Toward Bridging Future Irrigation Deficits Utilizing the Shark Algorithm Integrated with a Climate Change Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Objective
2. Methods
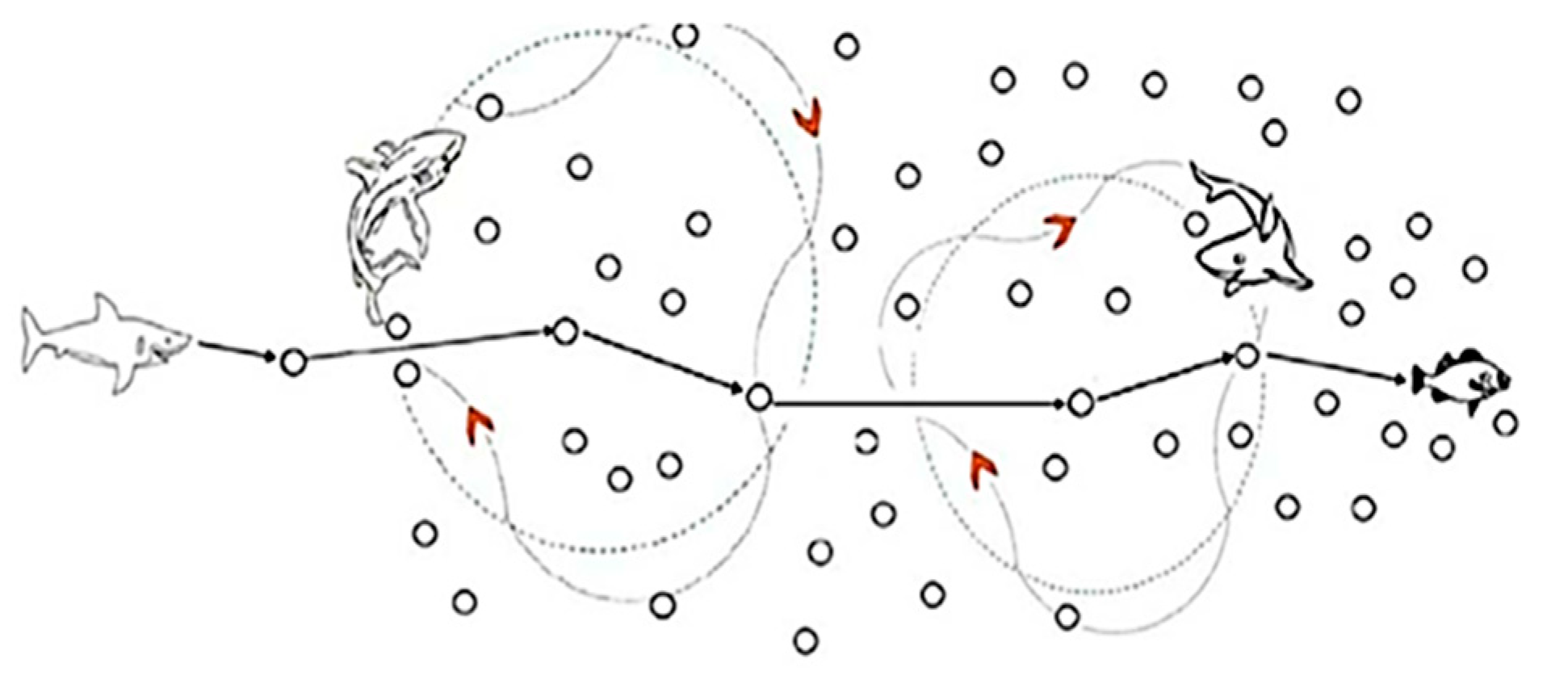
2.1. Shark Algorithm
- 1-
- Fish, as the prey of sharks, have been injured, and their bodies distribute blood. Thus, the wounded fish have a low velocity in the water.
- 2-
- Blood is regularly distributed in the water, and the odor particles that are closer to the fish allow the sharks to find the injured fish sooner.
- 3-
- There is a blood resource for each shark that each shark should find.
2.2. LARS-WG Model
- -
- Once all of the above parameter data files have been completed using (*.sce), all the required data are ready to use the LARS-WG model;
- -
- The average monthly rate of changes of wet and dry events;
- -
- Rate of change of the average monthly precipitation considering the long-term period;
- -
- Rate of change of the daily temperature (fluctuations) considering the long-term period;
- -
- The absolute difference of maximum and minimum monthly average temperature;
- -
- Absolute change of the monthly average radiation (long-term).
2.3. IHACRES Model
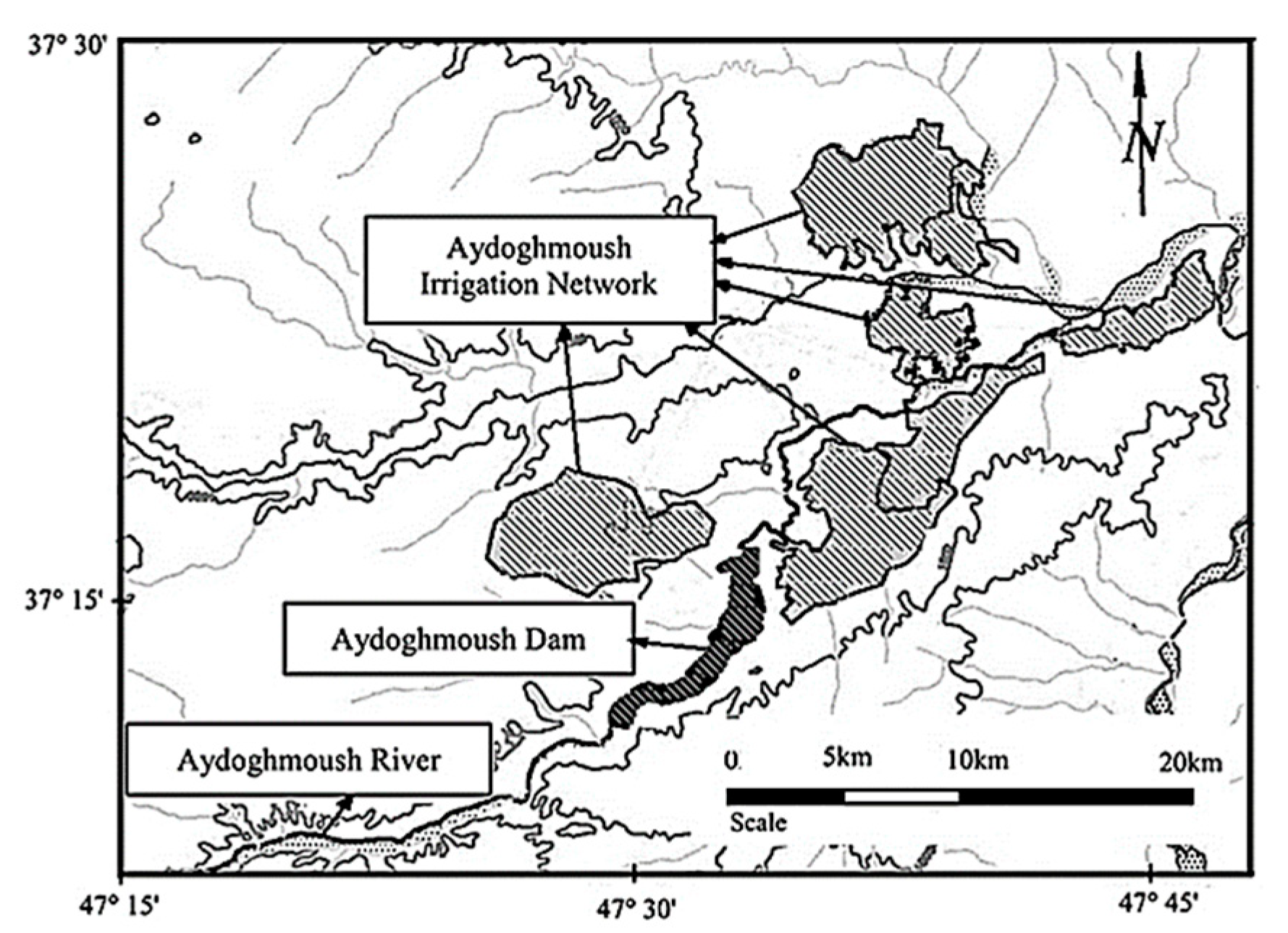
3. Case Study
- Reliability index
- Vulnerability index
- Resiliency index
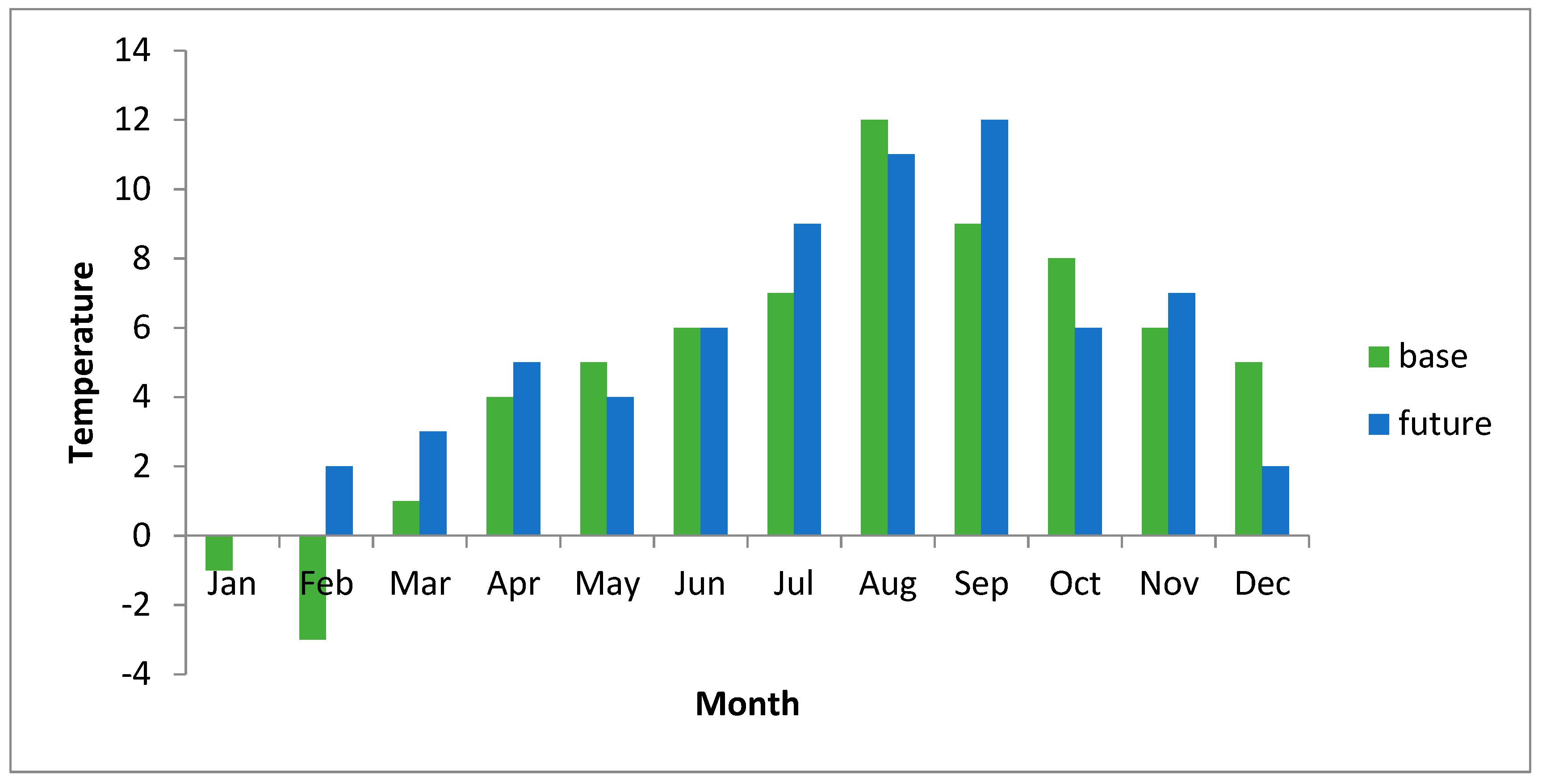
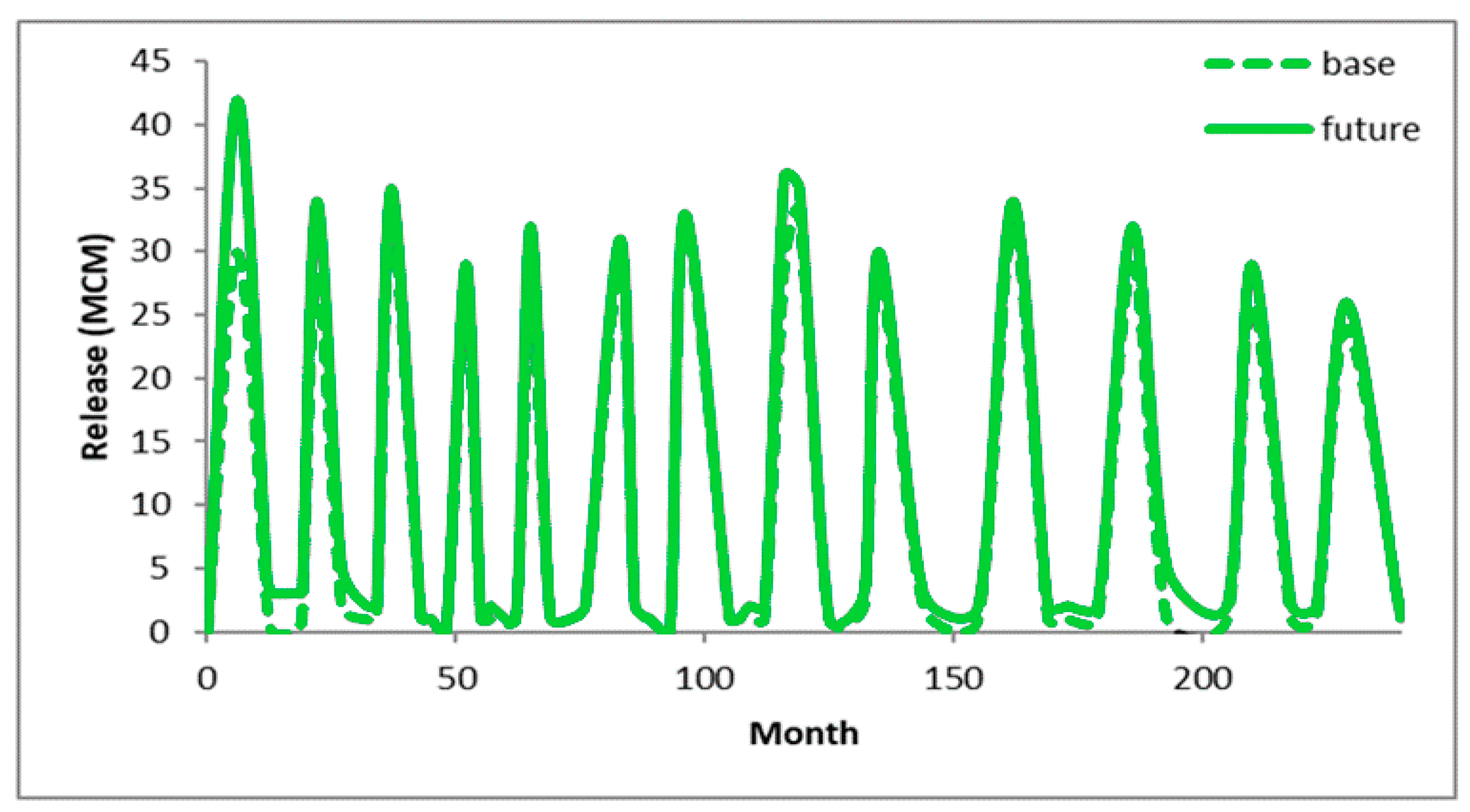
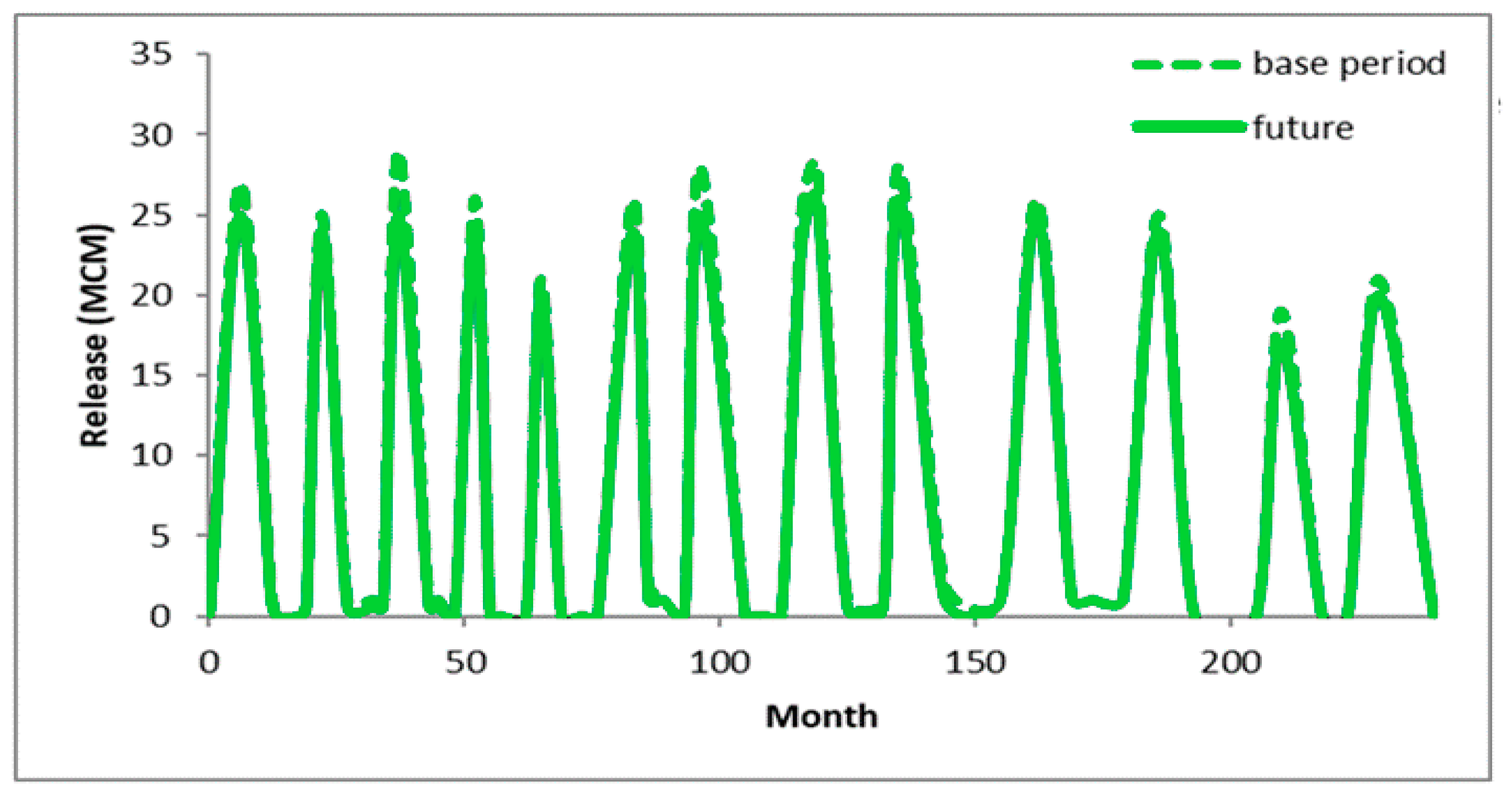
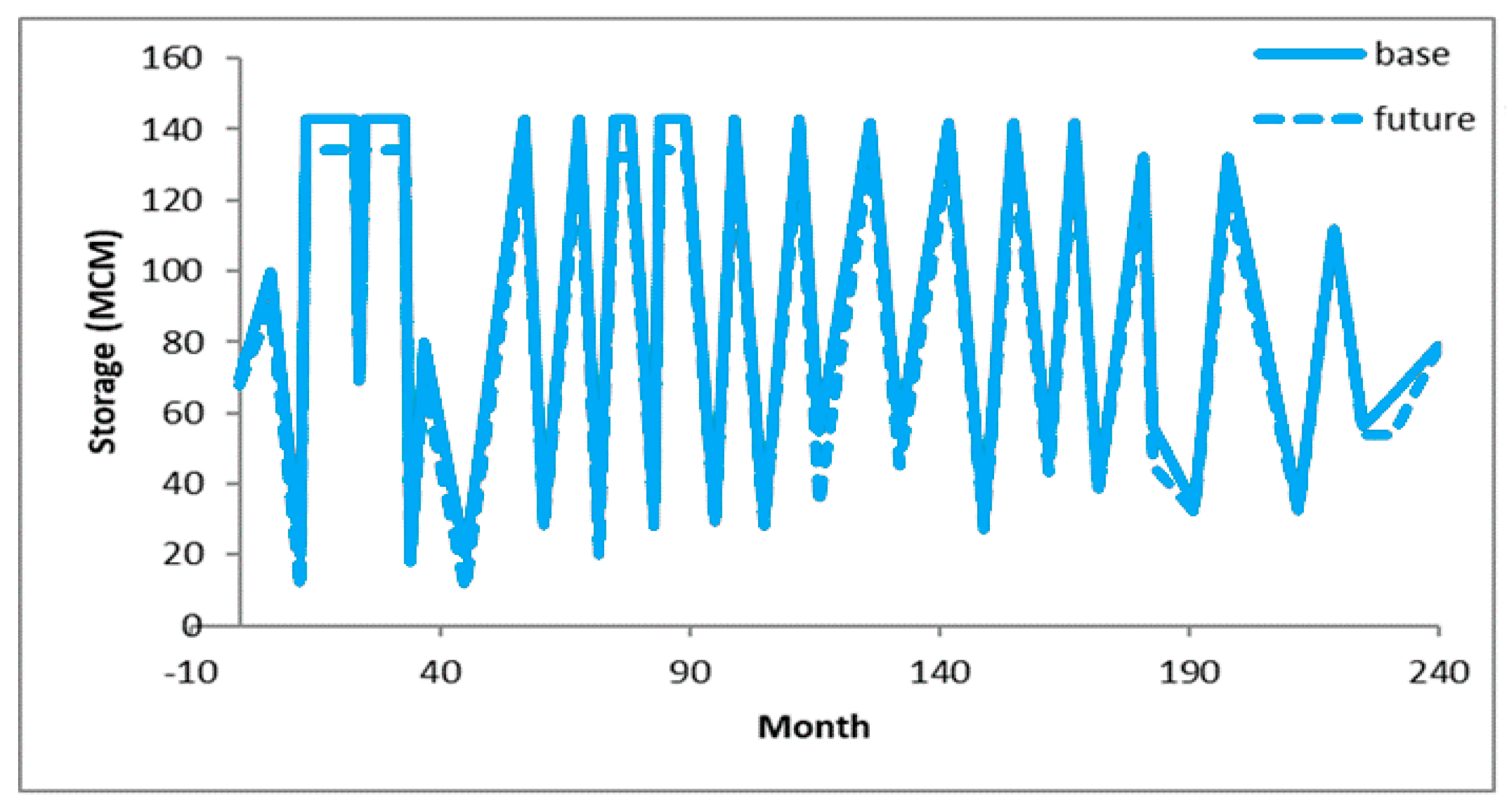
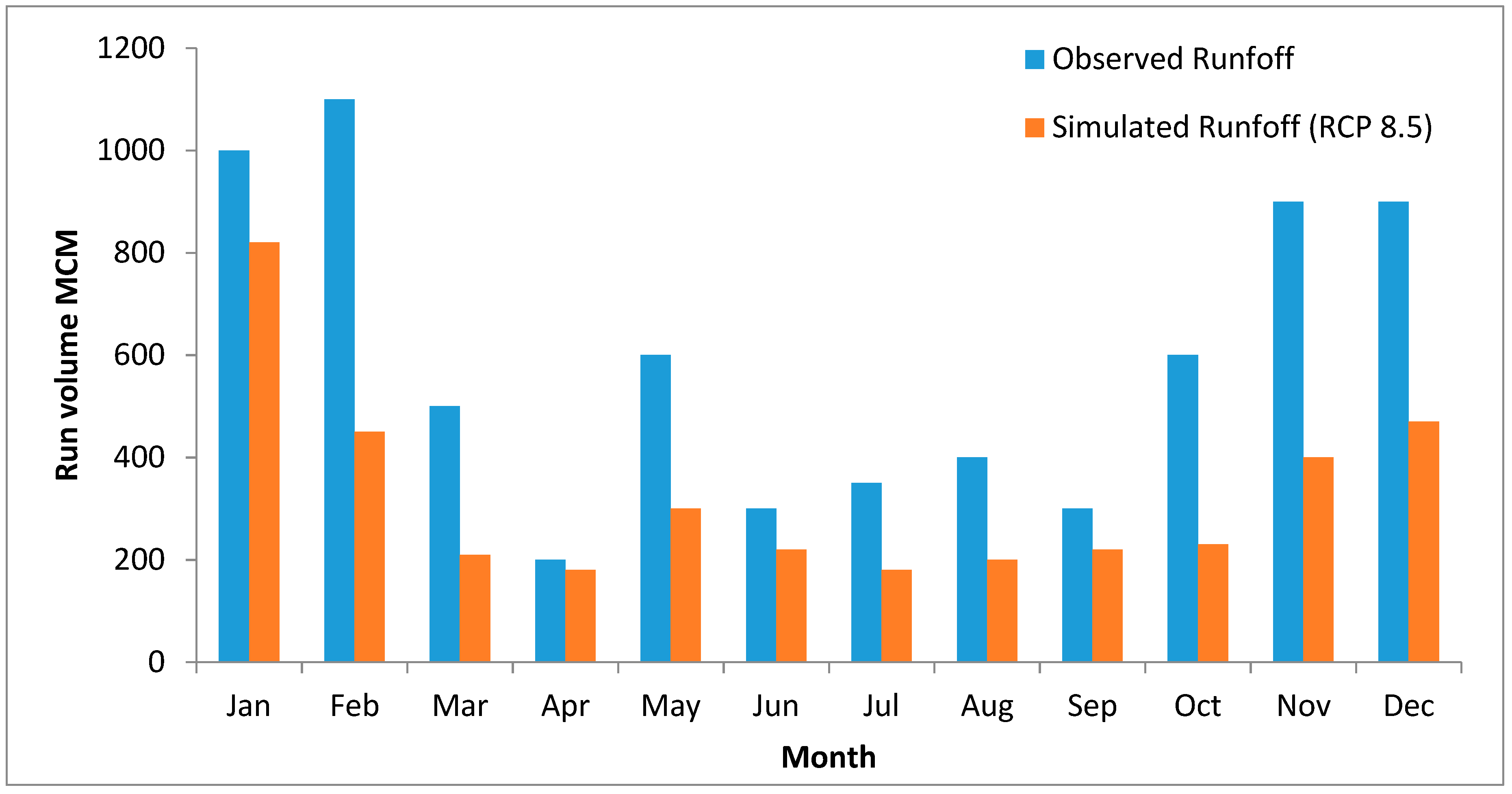
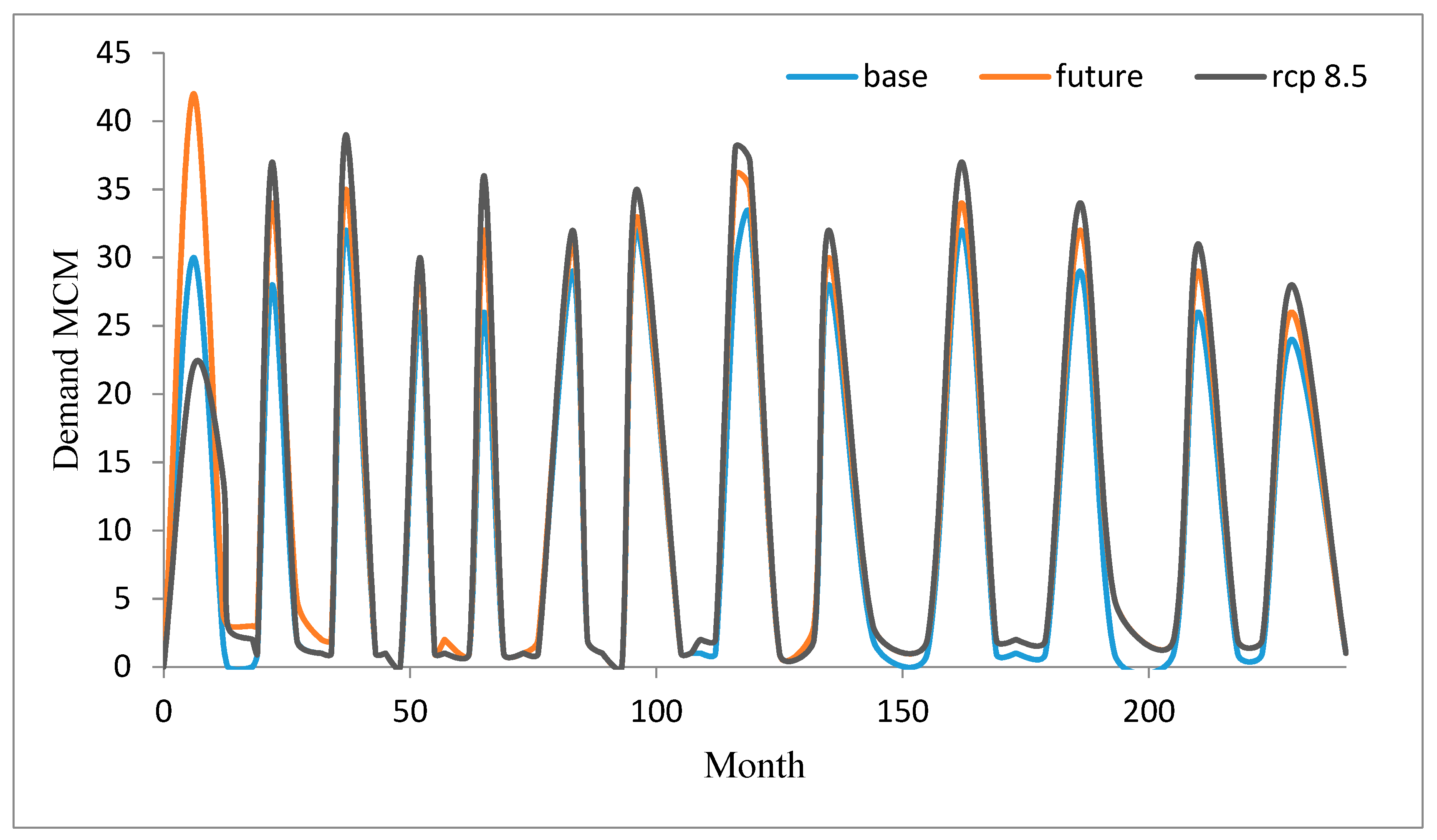
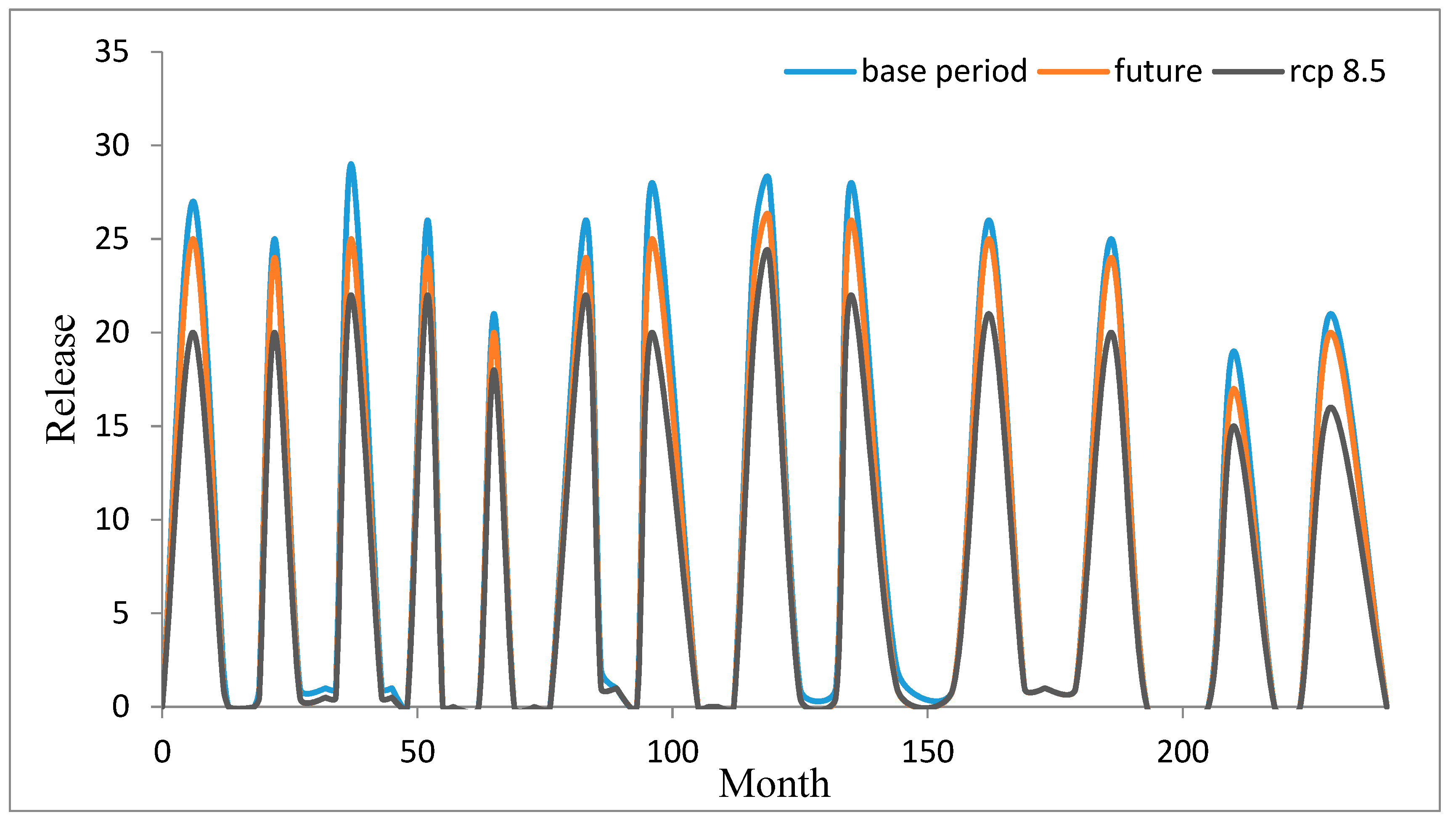
