Two-Step Feature Selection for Identifying Developmental Differences in Resting fMRI Intrinsic Connectivity Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
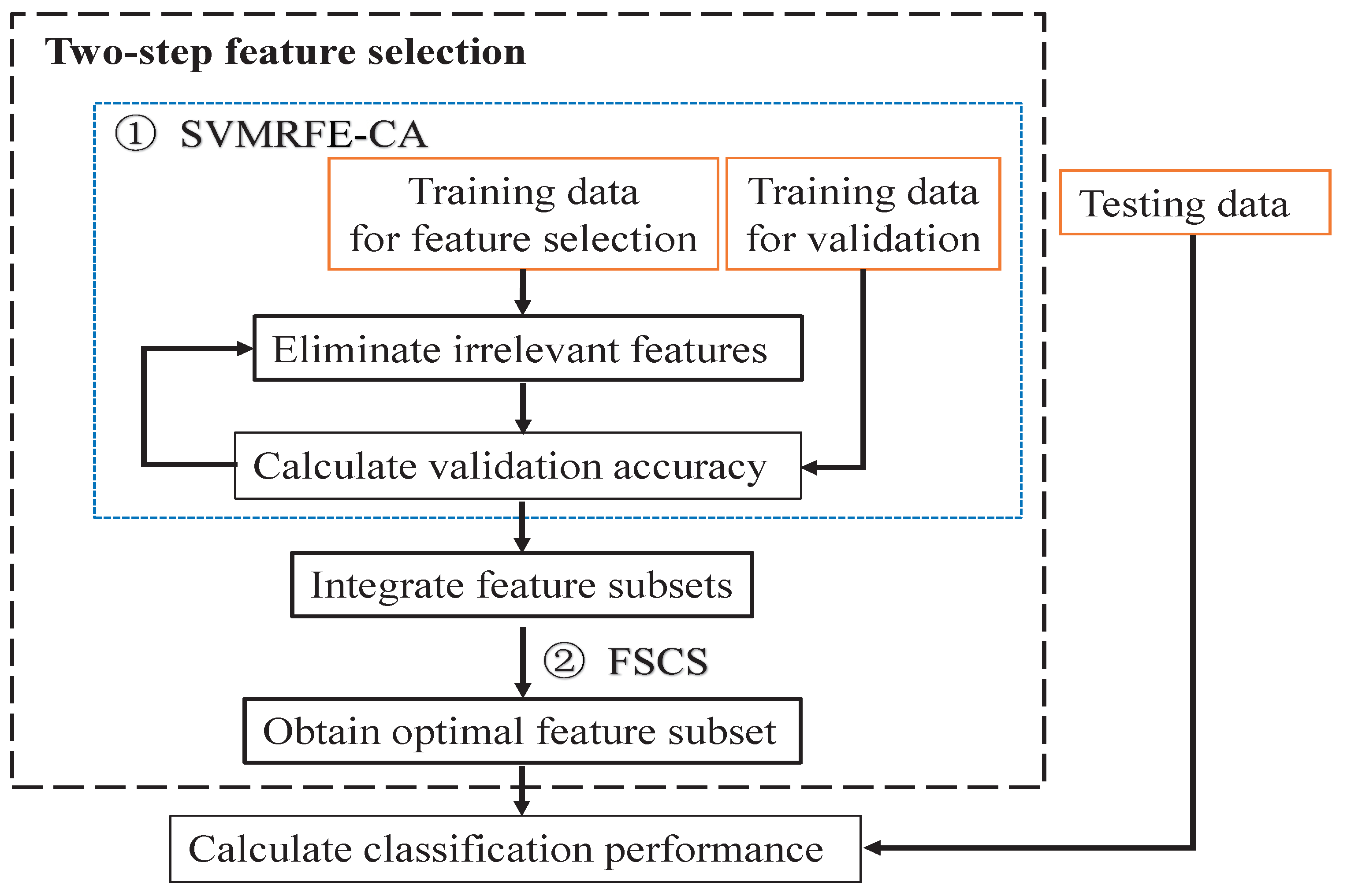
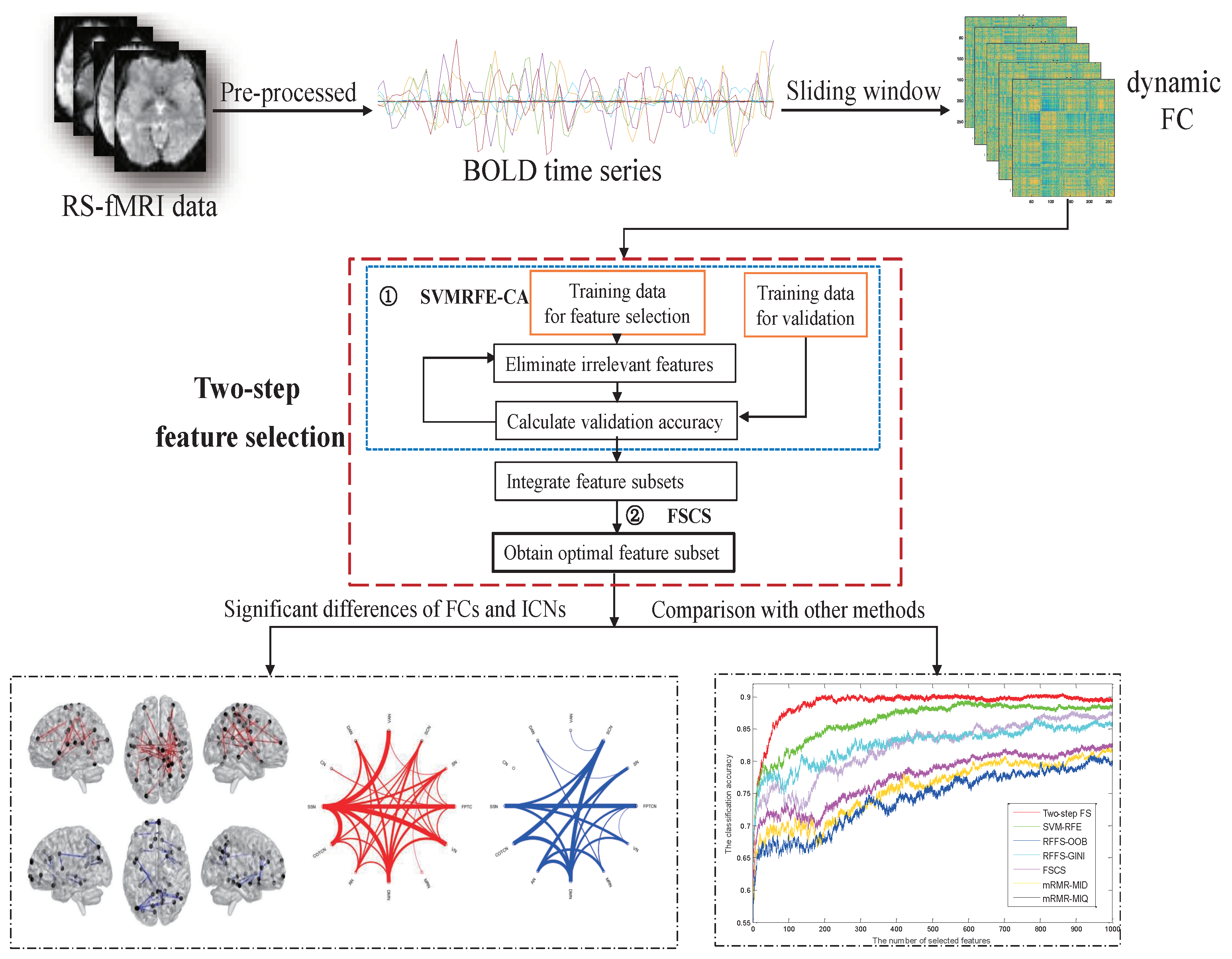
2. Methods
| Algorithm 1: Two-step feature selection method |
|
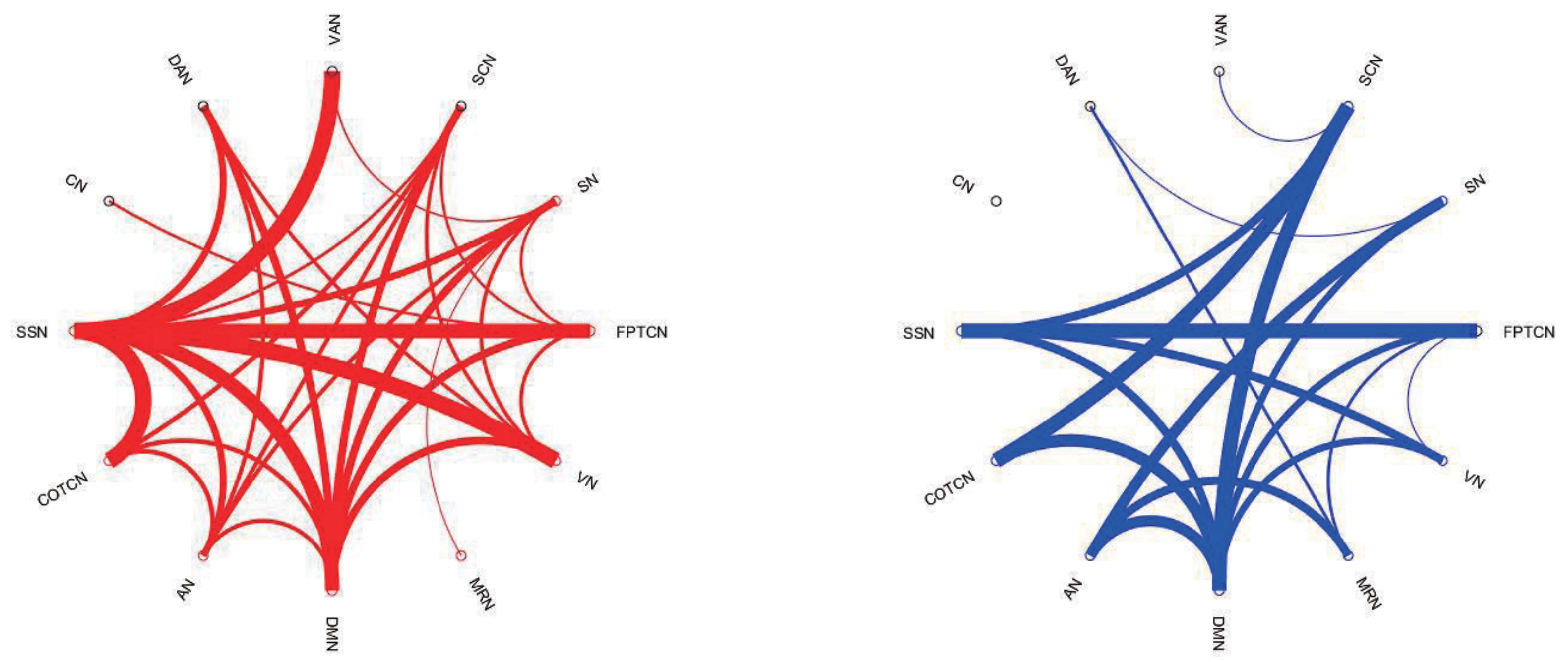
3. Results on Philadelphia Neuro Developmental Cohort (PNC) Data
3.1. Data Collection and Preprocessing
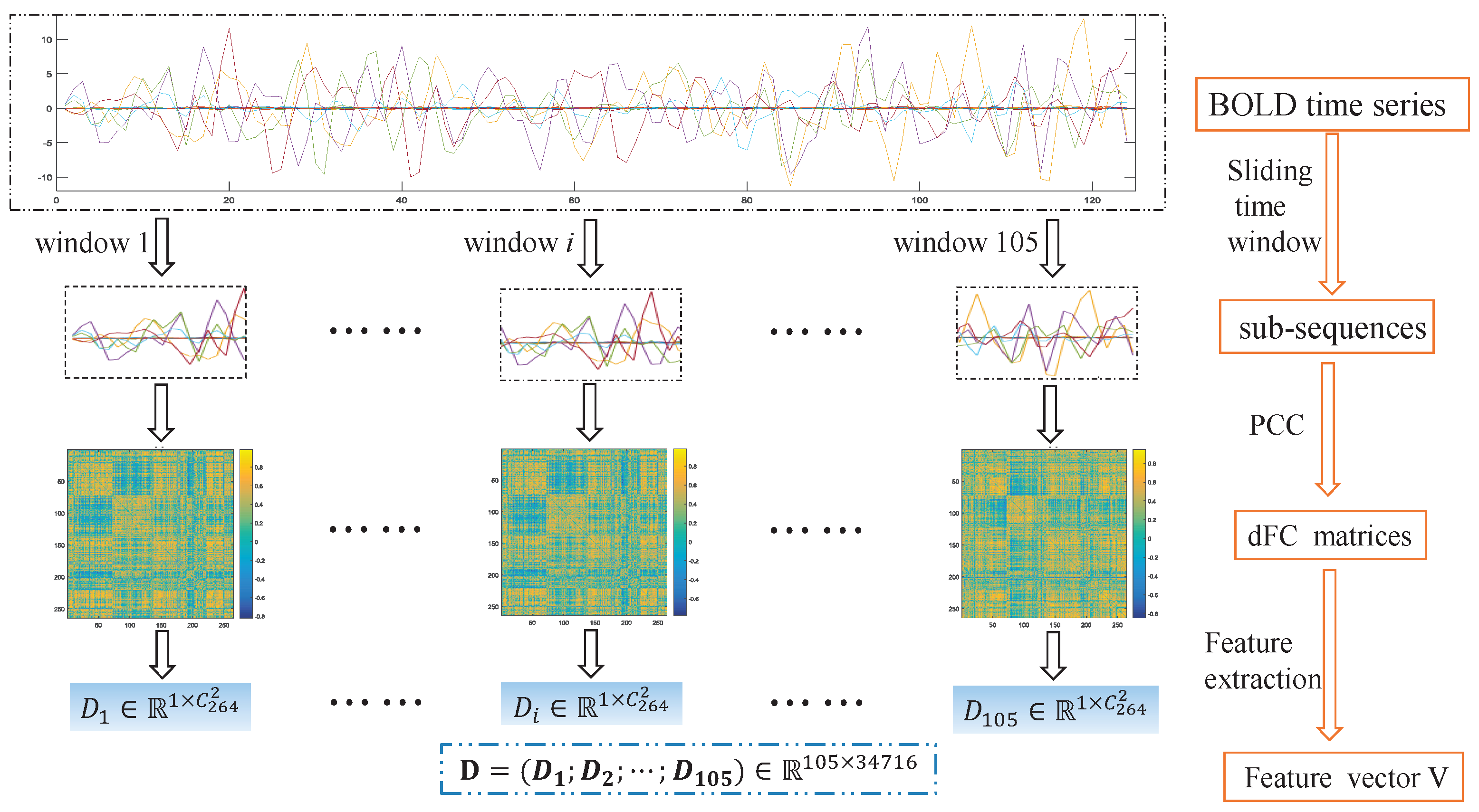
3.2. Dynamic Functional Network Connectivity Analysis
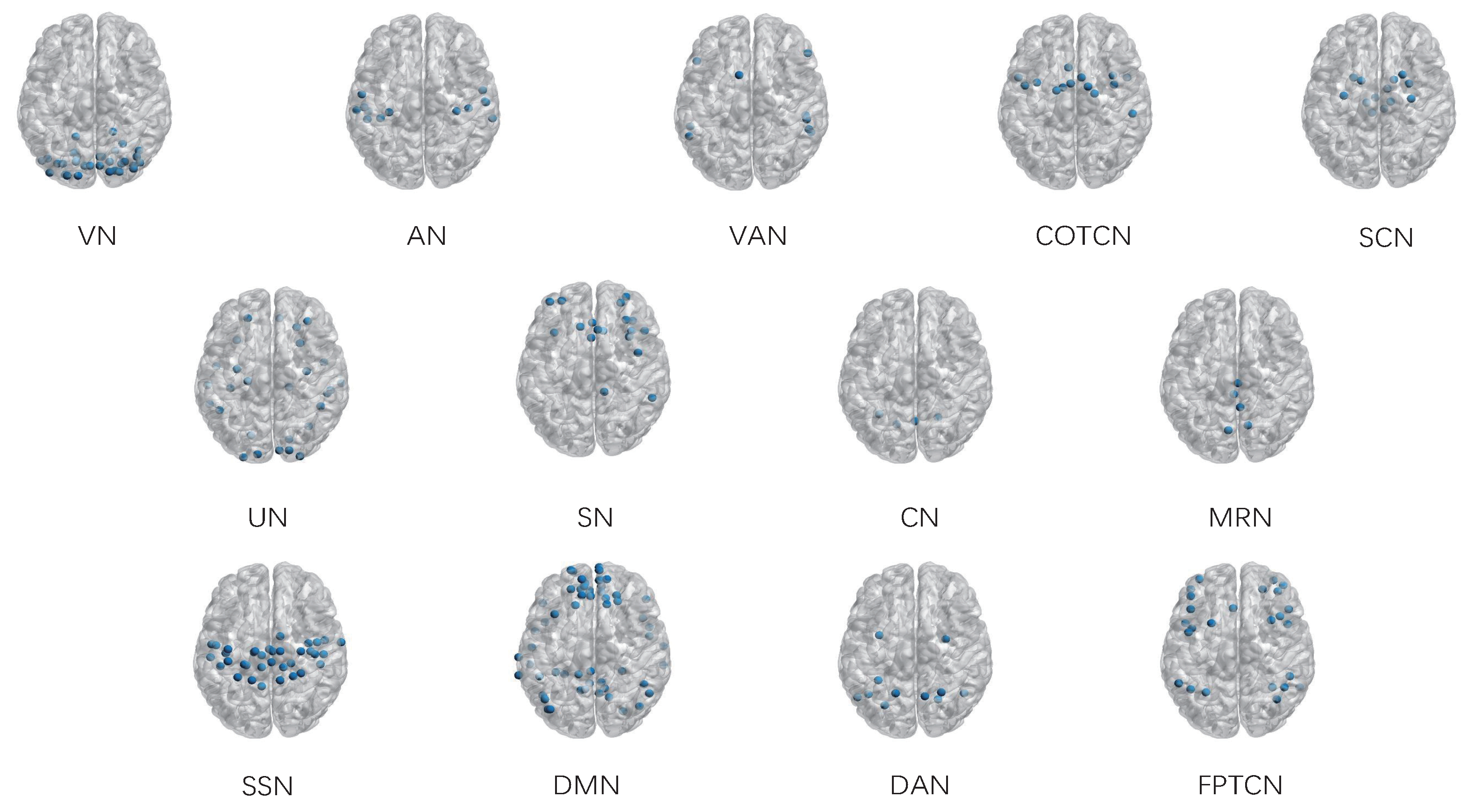
3.3. The Identification of Essential Differences of ICNs during Development
3.4. The Validation of the Selected Different ICNs by Graph Theory
3.5. Comparison with Other Feature Selection Methods
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, Q.; Du, Y.; Chen, J.; Sui, J.; Adali, T.; Pearlson, G.D.; Calhoun, V.D. Application of graph theory to assess static and dynamic brain connectivity: Approaches for building brain graphs. Proc. IEEE 2018, 106, 886–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, S.J.D.; Formisano, E.; Muckli, L.; De Lange, F.P. Laminar fMRI: Applications for cognitive neuroscience. Neuroimage 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heurling, K.; Leuzy, A.; Jonasson, M.; Frick, A.; Zimmer, E.R.; Nordberg, A.; Lubberink, M. Quantitative positron emission tomography in brain research. Brain Res. 2017, 1670, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswal, B.; Yetkin, F.Z.; Haughton, V.M.; Hyde, J.S. Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 1995, 34, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betzel, R.F.; Byrge, L.; He, Y.; Goni, J.; Zuo, X.N.; Sporns, O. Changes in structural and functional connectivity among resting-state networks across the human lifespan. Neuroimage 2014, 102, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, H.I.; Wee, C.Y.; Lee, S.W.; Shen, D. State-space model with deep learning for functional dynamics estimation in resting-state fMRI. Neuroimage 2016, 129, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, E.S.; Shen, X.; Scheinost, D.; Rosenberg, M.D.; Huang, J.; Chun, M.M.; Papademetris, X.; Constable, R.T. Functional connectome fingerprinting: Identifying individuals using patterns of brain connectivity. