In-Situ Nanoparticles: A New Strengthening Method for Metallic Structural Material
Abstract
1. Introduction
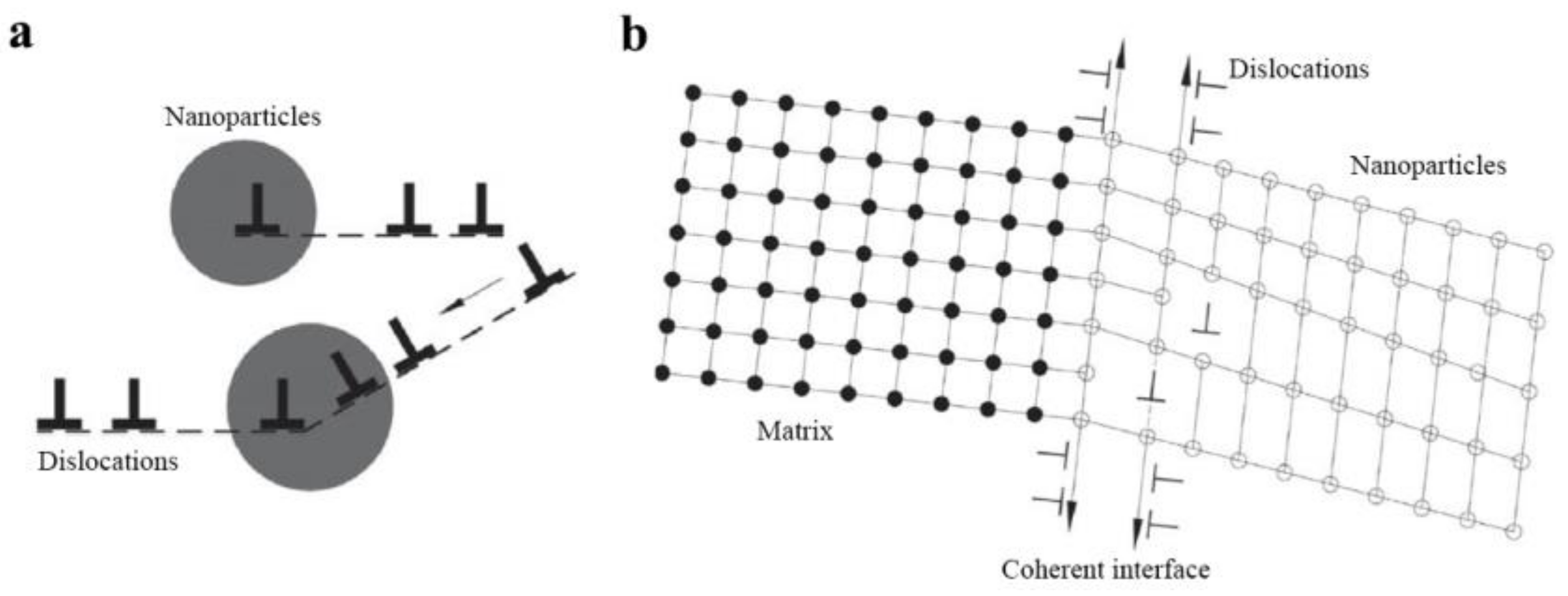
2. Strengthening Mechanism of In-Situ Nanoparticles
3. Materials Fabrication
3.1. In-Situ Nanoparticle Reinforced Steel
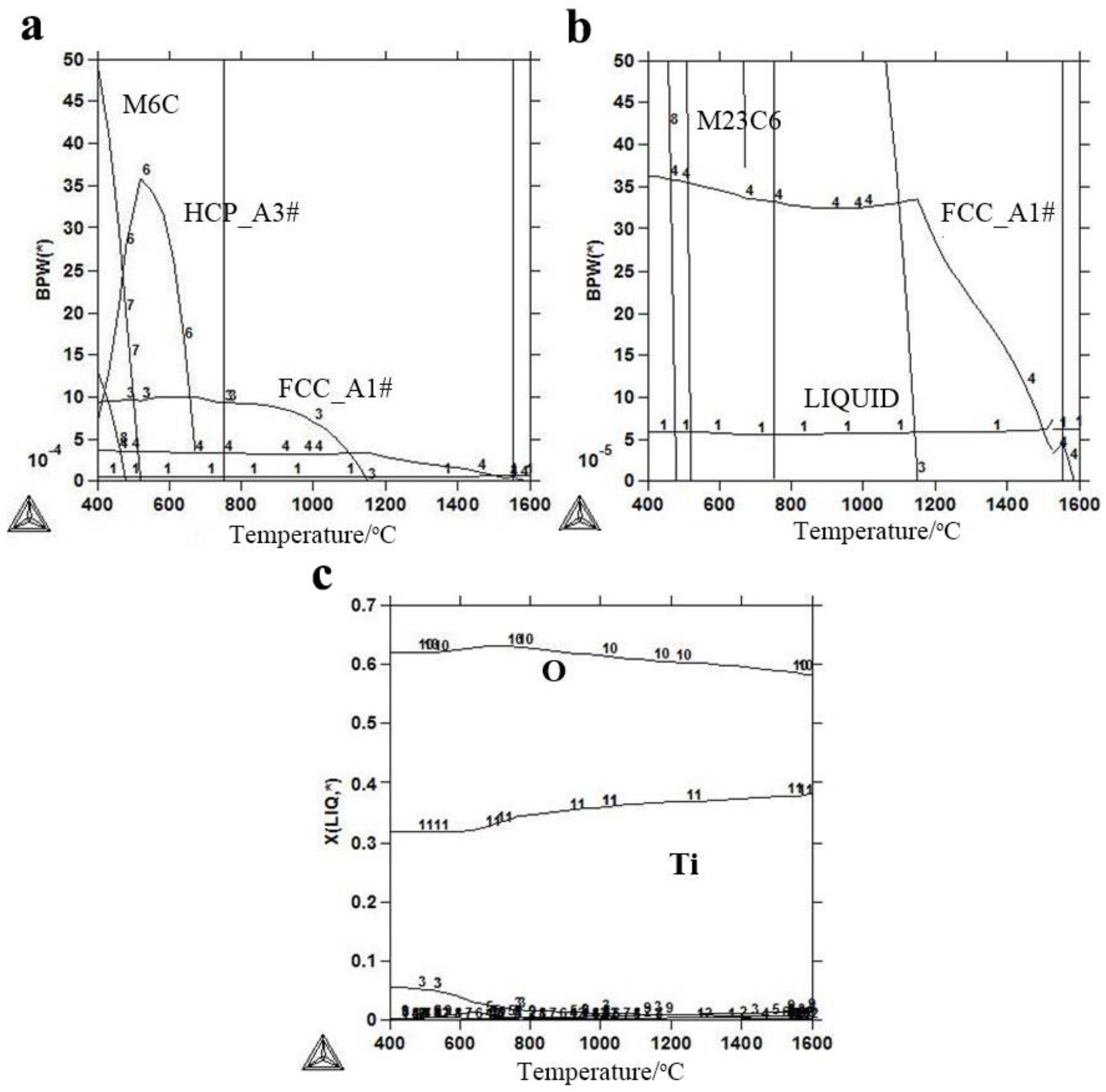
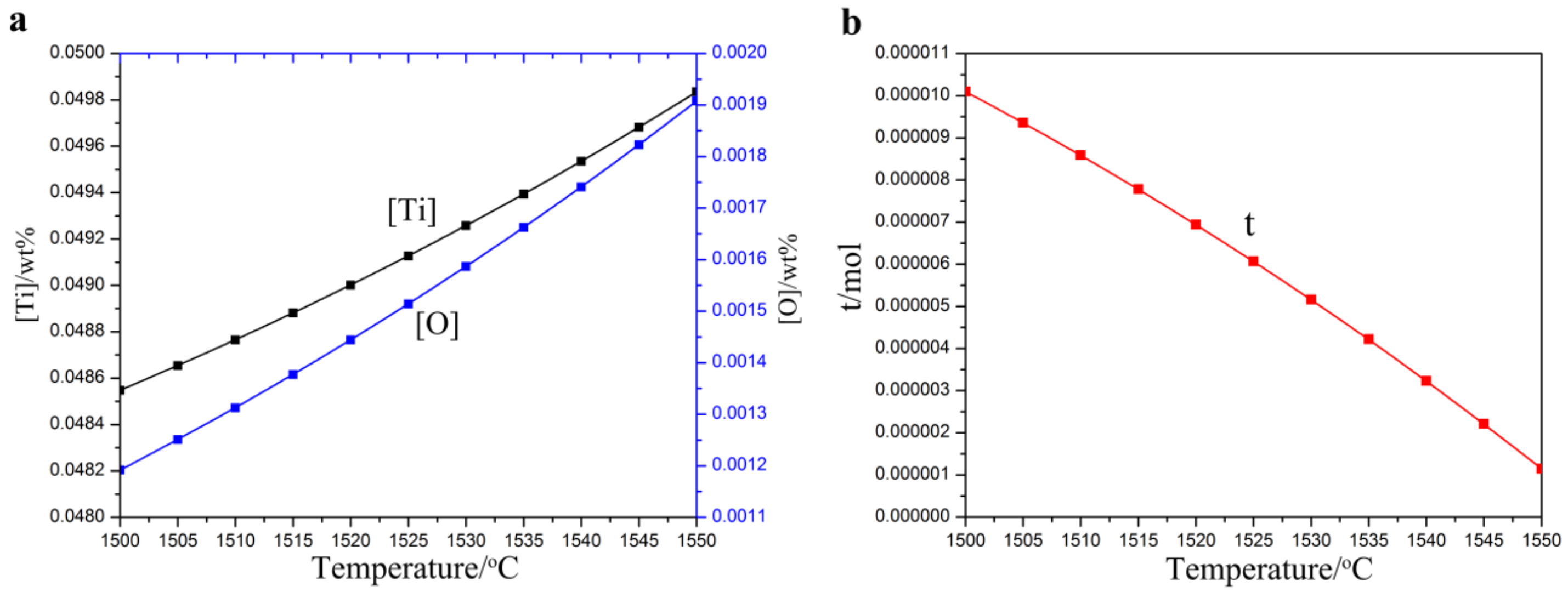
3.1.1. Thermodynamic Calculation
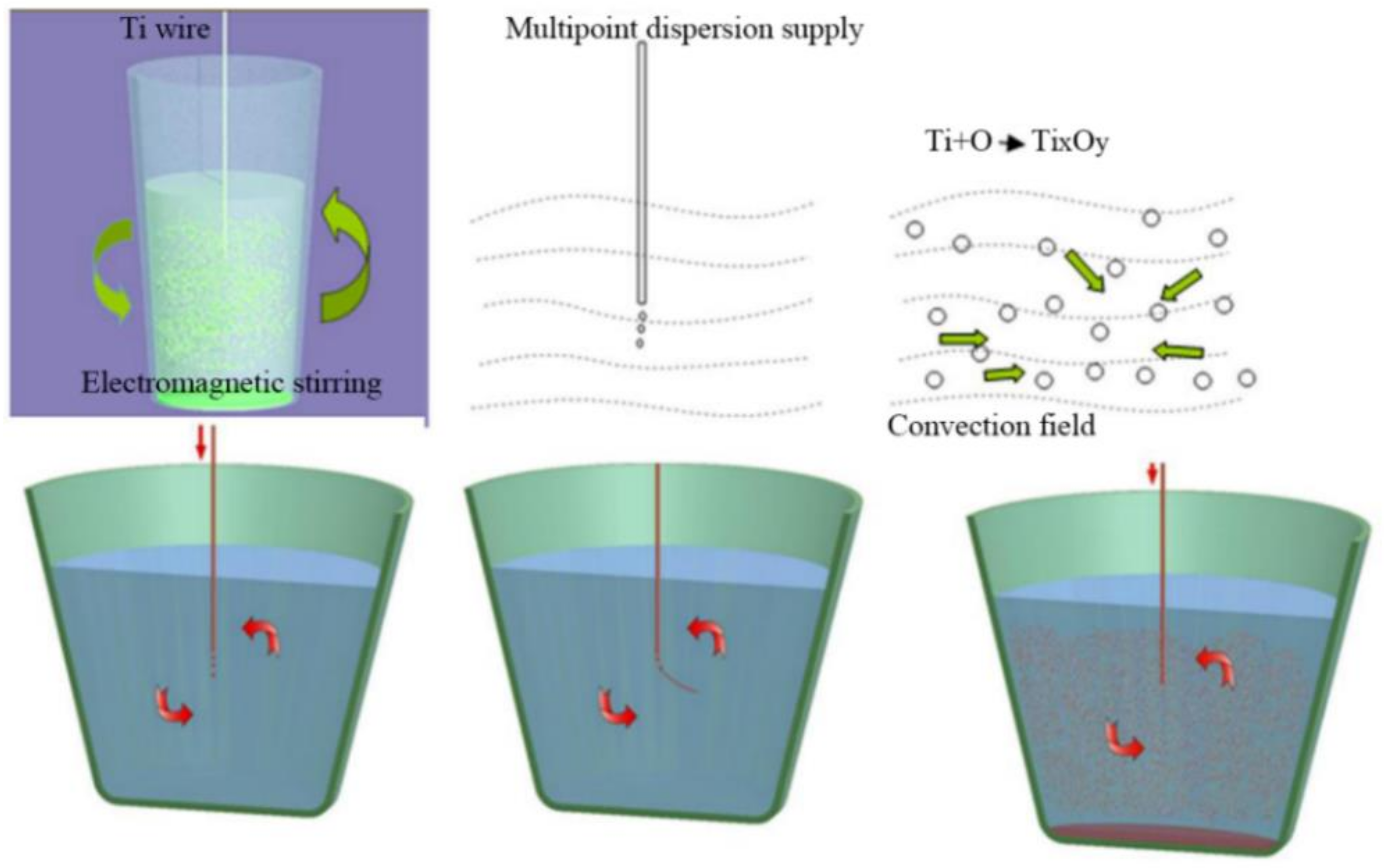
3.1.2. Fabrication Technique
3.2. In-Situ Nanoparticle Reinforced Cu Alloys
3.2.1. Thermodynamic Calculation
3.2.2. DSC (Differential Scanner Calorimetry) Analysis
3.2.3. Fabrication Technique
4. In-Situ Nanoparticles
4.1. Nanoparticles in As-Cast Steel
4.2. Nanoparticles in As-Cast Cu Alloys
5. Optimizing Microstructure
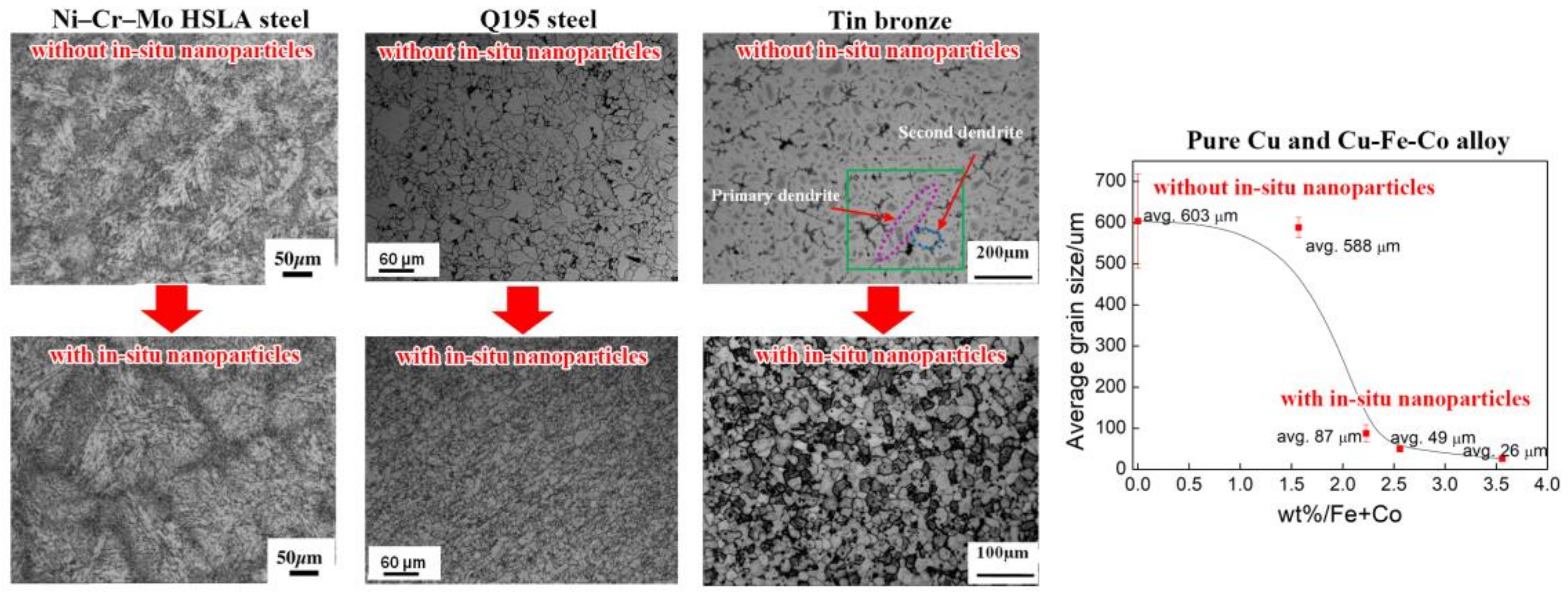
5.1. Grain Refinement
5.2. Inhibiting Segregation
5.3. Optimizing Inclusions
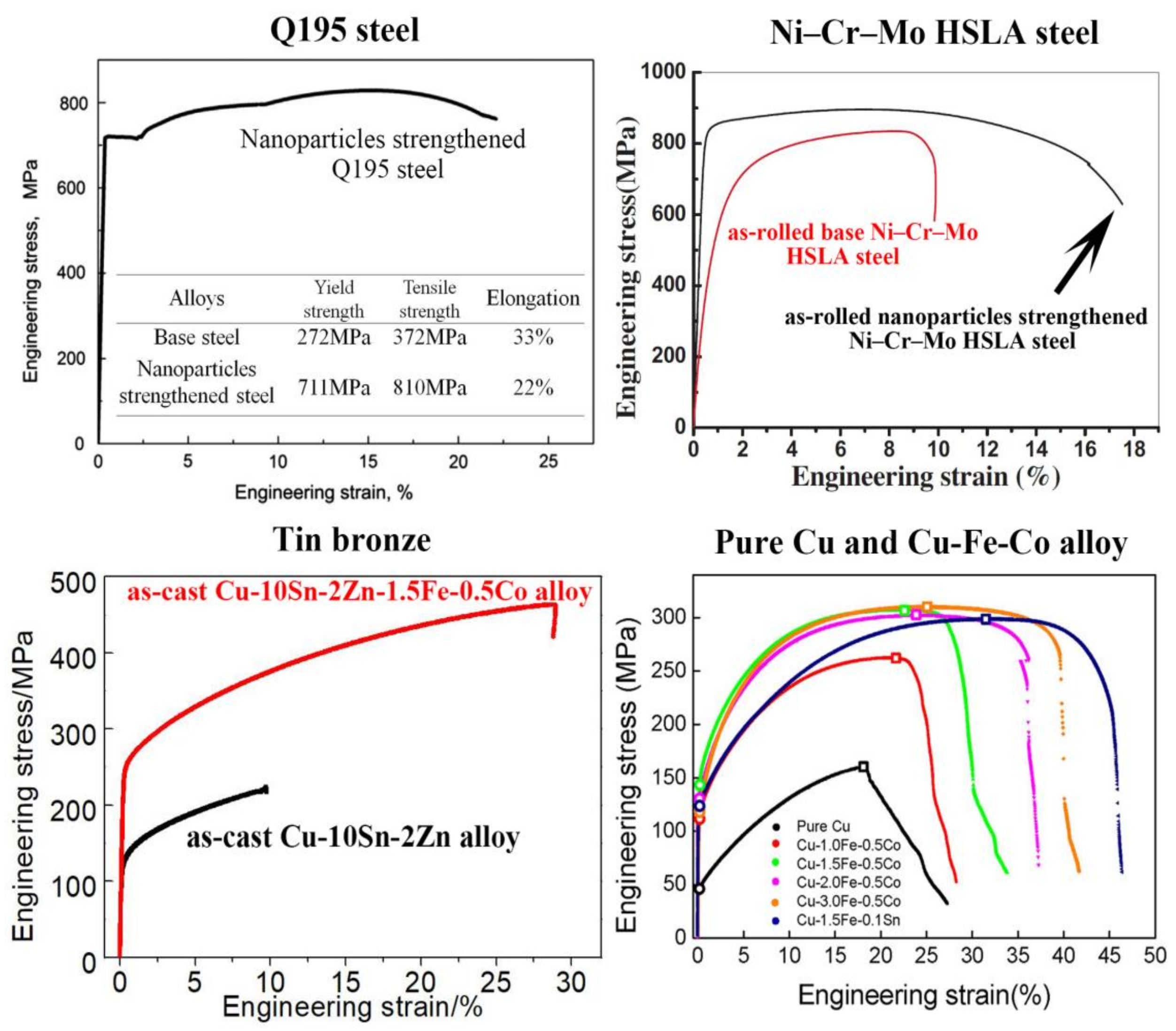
6. Improving Mechanical Property
7. Conclusions and Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agrawal, A.; Dube, R. Methods of fabricating Cu-Al-Ni shape memory alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 750, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, T.; Pan, S.; Wang, Z. Effect of morphologies of martensite–austenite constituents on impact toughness in intercritically reheated coarse-grained heat-affected zone of HSLA steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 710, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Huang, X.; Xin, Y.; Huang, G.; Li, Q.; Tan, C.; Liu, Q. The effect of hot rolling regime on texture and mechanical properties of an as-cast Mg–2Zn–2Gd plate. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 731, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Xin, Y.; Huang, G.; Li, Q.; Guo, F.; Liu, Q. Tailoring the texture and mechanical anisotropy of a Mg–2Zn–2Gd plate by varying the rolling path. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 653, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dursun, T.; Soutis, C. Recent developments in advanced aircraft aluminium alloys. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K. The future of metals. Science 2010, 328, 319–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, E. Deformation and Ageing of Mild Steel: III Discussion of Results. Proc. Phys. Soc. Lond. Ser. B 1951, 64, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petch, N.J. The cleavage of polycrystals. J. Iron Steel Inst. 1953, 174, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Langdon, T.G. Advances in ultrafine-grained materials. Mater. Today 2013, 16, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J. Achieving high strain rate superplasticity in Mg–Y–Nd–Zr alloy processed by homogenization