Abstract
Since physical parameters are much more sensitive than modal parameters, structural parameter identification with an extended Kalman filter (EKF) has received extensive attention in structural health monitoring for civil engineering structures. In this paper, EKF-based parameter identification technique is studied with numerical and experimental approaches. A four-degree-of-freedom (4-DOF) system is simulated and analyzed as an example. Different integration methods are examined and their influence to the final identification results of the structural stiffness and damping is also studied. Furthermore, the effect of different kinds of noise is studied as well. Identification results show that the convergence speed and estimation accuracy under Gaussian noises are better than those under non-Gaussian noises. Finally, experiments with a five-story steel frame are conducted to verify the damage identification capacity of the EKF. The results show that stiffness with different damage degrees can be identified effectively, which indicates that the EKF is capable of being applied for damage identification and health monitoring for civil engineering structures.
1. Introduction
Structural parameter identification is one of the most important aspects of the structural health monitoring and has received considerable attention. As a result, various analysis methods for structural parameter identification have been proposed and significant progress has been made over the past few decades. Damage detection techniques can be mainly classified as frequency-domain-based and time-domain-based methods. In particular, the time-domain analyses have been used extensively, such as the least-squares method [1,2], Monte Carlo method [3,4,5], and filtering methods [6,7,8]. Besides, the methods of wavelet analysis [9,10,11] and Hilbert–Huang transform [12,13,14], in which the vibration signals are decomposed into the frequency/time-domain signals, have also received much attention.
The well-known Kalman filter (KF) [15,16] has also been applied to the system identification. Based on the KF, Jazwinski [17] has promoted and studied the extended Kalman filter (EKF), which extended the KF theory into the nonlinear field, with great achievements acquired. Afterwards, Yun and Shinozuka [18] used the EKF for identification of the parameters involved in multi-degree-of-freedom (multi-DOF) nonlinear structural dynamic systems under various output noise conditions. Corigliano and Mariani [19] analyzed the single-DOF and multi-DOF dynamic systems based on EKF to detect the possible sources of the inaccuracy when the structures suffered the strength degradation. In recent years, several approaches to EKF-based system identification have been made for damage detection in the time domain which shows the good accuracy and arithmetic robustness. Best and Bogdanski [20] presented a new method working iteratively in the time domain using an EKF and it can also be used as a black box tool for model order reduction. González [21] developed an effective methodology based on the EKF to predict the beam tip displacement under Gaussian noises. Sen and Bhattacharya [22] employed a constrained version of the dual EKF technique, and its robustness and efficacy was verified by numerical analysis of a six-story shear frame and a three-dimensional space truss. Zhang [23] proposed a new method based on an EKF with l1-norm regularization via free vibration responses, which shows good robustness and excellent accuracy of damage identification with the unknown initial structural state. Jin [24] presented a novel real-time structural damage detection method by integrating an EKF and dynamic statistical process control, with which high detection accuracy was provided.
Generally speaking, the EKF is particularly suitable for real-time damage identification. However, inappropriate integration methods and integration steps will have negative effect on identified results, especially when it is applied to practical structures. On the other hand, observations are usually contaminated with all kinds of noises affecting the convergence of the algorithm and accuracy of the target structural parameters as well, which also should be investigated in depth. In this paper, the EKF will be studied focusing on identification of both stiffness and damping of multi-DOF systems, which are the two most important parameters of structural dynamic systems. Numerical simulation is firstly carried out to choose the suitable integration method and integration step. After that, the identification accuracies under different levels of both Gaussian and non-Gaussian noises are analyzed and compared. To verify the capability of EKF to identify the structural parameters as well as the damages for real structures, experiments on a five-story steel frame structure are further conducted.
2. EKF-Based Parameters Identification
For a linear n-DOF dynamic system, the motion equation can be written as:
where M, C, and K are the mass, damping, and stiffness matrices, respectively; vectors , and denote displacement, velocity, and acceleration response, respectively; F(t) is the external force vector.
Its state space equation can be expressed as:
where , , and , where 0n and In are an n-order zero matrix and an n-order unit matrix, respectively. The matrix exponential function of e−At is introduced to solve Equation (2).
Let , which is the state transition matrix. The system state at any time t can be obtained as:
Equation (3) is a continuous state equation. However, the continuous expression of external excitation time history function is often very difficult to be obtained, and discretization of the equation is therefore required. The discrete equation can be written as:
The uniform sampling is usually assumed, and the external excitation can be regarded as linear within the small interval , and can be calculated by:
where .
Let . Equation (4) can be finally expressed as:
where Xk is the system state at time k, and Fk and Fk+1 are the sampled values at the time k and k + 1, respectively. Thus, the discrete-time state equation of linear dynamic system is then obtained.
