Abstract
Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) are an environmentally friendly technology that can recover electricity directly from several wastes at ambient temperatures. This work explores the use of mineral oil refinery wastewater as feedstock in single-chamber air-cathode MFC devices. A polymer inclusion membrane based on the ionic liquid methyltrioctylammonium chloride, [MTOA+][Cl−], at a concentration of 70% w/w, was used as separator, showing a good efficiency in power production and chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal. The power and the chemical oxygen demand removal reached values of 45 mW/m3 and over 80%, respectively. The evolution of other parameters of the wastewater including nitrites, phosphates and sulphates were also studied. Kjeldahl nitrogen and sulphates were significantly reduced during MFC operation. The results show that mineral oil refinery wastewater can be used as feedstock in air breathing cathode-microbial fuel cells based on polymer ionic liquid inclusion membranes. This configuration could represent a good alternative for wastewater depuration while producing energy during the process.
1. Introduction
Water availability is a global issue requiring pressing solutions. Currently, around 40% of the world population is facing a scarcity of clean water, and this situation is likely to worsen in the next decades. The lack of access to safe water and sanitation causes serious health problems and has large unquantified impacts on economic productivity. Moreover, over 80% of the world’s wastewater is discharged into the environment without any treatment, damaging ecosystems and triggering the spread of communicable diseases [1]. Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) are a promising technology that could help to tackle this problem. MFCs are systems in which organic matter is oxidized by microbes under anaerobic conditions in the anodic compartment. Protons and electrons are released due to the oxidation process. While electrons are transferred to the cathode by an external circuit, protons travel from the anode to the cathode typically through a separator. At the cathode, electrons and protons combine to form water according to the schematic representation showed in Figure 1. Electricity can be produced from a single substrate (e.g., acetate, lactate or glucose), but what is truly innovative is that electricity can also be generated from complex substrates such as domestic sewage and industrial wastewater [2,3]. When these complex substrates are used to feed MFCs, this technology offers the two-fold benefit of energy production and wastewater treatment.
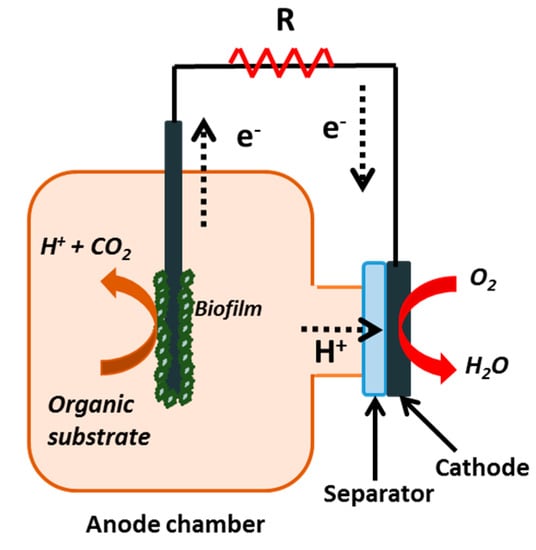
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of a microbial fuel cell (MFC).
Compared with other available options for wastewater treatment, MFCs offer prominent advantages. These include direct electricity generation, energy savings due to the lack of aeration sources and low sludge production compared with conventional wastewater treatment with no downstream processes. Regarding this, nearly half of the cost of current standard wastewater processes is due to the energy input, especially for the needs of aeration and the treatment of the sludge generated during the treatment process [4]. Other benefits are operational advantages such as the possibility of using many types of wastes, low operational costs and resistance to environmental stress [5,6].
