Multi-Plane Ultrafast Compound 3D Strain Imaging: Experimental Validation in a Carotid Bifurcation Phantom
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
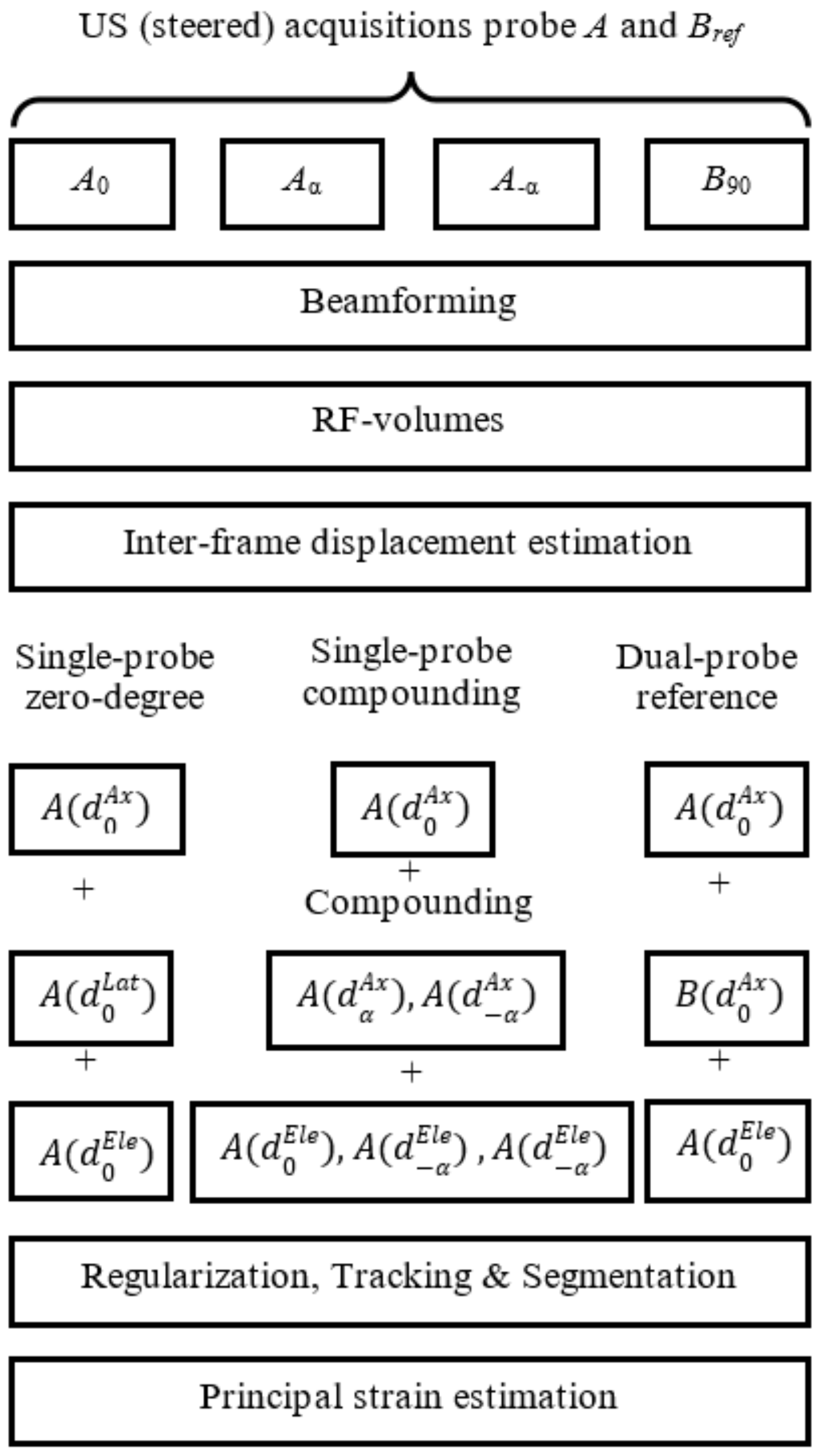
2. Materials and Methods
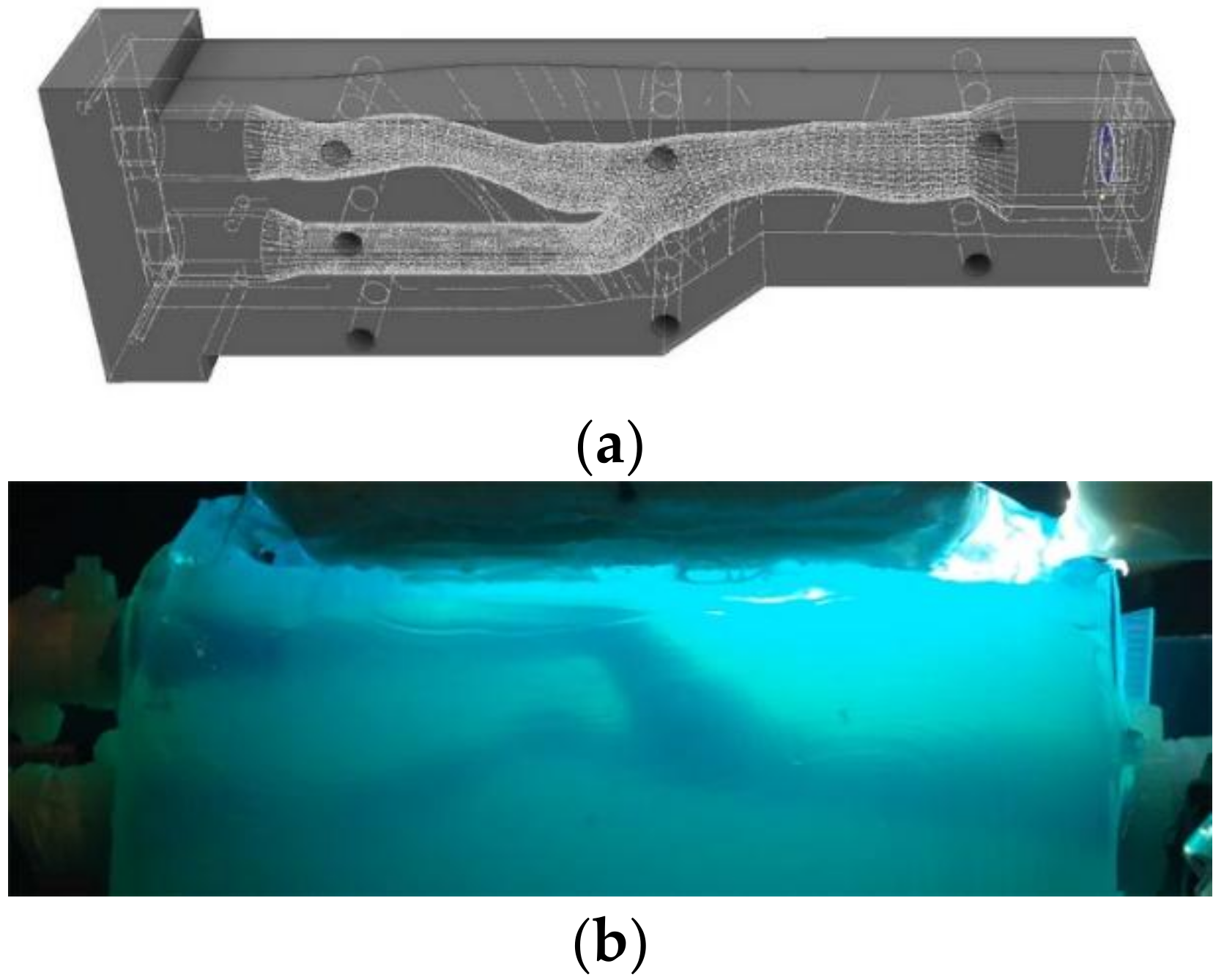
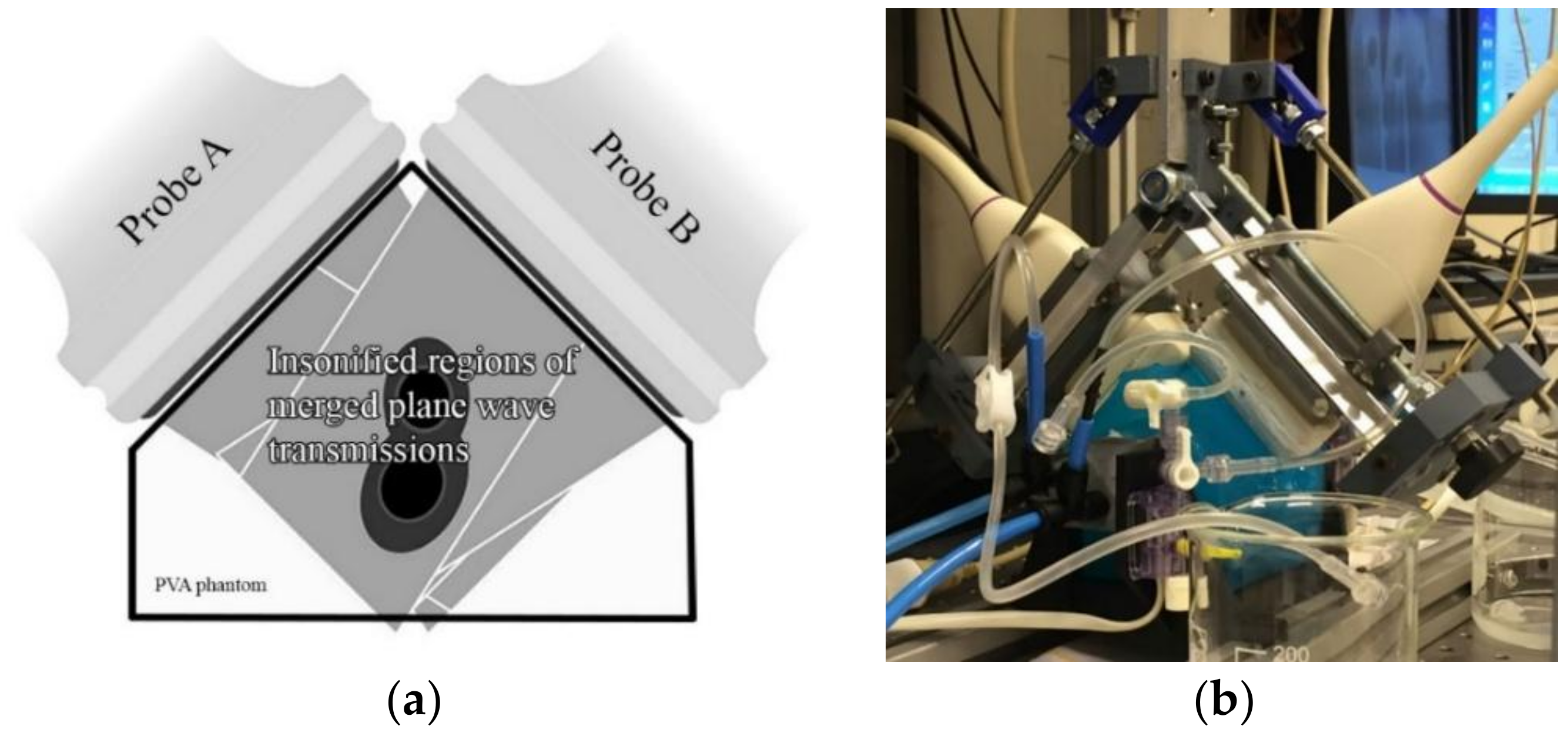
2.1. Experimental Setup
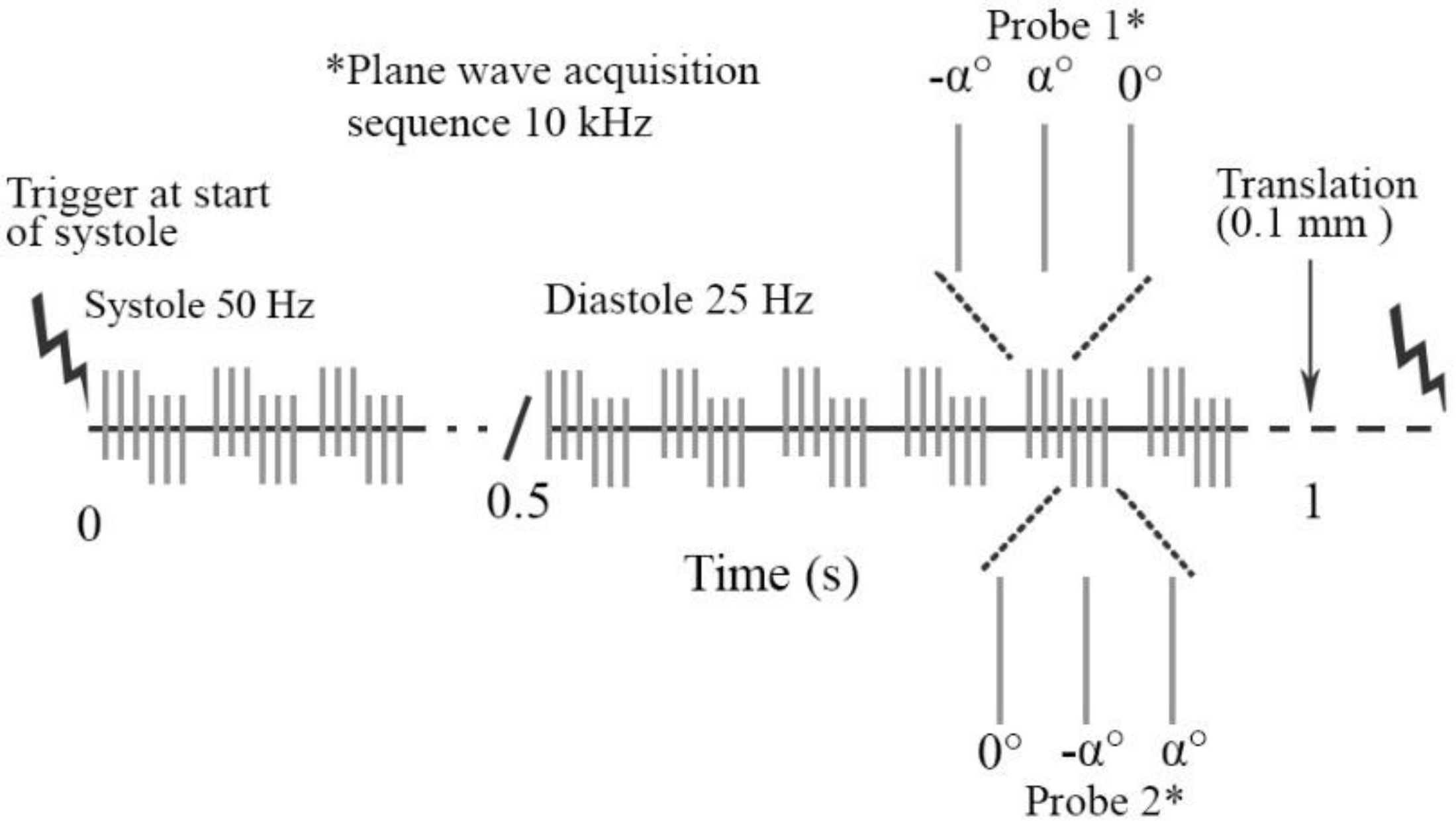
2.2. Ultrasound Data Acquisition
2.3. Post Processing RF Element Data
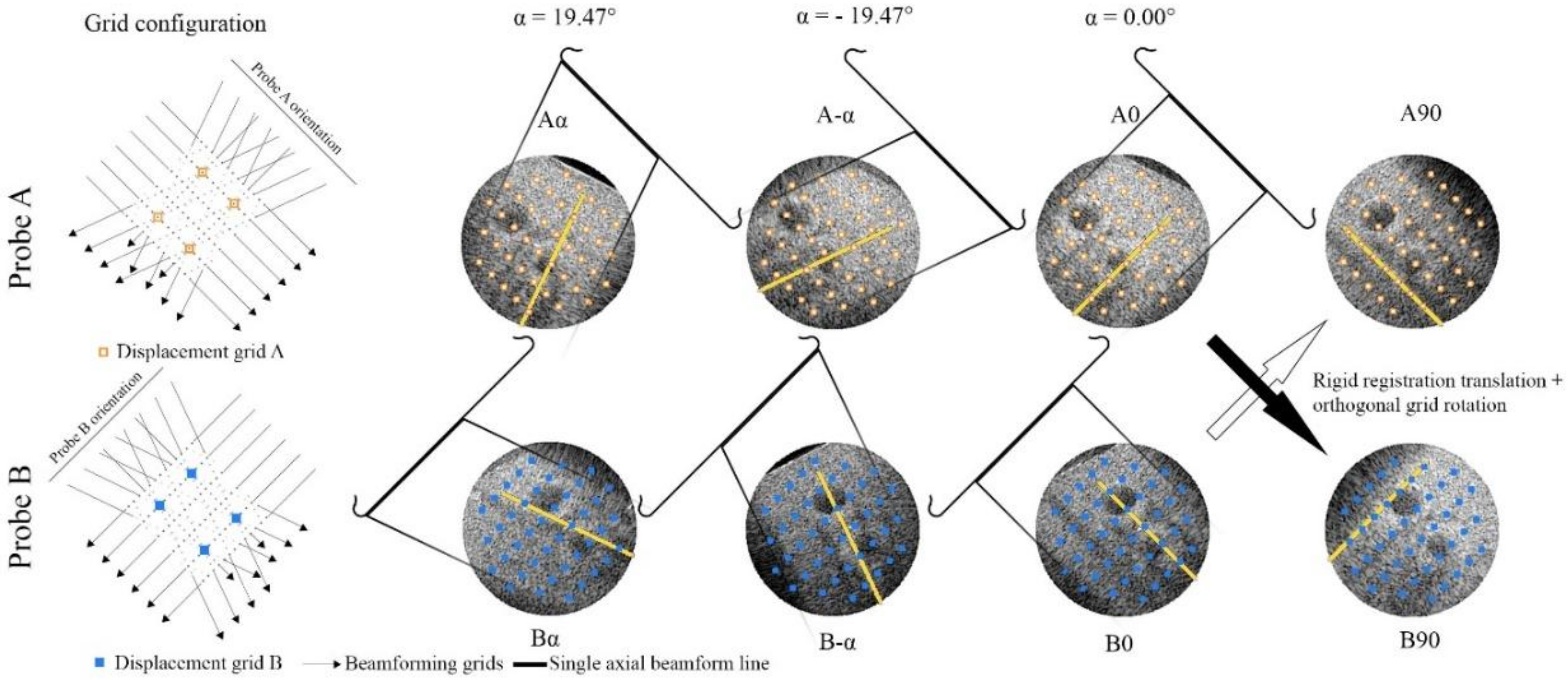
2.4. 3D Interframe Displacement Estimation
2.4.1. Single-Probe Zero-Degree
2.4.2. Single-Probe Compounding
2.4.3. Dual-Probe Reference
2.5. Regularization Tracking and Segmentation
2.6. Strain Estimation
2.7. Evaluation
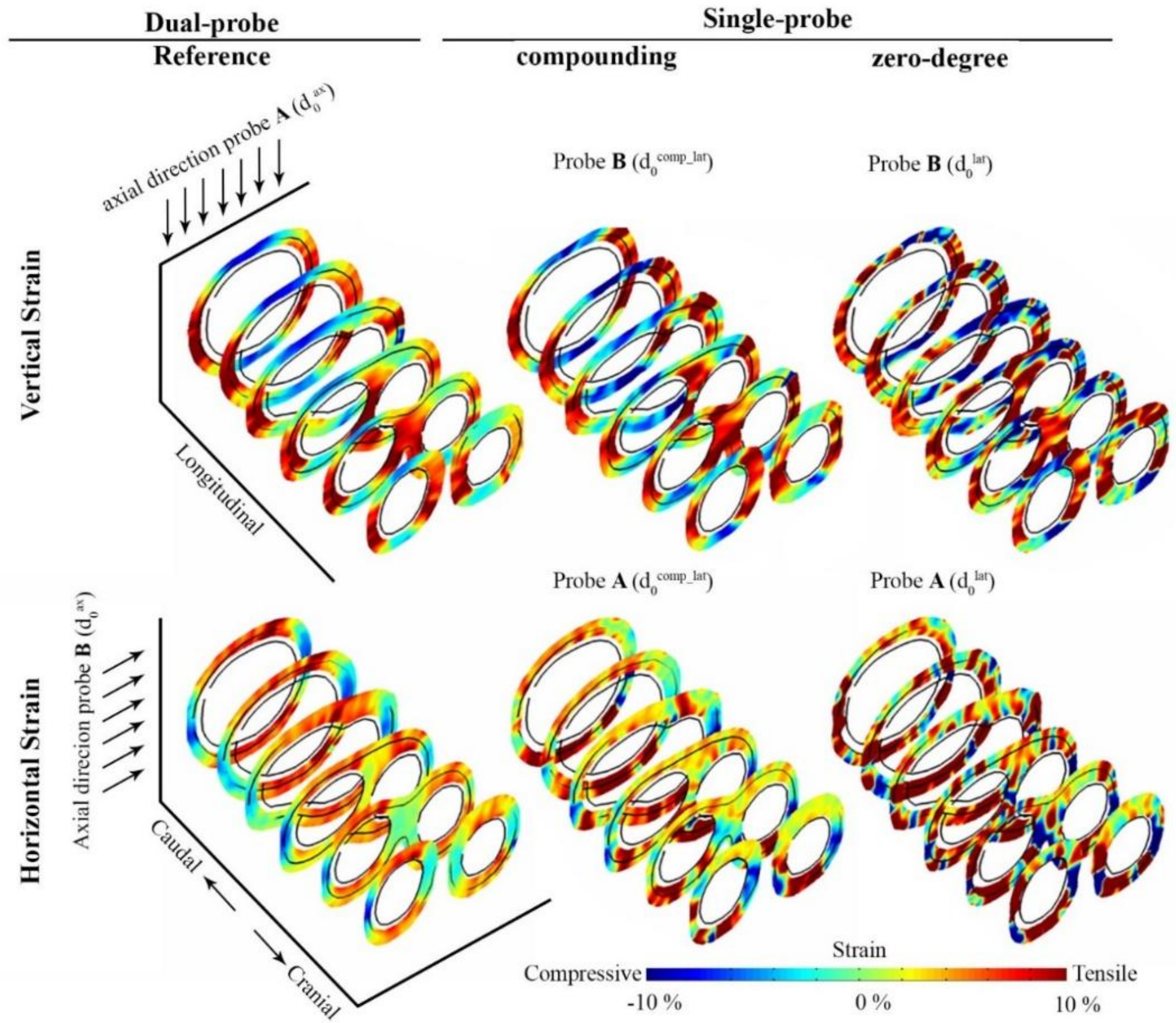
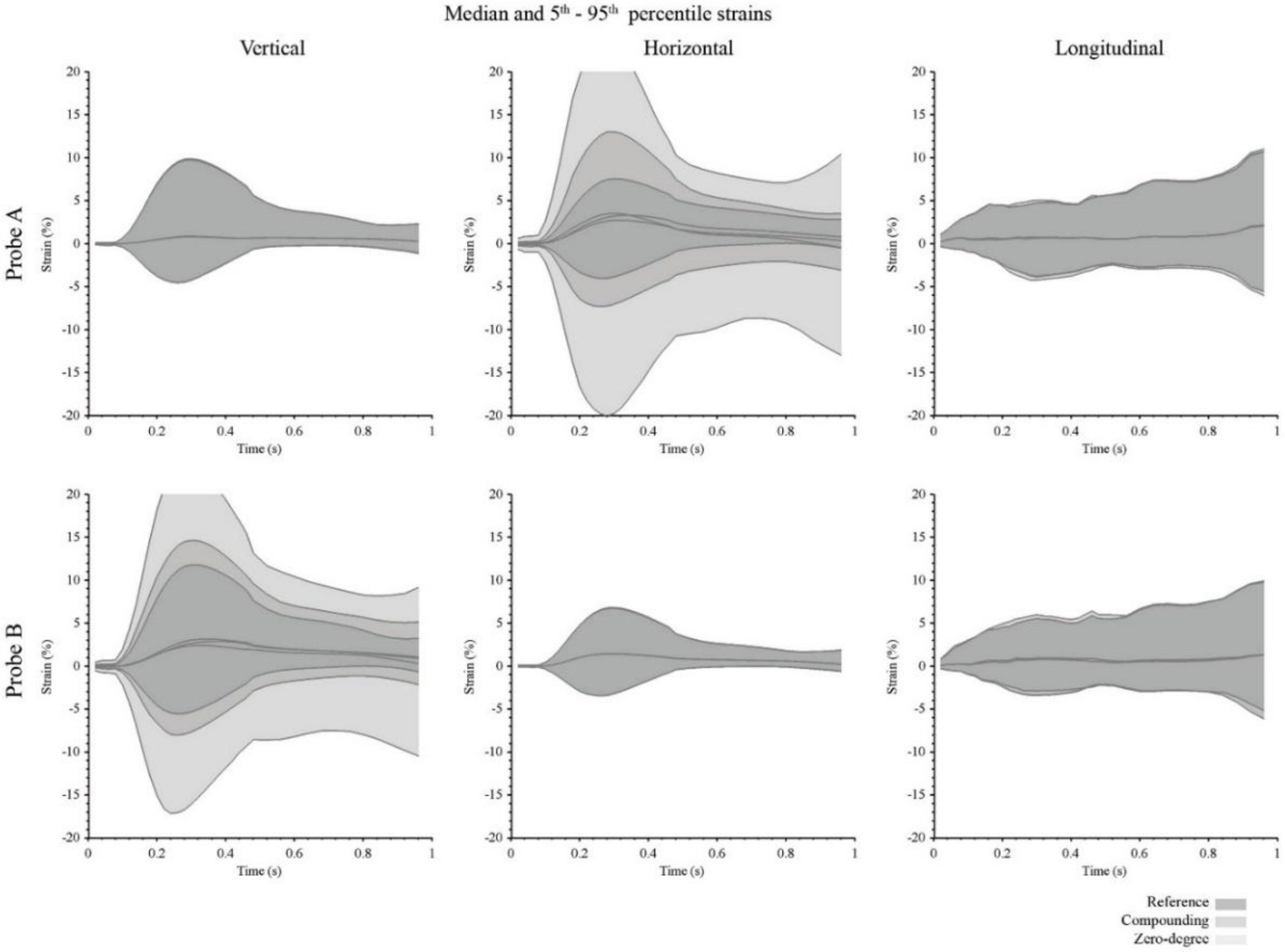
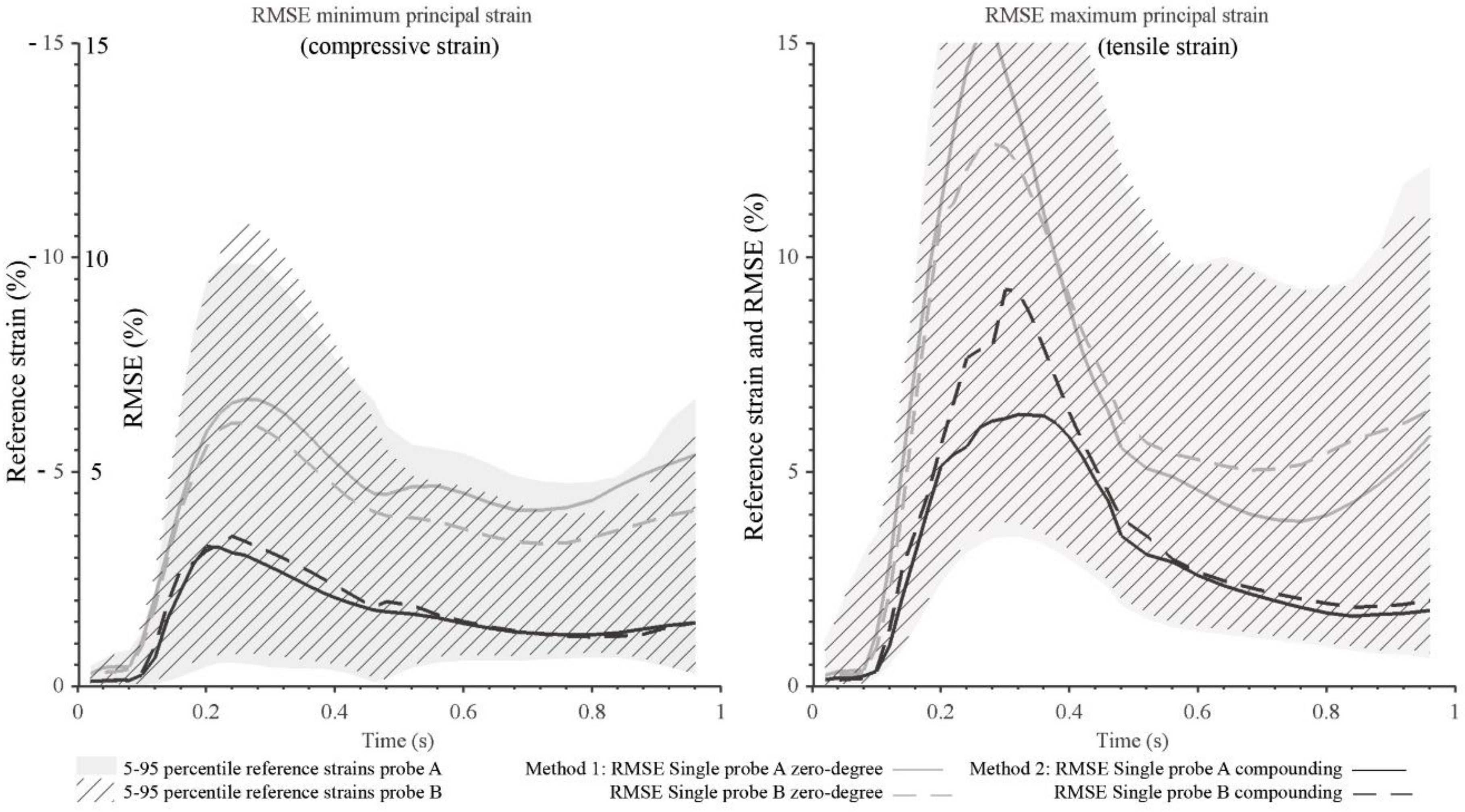
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ophir, J.; Céspedes, I.; Ponnekanti, H.; Yazdi, Y.; Li, X. Elastography: A quantitative method for imaging the elasticity of biological tissues. Ultrason. Imaging 1991, 13, 111–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, H.H.; de Borst, G.J.; Bots, M.L.; Moll, F.L.; Pasterkamp, G.; de Korte, C.L. Validation of noninvasive in vivo compound ultrasound strain imaging using histologic plaque vulnerability features. Stroke 2016, 47, 2770–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohayon, J.; Finet, G.; Le Floc’h, S.; Cloutier, G.; Gharib, A.M.; Heroux, J.; Pettigrew, R.I. Biomechanics of atherosclerotic coronary plaque: Site, stability and in vivo elasticity modeling. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 42, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinal, M.H.R.; Heusinkveld, M.H.G.; Qin, Z.; Lopata, R.G.P.; Naim, C.; Soulez, G.; Cloutier, G. Carotid artery plaque vulnerability assessment using noninvasive ultrasound elastography: Validation with MRI. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 209, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.W.; He, Q.; Huang, M.W.; Huang, L.Y.; Zhao, X.H.; Yuan, C.; Luo, J.W. Non-invasive identification of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques using texture analysis in ultrasound carotid elastography: An in vivo feasibility study validated by magnetic resonance imaging. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaar, J.A.; Muller, J.E.; Falk, E.; Virmani, R.; Fuster, V.; Serruys, P.W.; Colombo, A.; Stefanadis, C.; Ambrose, J.A.; Moreno, P.; et al. Terminology for high-risk and vulnerable coronary artery plaques. Eur. Heart J. 2004, 25, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lendon, C.L.; Davies, M.J.; Born, G.V.R.; Richardson, P.D. Atherosclerotic plaque caps are locally weakened when macrophage density is increased. Atherosclerosis 1991, 87, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellings, W.E.; Peeters, W.; Moll, F.L.; Piers, S.R.D.; van Setten, J.; Van der Spek, P.J.; de Vries, J.P.P.M.; Seldenrijk, K.A.; De Bruin, P.C.; Vink, A.; et al. Composition of carotid atherosclerotic plaque is associated with cardiovascular outcome a prognostic study. Circulation 2010, 121, 1941–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Korte, C.L.; Céspedes, E.I.; van der Steen, A.F.W.; Pasterkamp, G.; Bom, N. Intravascular ultrasound elastography: Assessment and imaging of elastic properties of diseased arteries and vulnerable plaque. Eur. J. Ultrasound 1998, 7, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribbers, H.; Lopata, R.G.; Holewijn, S.; Pasterkamp, G.; Blankensteijn, J.D.; de Korte, C.L. Noninvasive two-dimensional strain imaging of arteries: Validation in phantoms and preliminary experience in carotid arteries in vivo. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2007, 33, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, M.; Varghese, T.; Wang, X.; Mitchell, C.; Kliewer, M.A.; Dempsey, R.J. Methods for robust in vivo strain estimation in the carotid artery. Phys. Med. Biol. 2012, 57, 7329–7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, C.; Soulez, G.; Maurice, R.L.; Giroux, M.F.; Cloutier, G. Noninvasive vascular elastography: Toward a complementary characterization tool of atherosclerosis in carotid arteries. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2007, 33, 1841–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, T.; Fukuda, S.; Shimada, K.; Maeda, K.; Yoshida, K.; Sunada, H.; Inanami, H.; Tanaka, H.; Jissho, S.; Taguchi, H.; et al. Direct measurement of wall stiffness for carotid arteries by ultrasound strain imaging. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2009, 22, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poree, J.; Chayer, B.; Soulez, G.; Ohayon, J.; Cloutier, G. Noninvasive vascular modulography method for imaging the local elasticity of atherosclerotic plaques: Simulation and in vitro vessel phantom study. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2017, 64, 1805–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khamdaeng, T.; Luo, J.; Vappou, J.; Terdtoon, P.; Konofagou, E.E. Arterial stiffness identification of the human carotid artery using the stress-strain relationship in vivo. Ultrasonics 2012, 52, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Korte, C.L.; Sierevogel, M.; Mastik, F.; Strijder, C.; Velema, E.; Pasterkamp, G.; van der Steen, A.F.W. Identification of atherosclerotic plaque components with intravascular ultrasound elastography in vivo: A yucatan pig study. Circulation 2002, 105, 1627–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanai, H.; Hasegawa, H.; Ichiki, M.; Tezuka, F.; Koiwa, Y. Elasticity imaging of atheroma with transcutaneous ultrasound preliminary study. Circulation 2003, 107, 3018–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, H.H.; Lopata, R.G.; Idzenga, T.; de Korte, C.L. Full 2d displacement vector and strain tensor estimation for superficial tissue using beam-steered ultrasound imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2010, 55, 3201–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, H.H.; Saris, A.E.; Vaka, N.R.; Nillesen, M.M.; de Korte, C.L. Ultrafast vascular strain compounding using plane wave transmission. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korukonda, S.; Nayak, R.; Carson, N.; Schifitto, G.; Dogra, V.; Doyley, M.M. Noninvasive vascular elastography using plane-wave and sparse-array imaging. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2013, 60, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poree, J.; Garcia, D.; Chayer, B.; Ohayon, J.; Cloutier, G. Noninvasive vascular elastography with plane strain incompressibility assumption using ultrafast coherent compound plane wave imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 34, 2618–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, M.; Verbrugghe, P.; Smoljkic, M.; Verhoeven, J.; Heyde, B.; Famaey, N.; Herijgers, P.; D’Hooge, J. Strain assessment in the carotid artery wall using ultrasound speckle tracking: Validation in a sheep model. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 1107–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fekkes, S.; Swillens, A.E.S.; Hansen, H.H.G.; Saris, A.E.C.M.; Nillesen, M.M.; Iannaccone, F.; Segers, P.; de Korte, C.L. 2-d versus 3-d cross-correlation-based radial and circumferential strain estimation using multiplane 2-d ultrafast ultrasound in a 3-d atherosclerotic carotid artery model. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2016, 63, 1543–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinthio, M.; Ahlgren, A.R.; Bergkvist, J.; Jansson, T.; Persson, H.W.; Lindstrom, K. Longitudinal movements and resulting shear strain of the arterial wall. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 291, H394–H402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svedlund, S.; Eklund, C.; Robertsson, P.; Lomsky, M.; Gan, L.M. Carotid artery longitudinal displacement predicts 1-year cardiovascular outcome in patients with suspected coronary artery disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 1668–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landry, A.; Spence, J.D.; Fenster, A. Quantification of carotid plaque volume measurements using 3d ultrasound imaging. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2005, 31, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinke, W.; Hennerici, M. Three-dimensional ultrasound imaging of carotid artery plaques. J. Cardiovasc. Technol. 1989, 8, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Fenster, A.; Parraga, G.; Bax, J. Three-dimensional ultrasound scanning. Interface Focus 2011, 1, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldassarre, D.; Amato, M.; Bondioli, A.; Sirtori, C.R.; Tremoli, E. Carotid artery intima-media thickness measured by ultrasonography in normal clinical practice correlates well with atherosclerosis risk factors. Stroke 2000, 31, 2426–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landry, A.; Spence, J.D.; Fenster, A. Measurement of carotid plaque volume by 3-dimensional ultrasound. Stroke 2004, 35, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delcker, A.; Diener, H.C. 3d ultrasound measurement of atherosclerotic plaque volume in carotid arteries. Bildgeb. Imaging 1994, 61, 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Boekhoven, R.W.; Rutten, M.C.M.; van Sambeek, M.R.; van de Vosse, F.N.; Lopata, R.G.P. Towards mechanical characterization of intact endarterectomy samples of carotid arteries during inflation using echo-ct. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boekhoven, R.W.; Rutten, M.C.M.; van Sambeek, M.R.; van de Vosse, F.N.; Lopata, R.G.P. Echo-computed tomography strain imaging of healthy and diseased carotid specimens. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2014, 40, 1329–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Friedman, M.H. Measurement of the 3d arterial wall strain tensor using intravascular b-mode ultrasound images: A feasibility study. Phys. Med. Biol. 2010, 55, 6377–6394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, H.H.; de Borst, G.J.; Bots, M.L.; Moll, F.L.; Pasterkamp, G.; de Korte, C.L. Compound ultrasound strain imaging for noninvasive detection of (fibro)atheromatous plaques: Histopathological validation in human carotid arteries. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9, 1466–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, R.; Huntzicker, S.; Ohayon, J.; Carson, N.; Dogra, V.; Schifitto, G.; Doyley, M.M. Principal strain vascular elastography: Simulation and preliminary clinical evaluation. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 682–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fromageau, J.; Gennisson, J.L.; Schmitt, C.; Maurice, R.L.; Mongrain, R.; Cloutier, G. Estimation of polyvinyl alcohol cryogel mechanical properties with four ultrasound elastography methods and comparison with gold standard testings. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2007, 54, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, H.H.G.; Lopata, R.G.P.; Idzenga, T.; De Korte, C.L. Fast strain tensor imaging using beam steered plane wave ultrasound transmissions. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), San Diego, CA, USA, 11–14 October 2010; pp. 1344–1347. [Google Scholar]
- Akyildiz, A.C.; Speelman, L.; Gijsen, F.J.H. Mechanical properties of human atherosclerotic intima tissue. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varghese, T.; Ophir, J. A theoretical framework for performance characterization of elastography: The strain filter. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 1997, 44, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saris, A.E.C.M.; Nillesen, M.M.; Fekkes, S.; Hansen, H.H.G.; de Korte, C.L. Robust blood velocity estimation using point-spread-function-based beamforming and multi-step speckle tracking. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Taipei, Taiwan, 21–24 October 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Aglyamov, S.R.; Park, S.; O’Donnell, M.; Emelianov, S.Y. An autocorrelation-based method for improvement of sub-pixel displacement estimation in ultrasound strain imaging. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2011, 58, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kallel, F.; Ophir, J. A least-squares strain estimator for elastography. Ultrason. Imaging 1997, 19, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chee, A.J.Y.; Ho, C.K.; Yiu, B.Y.S.; Yu, A.C.H. Walled carotid bifurcation phantoms for imaging investigations of vessel wall motion and blood flow dynamics. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2016, 63, 1852–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boekhoven, R.W.; Rutten, M.C.M.; van de Vosse, F.N.; Lopata, R.G.P. Design of a fatty plaque phantom for validation of strain imaging. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium, Chicago, IL, USA, 3–6 September 2014; pp. 2619–2622. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Dang, C.; Garcia, M.; Gregersen, H.; Kassab, G.S. Surrounding tissues affect the passive mechanics of the vessel wall: Theory and experiment. Am. J. Physiol. Heart C 2007, 293, H3290–H3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berne, R.M.; Levy, M.N. Physiology, 3rd ed.; Mosby Year Book: Saint Louis, France, 1993. [Google Scholar]



| Beamforming Grid (µm) | Displacement Grid (µm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Zero-Degree | −α, +α, Orthogonal | ||
| dx | 64.2 | 30.2 | 64.2 |
| dy | 10.1 | 10.7 | 9.1 |
| dz | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Axis Direction | 3D Interframe Displacement Estimation | 3D Strain Estimation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Window Size ± Search Range (Beamforming Grid Samples) | Regularization (Displacement Grid Samples) | Least Square Window Sizes (Ax, Lat, Ele) | |||||
| Sample Iteration | Sub-Sample Iteration | Median Filtering (Kernel Sample Size Ax, Lat, Ele) | |||||
| Inter–Frame | Tracked | Ax | Lat | Ele | |||
| Axial | 81 ± 15 | 33 ± 5 | 7, 11, 3 | 7, 11, 3 | 17, 7, 3 | 5, 25,3 | 5, 7, 15 |
| Lateral | 13 ± 4 | 7 ± 4 | 7, 11, 3 | 7, 11, 3 | 17, 7, 3 | 5, 25, 3 | 5, 7, 15 |