Kalman [15] proposed the traditional KF in 1960, which is an optimal linear recursive estimator designed for linear time-varying dynamic systems. By using the linearized models, EKF expands its identification ability to nonlinear systems. In order to identify the parameters of the deterministic dynamical system by the EKF, the structural parameters can be considered as the state variables. Thus, the corresponding discrete formulation of the parameters identification problem in the EKF can be expressed as:
where Xk+1 and Z are the state vector and the observation vector, respectively; wk is the process noise represented by zero-mean white Gaussian noises with a covariance matrix Q, and v is the observation noise represented by zero-mean white Gaussian noises with a covariance matrix R, and the function h(X) is the theoretical solution of structural response at the measure point x.
The EKF algorithm is realized using a sequence of equations which generate a time-varying estimate of state error covariance and Kalman gain. The procedure of the EKF algorithm can be computed as:
State prediction:
Error covariance prediction:
Gain matrix:
State filtering:
Error covariance update:
where Q is the system noise, R is the observed noise, , , and .
Equation (12) combines Euler integration of the system using the time step T with state and parameter adaptation driven by the output error. Due to the Euler integration, T must be very small so as to ensure the filter accuracy.
3. Numerical Simulations
3.1. Numerical Model
A four-DOF linear system is considered in this paper as shown in Figure 1. The mass, stiffness and damping of each story are 200 kg, 7200 N/m, and 120 N·s/m, respectively. Assuming the structure is excited by the Hanshin earthquake wave, which has the peak ground acceleration (PGA) of 0.5 g as shown in Figure 2, the motion equation of the structure can be written as:
where M, C, and K are the mass, damping, and stiffness matrices, respectively, and vectors x, and denote the displacement, velocity, and acceleration response, respectively; and are the earthquake acceleration and four-order unit column vector, respectively; is the equivalent external force vector caused by the base movement. The dynamic response can be calculated using Newmark-β method (γ is 1/2, β is 1/6, and the time step is 0.02 s).
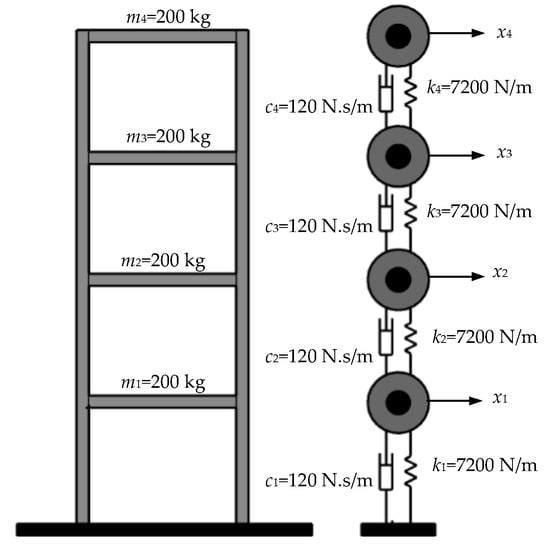
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the four-degree-of-freedom system.
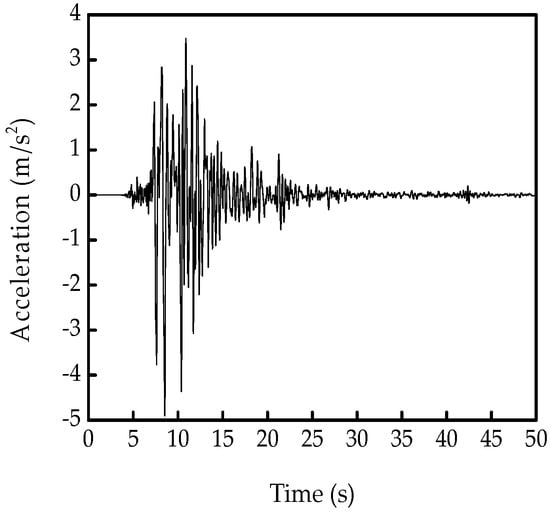
Figure 2.
The Hanshin earthquake wave.
In this paper, the observation vector is the absolute acceleration of structure which can be expressed as:
The stiffness ki (i = 1, 2, 3, 4) and damping ci (i = 1, 2, 3, 4) are the system parameters to be identified. Therefore, the augmented state vector can be expressed as:
where .
Then, the system equation and the observation equation can be written as:
In the actual operation, the system equation has the system noise, and the observation equation also has the observation noise (observation error). Therefore, the covariance matrix of the system noise and the observed noise are assumed as follows: , and R = I4. Moreover, the initial state vector and the covariance matrix are given. With this, the stiffness and damping parameters of the four-DOF system can be identified by the EKF algorithm.
3.2. Parameter Identification with Different Integration Methods
In EKF, realizing the state prediction (Equation (9)) is a critical issue for accurately identifying the structural parameters, especially the damping. In this paper, three integral methods, such as the rectangular integration, the trapezoidal integration and the fourth-order Runge–Kutta integration, are introduced to identify the stiffness and damping of the structure. Their corresponding estimation results will then be compared and discussed.