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1664–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennigen, E.; Miller, R.L.; Rashid, B.; Fryer, S.L.; Loewy, R.L.; Stuart, B.K.; Mathalon, D.H.; Calhoun, V.D. Reduced higher-dimensional resting state fMRI dynamism in clinical high-risk individuals for schizophrenia identified by meta-state analysis. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 201, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calhoun, V.D.; Miller, R.; Pearlson, G.D.; Adal, T. The chronnectome: Time-varying connectivity networks as the next frontier in fMRI data discovery. Neuron 2014, 84, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornito, A.; Zalesky, A.; Breakspear, M. The connectomics of brain disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.E.; Rubinov, M.; Chang, C. Methods and considerations for dynamic analysis of functional MR imaging data. Neuroimaging Clin. 2017, 27, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preti, M.G.; Bolton, T.A.; Van, D.V.D. The dynamic functional connectome: State-of-the-art and perspectives. Neuroimage 2016, 160, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindriks, R.; Adhikari, M.H.; Murayama, Y.; Ganzetti, M.; Mantini, D.; Logothetis, N.K.; Deco, G. Can sliding-window correlations reveal dynamic functional connectivity in resting-state fMRI? Neuroimage 2016, 127, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakil, S.; Lee, C.H.; Keilholz, S.D. Evaluation of sliding window correlation performance for characterizing dynamic functional connectivity and brain states. Neuroimage 2016, 133, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Fryer, S.L.; Fu, Z.; Lin, D.; Sui, J.; Chen, J.; Damaraju, E.; Mennigen, E.; Stuart, B.; Loewy, R.L.; et al. Dynamic functional connectivity impairments in early schizophrenia and clinical high-risk for