A Steam Ejector Refrigeration System Powered by Engine Combustion Waste Heat: Part 2. Understanding the Nature of the Shock Wave Structure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Algorithms
2.1. Governing Equations
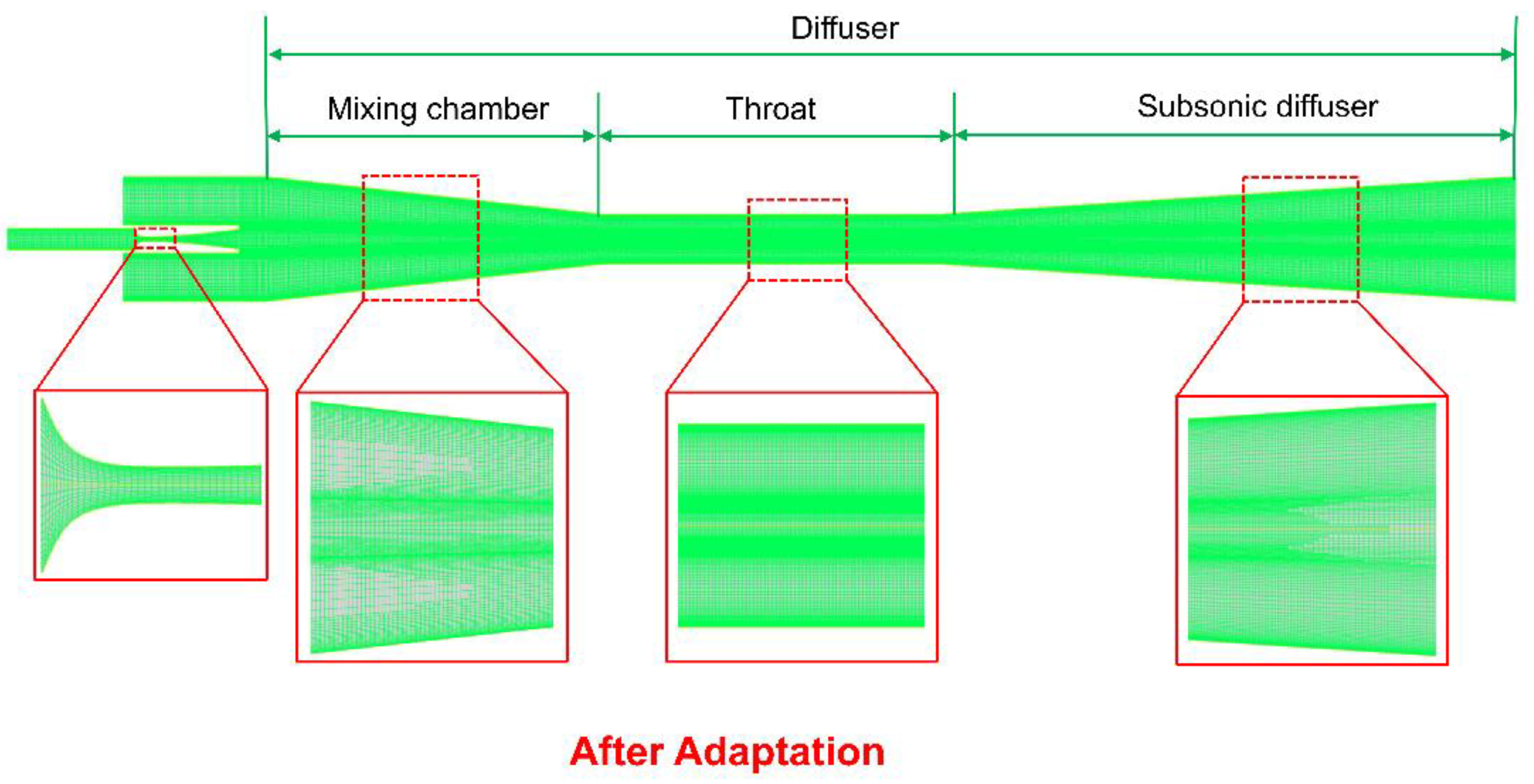
2.2. Geometry and Mesh Approach
2.3. Numerical Solution Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
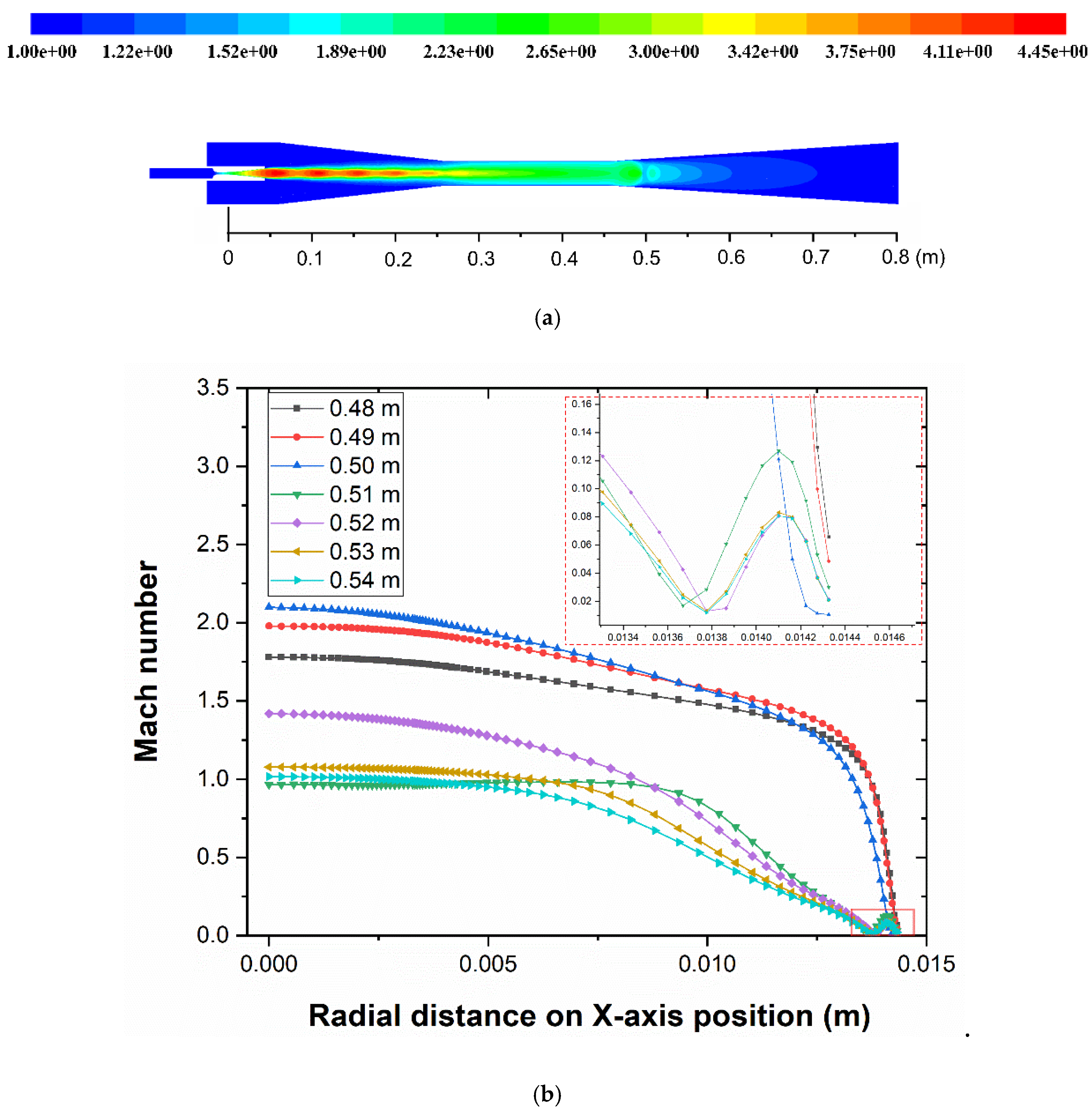
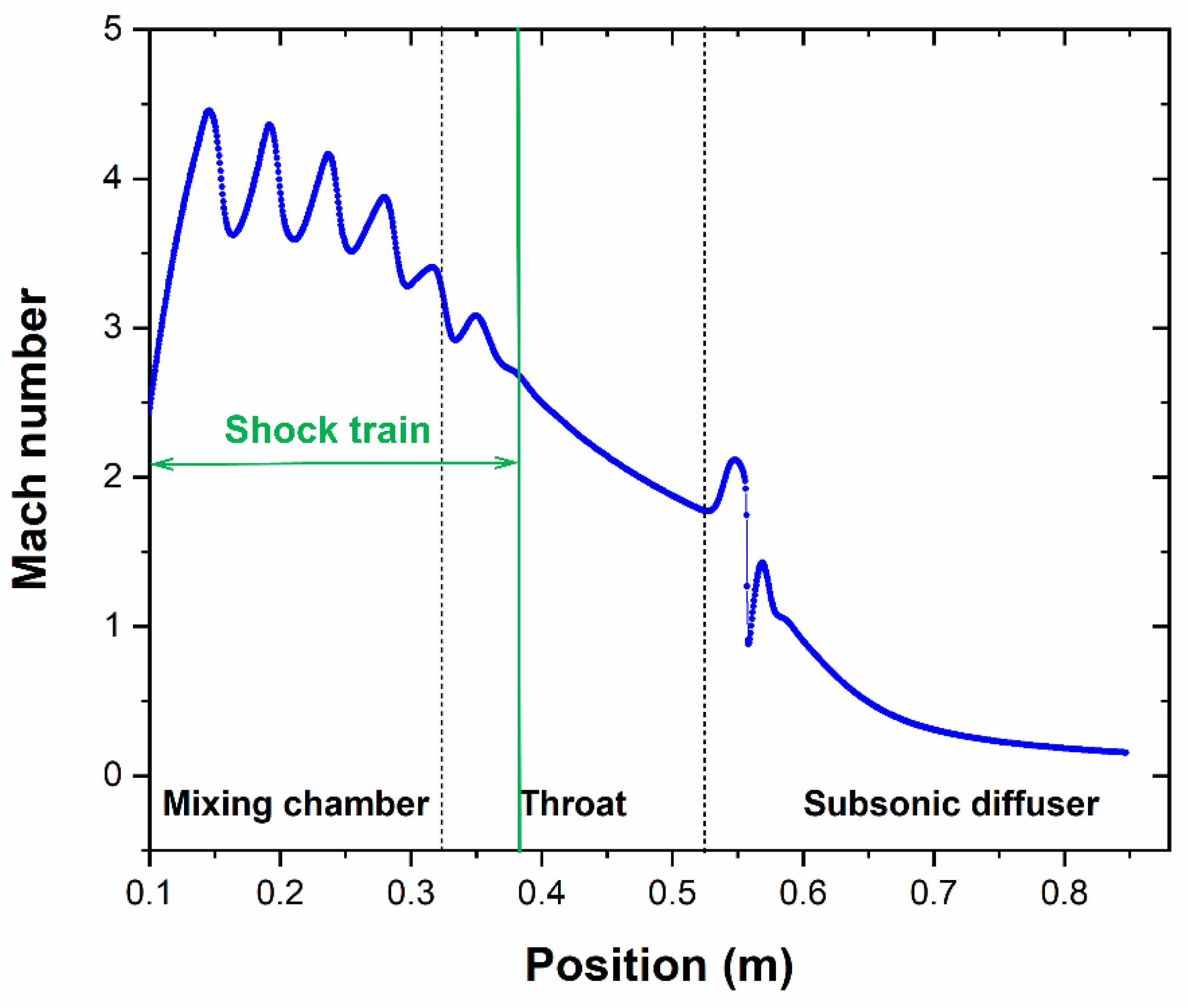
3.1. Structural Division of Shock Wave Structure in the Ejector
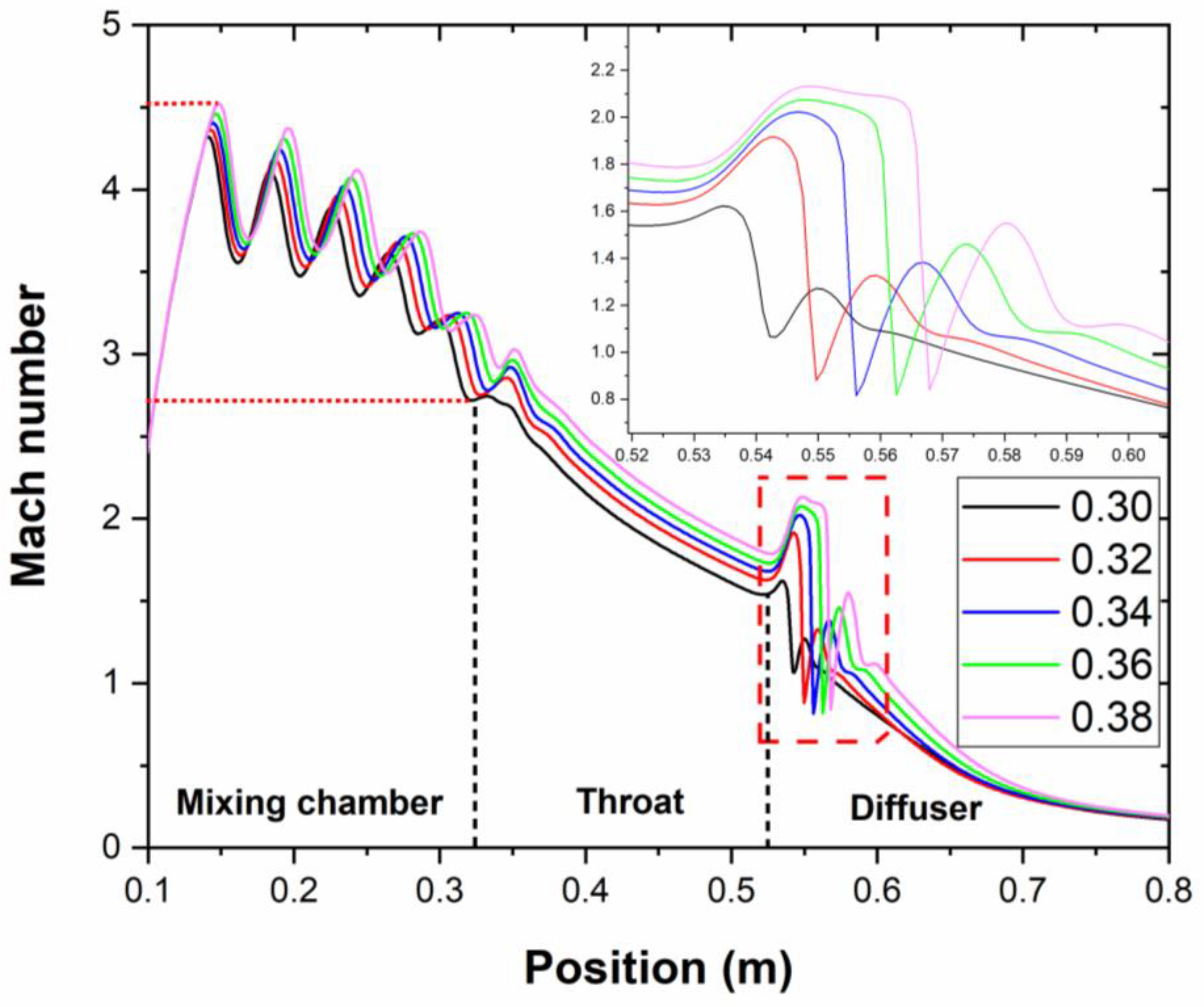
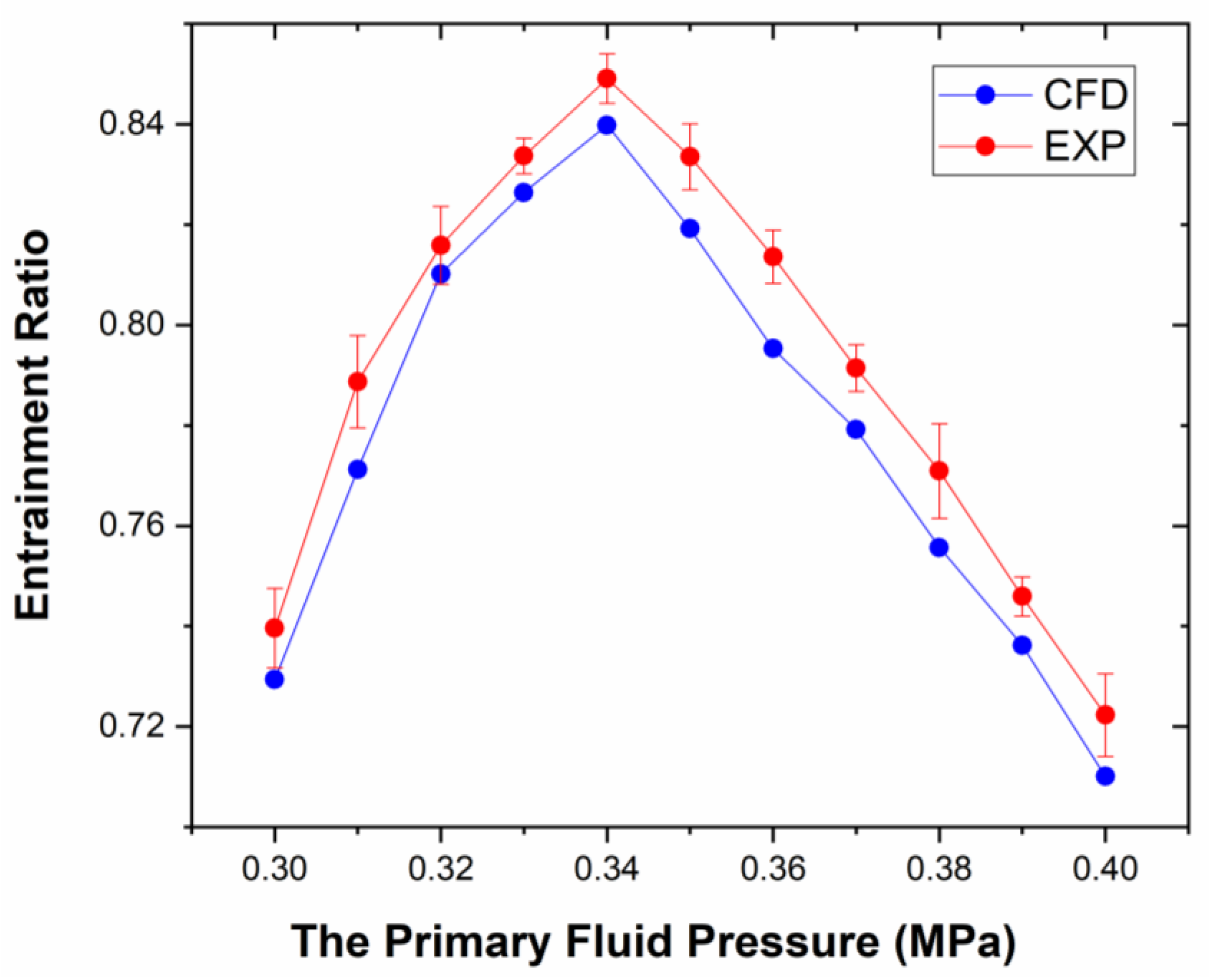
3.2. Effect of the Shock Wave Structure on the Pumping Performance
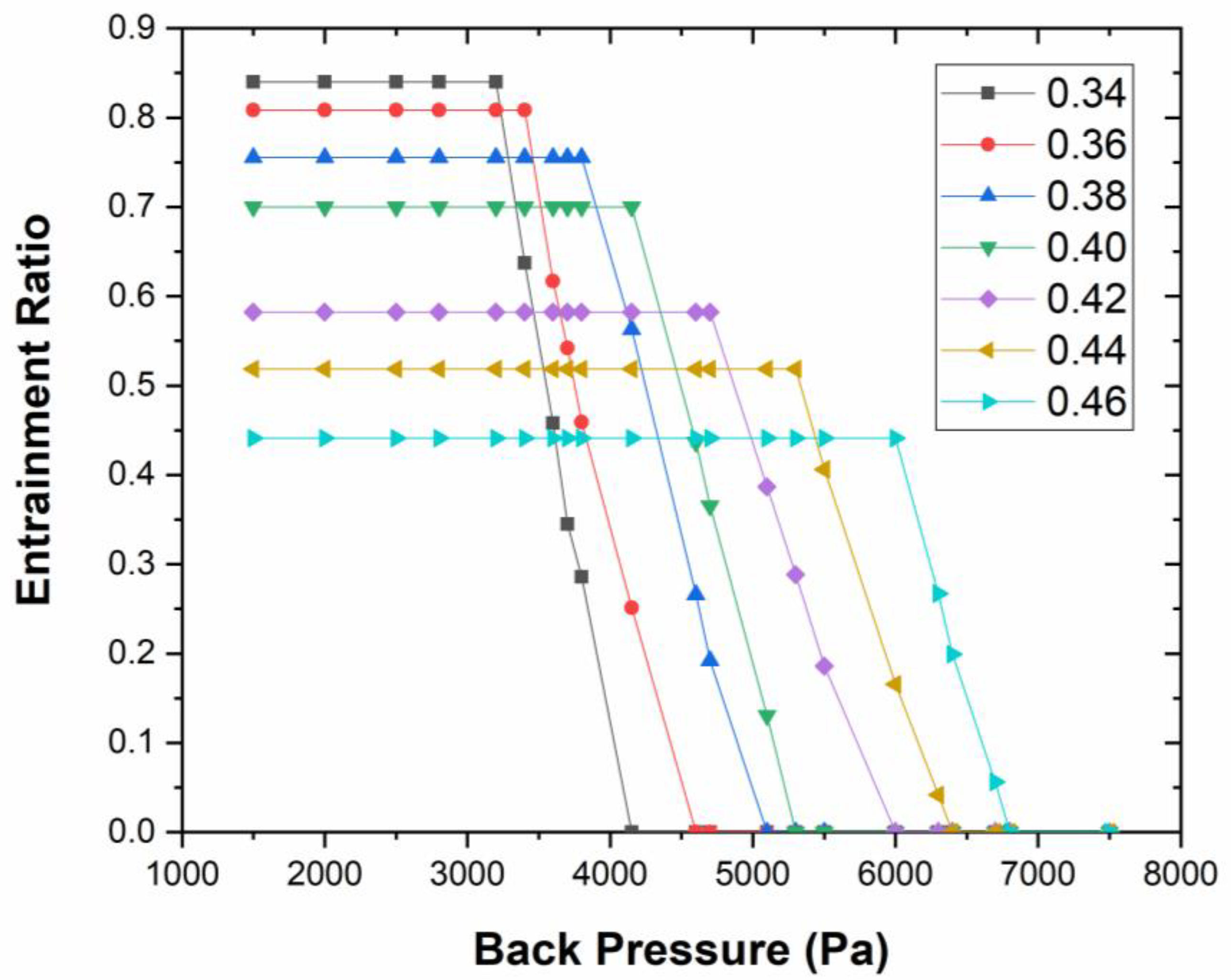
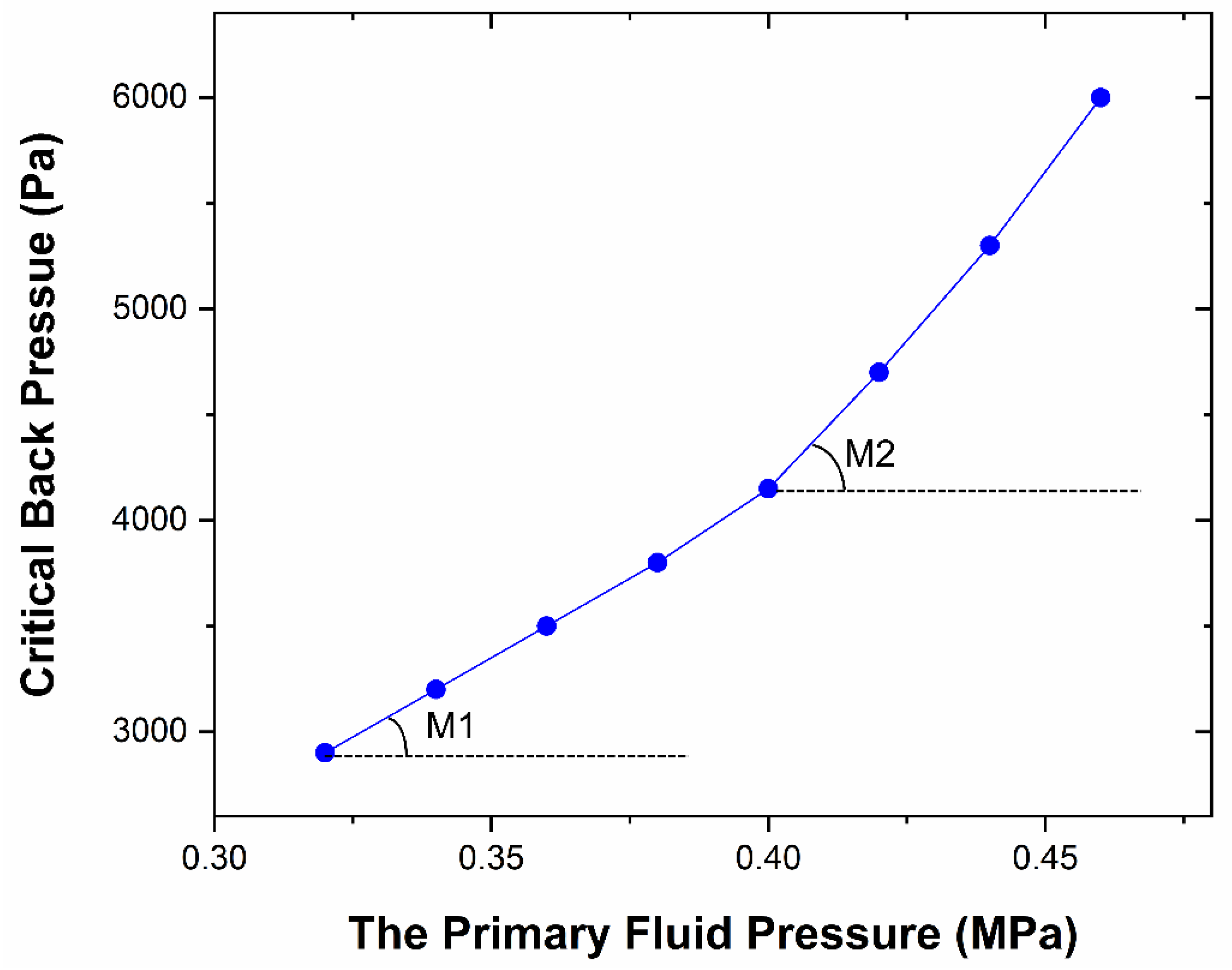
3.3. Effect of the Shock Wave on the Critical Back Pressure
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, J.; Yu, M.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Li, C.; Pan, X. Experimental investigation on low-temperature thermal energy driven steam ejector refrigeration system for cooling application. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 123, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eames, I.W.; Aphornratana, S.; Haider, H. A theoretical and experimental study of a small-scale steam jet refrigerator. Int. J. Refrig. 1995, 18, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besagni, G.; Mereu, R.; Inzoli, F. Ejector refrigeration: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 53, 373–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Han, J. Optimization analysis of structure parameters of steam ejector based on CFD and orthogonal test. Energy 2018, 151, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Yuen, A.C.Y.; Chen, T.B.Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Cao, R.; Yang, W.; Yeoh, G.H.; Timchenko, V. Computational study of wet steam flow to optimize steam ejector efficiency for potential fire suppression application. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.M.; Sun, C.Y. Experimental Study of the Performance Characteristics of a Steam-Ejector Refrigeration System. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 1997, 15, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aphornratana, S.; Eames, I.W. A small capacity steam-ejector refrigerator: Experimental investigation of a system using ejector with movable primary nozzle. Int. J. Refrig. 1997, 20, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eames, I.W.; Wu, S.; Worall, M.; Aphornratana, S. An experimental investigation of steam ejectors for applications in jet-pump refrigerators powered by low-grade heat. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 1999, 213, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunnanond, K.; Aphornratana, S. An experimental investigation of a steam ejector refrigerator: The analysis of the pressure profile along the ejector. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2004, 24, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, W.; Omer, S.A.; Riffat, S.B. Experimental investigation of a novel steam ejector refrigerator suitable for solar energy applications. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2010, 30, 1320–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, S.; Oliveira, A.C.; Ma, X.; Omer, S.A.; Zhang, W.; Riffat, S.B. Comparison of CFD and experimental performance results of a variable area ratio steam ejector. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 2011, 6, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, S.; Oliveira, A.C.; Ma, X.; Omer, S.A.; Zhang, W.; Riffat, S.B. Experimental and numerical analysis of a variable area ratio steam ejector. Int. J. Refrig. 2011, 34, 1668–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, V.V.; Ahmed, M.R. Experimental and computational studies on a steam jet refrigeration system with constant area and variable area ejectors. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 79, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, A.S.; Joseph Sekhar, S. Experimental Studies on the Effect of Suction Chamber Angle on the Entrainment of Passive Fluid in a Steam Ejector. J. Fluids Eng. 2017, 140, 011106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, A.S.; Sekhar, S.J. Experimental and numerical investigations on the effect of suction chamber angle and nozzle exit position of a steam-jet ejector. Energy 2018, 164, 1097–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, R.; Li, X.; Tian, Q. Experimental investigation on a R134a ejector refrigeration system under overall modes. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 137, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Kang, C.; Ma, H. An experimental investigation of steam ejector refrigeration system powered by extra low temperature heat source. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 81, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śmierciew, K.; Gagan, J.; Butrymowicz, D.; Łukaszuk, M.; Kubiczek, H. Experimental investigation of the first prototype ejector refrigeration system with HFO-1234ze(E). Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 110, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dong, J.; Li, A.; Lei, H.; Tu, J. Numerical study of primary steam superheating effects on steam ejector flow and its pumping performance. Energy 2014, 78, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, A.; Chen, T.; Yang, W.; Wang, C.; Li, A.; Yeoh, G.; Chan, Q.; Chan, M. Natural Ventilated Smoke Control Simulation Case Study Using Different Settings of Smoke Vents and Curtains in a Large Atrium. Fire 2019, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, A.C.Y.; Yeoh, G.H.; Cheung, S.C.P.; Chan, Q.N.; Chen, T.B.Y.; Yang, W.; Lu, H. Numerical study of the development and angular speed of a small-scale fire whirl. J. Comput. Sci. 2018, 27, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, A.C.Y.; Yeoh, G.H.; Timchenko, V.; Cheung, S.C.P.; Chen, T. Study of three LES subgrid-scale turbulence models for predictions of heat and mass transfer in large-scale compartment fires. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 2016, 69, 1223–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.B.Y.; Yuen, A.C.Y.; Wang, C.; Yeoh, G.H.; Timchenko, V.; Cheung, S.C.P.; Chan, Q.N.; Yang, W. Predicting the fire spread rate of a sloped pine needle board utilizing pyrolysis modelling with detailed gas-phase combustion. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 125, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Tang, Y. Numerical study for the influences of primary steam nozzle distance and mixing chamber throat diameter on steam ejector performance. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2018, 132, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, S.; Oliveira, A.C.; Diaconu, B. Numerical assessment of steam ejector efficiencies using CFD. Int. J. Refrig. 2009, 32, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Tan, L.; Xu, Y.; Yuan, Y. Three-dimensional CFD modeling and simulation on the performance of steam ejector heat pump for dryer section of the paper machine. Vacuum 2015, 122, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Wang, W.; Han, Z.; Ma, H.; Deng, Y.; Su, F.; Pan, X. Experimental investigation of the steam ejector in a single-effect thermal vapor compression desalination system driven by a low-temperature heat source. Energies 2018, 11, 2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhu, X.; Ren, X.; Qiu, Q.; Shen, S. Numerical investigation on the effect of nozzle position for design of high performance ejector. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 126, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, S.; Oliveira, A.C.; Diaconu, B. Influence of geometrical factors on steam ejector performance—A numerical assessment. Int. J. Refrig. 2009, 32, 1694–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, T.; Day, B. Numerical analysis of the performance of a thermal ejector in a steam evaporator. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2010, 30, 2708–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, Z.; Han, B.; Li, Y. Numerical investigation of the influences of mixing chamber geometries on steam ejector performance. Desalination 2014, 353, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Long, X.; Yao, X. Numerical investigation on the mixing process in a steam ejector with different nozzle structures. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2012, 56, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruangtrakoon, N.; Thongtip, T.; Aphornratana, S.; Sriveerakul, T. CFD simulation on the effect of primary nozzle geometries for a steam ejector in refrigeration cycle. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2013, 63, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riffat, S.B.; Omer, S.A. CFD modelling and experimental investigation of an ejector refrigeration system using methanol as the working fluid. Int. J. Energy Res. 2001, 25, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriveerakul, T.; Aphornratana, S.; Chunnanond, K. Performance prediction of steam ejector using computational fluid dynamics: Part 1. Validation of the CFD results. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2007, 46, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriveerakul, T.; Aphornratana, S.; Chunnanond, K. Performance prediction of steam ejector using computational fluid dynamics: Part 2. Flow structure of a steam ejector influenced by operating pressures and geometries. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2007, 46, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, N.H.; Karameldin, A.; Shamloul, M.M. Modelling and simulation of steam jet ejectors. Desalination 1999, 123, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Agarwal, R.K. CFD Simulation of a Supersonic Steam Ejector for Refrigeration Application. In Proceedings of the ASME/JSME/KSME 2015 Joint Fluids Engineering Conference, Seoul, Korea, 26–31 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Desevaux, P.; Mellal, A.; Alves de Sousa, Y. Visualization of secondary flow choking phenomena in a supersonic air ejector. J. Vis. 2004, 7, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, K. Shock