The f(X, F) can be regarded as an invariant constant if the is small enough. Then, the rectangular integral can be introduced to the state prediction, and Equation (9) can be approximated as:
A trapezoidal approach to approximating each area can be used to improve the accuracy of the approximate value, known as the improved Euler integration or trapezoidal integration. The f(X, F) can be approximately regarded as linear in the interval , and Equation (9) can be expressed by:
The nth-order Runge–Kutta integration can approximately calculate n values in each step. Actually, the rectangular integration and the trapezoidal integration can be also regarded as the first-order and second-order Runge–Kutta integration, respectively. Here, the fourth-order Runge–Kutta integration was introduced to solve the state prediction problem, and can be expressed as:
where , and the linearity is also assumed in the interval .
3.2.1. Stiffness Identification
Identification results of stiffness and damping of the four-DOF system were used to compare the effect of the three integration methods. During such an analysis, the integration time step is adopted with a small value of 0.02 s. To make things easier, the influence of noise is not considered here. The estimation results of the stiffness by the three integration methods are shown in Figure 3. Obviously, the identification results by the three integration methods are in good agreement with the actual value, and the estimation precisions are all higher than 98%.
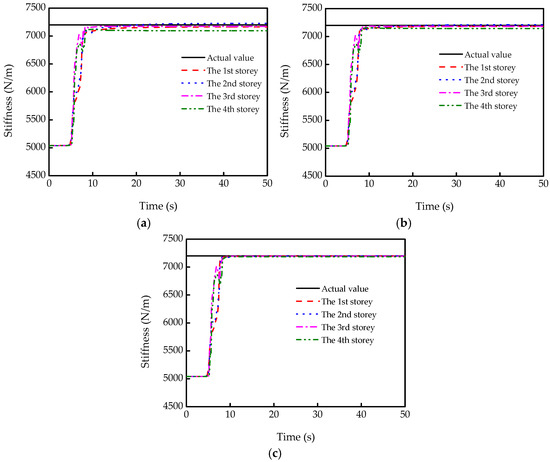
Figure 3.
Stiffness estimation by three integration methods: (a) rectangular integration; (b) trapezoidal integration; (c) fourth-order Runge–Kutta integration.
Moreover, the effect of time step on the identification results of the stiffness by the three integration methods was also discussed, in which the 2nd story was selected as the analyzing target. From Figure 4, it can be found the relative errors of stiffness estimates are very small, and even the simple rectangular integral can achieve good results. Nevertheless, the error slightly increases with the increased time step, especially when the time step is larger than 0.005 s.
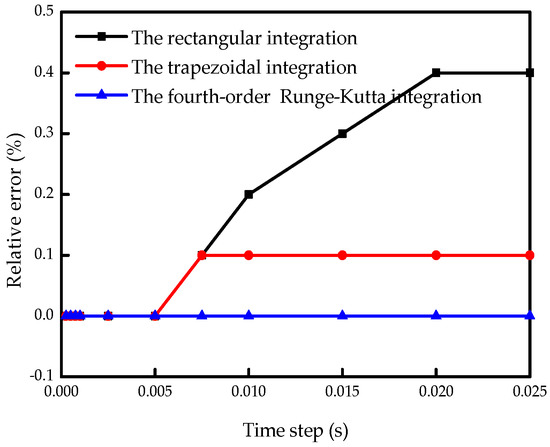
Figure 4.
Relative stiffness errors by three integration methods.
3.2.2. Damping Identification
Although the performance of the three integration methods is satisfactory for the stiffness estimation, the damping of multi-DOF system is often difficult to be identified. Poor integration methods often make the identified damping results far away from the actual values. From Figure 5, it can be seen that the rectangular integration and the trapezoidal integration perform poorly even when the time step is set to be as small as 0.005 s. Relative damping errors with the rectangular integration and trapezoidal integration reach as high as 30% and 15.1%, respectively. Still, it should also be noted that the trapezoidal integration algorithm is better than the rectangular integration algorithm for estimating the damping. Obviously, the fourth-order Runge–Kutta integration estimates the damping perfectly, which almost converges to the actual damping value.
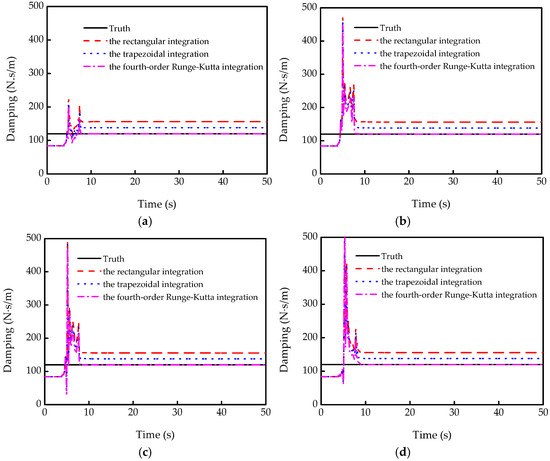
Figure 5.
Damping estimation by three integration methods: (a) the 1st story; (b) the 2nd story; (c) the 3rd story; (d) the 4th story.
