Biodegradation of Sulfamethoxazole in Milkfish (Chanos chanos) Pond Sediments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Sediment Sampling and Sampling Site
2.3. Experimental Setting
2.4. Analysis of Sulfonamides
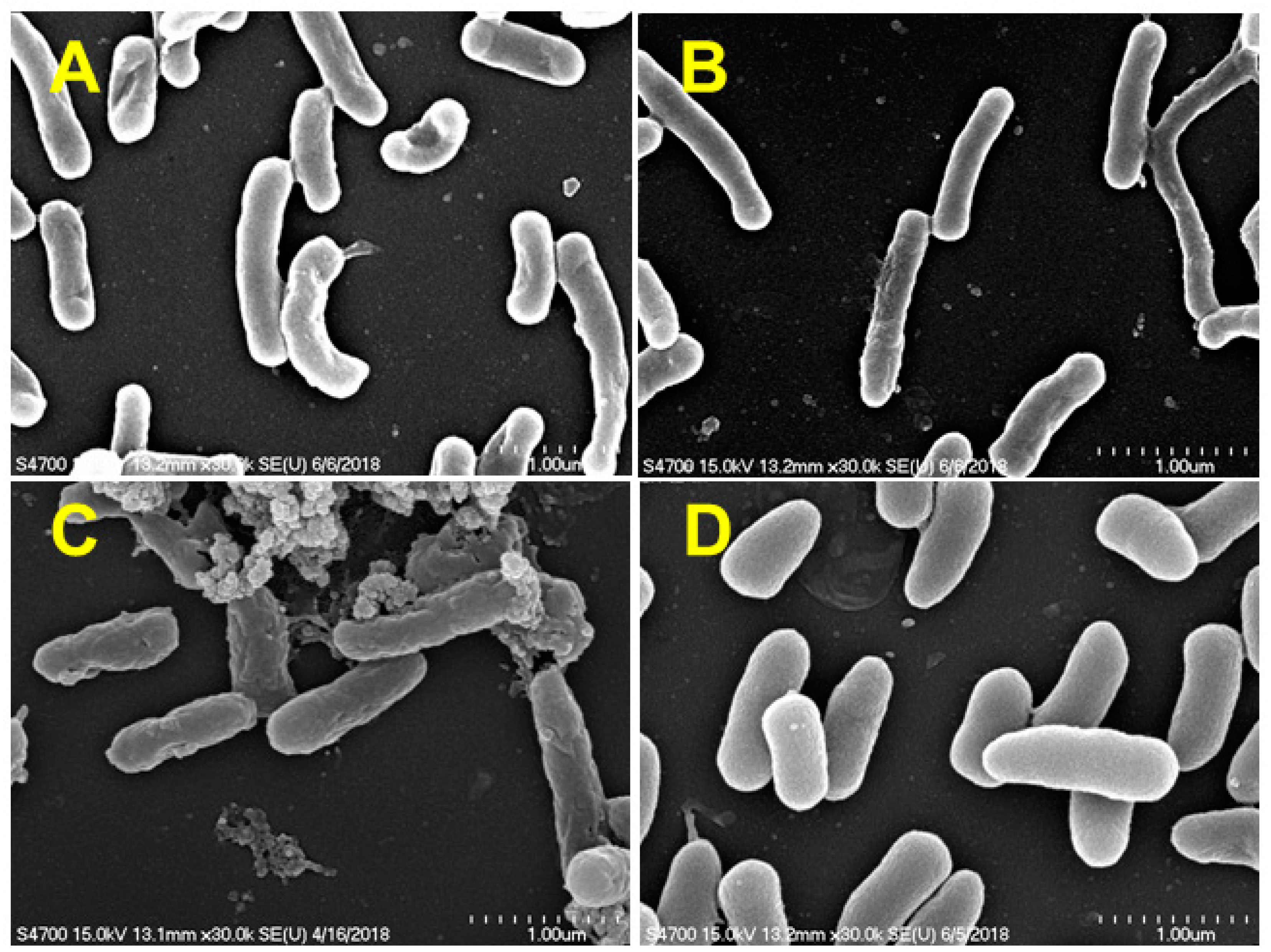
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscope
2.6. Next-Generation Sequencing and Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
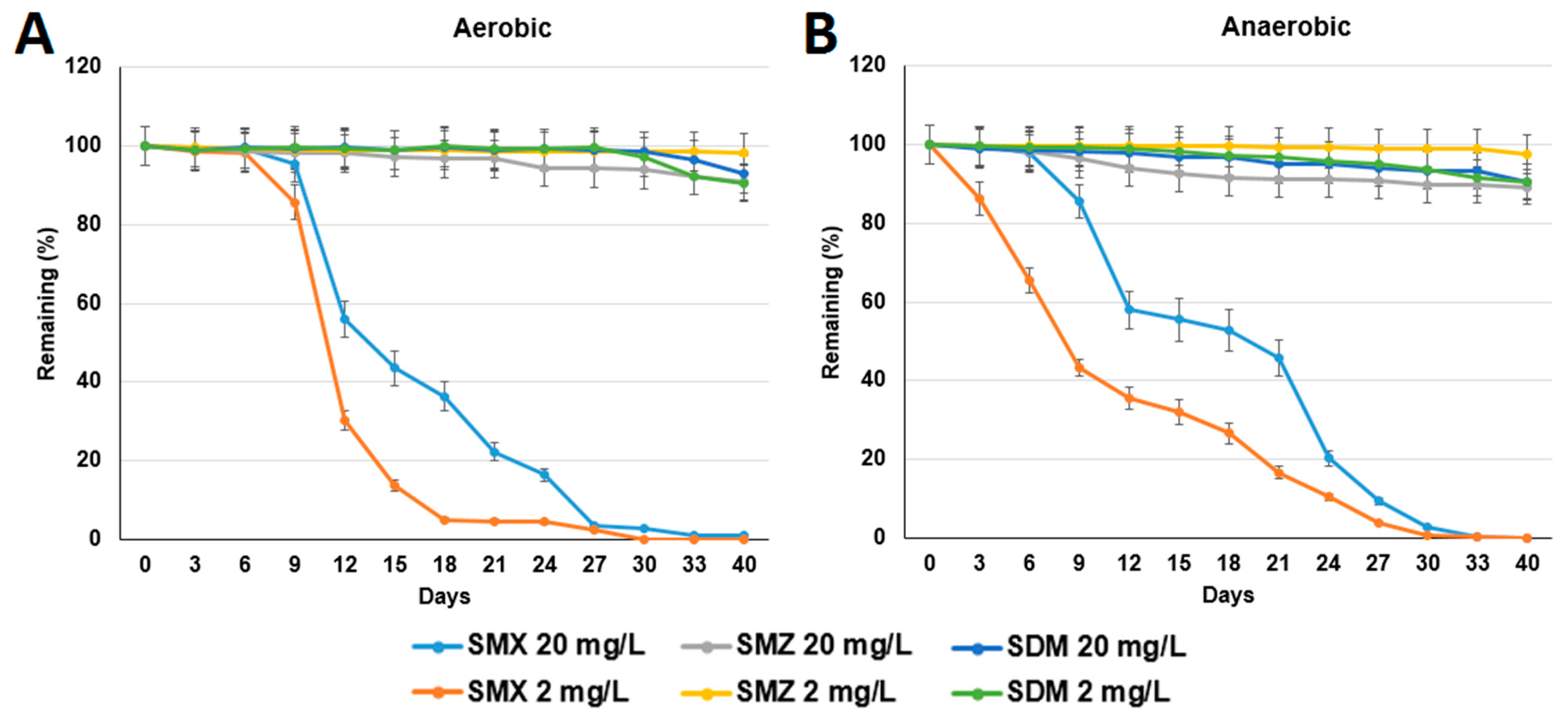
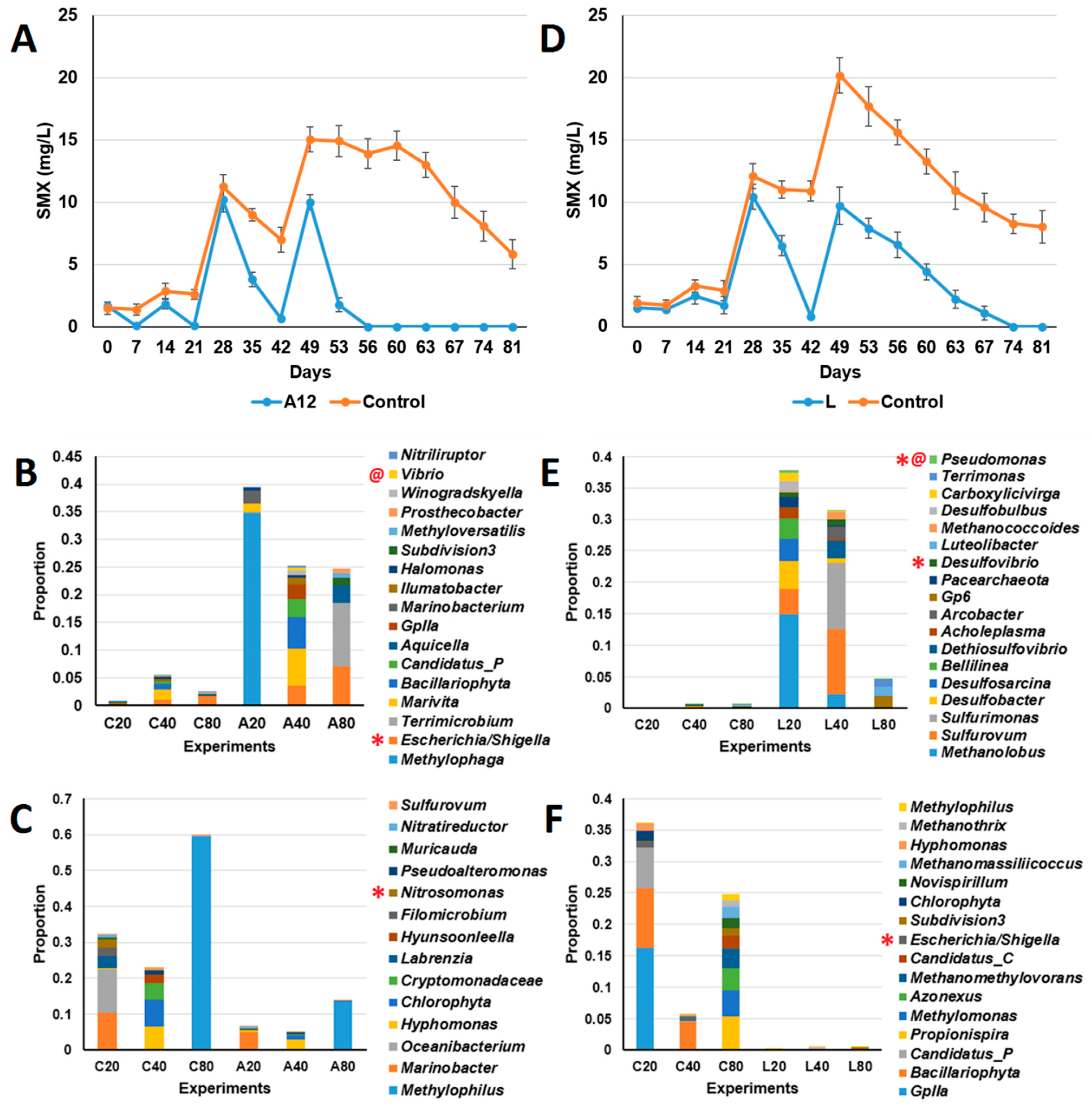
3.1. Test of Sulfonamide Degradation in Milkfish Pond Sediments
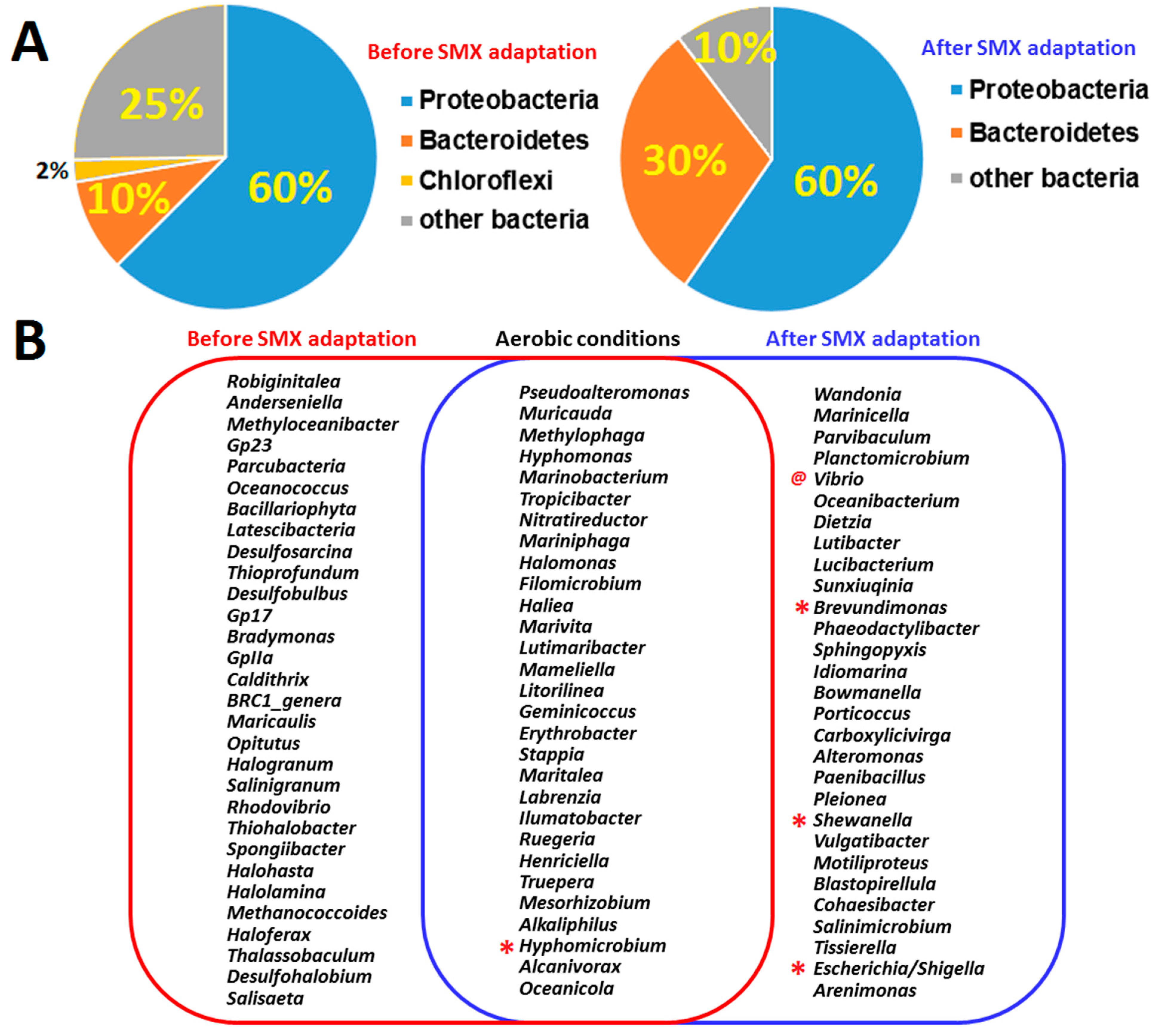
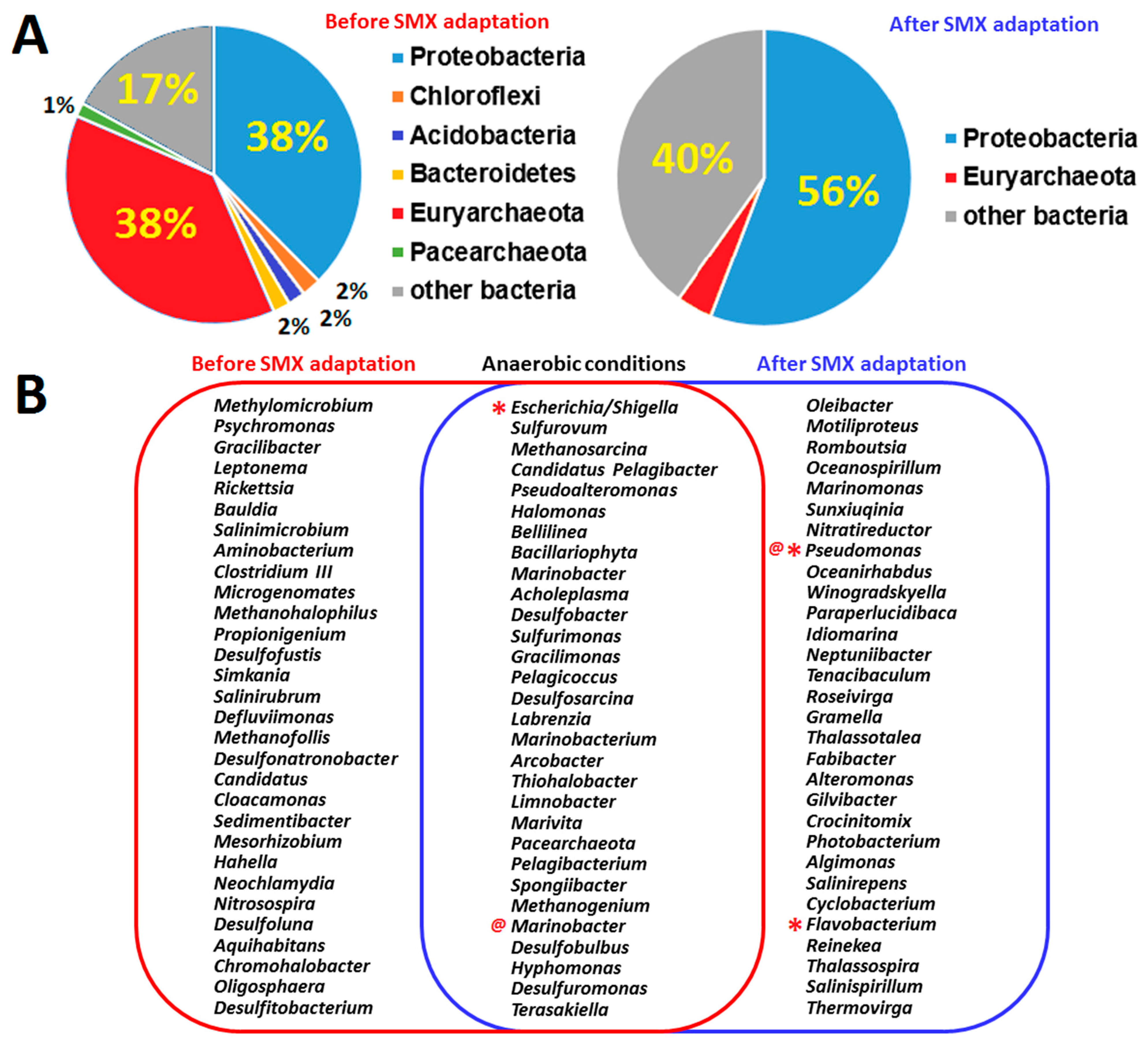
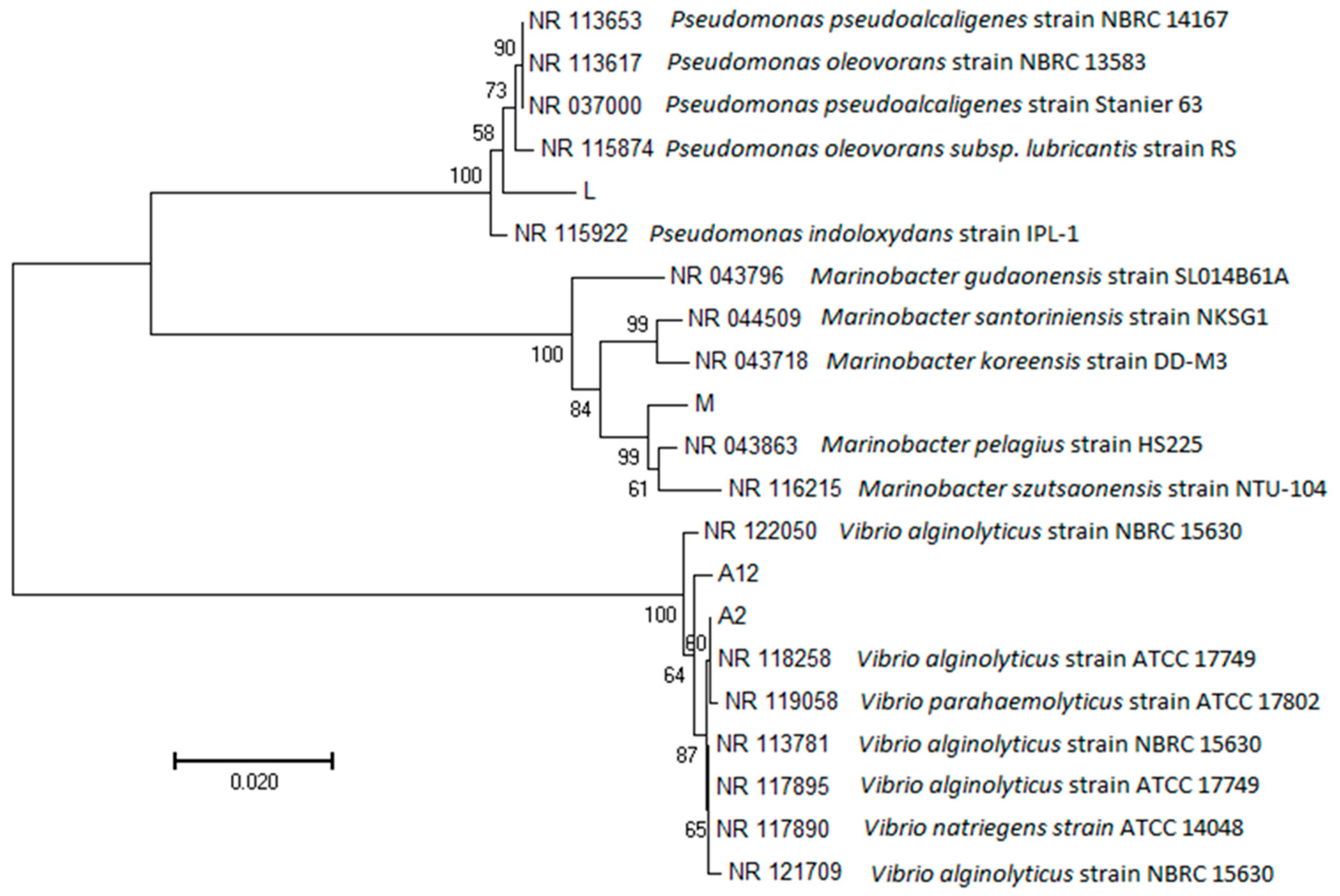
3.2. Isolation and Identification of Sulfamethoxazole-Degrading Bacteria
3.3. Test of Sulfamethoxazole-Degrading Ability of Isolated Bacteria
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Opiyo, M.A.; Marijani, E.; Muendo, P.; Odede, R.; Leschen, W.; Charo-Karisa, H. A review of aquaculture production and health management practices of farmed fish in Kenya. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Med. 2018, 6, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, A.; Takada, H.; Koike, T.; Takeshita, A.; Saha, M.; Rinawati; Nakada, N.; Murata, A.; Suzuki, T.; Suzuki, S.; et al. Ubiquitous occurrence of sulfonamides in tropical Asian waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 452–453, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, N.; Wang, B.; Fang, H.; Fu, C.; Tang, C.; Jiang, F.; Zhou, Y.; He, G.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Antibiotics detected in urines and adipogenesis in school children. Environ. Int. 2016, 89, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Li, L.; Zhang, C.; Kamira, B.; Qiu, L.; Fan, L.; Wu, W.; Meng, S.; Hu, G.; Chen, J. Occurrence and human dietary assessment of sulfonamide antibiotics in cultured fish around Tai Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 17493–17499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzariai, A.; Hafidi, M.; Khadra, A.; Aemig, Q.; El Fels, L.; Barret, M.; Merlina, G.; Patureau, D.; Pinelli, E. Human and veterinary antibiotics during composting of sludge or manure: Global perspectives on persistence, degradation, and resistance genes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 359, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Microbial degradation of sulfamethoxazole in the environment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 3573–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabanal, H.R. Development of the aquaculture industry in Southeast Asia. In Perspectives in Aquaculture Development in Southeast Asia and Japan; Juario, J.V., Benitez, L.V., Eds.; SEAFDEC Aquaculture Department: Tigbauan, Philippines, 1988; pp. 3–37. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, F.S.; Tseng, M.C.; Yeh, S.P. Milkfish (Chanos chanos) culture: Situations and trends. J. Fish. Soc. Taiwan 2006, 33, 229–244. [Google Scholar]
