Feature Weighting Based on Inter-Category and Intra-Category Strength for Twitter Sentiment Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel mathematical model called Category Discriminative Strength (CDS) is proposed, which measures the strength of the terms in differentiating the categories. Also, the Intra-Distribution Measure (IDM) is introduced to characterize the partial significance of the terms inside a category.
- A modified Chi-square statistics model is introduced to measure the intra-category dependency of the features.
- A fine-grained feature clustering strategy is presented, which properly defines the margin of discriminative features and aggregates the features of similar distributions for efficient feature weighting.
- An adaptive weighting strategy is proposed to properly decide the weight of each feature, and the inter-category and intra-category relevance of the features are included to maximize the efficiency of the weighting.
2. Related Work
2.1. Twitter Sentiment Analysis and Opinion Mining
2.2. Lexicon-Based Approach
2.3. Machine Learning-Based Approach
2.4. Feature Weighting
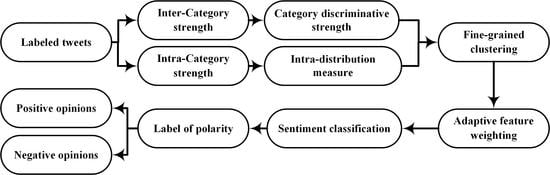
3. The Proposed Scheme
3.1. Motivation
3.2. Category Discriminative Strength
3.3. Intra-Distribution Measure (IDM)
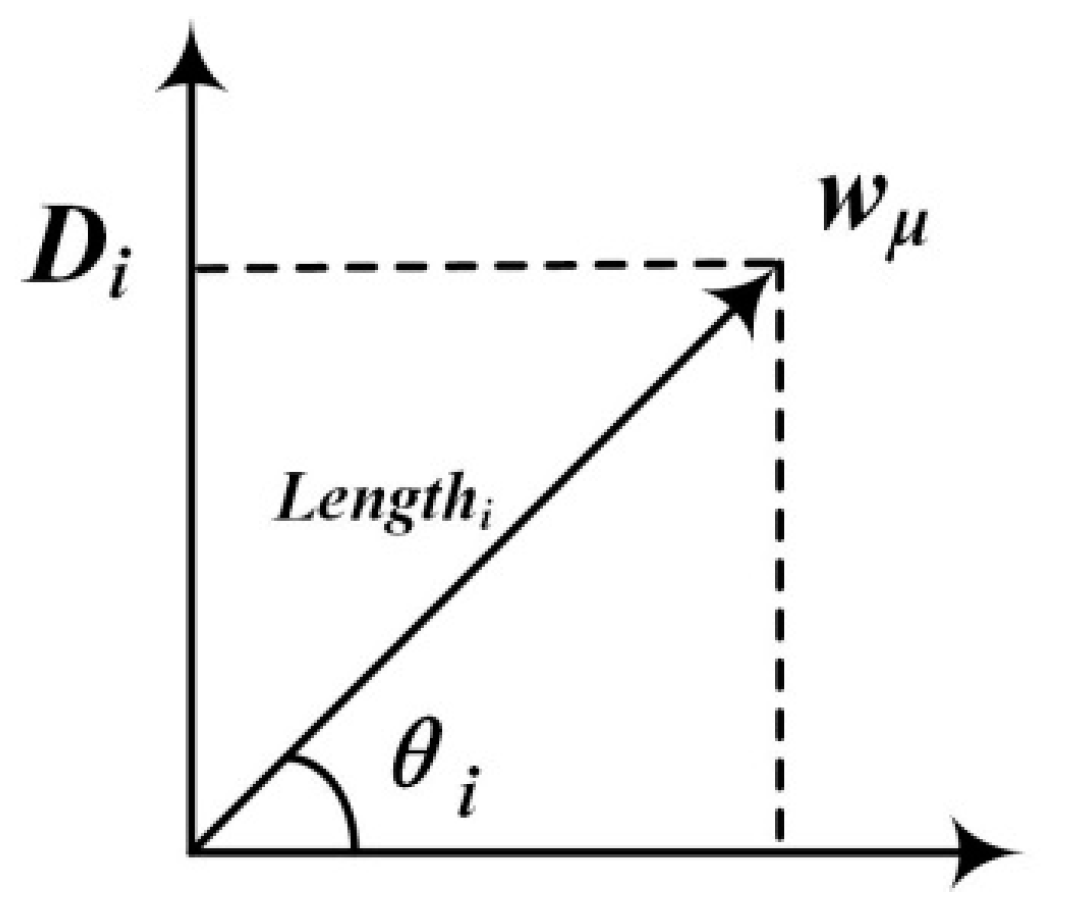
3.4. Feature Clustering and Weighting
3.5. Sentiment Estimation
4. Performance Evaluation
4.1. Experiment Setting
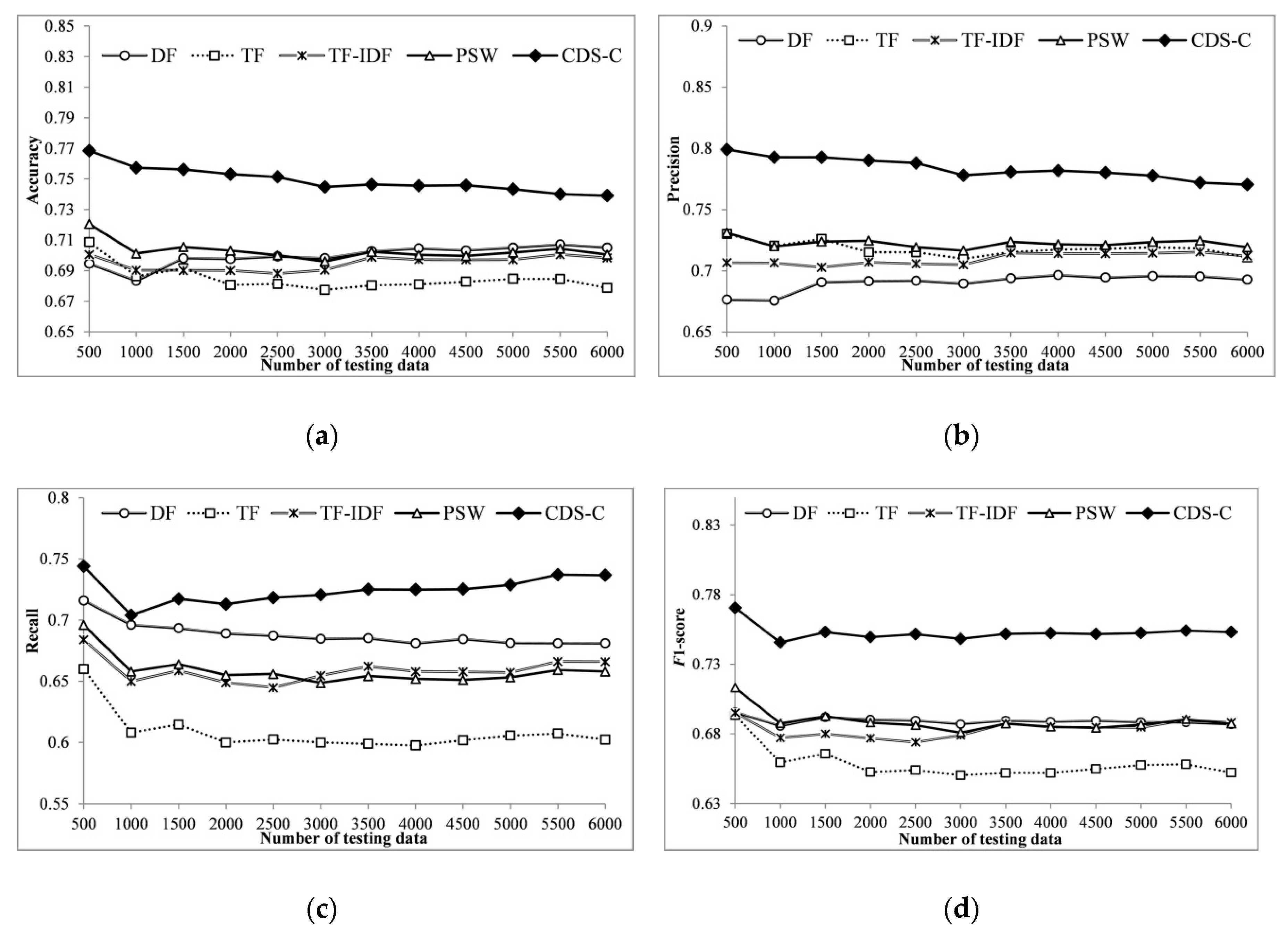
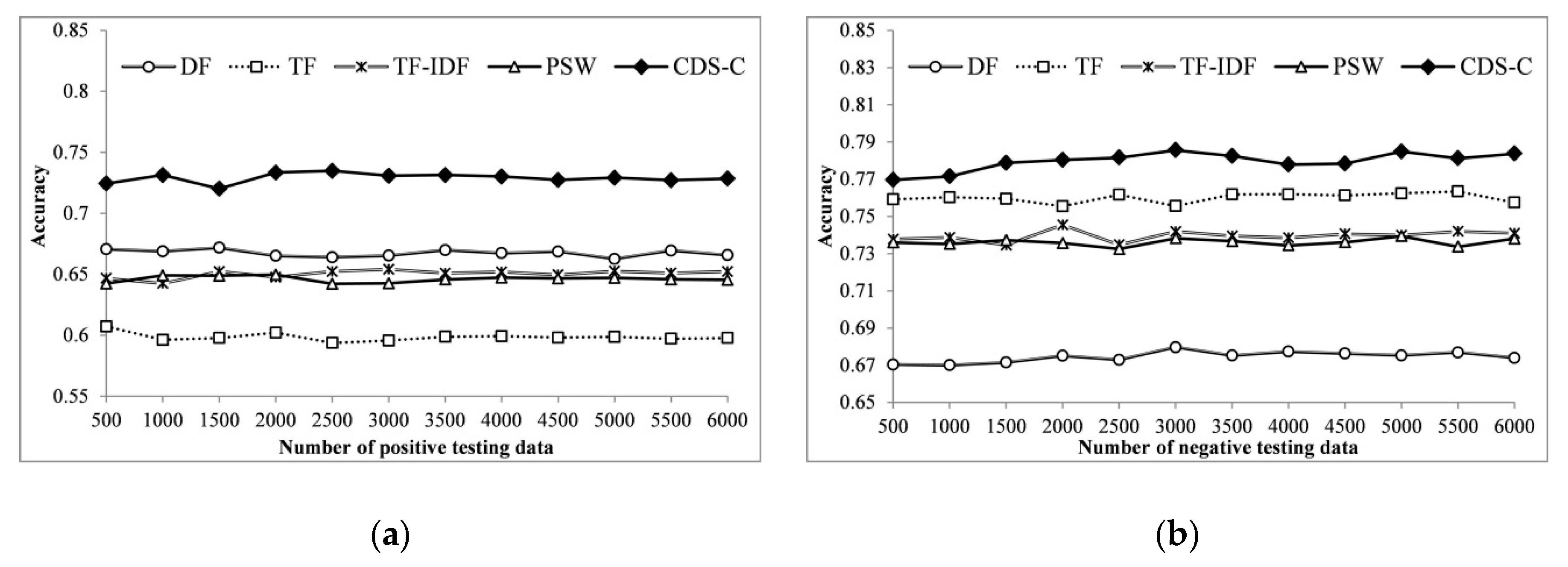
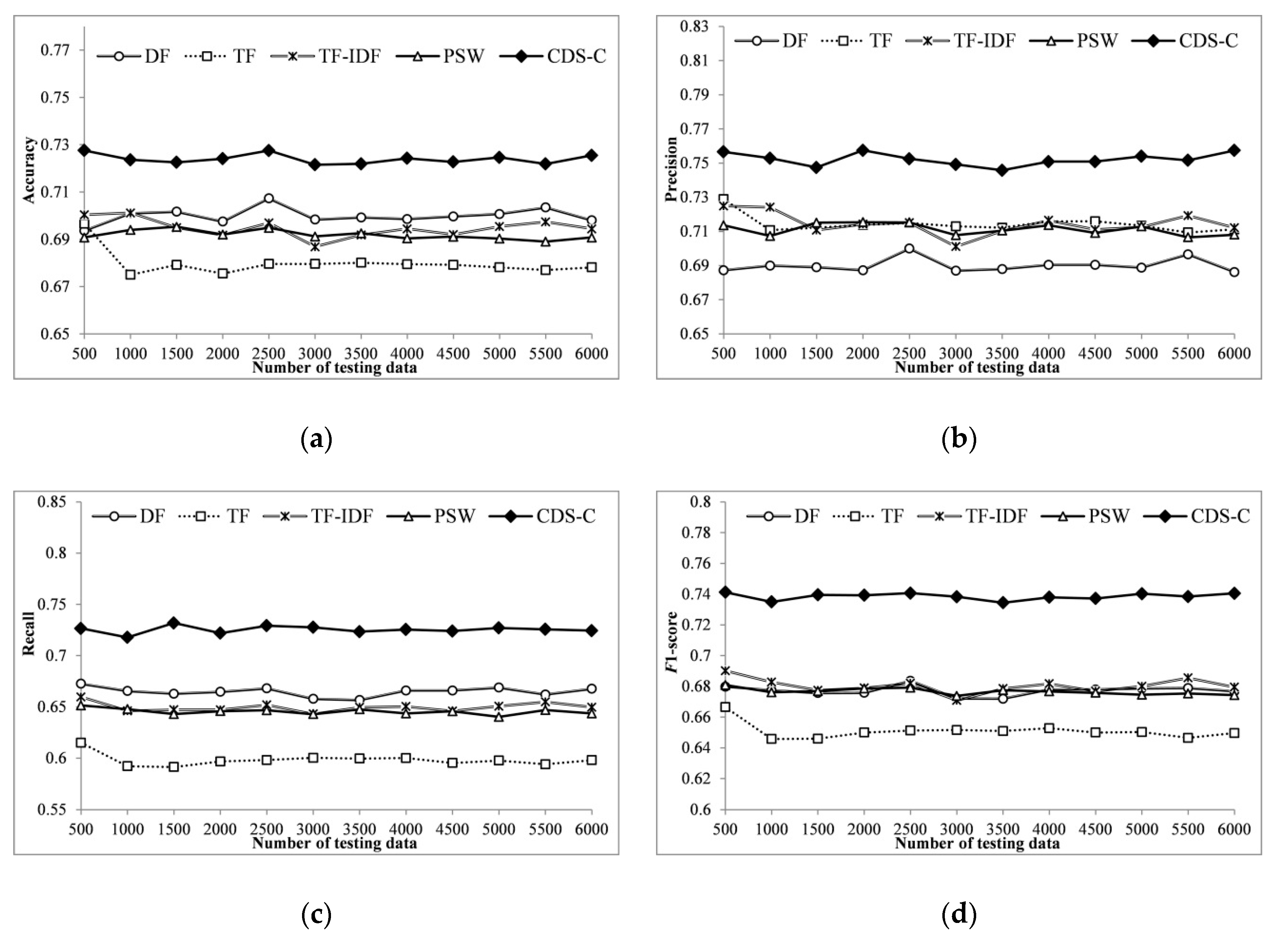
4.2. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deng, Z.H.; Tang, S.W.; Yang, D.Q.; Ming, Z.; Li, L.Y.; Xie, K.Q. A comparative study on features weight in text categorization. In Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific Web Conference, Berlin, Germany, 4 April 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Z.H.; Luo, K.H.; Yu, H.L. A study of supervised term weighting scheme for sentiment analysis. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 3506–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Lv, R.; Zhu, Y.; Ji, P.; Sun, H.; Shi, Y.Q. Fingerprint liveness detection using gradient-based texture features. Signal Image Video Process. 2017, 11, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salima, B.; Barigou, F.; Belalem, G. Sentiment analysis at document level. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart Trends for Information Technology and Computer Communications, Singapore, 6 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Parlar, T.; Özel, S.A.; Song, F. QER: A new feature selection method for sentiment analysis. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2018, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, M. A feature selection approach based on interclass and intraclass relative contributions of terms. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2016, 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Wang, H.; Gao, S. Sentimental feature selection for sentiment analysis of Chinese online reviews. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2018, 9, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debole, F.; Sebastiani, F. Supervised term weighting for automated text categorization. In Proceedings of the Text Mining and Its Applications, 1st ed.; Janusz, K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2004; Volume 138, pp. 81–97. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, Z.; Long, J.; Zhang, H. Turning from TF-IDF to TF-IGM for term weighting in text classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 66, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Youn, H.Y. A Novel Feature-Based Text Classification Improving the Accuracy of Twitter Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the Advances in Computer Science and Ubiquitous Computing, Singapore, 18 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, A.; Jun, Z.; Lei, P.; Yang, X. Enhanced twitter sentiment analysis by using feature selection and combination. In Proceedings of the Security and Privacy in Social Networks and Big Data, Hangzhou, China, 16–18 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jose, A.K.; Bhatia, N.; Krishna, S. Twitter