| Elevational | 3 ± 0 | 3 ± 2 | 28, 20, 5 | 7, 11, 3 | 33, 11, 7 | 9, 49, 7 | 9, 11, 61 |
| Strain (%) at Max. Systolic Pressure t = 0.30 s | Residual Strain (%) t = 0.96 s | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probe | Reference | Compounding | Zero-Degree | Reference | Compounding | Zero-Degree | |
| Vertical | A | −4.2–9.7 | −4.3–9.8 | −4.9–9.7 | −1.1–2.3 | −1.1–2.3 | −1.2–2.3 |
| B | −5.3–11.8 | −7.6–14.6 | −16.0–23.0 | −0.7–3.2 | −2.2–5.1 | −10.5–9.1 | |
| Horizontal | A | −3.9–7.5 | −7.0–13.0 | −19.7–23.6 | −0.5–2.8 | −3.1–3.5 | −13.1–0.4 |
| B | −3.2–6.8 | −3.2–6.7 | −3.2–6.7 | −0.6–1.8 | −0.6–1.9 | −0.6–1.8 | |
| Longitudinal | A | −3.8–4.7 | −4.3–5.0 | −3.9–4.7 | −5.6–10.7 | −6.0–11.0 | −5.6–10.7 |
| B | −3.4–5.5 | −2.9–6.0 | −3.4–5.5 | −6.1–9.9 | −5.2–9.8 | −6.1–9.9 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fekkes, S.; Saris, A.E.C.M.; Menssen, J.; Nillesen, M.M.; Hansen, H.H.G.; De Korte, C.L. Multi-Plane Ultrafast Compound 3D Strain Imaging: Experimental Validation in a Carotid Bifurcation Phantom. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8040637
Fekkes S, Saris AECM, Menssen J, Nillesen MM, Hansen HHG, De Korte CL. Multi-Plane Ultrafast Compound 3D Strain Imaging: Experimental Validation in a Carotid Bifurcation Phantom. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(4):637. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8040637
Chicago/Turabian StyleFekkes, Stein, Anne E. C. M. Saris, Jan Menssen, Maartje M. Nillesen, Hendrik H. G. Hansen, and Chris L. De Korte. 2018. "Multi-Plane Ultrafast Compound 3D Strain Imaging: Experimental Validation in a Carotid Bifurcation Phantom" Applied Sciences 8, no. 4: 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8040637
APA StyleFekkes, S., Saris, A. E. C. M., Menssen, J., Nillesen, M. M., Hansen, H. H. G., & De Korte, C. L. (2018). Multi-Plane Ultrafast Compound 3D Strain Imaging: Experimental Validation in a Carotid Bifurcation Phantom. Applied Sciences, 8(4), 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8040637