- OECD/OCDE. Aerobic Mineralisation in Surface Water—Simulation Biodegradation Test. In Oecd Guideline for the Testing of Chemicals; INGENTA: Oxford, UK, 2004; p. 309. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.W.; Tsai, L.L.; Chang, B.V. Anaerobic degradation of sulfamethoxazole in mangrove sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1446–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahed, M.A.; Aziz, H.A.; Isa, M.H.; Mohajeri, L.; Mohajeri, S.; Kutty, S.R. Kinetic modeling and half life study on bioremediation of crude oil dispersed by Corexit 9500. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benotti, M.J.; Brownawell, B.J. Microbial degradation of pharmaceuticals in estuarine and coastal seawater. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chang, Q.; Li, S.; Gao, M.; She, Z.; Guo, L.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, C.; Zheng, D.; Xu, Q. Impact of sulfadiazine on performance and microbial community of a sequencing batch biofilm reactor treating synthetic mariculture wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 235, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, B.; Lemmer, H.; Horn, H.; Muller, E. Characterization of pure cultures isolated from sulfamethoxazole-acclimated activated sludge with respect to taxonomic identification and sulfamethoxazole biodegradation potential. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.W.; Wen, Y.Y.; Niu, Z.L.; Yin, K.; Xu, D.X.; Chen, L.X. Isolation and characterization of sulfonamide-degrading bacteria Escherichia sp. HS21 and Acinetobacter sp. HS51. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhao, F. Rapid degradation of sulphamethoxazole and the further transformation of 3-amino-5-methylisoxazole in a microbial fuel cell. Water Res. 2016, 88, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, N. A soil Flavobacterium sp. that degrades sulphanilamide and asulam. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1978, 45, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzierzewicz, Z.; Cwalina, B.; Weglarz, L.; Wi?niowska, B.; Szczerba, J. Susceptibility of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans intestinal strains to sulfasalazine and its biotransformation products. Med. Sci. Monit. 2004, 10, BR185–BR190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Jia, G.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Y. Occurrence, distribution and ecological risks of antibiotics and pesticides in coastal waters around Liaodong Peninsula, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limbu, S.M.; Zhou, L.; Sun, S.X.; Zhang, M.L.; Du, Z.Y. Chronic exposure to low environmental concentrations and legal aquaculture doses of antibiotics cause systemic adverse effects in Nile tilapia and provoke differential human health risk. Environ. Int. 2018, 115, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Steele, J.C.; Meng, X.Z. Usage, residue, and human health risk of antibiotics in Chinese aquaculture: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, B.-V.; Chao, W.-L.; Yeh, S.-L.; Kuo, D.-L.; Yang, C.-W. Biodegradation of Sulfamethoxazole in Milkfish (Chanos chanos) Pond Sediments. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9194000
Chang B-V, Chao W-L, Yeh S-L, Kuo D-L, Yang C-W. Biodegradation of Sulfamethoxazole in Milkfish (Chanos chanos) Pond Sediments. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(19):4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9194000
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Bea-Ven, Wei-Liang Chao, Shinn-Lih Yeh, Dong-Lin Kuo, and Chu-Wen Yang. 2019. "Biodegradation of Sulfamethoxazole in Milkfish (Chanos chanos) Pond Sediments" Applied Sciences 9, no. 19: 4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9194000
APA StyleChang, B.-V., Chao, W.-L., Yeh, S.-L., Kuo, D.-L., & Yang, C.-W. (2019). Biodegradation of Sulfamethoxazole in Milkfish (Chanos chanos) Pond Sediments. Applied Sciences, 9(19), 4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9194000