Sentiment Analysis; Seminar Report; National Institute of Technology Calicut: Kerala, India, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Krouska, A.; Troussas, C.; Virvou, M. The effect of preprocessing techniques on Twitter Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information, Intelligence, Systems & Applications, Chalkidiki, Greece, 13–15 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wikipedia Sentiment Analysis. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sentiment_ analysis (accessed on 12 November 2018).
- Pang, B.; Lee, L. Opinion Mining and Sentiment Analysis, 1st ed.; Now Publishers Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 1–135. [Google Scholar]
- Mingqing, H.; Bin, L. Mining and summarizing customer reviews. In Proceedings of the Tenth ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Washington, DC, USA, 22–25 August 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, F.A. A new ANEW: Evaluation of a word list for sentiment analysis in microblogs. arXiv, 2011; arXiv:1103.2903. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, S.M.; Kiritchenko, S.; Zhu, X. NRC-Canada Building the state-of-the-art in sentiment analysis of tweets. arXiv, 2013; arXiv:1308.6242. [Google Scholar]
- Kolchyna, O.; Souza, T.T.; Treleaven, P.; Aste, T. Twitter sentiment analysis: Lexicon method, machine learning method and their combination. arXiv, 2015; arXiv:1507.00955. [Google Scholar]
- Hailong, Z.; Wenyan, G.; Bo, J. Machine Learning and Lexicon Based Methods for Sentiment Classification: A Survey. In Proceedings of the Web Information System and Application Conference, Tianjin, China, 12–14 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- De Diego, I.M.; Fernández-Isabel, A.; Ortega, F.; Moguerza, J.M. A visual framework for dynamic emotional web analysis. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2018, 145, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambria, E. Affective computing and sentiment analysis. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2016, 31, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, M.T.; Pardo, T.A.; Ruiz, E.E.S. Creating a Portuguese context sensitive lexicon for sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Processing of the Portuguese Language, Cham, Switzerland, 24 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Moslmi, T.; Albared, M.; Al-Shabi, A.; Omar, N.; Abdullah, S. Arabic senti-lexicon: Constructing publicly available language resources for Arabic sentiment analysis. J. Inf. Sci. 2018, 44, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, R. Techniques and applications for sentiment analysis. Commun. ACM 2013, 56, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giachanou, A.; Crestani, F. Like it or not: A survey of Twitter sentiment analysis methods. ACM Comput. Surv. 2016, 49, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Isabel, A.; Prieto, J.C.; Ortega, F.; de Diego, I.M.; Moguerza, J.M.; Mena, J.; Galindo, S.; Napalkova, L. A unified knowledge compiler to provide support the scientific community. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2018, 161, 157–171. [Google Scholar]
- Jaramillo, F.; Orchard, M.; Muñoz, C.; Antileo, C.; Sáez, D.; Espinoza, P. On-line estimation of the aerobic phase length for partial nitrification processes in SBR based on features extraction and SVM classification. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 331, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.; Maldonado, S.; Carrasco, M. Double regularization methods for robust feature selection and SVM classification via DC programming. Inf. Sci. 2018, 429, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, S.; López, J. Dealing with high-dimensional class-imbalanced datasets: Embedded feature selection for SVM classification. Appl. Soft. Comput. 2018, 67, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achlerkar, P.D.; Samantaray, S.R.; Manikandan, M.S. Variational mode decomposition and decision tree based detection and classification of power quality disturbances in grid-connected distributed generation system. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9, 3122–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, Q.; Li, T.; Chen, D. Differentially private classification with decision tree ensemble. Appl. Soft. Comput. 2018, 62, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Du, C.; Xu, Y.; Tian, Y.C. Cost-sensitive and hybrid-attribute measure multi-decision tree over imbalanced data sets. Inf. Sci. 2018, 422, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, P.; Jia, C. Differentially private naive bayes learning over multiple data sources. Inf. Sci. 2018, 444, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H. An information-theoretic filter approach for value weighted classification learning in naive Bayes. Data Knowl. Eng. 2018, 113, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S. Bayesian Naïve Bayes classifiers to text classification. J. Inf. Sci. 2018, 44, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiani, F. Machine learning in automated text categorization. ACM Comput. Surv. 2002, 34, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.T.; Goh, W.B.; Low, K.L. Feature selection, perceptron learning, and a usability case study for text categorization. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 27–31 July 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Schütze, H.; Hull, D.A.; Pedersen, J.O. A comparison of classifiers and document representations for the routing problem. In Proceedings of the 18th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Seattle, WA, USA, 9–13 July 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Wiener, E.; Pedersen, J.O.; Weigend, A.S. A neural network approach to topic spotting. In Proceedings of the 4th Annual Symposium on Document Analysis and Information Retrieval (SDAIR-95), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24–26 April 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, D.; Qin, B.; Liu, T. Document modeling with gated recurrent neural network for sentiment classification. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Lisbon, Portugal, 17–21 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Supratak, A.; Pan, W.; Wu, C.; Matthews, P.M.; Guo, Y. Mixed neural network approach for temporal sleep stage classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2018, 26, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Peng, H.; Khan, T.; Cambria, E.; Hussain, A. Sentic LSTM: A Hybrid Network for Targeted Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis. Cogn. Comput. 2018, 10, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Shi, T.; Xiong, N.N.; Sun, X.; Jeon, B. A Privacy-Preserving Handwritten Signature Verification Method Using Combinational Features and Secure KNN. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 46695–46705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Jeon, B.; Sun, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H. Student’s t-hidden Markov model for unsupervised learning using localized feature selection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2018, 28, 2586–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Chen, L. Term-frequency based feature selection methods for text categorization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computing, Shenzhen, China, 13–15 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Z.; Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, Q. A secure and dynamic multi-keyword ranked search scheme over encrypted cloud data. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2015, 27, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kim, K.; Lee, B.; Youn, H.Y. Word clustering based on POS feature for efficient twitter sentiment analysis. Hum.-Centric Comput. Inf. Sci. 2018, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, L.D.; McCallum, A.K. Distributional clustering of words for text classification. In Proceedings of the 21st Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Melbourne, Australia, 24–28 August 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Stanford Naïve Bayes Text Classification. Available online: http://nlp.stanford.edu/IR-book /html/htmledition/naive-bayes-text-classification-1.html (accessed on 13 November 2018).