The relative errors of the damping with the three integration methods were compared and are shown in Figure 6. It can be clearly found that the time step is very sensitive for the rectangular integration and the trapezoidal integration to identify the damping. Good results cannot be achieved until the time step reaches 0.001 s. However, the time step has little effect on the Runge–Kutta integration; good and stable results can be obtained although the time step is 0.025 s. By comparison, the fourth-order Runge–Kutta integration proves to be a good choice in such applications rather than the rectangular integration and the trapezoidal integration.
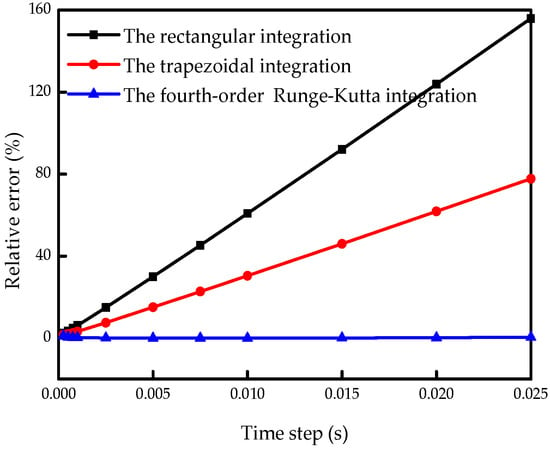
Figure 6.
Relative damping errors by three integration methods.
3.3. Parameter Identification under Gaussian and Non-Gaussian Noises
Simulation models with Gaussian noises dominate the research field of structural parameter identification. Normally, it is assumed that the noise has a Gaussian distribution, and its rationality can be proved by the central limit theorem. However, considering the real structures are often subjected to the complex environment, it contains more or less non-Gaussian noise actually. In the case when the non-Gaussian noise is prominent, the system tends to be unsuitable if the Gaussian hypothesis is still made. Therefore, it is of great theoretical and practical significance to study the structural parameter estimation under non-Gaussian noises.
The distributions of Gaussian and non-Gaussian noises are shown in Figure 7. The noise is added to the absolute acceleration to simulate the observed acceleration. When the noise has a Gaussian distribution, the observed acceleration is:
where a is the Gaussian noise level, is the root mean square value of the absolute acceleration, and random1 is the standard normal distribution.
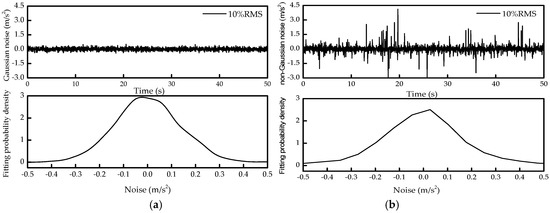
Figure 7.
The distribution curves of Gaussian and non-Gaussian noises: (a) 10% root mean square RMS for Gaussian noise; (b) 10% root mean square for non-Gaussian noise.
The observed acceleration with the additive non-Gaussian noise can be expressed as:
where random2 follows the t distribution with the DOF being 2 and the mean value being 1.
3.3.1. Parameter Identification under Gaussian Noises
In numerical analysis, based on the previous analysis and discussion, the fourth-order Runge–Kutta integration is selected, and the integration time step is adopted as 0.02 s. The identified results at different Gaussian noise levels (low noise level conditions) are shown in Figure 8. Notably, the identified curves of the stiffness and damping are almost in accordance with the actual values even when the noise level reaches 10%, which indicates that the parameters of the four-DOF system can be identified precisely by the EKF under Gaussian noises.
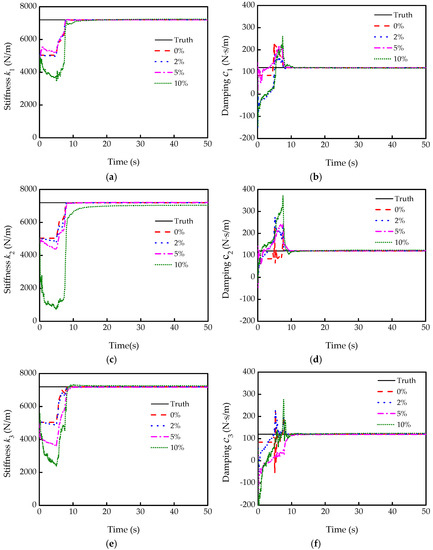
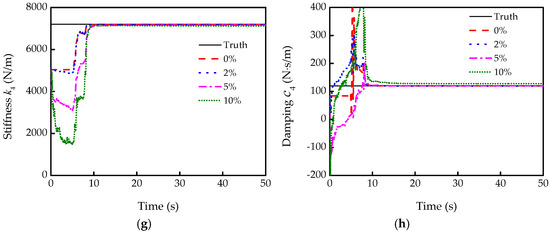
Figure 8.
Identification results under different Gaussian noise levels: (a,c,e,g) are the stiffness k1, k2, k3, and k4, respectively; (b,d,f,h) are the damping c1, c2, c3, and c4, respectively.