MFCs usually include a separator between the anode and the cathode that prevents short circuits due electrode separation and improves Coulombic efficiency (CE) since it hinders the diffusion of oxygen to the anode [7,8]. Very recently, polymer inclusion membranes based on ionic liquids have shown to be efficient separators in MFCs acting as proton exchange membranes. These membranes showed a good performance when compared with conventional materials such as Nafion and their cost are lower compared with this commercial membrane [9,10,11]. Ionic liquids (ILs) are organic salts that remain liquid near room temperature. They consist of an organic cation such as imidazolium, pyridinium, pyrrolidinium, phosphonium, ammonium, and a polyatomic inorganic anion or organic anion such us tetrafluoroborate, hexafluorophosphate, chloride, trifluoromethylsulfonate, and bis[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]imide). Some of their advantages include task-specific functionality since these compounds can be tailored by selecting the proper cations and anions in their structure for a given purpose. They generally have high viscosities, negligible vapor pressure and non-flammability in addition to good electrochemical features such as high ion conductivity and wide electrochemical stability window [12]. Due to these properties, it can be adventurous to use ionic liquid-based separators for wastewater treatment in MFCs. However, the study of the performance of MFC devices including such types of membranes is scarce in the literature.
Several types of complex substrates have been investigated for bioenergy generation in these devices, including domestic, food processing and swine wastewater [13,14,15,16,17,18]. Brewery wastewater of high organic matter loading has been a preferable option for feeding MFCs. Other carbon sources such as starch-processing wastewater have shown to be suitable for microbial consortium enrichment. More recently, effluents containing azo dyes from dye-manufacturing textile industries have been treated in MFC devices, proving their removal capacity of xenobiotic compounds. Thus, the use of MFC technology could offer a great potential for wastewater treatment before discharge [19,20,21].
In this work, the application of MFC technology specifically for the treatment of wastewater from industries involved in the production of white mineral oils and petroleum sulfonates is evaluated. This type of wastewater has not been previously studied in these devices. For this purpose, single-chamber MFCs using polymer membranes based on the ionic liquid methyltrioctylammonium chloride, [MTOA+][Cl−], were used. The chemical and electrical performance of the MFCs fed with industrial oil wastewater were analyzed. Wastewater physico-chemical parameters such as chemical oxygen demand (COD), total suspended solids (TSS) and concentration of nitrite, orthophosphate and ammonium sulphate were analyzed. The ionic liquid-based polymer membranes employed were characterized with a scanning electron microscopy with energy dispersive X-ray analysis (SEM-EDX).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation and SEM-EDX Characterization of Polymer Ionic Liquid Inclusion Membrane
The ionic liquid methyltrioctylammonium chloride, [MTOA+][Cl−], (purity > 97%), poly(vinylchloride) (PVC) of high molecular weight and tetrahydrofuran (THF) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich-Fluka Chemical Co. (Madrid, Spain)
The polymer ionic liquid inclusion membranes (PILIMs) used as separators in MFCs were prepared by casting method dissolving 210 mg of [MTOA+][Cl−] and 70 mg of PVC in 3 mL of THF according to a previous reported method [9].
A Hitachi S-3500N scanning electron microscope (Berkshire, UK) coupled to a Bruker AXS X-ray analyser (Karlsruhe, Germany) was used for energy dispersive X-ray analysis in order to study the morphology, chemical composition and distribution of the chemical elements present in the membranes. The PILIMs were characterized immediately after preparation (fresh membrane) and after being used in microbial fuel cells.
2.2. Microbial Fuel Cell Set-Up
Experiments were performed in air-cathode single-chamber MFCs. They consisted of 250 mL glass reactors using graphite granules and a graphite bar as anode and carbon cloth sprayed with platinum (0.5 mg/cm2, Cimyt-Quimica, Barcelona, Spain) as described in other works of the research group [11]. The anode chamber was fed with 160 mL of wastewater. MFCs were operated during 9 days (217 h) at a fixed temperature of 25 °C with an external resistance load of 1 KΩ. Two replicates of each reactor were set-up. The values reported are average values.
Two other types of reactors were also added to the experimentation, which were named the baseline (containing only carbon granules as a biofilm support with 100 mL of graphite granules and 160 mL of wastewater without an external connection) and control (only with 160 mL of wastewater; no graphitic components). They served to compare the outputs from MFC operational conditions to those from an anaerobic digester with biofilm and to those from an anaerobic reactor with suspended microflora, respectively.