psychosis. Neuroimage 2017, 180, 632–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, E.A.; Damaraju, E.; Plis, S.M.; Erhardt, E.B.; Eichele, T.; Calhoun, V.D. Tracking whole-brain connectivity dynamics in the resting state. Cereb. Cortex 2014, 24, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eavani, H.; Satterthwaite, T.D.; Filipovych, R.; Gur, R.E.; Gur, R.C.; Davatzikos, C. Identifying sparse connectivity patterns in the brain using resting-state fMRI. Neuroimage 2015, 105, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Worsley, K. The geometry of correlation fields with an application to functional connectivity of the brain. Ann. Appl. Probab. 1999, 9, 1021–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Allen, E.A.; Sui, J.; Arbabshirani, M.R.; Pearlson, G.; Calhoun, V.D. Brain connectivity networks in schizophrenia underlying resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 2415–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, H.I.; Lee, S.W.; Shen, D. Deep ensemble learning of sparse regression models for brain disease diagnosis. Med Image Anal. 2017, 37, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, N.F.; Osuch, E.A.; Zhu, M.H.; Ma, X.Y.; Wammes, M.; Jiang, T.Z.; Sui, J.; Calhoun, V.D. Discriminating Bipolar Disorder from Major Depression using Whole-Brain Functional Connectivity: A Feature Selection Analysis with SVM-FoBa Algorithm. J. Signal Process. Syst. 2018, 90, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.; Lu, L.; Yang, L.; Kennedy, P.J. Identifying Brain Abnormalities with Schizophrenia Based on a Hybrid Feature Selection Technology. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, G.; Sahin, F. A Survey on Feature Selection Methods; Pergamon Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yuhui, D.; Zening, F.; Calhoun, V.D. Classification and Prediction of Brain Disorders Using Functional Connectivity: Promising but Challenging. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 525. [Google Scholar]
