User-In-The-Loop Content Delivery in Cellular Communication Networks with Heterogeneous User Behaviors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. System Model
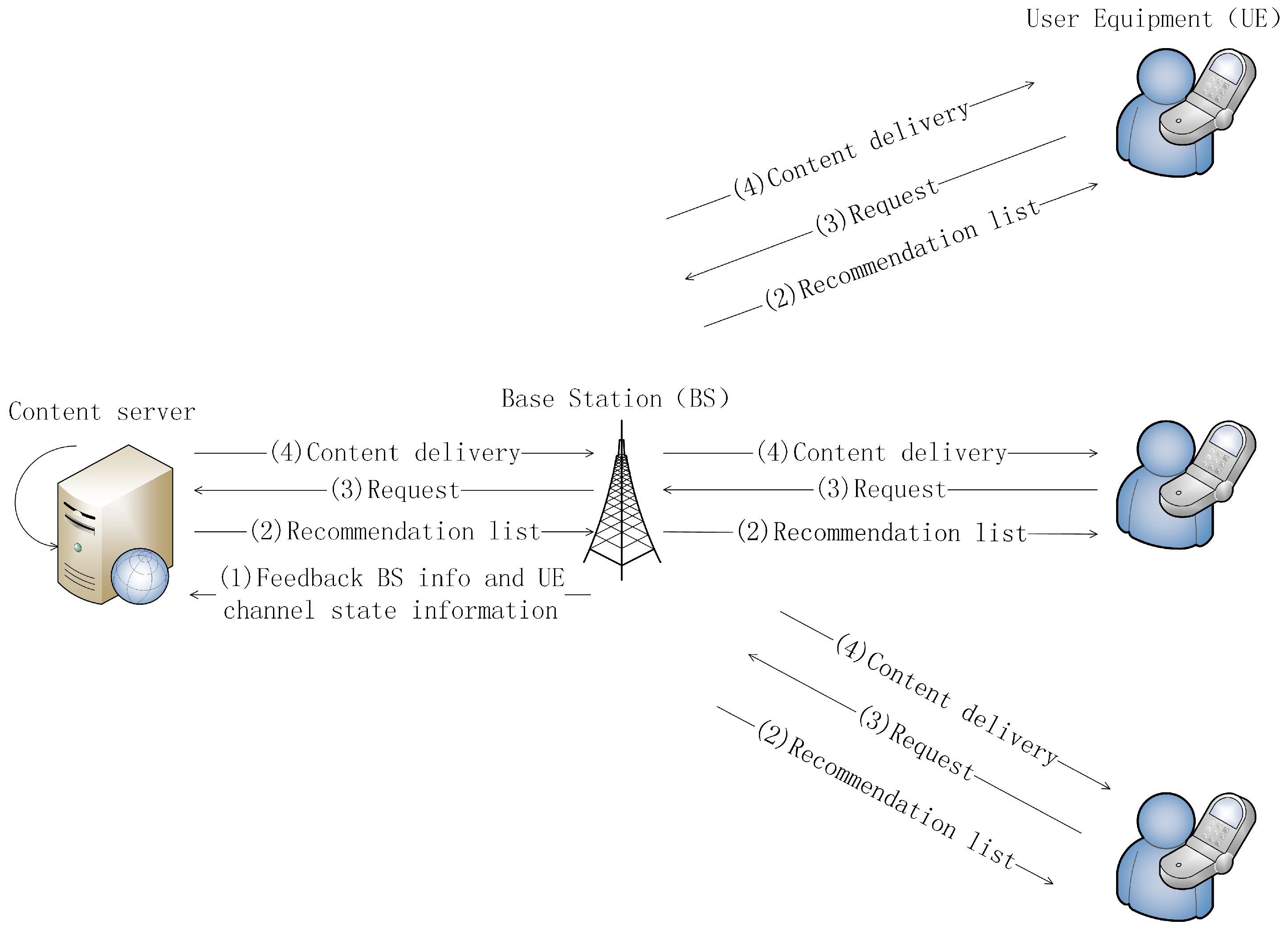
2.1. System Architecture
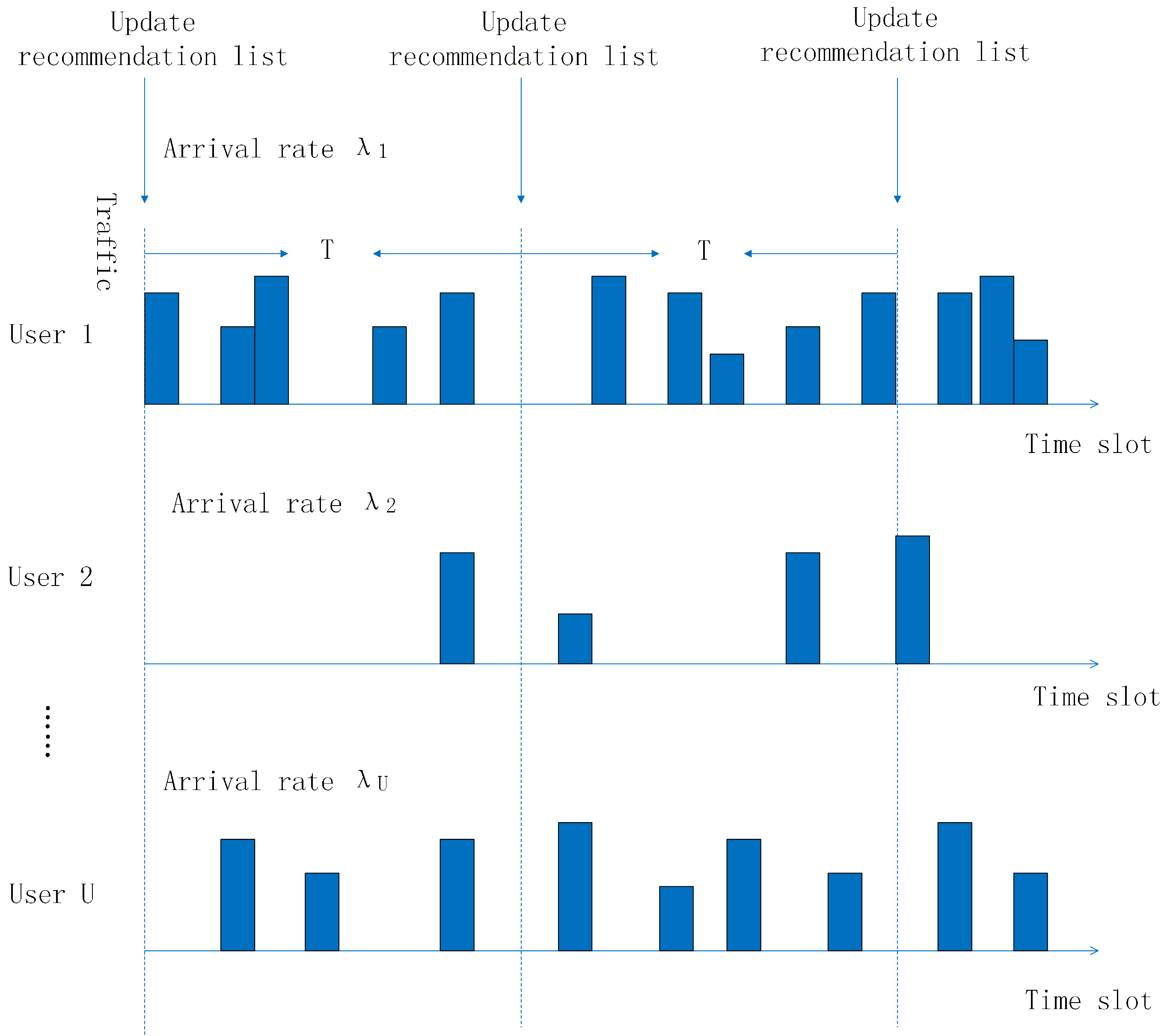
2.2. Traffic Demand Model
2.3. Air Interface Model
2.4. Problem Formulation
3. Theoretical Performance Limits
3.1. Upper Bound
3.2. Lower Bound
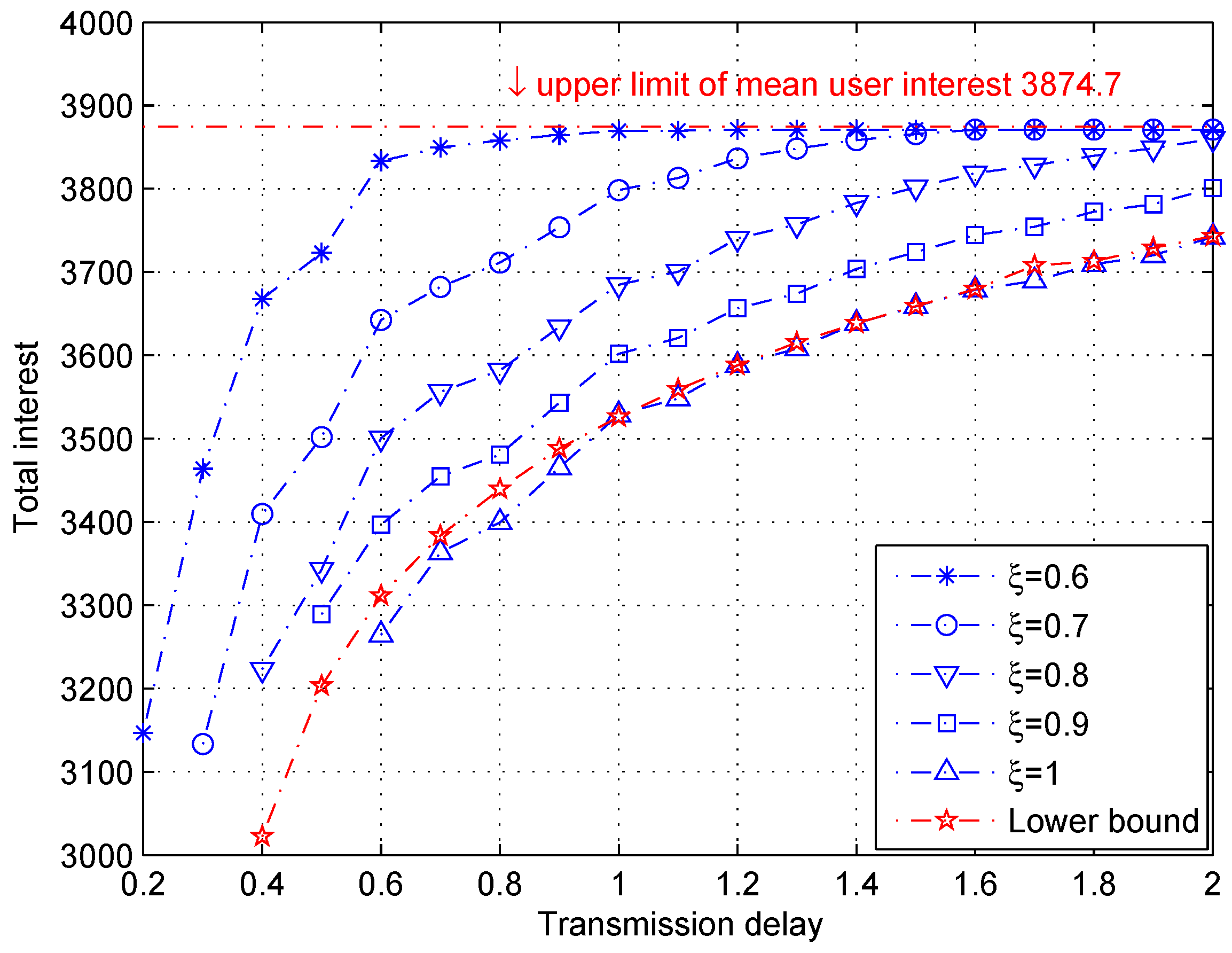
3.3. Simulation Validation
4. Heuristic Algorithms for UiL Content Delivery Systems
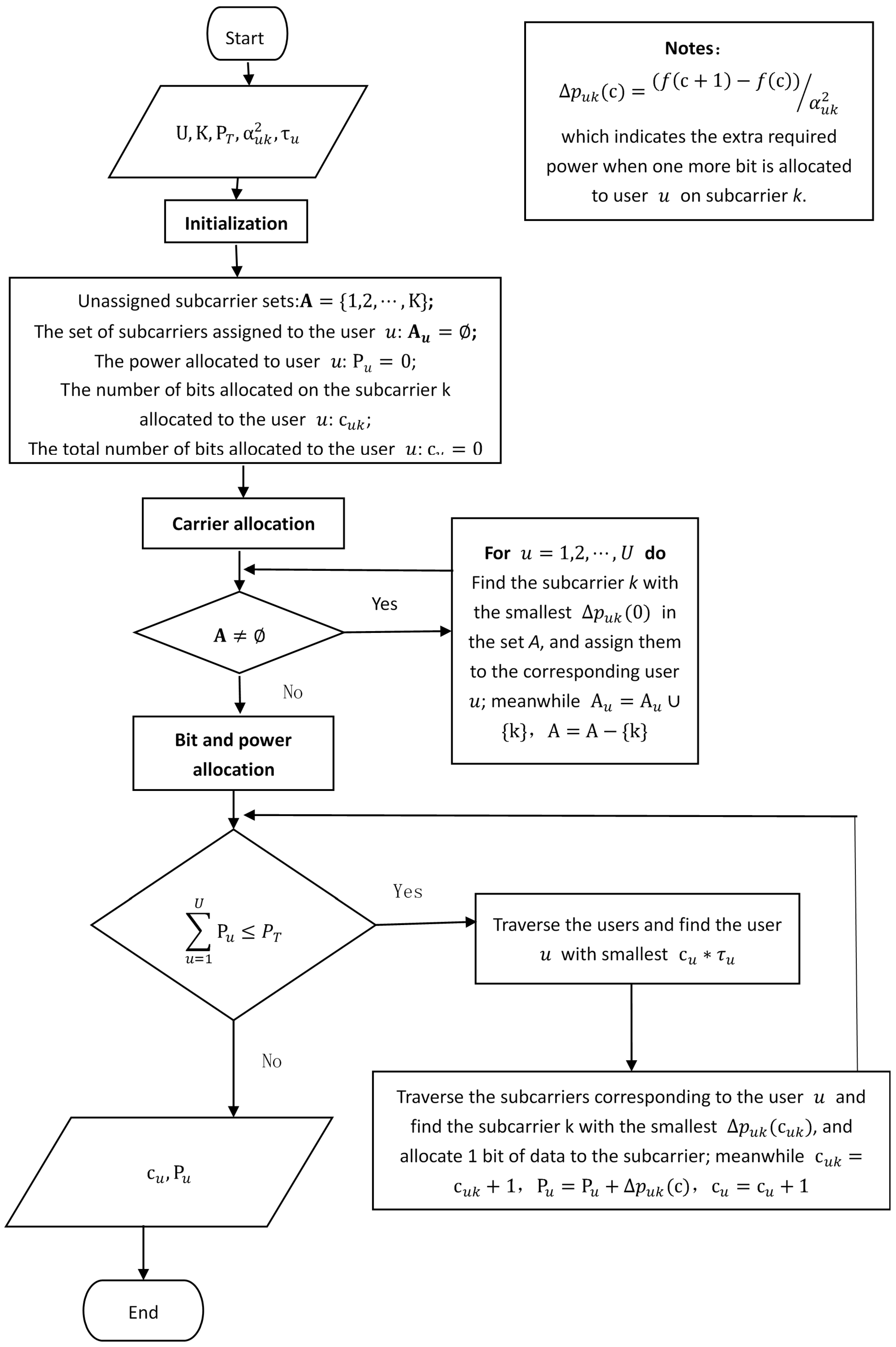
4.1. Capacity Allocation with Multiple Users
4.2. Recommendation of Content Lists
5. Simulation Results and Performance Evaluation
5.1. Realistic Models and Parameters
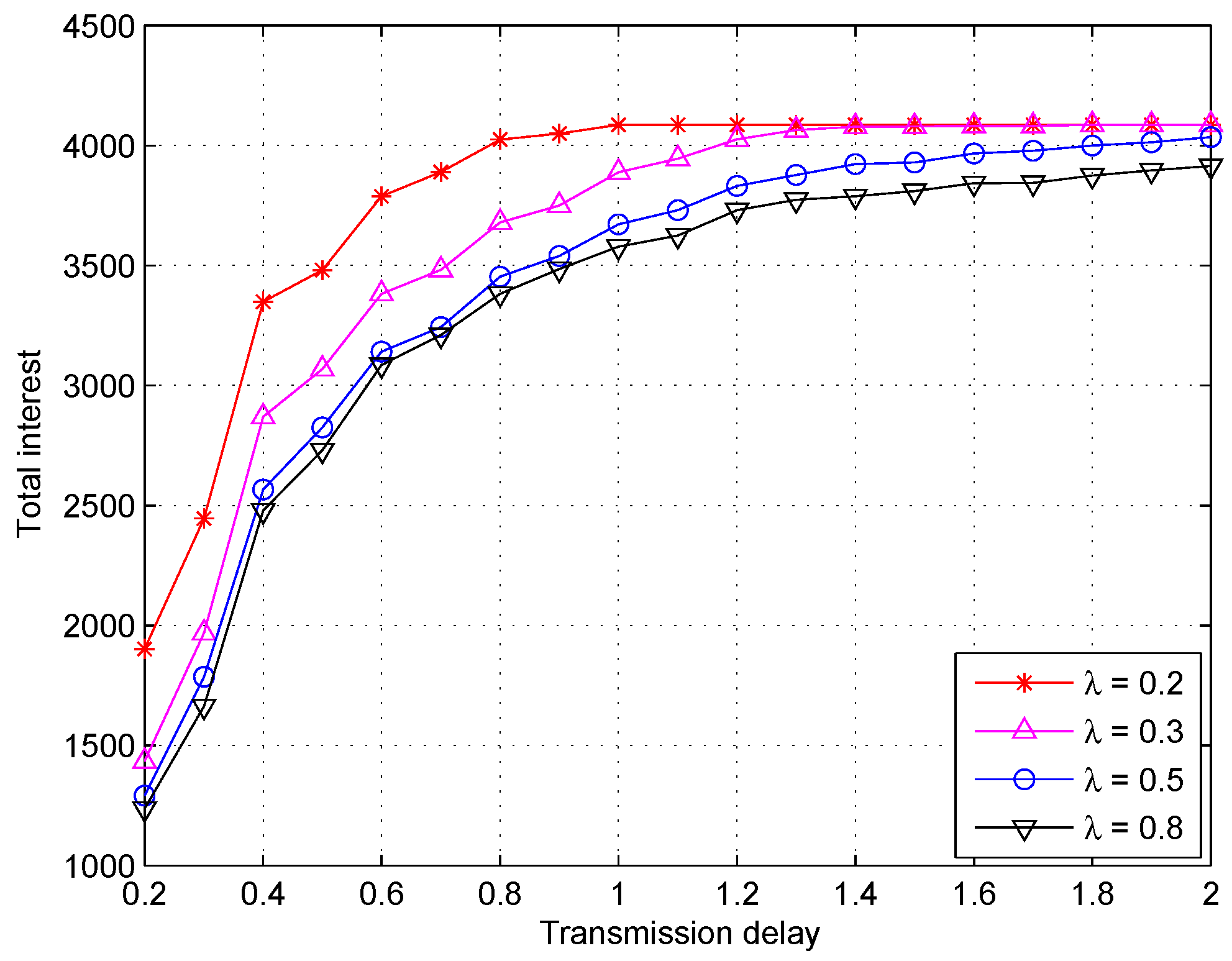
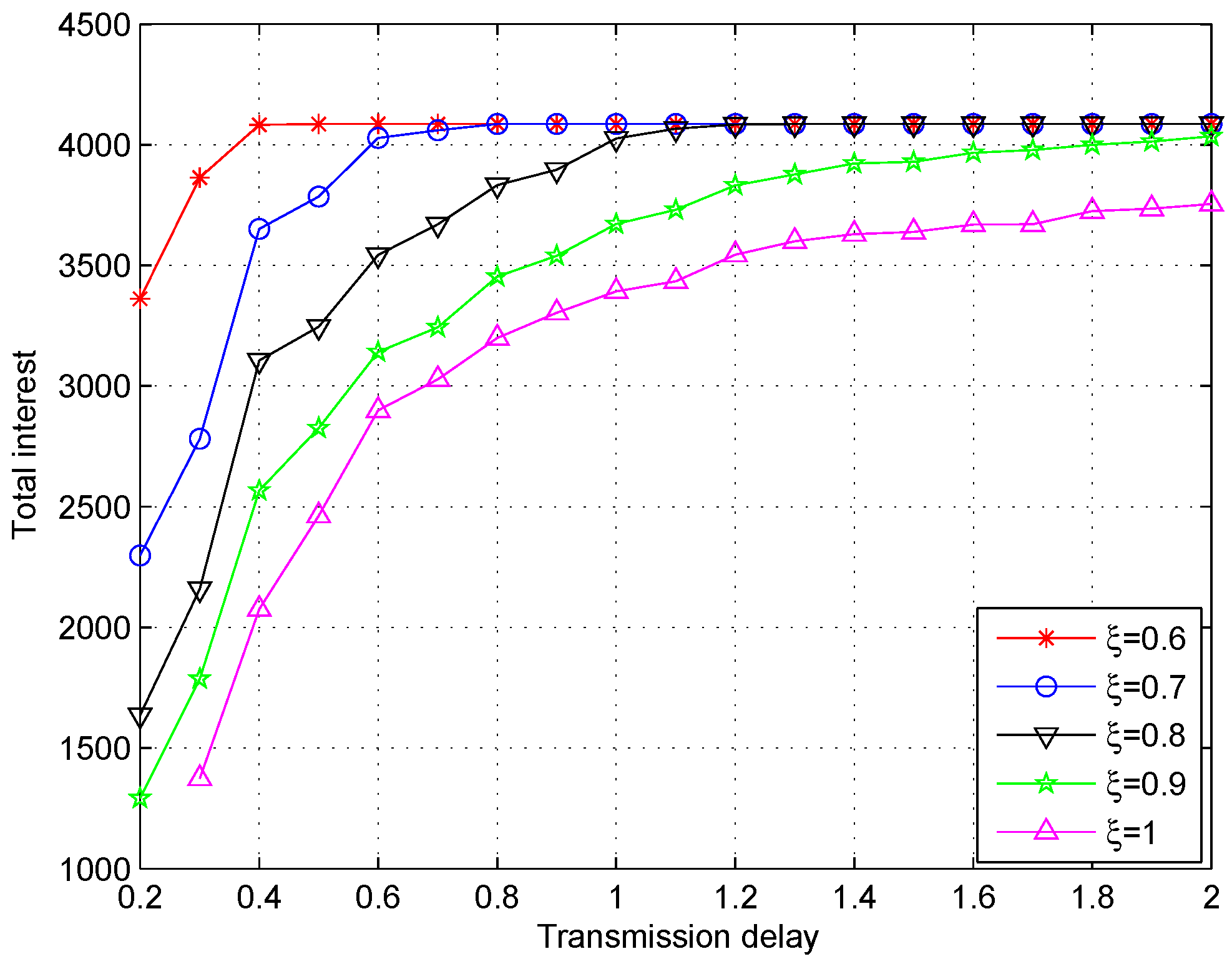
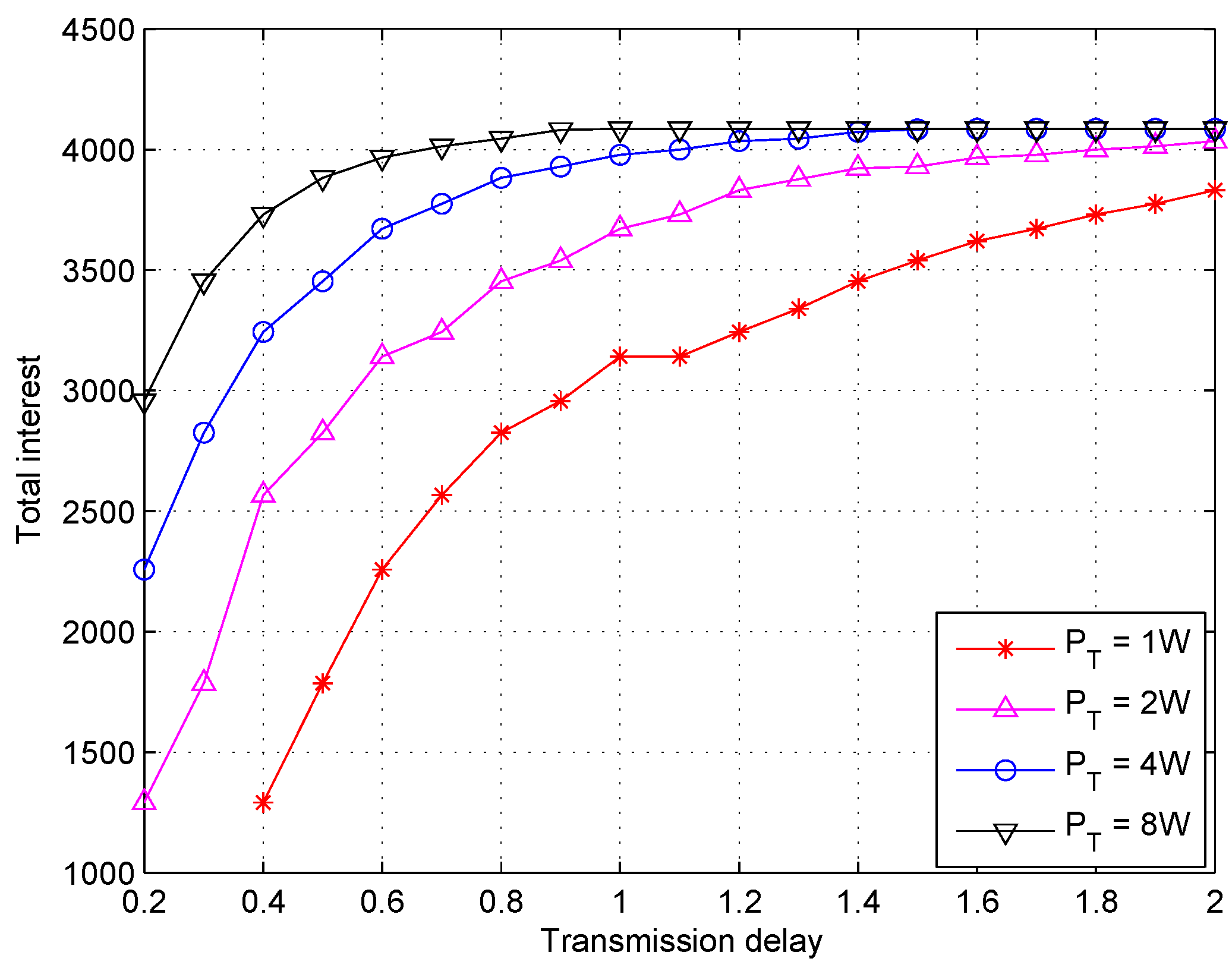
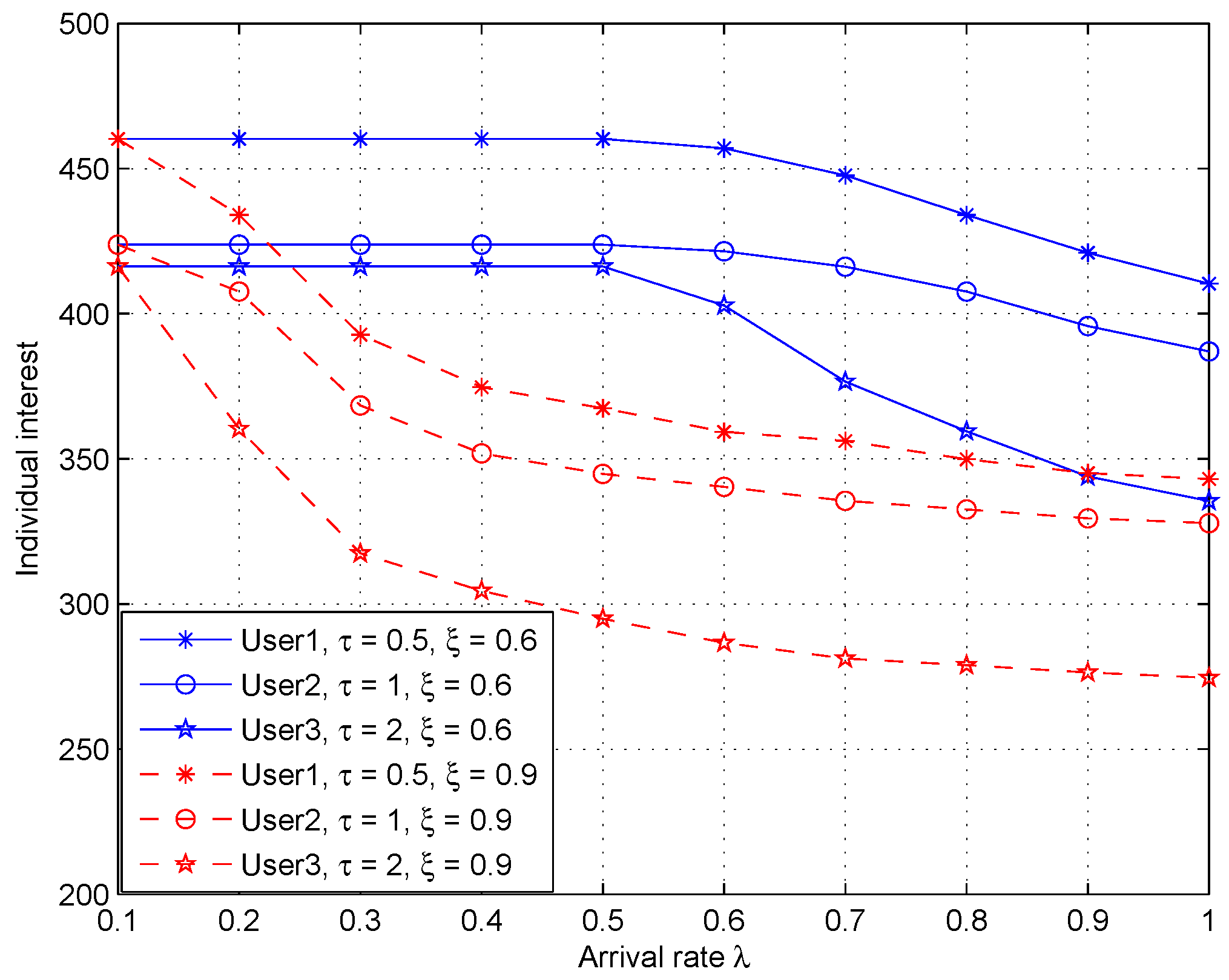