2.3. Substrate
The substrate used for the experiments was obtained from a local industry dedicated to the production of white mineral oils and petroleum sulfonates located in the southeast of Spain. Before and after the experiments, an exhaustive characterization of the wastewater was performed. The initial values of the physicochemical parameters of the wastewater monitored in this work are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Comparison of physicochemical parameters before and after water treatment in microbial fuel cells (MFCs), baseline and control.
2.4. Wastewater Characterization
Sampling was done by removing a 5 mL aliquot with a plastic syringe from glass reactors. The sample was centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 5 min and then subjected to filtration (standard membrane filter of 0.45 microns). In addition, 3 mL of the filtered aliquot was employed for COD analysis according to the French Standarization Association (AFNOR) method T90-101 with a Spectroquant Nova 30 spectrophotometer (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany). Soluble COD removal or CODR is defined as the ratio between the total COD consumed in the process (difference between initial COD value or [COD]0 and the COD value at a given time or [COD]):
Total suspended solids, hardness, alkalinity and ion analysis were performed using AFNOR standard methods [22,23].
2.5. Polarization Method
Polarization tests were performed with a variable resistor box in the range from 11 MΩ to 1 Ω. For each case, voltage was taken once the cell reached the pseudo-steady state under the correspondent resistor value (typically after 1 min). For each external resistance load, current density was determined as I = E/Rext and the power density alternatively as P = E2/Rext. Both values are normalized to anode capacity (wastewater volume used to feed the MFCs). Polarization and power curves depict voltage and power output, respectively, versus current density measured in polarization tests.
2.6. Coulombic Efficiency
Coulombic efficiency (YQ) is defined as the ratio between the number of coulombs transferred to the anode from the substrate and the theoretical maximum number of coulombs that could be produced if the entire substrate were available for current generation:
The number of total coulombs obtained is determined by integrating current versus time. The above equation can be rewritten in order to obtain the Coulombic efficiency in an MFC in batch mode as follows [24]:
where Mm is the molecular mass of oxygen (32 g/mol), i(t) is the rated current (A = C/s), F is the Faraday constant (96,485 C/mol of e−), ΔCOD is the variation of COD during the time t ([COD]0 − [COD]), b is the mols of electrons produced per mol of oxygen (b = 4) and V is the volume of liquid in the anode chamber (0.25 L).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Industrial Wastewater Treatment by Microbial Fuel Cells
The physicochemical parameters of the wastewater used for the MFC experiments, baseline and control, are shown in Table 1, including initial and final values, which are common for all operational conditions, and final values after 217 h (test time).
The wastewater analysis shows that the pH shifts from an initial value over 8 in the anode chamber to neutral values at the end time for all systems (MFCs, baseline and control). In MFC systems, the pH of the anodic chamber greatly influences the metabolic activity of microbes affecting the mechanism of proton and electron generation from electroactive bacteria. Since the final pH values are neutral, protons produced are not accumulated during time operation in the anodic chamber in MFCs but transferred through the ionic liquid membrane to the cathode at which they combine with oxygen. Accordingly, alkalinity also decreases in MFCs from 67.60 mg/L to 19.60 mg/L in the MFC anode chamber.
Another significant parameter for wastewater treatment is the evolution of the COD loading. As can be seen from Table 1, a high removal rate is achieved in the MFC system after nine days of operation. COD loading reduces from 1760 mg/L to 334 mg/L, which accounts for 81.0% in terms of COD removal. The digestion of the wastewater performed in the presence of graphite granules only (baseline) and the absence of graphitic components (control) for comparison purposes, offers removal rates of only 31.8% and 37.9%, respectively. These values show that the degradation of soluble organic matter is clearly promoted in MFC operation versus conventional anaerobic digestion. Regarding the levels of TSS, higher values of these parameters were found in MFC and baseline conditions in comparison with the control. The increase in this parameter for such conditions is related to the presence of graphite granules in the two first configurations, which would increase the level by adding solids from the graphite phase to the anode bulk solution.
