Fabrication of Hydrophobic Coatings Using Sugarcane Bagasse Waste Ash as Silica Source
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Preparation of SBA Coating Solution
2.2. Fabrication of Hydrophobic Surfaces
2.3. Characterization:
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Field-Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM)
3.2. Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS)
3.3. X-Ray Fluorescent Spectroscopy (XRF)
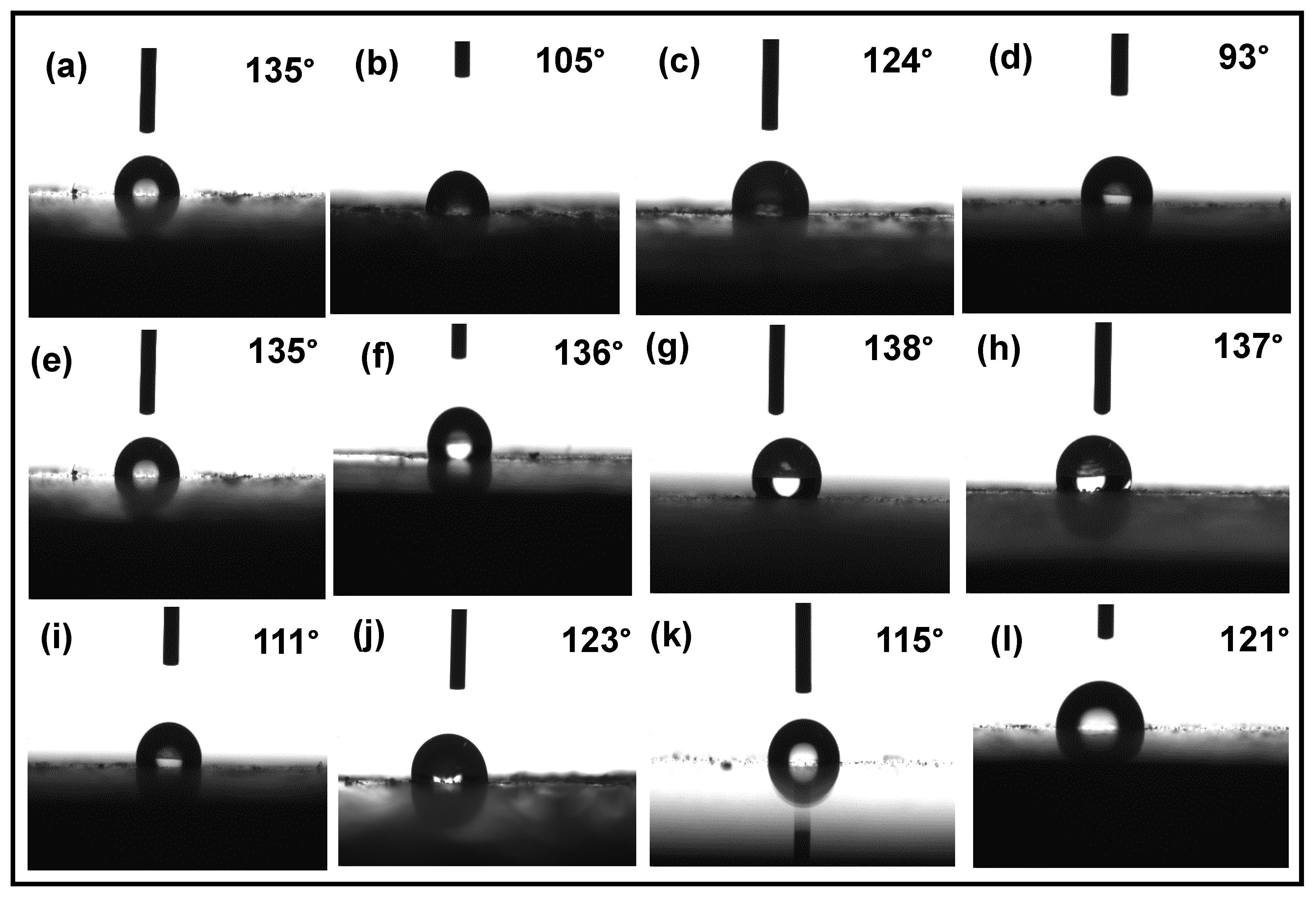
3.4. Water Contact Angle Test
4. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laurent, A.; Bakas, I.; Clavreul, J.; Bernstad, A.; Niero, M.; Gentil, E.; Hauschild, M.Z.; Christensen, T.H. Review of LCA studies of solid waste management systems–Part I: Lessons learned and perspectives. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, S.A.; Sales, A.; Almeida, F.d.C.R.; Moretti, J.P.; Portella, K.F. Concretes made with sugarcane bagasse ash: Evaluation of the durability for carbonation and abrasion tests. Ambient. Constr. 2011, 11, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Kamal, M.; Haroon, M. Potential of cement-treated sugar cane bagasse ash (SCBA) as highway construction material. Road Trans. Res. 2015, 24, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Arumugam, A.; Ponnusami, V. Modified SBA-15 synthesized using sugarcane leaf ash for nickel adsorption. Indian J. Chem. Technol. 2013, 20, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Drummond, A.-R.F.; Drummond, I.W.; Research, E.C. Pyrolysis of sugar cane bagasse in a wire-mesh reactor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1996, 35, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, N.; Damayanti, M.; Pratama, S.W.I. The influence of sugarcane bagasse ash as fly ash on cement quality. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1801, 040009. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, A.M.; Rothstein, J.P.; Kavehpour, H.P. Experimental study of dynamic contact angles on rough hydrophobic surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 513, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Kulkarni, M.A.; Chembu, N.G.; Banpurkar, A.; Kumaraswamy, G. Aqueous dispersions of lipid nanoparticles wet hydrophobic and superhydrophobic surfaces. Soft Matter. 2018, 14, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, T.; Bagchi, B. Temperature effects on the hydrophobic force between two graphene-like surfaces in liquid water. J. Chem. Sci. 2018, 130, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.-H.; Ha, J.-H.; Song, H.; Bae, J.; Park, S.-H. Enhanced adhesion properties of conductive super-hydrophobic surfaces by using zirco-aluminate coupling agent. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 68, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-P.; Sun, Y.-L.; Luo, C.-W.; Chao, Z.-S. UV-resistant hydrophobic CeO2 nanomaterial with photocatalytic depollution performance. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 13439–13443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharudin, K.A.; Sreekantan, S.; Basiron, N.; Chun, L.K.; Kumaravel, V.; Abdullah, T.K.; Ahmad, Z.A. Improved super-hydrophobicity of eco-friendly coating from palm oil fuel ash (POFA) waste. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 337, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basiron, N.; Sreekantan, S.; Saharudin, K.A.; Ahmad, Z.A.; Kumaravel, V. Improved Adhesion of Nonfluorinated ZnO Nanotriangle Superhydrophobic Layer on Glass Surface by Spray-Coating Method. J. Nanomater. 2018, 2018, 7824827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürstner, R.; Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C.; Walzel, P. Wetting and self-cleaning properties of artificial superhydrophobic surfaces. Langmuir 2005, 21, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmur, A. The lotus effect: Superhydrophobicity and metastability. Langmuir 2004, 20, 3517–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; McCarthy, T.J. The “lotus effect” explained: Two reasons why two length scales of topography are important. Langmuir 2006, 22, 2966–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kichigina, G.A.; Kushch, P.P.; Krivonogova, E.A.; Kiryukhin, D.P.; Dorohov, V.G.; Barelko, V.V. Tetrafluoroethylene Telomeres Used to Prepare Fluorine-Containing Hydrophobic Silica Fabric. Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res. 2018, 9, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, U.; Awais, M.; Hussain, S.Z.; Hussain, I.; Husain, S.W.; Subhani, T. Durable and self-healing superhydrophobic surfaces for building materials. Mater. Lett. 2017, 192, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, I.; Lorenzi, A.; Ranzenigo, L.; Lazzarini, L.; Predieri, G.; Lottici, P.P. Synthesis and characterization of photocatalytic hydrophobic hybrid TiO2-SiO2 coatings for building applications. Build. Environ. 2017, 111, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midtdal, K.; Jelle, B.P. Self-cleaning glazing products: A state-of-the-art review and future research pathways. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2013, 109, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Guo, D.; Yu, C.; Li, K.; Liu, M.; Jiang, L. Water-repellent properties of superhydrophobic and lubricant-infused “slippery” surfaces: A brief study on the functions and applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 8, 3615–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mates, J.E.; Bayer, I.S.; Palumbo, J.M.; Carroll, P.J.; Megaridis, C.M. Extremely stretchable and conductive water-repellent coatings for low-cost ultra-flexible electronics. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, R.; Glinel, K.; De Smet, D.; Vanneste, M.; Mannu, N.; Kartheuser, B.; Nysten, B.; Jonas, A.M. Environmentally Friendly Super-Water-Repellent Fabrics Prepared from Water-Based Suspensions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 15346–15351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.T.; Hunter, S.R.; Aytug, T. Superhydrophobic materials and coatings: A review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2015, 78, 086501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Q.; Li, X.; Deng, C.; Zhang, Q.; Yi, D.; Wang, X.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Y. Silica nanowires with tunable hydrophobicity for lipase immobilization and biocatalytic membrane assembly. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 531, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Huang, F.-H.; Chang, H.-H.; Don, T.-M.; Chen, C.-C.; Cheng, L.-P. Preparation of water-resistant antifog hard coatings on plastic substrate. Langmuir 2012, 28, 17193–17201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.; Yu, X.; Jia, J.; Tu, S.-T.; Yan, J.; Dahlquist, E. Fabrication and characterization of superhydrophobic polypropylene hollow fiber membranes for carbon dioxide absorption. Appl. Energy. 2012, 90, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Cheng, Y.; Wei, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z. Suspension of surface-modified nano-SiO2 in partially hydrolyzed aqueous solution of polyacrylamide for enhanced oil recovery. Colloids Surf. A 2017, 524, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.K.; Son, H.A.; Kim, H.T.; Kim, J.W. Nanofluid Enhanced Oil Recovery Using Hydrophobically Associative Zwitterionic Polymer-Coated Silica Nanoparticles. Energy Fuels. 2017, 31, 7777–7782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Ma, M.; Zang, D.; Gao, Z.; Wang, C. Fabrication of superhydrophobic/superoleophilic cotton for application in the field of water/oil separation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Xiang, T.; Li, C.; Zheng, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Dong, C.; Chan, W. Fabrication of self-cleaning super-hydrophobic nickel/graphene hybrid film with improved corrosion resistance on mild steel. Mater. Design. 