Locating the Source of Diffusion in Complex Networks via Gaussian-Based Localization and Deduction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Problem Definition
2.2. Source Localization on Arbitrary Trees
2.3. Source Localization on General Graphs
2.4. Computational Complexity Analysis
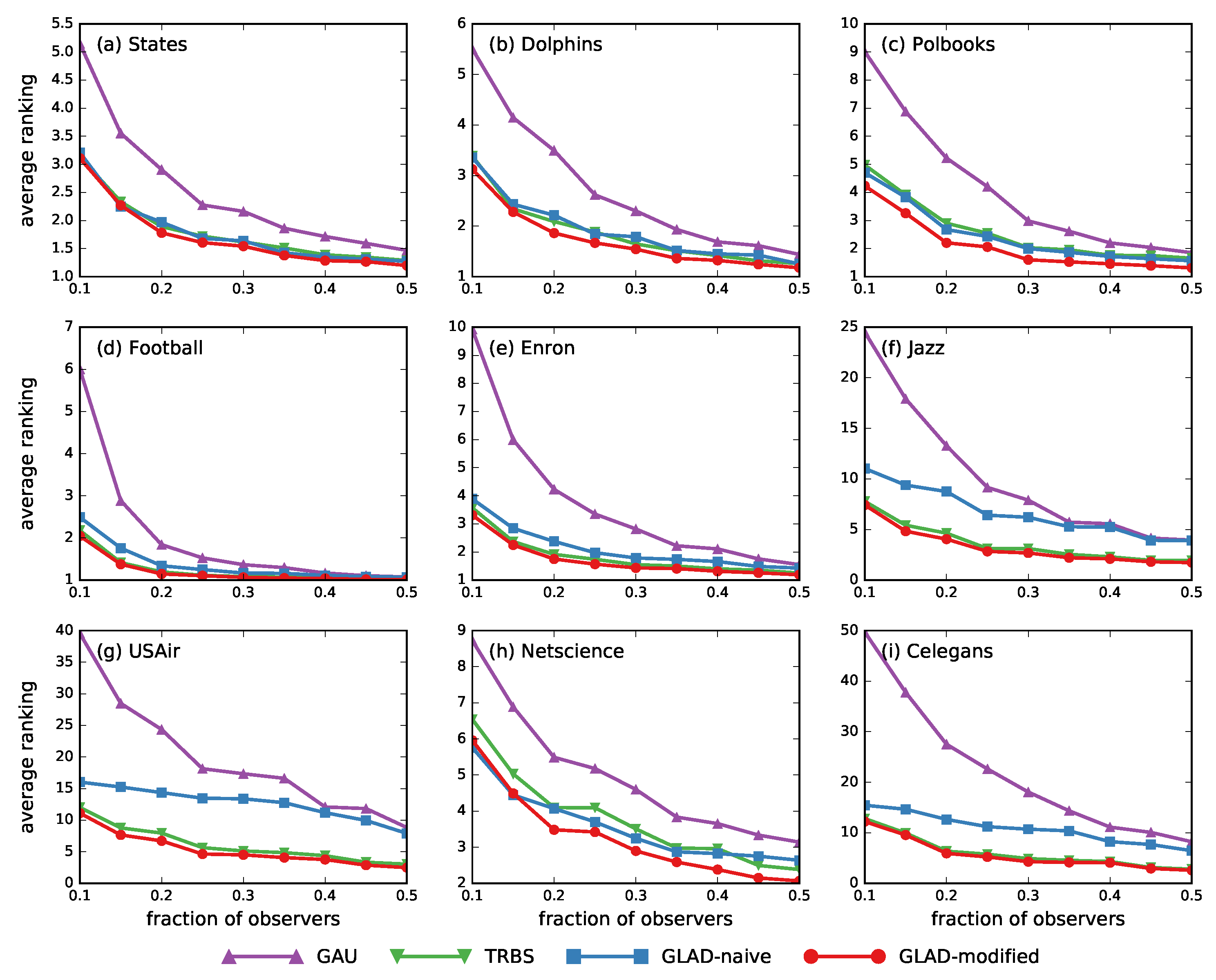
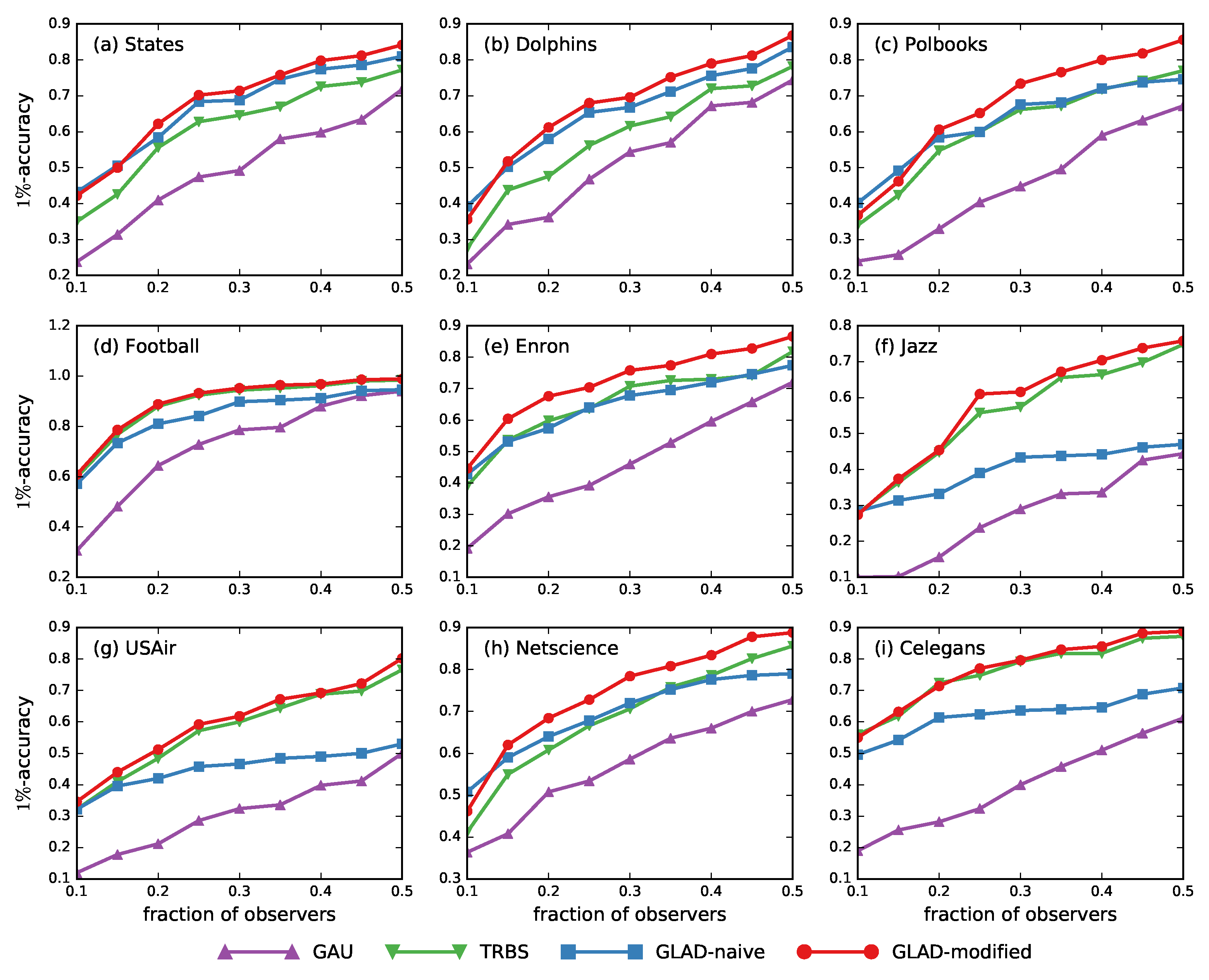
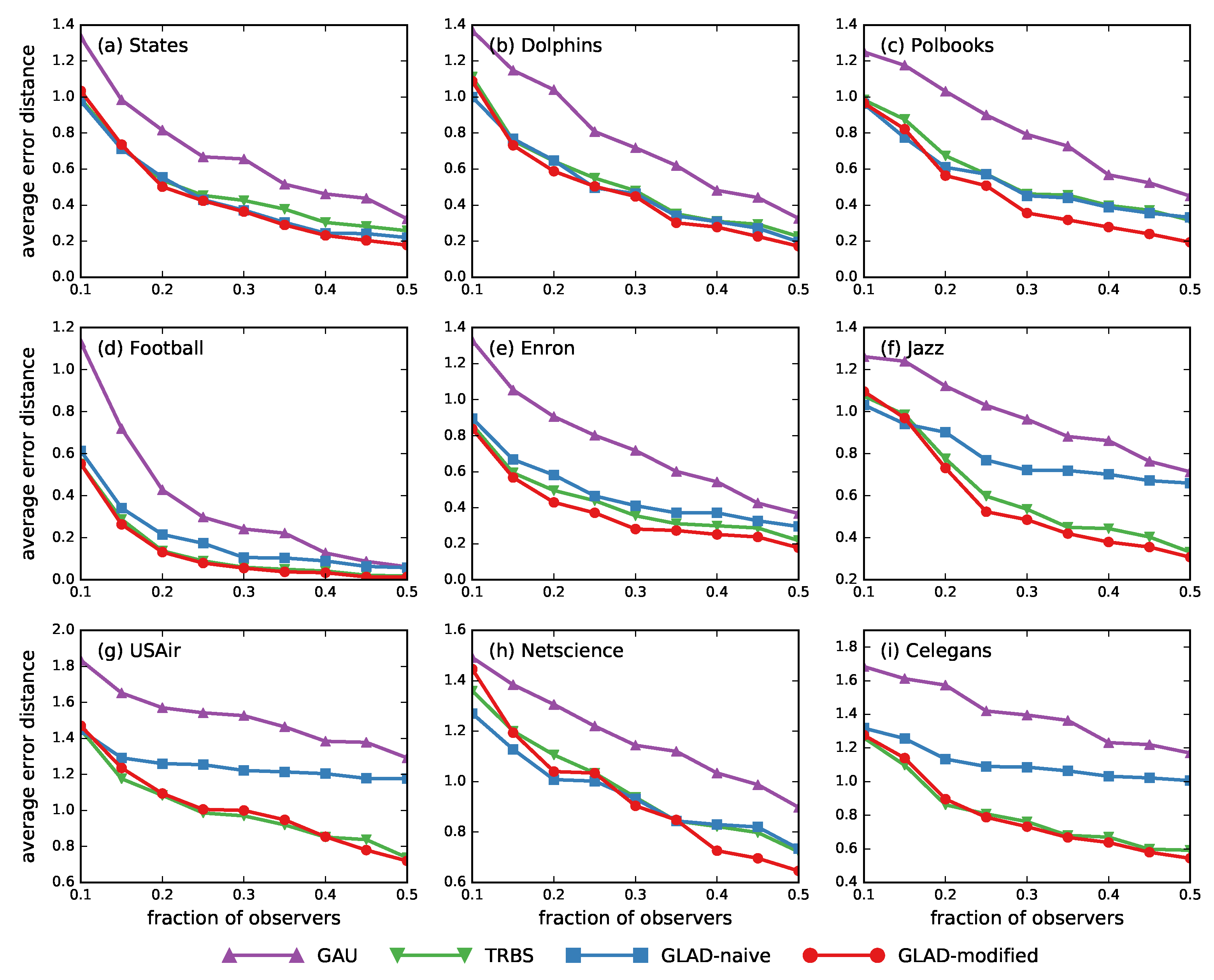
3. Experiments and Analysis
3.1. Metrics and Benchmark Methods
- Gaussian heuristic (GAU). In [19], Pinto et al. first showed the possibility of estimating the location of the source from measurements collected by sparsely placed observers. They modeled the diffusion delays along edges with Gaussian distribution , and built an MLE as the optimal solution for the source localization problem in arbitrary trees. Compared with our method, Pinto assumed that both and were known parameters, whereas we allowed to be unknown and determined it via estimation process.