Regarding the analysis of the ion species present in the wastewater used, different tendencies can be observed depending on the case. Nitrite, sulphate and ammonium show a decreasing tendency in all conditions, but generally more accentuated under MFC operation. Considering the complexity of the anode conditions in MFCs, it is likely that several mechanisms are involved for each ion species. In the absence of oxygen, nitrites and sulphates can act as electron donors and be employed as nutrients by bacteria. The higher decrease rates in MFC when compared with baseline and control conditions can be attributed to the growth of the biofilm, and the faster water oxidation rate as previously commented. Given that the initial concentration of sulphate is significantly high (263.50 mg/L), it is worth noting that the reduction of this ion species in the MFC systems reaches 51.23%. The concentration of ammonium also decreases in comparison with the initial values. Ammonium is another nutrient used by microorganisms. This reduction is also higher in MFCs than in the baseline and control. This trend is also observable for Kheldahl nitrogen, which is reduced by a 50% in MFCs, showing higher removal rates compared with the rest of the conditions.
Regarding the concentration of total phosphates, it can be observed that there is a significant increase in their concentrations in comparison with their initial values (0.51 mg/L) in those systems in which graphite are present (MFC and baseline). The final values for these two parameters are in the interval 14.41–19.27 mg/L. In previous works, it has also been also reported that these ion species can be released to the medium from the class of graphite used in this work due to its composition [25].
In the case of chloride, this parameter clearly increases in the case of MFCs. This is caused by the release to the media of a small amount of ionic liquid that forms the membrane as discussed in the following section. Finally, the hardness remained practically unchanged for baseline and control, but increased by 22% in the MFCs.
3.2. Ionic Liquid-Based Membranes Applied to Wastewater Treatment
As stated in the Materials and Methods section, a polymer inclusion membrane based on the ionic liquid [MTOA+][Cl−] was employed as separator for the treatment of white oil refinery industry wastewater in the MFC system. The ionic liquid membrane was characterized before (fresh membrane) and after MFC operation by scanning electron microscope with the purpose of obtaining information about morphology, topography and chemical composition. Figure 2A,B show the SEM micrographs of the [MTOA+][Cl−] membrane before and after use in MFCs, respectively. The fresh membrane offers a homogenous appearance with no porosity observable. The surface of the membrane is virtually smooth and clean. Figure 2B shows that, after being employed as a separator in the MFC system, the membrane becomes rougher due to the formation of deposits over the surface that has been in contact with the oil industry wastewater.
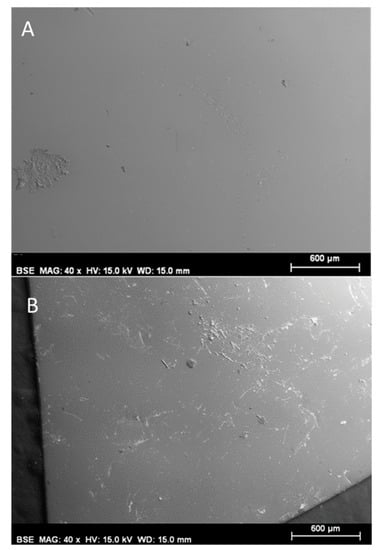
Figure 2.
Scanning electron micrograph of the membrane with [MTOA+][Cl−] ionic liquid after being used in MFC with white oil refinery industry wastewater.