5.2. Simulations Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ekstrand, M.D.; Riedl, J.T.; Konstan, J.A. Collaborative filtering recommender systems. Found. Trends Hum. Comput. Interact. 2011, 4, 81–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, F.; Rokach, L.; Shapira, B. Recommender systems: introduction and challenges. In Recommender Systems Handbook; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.; Sheng, Q.Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, E.W.; Qin, Y. Collaborative Location Recommendation by Integrating Multi-dimensional Contextual Information. ACM Trans. Internet Technol. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.L.; Nie, L.; Gao, Y.; Nie, W.; Zha, Z.J.; Chua, T.S. Semantic-based location recommendation with multimodal venue semantics. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2015, 17, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, A.; Kartsakli, E.; Perillo, C.; Verikoukis, C. Shedding Light on the Internet: Stakeholders and Network Neutrality. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 55, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, W.; Chen, M. CPCDN: Content delivery powered by context and user intelligence. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2015, 17, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lum, W.Y.; Lau, F.C.M. A context-aware decision engine for content adaptation. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2002, 1, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Shoukry, O.; ElMohsen, M.A.; Tadrous, J. Proactive scheduling for content pre-fetching in mobile networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Sydney, Australia, 10–14 June 2014; pp. 2848–2854. [Google Scholar]
- Shoukry, O.K.; Fayek, M.B. Evolutionary scheduler for content pre-fetching in mobile networks. In Proceedings of the 2013 AAAI Fall Symposium Series, Arlington, VA, USA, 15–17 November 2013; pp. 386–391. [Google Scholar]
