Deep Learning Based Lithology Classification Using Dual-Frequency Pol-SAR Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pol-SAR Features Extraction
2.1.1. Cross Polarized Ratio
2.1.2. Co-Polarized Correlation Coefficient
2.1.3. Freeman–Durden Decomposition
2.2. Stacked Sparse Autoencoder
2.2.1. Sparse Autoencoder
2.2.2. Stacked Sparse Autoencoder
2.3. Lithology Classification Based on Deep Learning
2.3.1. Pol-SAR Data Pre-Processing
2.3.2. Lithology Feature Extraction
2.3.3. Lithology Classification
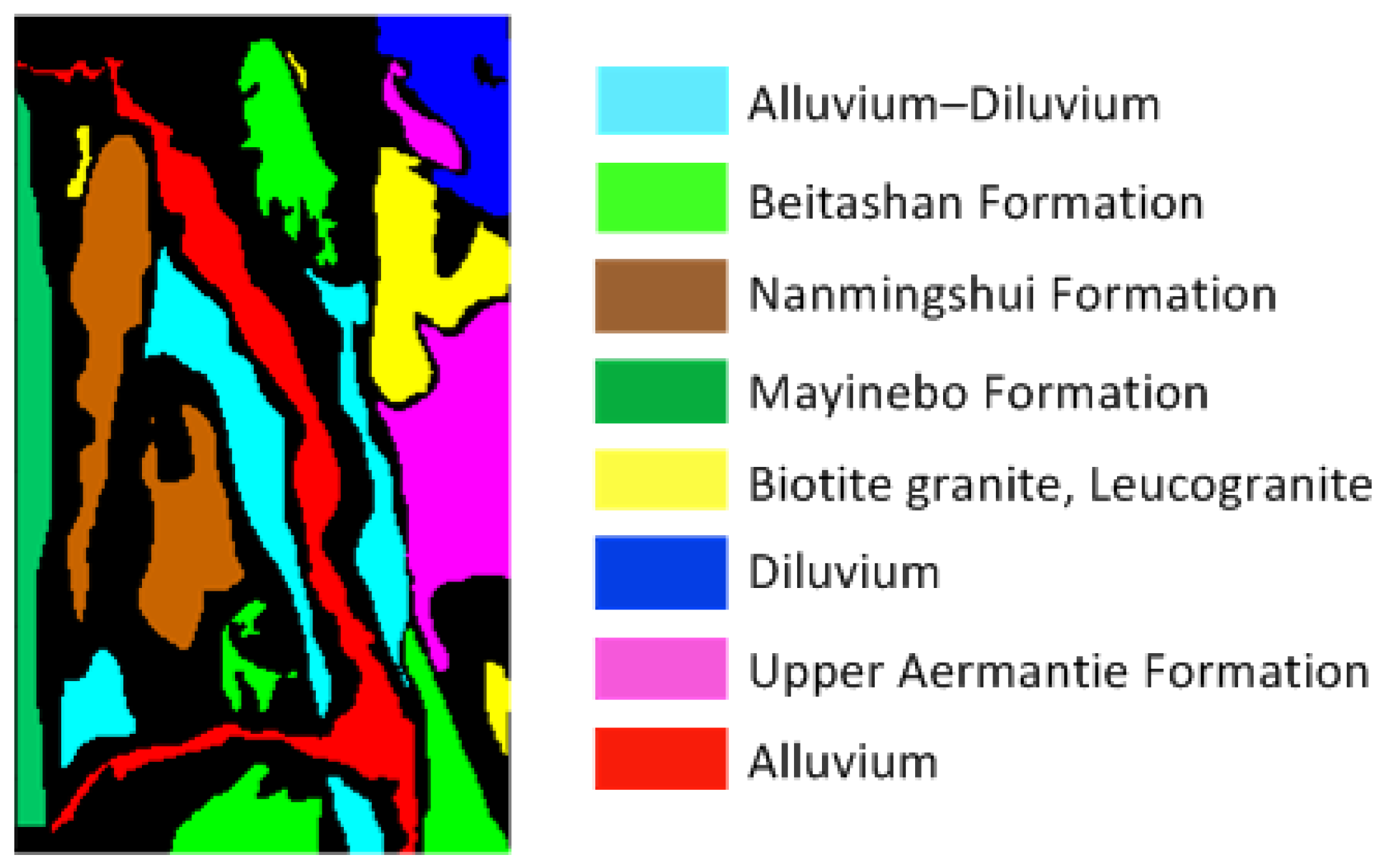
2.4. Dataset Description
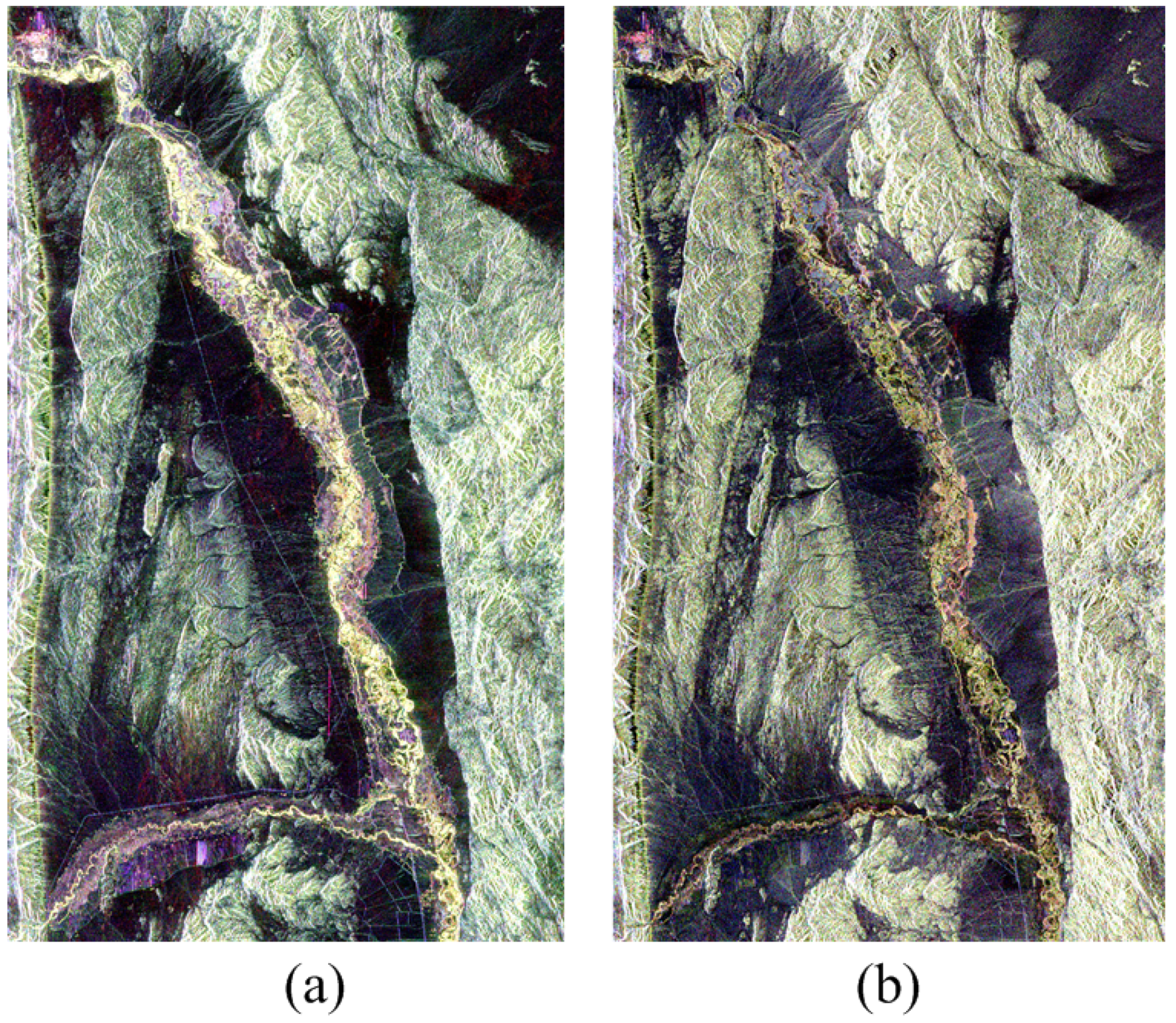
3. Results
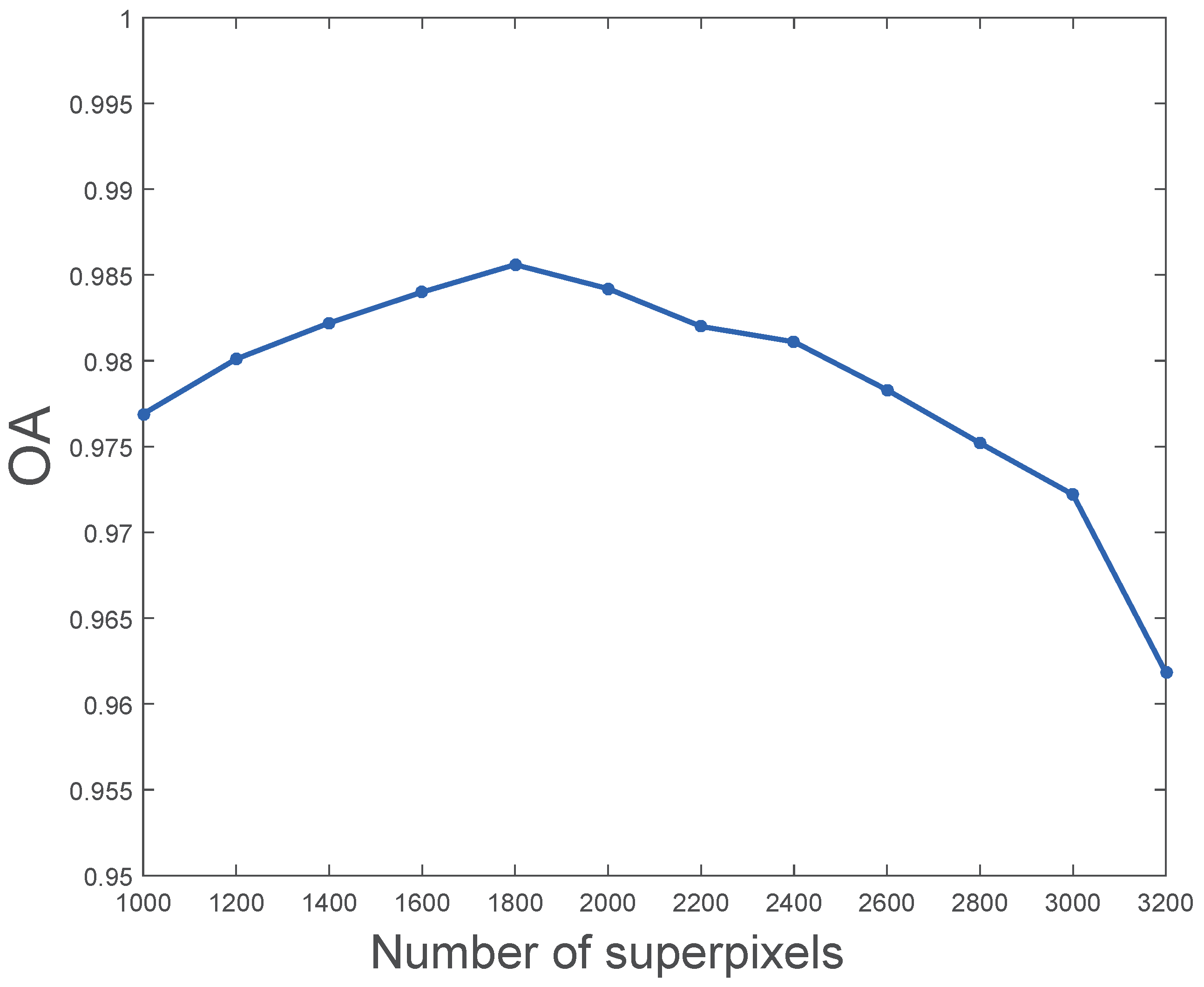
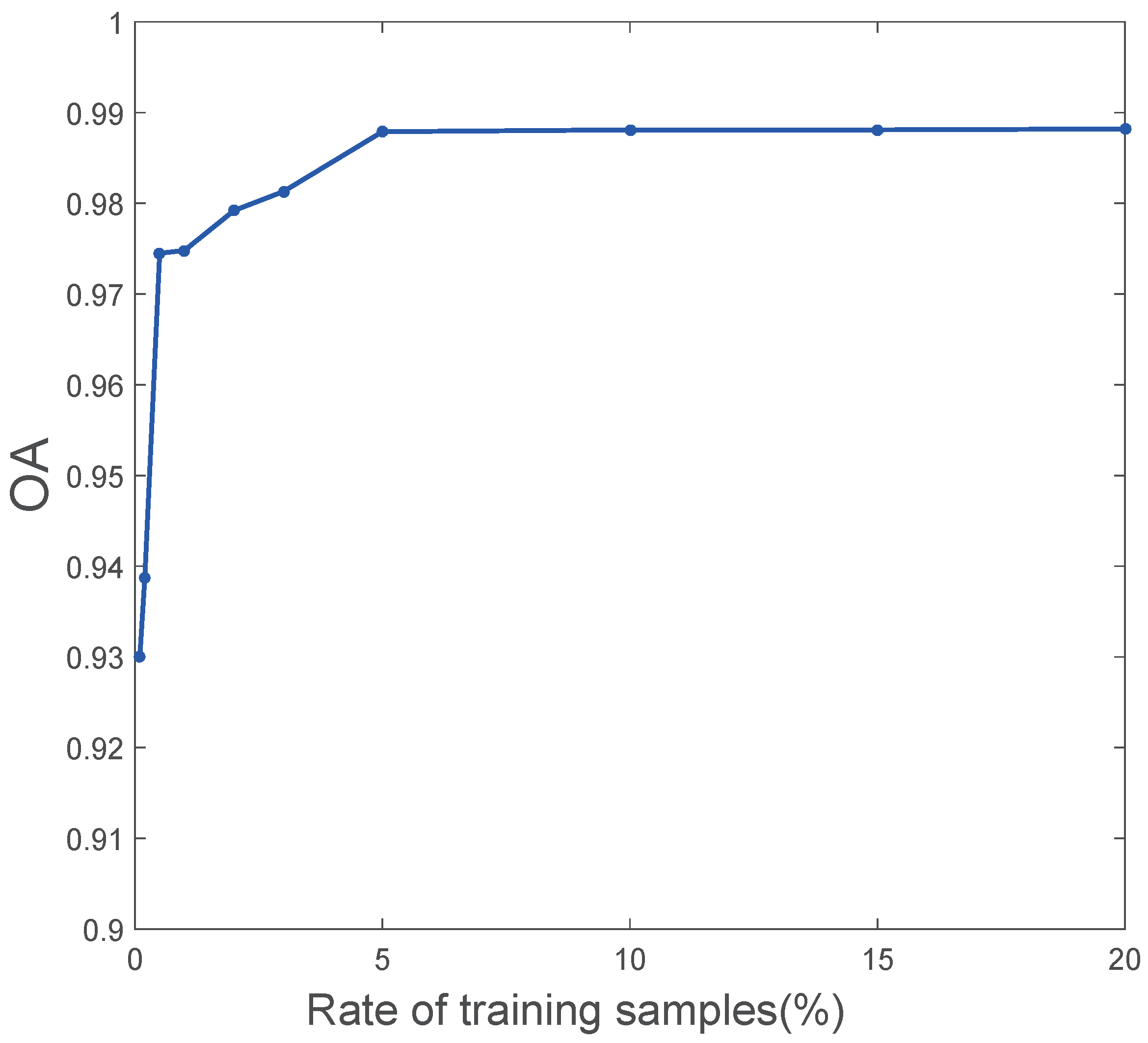
3.1. Experimental Parameters
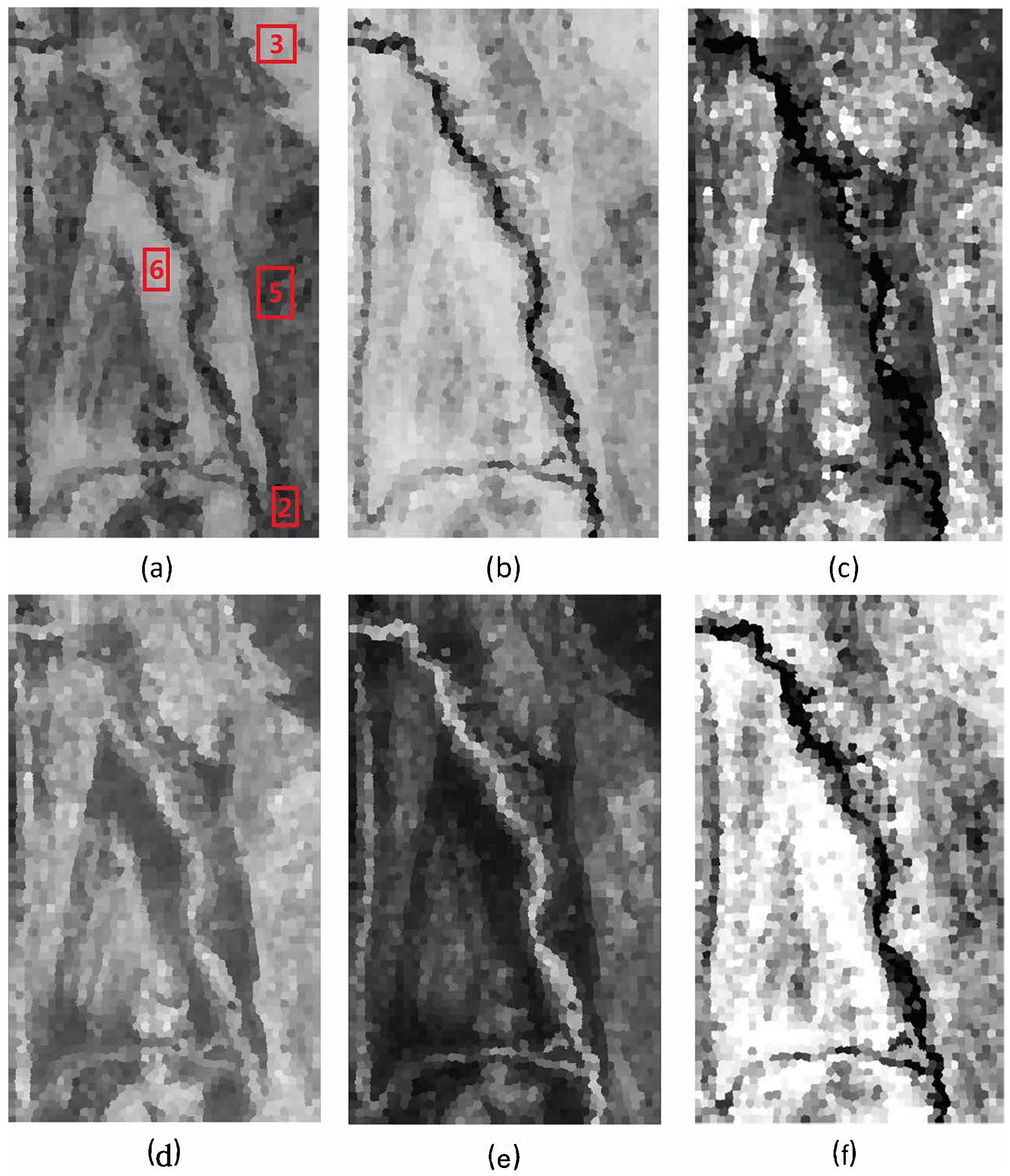
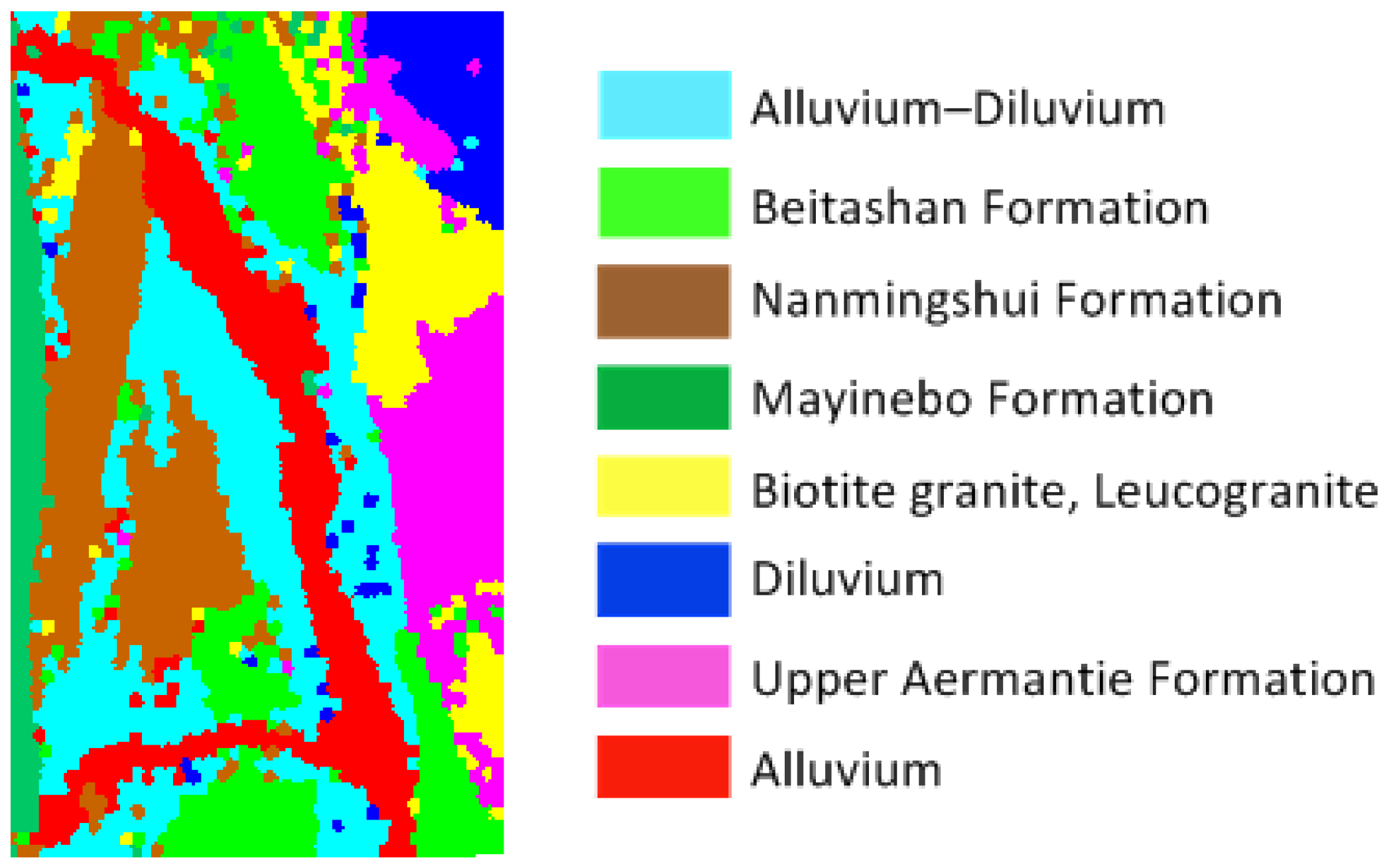
3.2. Classification Results
3.3. Comparison with Other Classifiers
3.3.1. Classification Accuracy
3.3.2. Computational Burden
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cuizhen, W. Polarimetric SAR Data Analysis and Target Information Extraction; Institute of Remote Sensing Application, Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 1999. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y. Lithology identification using an optimized KNN clustering method based on entropy-weighted cosine distance in Mosozo strata of Gaoqing Field, Jiyang depression. