DC-Microgrid Operation Planning for an Electric Vehicle Supply Infrastructure
Abstract
1. Introduction
- -
- A model of degradation costs and capacity for energy storage devices is included;
- -
- Specific features of active power losses in DC microgrids and in converters are taken into account;
- -
- The economic objective involves a microgrid and an EV aggregator;
- -
- An iterative procedure is exploited in order to consider non-linear realistic models and keep linear programming properties;
- -
- Performance indicators related to EV exploitation for electric system integration are adopted to prove procedure validity.
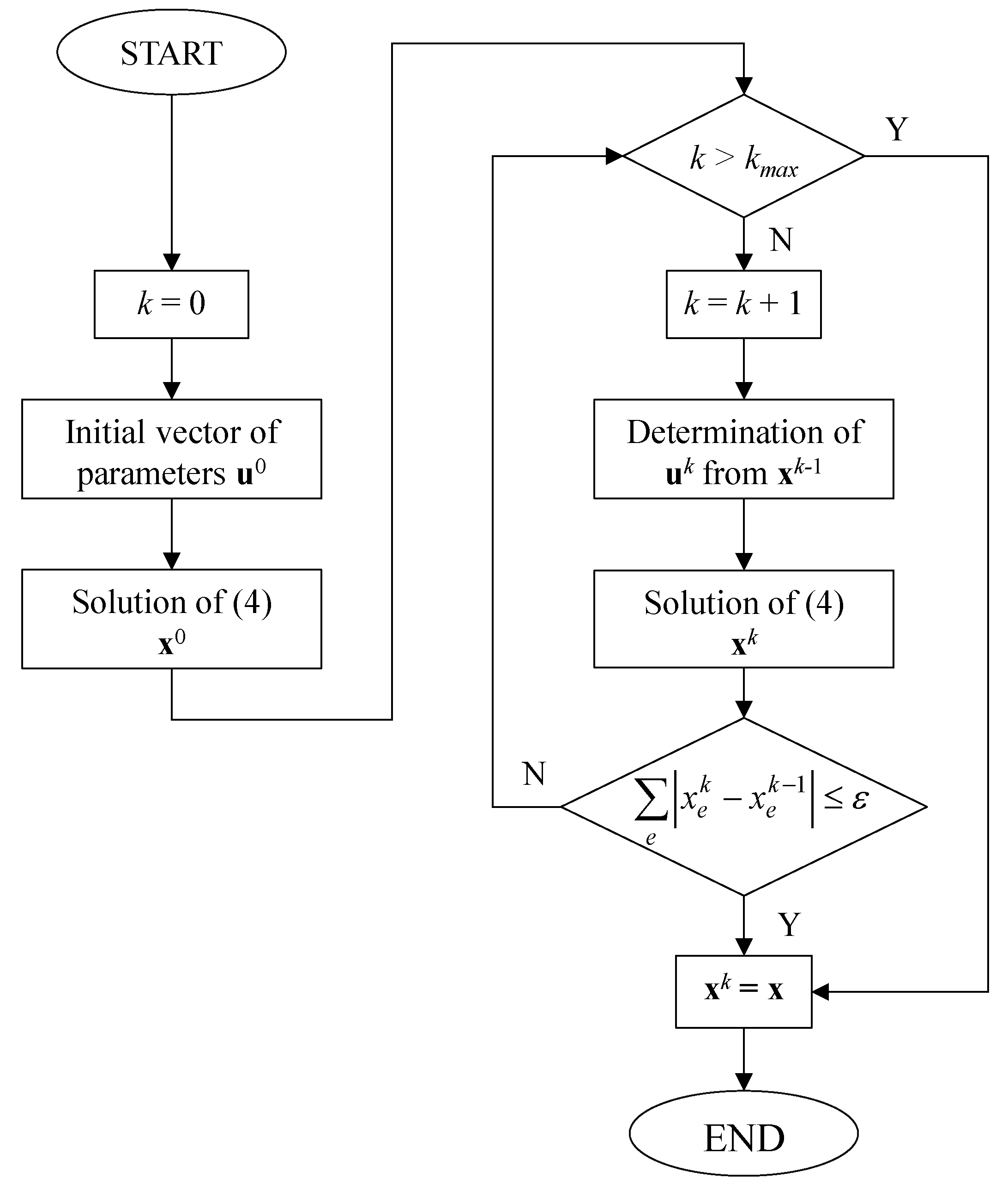
2. Methodology
2.1. General Assumptions
2.2. Mixed Integer Linear Problem Formulation
2.3. Reference Non-Linear Approach
3. System under Study
4. Tests and Results
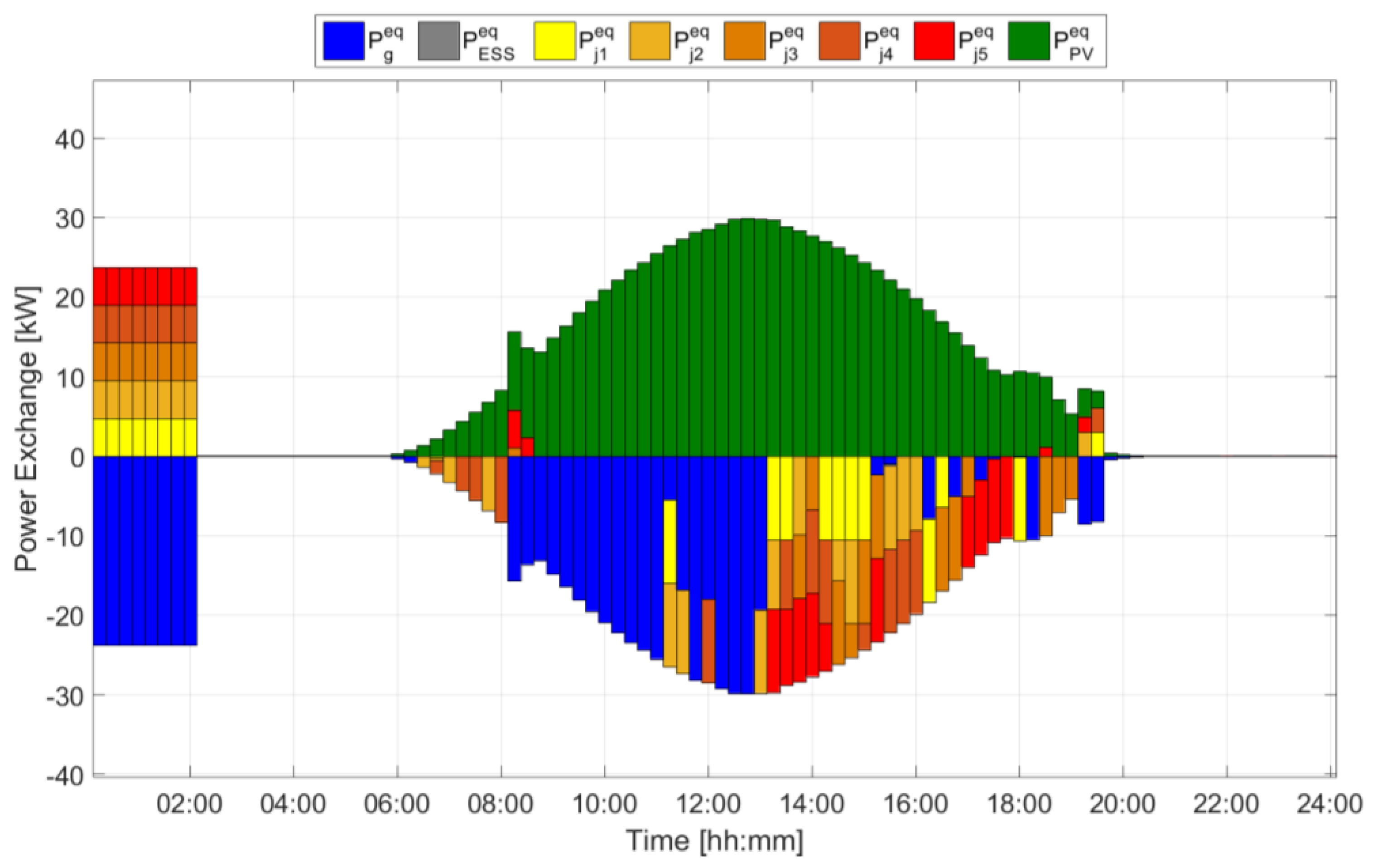
4.1. Test Cases: Different Operation Days
4.2. Results, Indicators, and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Indices and auxiliaries | |
| Number of storage systems | |
| Number of electric vehicles | |
| Number of time steps | |
| Storage index | |
| Electric vehicle index | |
| Time step index | |
| Objective function [€] | |
| Time step duration [h] | |
| Iteration index | |
| Maximum number of iterations | |
| Solution convergence threshold | |
| Input parameters | |
| Unitary revenue for the energy injected into the utility grid at time step t [€/kWh] | |
| Unitary revenue for the discharge energy of the j-th EV at time step t [€/kWh] | |
| Unitary cost for the energy withdrawal from the grid at time step t [€/kWh] | |
| Unitary cost for the charge energy of the j-th EV at time step t [€/kWh] | |
| Degradation cost of the i-th storage [€/kWh] | |
| Degradation cost of the j-th EV [€/kWh] | |
| Maximum power exchange with utility grid [kW] | |
| Maximum charge/discharge power for the i-th storage [kW] | |
| Maximum charge/discharge power for the j-th EV [kW] | |
| Max/min SOC of the i-th storage [kWh] | |
| Max/min SOC of the j-th EV [kWh] | |
| Photovoltaic production power at time step t [kW] | |
| Charge/discharge efficiency of the i-th storage at time step t | |
| Charge/discharge efficiency of the j-th EV at time step t | |
| Self-discharge of the i-th storage [kW] | |
| Initial SOC of the i-th storage [kWh] | |
| Self-discharge of the j-th EV [kW] | |
| Initial SOC of the j-th EV [kWh] | |
| SOC reduction of the j-th EV for mobility needs in the time step t [kWh] | |
| State variables | |
| Power withdrawn from AC grid at time step t [kW] | |
| Power injected into the AC grid at time step t [kW] | |
| Charge power of the i-th storage at time step t [kW] | |
| Discharge power of the i-th storage at time step t [kW] | |
| Charge power of the j-th EV at time step t [kW] | |
| Discharge power of the j-th EV at time step t [kW] | |
| SOC of the i-th storage at time step t [kWh] | |
| SOC of the j-th EV at time step t [kWh] | |
| Binary variable of the grid power exchange state (1 if the microgrid is draining power from the external grid, 0 if the microgrid is injecting power) | |
| Binary variable of the i-th storage charging state (1 charging, 0 discharging) | |
| Binary variable of the j-th EV charging state (1 charging, 0 discharging) | |
References
- Urbanelli, A.; Sallati, A.; Ciasca, F.; Aluisio, B.; Vergine, C.; Zeni, L.; Petrucci, M.; Forte, G.; Trovato, M. Electric vehicle grid impacts—Opportunities and evaluation on the Italian Transmission Grid. In Proceedings of the 2018 AEIT International Annual Conference, Bari, Italy, 3–5 October 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International standard IEC 62196-1. Plugs, Socket-Outlets, Vehicle Connectors and Vehicle Inlets—Conductive Charging of Electric Vehicles—Part 1: General Requirements, 3rd ed.; International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Abousleiman, R.; Scholer, R. Smart Charging: System design and implementation for interaction between plug-in electric vehicles and the power grid. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2015, 1, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, Z.; Ahmad, I.; Habibi, D.; Phung, Q.V. Smart Charging Strategy for Electric Vehicle Charging Stations. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2018, 4, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Vayá, M.; Andersson, G. Optimal bidding strategy of a plug-in electric vehicle aggregator in day-ahead electricity markets under uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2015, 30, 2375–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, A.R.; Salam, Z.; Aziz, M.J.B.A.; Yee, K.P.; Ashique, R.H. Electric vehicles charging using photovoltaic: Status and technological review. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbordone, D.; Bertini, I.; Di Pietra, B.; Falvo, M.C.; Genovese, A.; Martirano, L. EV fast charging stations and energy storage technologies: A real implementation in the smart micro grid paradigm. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2015, 120, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashique, R.H.; Salam, Z.; Bin Abdul Aziz, M.J.; Bhatti, A.R. Integrated photovoltaic-grid dc fast charging system for electric vehicle: A review of the architecture and control. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 1243–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Kaur, T.; Khanna, R.; Singh, P. A State of the art of DC microgrids for Electric Vehicle Charging. In Proceedings of the 4th IEEE ISPC 2k17 Conference, Solan, India, 21–23 September 2017; pp. 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboli, R.; Ramezani, M.; Falaghi, H. Joint optimization of day-ahaed and uncertain near real-time operation of microgrids. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2019, 107, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zeng, H.; Lu, C.; Boulet, B. Two-Stage Energy Management for Office Buildings With Workplace EV Charging and Renewable Energy. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2017, 3, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamankesh, H.; Agelidis, V.G.; Kavousi-Fard, A. Optimal scheduling of renewable micro-grids considering plug-in hybrid electric vehicle charging demand. Energy 2016, 100, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Cachinero, P.; Munoz-Hernandez, J.I.; Contreras, J. A Linear Model for Operating Microgrids with Renewable Resources, Battery Degradation Costs and Electric Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2018 EEM International Conference, Lodz, Poland, 27–29 June 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Xiao, J.; Koh, L.H.; Wang, P.; Ding, Z. Strategic Day-ahead Bidding for Energy Hubs with Electric Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE EI2 Conference, Beijing, China, 20–22 October 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahramara, S.; Golpira, H. Robust optimization of micro-grids operation problem in the presence of electric vehicles. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 37, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhou, K.; Yang, S.; Liu, H. Multi-objective optimal load dispatch of microgrid with stochastic access of electric vehicles. J. Cleaner Prod. 2018, 195, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuran, M.S.; Carneiro Viana, A.; Iannone, L.; Kofman, D.; Mermoud, G.; Vasseur, J.P. A Smart Parking Lot Management System for Scheduling the Recharging of Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 6, 2942–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, T.; Wang, R. Energy management model of charging station micro-grid considering random arrival of electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Energy Internet, Beijing, China, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, M.; Yazdani, A. An Energy Management Strategy for a DC Distribution System for Power System Integration of Plug-In Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 7, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Kam, M.; Van Sark, W. Smart charging of electric vehicles with photovoltaic power and vehicle-to-grid technology in a microgrid; a case study. Appl. Energy 2015, 152, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Teng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Jiang, R.; Huang, Q. Scheduling Optimization of Microgrid Considering Electric Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Power and Renewable Energy, Chengdu, China, 20–23 September 2017; pp. 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliasghari, P.; Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B.; Alipour, M.; Abapour, M.; Zare, K. Optimal scheduling of plug-in electric vehicles and renewable microgrid in energy and reserve markets considering demand response program. J. Cleaner Prod. 2018, 186, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honarmand, M.; Zakariazadeh, A.; Jadid, S. Integrated scheduling of renewable generation and electric vehicles parking lot in a smart microgrid. Energy Convers. Manage. 2014, 86, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaee, S.; Mortazavi, S.S.; Niknam, T. Stochastic scheduling of local distribution systems considering high penetration of plug-in electric vehicles and renewable energy sources. Energy 2017, 121, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluisio, B.; Conserva, A.; Dicorato, M.; Forte, G.; Trovato, M. Optimal operation planning of V2G-equipped Microgrid in the presence of EV aggregator. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 152, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortaz, E.; Valenzuela, J. Microgrid energy scheduling using storage from electric vehicles. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 143, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Duan, S. Optimal Integration of Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles in Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2014, 10, 1917–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Nunna, H.S.V.S.; Battula, S.; Doolla, S.; Srinivasan, D. Energy Management in Smart Distribution Systems With Vehicle-to-Grid Integrated Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9, 4004–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, N.; Xu, W. Coordinated Dispatch Strategy of Virtual Power Plant Considering Electric Vehicle and Battery Management. In Proceedings of the 2018 37th CCC Conference, Wuhan, China, 25–27 July 2018; pp. 8798–8802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshminarayanan, V.; Pramanick, S.; Rajashekara, K.; Ben-Brahim, L.; Gastli, A. Optimal energy management scheme for electric vehicle integration in microgrid. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE NAPS Conference, Morgantown, WV, USA, 17–19 September 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tushar, W.; Yuen, C.; Huang, S.; Smith, D.B.; Poor, H.V. Cost Minimization of Charging Stations With Photovoltaics: An Approach With EV Classification. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 17, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liu, N.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, J. Multi-objective Optimal Scheduling of a DC Micro-grid Consisted of PV System and EV Charging Station. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE ISGT Asia Conference, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 20–23 May 2014; pp. 