- Tadrous, J.; Eryilmaz, A.; Gamal, H.E. Proactive content download and user demand shaping for data networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2015, 23, 1917–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Baras, J.S. Joint optimization for social content delivery in wireless networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 23–27 May 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, X.; Baras, J.S. Joint optimization for social content delivery in heterogeneous wireless networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 14th International Symposium on Modeling and Optimization in Mobile, Ad Hoc, and Wireless Networks, Tempe, AZ, USA, 9–13 May 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, L.; Cao, G. Adaptive power-aware prefetch in wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2004, 3, 1648–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor, A.C.; Gunduz, D. Proactive wireless caching at mobile user devices for energy efficiency. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems, Brussels, Belgium, 25–28 August 2015; pp. 186–190. [Google Scholar]
- Tadrous, J.; Eryilmaz, A.; El Gamal, H. Joint smart pricing and proactive content caching for mobile services. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2016, 24, 2357–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadrous, J.; Eryilmaz, A.; El Gamal, H. Pricing for demand shaping and proactive download in smart data networks. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops, Turin, Italy, 14–19 April 2013; pp. 321–326. [Google Scholar]
- Giatsoglou, N.; Ntontin, K.; Kartsakli, E.; Antonopoulos, A.; Verikoukis, C. D2D-Aware device caching in mmWave-cellular networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2017, 35, 2025–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, A.; Kartsakli, E.; Verikoukis, C. Game theoretic D2D content dissemination in 4G cellular networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Caire, G.; Molisch, A.F. Wireless device-to-device caching networks: Basic principles and system performance. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2016, 34, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Shi, H.; Hong, X.; Shi, J. Joint Content Recommendation and Delivery in Mobile Wireless Networks with Outage Management. Entropy 2018, 20, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobadilla, J.; Ortega, F.; Hernando, A. Recommender systems survey. Knowl. Based Syst. 2013, 46, 109–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y. A survey of collaborative filtering based social recommender systems. Comput. Commun. 2014, 41, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adomavicius, G.; Tuzhilin, A. Context-aware recommender systems. In Recommender Systems Handbook; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 191–226. [Google Scholar]
- Koren, Y.; Bell, R.; Volinsky, C. Matrix factorization techniques for recommender systems. Computer 2009, 42, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, A. Wireless Communications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hasna, M.O.; Alouini, M.S. End-to-end performance of transmission systems with relays over Rayleigh-fading channels. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2003, 2, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Giannakis, G.B. A simple and general parameterization quantifying performance in fading channels. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2003, 51, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, M.C. Signal Processing and Detection. Available online: http://web.stanford.edu/group/cioffi/ee379a/course_reader/chap1.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2018).
- Kay, S.M. Fundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing, Vol. II: Detection Theory; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kyle, S. Random Samples. Available online: http://www.randomservices.org/random/sample/OrderStatistics.html (accessed on 23 March 2018).