- Time-reversal backward spreading (TRBS). The time-reversal backward spreading algorithm proposed by Shen et al. [21] was an efficient method to infer the diffusion source based on a weighted network structure and partial timestamps. In their method, the variance of the differences between the true arrival times and the expected arrival from a node to all observers was calculated, as a measurement to evaluate the extent to which it is the diffusion source.
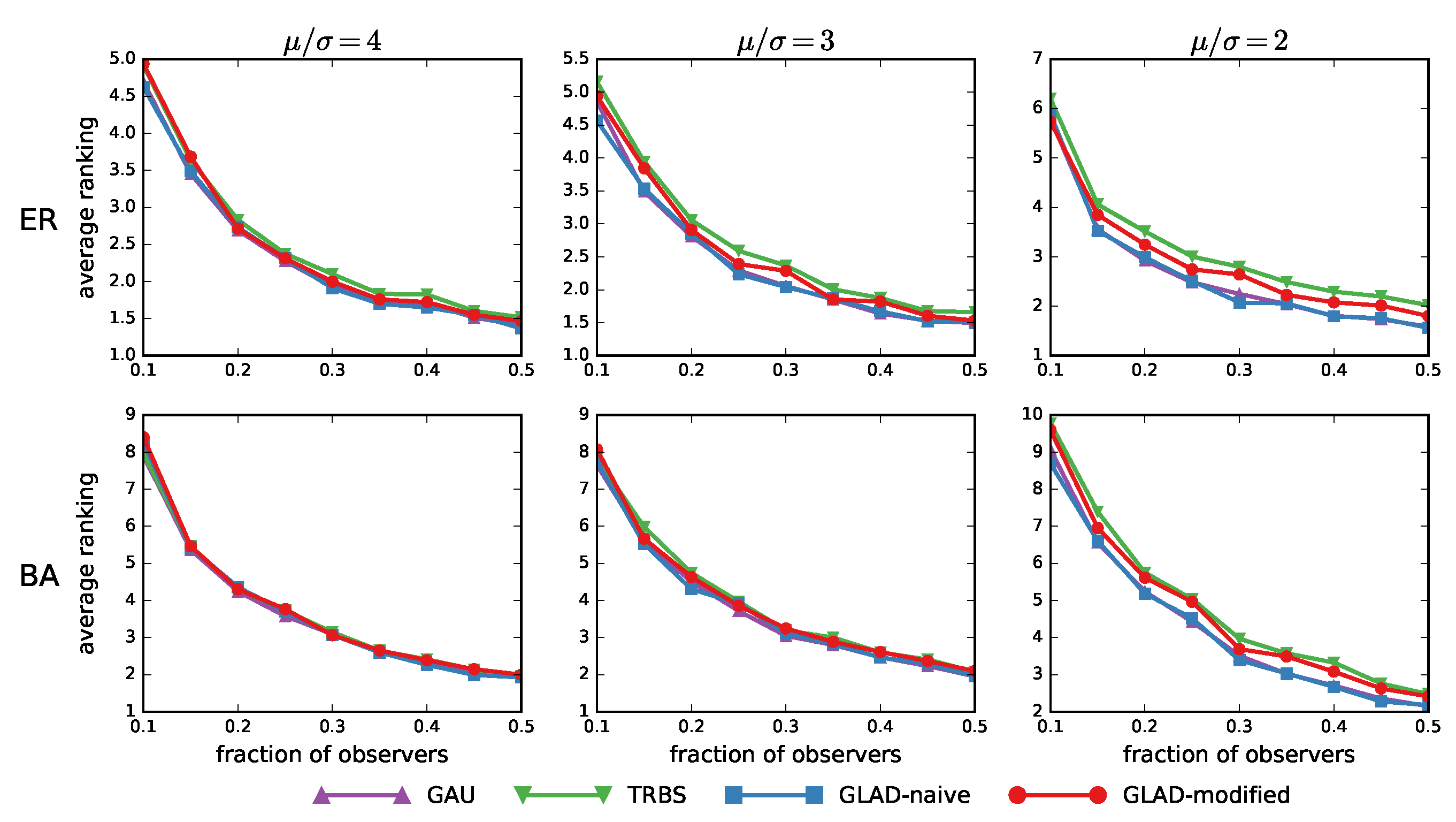
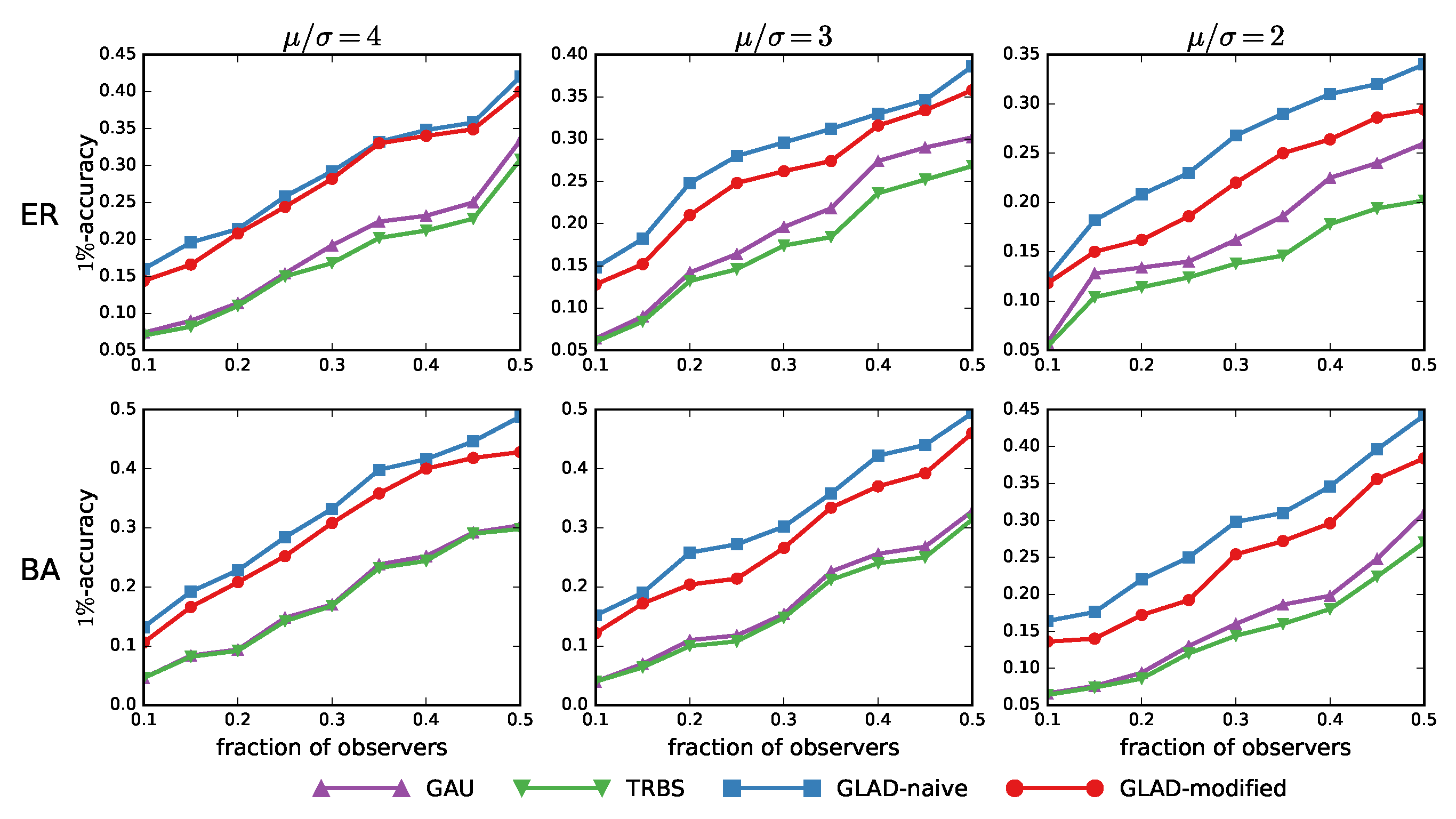
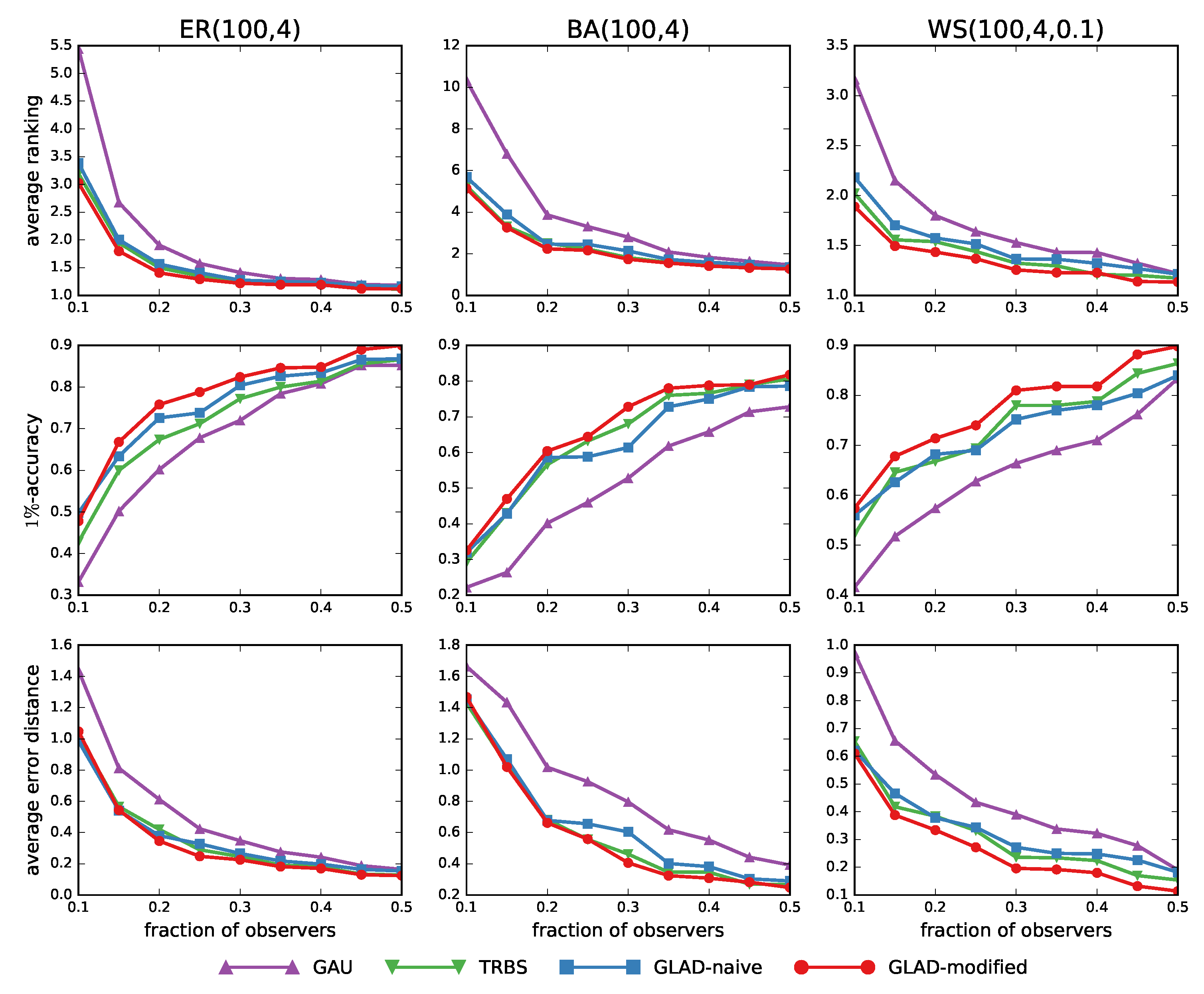
3.2. Results on Arbitrary Trees
3.3. Results on General Graphs
4. Discussion
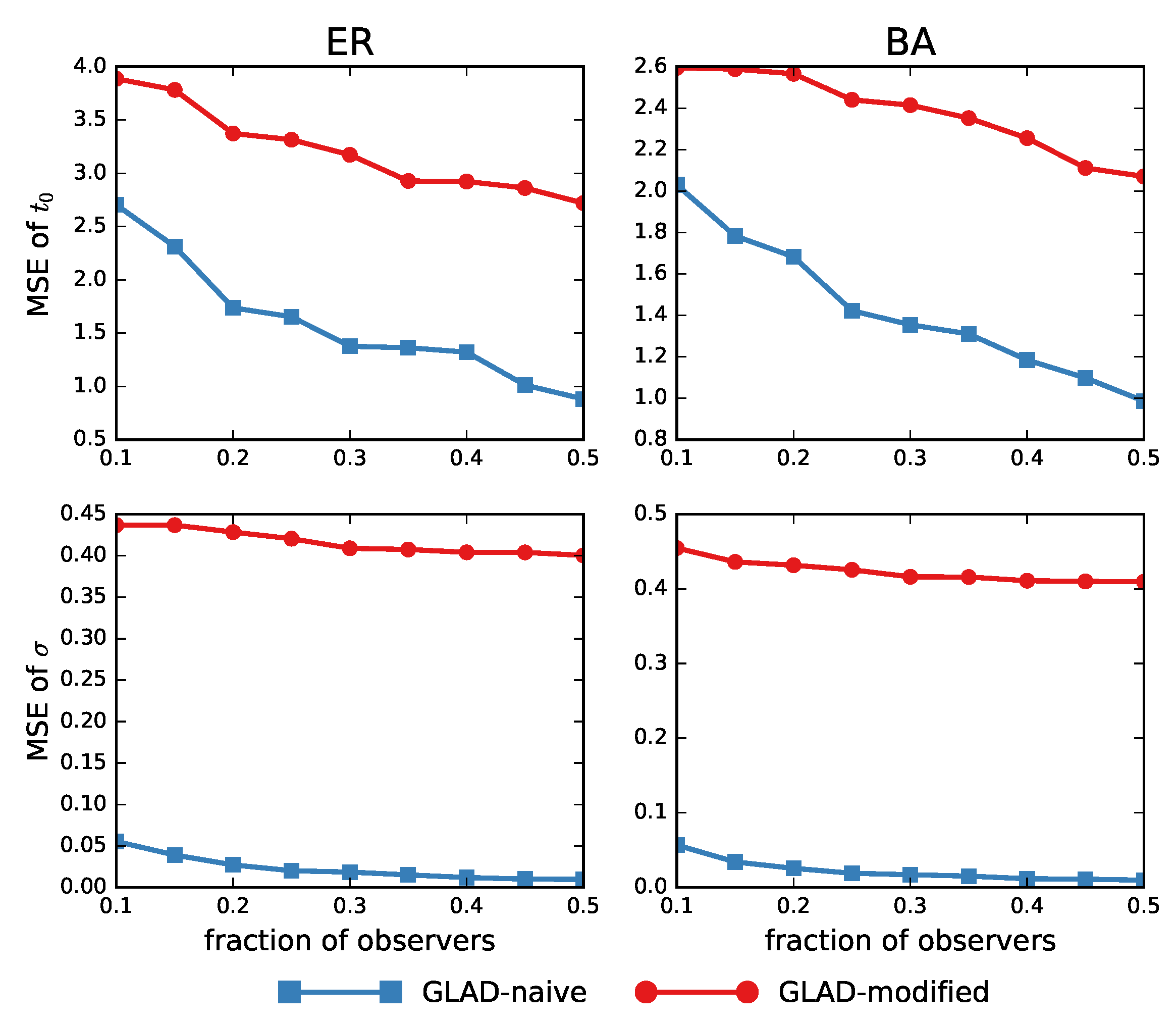
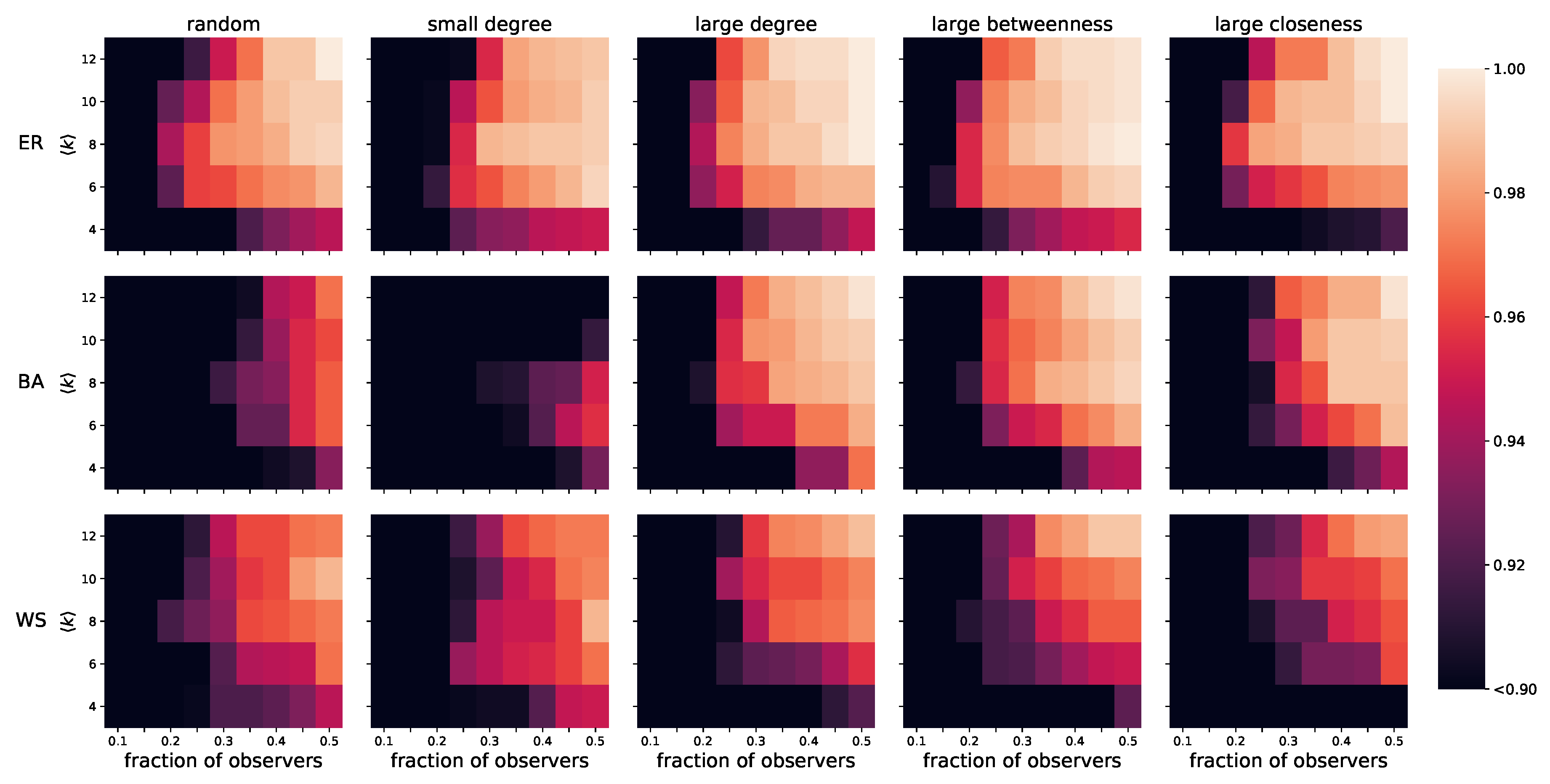
4.1. Different Strategies for Observer Placements
4.2. Relationship with the TRBS Algorithm
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pastor-Satorras, R.; Castellano, C.; Van Mieghem, P.; Vespignani, A. Epidemic processes in complex networks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2015, 87, 925–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chierichetti, F.; Lattanzi, S.; Panconesi, A. Rumor