Figure 3 and Table 2 (EDX normalize %wt) includes the EDX spectrum and the EDX analysis results (in %wt) of the ionic liquid membrane before and after MFC operation. In Figure 3, a reduction of the Cl content of the membrane is observed, which, according to the EDX analysis, corresponds to a percentage of 3.28%. Given that the Cl content of the membrane stems from the ionic liquid composition and PVC (polymer matrix), it can be concluded that a certain amount of the ionic liquid has been released from the membrane to the medium, since PVC is recognized as an insoluble polymer. The same applies to the content of the nitrogen, although, in this case, the reduction percentage is higher, since nitrogen is not present in the polymer but only in the ionic liquid. The stability of polymer ionic liquid membranes based on [MTOA+][Cl−] in contact with water has been previously studied [9], showing that they are capable of retaining an important amount of ionic liquid after long-time water contact. As noted before, the membrane showed that some deposits were formed over the membrane surface (Figure 2). After MFC operation, new chemical elements (S, Ca, Fe, Zn) were found absorbed in the membranes, which would come from the white oil refinery wastewater used as fuel. In addition, higher concentrations of oxygen and carbon concentration were found in the used membranes compared with their concentration in the fresh separator. Both findings could be related to the deposition of CO2 generated during the microbial activity on the membrane.
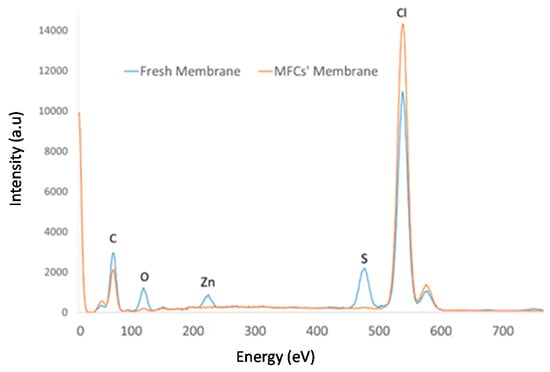
Figure 3.
Energy dispersive X-ray (EDX)spectra of the [MTOA+][Cl−] (70% w/w) membrane, fresh and after operation in MFCs with white oil refinery wastewater.

Table 2.
EDX spectrum data of membranes before and after use in MFCs in contact with oil industry wastewater.
3.3. Electric Performance
Figure 4 displays the voltage response of the MFC system, showing that the pseudo-stationary sate is reached after 50 h of operation. Typically, the breaking of the long organic chains and the formation of biofilm take place in the first hours of operation (24 h). Beyond this point, an increase in voltage output is observed and a further stabilization of the system is appreciated after 50 h. Figure 5 illustrates the results of the polarization tests performed after 72 h of operation. As can be seen, the maximum level of power density is 45 (mW/m3) at a current density of around 500 mA/m3, corresponding to an internal resistance of 0.98 kΩ. This level of power could be increased by mixing wastewater with other microbial promoting substrates [26,27], although this proves that direct white oil refinery wastewater with natural occurring bacteria without previous treatment (direct use of wastewater effluent) can be used for energy production. Finally, as regards the evolution of the Coulombic efficiency for the MFC system, after operation, the Coulombic efficiency of the system reaches only 1.5%. This low level of Coulombic efficiency can be attained in MFCs fed with wastewater that are not strengthened by the addition of other microbial cultures specifically selected for electricity production.
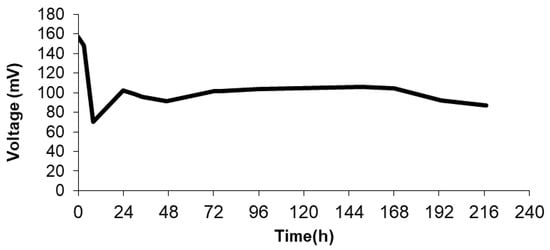
Figure 4.
Voltage output in MFC using polymer inclusion membrane based on 70% w/w of [MTOA+][Cl−] using white oil refinery wastewater as feedstock.
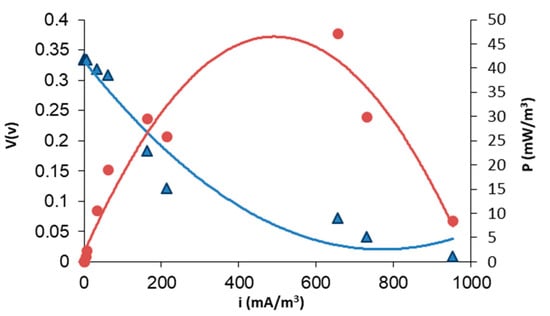
Figure 5.