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jothiprakash, V.; Shanthi, G. Single Reservoir Operating Policies Using Genetic Algorithm. Water Resour. Manag. 2006, 20, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghian, M.; Rosbjerg, D.; Haghighi, A.; Madsen, H. Optimization of Conventional Rule Curves Coupled with Hedging Rules for Reservoir Operation. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2014, 140, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo Martínez, C.I.; Alfonso Piña, W.H.; Moreno, S.F. Prevention, mitigation and adaptation to climate change from perspectives of urban population in an emerging economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 178, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearnside, P.M. Tropical hydropower in the clean development mechanism: Brazil’s Santo Antônio Dam as an example of the need for change. Clim. Chang. 2015, 131, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, L.A.; Masih, I.; Jiang, Y.; Douven, W. Impact of reservoir operation and climate change on the hydrological regime of the Sesan and Srepok Rivers in the Lower Mekong Basin. Clim. Chang. 2016, 149, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kling, H.; Fuchs, M.; Paulin, M. Runoff conditions in the upper Danube basin under an ensemble of climate change scenarios. J. Hydrol. 2012, 424, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.J.; Ponnambalam, K.; Karray, F. Reservoir Operation Using a Dynamic Programming Fuzzy Rule–Based Approach. Water Resour. Manag. 2005, 19, 655–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, A.; Bozorg Haddad, O.; Mariño, M.A. Algorithm for Increasing the Speed of Evolutionary Optimization and its Accuracy in Multi-objective Problems. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 2231–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullenward, D.; Victor, D.G. The Dam Debate and its Discontents. Clim. Chang. 