spreading in social networks. Theor. Comput. Sci. 2011, 412, 2602–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, R.; Albert, I.; Nakarado, G.L. Structural vulnerability of the North American power grid. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 69, 25103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, D.; Zaman, T. Rumors in a Network: Who’s the Culprit? IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2011, 57, 5163–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Ying, L. Information source detection in the SIR model: A sample-path-based approach. IEEE ACM Trans. Netw. 2016, 24, 408–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokhov, A.Y.; Mézard, M.; Ohta, H.; Zdeborová, L. Inferring the origin of an epidemic with a dynamic message-passing algorithm. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 90, 12801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altarelli, F.; Braunstein, A.; Dall’Asta, L.; Lage-Castellanos, A.; Zecchina, R. Bayesian inference of epidemics on networks via Belief Propagation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 118701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockmann, D.; Helbing, D. The Hidden Geometry of Complex, Network-Driven Contagion Phenomena. Science 2013, 342, 1337–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Ying, L. Source Localization in Networks: Trees and Beyond. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1510.01814. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.L.; Han, X.; Lai, Y.C.; Wang, W.X. Optimal localization of diffusion sources in complex networks. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 170091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Tay, W.P.; Leng, M. Identifying Infection Sources and Regions in Large Networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 61, 2850–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dong, W.; Zhang, W.; Tan, C.W. Rumor source detection with multiple observations: Fundamental limits and algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2014 ACM International Conference on Measurement and