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, L.; Li, C.; Kong, G. Two feature weighting approaches for naive bayes text classifiers. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2016, 100, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford Log-Linear Part-of-Speech Tagger. Available online: http://nlp.stanford.edu/softw are/tagger.shtml (accessed on 5 October 2018).
- Matlab-Stanford-Postagger. Available online: https://github.com/musically-ut/matlab-stanf ord-postaggr (accessed on 3 May 2018).
- Sentiment 140. Available online: http://help.sentiment140.com/home (accessed on 6 May 2018).
- Liangxiao, J.; Dianhong, W.; Zhihua, C. Discriminatively weighted naïve bayes and its application in text classification. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Tools 2012, 21, 1250007. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, B.; Lee, L.; Vaithyanathan, S. Thumbs up?: Sentiment classification using machine learning techniques. In Proceedings of the ACL–02 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 6–7 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Huang, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, B.; Liu, T. Aurora image classification based on multi-feature latent dirichlet allocation. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, X.; Jian, L.; Liu, K.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, W. A sparse representation-based image resolution improvement method by processing multiple dictionary pairs with latent Dirichlet allocation model for street view images. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 38, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, C. Ldagibbs: A command for topic modeling in Stata using latent Dirichlet allocation. Stata J. 2018, 18, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.; Choi, I.; Choi, N. Topic Analysis of the Research Domain in Knowledge Organization: A Latent Dirichlet Allocation Approach. Knowl. Organ. 2018, 45, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Subset | Property | POS Tag |
|---|---|---|
| Emotion | Adverb, Adjective, Verb | JJ, JJR, …, RB, RBR, …, VB, VBD, … |
| Normal | Norm | NN, NNS, NNP, NNPS… |
| Remain | Remaining | Remaining |
| Feature Selection | ∈ cj | ∉ cj | Sum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Containing wi | A | B | A + B |
| Not containing wi | C | D | C + D |
| Sum | A + C | B + D | A + B + C + D |
| Tested Tweet | Content | Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ‘ok I’m sick and spent an hour sitting in the shower cause I was too sick to stand and held back the puke like a champ. BED now‘ | 0 |
| 2 | ‘@KourtneyKardash yep Mornings are the Best! nighttime is chill time‘ | 4 |
| Test | Scheme | P(neg|test) | P(pos|test) | Polarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | TF | −109.0824 | −112.5455 | negative |
| TF-IDF | −131.0328 | −135.1276 | negative | |
| DF | −104.6422 | −106.6193 | negative | |
| PSW | −92.5987 | −95.7893 | negative | |
| CDS-C | −92.7449 | −96.1055 | negative | |
| 2 | TF | −40.8930 | −40.6772 | positive |
| TF-IDF | −47.3391 | −46.0011 | positive | |
| DF | −40.8216 | −39.3454 | positive | |
| PSW | −39.4379 | −37.6068 | positive | |
| CDS-C | −40.1410 | −38.9358 | positive |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Youn, H.Y. Feature Weighting Based on Inter-Category and Intra-Category Strength for Twitter Sentiment Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010092
Wang Y, Youn HY. Feature Weighting Based on Inter-Category and Intra-Category Strength for Twitter Sentiment Analysis. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(1):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010092
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yili, and Hee Yong Youn. 2019. "Feature Weighting Based on Inter-Category and Intra-Category Strength for Twitter Sentiment Analysis" Applied Sciences 9, no. 1: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010092
APA StyleWang, Y., & Youn, H. Y. (2019). Feature Weighting Based on Inter-Category and Intra-Category Strength for Twitter Sentiment Analysis. Applied Sciences, 9(1), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010092