- Kuncheva, L.I. Ensemble Feature Selection. In Combining Pattern Classifiers: Methods and Algorithms, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, B.; Zille, P.; Stephen, J.M.; Wilson, T.; Calhoun, V.D.; Wang, Y.P. Estimation of dynamic sparse connectivity patterns from resting state fMRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1224–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zille, P.; Calhoun, V.D.; Stephen, J.M.; Wilson, T.; Wang, Y.P. Fused estimation of sparse connectivity patterns from rest fMRI: Application to comparison of children and adult brains. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 2165–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.; Hallquist, M.N.; Luna, B. The development of hub architecture in the human functional brain network. Cereb. Cortex 2013, 23, 2380–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, J.D.; Cohen, A.L.; Nelson, S.M.; Wig, G.S.; Petersen, S.E. Functional network organization of the human brain. Neuron 2011, 72, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, S.M.; Cohen, A.L.; Power, J.D.; Wig, G.S.; Petersen, S.E. A parcellation scheme for human left lateral parietal cortex. Neuron 2010, 67, 156–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.L.; Fair, D.A.; Dosenbach, N.U.F.; Miezin, F.M.; Dierker, D.; Essen, D.C.V.; Schlaggar, B.L.; Petersen, S.E. Defining functional areas in individual human brains using resting functional connectivity MRI. Neuroimage 2008, 41, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.D.; Geoffrey, W.; Song, J.N. Accurate in silico identification of species-specific acetylation sites by integrating protein sequence-derived and functional features. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolles, D.D.; Van Buchem, M.A.; Crone, E.A.; Rombouts Serge, A.R.B. A comprehensive study of whole-brain functional connectivity in children and young adults. Cereb. Cortex 2011, 21, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchison, R.M.; Morton, J.B. Tracking the brains functional coupling dynamics over development. Neuroscience 2015, 35, 6849–6859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, J.; Thompson, P.M.; Stern, J.M.; Staba, R.J.; Bragin, A.; Mody, I. Connectomics and epilepsy. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2013, 26, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broyd, S.J.; Demanuele, C.; Debener, S.; Helps, S.K.; James, C.J.; Sonuga-Barke, E.J.S. Default-mode brain dysfunction in mental disorders: A systematic review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2009, 33, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.S.; Ferguson, M.A.; Lopez-Larson, M.; Yurgelun-Todd, D. Connectivity gradients between the default mode and attention control networks. Brain Connect. 2011, 1, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giedd, J.N. The teen brain: Insights from neuroimaging. J. Adolescent Health 2008, 42, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyon, I.; Weston, J.; Barnhill, S.; Vapnik, V. Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines. Mach. Learn. 2002, 46, 389–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Tuck, D.P. MSVM-RFE: Extensions of SVM-RFE for multiclass gene selection on DNA microarray data. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Zhang, D. Feature selection and analysis on correlated gas sensor data with recursive feature 536 elimination. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 212, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sharmila, D.J.S.; Singh, S. SVMRFE based approach for prediction of most discriminatory gene target for type II diabetes. Genom. Data 2017, 12, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyon, I.; Elisseeff, A. An Introduction to Variable and Feature Selection. J. Mach. Learn. 2003, 3, 1157–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Dao, F.Y.; Lv, H.; Wang, F.; Feng, C.Q.; Ding, H.; Chen, W.; Lin, H. Identify origin of replication in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using two-step feature selection technique. Bioinformatics 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satterthwaite, T.D.; Elliott, M.A.; Ruparel, K.; Calkins, M.E.; Jackson, C.; Elliott, M.A.; Roalf, D.R.; Hopson, R.; Prabhakaran, K.; Behr, M.; et