3.3.2. Parameter Identification under Non-Gaussian Noises
Parameter estimation at different non-Gaussian noise levels (low noise level conditions) is also conducted, as shown in Figure 9. The identified results of the stiffness and damping also can converge fairly fast. However, the identified damping has deviated from the true value when the non-Gaussian noise level reaches 10%. Furthermore, the comparison of the estimation results between the EKF with Gaussian and that with non-Gaussian is listed in Table 1. It can be clearly seen that the identification accuracies of the stiffness and damping with EKF are affected more by the non-Gaussian noise than that by the Gaussian noise. When the non-Gaussian noise level reaches 10%, the maximum estimation error of damping reaches 19.436%. Hence, the identified values by EKF may be inaccurate when subjected to a certain level of non-Gaussian noise.
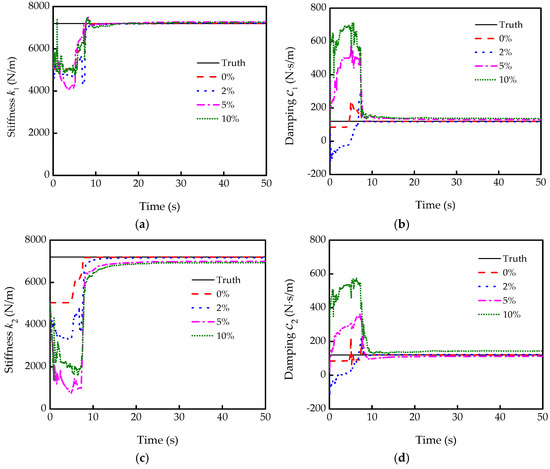
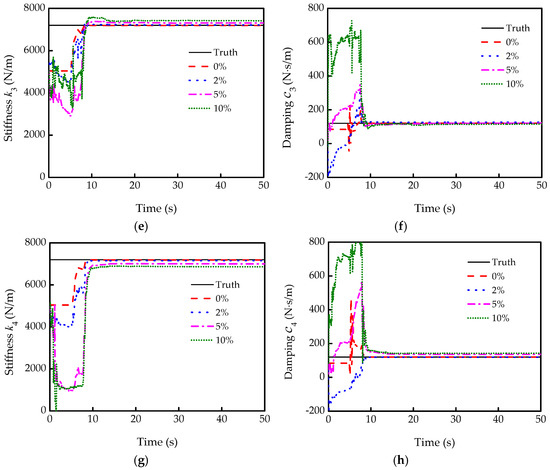
Figure 9.
Identification results under different levels of non-Gaussian noise: (a,c,e,g) are the stiffness k1, k2, k3, and k4, respectively; (b,d,f,h) are the damping c1, c2, c3, and c4, respectively.

Table 1.
Estimation errors of the identified results under Gaussian and non-Gaussian noise conditions.
4. Experiments
4.1. Excitation System
An excitation system was used for the experiment as shown in Figure 10. The generated specified vibration waveform signal by the computer was then put into the power amplifier. After that, the amplified signal actuated the vibration exciter to output the expected force which was used to excite the frame structure. Here, a vibration exciter, Modal Shop 2100E11, was adopted in the experiment. It is a lightweight electrodynamic modal exciter, and is capable of providing 440 N of peak force excitation in a small footprint weighing just 15 kg.

Figure 10.
Experiment setup.
4.2. Experimental Model and Damage Cases
The performance of the EKF for damage identification was verified by a five-story steel frame experiment. Three different damage cases were considered with the corresponding experimental models shown in Figure 11. Case 1 represents the intact case with no damage occurred. However, in cases 2 and 3, certain extents of damages were introduced to the 5th and 4th stories, respectively.
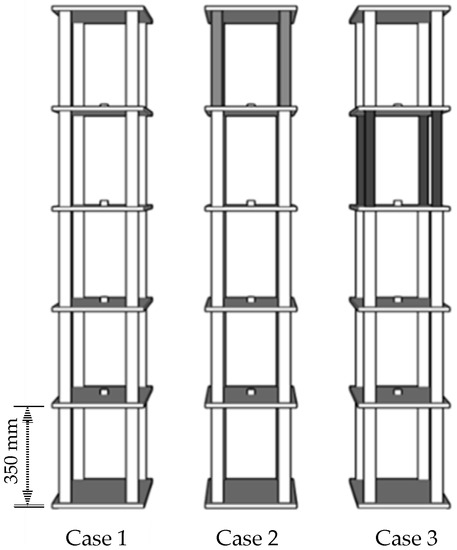
Figure 11.
The sketch of the five-story steel frame under different damage cases.
In the damage design, the stiffness reduction was simulated by reducing the cross section area of the columns. In terms of this steel frame, the story stiffness was composed by the lateral stiffness of 4 steel bars. Hence, the theoretical stiffness of each story can be calculated by the following equation:
where ki is the stiffness of ith story; E is the elastic modulus of the bar and equal to 2.06 × 105 N/mm2; I is the moment of inertia and equal to bh3/12; l is the height of each story and equal to 350 mm.