train and pseudo-shock phenomena in supersonic internal flows. J. Therm. Sci. 2003, 12, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, H.; Zhang, G.; Guo, L.; Tu, J. CFD simulation on the boundary layer separation in the steam ejector and its influence on the pumping performance. Energy 2019, 167, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariafar, K.; Buttsworth, D.; Al-Doori, G.; Sharifi, N. Mixing layer effects on the entrainment ratio in steam ejectors through ideal gas computational simulations. Energy 2016, 95, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dong, J.; Zhang, G.; Fu, Q.; Li, H.; Han, Y.; Tu, J. The primary pseudo-shock pattern of steam ejector and its influence on pumping efficiency based on CFD approach. Energy 2019, 167, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dong, J.; Lei, H.; Li, A.; Wang, R.; Chen, W.; Tu, J. Modeling and simulation of steam-jet vacuum pump. Zhenkong Kexue yu Jishu Xuebao/Vacuum Sci. Technol. 2013, 33, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar]
- Yuen, A.C.Y.; Yeoh, G.H.; Timchenko, V.; Chen, T.B.Y.; Chan, Q.N.; Wang, C.; Li, D.D. Comparison of detailed soot formation models for sooty and non-sooty flames in an under-ventilated ISO room. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 115, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, A.C.Y.; Yeoh, G.H.; Timchenko, V.; Cheung, S.C.P.; Barber, T.J. Importance of detailed chemical kinetics on combustion and soot modelling of ventilated and under-ventilated fires in compartment. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 96, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Yeoh, G.H.; Timchenko, V.; Yuen, A.C.Y.; Wang, X. Numerical Study of Condensation Effect on a Steam Ejector by Wet Steam Model. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Flow Dynamics (ICFD2016), Sendai, Japan, 10–12 October 2016; Volume 12, pp. 492–493. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.B.Y.; Yuen, A.C.Y.; Yeoh, G.H.; Timchenko, V.; Cheung, S.C.P.; Chan, Q.N.; Yang, W.; Lu, H. Numerical study of fire spread using the level-set method with large eddy simulation incorporating detailed chemical kinetics gas-phase combustion model. J. Comput. Sci. 2018, 24, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, A.C.Y.; Chen, T.B.Y.; Yeoh, G.H.; Yang, W.; Cheung, S.C.P.; Cook, M.; Yu, B.; Chan, Q.N.; Yip, H.L. Establishing pyrolysis kinetics for the modelling of the flammability and burning characteristics of solid combustible materials. J. Fire Sci. 2018, 36, 494–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, A.C.Y.; Yeoh, G.H. Numerical simulation of an enclosure fire in a large test hall. Comput. Therm. Sci. 2013, 5, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, A.C.Y.; Yeoh, G.H.; Timchenko, V.; Cheung, S.C.P.; Chan, Q.N.; Chen, T. On the influences of key modelling constants of large eddy simulations for large-scale compartment fires predictions. Int. J. Comut. Fluid Dyn. 2017, 31, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besagni, G.; Mereu, R.; Inzoli, F. CFD study of ejector flow behavior in a blast furnace gas galvanizing plant. J. Therm. Sci. 2015, 24, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besagni, G.; Mereu, R.; Chiesa, P.; Inzoli, F. An Integrated Lumped Parameter-CFD approach for off-design ejector performance evaluation. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 105, 697–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocco, L. One-dimensional treatment of steady gas dynamics. Fundam. Gas Dyn. 1958, Chap-B, 64–349. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.J.; Chang, J.M.; Wang, C.P.; Petrenko, V.A. 1-D analysis of ejector performance. Int. J. Refrig. 1999, 22, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Geometrical Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Diameter of the nozzle inlet | 12 mm |
| Diameter of the nozzle outlet | 11 mm |
| Diameter of the nozzle throat | 2.5 mm |
| Expand the angle of the nozzle | 10° |
| Nozzle exit position | 10 mm |
| Diameter of the mixing chamber inlet | 70 mm |