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Damiran, Z.; Lim, W.H. Optimal Charging and Discharging Scheduling for Electric Vehicles in a Parking Station with Photovoltaic System and Energy Storage System. Energies 2017, 10, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Zhang, B.; Kezunovic, M. Optimized Operational Cost Reduction for an EV Charging Station Integrated With Battery Energy Storage and PV Generation. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2019, 10, 2096–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.-T.; Lu, C.N. Dispatch of EV Charging Station Energy Resources for Sustainable Mobility. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2015, 1, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xiong, J.; Xu, A.; Su, W. Two-Stage Economic Operation of Microgrid-Like Electric Vehicle Parking Deck. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 7, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, H.; Khodaei, A. AC versus DC Microgrid Planning. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 8, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, T.; Ansari, Z.A. An Overview of Intelligent Energy Management System for DC Microgrid: System and Communication Architecture and Application in Power Distribution System. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 13th International Conference on Industrial and Information Systems (ICIIS), Rupnagar, India, 1–2 December 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, Z.; Fang, J.; Ning, F.; Shen, Z.J. Hierarchical structure and bus voltage control of DC microgrid. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 3670–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sechilariu, M.; Locment, F.; Trigueiro Dos Santos, L. A Conceptual Framework for Full Optimal Operation of a Grid-Connected DC Microgrid. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Electronics for Sustainable Energy Systems (IESES), Hamilton, New Zealand, 31 January–2 February 2018; pp. 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, M.F.; Elbouchikhi, E.; Benbouzid, M. Optimal operational planning of scalable DC microgrid with demand response, islanding, and battery degradation cost considerations. Appl. Energy 2019, 237, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Gonzalez, W.; Montoya, O.D.; Holguin, E.; Garces, A.; Grisales-Noreña, L.F. Economic dispatch of energy storage systems in dc microgrids employing a semidefinite programming model. J. Energy Storage 2019, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, M.; Shokridehaki, F.; Akorede, M.R.; Marzband, M.; Vechiu, I.; Pouresmaeil, E. CVaR-based energy management scheme for optimal resilience and operational cost in commercial building microgrids. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2018, 100, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sakkaf, S.; Kassas, M.; Khalid, M.; Abido, M.A. An Energy Management System for Residential Autonomous DC Microgrid Using Optimized Fuzzy Logic Controller Considering Economic Dispatch. Energies 2019, 12, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovine, A.; Rigaut, T.; Damm, G.; De Santis, E.; Di Benedetto, M.D. Power management for a DC MicroGrid integrating renewables and storages. Control Eng. Pract. 2019, 85, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, R.R.; Ballal, M.; Suryawanshi, H.M.; Mishra, M.K. An Adaptive Approach for Effective Power Management in DC Microgrid Based on Virtual Generation in Distributed Energy Sources. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inform. 2019, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nougain, V.; Panigrahi, B.K. Real Time Energy Management System and Control Strategy for DC Microgrid. In Proceedings of the 2018 8th IEEE India International Conference on Power Electronics (IICPE), Jaipur, India, 13–15 December 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluisio, B.; Dicorato, M.; Ferrini, I.; Forte, G.; Sbrizzai, R.; Trovato, M. Optimal sizing procedure for Electric Vehicle Supply Infrastructure based on DC microgrid with station commitment. Energies 2019, 12, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Vazquez, M.A. Optimal scheduling of electric vehicle charging and vehicle-to-grid services at household level including battery degradation and price uncertainty. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2014, 8, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, M.; Gross, G. Measurement techniques for online battery state of health estimation in vehicle-to-grid applications. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2014, 63, 1224–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluisio, B.; Dicorato, M.; Forte, G.; Trovato, M. A Monte-Carlo Based procedure for optimal sizing of integrated Electric Vehicle Supply Infrastructure. In Proceedings of the IEEE ISGT Europe 2017 Conference, Turin, Italy, 26–29 September 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluisio, B.; Dicorato, M.; Ferrini, I.; Forte, G.; Trovato, M. AC and DC solutions for Electric Vehicle microgrid: Sizing and reliability analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2018 EEEIC/I&CPS Europe International Conference, Palermo, Italy, 12–15 June 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemhauser, G.L.; Wolsey, L.A. Integer and Combinatorial Optimization; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Fortin, M.; Glowniski, R. Augmented Lagrangian Methods: Applications to the Numerical Solution of Boundary-Value Problems, 1st ed.; North-Holland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: www.wunderground.com, weather stations network (accessed on 31 January 2018).
