Fast Multi-Objective Antenna Optimization Based on RBF Neural Network Surrogate Model Optimized by Improved PSO Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Problem Formulation and Preliminaries
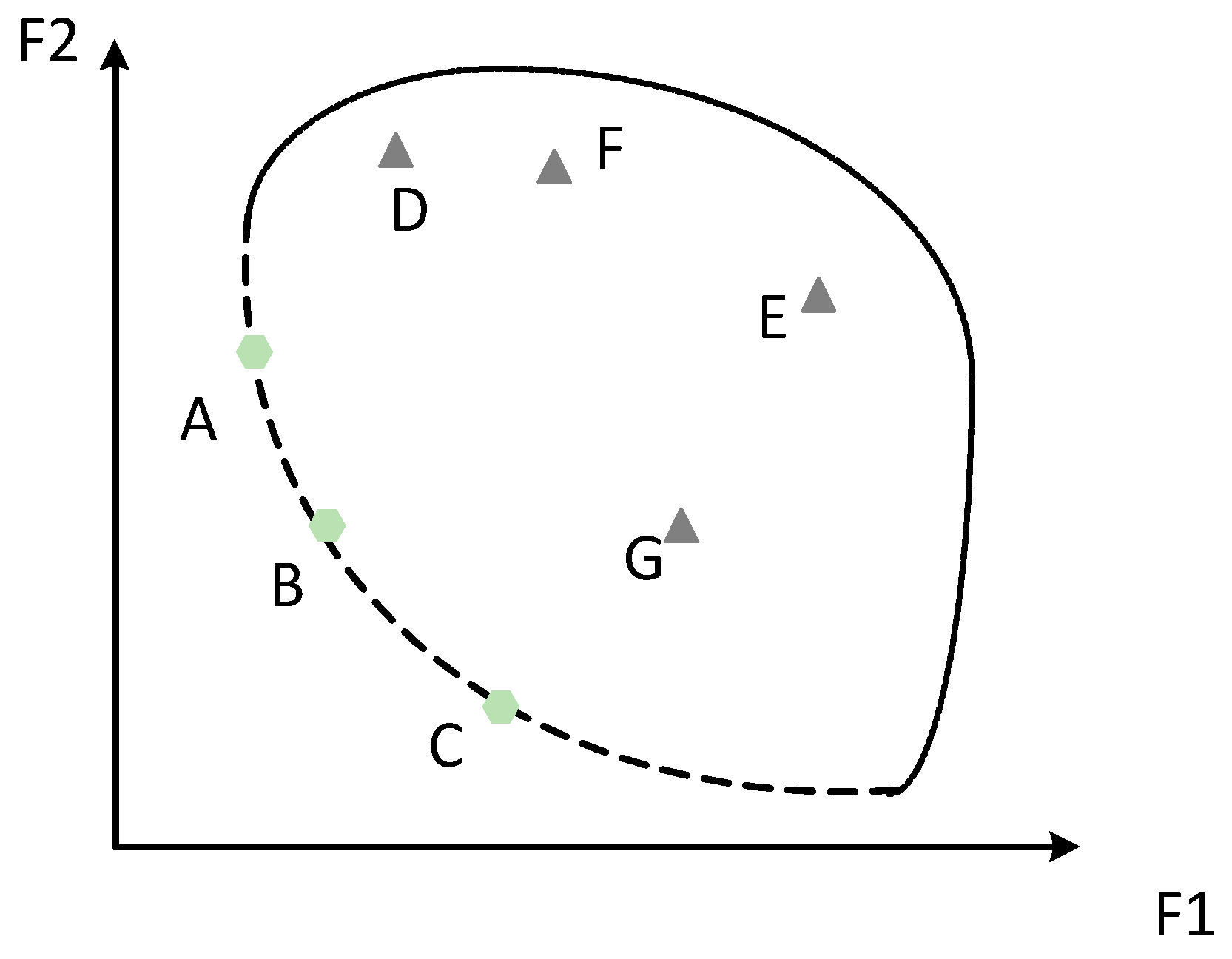
2.1. Problem Formulation
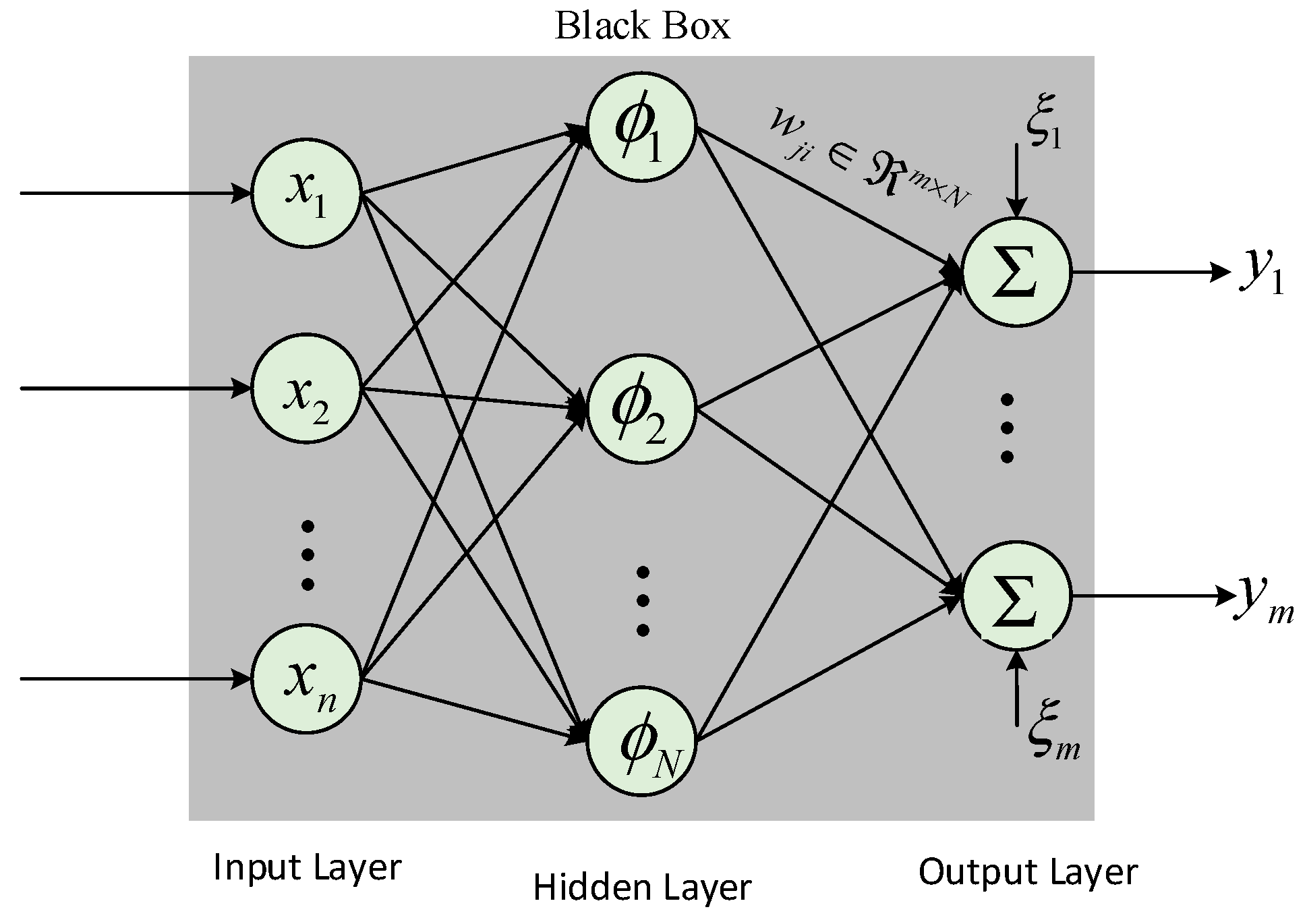
2.2. RBF Neural Networks
2.3. PSO Algorithm
3. Improved PSO-RBFNN Model