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 166, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.A.; Swartz, A.A.; Yueh, H.A.; Novak, L.M.; Shin, R.T. Identification of Terrain Cover Using the Optimum Polarimetric Classifier. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 1988, 2, 171–194. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.S.; Grunes, M.R. Classification of multi-look polarimetric SAR data based on complex Wishart distribution. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 15, 2299–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Pottier, E. An entropy based classification scheme for land applications of polarimetric SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.; Durden, S.L. A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Yeh, G.O.; Li, X.; Lin, Z. A novel algorithm for land use and land cover classification using RADARSAT-2 polarimetric SAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdianpari, M.; Salehi, B.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Brisco, B.; Mahdavi, S.; Amani, M.; Granger, J.E. Fisher Linear Discriminant Analysis of coherency matrix for wetland classification using PolSAR imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 206, 300–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.; Vincent, P. Presentation Learning: A Review and New Perspective. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 1798–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, P.; Larochelle, H.; Lajoie, I.; Bengio, Y.; Manzagol, P.A. Stacked Denosing Autoencoder: Learning Useful Representation in a Deep Network with a Local Denosing Criterion. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2010, 11, 3371–3408. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.H.T. Dual-Branch Deep Convolution Neural Network for Polarimetric SAR Image Classification. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansch, R.; Hellwich, O. Classification of Polarimetric SAR Data by Complex Valued Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Hannover Workshop 2009—High-Resolution Earth Imaging for Geospatial Information, Hannover, Germany, 2–5 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Q.; Dou, Y.; Niu, X.; Xu, J.; Li, B. Classification of land cover based on deep belief networks using polarimetric RADARSAT-2 data. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 4679–4682. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, F.; Jin, Y.Q. Polarimetric SAR Image Classification Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 13, 1935–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, K.; Lin, S.; Hou, B. Multilayer feature learning for polarimetric synthetic radar data classification. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 2818–2821. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, W.; Zhang, D. Stacked Sparse Autoencoder in PolSAR Data Classification Using Local Spatial Information. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 13, 1359–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Ma, X.; Fan, J.; Wang, H. Semisupervised Classification of Polarimetric SAR Image via Superpixel Restrained Deep Neural Network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 15, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Kou, H.; Jiao, L. Classification of Polarimetric SAR Images Using Multilayer Autoencoders and Superpixels. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 3072–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloud, S. Target decomposition theorems in radar scattering. Electron. Lett. 1985, 21, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenguang, W.; Jun, W.; Peng, L.; Shiyi, M. A new ship detection method based on polarimetric SAR classification. Chin. J. Electron. 2008, 7, 769–774. [Google Scholar]
- Borgeaud, M.; Nell, J. Comparisons Of Theoretical Surface Scattering Models For Polarimetric Microwave Remote Sensing. In Proceedings of the IGARSS ’92 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Houston, TX, USA, 26–29 May 1992; pp. 180–182. [Google Scholar]
- Borgeaud, M.; Noll, J. Analysis of theoretical surface scattering models for polarimetric microwave remote sensing of bare soils. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 2931–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, A.; Ligthart, L.; Logvin, A.; Besieris, I.M.; Ligthart, L.P.; Pusone, E.G. Mathematical and Physical Modelling of Microwave Scattering and Polarimetric Remote Sensing; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 261–264. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Ekanadham, C.; Ng, A.Y. Sparse deep belief net model for visual area V2. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing System, Kitakyushu, Japan, 13–16 November 2007; pp. 873–880. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, A. Sparse autoencoder. In CS294A Lecture Notes; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lecun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengio, Y.; Lamblin, P.; Dan, P.; Larochelle, H. Greedy layer-wise training of deep networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2007, 19, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.S.; Grunes, M.R.; Grandi, G.D. Polarimetric SAR speckle filtering and its implication for classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 37, 2363–2373. [Google Scholar]