Modeling of Computer Systems, Austin, TX, USA, 16–20 June 2014; Volume 42, pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, W.; Tay, W.P.; Leng, M. How to Identify an Infection Source With Limited Observations. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2014, 8, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antulov-Fantulin, N.; Lancic, A.; Smuc, T.; Stefancic, H.; Sikic, M. Identification of Patient Zero in Static and Temporal Networks: Robustness and Limitations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 248701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louni, A.; Subbalakshmi, K.P. A two-stage algorithm to estimate the source of information diffusion in social media networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), Toronto, ON, Canada, 27 April–2 May 2014; pp. 329–333. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, C.T. Locating the Epidemic Source in Complex Networks with Sparse Observers. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zejnilovic, S.; Gomes, J.P.; Sinopoli, B. Network observability and localization of the source of diffusion based on a subset of nodes. In Proceedings of the 2013 51st Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing (Allerton), Monticello, IL, USA, 2–4 October 2013; pp. 847–852. [Google Scholar]
- Zejnilovic, S.; Xavier, J.M.F.; Gomes, J.P.; Sinopoli, B. Selecting observers for source localization via error exponents. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Hong Kong, China, 14–19 June 2015; pp. 2914–2918. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, P.C.; Thiran, P.; Vetterli, M. Locating the Source of Diffusion in Large-Scale Networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 68702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Chen, Z.; Ying, L. Locating the contagion source in networks with partial timestamps. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2016, 30, 1217–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Cao, S.; Wang, W.-X.; Di, Z.; Stanley, H.E. Locating the source of diffusion in complex networks by time-reversal backward spreading. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 93, 32301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Shen, Z.; Wang, W.-X.; Fan, Y.; Di, Z. Multi-source localization on complex networks with limited observers. EPL 2016, 113, 18006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.-L.; Shen, Z.; Tang, C.-B.; Xie, B.-B.; Lu, J.-F. Localization of diffusion sources in complex networks with sparse observations. Phys. Lett. A 2018, 382, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, R.A.; Ahmed, N.K. The Network Data Repository with Interactive Graph Analytics and Visualization. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Austin, TX, USA, 25–30 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lusseau, D. The emergent properties of a dolphin social network. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, S186–S188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Social Network Analysis Software & Services for Organizations, Communities, and Their Consultants. Available online: http://www.orgnet.com (accessed on 8 September 2008).
