Semi-Analytic Monte Carlo Model for Oceanographic Lidar Systems: Lookup Table Method Used for Randomly Choosing Scattering Angles
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory and Modeling
2.1. Determining Photon-Free Path Length in Inhomogeneous Water
2.2. Determining Scattering Angle: Lookup Table Method
2.3. Semi-Analytic MC Model
2.4. Boundary Consideration
3. Simulation Results
3.1. Simulation Comparison between Inverse Function for HG cdf and LUT Method for FF cdf
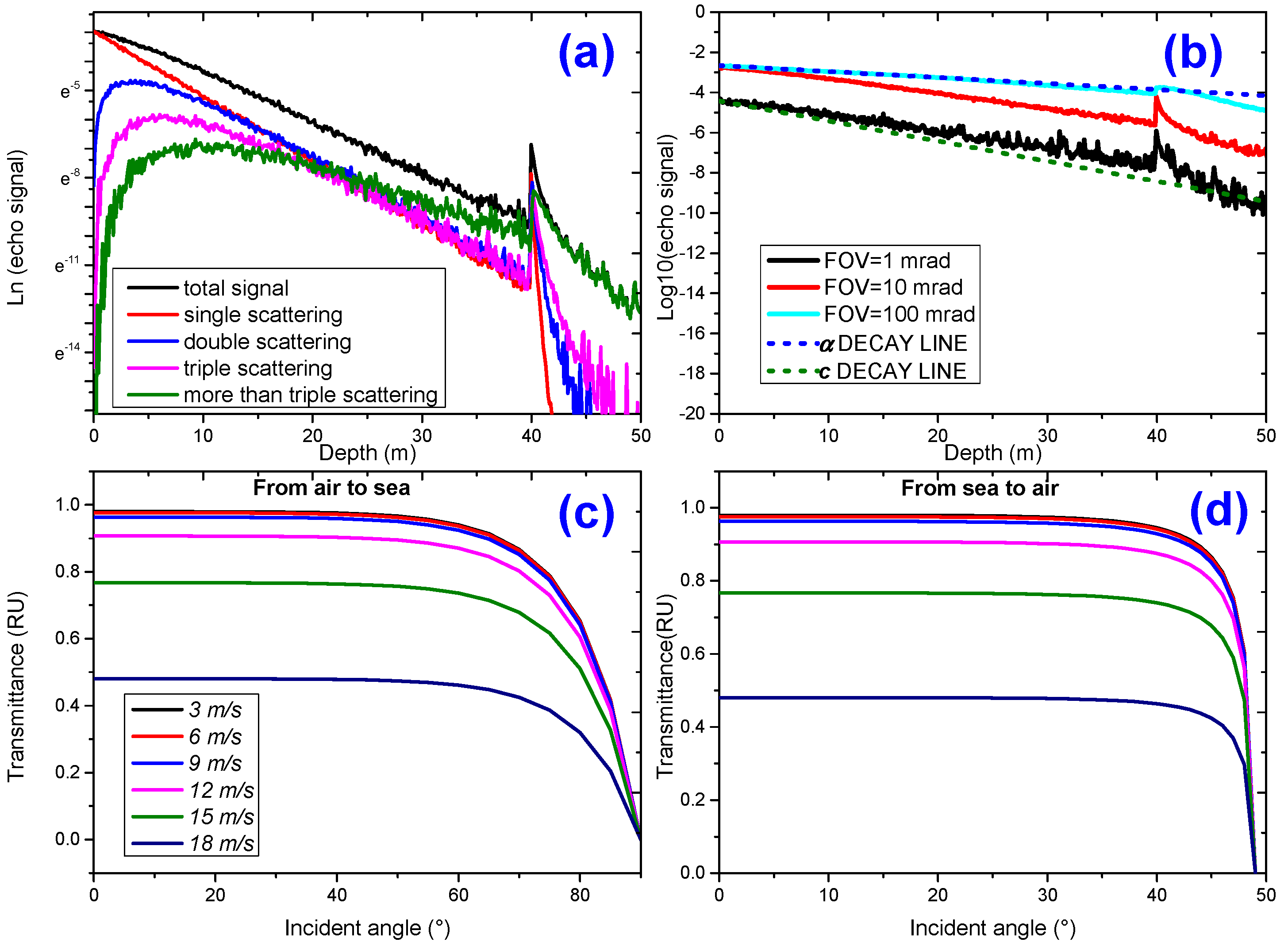
3.2. Multiple Scattering and Wind-Driven Roughened Sea Surface Effect
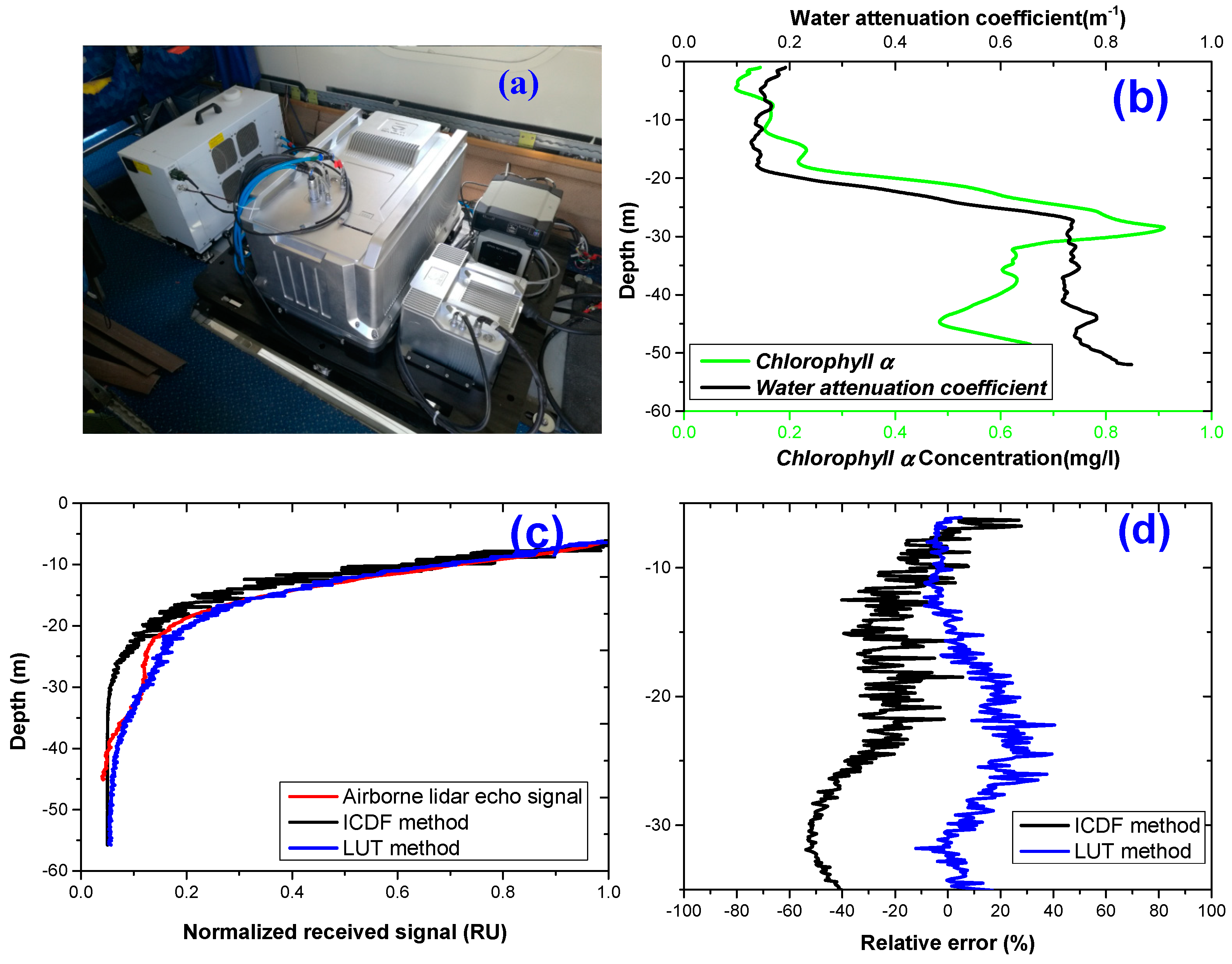
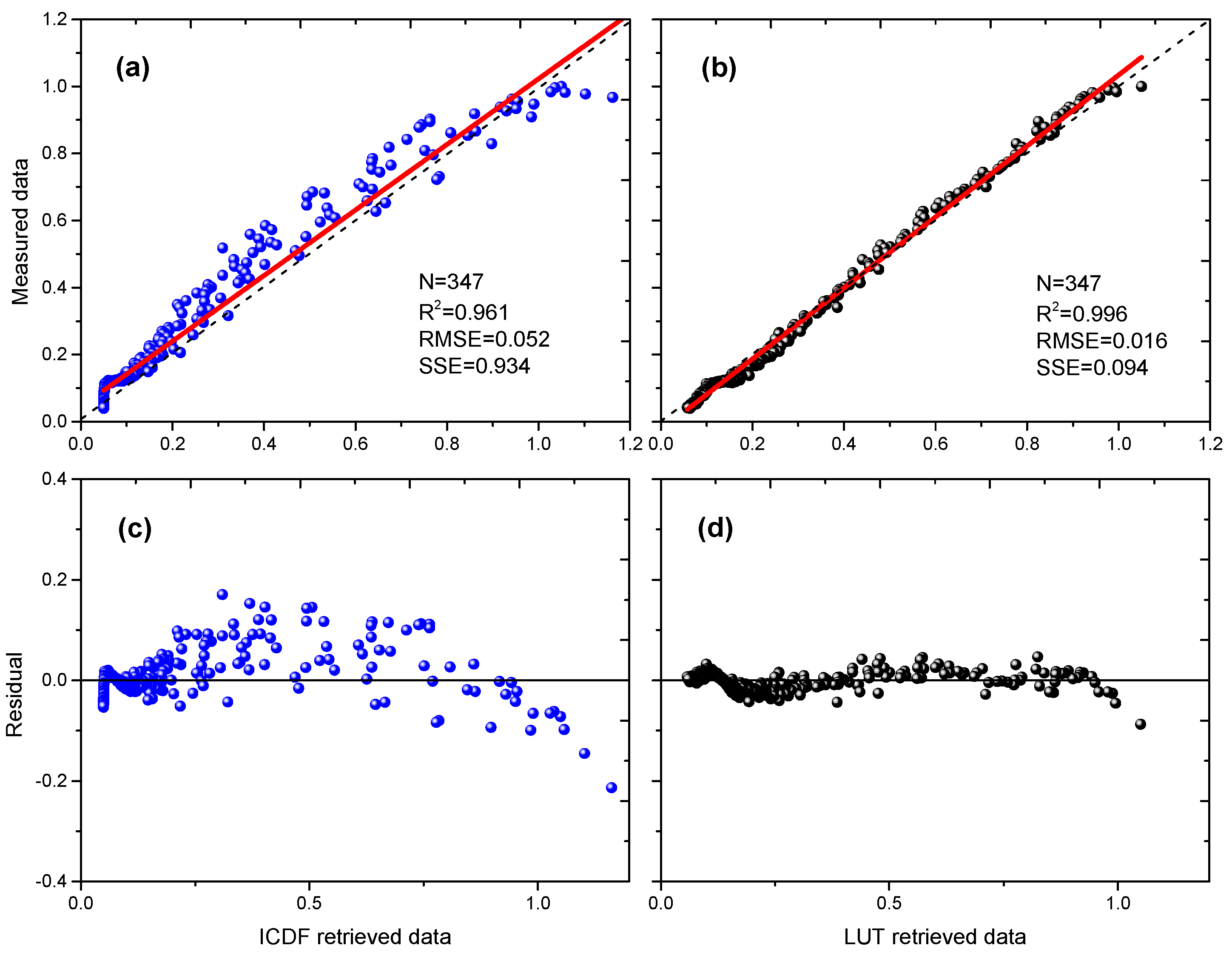
3.3. Simulated-Signal vs. Airborne Lidar Measured-Signal
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mobley, C.D. Light and Water: Radiative Transfer in Natural Waters; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, P.W.; Kattawar, G.W.; Yang, P. Impulse response solution to the three-dimensional vector radiative transfer equation in atmosphere-ocean systems. I. Monte Carlo method. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, P.-W.; Kattawar, G.W.; Yang, P. Impulse response solution to the three-dimensional vector radiative transfer equation in atmosphere-ocean systems. II. The hybrid matrix operator--Monte Carlo method. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramella-Roman, J.C.; Prahl, S.A.; Jacques, S.L. Three Monte Carlo programs of polarized light transport into scattering media: Part I. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 4420–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramella-Roman, J.C.; Prahl, S.A.; Jacques, S.L. Three Monte Carlo programs of polarized light transport into scattering media: Part II. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 10392–10405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrocal, E.; Sedarsky, D.L.; Paciaroni, M.E.; Meglinski, I.V.; Linne, M.A. Laser light scattering in turbid media Part I: Experimental and simulated results for the spatial intensity distribution. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 10649–10665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, H.R. Interpretation of airborne oceanic lidar: Effects of multiple scattering. Appl. Opt. 1982, 21, 2996–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole, L.R.; Venable, D.D.; Campbell, J.W. Semianalytic Monte Carlo radiative transfer model for oceanographic lidar systems. Appl. Opt. 1981, 20, 3653–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Pan, D.; Mao, Z.; Liu, H. Semi-analytic Monte Carlo radiative transfer model of laser propagation in inhomogeneous sea water within subsurface plankton layer. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 111, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuki, S. Multiple scattering of polarized light in turbid infinite planes: Monte Carlo simulations. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2016, 33, 988–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrocal, E.; Meglinski, I.; Jermy, M. New model for light propagation in highly inhomogeneous polydisperse turbid media with applications in spray diagnostics. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 9181–9195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M. Electric field Monte Carlo simulation of polarized light propagation in turbid media. Opt. Express 2004, 12, 6530–6539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seteikin, A.Y. Monte Carlo analysis of laser radiation propagation in multilayer biological materials. Opt. Spectrosc. 2005, 99, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henyey, L.C.; Greenstein, J.L. Diffuse radiation in the galaxy. Astrophys. J. 1941, 93, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, G.R.; Forand, J.L. Analytic phase function for ocean water. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 1994, 2258, 194–201. [Google Scholar]
- Jacques, S.L. Monte Carlo modeling of light transport in tissue (steady state and time of flight). In Optical-Thermal Response of Laser-Irradiated Tissue; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 109–144. [Google Scholar]
- Petzold, T.J. Volume Scattering Functions for Selected Ocean Waters; Scripps Institution of Oceanography: La Jolla, CA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, G.R. Computer-based underwater imaging analysis. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 1999, 3761, 62–70. [Google Scholar]
- Lawless, J.F. Statistical Models and Methods for Lifetime Data, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Estes, L.E.; Fain, G.; Harris, J.D. Laser beam propagation through the ocean’s surface. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 96 MTS/IEEE Conference Proceedings, The Coastal Ocean—Prospects for the 21st Century, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 23–26 September 1996; Volume 8, pp. 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Ao, F.-L.; Ou, Y. The study of blue and green laser through seawater interface. In Proceedings of the 15th Annual Conference of Information Theory and the First National Network Coding Academic Conference Proceedings of the China Electronics Society, Qing Dao, ShanDong, China, 15–20 Augest 2008; pp. 297–301. [Google Scholar]