- Achanta, R.; Shaji, A.; Smith, K.; Lucchi, A.; Fua, P.; Susstrunk, S. SLIC superpixels compared to State-of-the-Art Superpixel Methods. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 2274–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano, A.; Vergara, L.; Ahmed, B.; Salazar, A. Fusion of scores in a detection context based on alpha integration. Neural Comput. 2015, 27, 1983–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


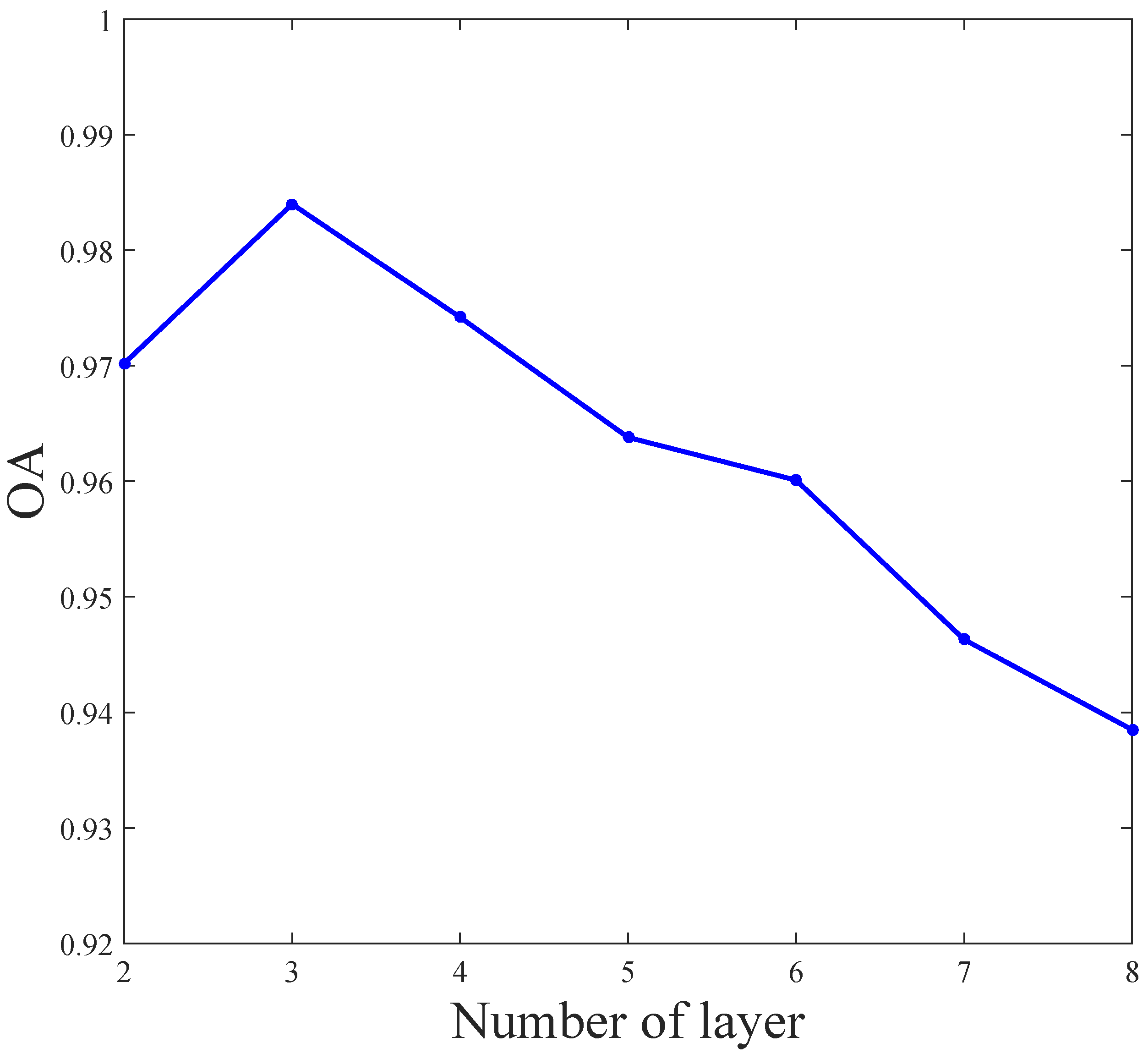



| Features Variation () | ||
|---|---|---|
| Increased surface roughness | Decreased surface roughness | |
| Increased permittivity | Decreased permittivity | |
| Increased volume scattering | Decreased volume scattering | |
| Increased surface scattering | Decreased surface scattering |
| Class Label | All Pixels | Training Pixels | Testing Pixels | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alluvium | 1 | 343,987 | 17,199 | 326,788 |
| Beitashan Formation | 2 | 322,833 | 16,142 | 306,691 |
| Diluvium | 3 | 167,735 | 8,387 | 159,348 |
| Biotite granite, Leucogranite | 4 | 211,923 | 10,596 | 201,327 |
| Upper Aermantie Formation | 5 | 318,968 | 15,948 | 303,020 |
| Alluvium–Diluvium | 6 | 371,692 | 18,585 | 353,107 |
| Nanmingshui Formation | 7 | 352,351 | 17,618 | 334,733 |
| Mayinebo Formation | 8 | 212,628 | 10,631 | 208,375 |
| Total | - | 2,302,117 | 115,106 | 2,187,011 |
| 1.08 | 1.06 | 1.26 | 1.03 | 1.08 | 1.21 | 1.01 | 1.03 | 1.20 | 1.02 | 1.06 | 1.31 | |