- Girvan, M.; Newman, M.E.J. Community structure in social and biological networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7821–7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leskovec, J.; Lang, K.J.; Dasgupta, A.; Mahoney, M.W. Community structure in large networks: Natural cluster sizes and the absence of large well-defined clusters. Internet Math. 2009, 6, 29–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleiser, P.M.; Danon, L. Community structure in jazz. Adv. Complex Syst. 2003, 6, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.J. Finding community structure in networks using the eigenvectors of matrices. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 74, 36104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.G.; Southgate, E.; Thomson, J.N.; Brenner, S. The structure of the nervous system of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 1986, 314, 1–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Network Data. Available online: http://www-personal.umich.edu/~mejn/netdata/ (accessed on 19 April 2013).
- Freeman, L.C. A set of measures of centrality based on betweenness. Sociometry 1977, 40, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavelas, A. Communication patterns in task-oriented groups. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1950, 22, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Ji, F.; Tay, W.P. Estimating Infection Sources in Networks Using Partial Timestamps. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2018, 13, 3035–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, C.; Guo, L. Locating multiple sources in social networks under the SIR model: A divide-and-conquer approach. J. Comput. Sci. 2015, 10, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, C.; Guo, L. Discovering Multiple Diffusion Source Nodes in Social Networks. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2014, 29, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Ji, F.; Tay, W.P. Multiple sources identification in networks with partial timestamps. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP), Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–16 November 2017; pp. 638–642. [Google Scholar]
- Kivelä, M.; Arenas, A.; Barthelemy, M.; Gleeson, J.P.; Moreno, Y.; Porter, M.A. Multilayer networks. J. Complex Netw. 2014, 2, 203–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holme, P. Modern temporal network theory: A colloquium. Eur. Phys. J. B 2015, 88, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| MLE | B | C | D | E | G | H | I | K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.404 | −0.596 | −0.177 | −1.177 | 0.489 | −0.511 | −0.424 | −1.424 | |
| 1.056 | 1.056 | 0.583 | 0.583 | 1.108 | 1.108 | 0.099 | 0.099 | |
| 5.700 | 6.617 | 2.133 | 3.050 | 5.989 | 6.906 | −8.499 | −7.583 |
| Type | Name | N | M | H | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random | ER(100,4) | 100 | 200 | 4.000 | 9.620 | 1.211 | 3.418 | 0.038 |
| Scale-free | BA(100,4) | 100 | 200 | 4.000 | 21.756 | 1.723 | 3.104 | 0.102 |
| Small-world | WS(100,4,0.1) | 100 | 200 | 4.000 | 6.452 | 1.047 | 4.263 | 0.286 |
| Type | Name | N | M | H | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geography | States | 49 | 107 | 4.367 | 8 | 1.130 | 4.163 | 0.507 |
| Animal | Dolphins | 62 | 159 | 5.129 | 12 | 1.327 | 3.357 | 0.303 |
| Co-purchasing | Polbooks | 105 | 441 | 8.400 | 25 | 1.421 | 3.079 | 0.488 |
| Sport | Football | 115 | 613 | 10.661 | 12 | 1.007 | 2.508 | 0.403 |
| Enron | 143 | 623 | 8.713 | 42 | 1.483 | 2.967 | 0.453 | |
| Social | Jazz | 198 | 2742 | 27.697 | 100 | 1.395 | 2.235 | 0.633 |
| Transport | USAir | 332 | 2126 | 12.807 | 139 | 3.464 | 2.738 | 0.749 |
| Co-authorship | Netscience | 379 | 914 | 4.823 | 34 | 1.663 | 6.042 | 0.798 |
| Biological | Celegans | 453 | 2025 | 8.940 | 237 | 4.485 | 2.664 | 0.655 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, X.; Yi, D. Locating the Source of Diffusion in Complex Networks via Gaussian-Based Localization and Deduction. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3758. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9183758
Li X, Wang X, Zhao C, Zhang X, Yi D. Locating the Source of Diffusion in Complex Networks via Gaussian-Based Localization and Deduction. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(18):3758. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9183758
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiang, Xiaojie Wang, Chengli Zhao, Xue Zhang, and Dongyun Yi. 2019. "Locating the Source of Diffusion in Complex Networks via Gaussian-Based Localization and Deduction" Applied Sciences 9, no. 18: 3758. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9183758
APA StyleLi, X., Wang, X., Zhao, C., Zhang, X., & Yi, D. (2019). Locating the Source of Diffusion in Complex Networks via Gaussian-Based Localization and Deduction. Applied Sciences, 9(18), 3758. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9183758