Columns with three different sizes were considered as shown in Figure 12, consistent with the three damage cases. Then, the damage case 2 was achieved by replacing the columns of 5th story. The same action was made to the 4th story to realize the damage case 3. Columns’ parameters of theoretical and actual story stiffness are tabulated in Table 2. Considering the manufacturing error of the steel bars as well as the installing effect, the static test method was further developed to determine the actual story stiffness with steel bars of three different sizes. In each story, there were four columns and their sizes were assumed to be the same.
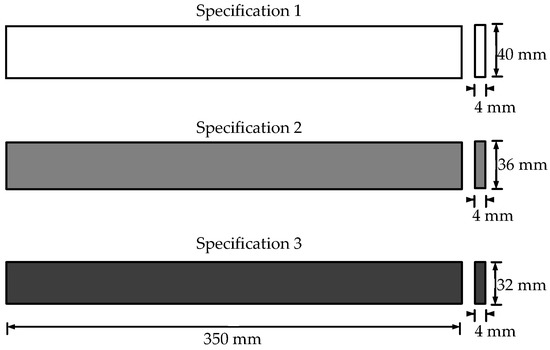
Figure 12.
Three specifications of the steel bars in the experiment.

Table 2.
The parameters of the steel column bars and the story stiffness.
For the intact case (case 1), all columns had the size of specification 1. Structural damage was then introduced by replacing the initial columns with the thinner columns (specification 2 or 3) so that the story stiffness was decreased. The details of the three damage cases can be found in Table 3. Actually, the damage degree, which was defined as the reduction extent of the story stiffness in this paper, of each case is 0%, 10.5%, and 22.7%, respectively.

Table 3.
The details of damage cases.
4.3. Experiment Implementation
The accelerometer has the advantages of high precision, high sensitivity, low power consumption, small size and good linearity. It is widely used in applications, such as dynamic testing, parameter identification, health monitoring, of practical structures [25,26]. In the experiment, accelerometers (model 991C, developed by the Institute of Engineering Mechanics of Chinese Earthquake Administration) were mounted on the slabs of each story to collect the horizontal accelerations of each floor as the observations, while the exciter was anchored on counterforce wall exerting force on the slab of the 5th story, as shown in Figure 13. As shown in Figure 14, the model 991C accelerometer applied in this experiment had two output interfaces, one for acceleration and the other for velocity, but only acceleration output was collected and analyzed here. It inherits the excellent characteristics of passive servo vibration sensors, possessing good impact resistance with no need for zero adjustment before testing, and is suitable for vibration measurement in many occasions. The main performance specification of the accelerometers is listed in Table 4. Acceleration data were collected by the Quantum X data acquisition system produced by HBM Co. Ltd. The sampling frequency of the signal was set to be 50 Hz for all cases. The total masses of the five stories including the sensor weight were: m1 = 24.99 kg, m2 = 24.94 kg, m3 = 24.93 kg, m4 = 24.75 kg, and m5 = 24.80 kg.
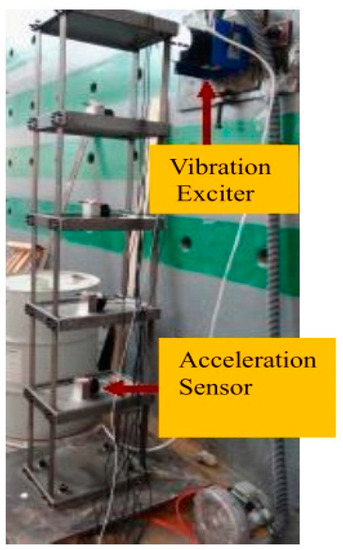
Figure 13.
The five-story steel frame.

Figure 14.
Model 991C accelerometer.

Table 4.
The main performance indicators of the Accelerometer.
In various cases, the Modal Shop 2100E11 was used to excite a random-force time history as shown in Figure 15. When the structure was subjected to vibration, the horizontal acceleration response of each story could be obtained through the acceleration sensors. To limit the length of the paper, only parts of the results are presented here. The data of one test were depicted here to illustrate the horizontal acceleration of each story, as shown in Figure 16.
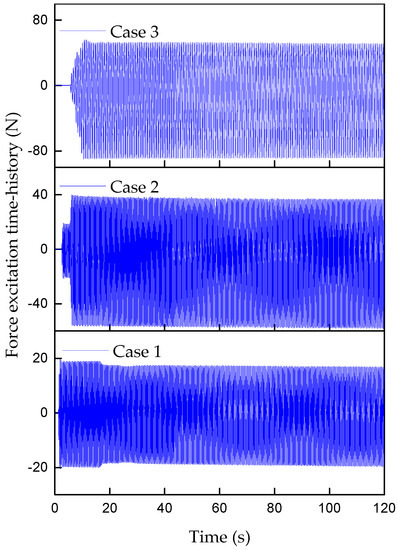
Figure 15.
The time histories of force excitation in three damage cases.