| 1.00 | 1.03 | 1.10 | 1.02 | 1.15 | 1.18 | 1.01 | 1.01 | 1.04 | 1.03 | 1.11 | 1.27 |
| Predicted | Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 | Class 4 | Class 5 | Class 6 | Class 7 | Class 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real | |||||||||
| Class 1 | 306,036 | 0 | 155 | 0 | 187 | 1,767 | 1,413 | 30 | |
| Class 2 | 205 | 286,749 | 0 | 21 | 889 | 3 | 2,682 | 0 | |
| Class 3 | 0 | 0 | 147,703 | 60 | 0 | 3,198 | 0 | 0 | |
| Class 4 | 0 | 0 | 49 | 189,009 | 1,436 | 28 | 208 | 0 | |
| Class 5 | 0 | 191 | 795 | 307 | 285,751 | 27 | 0 | 0 | |
| Class 6 | 0 | 18 | 6,420 | 0 | 221 | 327,856 | 7 | 0 | |
| Class 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 204 | 0 | 406 | 316,459 | 46 | |
| Class 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 38 | 83 | 119,343 | |
| The Proposed Method | M1 | M2 | M3 | SVM | Hou’s Method | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | 0.9885 | 0.9154 | 0.9719 | 0.9863 | 0.9813 | 0.9885 |
| Class 2 | 0.9869 | 0.5497 | 0.5754 | 0.9450 | 0.7250 | 0.5475 |
| Class 3 | 0.9784 | 0.7628 | 0.9982 | 0.9439 | 0.9640 | 0.9578 |
| Class 4 | 0.9910 | 0.7912 | 0.7147 | 0.8716 | 0.8185 | 0.8772 |
| Class 5 | 0.9954 | 0.6190 | 0.8800 | 0.9121 | 0.7145 | 0.6922 |
| Class 6 | 0.9801 | 0.6843 | 0.8690 | 0.9743 | 0.9443 | 0.8744 |