Polarization test of MFCs using white oil industry wastewater as feedstock and a polymer inclusion membrane based on [MTOA+][Cl−]. Polarization curve for MFCs (V vs. I). Power output curve (P vs. I). Calculations are based on anode liquid volume.
4. Conclusions
The present work studies the use of white oil industry wastewater as direct feedstock in MFCs. MFC systems incorporated an ionic liquid membrane based on methyltrioctylammonium chloride, [MTOA+][Cl−], as an effective separator for the treatment of white oil refinery wastewater. A high removal of COD of 80% was achieved after nine days of operation, with 105 mV as voltage output and 45 mW/m3 of power density, respectively. A reduction of other species such as Kjeldahl nitrogen, nitrite, sulfate and ammonium was also found, with a high removal percentage of over 50% in the case of sulfate. Moreover, the analysis of the ionic liquid membrane after use showed a good behavior of this type of separator in contact with the substrate in terms of stability, indicating that MFCs containing ionic liquid based separators are suitable for bioenergy production and simultaneous treatment of white oil refinery wastewater. These preliminary results could be for the application of MFC technology for the treatment of wastewater effluents in white oil refinery industries. Future works may be comprised of several strategies for strengthening electrical performance by mixing different microbial and substrate sources when using white oil refinery industry wastewater as feedstock.
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (MICINN) and by the FEDER (Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional), Ref. CICYT ENE2011-25188 and by the SENECA Foundation 18975/JLI/2013 grants.
Author Contributions
Francisco José Hernández Fernández, Antonia Pérez de los Ríos, Carlos Godínez and Luis Javier Lozano Blanco conceived, designed and supervised the experiments. Hasna Addi and Francisco Mateo-Ramírez performed the experiments and contributed to the preparation of the paper; Víctor Manuel Ortiz-Martínez and María José Salar-García contributed to the preparation of the paper and analyzed the data; El Mostapha Lotfi and Mohammed El Mahi supervised the experiments and contributed to the preparation of the paper and data analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dannys, E.; Green, T.; Wettlaufer, A.; Mouli, C.; Madhurnathakam, R.; Elkamel, A. Wastewater Treatment with Microbial Fuel Cells: A Design and Feasibility Study for Scale-up in Microbreweries. J. Bioprocess Biotech. 2016, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.V.; Velvizhi, G.; Modestra, J.A.; Srikanth, S. Microbial fuel cell: Critical factors regulating bio-catalyzed electrochemical process and recent advancements. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 40, 779–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio, Y.; Fernández-Marchante, C.M.; Lobato, J.; Cañizares, P.; Rodrigo, M.A. Influence of the fuel and dosage on the performance of double-compartment microbial fuel cells. Water Res. 2016, 99, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassallo, P.; Paoli, C.; Fabiano, M. Energy required for the complete treatment of municipal wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gude, V.G. Wastewater treatment in microbial fuel cells—An overview. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 122, 287–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaey, K.; Verstraete, W. Microbial fuel cells: Novel biotechnology for energy generation. Trends Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prestigiacomo, C.; Fernandez-Marchante, C.M.; Fernández-Morales, F.J.; Cañizares, P.; Scialdone, O.; Rodrigo, M.A. New prototypes for the isolation of the anodic chambers in microbial fuel cells. Fuel 2016, 181, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio, Y.; Fernandez-Marchante, C.M.; Lobato, J.; Cañizares, P.; Rodrigo, M.A. Influence of the ion-exchange membrane on the performance of double-compartment microbial fuel cells. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 808, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Fernández, F.J.; de los Ríos, A.P.; Mateo-Ramírez, F.; Juarez, M.D.; Lozano-Blanco, L.J.; Godínez, C. New application of polymer inclusion membrane based on ionic liquids as proton exchange membrane in microbial fuel cell. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 160, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koók, L.; Nemestóthy, N.; Bakonyi, P.; Zhen, G.; Kumar, G.; Lu, X.; Su, L.; Saratale, G.D.; Kim, S.H.; Gubicza, L. Performance evaluation of microbial electrochemical systems operated with Nafion and supported ionic liquid membranes. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salar-García, M.J.; Ortiz-Martínez, V.M.; de los Ríos, A.P.; Hernández-Fernández, F.J. A method based on impedance spectroscopy for predicting the behavior of novel ionic liquid-polymer inclusion membranes in microbial fuel cells. Energy 2015, 89, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, T.L.; Drummond, C.J. Protic Ionic Liquids: Properties and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 206–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, Y.; Logan, B.E. Effectiveness of domestic wastewater treatment using microbial fuel cells at ambient and mesophilic temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, B.; Kim, J.; Oh, A.S.; Regan, J.M.; Logan, B.E. Electricity generation from swine wastewater using microbial fuel cells. Water Res. 2005, 39, 4961–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansoorian, H.J.; Mahvi, A.H.; Jafari, A.J.; Amin, M.M.; Rajabizadeh, A.; Khanjani, N. Bioelectricity generation using two chamber microbial fuel cell treating wastewater from food processing. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2013, 10, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asensio, Y.; Fernandez-Marchante, C.; Villaseñor, J.; Lobato, J.; Cañizares, P.; Rodrigo, M.A. Algal biomass as fuel for stacked-MFCs for profitable, sustainable and carbon neutral bioenergy generation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschitor, A.; Soreanu, G.; Fernandez-Marchante, C.M.; Lobato, J.; Canizares, P.; Cretescu, I.; Rodrigo, M.A. Bioelectro-Claus processes using MFC technology: Influence of co-substrate. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 189, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penteado, E.D.; Fernandez-Marchante, C.M.; Zaiat, M.; Cañizares, P.; Gonzalez, E.R.; Rodrigo, M.A.R. Energy recovery from winery wastewater using a dual chamber microbial fuel cell. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 91, 1802–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angosto, J.M.; Fernández-López, J.A.; Godínez, C. Brewery and liquid manure wastewaters as potential feedstocks for microbial fuel cells: A performance study. Environ. Technol. 2015, 36, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansoorian, H.J.; Mahvi, A.H.; Jafaric, A.J.; Khanjanid, N. Evaluation of dairy industry wastewater treatment and simultaneous bioelectricity generation in a catalyst-less and mediator-less membrane microbial fuel cell. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2016, 20, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, D.; Bogaert, G.V.; Diels, L.; Vanbroekhoven, K. A review of the substrates used in microbial fuel cells (MFCs) for sustainable energy production. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodier, J. L’Analyse de l’Eau:Eaux Naturelles, Eaux Résiduaires, Eau de Mer, 7th ed.; Dunod Edition: Paris, France, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Qualité de l'eau-Détermination de la Demande Chimique en Oxygène (DCO); NF T90-101; AFNOR: Paris, France, 2001.
- Logan, B.E. Microbial Fuel Cells; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mateo-Ramírez, F.; Hasna, A.; Hernández-Fernández, F.J.; Godínez, C.; de los Ríos, A.P.; Lotfi, E.M.; Mahi, M.E.; Lozano Blanco, L.J. Air breathing cathode-microbial fuel cell with separator based on ionic liquid applied to slaughterhouse wastewater treatment and bio-energy production. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 92, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köroğlu, E.O.; Özkaya, B.; Çetinkaya, A.Y. Microbial fuel cells for energy recovery from waste. Int. J. Energy Sci. 2014, 4, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirik, K. Optimization of bioelectricity generation in fed-batch microbial fuel cell: Effect of electrode material, initial substrate concentration, and cycle time applied. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 173, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).