- Duffie, J.A.; Beckman, W.A. Solar Engineering of Thermal Processes, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
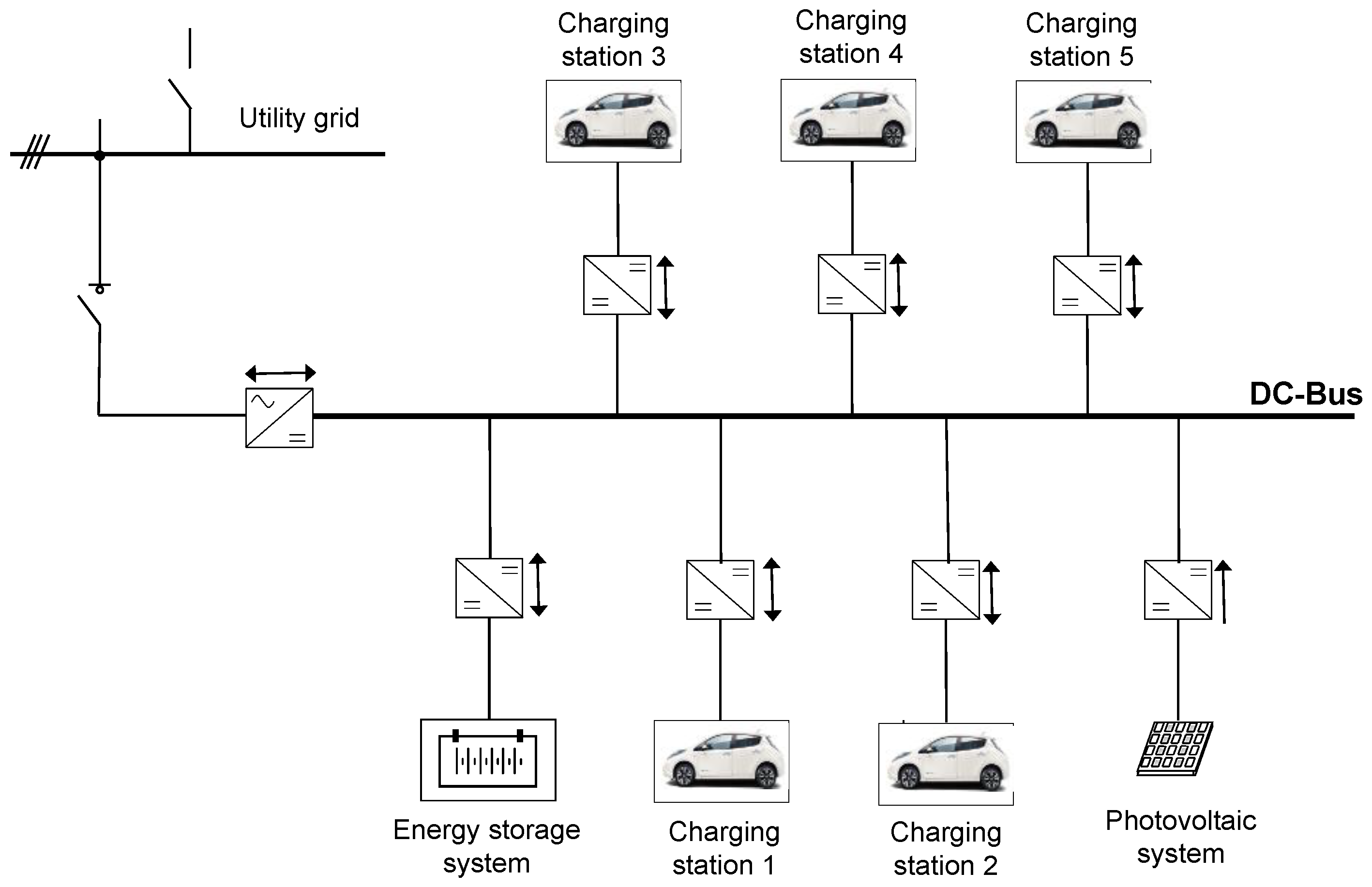
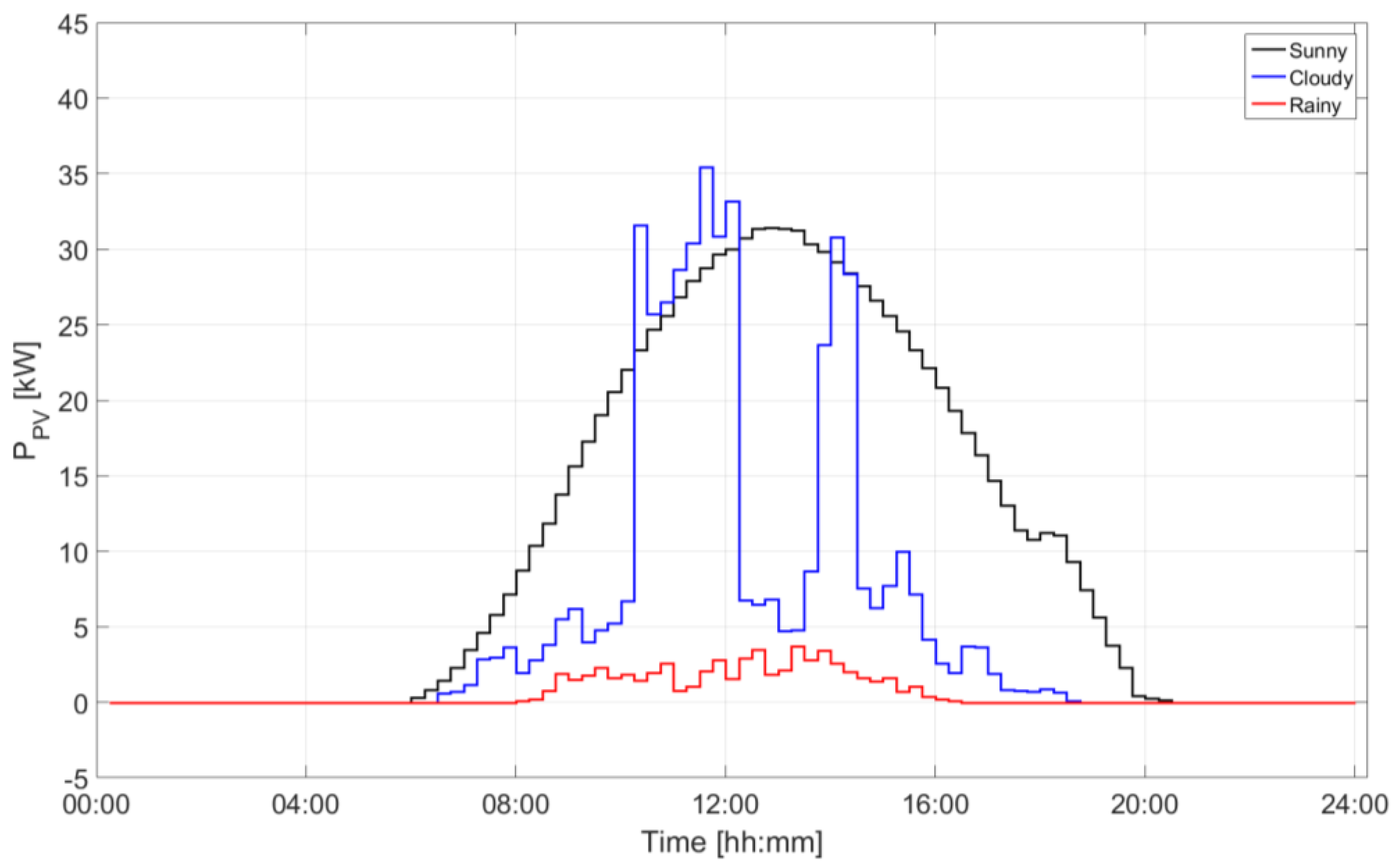
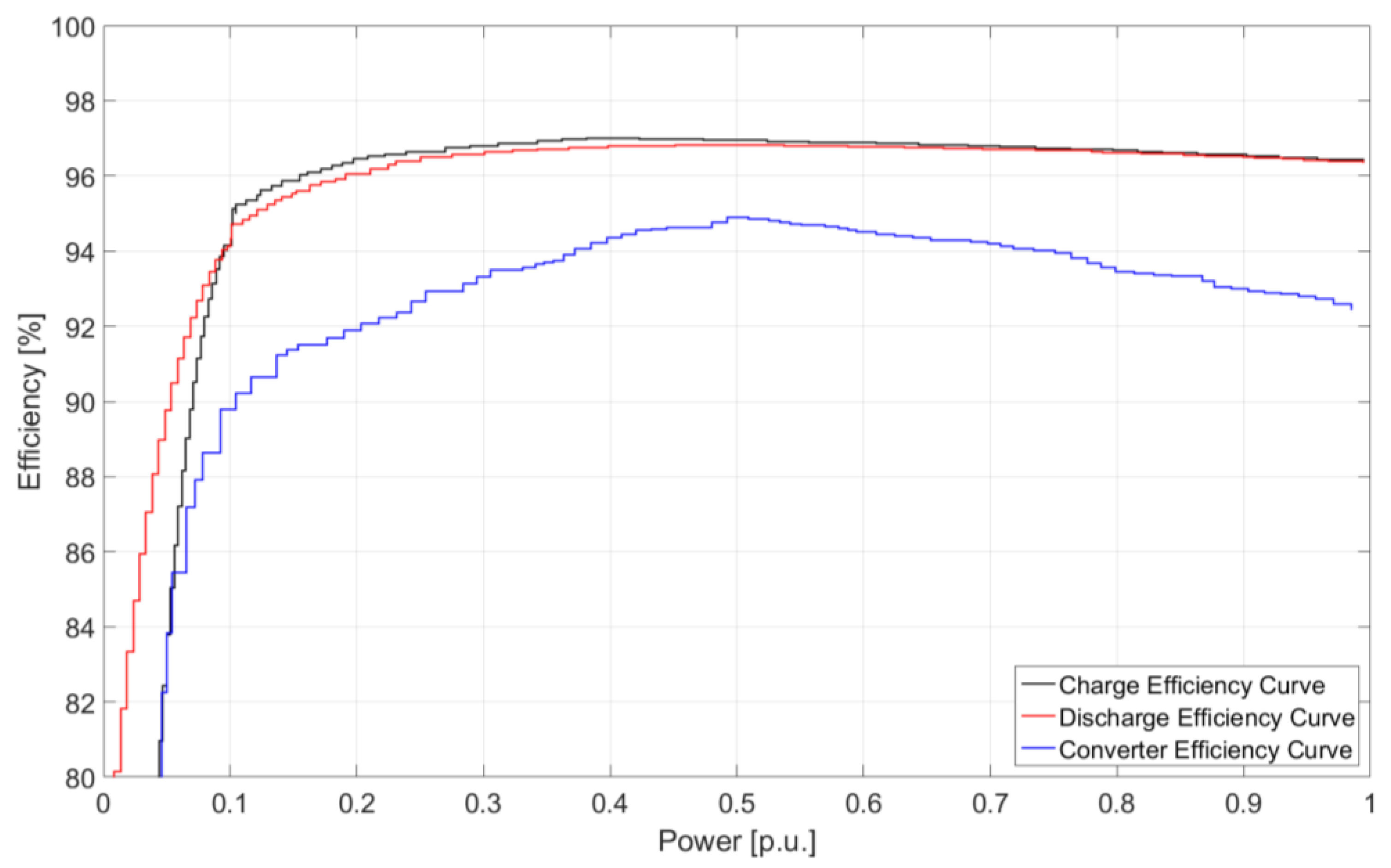

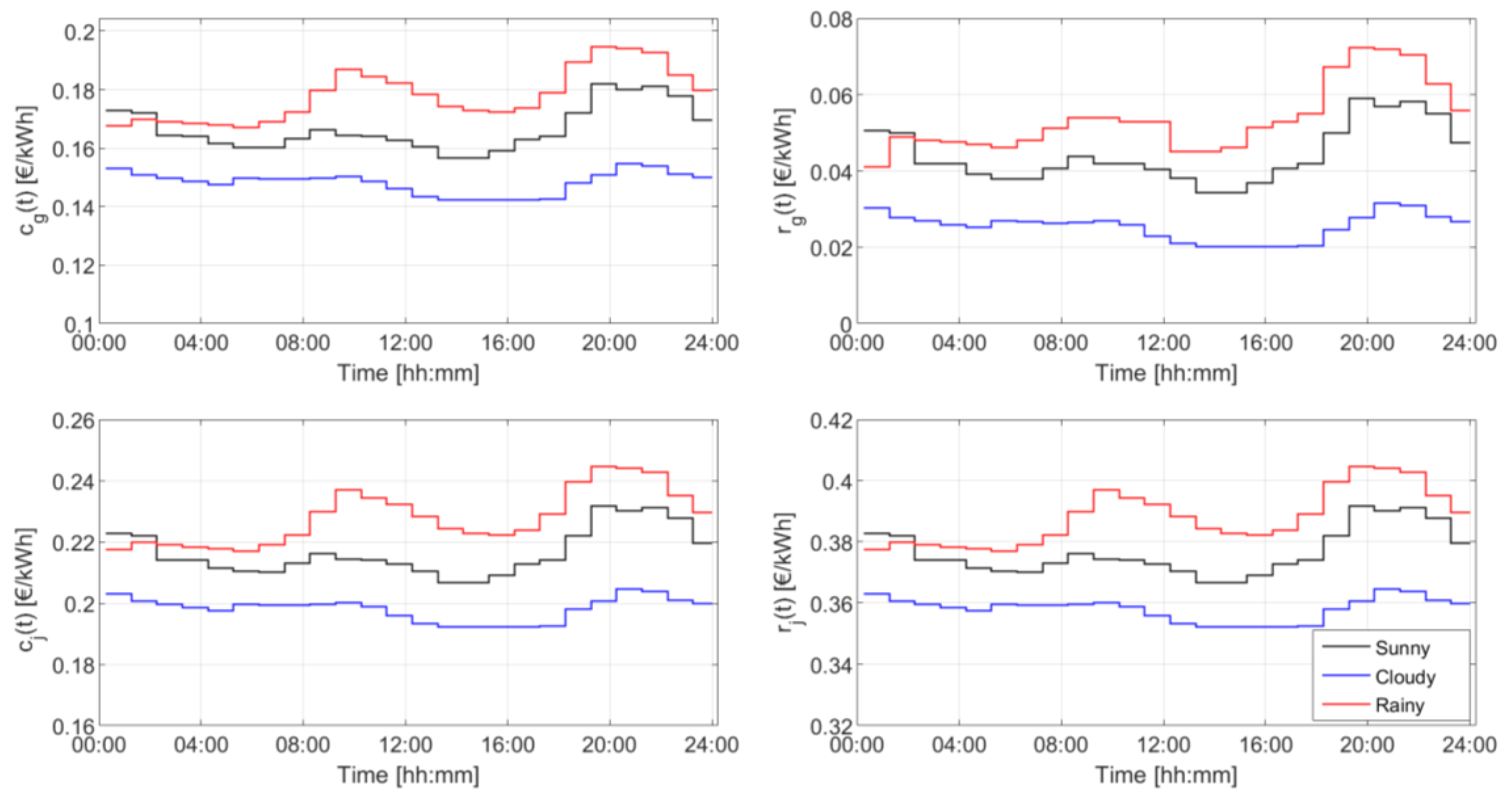
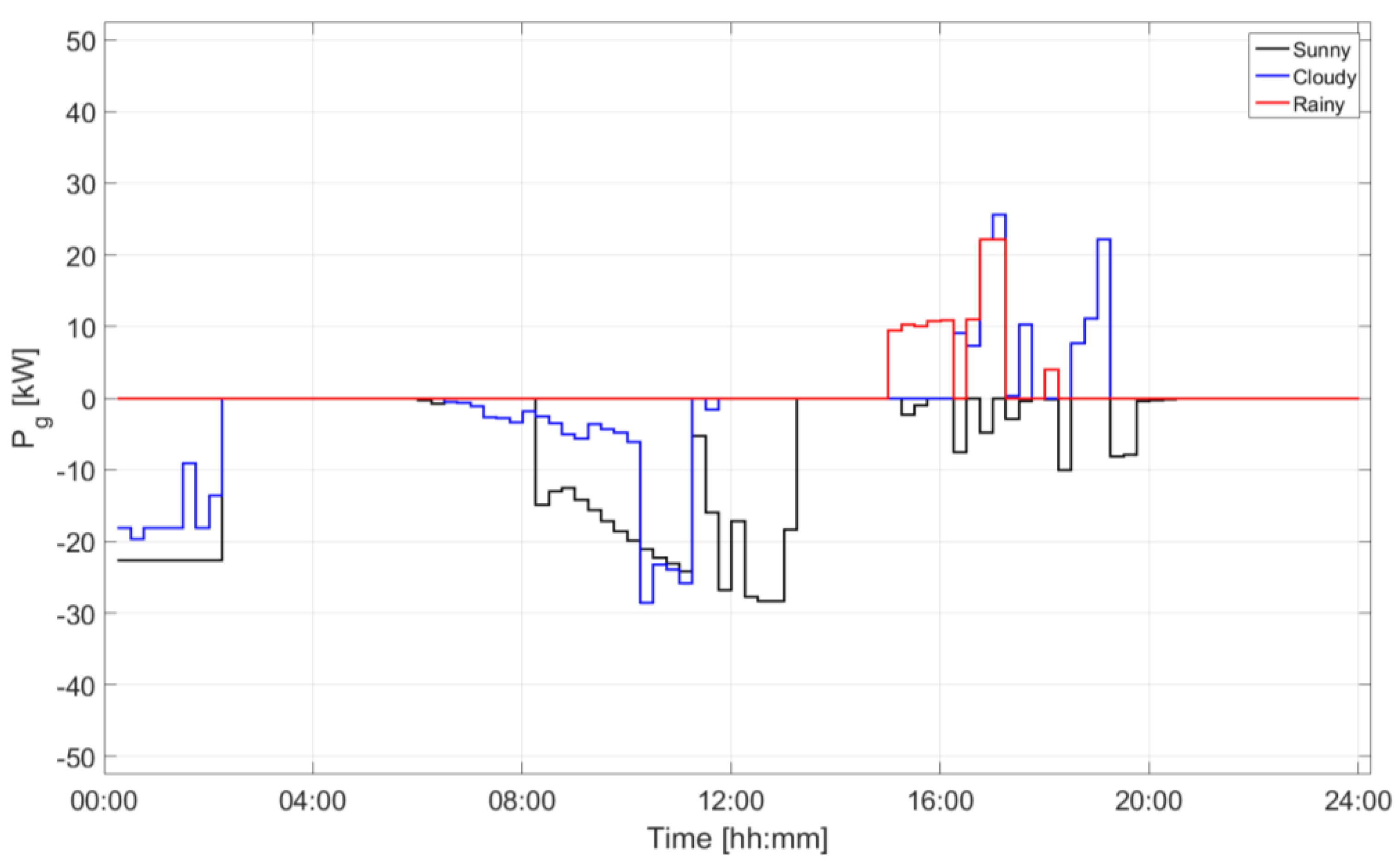
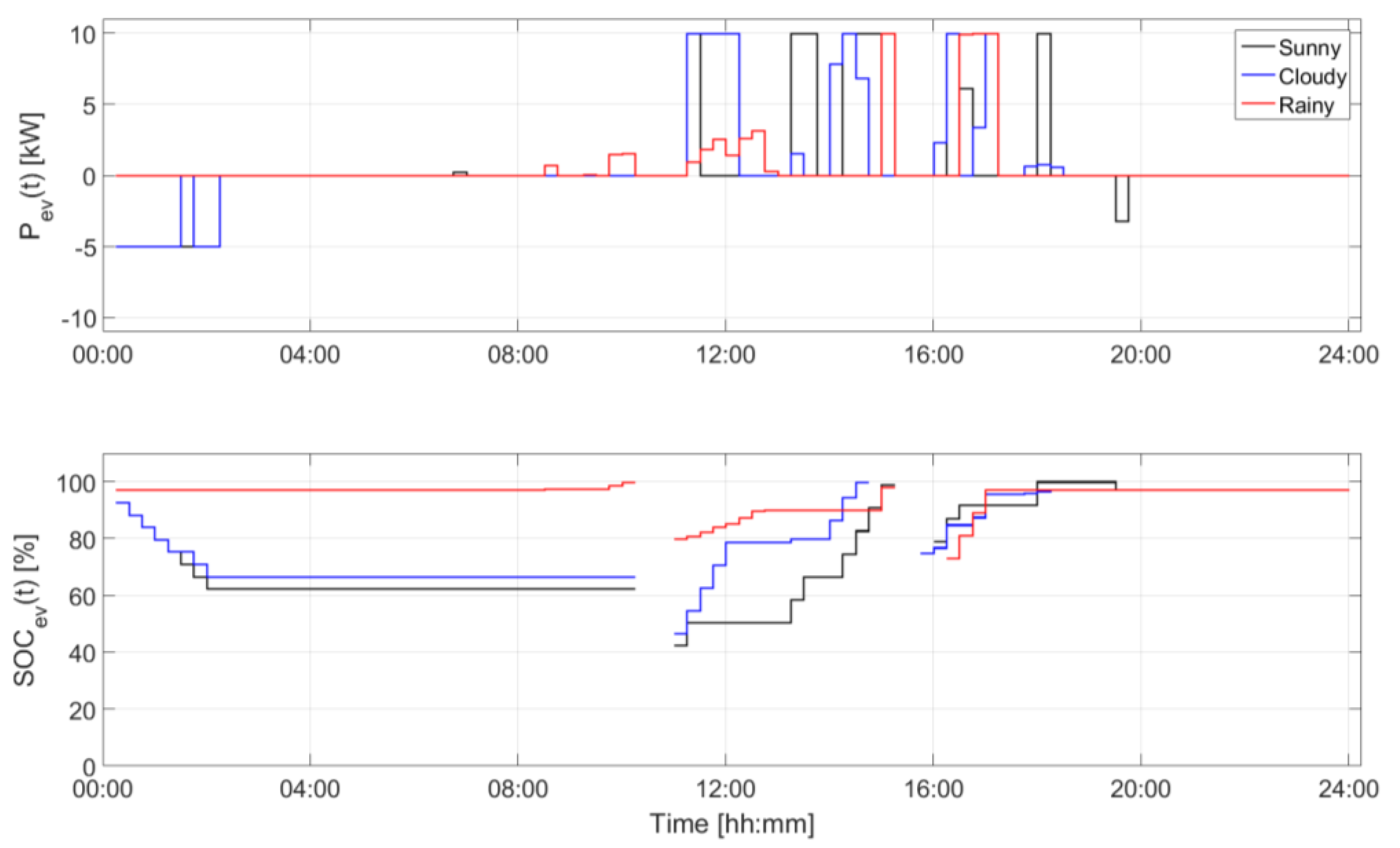
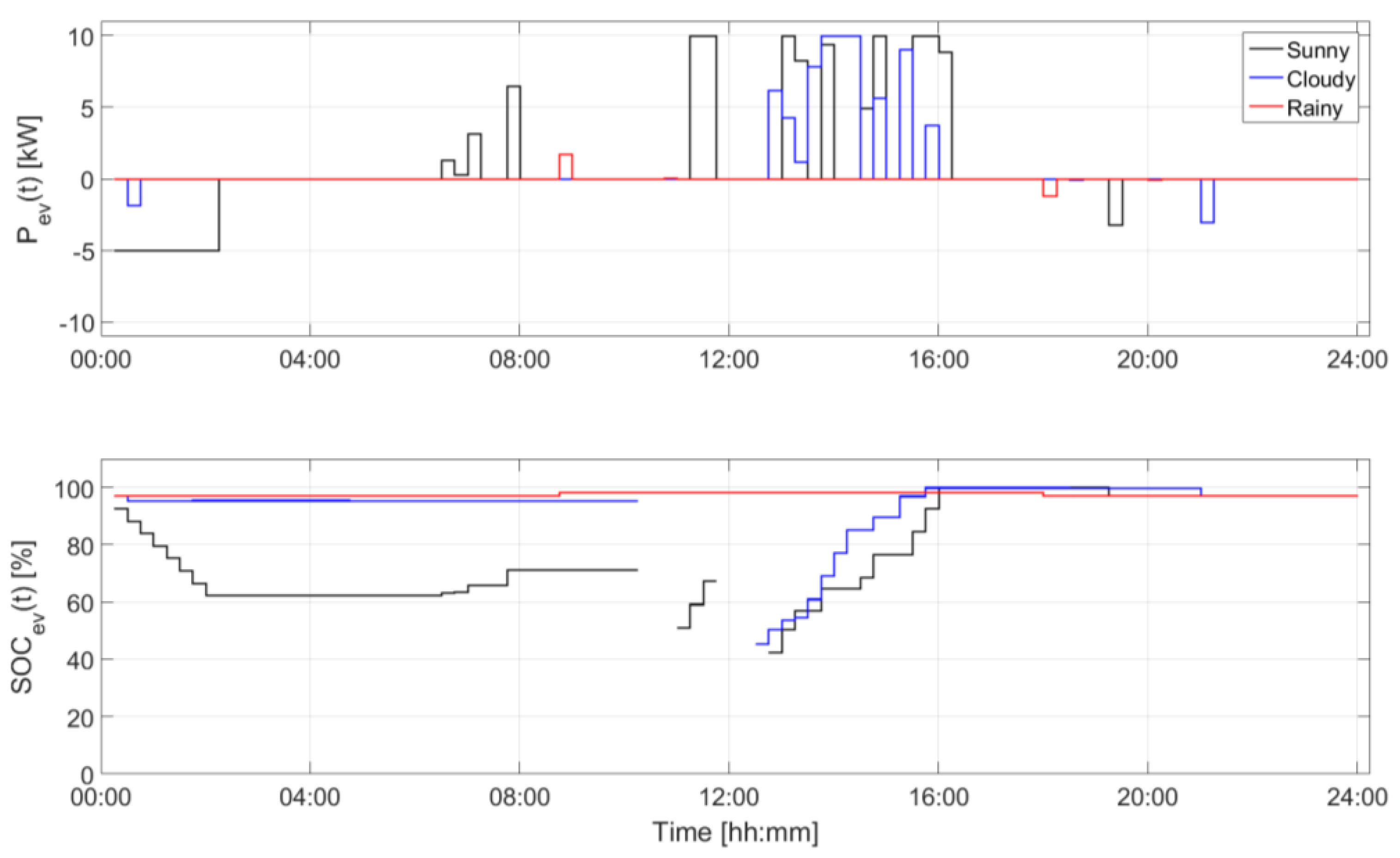
| Device | Installed Size (kW) | Installed Size (kWh) | State of Charge Max/Min (p.u.) | Converter Size (kW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Photovoltaic (PV) | 40 | --- | --- | 40 |
| Energy storage system (ESS) | 30 | 60 | 0.95/0.25 | 30 |
| Charging station (CS) | --- | --- | --- | 10 |
| Utility grid | --- | --- | --- | 50 |
| Electric vehicle (EV) | --- | 24 | 1.0/0.2 | --- |
| Parameter | Symbol | Nominal Value |
|---|---|---|
| EV charge efficiency | 0.95 | |