3.1. Improved PSO Algorithm
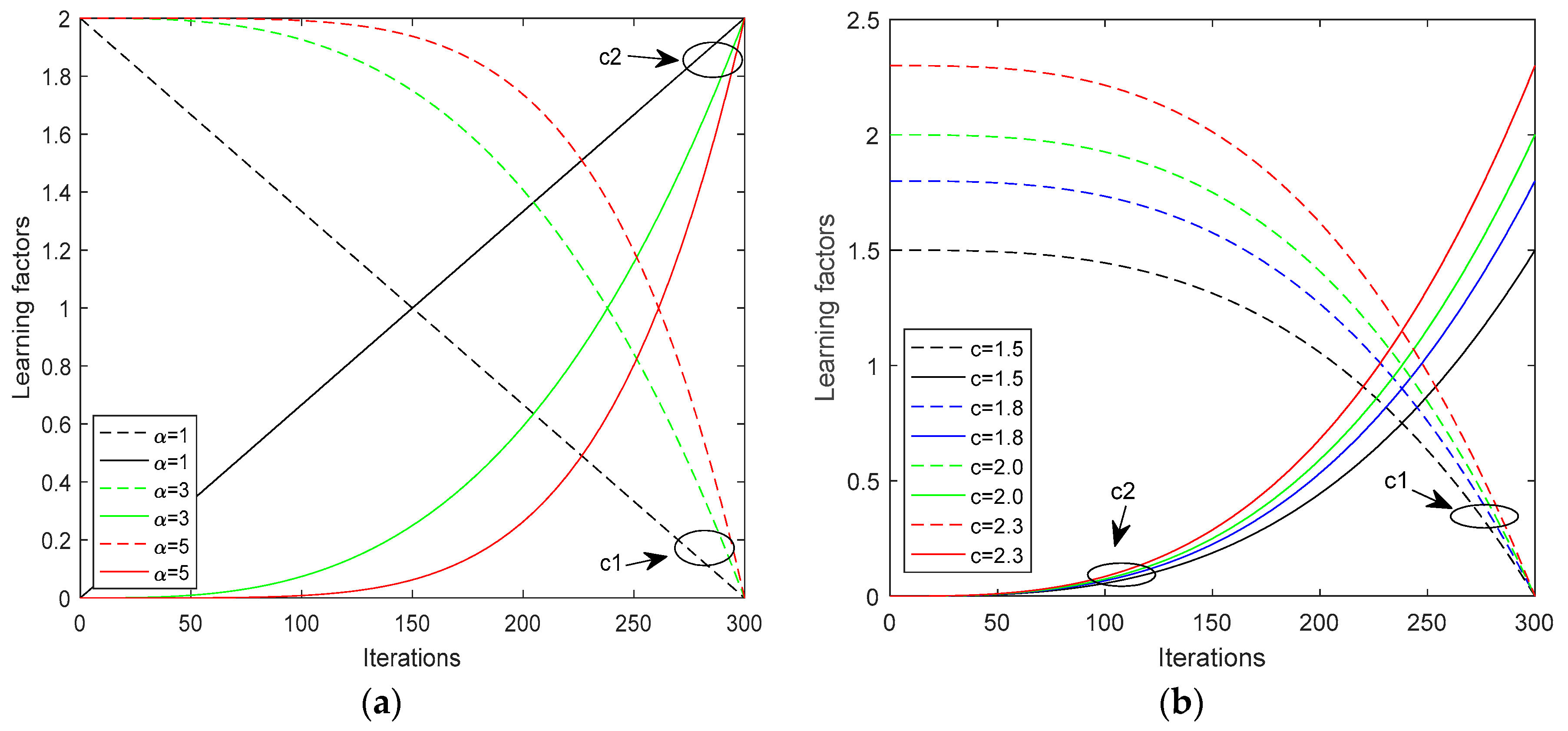
3.1.1. Time-Varying Learning Factors
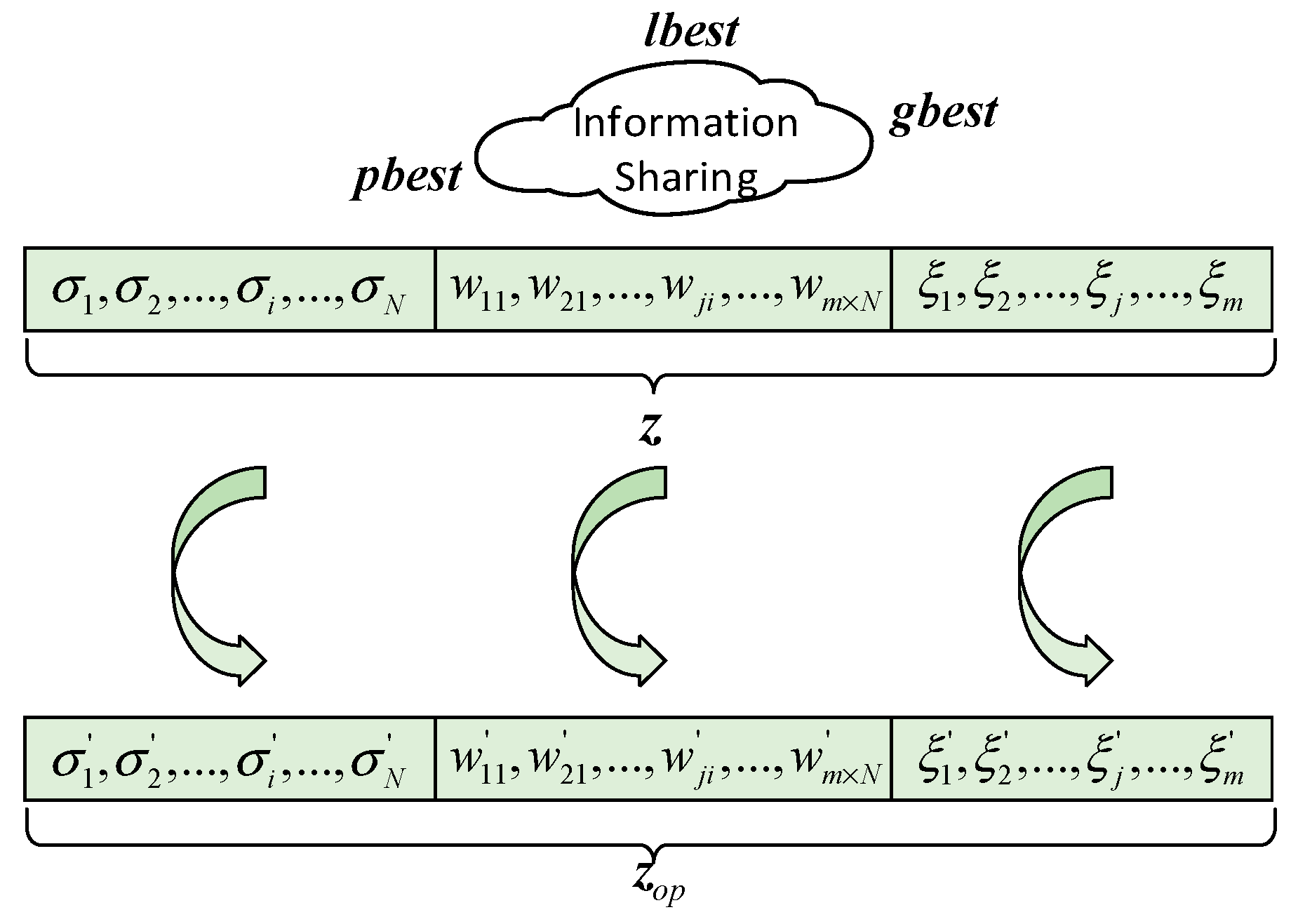
3.1.2. The Addition of Local Best Information
3.2. Improved PSO-RBFNN
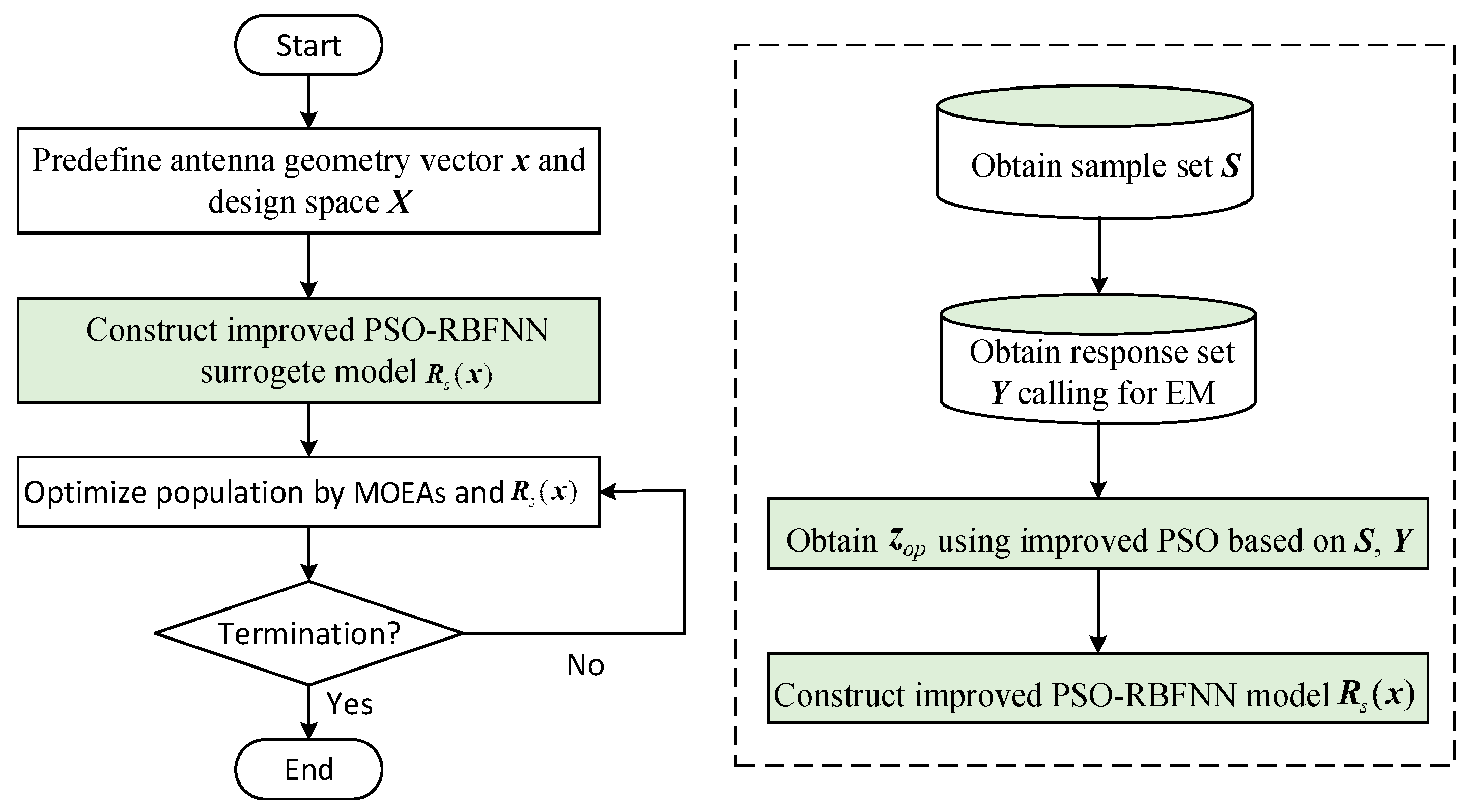
4. Fast Multi-Objective Antenna Optimization Framework Combining MOEAs and Improved PSO-RBFNN Surrogate Model
- Predefine antenna geometry vector x and design space X;
- Obtain the sample set S by sampling randomly in the design space X and obtain the response set Y by calling for EM simulation software;
- Obtain the optimal RBFNN parameters using improved PSO based on S, Y;
- Construct the improved PSO-RBFNN model ;
- Optimize the population by MOEAs and ;
- Stop when the termination condition is satisfied; otherwise, turn to step 5.