2017, 117, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangiuli, D.; Lettieri, M.; Masieri, M.; Calia, A. Field study in an urban environment of simultaneous self-cleaning and hydrophobic nanosized TiO2-based coatings on stone for the protection of building surface. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2919–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Hu, J.; Lin, X.; Fang, L.; Wu, F.; Liao, X.; Luo, H.; Shi, L. Robust and anti-corrosive PDMS/SiO2 superhydrophobic coatings fabricated on magnesium alloys with different-sized SiO2 nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 457, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayake, R.M.N.M.; Mantilaka, M.M.M.G.P.G.; Hara, M.; Huang, H.-H.; Wijayasinghe, H.W.M.A.C.; Yoshimura, M.; Pitawala, H.M.T.G.A. Graphite intercalated polyaniline composite with superior anticorrosive and hydrophobic properties, as protective coating material on steel surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 410, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Pranantyo, D.; Kang, E.T.; Wright, D.S.; Luo, H.K. In Situ Self-Assembled Polyoxotitanate Cages on Flexible Cellulosic Substrates: Multifunctional Coating for Hydrophobic, Antibacterial, and UV-Blocking Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Xiong, X.; Jiang, B.; Weng, C. Fabrication of high aspect ratio nanopillars and micro/nano combined structures with hydrophobic surface characteristics by injection molding. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.-H.; Chiu, C.-Y.; Yang, J.-T.; Yeh, J.A. Investigation and application of an ultrahydrophobic hybrid-structured surface with anti-sticking character. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2009, 19, 085022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Ma, M.; Wang, C.; Li, J. Improvement of mechanical robustness of the superhydrophobic wood surface by coating PVA/SiO2 composite polymer. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 280, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Chung, T.-S.; O’Brien, G.S.; Kosar, W. Hydrophobic/hydrophilic PVDF/Ultem® dual-layer hollow fiber membranes with enhanced mechanical properties for vacuum membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 523, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, M.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Ma, F.; Yu, Z.; Feng, W.; Chen, Y. Superhydrophobic and anti-icing properties of sol–gel prepared alumina coatings. Rus. J. Non-Ferrous Met. 2016, 57, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulinich, S.A.; Farhadi, S.; Nose, K.; Du, X.W. Superhydrophobic surfaces: Are they really ice-repellent? Langmuir 2011, 27, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huovinen, E.; Hirvi, J.; Suvanto, M.; Pakkanen, T.A. Micro–micro hierarchy replacing micro–nano hierarchy: A precisely controlled way to produce wear-resistant superhydrophobic polymer surfaces. Langmuir 2012, 28, 14747–14755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barshilia, H.C.; Gupta, N. Superhydrophobic polytetrafluoroethylene surfaces with leaf-like micro-protrusions through Ar + O2 plasma etching process. Vacuum 2014, 99, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martines, E.; Seunarine, K.; Morgan, H.; Gadegaard, N.; Wilkinson, C.D.; Riehle, M.O. Superhydrophobicity and superhydrophilicity of regular nanopatterns. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 2097–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghdoost, A.; Pitchumani, R. Fabricating superhydrophobic surfaces via a two-step electrodeposition technique. Langmuir 2013, 30, 4183–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husni, H.; Nazari, M.R.; Yee, H.M.; Rohim, R.; Yusuff, A.; Ariff, M.A.M.; Ahmad, N.N.R.; Leo, C.P.; Junaidi, M.U.M. Superhydrophobic rice husk ash coating on concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 144, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Sun, Q.; Guo, Y.; Dong, S. Effects of modifiers on the hydrophobicity of SiO2 films from nano-husk ash. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 276, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.S.; Barakat, R.; Alhilali, A.; Saleh, M.; Cheeseman, C.R. Hydrophobic concrete using waste paper sludge ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 70, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spathi, C.; Young, N.; Heng, J.Y.Y.; Vandeperre, L.J.M.; Cheeseman, C.R. A simple method for preparing super-hydrophobic powder from paper sludge ash. Mater. Lett. 2015, 142, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, I.S.; Davis, A.J.; Biswas, A. Robust superhydrophobic surfaces from small diffusion flame treatment of hydrophobic polymers. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, I.S.; Davis, A.J.; Loth, E.; Steele, A. Water jet resistant superhydrophobic carbonaceous films by flame synthesis and tribocharging. Mater. Today Commun. 2015, 3, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aigbodion, V.S.; Hassan, S.B.; Ause, T.; Nyior, G.B. Potential utilization of solid waste (bagasse ash). Int. J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 2010, 9, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, V.S.; Urbonaite, S.; Svensson, G. Characterization of unburned carbon in bagasse fly ash. Fuel 2008, 87, 2972–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, G.C.; Toledo Filho, R.D.; Tavares, L.M.; Fairbairn, E.M.R. Experimental characterization of binary and ternary blended-cement concretes containing ultrafine residual rice husk and sugar cane bagasse ashes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 29, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chusilp, N.; Jaturapitakkul, C.; Kiattikomol, K. Effects of LOI of ground bagasse ash on the compressive strength and sulfate resistance of mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 3523–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahurudeen, A.; Kanraj, D.; Dev, V.G.; Santhanam, M. Performance evaluation of sugarcane bagasse ash blended cement in concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015, 59, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worathanakul, P.; Payubnop, W.; Muangpet, A. Characterization for post-treatment effect of bagasse ash for silica extraction. Int. J. Chem. Mol. Eng. 2009, 3, 398–400. [Google Scholar]

| Weight% | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Components | Raw Sample | After Acid Treatment | After Acid Treatment |
| SBA 500 °C | SBA 750 °C | ||
| SiO2 | 54.20 | 87.63 | 94.2 |
| CaO | 3.77 | 1.26 | 2.16 |
| SO3 | 16.10 | 0.45 | 1.34 |
| Al2O3 | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.94 |
| K2O | 1.26 | 0.28 | 0.41 |
| MgO | 20.72 | 0.19 | 0.39 |
| P2O5 | 7.36 | 0.07 | 0.20 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.78 | 0.06 | 0.11 |
| TiO2 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 |
| MnO | 1.45 | - | 0.01 |
| CuO | 0.06 | - | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Natarajan, S.; Subramaniyam, S.T.; Kumaravel, V. Fabrication of Hydrophobic Coatings Using Sugarcane Bagasse Waste Ash as Silica Source. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010190
Natarajan S, Subramaniyam ST, Kumaravel V. Fabrication of Hydrophobic Coatings Using Sugarcane Bagasse Waste Ash as Silica Source. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(1):190. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010190
Chicago/Turabian StyleNatarajan, Sriharan, Senthil Thottipalayam Subramaniyam, and Vignesh Kumaravel. 2019. "Fabrication of Hydrophobic Coatings Using Sugarcane Bagasse Waste Ash as Silica Source" Applied Sciences 9, no. 1: 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010190
APA StyleNatarajan, S., Subramaniyam, S. T., & Kumaravel, V. (2019). Fabrication of Hydrophobic Coatings Using Sugarcane Bagasse Waste Ash as Silica Source. Applied Sciences, 9(1), 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010190