al. The philadelphia neurodevelopmental cohort: A publicly available resource for the study of normal and abnormal brain development in youth. Neuroimage 2016, 124, 1115–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, S.; Vankov, E.R.; Yeh, H.J.; Guindani, M.; Vannucci, M.; Haneef, Z.; Stern, J. Temporal and spectral characteristics of dynamic functional connectivity between resting-state networks reveal information beyond static connectivity. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marusak, H.A.; Calhoun, V.D.; Brown, S.; Crespo, L.M.; Thomason, M.E. Dynamic functional connectivity of neurocognitive networks in children. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2016, 38, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damaraju, E.; Allen, E.A.; Belger, A.; Ford, J.M.; McEwen, S.; Mathalon, D.H.; Muellwe, B.A.; Pearlson, G.D.; Potkin, S.G.; Preda, A.; et al. Dynamic functional connectivity analysis reveals transient states of dysconnectivity in schizophrenia. Neuroimage Clin. 2014, 5, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirer, W.R.; Ryali, S.; Rykhlevskaia, E.; Menon, V.; Greicius, M.D. Decoding subject-driven cognitive states with whole-brain connectivity patterns. Cereb. Cortex 2012, 22, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Fox, P.T.; Miller, K.L.; Glahn, D.C.; Beckmann, C.F. Correspondence of the brain’s functional architecture during activation and rest. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13040–13045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Miller, K.L.; Salimi-Khorshidi, G.; Webster, M.; Beckmann, C.F.; Nichols, T.E.; Ramsey, J.D.; Woolrich, M.W. Network modelling methods for fMRI. NeuroImage 2011, 54, 875–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingrui, X.; Jinhui, W.; Yong, H. BrainNet viewer: A network visualization tool for human brain connectomics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68910. [Google Scholar]