| EV discharge efficiency | 0.95 | |
| Grid converter efficiency | 0.93 | |
| DC/DC converter efficiency | 0.965 | |
| Storage charge efficiency | 0.9 | |
| Storage discharge efficiency | 0.9 | |
| Connection losses coefficient | 0.035÷0.055 |
| Proposed Iterative MILP | Reference Non-Linear with GA | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EV 1 | EV 2 | EV 3 | EV 4 | EV 5 | EV 1 | EV 2 | EV 3 | EV 4 | EV 5 | ||
[€] | Sunny | 4.14 | 4.14 | 3.93 | 4.14 | 4.85 | 4.15 | 4.15 | 3.84 | 4.2 | 4.48 |
| Cloudy | 3.17 | 0.45 | 3.62 | 3.45 | 3.17 | 3.19 | 0.5 | 3.27 | 3.46 | 3.17 | |
| Rainy | 0 | 0.13 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.15 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.31 | |
[€] | Sunny | 5.04 | 5.38 | 5 | 4.74 | 4.83 | 5.2 | 5.52 | 5.07 | 4.85 | 4.74 |
| Cloudy | 4.56 | 3.27 | 4.54 | 2.01 | 4.58 | 4.66 | 3.36 | 4.43 | 2.07 | 4.69 | |