2006, 75, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.; Culver, T.B.; Block, P.J.; McCartney, M.P. Evaluating the impact and uncertainty of reservoir operation for malaria control as the climate changes in Ethiopia. Clim. Chang. 2016, 136, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, J.T.; Wood, A.W.; Hamlet, A.F.; Palmer, R.N.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Mitigating the Effects of Climate Change on the Water Resources of the Columbia River Basin. Clim. Chang. 2004, 62, 233–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, N.S.; Wood, A.W.; Voisin, N.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Palmer, R.N. The Effects of Climate Change on the Hydrology and Water Resources of the Colorado River Basin. Clim. Chang. 2004, 62, 337–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumbroso, D.M.; Woolhouse, G.; Jones, L. A review of the consideration of climate change in the planning of hydropower schemes in sub-Saharan Africa. Clim. Chang. 2015, 133, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; El-Shafie, A. Intelligent Systems in Optimizing Reservoir Operation Policy: A Review. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 3387–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shafie, A.H.; El-Manadely, M.S. An integrated neural network stochastic dynamic programming model for optimizing the operation policy of Aswan High Dam. Hydrol. Res. 2010, 42, 50–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azamathulla, H.M.; Wu, F.C.; Ghani, A.A.; Narulkar, S.M.; Zakaria, N.A.; Chang, C.K. Comparison between genetic algorithm and linear programming approach for real time operation. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2008, 2, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noory, H.; Liaghat, A.M.; Parsinejad, M.; Haddad, O.B. Optimizing Irrigation Water Allocation and Multicrop Planning Using Discrete PSO Algorithm. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2012, 138, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.J.; Kumar, D.N. Optimal reservoir operation using multi-objective evolutionary algorithm. Water Resour. Manag. 2006, 20, 861–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, A.; Bozorg Haddad, O.; Mariño, M.A.; Adams, B.J. Honey-bee mating optimization (HBMO) algorithm for optimal reservoir operation. J. Frankl. Inst. 2007, 344, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozorg Haddad, O.; Afshar, A.; Mariño, M.A. Design-Operation of Multi-Hydropower Reservoirs: HBMO Approach. Water Resour. Manag. 2008, 22, 1709–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.-C.; Chang, F.-J. Multi-objective evolutionary algorithm for operating parallel reservoir system. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah-Mehdipour, E.; Bozorg Haddad, O.; Mariño, M.A. Real-Time Operation of Reservoir System by Genetic Programming. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 4091–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozorg-Haddad, O.; Karimirad, I.; Seifollahi-Aghmiuni, S.; Loáiciga, H.A. Development and Application of the Bat Algorithm for Optimizing the Operation of Reservoir Systems. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2015, 141, 04014097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashofteh, P.-S.; Haddad, O.B.; Akbari-Alashti, H.; Mariño, M.A. Determination of Irrigation Allocation Policy under Climate Change by Genetic Programming. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2015, 141, 4014059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahandideh-Tehrani, M.; Bozorg Haddad, O.; Loáiciga, H.A. Hydropower Reservoir Management Under Climate Change: The Karoon Reservoir System. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 749–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Haddad, O.B.; Loáiciga, H.A. Adaptive Reservoir Operation Rules Under Climatic Change. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 29, 1247–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzabiras, J.; Vasiliades, L.; Sidiropoulos, P.; Loukas, A.; Mylopoulos, N. Evaluation of Water Resources Management Strategies to Overturn Climate Change Impacts on Lake Karla Watershed. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 5819–5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Guo, S.; Li, L.; Hong, X.; Wang, L. Multi-Objective Operating Rules for Danjiangkou Reservoir Under Climate Change. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 30, 1183–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehteram, M.; Mousavi, S.F.; Karami, H.; Farzin, S.; Singh, V.P.; Chau, K.; El-Shafie, A. Reservoir operation based on evolutionary algorithms and multi-criteria decision-making under climate change and uncertainty. J. Hydroinform. 2018, 20, 332–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehteram, M.; Karami, H.; Mousavi, S.F.; El-Shafie, A.; Amini, Z. Optimizing dam and reservoirs operation based model utilizing shark algorithm approach. Knowl. Based Syst. 2017, 122, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajeh, S.; Paimozd, S.; Moghaddasi, M. Assessing the Impact of Climate Changes on Hydrological Drought Based on Reservoir Performance Indices (Case Study: ZayandehRud River Basin, Iran). Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 2595–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshan, G.; Ghanghermeh, A.; Nasrabadi, T.; Meimandi, J.B. Effect of Global Warming on Intensity and Frequency Curves of Precipitation, Case Study of Northwestern Iran. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedinia, O.; Amjady, N.; Ghadimi, N. Solar energy forecasting based on hybrid neural network and improved metaheuristic algorithm. Comput. Intell. 2017, 34, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashofteh, P.S.; Haddad, O.B.; Mariño, M.A. Climate Change Impact on Reservoir Performance Indexes in Agricultural Water Supply. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2013, 139, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racsko, P.; Szeidl, L.; Semenov, M. A serial approach to local stochastic weather models. Ecol. Model. 1991, 57, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadzadeh Araji, H.; Wayayok, A.; Massah Bavani, A.; Amiri, E.; Abdullah, A.F.; Daneshian, J.; Teh, C.B.S. Impacts of climate change on soybean production under different treatments of field experiments considering the uncertainty of general circulation models. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 205, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazavi, R.; Ebrahimi, H. Predicting the impacts of climate change on groundwater recharge in an arid environment using modeling approach. Int. J. Clim. Chang. Strateg. Manag. 2019, 11, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanikhani, H.; Kisi, O.; Amirataee, B. Impact of climate change on runoff in Lake Urmia basin, Iran. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2017, 132, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashofteh, P.