- Baggio, H.C.; Sala-Llonch, R.; Segura, B.; Marti, M.J.; Valldeoriola, F.; Compta, Y.; Tolosa, E.; Junque, C. Functional brain networks and cognitive deficits in Parkinson’s disease. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2014, 35, 4620–4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.H.; Zuo, X.N.; Dai, Z.J.; Xia, M.R.; Zhao, Z.L.; Zhao, X.L.; Jia, J.P.; Han, Y.; He, Y. Disrupted functional brain connectome in individuals at risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 73, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Long, F.; Ding, C. Feature selection based on mutual information criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. 2005, 27, 1226–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menze, B.H.; Kelm, M.B.; Masuch, R.; Himmelreich, U.; Bachert, P.; Petrich, W.; Hamprecht, F.A. A comparison of random forest and its Gini importance with standard chemometric methods for the feature selection and classification of spectral data. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londei, A.; D’Ausilio, A.; Basso, D.; Sestieri, C.; Gratta, C.D.; Romani, G.L.; Belardinelli, M.O. Sensory-motor brain network connectivity for speech comprehension. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2010, 31, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffield, J.M.; Repovs, G.; Harms, M.P.; Carter, C.S.; Gold, J.M.; MacDonald, A.W.; Ragland, D.; Silverstein, S.M.; Godwin, D.; Barch, D.M. Fronto-parietal and cingulo-opercular network interity and cognition in health and schizophrenia. Neuropsychologia 2015, 73, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubillo, A.; Halari, R.; Smith, A.; Taylor, E.; Rubia, K. A review of fronto-striatal and fronto-cortical brain abnormalities in children and adults with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and new evidence for dysfunction in adults with ADHD during motivation and attention. Cortex 2012, 48, 194–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Children | Young Adults | |
|---|---|---|
| Number | 193 | 204 |
| Gender (male/female) | 91/102 | 81/123 |
| Age (Mean ± SD, months) | 124.06 ± 11.33 | 231.50 ± 12.14 |
| Ethnicity | ||
| ASIAN | 3 (1.5%) | 0 (0%) |