| Rainy | 3.19 | 0.1 | 1.78 | 3.52 | 0.22 | 3.3 | 0.11 | 1.82 | 3.55 | 0.22 | |
[p.u.] | Sunny | 0.45 | 0.42 | 0.44 | 0.48 | 0.55 | 0.44 | 0.41 | 0.42 | 0.47 | 0.52 |
| Cloudy | 0.37 | 0.07 | 0.43 | 0.92 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.08 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 0.36 | |
| Rainy | 0 | 0.74 | 0 | 0 | 0.82 | 0 | 0.77 | 0.02 | 0 | 0.83 | |
[%] | Sunny | 9 | 9 | 8.57 | 9 | 10.57 | 9.03 | 9.03 | 8.35 | 9.13 | 9.76 |
| Cloudy | 7.29 | 1.03 | 8.33 | 7.95 | 7.29 | 7.33 | 1.16 | 7.53 | 7.95 | 7.3 | |
| Rainy | 0 | 0.28 | 0 | 0 | 0.64 | 0 | 0.32 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.65 | |
| Sunny | 0.64 | 0.64 | 0.60 | 0.64 | 0.76 | 0.64 | 0.64 | 0.59 | 0.65 | 0.70 | |
| Cloudy | 0.50 | 0.08 | 0.58 | 0.55 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.09 | 0.52 | 0.55 | 0.50 | |
| Rainy | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.05 | |