-S.; Haddad, O.B.; Loáiciga, H.A. Evaluation of Climatic-Change Impacts on Multiobjective Reservoir Operation with Multiobjective Genetic Programming. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2015, 141, 4015030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

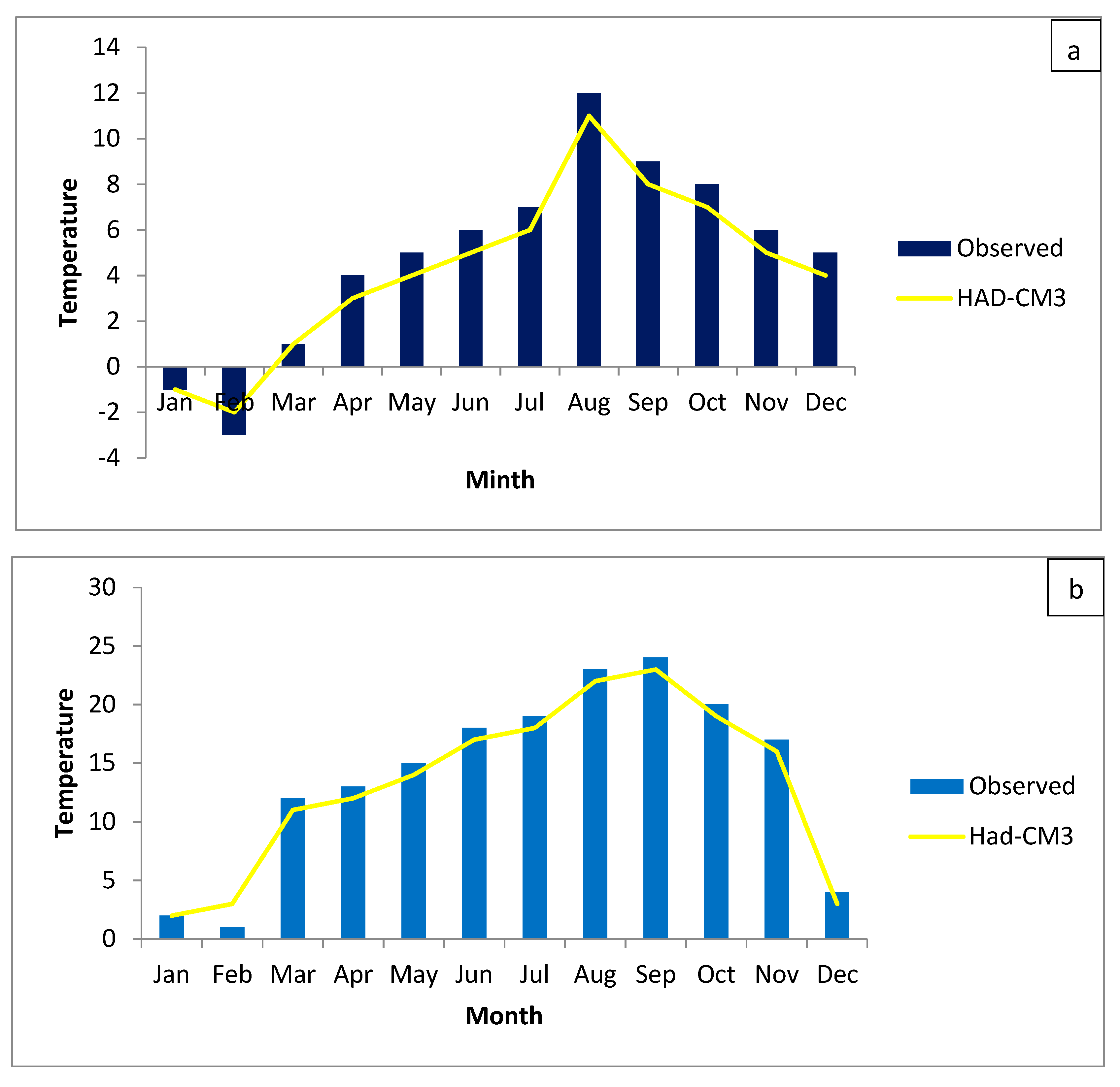
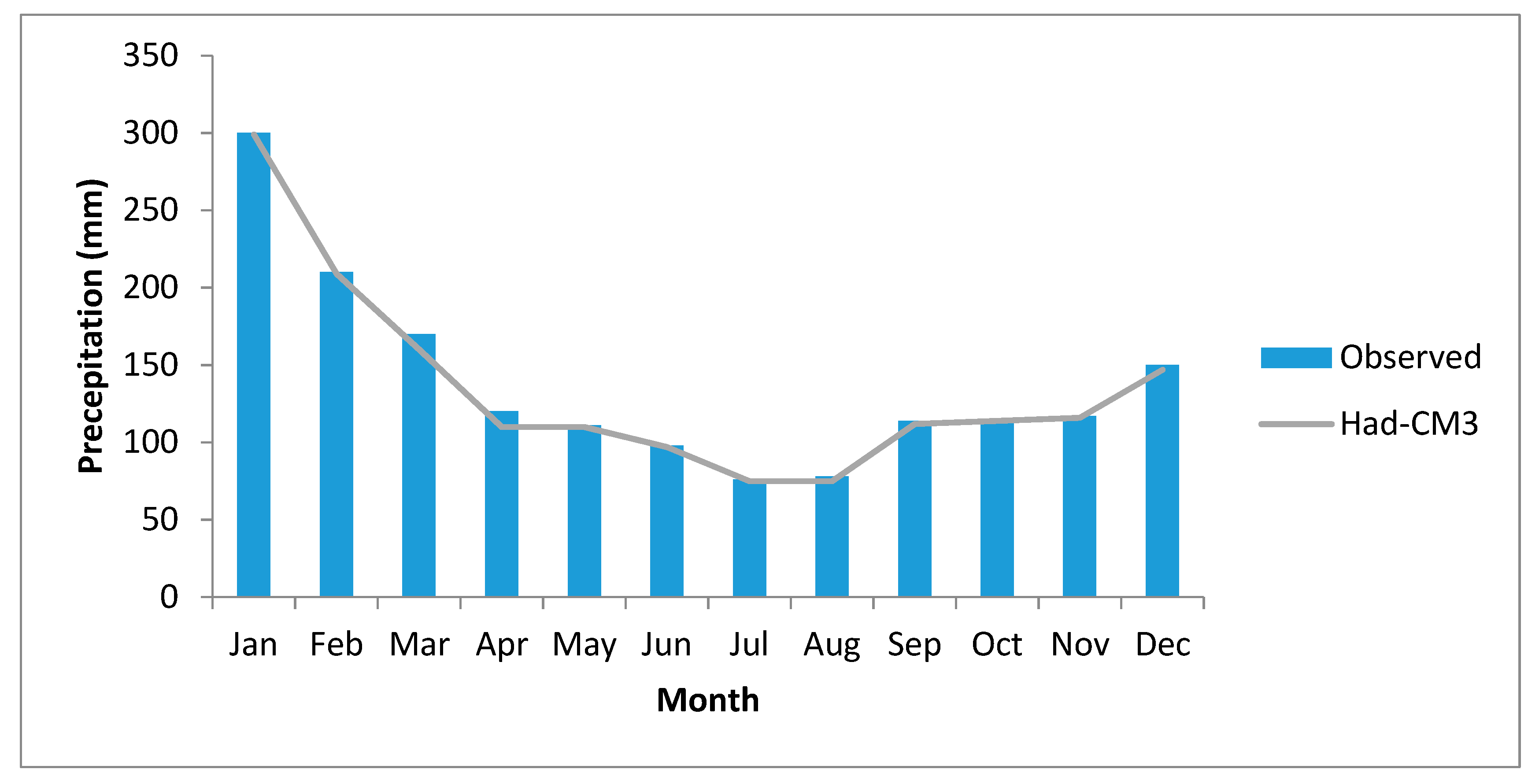
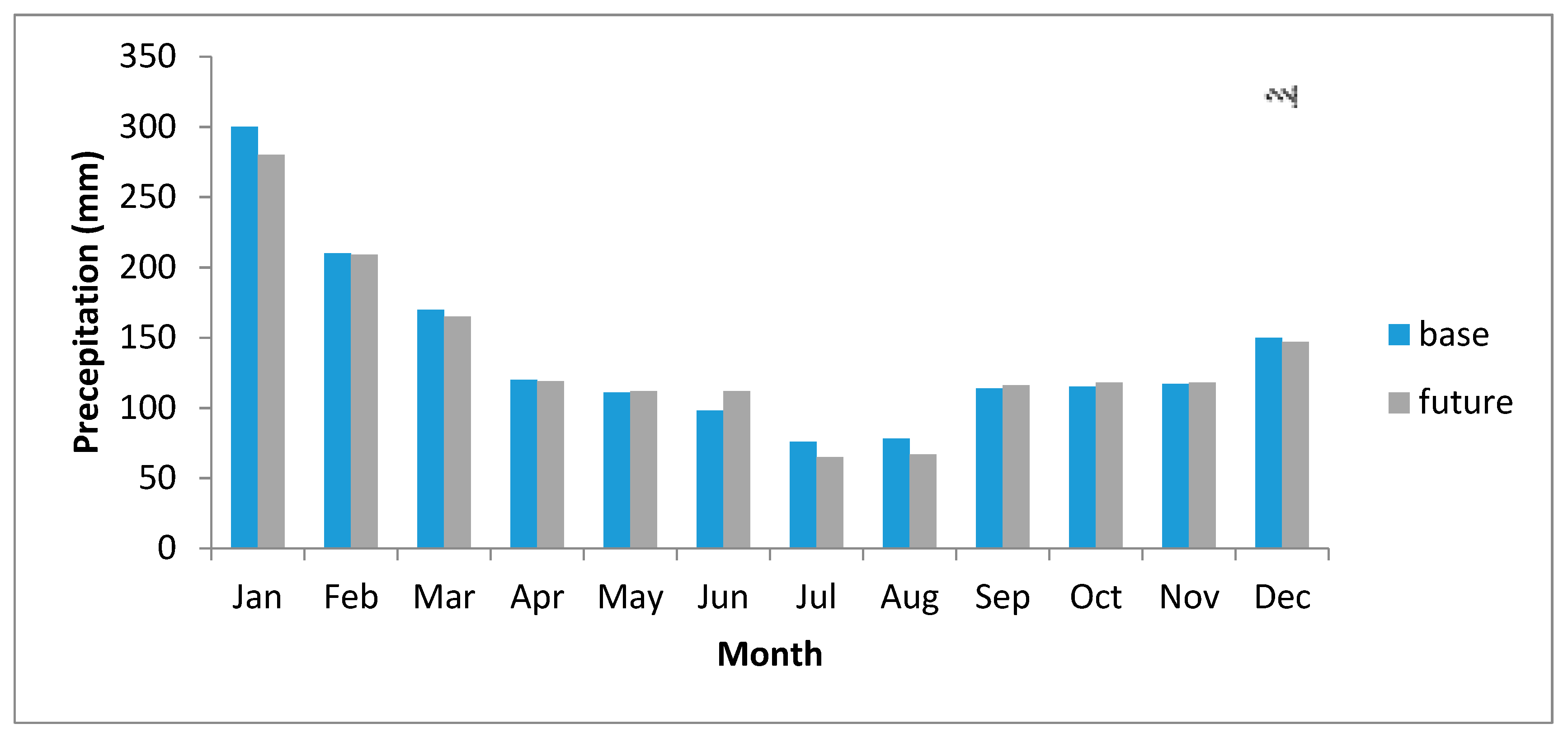
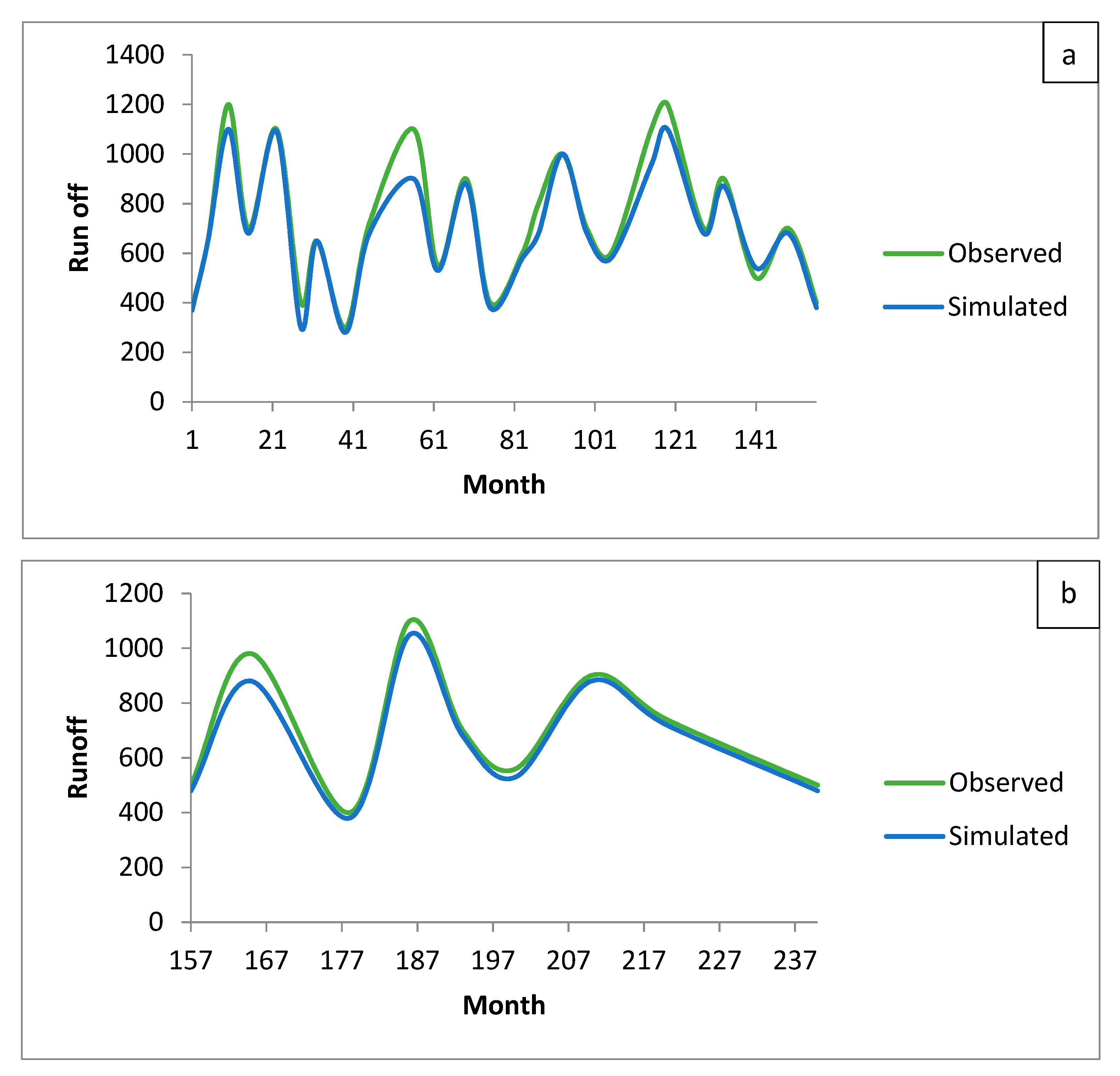
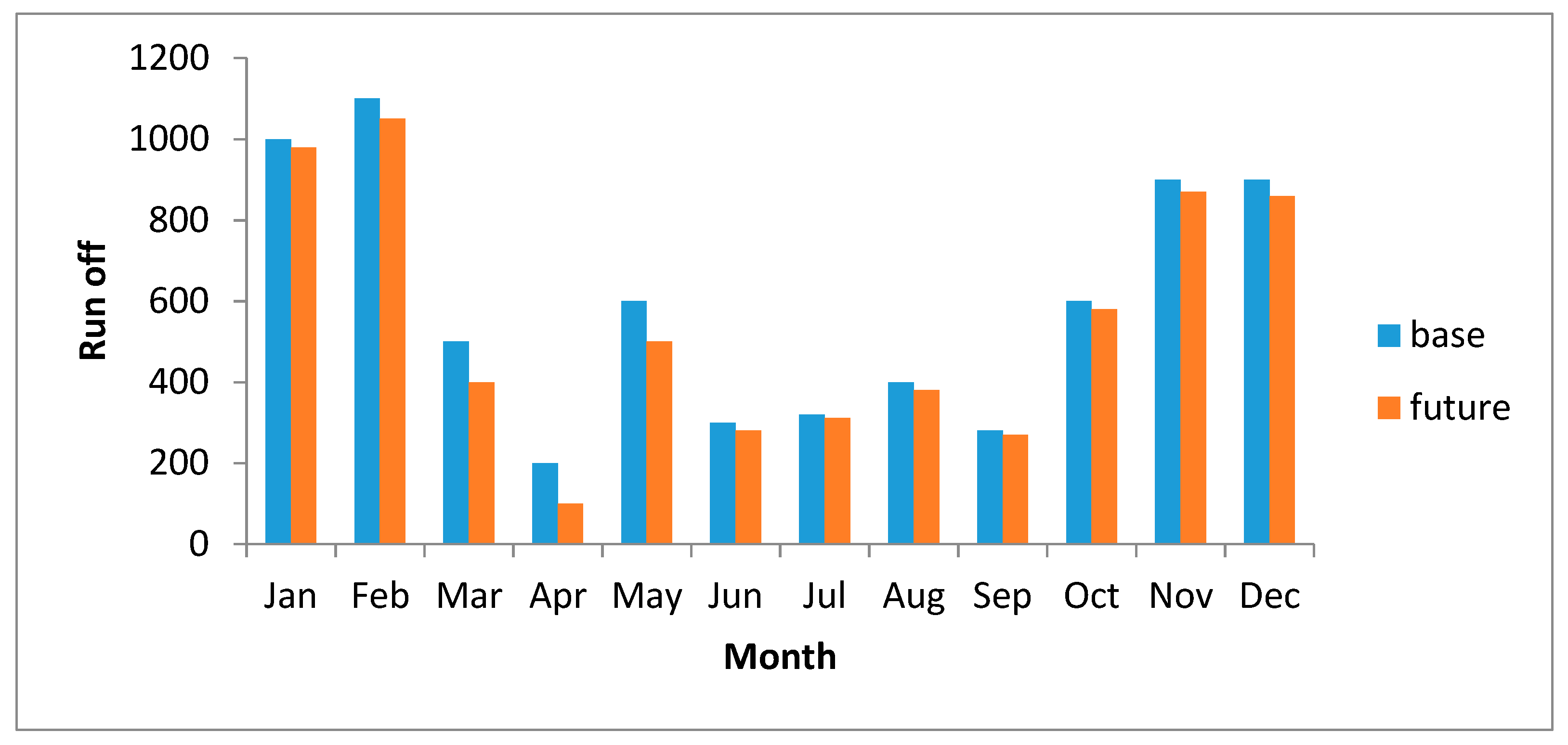


| Parameter | R2 | RMSE | MBE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum temperature | 0.94 | 4 | 2 |
| Minimum temperature | 0.96 | 3.5 | 1.5 |
| Parameter | R2 | RMSE (106 m3) | MBE (106 m3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | 0.96 | 3 | 1 |
| Verification | 0.92 | 5 | 3 |
| Base Period | |||||
| Population Size | Objective Function | α | Objective Function | M | Objective Function |
| 10 | 1.454 | 0.58 | 1.565 | 10 | 1.454 |
| 30 | 1.312 | 0.68 | 1.476 | 20 | 1.412 |
| 50 | 1.455 | 0.78 | 1.312 | 30 | 1.311 |
| 70 | 1.576 | 0.88 | 1.415 | 40 | 1.398 |
| Future Period | |||||
| 10 | 1.678 | 0.58 | 1.594 | 10 | 1.611 |
| 30 | 1.612 | 0.68 | 1.525 | 20 | 1.567 |
| 50 | 1.525 | 0.78 | 1.567 | 30 | 1.525 |
| 70 | 1.567 | 0.88 | 1.578 | 40 | 1.545 |
| Run | Base Period | Future Period |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.455 | 1.529 |
| 2 | 1.457 | 1.525 |
| 3 | 1.455 | 1.525 |
| 4 | 1.455 | 1.525 |
| 5 | 1.455 | 1.525 |
| 6 | 1.455 | 1.525 |
| 7 | 1.455 | 1.525 |
| 8 | 1.455 | 1.525 |
| 9 | 1.455 | 1.525 |
| 10 | 1.455 | 1.525 |
| Average solution | 1.455 | 1.525 |
| Variation coefficient | 0.0006 | 0.0008 |
| Global solution | 1.454 |