| AFRICAN | 77 (39.9%) | 74 (36.3%) |
| AMERICAN | 0 (0%) | 2 (1%) |
| OTHER/MIXED | 20 (10.4%) | 17 (8.3%) |
| CAUCASIAN/WHITE | 92 (47.7%) | 111 (54.4%) |
| HAWAIIAN/PACIFIC | 1 (0.5%) | 0 (0%) |
| Measure | Definition |
|---|---|
| Cc: Clustering coefficient | |
| Lp: Characteristic path length | |
| : local efficiency | |
| : global efficiency |
| Methods | CAR | SS | SC | PPV | NPV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two-step FS | 0.9063 | 0.8951 | 0.9041 | 0.9026 | 0.8942 |
| SVM-RFE | 0.8922 | 0.8787 | 0.8930 | 0.8975 | 0.8827 |
| RFFS-OOB | 0.8756 | 0.8601 | 0.8734 | 0.8651 | 0.8669 |
| RFFS-GINI | 0.8645 | 0.8514 | 0.8584 | 0.8581 | 0.8512 |
| FSCS | 0.8253 | 0.8305 | 0.8285 | 0.8208 | 0.8378 |
| mRMR-MID | 0.8190 | 0.8129 | 0.8140 | 0.8108 | 0.8301 |
| mRMR-MIQ | 0.8059 | 0.8107 | 0.8175 | 0.8108 | 0.8308 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiao, C.; Gao, B.; Lu, L.-J.; Calhoun, V.D.; Wang, Y.-P. Two-Step Feature Selection for Identifying Developmental Differences in Resting fMRI Intrinsic Connectivity Networks. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4298. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204298
Qiao C, Gao B, Lu L-J, Calhoun VD, Wang Y-P. Two-Step Feature Selection for Identifying Developmental Differences in Resting fMRI Intrinsic Connectivity Networks. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(20):4298. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204298
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiao, Chen, Bin Gao, Lu-Jia Lu, Vince D. Calhoun, and Yu-Ping Wang. 2019. "Two-Step Feature Selection for Identifying Developmental Differences in Resting fMRI Intrinsic Connectivity Networks" Applied Sciences 9, no. 20: 4298. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204298
APA StyleQiao, C., Gao, B., Lu, L.-J., Calhoun, V. D., & Wang, Y.-P. (2019). Two-Step Feature Selection for Identifying Developmental Differences in Resting fMRI Intrinsic Connectivity Networks. Applied Sciences, 9(20), 4298. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204298