5. Verification Case Study and Discussions
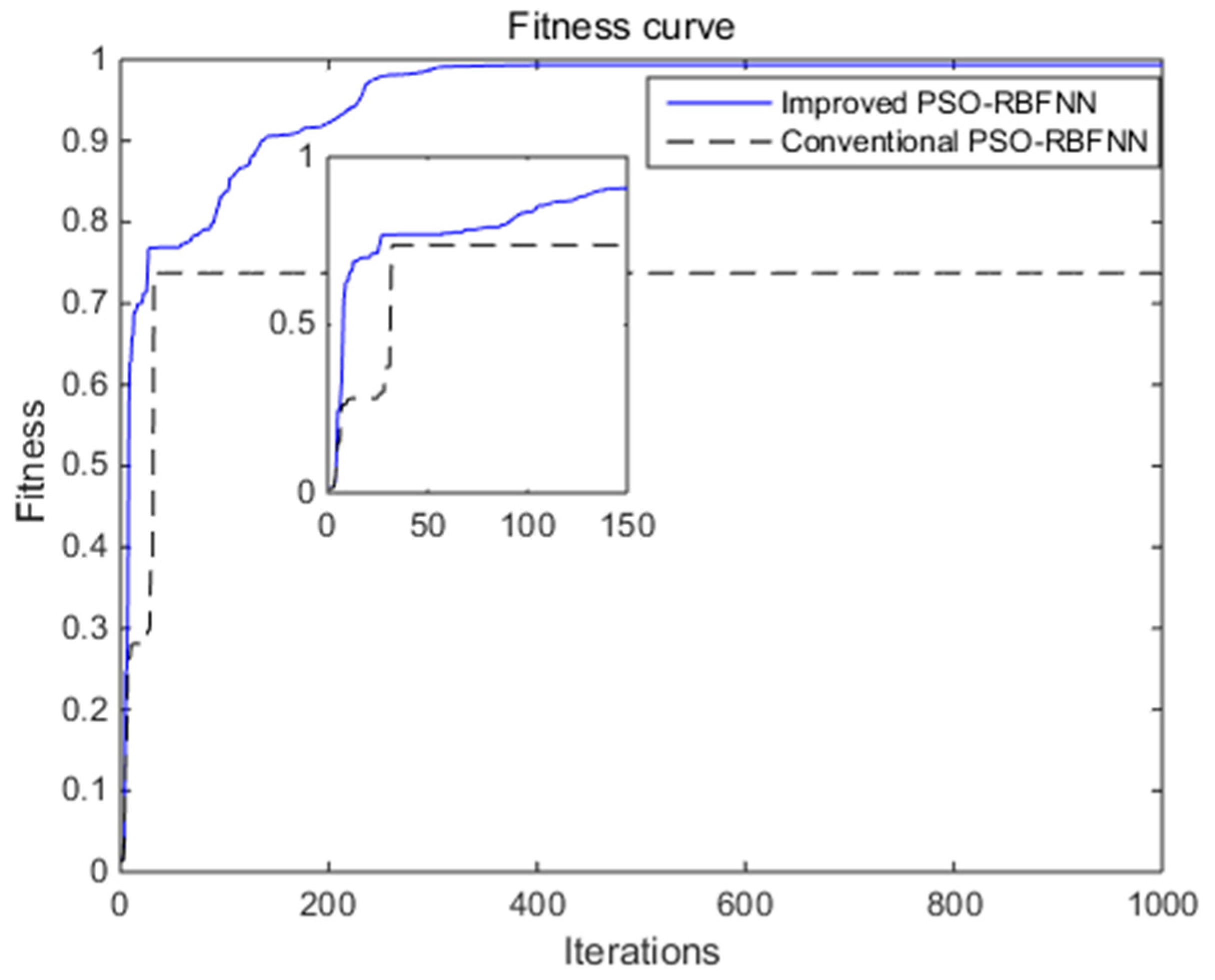
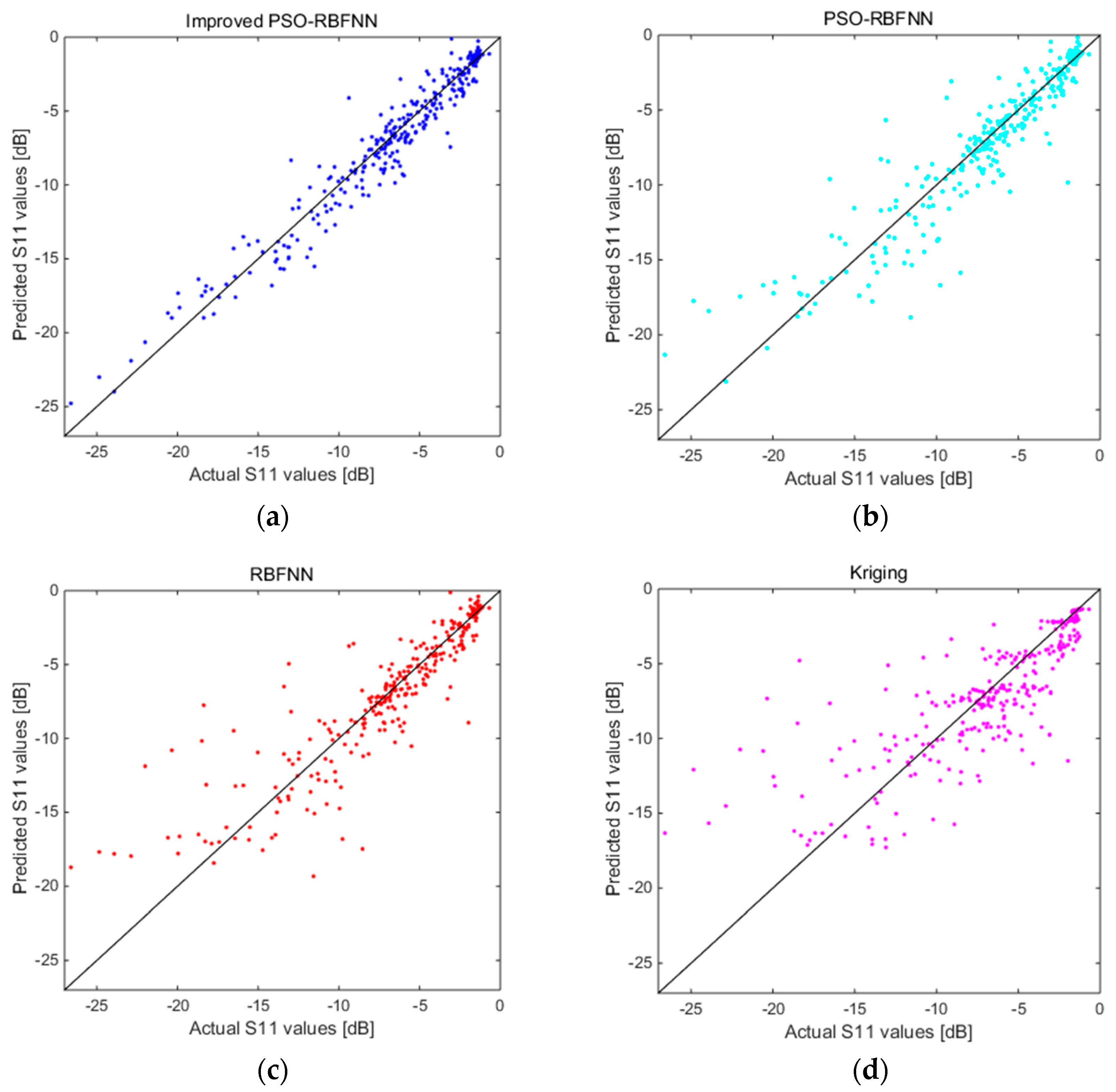
5.1. The Improved PSO-RBFNN Antenna Surrogate Model
5.2. Pareto-Optimal Designs of Planar Miniaturized Multiband Antenna
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, K.; Jang, D.H.; Kang, S.I.; Lee, J.H.; Chung, T.K.; Kim, H.S. Hybrid algorithm combing genetic algorithm with evolution strategy for antenna design. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2016, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Li, Q.; Deng, L. Design of fragment-type antenna structure using an improved BPSO. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, R.; Saldanha, R.R.; Gomes, B.N.; Lisboa, A.C.; Martins, A.X. A multi-objective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition for optimal design of Yagi-Uda antennas. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noras, J.M.; Abd-Alhameed, R.A.; Abdulraheem, Y.I.; Abdullah, A.S.; Mohammed, H.J.; Ali, R.S. Design of a uniplanar printed triple band-rejected ultra-wideband antenna using particle swarm optimisation and the firefly algorithm. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2016, 10, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Koziel, S.; Ogurtsov, S. Multi-objective design of antennas using variable-fidelity simulations and surrogate models. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 5931–5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Li, Q.; Deng, L. Fast multi-objective optimization of multi-parameter antenna structures based on improved MOEA/D with surrogate-assisted model. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2017, 72, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Aliakbarian, H.; Ma, Z.; Vandenbosch, G.A.; Gielen, G.; Excell, P. An Efficient method for antenna design optimization based on evolutionary computation and machine learning techniques. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.P. Efficient Resonant Frequency Modeling for Dual-Band Microstrip Antennas by Gaussian Process Regression. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 14, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Dong, J.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, S. Fast Antenna Design Using Multi-Objective Evolutionary Algorithms and Artificial Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Antennas, Propagation and EM Theory (ISAPE), Hangzhou, China, 3–6 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Qin, W.; Wang, M. Fast Multi-Objective Optimization of Multi-Parameter Antenna Structures Based on Improved BPNN Surrogate Model. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 77692–77701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.D.A.; Soliman, E.A.; El-Gamal, M.A. Optimization and characterization of electromagnetically coupled patch antennas using RBF neural networks. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2006, 20, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Yadav, R.N.; Singh, R.P. Directivity estimations for short dipole antenna arrays using radial basis function neural networks. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 14, 1219–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L. A taxonomy of global optimization methods based on response surfaces. J. Glob. Optim. 2001, 21, 345–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santner, T.J.; Williams, B.J.; Notz, W.I. The Design and Analysis of Computer Experiments; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Thakare, V.V.; Singhal, P.K. Bandwidth Analysis by Introducing Slots in Microstrip Antenna Design Using ANN. Prog. Electromagn. Res. M 2009, 9, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D. Research on traffic flow prediction in the big data environment based on the improved RBF neural network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 13, 2000–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.M.; Verma, B. Nonlinear curve fitting to stopping power data using RBF neural networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 45, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.C.; Do, B.H. Radial Basis Function Based Neural Network for Motion Detection in Dynamic Scenes. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2013, 44, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, C.; Lei, S.; Liu, Y.; Song, Y. RBF Neural Network and ANFIS-Based Short-Term Load Forecasting Approach in Real-Time Price Environment. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2008, 23, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Sandberg, I.W. Universal approximation using radial-basis-function networks. Neural Comput. 1991, 3, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xu, Z.B.; Huang, G.B.; Wang, D.H. Global convergence of online BP training with dynamic learning rate. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2012, 23, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.B.; Zhang, R.; Jing, W.F. When does online bp training converge? IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2009, 20, 1529–1539. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.M. Self-generation RBFNs using evolutional PSO learning. Neurocomputing 2006, 70, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Sun, Y.; Ruan, X. A simulation analysis method based on PSO-RBF model and its application. Clust. Comput. 2018, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, P.A.; Hervas-Martinez, C.; Martinez-Estudillo, F.J. Logistic regression by means of evolutionary radial basis function neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2011, 22, 246–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.M.; Ko, C.N. Time series prediction using rbf neural networks with a nonlinear time-varying evolution pso algorithm. Neurocomputing 2009, 73, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziel, S.; Bekasiwewicz, A. Fast multi-objective surrogate-assisted design of multi-parameter antenna structures through rotational design space reduction. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2016, 10, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, J.; Darken, C.J. Fast learning in networks of locally-tuned processing units. Neural Comput. 1989, 1, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, K.; He, H.; Irwin, G.W. A new discrete-continuous algorithm for radial basis function networks construction. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2013, 24, 1785–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.L.; Liao, C.; Lin, W.; Chang, L.; Zhong, X.M. Hybrid-Surrogate-Model-Based Efficient Global Optimization for High-Dimensional Antenna Design. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2012, 124, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R.C. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the 1995 IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Lynn, N.; Suganthan, P.N. Heterogeneous comprehensive learning particle swarm optimization with enhanced exploration and exploitation. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2015, 24, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.J.; Li, X.; Mei, Y. A Time-Varying Transfer Function for Balancing the Exploration and Exploitation ability of a Binary PSO. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 59, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q. Prediction of building energy consumption based on PSO-RBF neural network. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on System Science and Engineering (ICSSE), Shanghai, China, 11–13 July 2014; pp. 60–63. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, N.; Rahmat-Samii, Y. Advances in particle swarm optimization for antenna designs: Real-number, binary, single-objective and multiobjective implementations. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2007, 55, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, H. MOEA/D: A multiobjective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2007, 11, 712–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


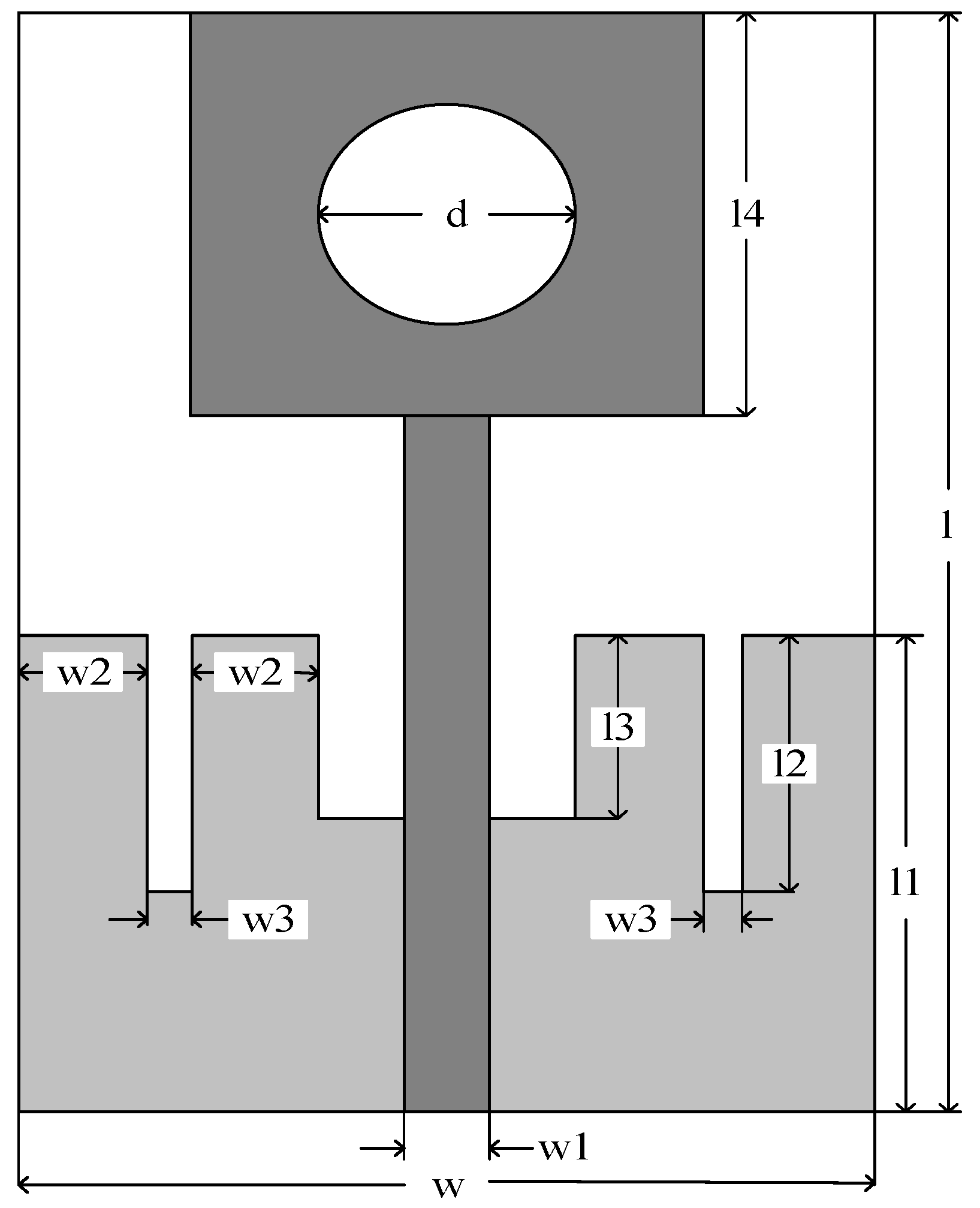
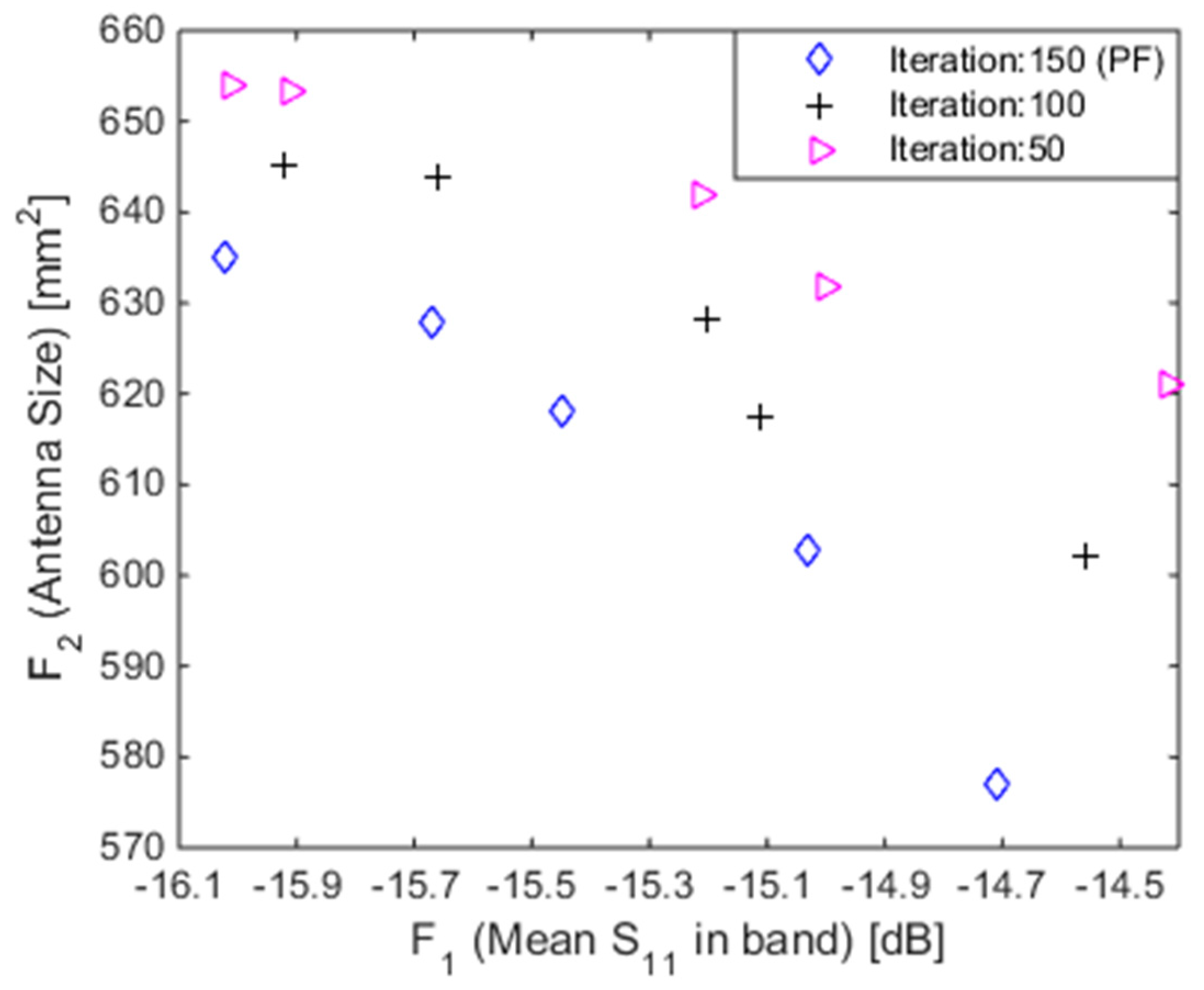
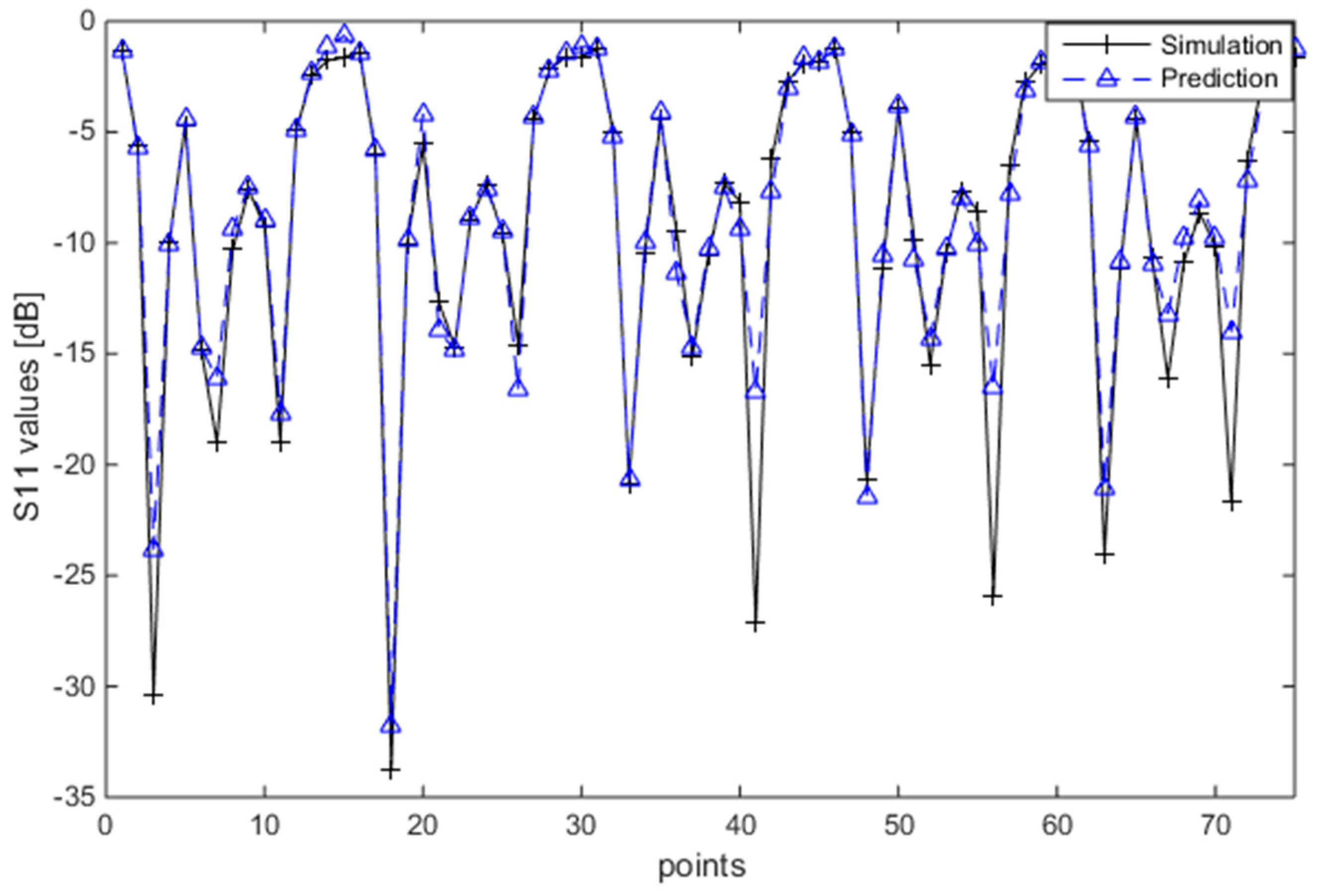
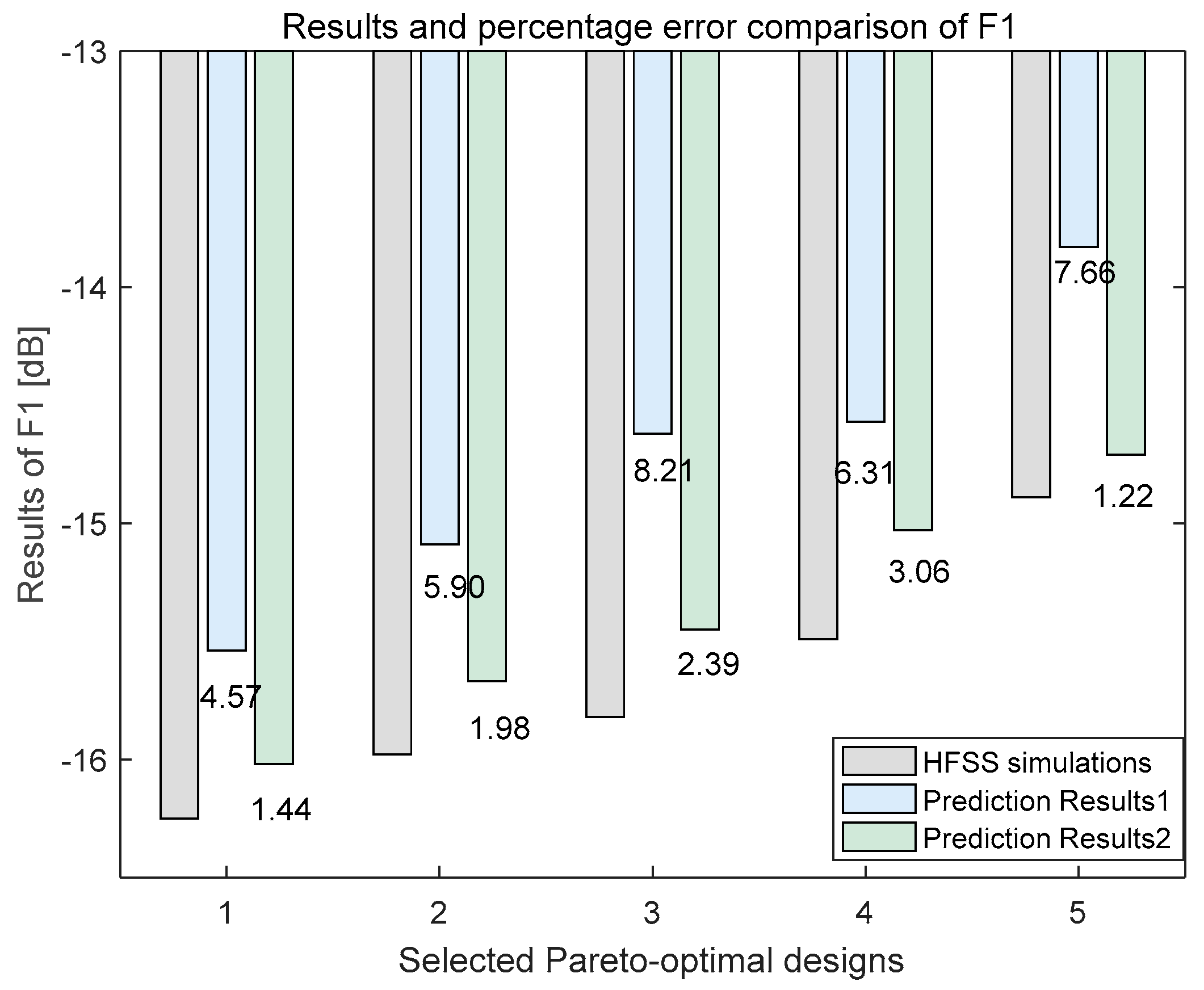
| Parameters | Range |
|---|---|
| d | [7, 10] |
| l | [26, 34] |
| l1 | [11, 14] |
| l2 | [8, 10] |
| l3 | [6, 8] |
| l4 | [10, 14] |
| w | [17, 23] |
| w1 | [2, 4] |
| w2 | [2, 4] |
| w3 | [0.5, 1.5] |