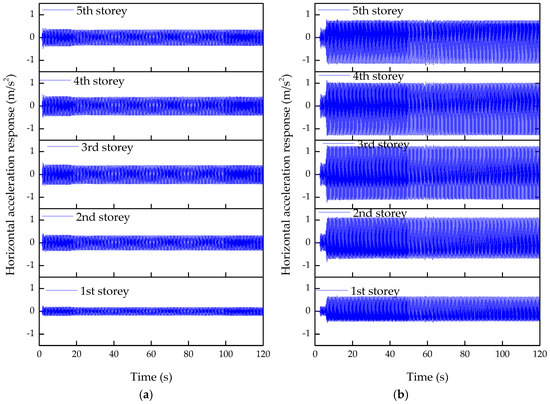
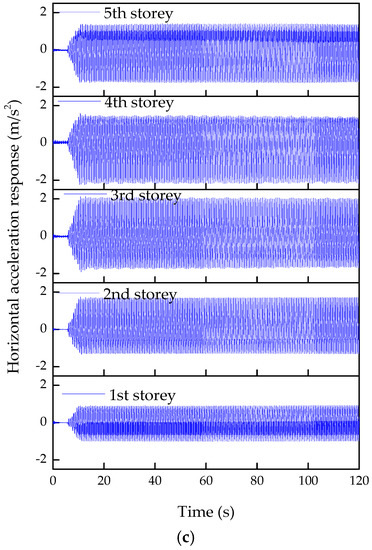
Figure 16.
Horizontal acceleration responses of each story in damage cases: (a) case 1; (b) case 2; (c) case 3.
4.4. Structural Parameter Identification
Based on the EKF algorithm, the identification results for the stiffness under different damage cases are shown in Figure 17. Identified stiffness of each story in case 1 is shown in Figure 17a, the EKF method exhibits excellent convergence, and all identified parameters can rapidly converge to their exact values even if the identified curve of the 5th story has some deviation. The damaged stiffness identification results for cases 2 and 3 are shown in Figure 17b,c, respectively. The stiffness can be also accurately identified. These results indicate the effective identification of the EKF for structural stiffness. Furthermore, the detection results for damage degree under different damage cases are shown in Figure 18. The mean degree of the four tests is used to determine the degree of damage. As shown in Figure 18a, the estimation results of each story are close to 0% when the five-story steel frame has no damage occur. In case 2, the 4th story has the damage with the degree of 10.5%, while others have no damage, as shown in Figure 18b. The identified damage degree is 14.3% which shows the sufficient recognition accuracy. Meanwhile, the identified damage degree of the 4th story in case 3 is 21.3%. Considering the actual damage degree of case 3 is 22.7%, damage at case 3 actually is also well identified. Such experimental results show that the EKF is applicable for detecting damage in multi-DOF systems.
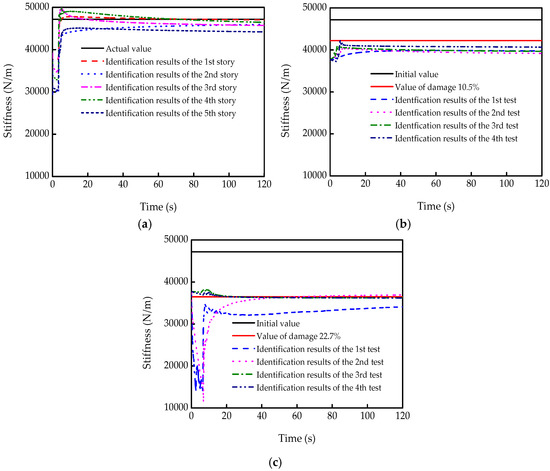
Figure 17.
Stiffness identification of each damage case: (a) case 1; (b) the 5th story in case 2; (c) the 4th story in case 3.
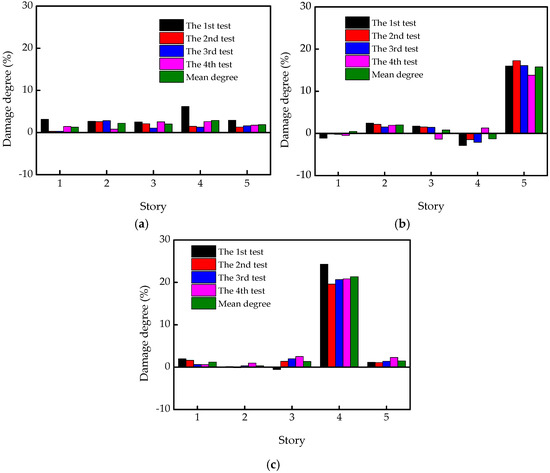
Figure 18.
Identified damages at different damage cases: (a) case 1; (b) case 2; (c) case 3.
5. Conclusions
This work investigated the feasibility and effectiveness of using the EKF algorithm to identify the structural damage in multi-DOF systems. Parameter identification and damage detection have been successfully investigated based on the numerical simulations and laboratory experiments. Firstly, the effect of different integration methods for estimating the structural stiffness and damping was studied. The results show the stiffness is not sensitive to the integration method, and the simple rectangular integral can achieve good result, while the damping is very sensitive to the integral method, which requires the fourth-order Runge–Kutta integration. Meanwhile, EKF-based identification was also studied for structures subjected to Gaussian and non-Gaussian noises. The identification results under Gaussian noises are better than those under non-Gaussian noises. Finally, experiments were conducted and structural damage indicated by the decrease of stiffness was detected effectively. It is shown that EKF is capable of being applied to damage identification and health monitoring for civil engineering structures.