| Proposed Iterative MILP | Reference Non-Linear with GA | ||
|---|---|---|---|
[€] | Sunny | 6.77 | 6.66 |
| Cloudy | 1.95 | 1.92 | |
| Rainy | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
[€] | Sunny | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Cloudy | 4.20 | 4.28 | |
| Rainy | 4.82 | 4.90 | |
[€] | Sunny | 8.66 | 9.53 |
| Cloudy | 16.40 | 17.06 | |
| Rainy | 15.88 | 16.08 |
| Proposed Iterative MILP | Reference Non-Linear with GA | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Simulation time [s] | Sunny | 26.06 | 7216.76 |
| Cloudy | 28.94 | 7222.93 | |
| Rainy | 44.11 | 7217.23 | |
| Iteration number or Generation number | Sunny | 4 | 12 |
| Cloudy | 5 | 13 | |
| Rainy | 10 | 16 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aluisio, B.; Bruno, S.; De Bellis, L.; Dicorato, M.; Forte, G.; Trovato, M. DC-Microgrid Operation Planning for an Electric Vehicle Supply Infrastructure. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132687
Aluisio B, Bruno S, De Bellis L, Dicorato M, Forte G, Trovato M. DC-Microgrid Operation Planning for an Electric Vehicle Supply Infrastructure. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(13):2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132687
Chicago/Turabian StyleAluisio, Benedetto, Sergio Bruno, Luca De Bellis, Maria Dicorato, Giuseppe Forte, and Michele Trovato. 2019. "DC-Microgrid Operation Planning for an Electric Vehicle Supply Infrastructure" Applied Sciences 9, no. 13: 2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132687
APA StyleAluisio, B., Bruno, S., De Bellis, L., Dicorato, M., Forte, G., & Trovato, M. (2019). DC-Microgrid Operation Planning for an Electric Vehicle Supply Infrastructure. Applied Sciences, 9(13), 2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132687