| Methods | HFSS | Kriging [5] | RBFNN [11] | PSO-RBFNN [24] | Improved PSO-RBFNN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total time | 1017.820 | 0.413 | 0.165 | 0.043 | 0.039 |
| Average time | 50.891 | 0.021 | 0.008 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| Designs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −16.02 | −15.67 | −15.45 | −15.03 | −14.71 | |
| 634.92 | 628.00 | 617.97 | 602.76 | 577.17 | |
| d | 8.58 | 8.61 | 8.76 | 8.69 | 8.27 |
| l | 31.20 | 31.40 | 29.26 | 29.26 | 28.90 |
| l1 | 12.70 | 12.50 | 12.00 | 11.95 | 11.09 |
| l2 | 8.80 | 8.80 | 9.04 | 9.04 | 8.79 |
| l3 | 6.92 | 6.90 | 7.28 | 7.21 | 7.01 |
| l4 | 11.43 | 11.43 | 11.73 | 11.73 | 11.37 |
| w | 20.35 | 20.00 | 21.12 | 20.60 | 19.97 |
| w1 | 3.23 | 3.23 | 3.34 | 3.31 | 3.13 |
| w2 | 3.10 | 3.10 | 3.27 | 3.27 | 3.27 |
| w3 | 1.01 | 1.00 | 1.19 | 1.17 | 1.01 |
| Optimization Method | Number of EM Simulations | CPU Time/h | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Relative | ||
| Method 1 | 15,100 | 213.51 | 100% |
| Method 2 | 200 | 2.93 | 1.37% |
| This work | 200 | 2.98 | 1.40% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, M. Fast Multi-Objective Antenna Optimization Based on RBF Neural Network Surrogate Model Optimized by Improved PSO Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132589
Dong J, Li Y, Wang M. Fast Multi-Objective Antenna Optimization Based on RBF Neural Network Surrogate Model Optimized by Improved PSO Algorithm. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(13):2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132589
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Jian, Yingjuan Li, and Meng Wang. 2019. "Fast Multi-Objective Antenna Optimization Based on RBF Neural Network Surrogate Model Optimized by Improved PSO Algorithm" Applied Sciences 9, no. 13: 2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132589
APA StyleDong, J., Li, Y., & Wang, M. (2019). Fast Multi-Objective Antenna Optimization Based on RBF Neural Network Surrogate Model Optimized by Improved PSO Algorithm. Applied Sciences, 9(13), 2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132589