- Kamps, U. A concept of generalized order statistics. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 1995, 48, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, K.M.; Kuenning, G.H. A study of irregularities in file-size distributions. In Proceedings of the 2002 International Symposium on Performance Evaluation of Computer and Telecommunication Systems, San Diego, CA, USA, 14–18 July 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Barford, P.; Crovella, M. Generating representative web workloads for network and server performance evaluation. ACM Sigmetrics Perform. Eval. Rev. 1998, 26, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlebus, E.; Divgi, G. A versatile probability distribution for light and heavy tails of web file sizes. In Proceedings of the 2009 Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Budapest, Hungary, 5–8 April 2009; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Douceur, J.R.; Bolosky, W.J. A large-scale study of file-system contents. ACM Sigmetrics Perform. Eval. Rev. 1999, 27, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, C.; Kaczor, G.; Markovi, D. Neuropsychological constraints to human data production on a global scale. Eur. Phys. J. B Condens. Matter Complex Syst. 2012, 85, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlitt, M.F.; Williamson, C.L. Internet web servers: Workload characterization and performance implications. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 1997, 5, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, M.; Kwak, H.; Rodriguez, P. I tube, you tube, everybody tubes: analyzing the world’s largest user generated content video system. In Proceedings of the 7th ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Internet Measurement, San Diego, CA, USA, 24–26 October 2007; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Adamic, L.A. Zipf, Power-Laws, and Pareto—A Ranking Tutorial. Available online: http://www.labs.hp.com/research/idl/papers/ranking/ranking.html (accessed on 23 March 2018).
- Hu, N.; Zhang, J.; Pavlou, P.A. Overcoming the J-shaped distribution of product reviews. Commun. ACM 2009, 52, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, J. Universality in movie rating distributions. Eur. Phys. J. B Condens. Matter Complex Syst. 2009, 71, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio, M.B.; Cocho, G.; Naumis, G.G. Universality in the tail of musical note rank distribution. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2008, 387, 5552–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Pavlou, P.A.; Zhang, J. Can online reviews reveal a product’s true quality? Empirical findings and analytical modeling of Online word-of-mouth communication. In Proceedings of the 7th ACM Conference on Electronic Commerce, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 11–15 June 2006; pp. 324–330. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, T.; Cai, H.J.; Zhang, Y. Polarized score distributions in music ratings and the emergence of popular artists. In Proceedings of the Science and Information Conference, London, UK, 7–9 October 2013; pp. 472–476. [Google Scholar]
- LTE; Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA); Radio Frequency (RF). Requirements for LTE Pico Node B. ETSI TR 136 931 v9.0.0. Available online: http://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_ts/136100_136199/136104/09.04.00_60/ts_136104v090400p.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2018).
- Kim, I.; Park, I.S.; Lee, Y.H. Use of linear programming for dynamic subcarrier and bit allocation in multiuser OFDM. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2006, 55, 1195–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, C.; Roli, A.; Alba, E. An introduction to metaheuristic techniques. In Parallel Metaheuristics: A New Class of Algorithms; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 47. [Google Scholar]
- Boussaid, I.; Lepagnot, J.; Siarry, P. A survey on optimization metaheuristics. Inf. Sci. 2013, 237, 82–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarts, E.; Korst, J. Simulated Annealing and Boltzman Machines: A Stochastic Approach to Combinatorial Optimization and Neural Computing; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Khajehzadeh, M.; Taha, M.R.; El-Shafie, A.; Eslami, N. A survey on meta-heuristic global optimization algorithms. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2011, 3, 569–578. [Google Scholar]


| Simulation Parameter | Parameter Value |
|---|---|
| Number of users U | 10 |
| Number of contents F | 500 |
| Number of channels K | 256 |
| Recommended form length N | 50 |
| System bandwidth B | 10 MHz |
| Noise power spectral density | −174 dBm/Hz [45] |
| Bit error rate BER | 1 × 10 [46] |
| Macrocell path loss model | 128.1 + 37.6 (d in km) [45] |
| Inter-site distance d | 330 m |
| Channel gain | Exponential distribution of parameter 1 |
| File distribution L | Logarithmic normal distribution with location parameter of and scale parameter of [33] |
| Interest matrix | Zipf distribution with parameter 1 [38]; Truncated Gaussian distribution between 1 and 5 with a mean of 3 and a variance of 2 [40]. |
| Simulation Parameter | Parameter Value |
|---|---|
| Initial temperature | 0.5 |
| Cooling method | |
| Maximum number of iterations | 500 |
| Population size | 30 |
| Crossover percentage | 0.5 |
| Mutation percentage | 0.4 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Lu, H.; Hong, X.; Shi, J. User-In-The-Loop Content Delivery in Cellular Communication Networks with Heterogeneous User Behaviors. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8050704
Zhang W, Li Y, Lu H, Hong X, Shi J. User-In-The-Loop Content Delivery in Cellular Communication Networks with Heterogeneous User Behaviors. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(5):704. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8050704
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Weicheng, Yaodong Li, Hai Lu, Xuemin Hong, and Jianghong Shi. 2018. "User-In-The-Loop Content Delivery in Cellular Communication Networks with Heterogeneous User Behaviors" Applied Sciences 8, no. 5: 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8050704
APA StyleZhang, W., Li, Y., Lu, H., Hong, X., & Shi, J. (2018). User-In-The-Loop Content Delivery in Cellular Communication Networks with Heterogeneous User Behaviors. Applied Sciences, 8(5), 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8050704