| Class 7 | 0.9979 | 0.8295 | 0.7000 | 0.9514 | 0.9155 | 0.8227 |
| Class 8 | 0.9990 | 0.6772 | 0.8141 | 0.9446 | 0.8910 | 0.6680 |
| OA | 0.9890 | 0.7299 | 0.8055 | 0.9470 | 0.8669 | 0.8005 |
| Kappa | 0.9873 | 0.6884 | 0.7742 | 0.9385 | 0.8458 | 0.7704 |
| The Proposed Method | M1 | M2 | M3 | SVM | Hou’s Method | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time consumed (s) | 1871 | 1781 | 1812 | 1839 | 4977 | 1867 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Ren, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M. Deep Learning Based Lithology Classification Using Dual-Frequency Pol-SAR Data. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091513
Wang W, Ren X, Zhang Y, Li M. Deep Learning Based Lithology Classification Using Dual-Frequency Pol-SAR Data. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(9):1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091513
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wenguang, Xin Ren, Yan Zhang, and Meng Li. 2018. "Deep Learning Based Lithology Classification Using Dual-Frequency Pol-SAR Data" Applied Sciences 8, no. 9: 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091513
APA StyleWang, W., Ren, X., Zhang, Y., & Li, M. (2018). Deep Learning Based Lithology Classification Using Dual-Frequency Pol-SAR Data. Applied Sciences, 8(9), 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091513