| Index | Reliability | Vulnerability | Resiliency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base | 96% | 14% | 34% |
| Future | 89% | 22% | 27% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ehteram, M.; El-Shafie, A.H.; Hin, L.S.; Othman, F.; Koting, S.; Karami, H.; Mousavi, S.-F.; Farzin, S.; Ahmed, A.N.; Bin Zawawi, M.H.; et al. Toward Bridging Future Irrigation Deficits Utilizing the Shark Algorithm Integrated with a Climate Change Model. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3960. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9193960
Ehteram M, El-Shafie AH, Hin LS, Othman F, Koting S, Karami H, Mousavi S-F, Farzin S, Ahmed AN, Bin Zawawi MH, et al. Toward Bridging Future Irrigation Deficits Utilizing the Shark Algorithm Integrated with a Climate Change Model. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(19):3960. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9193960
Chicago/Turabian StyleEhteram, Mohammad, Amr H. El-Shafie, Lai Sai Hin, Faridah Othman, Suhana Koting, Hojat Karami, Sayed-Farhad Mousavi, Saeed Farzin, Ali Najah Ahmed, Mohd Hafiz Bin Zawawi, and et al. 2019. "Toward Bridging Future Irrigation Deficits Utilizing the Shark Algorithm Integrated with a Climate Change Model" Applied Sciences 9, no. 19: 3960. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9193960
APA StyleEhteram, M., El-Shafie, A. H., Hin, L. S., Othman, F., Koting, S., Karami, H., Mousavi, S.-F., Farzin, S., Ahmed, A. N., Bin Zawawi, M. H., Hossain, M. S., Mohd, N. S., Afan, H. A., & El-Shafie, A. (2019). Toward Bridging Future Irrigation Deficits Utilizing the Shark Algorithm Integrated with a Climate Change Model. Applied Sciences, 9(19), 3960. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9193960