- Mobley, C.D.; Zhang, H.; Voss, K.J. Effects of Optically Shallow Bottoms on Upwelling Radiances: Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function Effects. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feygels, V.I.; Wright, C.W.; Kopilevich, Y.I.; Surkov, A.I. Narrow-field-of-view bathymetrical lidar: Theory and field test. In Proceedings of the SPIE’s 48th Annual Meeting on Optical Science and Technology, San Diego, CA, USA, 3–8 August 2003; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Allocca, A.D.M.; London, M.A.; Curran, T.P.; Concannon, B.M.; Contarino, V.M.; Prentice, J.; Mullen, L.J.; Kane, T.J. Ocean water clarity measurement using shipboard lidar systems. Proc. SPIE 2002, 4488, 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Concannon, B.M.; Prentice, J.E. LOCO with a Shipboard Lidar; Naval Air Systems Command: Patuxent River, MD, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
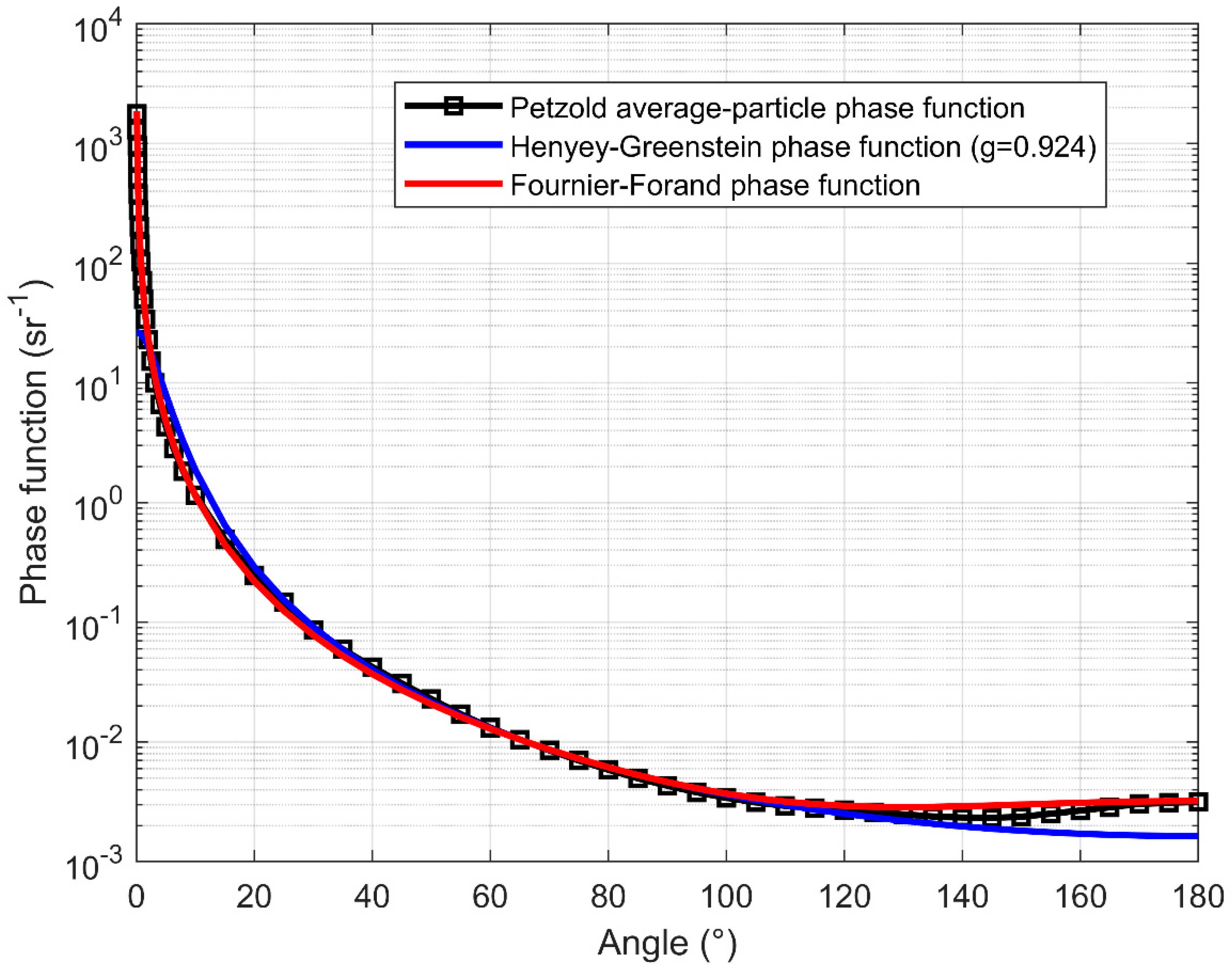
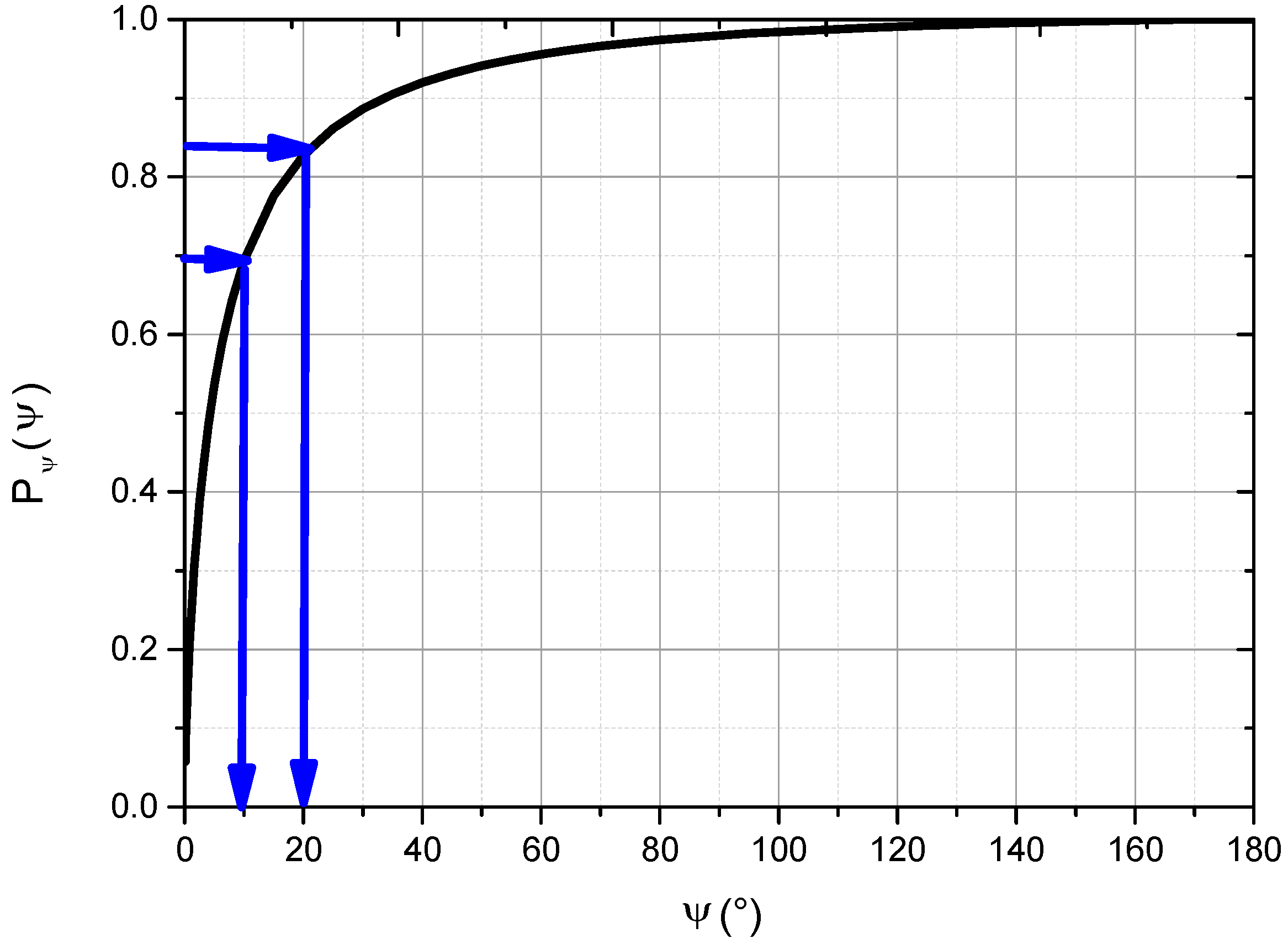
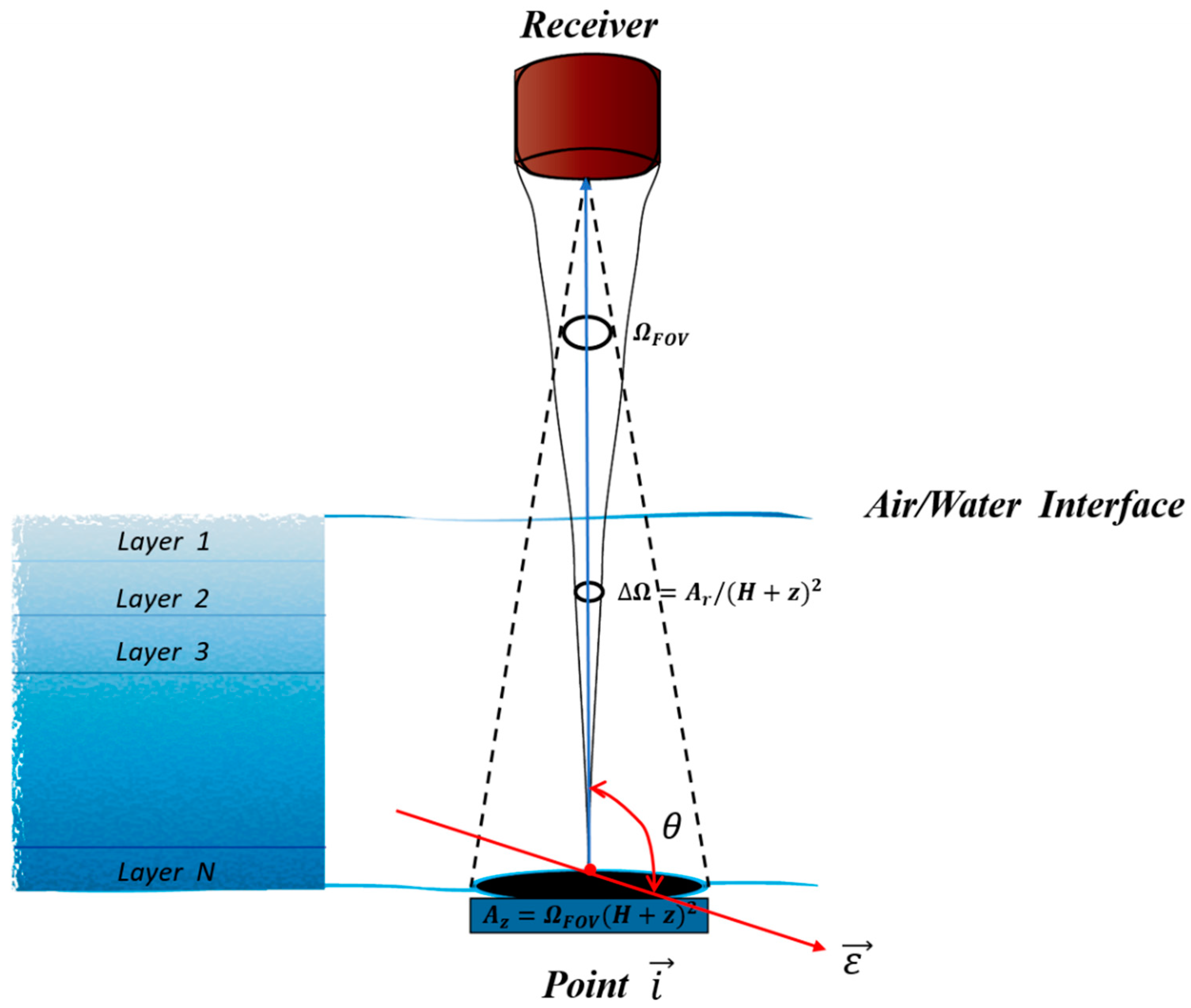
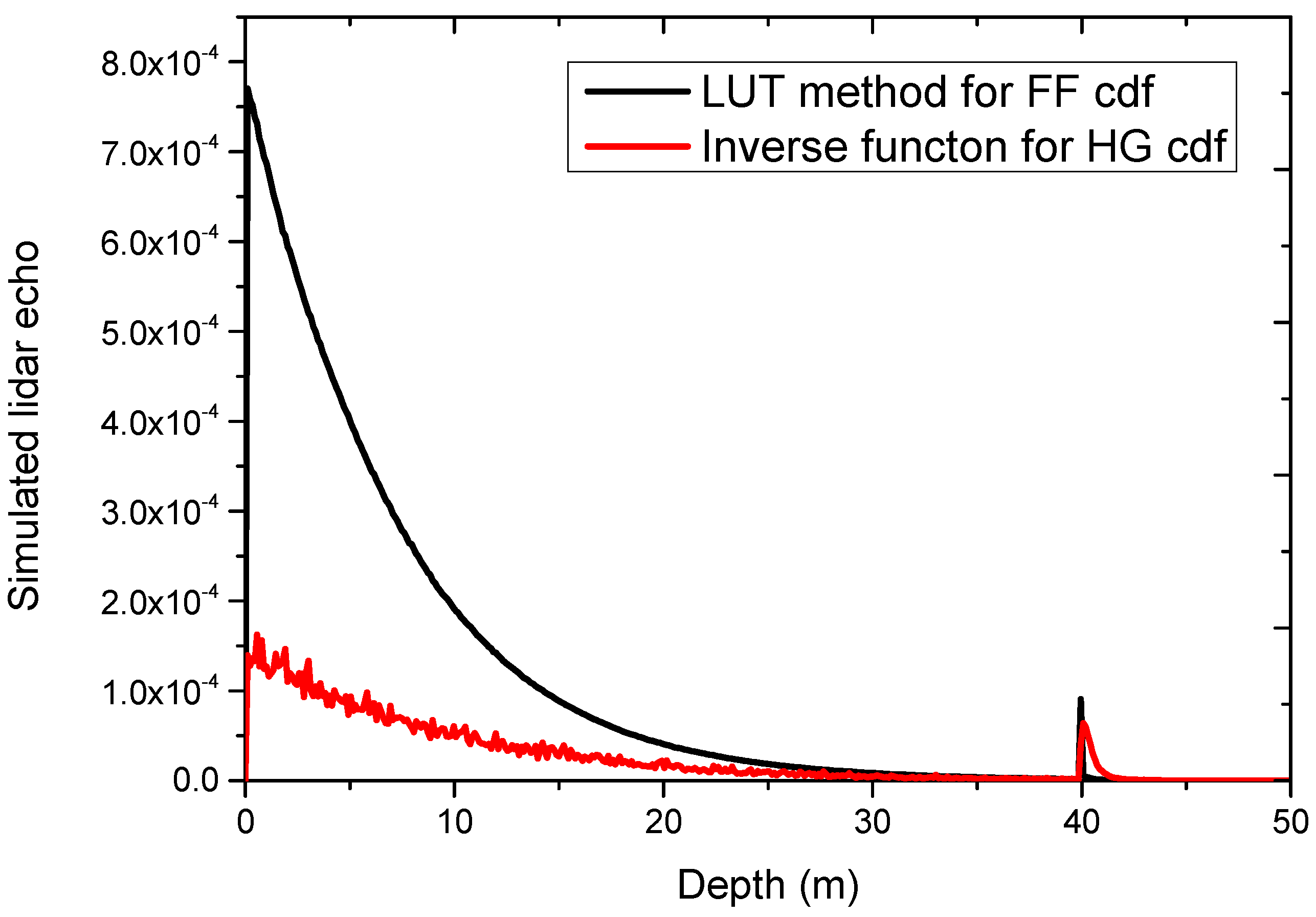
| SPFs | Angle Limit | Number of Samples | R2 | Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-G | all | 55 | 0.3766 | 323.9334 |
| [20°,140°] | 25 | 0.9950 | 0.0115 | |
| <20° | 22 | 0.2662 | 457.5366 | |
| >140° | 8 | 0.8217 | 4.2527 × 10−4 | |
| FF | all | 55 | 0.9996 | 14.7719 |
| [20°,140°] | 25 | 0.9992 | 0.0088 | |
| <20° | 22 | 0.9996 | 22.1625 | |
| >140° | 8 | 0.9260 | 2.1983 × 10−4 |
| Methods | Number of Samples | Min. | Max. | Mean | Standard Deviation (SD) | R2 between the Two Curves | RMSE between the Two Curves |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICDF | 498 | 1.11 × 10−9 | 1.63 × 10−4 | 2.48 × 10−5 | 3.53 × 10−5 | 0.948 | 8.03 × 10−6 |
| LUT | 498 | 1.54 × 10−8 | 7.70 × 10−4 | 9.82 × 10−5 | 1.73 × 10−4 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, P.; Pan, D.; Mao, Z.; Liu, H. Semi-Analytic Monte Carlo Model for Oceanographic Lidar Systems: Lookup Table Method Used for Randomly Choosing Scattering Angles. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010048
Chen P, Pan D, Mao Z, Liu H. Semi-Analytic Monte Carlo Model for Oceanographic Lidar Systems: Lookup Table Method Used for Randomly Choosing Scattering Angles. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(1):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010048
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Peng, Delu Pan, Zhihua Mao, and Hang Liu. 2019. "Semi-Analytic Monte Carlo Model for Oceanographic Lidar Systems: Lookup Table Method Used for Randomly Choosing Scattering Angles" Applied Sciences 9, no. 1: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010048
APA StyleChen, P., Pan, D., Mao, Z., & Liu, H. (2019). Semi-Analytic Monte Carlo Model for Oceanographic Lidar Systems: Lookup Table Method Used for Randomly Choosing Scattering Angles. Applied Sciences, 9(1), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010048