| Diameter of the throat | 28 mm |
| Length of the mixing chamber | 122.2 mm |
| Length of the throat | 90 mm |
| Length of the subsonic diffuser | 210 mm |
| Properties | Dynamic Viscosity | Thermal Conductive | Specific Heat Capacity | Molecular Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 1.34 × 10−5 kgm−1s−1 | 0.00261 Wm−1K−1 | 2014.00 J kg−1K−1 | 18.01534 kgkmol−1 |
| Operating Condition | Value |
|---|---|
| Primary fluid pressure | 360,000 Pa |
| Secondary fluid pressure | 2330 Pa |
| Back pressure | 3500 Pa |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, L.; Yuen, A.C.Y.; Liu, H.; Cao, R.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Tu, J.; Yeoh, G.H. A Steam Ejector Refrigeration System Powered by Engine Combustion Waste Heat: Part 2. Understanding the Nature of the Shock Wave Structure. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4435. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204435
Han Y, Wang X, Guo L, Yuen ACY, Liu H, Cao R, Wang C, Li C, Tu J, Yeoh GH. A Steam Ejector Refrigeration System Powered by Engine Combustion Waste Heat: Part 2. Understanding the Nature of the Shock Wave Structure. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(20):4435. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204435
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Yu, Xiaodong Wang, Lixin Guo, Anthony Chun Yin Yuen, Hengrui Liu, Ruifeng Cao, Cheng Wang, Cuiling Li, Jiyuan Tu, and Guan Heng Yeoh. 2019. "A Steam Ejector Refrigeration System Powered by Engine Combustion Waste Heat: Part 2. Understanding the Nature of the Shock Wave Structure" Applied Sciences 9, no. 20: 4435. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204435
APA StyleHan, Y., Wang, X., Guo, L., Yuen, A. C. Y., Liu, H., Cao, R., Wang, C., Li, C., Tu, J., & Yeoh, G. H. (2019). A Steam Ejector Refrigeration System Powered by Engine Combustion Waste Heat: Part 2. Understanding the Nature of the Shock Wave Structure. Applied Sciences, 9(20), 4435. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204435