Author Contributions
S.X. conceived and designed the simulation and experiments. L.X. finished the numerical simulation. Z.Z. and L.Z. performed the experiments. C.W. and H.T. analyzed the data. L.X. and Z.Z. wrote this paper.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Numbers: 51578140, 51478356, and 51778490), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFE0127600, and 2017YFC0805900), Shanghai Municipal Education Commission-Gaofeng Grant Support, and the open fund of the Key laboratory of concrete and pre-stressed concrete structure of Ministry of Education of China (CPCSME2015-01).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhang, Z.G.; Guan, D. Experimental Investigation of Feedback Control of The rmoacoustic Oscillations using Least Mean Square-based Algorithms. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 2015, 34, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.N.; Lin, S.L. Identification of Parametric Variations of Structures Based on Least Squares Estimation and Adaptive Tracking Technique. J. Eng. Mech. 2005, 131, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.P.M.; Meenagh, D.; Minford, P.; Wickens, M. A Monte Carlo procedure for checking identification in DSGE models. J. Econ. Dyn. Control 2017, 76, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, P.L.; Maskell, S. Estimating the parameters of dynamical systems from Big Data using Sequential Monte Carlo samplers. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 2017, 93, 379–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, C.; Fearnhead, P.; Mihaylova, L. Sequential Monte Carlo Methods for State and Parameter Estimation in Abruptly Changing Environments. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 2, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, A.; Shinmura, H.; Ohno, S.; Fujisawa, K. Model identification and parameter estimation of elastoplastic constitutive model by data assimilation using the particle filter. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2018, 42, 110–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Q.; Chen, J.; Brownjohn, J.M.W. Parameter identification of pedestrian’s spring-mass-damper model by ground reaction force records through a particle filter approach. J. Sound Vib. 2017, 411, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.L.; Meng, Z.Q.; Cao, T.T.; Zhang, Z.J.; Dai, Y.X. Particle filter-based robust state and parameter estimation for nonlinear process systems with variable parameters. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2017, 28, 065003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhshan, M.; Moula, E.; Shabani-nia, F.; Safarinejadian, B.; Khorshidi, S. Active noise control using wavelet function and network approach. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 2016, 35, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, S.L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W. Mode identification of broadband Lamb wave signal with squeezed wavelet transform. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 125, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.P. Use of the Morlet mother wavelet in the frequency-scale domain decomposition technique for the modal identification of ambient vibration responses. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 2017, 95, 488–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Pal, S.; Bag, S. A combined wavelet packet and Hilbert-Huang transform for defect detection and modelling of weld strength in friction stir welding process. J. Manuf. Process. 2016, 22, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, K.; Loussifi, H.; Braiek, N.B. A comparative study on the identification of the dynamical model of multi-mass electrical drives using wavelet transforms. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2014, 45, 2223–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhao, S.L.; Li, P.Y. Application of Hilbert-Huang Transform in Structural Health Monitoring: A State-of-the-Art Review. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 2014, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, R.E. A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems. J. Basic Eng. 1960, 82, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, R.E.; Bucy, R.S. New Results in Linear Filtering and Prediction Theory. J. Basic Eng. 1961, 83, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazwinsky, A.H. Stochastic Process and Filtering Theory; Mathematics in Science and Engineering: New York, NY, USA, 1970; p. 1730. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, C.B.; Shinozuka, M. Identification of nonlinear structural dynamic systems. J. Struct Mech. 1980, 8, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corigliano, A.; Mariani, S. Parameter identification in explicit structural dynamics: Performance of the extended Kalman filter. Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng. 2004, 193, 3807–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, M.C.; Bogdanski, K. Extending the Kalman filter for structured identification of linear and nonlinear systems. Int. J. Model. Identif. Control 2017, 27, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, D.; Badías, A.; Alfaro, I.; Chinesta, F.; Cueto, E. Model order reduction for real-time data assimilation through Extended Kalman Filters. Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng. 2017, 326, 679–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Bhattacharya, B. Online structural damage identification technique using constrained dual extended Kalman filter. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2017, 24, e1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Huang, J.Z.; Song, G.Q.; Chen, L. Structural damage identification by extended Kalman filter with l1-norm regularization scheme. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2017, 24, e1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.H.; Jang, S.; Sun, X.R. An integrated real-time structural damage detection method based on extended Kalman filter and dynamic statistical process control. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2016, 20, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedon, C.; Bergamo, E.; Izzi, M.; Noè, S. Prototyping and validation of MEMS accelerometers for structural health monitoring-The case study of the Pietratagliata cable-stayed bridge. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2018, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedon, C.; Morassi, A. Dynamic testing and parameter identification of a base-isolated bridge. Eng. Struct. 2014, 60, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).