treatment and equal channel angular pressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 633, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.H.; Park, K.T. Ultrafine grained steels processed by equal channel angular pressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 410–411, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, M.; Beyerlein, I.J.; Vogel, S.C.; Langdon, T.G. Characterization of creep properties and creep textures in pure aluminum processed by equal-channel angular pressing. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 2307–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, R.B.; Kawasaki, M.; Xu, C.; Langdon, T.G. Achieving superplastic behavior in fcc and hcp metals processed by equal-channel angular pressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 493, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, R.B.; Langdon, T.G. Strategies for achieving high strain rate superplasticity in magnesium alloys processed by equal-channel angular pressing. Scr. Mater. 2009, 61, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, T.S.; Lee, H.J.; Ahn, B.; Kawasaki, M.; Langdon, T.G. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties in a Zn–Al eutectoid alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Acta Mater. 2014, 72, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, G.; Horita, Z.; Langdon, T.G. Grain refinement and superplasticity in an aluminum alloy processed by highpressure torsion.pdf. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 393, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Infanta, J.M.; Zhilyaev, A.P.; Sharafutdinov, A.; Ruano, O.A.; Carreño, F. An evidence of high strain rate superplasticity at intermediate homologous temperatures in an Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 473, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Urrutia, I.; Muñoz-Morris, M.A.; Morris, D.G. Contribution of microstructural parameters to strengthening in an ultrafine-grained Al–7% Si alloy processed by severe deformation. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, D.P.; Jha, N.; Gull, B.; Das, S.; Badkul, A. Microarchitecture and compressive deformation behaviour of Al-alloy (LM13)–cenosphere hybrid Al-foam prepared using CaCO3 as foaming agent. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 560, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.M.; Mordike, B.L.; Nie, J.F. Creep properties of a Mg–Al–Ca alloy produced by different casting technologies. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 483–484, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Torbet, C.J.; Pollock, T.M.; Wayne, J.J. In situ characterization of fatigue damage evolution in a cast Al alloy via nonlinear ultrasonic measurements. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 2143–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.M. Microstructural and mechanical characterization of various modified 7XXX series spray formed alloys. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cao, F.; Guo, S.; Ning, Z.; Liu, Z.; Jia, Y.; Scudino, S.; Gemming, T.; Sun, J. Microstructures and properties evolution of spray-deposited Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloys with scandium addition. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 691, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Q.; Chen, L.Y.; Choi, H.; Li, X.C. Theoretical study and pathways for nanoparticle capture during solidification of metal melt. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2012, 24, 255304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groza, J.R.; Gibeling, J.C. Principles of particles election for dispersion-strengthened copper. Mater. Sci. Eng. Part A 1993, A171, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, K.; Mada, T.; Takahashi, J.; Todo, M.; Ooka, S. Effect of rubber particle size on the impact tensile fracture behavior of MBS resin with a bimodal particle size distribution. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 8700–8706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jung, J.; Lee, E.; Park, W.; Ahn, S.; Kim, N. Microstructure and properties of titanium boride dispersed Cu alloys fabricated by spray forming. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 277, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, G.; Cheng, X.; Wang, C. In situ (Al2O3 + Al3Zr)np/Al nanocomposites synthesized by magneto-chemical melt reaction. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 1463–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Chan, S. Tensile properties of nanometric Al2O3 particulate-reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Chem. Phys. 2004, 85, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maik, T.; Beffort, O.; Kleiner, S.; Vogt, U. Aluminum matrix composites based on preceramic-polymer-bonded SiC preforms. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 2377–2383. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.; Hoelzer, D.; Kenik, E.; Russell, K. Nanometer scale precipitation in ferritic MA/ODS alloy MA957. J. Nucl. Mater. 2004, 329–333, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Cheng, G.; Wang, M.; Zhao, P. Precipitation and growth of titanium nitride during solidification of clean steel. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. B 2003, 10, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, M.; Zuo, L.; Hou, B.; Wang, Z. Microstructure and mechanical property of in-situ nano-particle strengthened ferritic steel by novel internal oxidation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 609, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callister, W.D. Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, M. High-Strength, Low-Alloy Steels. Science 1980, 208, 862–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagorka, M.S.; Levi, C.G.; Lucas, G.E.; Ridder, S.D. The potential of rapid solidification in oxide-dispersion-strengthened. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1991, 104, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Lu, L.; Suresh, S. Strengthening materials by engineering coherent internal boundaries at the nanoscale. Science 2009, 324, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, G.; Chen, X.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Z.; Tang, H.; Fan, Y. Strengthening mechanisms of Fe nanoparticles for single crystal Cu–Fe alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 636, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, N.; Ohtake, Y.; Kita, K.; Kitagawa, K.; Tsuji, N. Increasing the ductility of ultrafine-grained copper alloy by introducing fine precipitates. Scr. Mater. 2009, 60, 590–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Shih, I.; Xu, J.J. Fabrication of a nanocomposite from in situ iron nanoparticle reinforced copper alloy. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 075605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Ding, D.; Tang, H.; Qiu, L.; Luo, X.; Shi, G. Strengthening and toughening strategies for tin bronze alloy through fabricating in-situ nanostructured grains. Mater. Des. 2015, 66, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Yao, M.; Gault, B.; Ponge, D.; Raabe, D.; Hirata, A.; et al. Ultrastrong steel via minimal lattice misfit and high-density nanoprecipitation. Nature 2017, 544, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meslet, A.; Aldo, M.; Woods, R.; Srivatsan, T.S. Influence of heat treatment on tensile response of an oxide dispersion strengthened copper-main. J Alloys Compd. 1999, 290, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vencl, A.; Rajkovic, V.; Zivic, F.; Mitrović, S.; Cvijović-Alagić, I.; Jovanovic, M.T. The effect of processing techniques on microstructural and tribological properties of copper-based alloys. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 280, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naser, J.; Rieheman, W.; Ferkel, H. Dispersion hardening of metals by nanoscaled ceramic powders. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1997, 234–236, 467–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, A.; Shehata, F.; Abdelhameed, M.; Elmahdy, M. Compressive and wear resistance of nanometric alumina reinforced copper matrix composites. Mater. Des. 2012, 36, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneibel, J.H.; Liu, C.T.; Hoelzer, D.T.; Mills, M.J.; Sarosi, P.; Hayashi, T.; Wendt, U.; Heyse, H. Development of porosity in an oxide dispersion-strengthened ferritic alloy containing nanoscale oxide particles. Scr. Mater. 2007, 57, 1040–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.Y.; Li, J.H.; Luo, M.; Ning, X.G.; Lu, Y.X.; Bi, J.Y.; Zhang, Z. In-situ formed Al2O3 and TiB2 particulates mixture-reinforced aluminum composite. Scr. Metall. Mater. 1994, 31, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X.; Wu, R.; Sakata, T.; Mori, H. HREM study of TiB-Ti interfaces in a TiB-TiC in situ composite-main. Scr. Mater. 2001, 44, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruvilla, A.K.; Prasad, K.S.; Bhanuprasad, V.V.; Mahajan, Y.R. Microstructure-property correlation in AlTiB2 (XD) composites. Scr. Metall. Mater. 1990, 24, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleiter, H. Nanostructured materials: Basic concepts and microstructure. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Wei, Z.; Ni, R.; Ma, B.; Wang, Z. Effect of Aging Temperature on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 1000 MPa Grade Low Carbon Bainitic Steel. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 152–154, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Qiu, L.; Hou, B.; Chen, X.; Chen, M.; Wang, Z. Study of Nano-precipitate in high strength low carbon steel during tempering by TEM. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 327, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Zuo, L.; Ma, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z. Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 800 MPa Grade Ultra Low Carbon Bainite Steel. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 415–417, 943–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Tang, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, K.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X. Effect of In Situ Nano-Particles on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ferritic Steel. Steel Res. Int. 2016, 87, 1389–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Chen, X.; Luo, X.; Chen, M.; Wang, Z.; Zuo, L. Heterogeneous nucleation effect of in situ nanoparticles on the metal–matrix microstructure. Mater. Lett. 2014, 137, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Chen, X.; Niu, Y.; Luo, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, M.; Shi, G. Thermal stability characteristics of in situ nano-particles formed in metal melt. Mater. Lett. 2016, 162, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Qiu, L.; Tang, H.; Luo, X.; Zuo, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. Effect of nanoparticles formed in liquid melt on microstructure and mechanical property of high strength naval steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 222, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H. Microstructure and Properties of in Situ Nano Particle Reinforced High Strength and Toughness Steel. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Booth-Morrison, C.; Dunand, D.; Seidman, D. Coarsening resistance at 400°C of precipitation-strengthened Al–Zr–Sc–Er alloys. Acta. Mater. 2011, 59, 7029–7042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipling, K.; Karnesky, R.; Lee, C.; Dunand, D.; Seidman, D. Precipitation evolution in Al–0.1Sc, Al–0.1Zr and Al–0.1Sc–0.1Zr (at.%) alloys during isochronal aging. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 5184–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Chen, X.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, T.; Luo, X. Dendrite remelting of petal-shaped iron-rich nanoparticles in Cu-2wt% Fe alloy at the nanoscale. Mater. Lett. 2016, 166, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Chen, X.; Ding, D.; Shi, G.; Wang, Z. Heterogeneous nucleation effect of in situ iron-rich nanoparticles on grain refinement of copper alloy. Mater. Lett. 2016, 168, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Chen, X.; Ding, D.; Shi, G.; Wang, Z. Formation mechanism of in-situ nanostructured grain in cast Cu–10Sn–2Zn–1.5Fe–0.5Co (wt.%) alloy. Mater. Des. 2016, 94, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Tang, H.; Chen, X.; Ding, D.; Shi, G.; Wang, Z. Morphological instability of spherical nano iron-rich crystal in copper melt. Mater. Lett. 2016, 172, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Chen, X.; Ding, D.; Shi, G.; Wang, Z. Crystallographic features of iron-rich nanoparticles in cast Cu–10Sn–2Zn–1.5Fe–0.5Co alloy. Mater. Charact. 2016, 113, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Chen, X.; Ding, D.; Wang, Z. Effect of in-situ nanoparticle wall on inhibiting segregation of tin bronze alloy. Mater. Lett. 2016, 175, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Pan, S.; Zhu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z. In situ observations of crack propagation in as-cast Cu-1.5Fe-0.5Co (wt%) alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 706, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Mao, H.; Rolf, S. Optimization of deformation properties in as-cast copper by microstructural engineering. Part I. microstructure. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 763, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.X.; Korzhavyi, P.; Demange, G.; Zapolsky, H.; Patte, R.; Boisse, J.; Wang, Z. Morphological instability of iron-rich precipitates in Cu Fe Co alloys. Acta Mater. 2019, 163, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K. Microstructure and Deformation Properties of Nanoparticle-Fine Grain (NPFG) Synergistically Reinforced Copper Alloys. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, W.; Wang, W.; Geng, D.; Wei, B. A DSC analysis of thermodynamic properties and solidification characteristics for binary Cu–Sn alloys. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 6518–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.N. Fundamentals of Material Science; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.K.; Chatterjee, S.; Tarafder, S. Tensile fracture behaviour of microstructurally engineered Cu bearing high strength low alloy steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 22, 1409–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chairuangsri, T.; Edmonds, D.V. The precipitation of copper in abnormal ferrite and pearlite in hyper-eutectoid steels. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 3931–3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, C.S.; Ashraf Imam, M.; Vold, C.L.; Dantsker, E.; Rath, B.B. Study of Precipitation Kinetics in High Strength Low Carbon Ferrous Alloys. Key Eng. Mater. 1993, 84, 145–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotan, H.; Darling, K.A.; Saber, M.; Scattergood, R.O.; Koch, C.C. Thermal stability and mechanical properties of nanocrystalline Fe–Ni–Zr alloys prepared by mechanical alloying. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 8402–8411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Q.L. Secondary Phases in Steels; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Z. Mechanisms of enhanced heterogeneous nucleation during solidification in binary Al–Mg alloys. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 1528–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, H.; Fan, Z. Effects of solute content on grain refinement in an isothermal melt. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 2704–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, I.; Hellawell, A. An analysis of the peritectic reaction with particular reference to Al-Ti alloys. Acta Metall. 1975, 23, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, A.; Bunn, A.; Tronche, A.; Evans, P.; Bristow, D. Modelling of inoculation of metallic melts: application to grain refinement of Aluminium by Al-Ti-B. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 2823–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumoto, E.; Alhadeff, R.; Martorano, M. Microsegregation and dendrite arm coarsening in tin bronze. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 18, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Park, C.; Lee, K. Implication of peritectic composition in historical high-tin bronze metallurgy. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 1268–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türk, A.; Durman, M.; Kayali, E. The effect of manganese on the microstructure and mechanical. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 42, 8298–8305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, E.; deJonge, N. Video-frequency scanning transmission electron microscopy of moving gold nanoparticles in liquid. Micron 2012, 43, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, P.; Greer, A. Modelling of crystal growth and solute redistribution during rapid solidification. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1988, 98, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M. Model for solute redistribution during rapid solidification. J. Appl. Phys. 1982, 53, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, F.; Cui, F. Analysis of Forming Mechanism of Lamination Defect of Steel Plate. J. Northeast. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2007, 28, 1002–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domizzi, G.; Anteri, G.; Ovejero-Garcia, J. Influence of sulphur content and inclusion distribution on the hydrogen induced blister cracking in pressure vessel and pipeline steels. Corros. Sci. 2001, 43, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, F. Physical Metallurgy and the Design of Steels; Applied Science Publication Limited: London, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Nes, E.; Ryum, N.; Hunderi, O. On the Zener drag. Acta Mater. 1985, 33, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecking, H.; Kocks, U.F. Kinetics of flow and strain-hardening. Acta Mater. 1981, 29, 1865–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Huo, X.; Sun, X.; Chai, Y. Strengthening mechanisms of a new 700MPa hot rolled Ti-microalloyed steel produced by compact strip production. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2010, 210, 1660–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callister, W. Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Reed-Hill, R. Physical Metallurgy Principle, 2nd ed.; PWS Kent: Whitstable, UK, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Orowan, E. Dislocations in Metals; AIME Publication: New York, NY, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
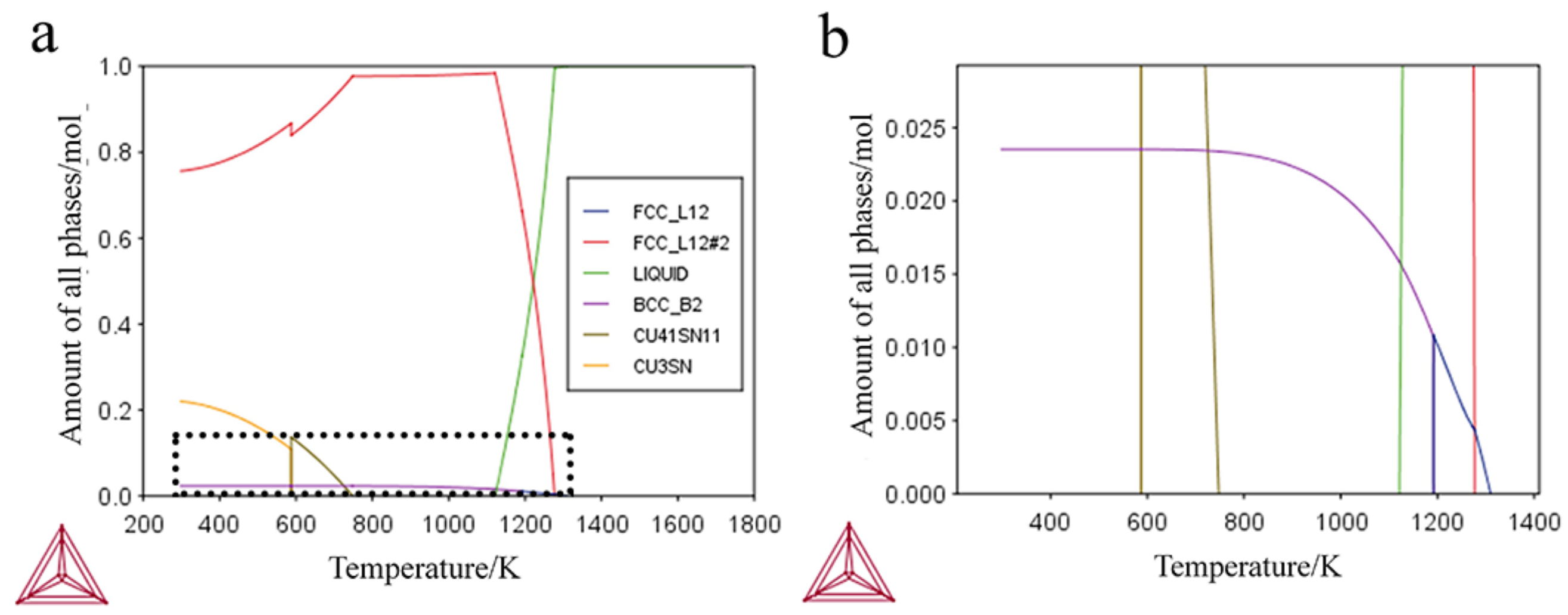
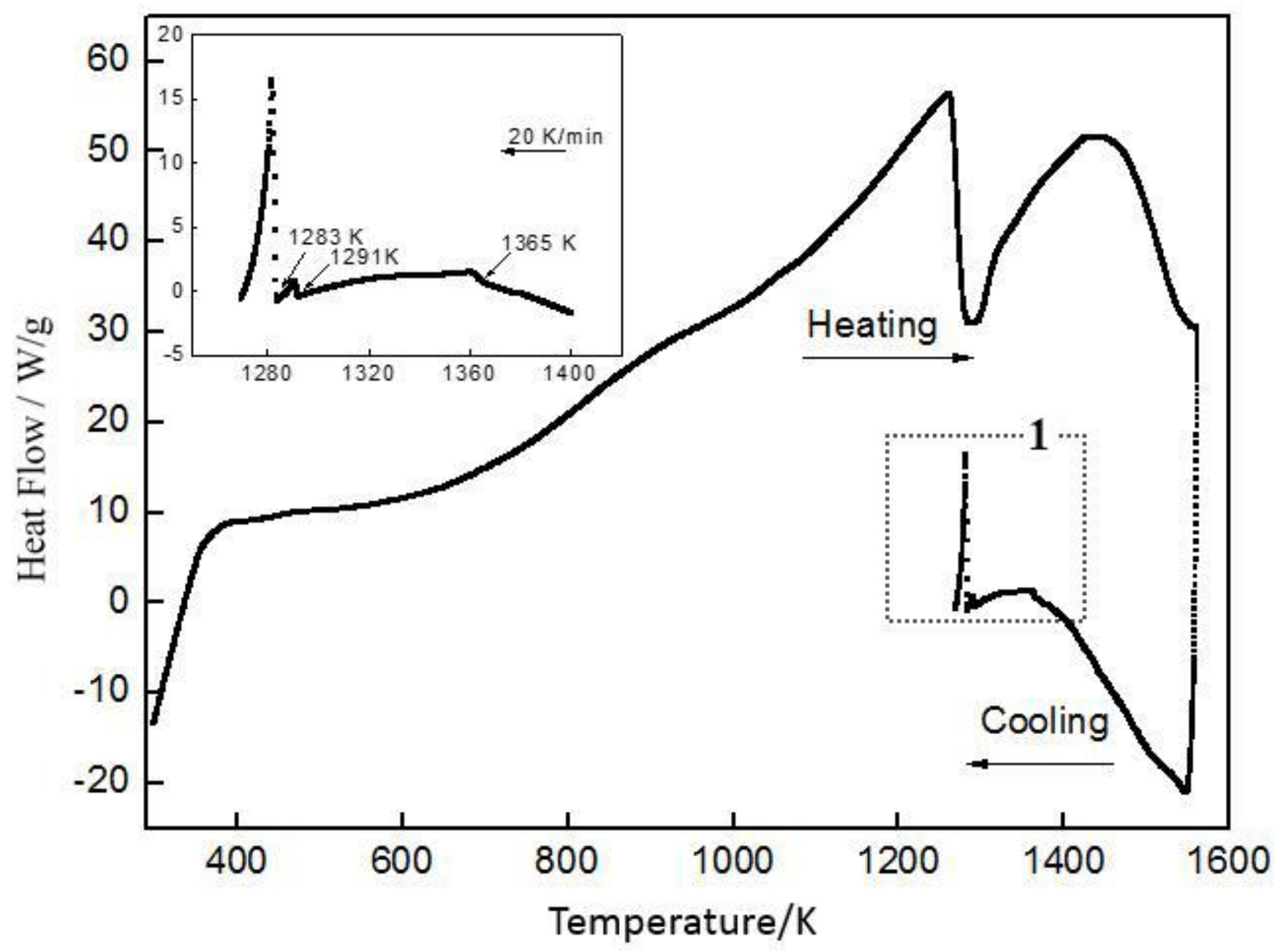
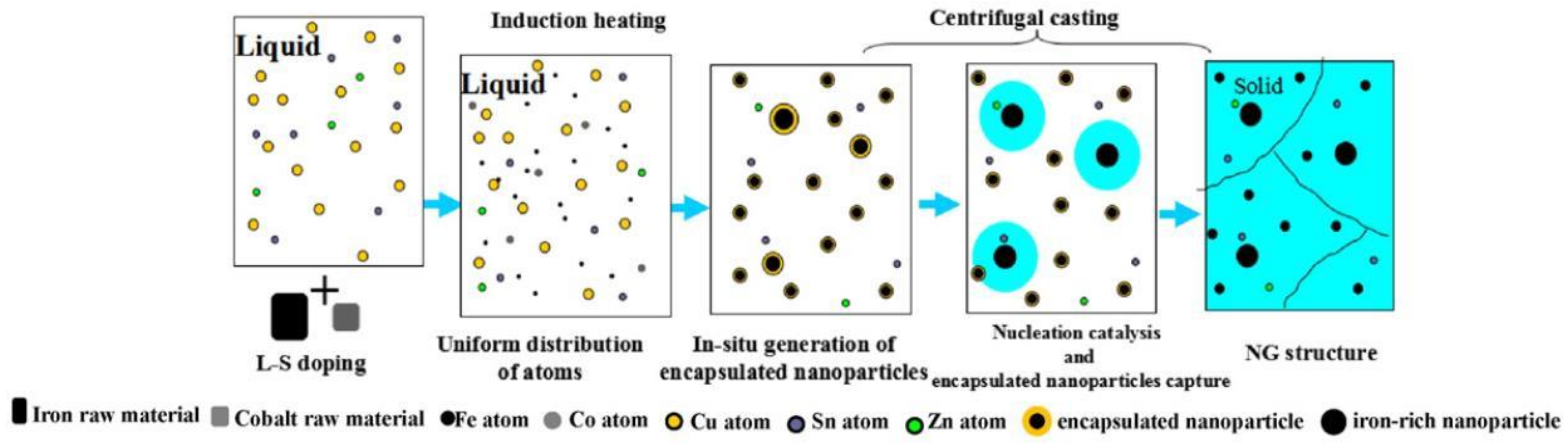
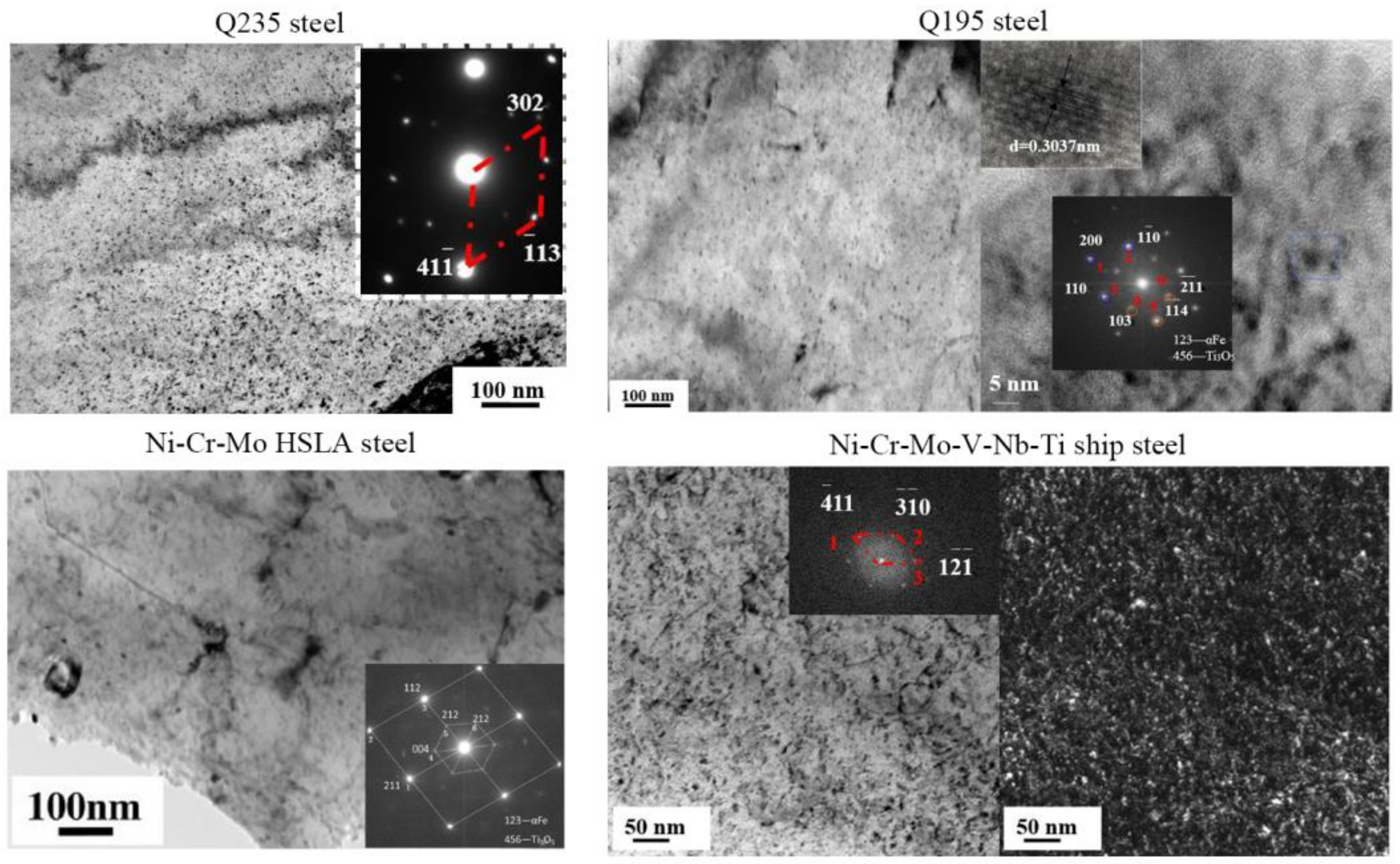
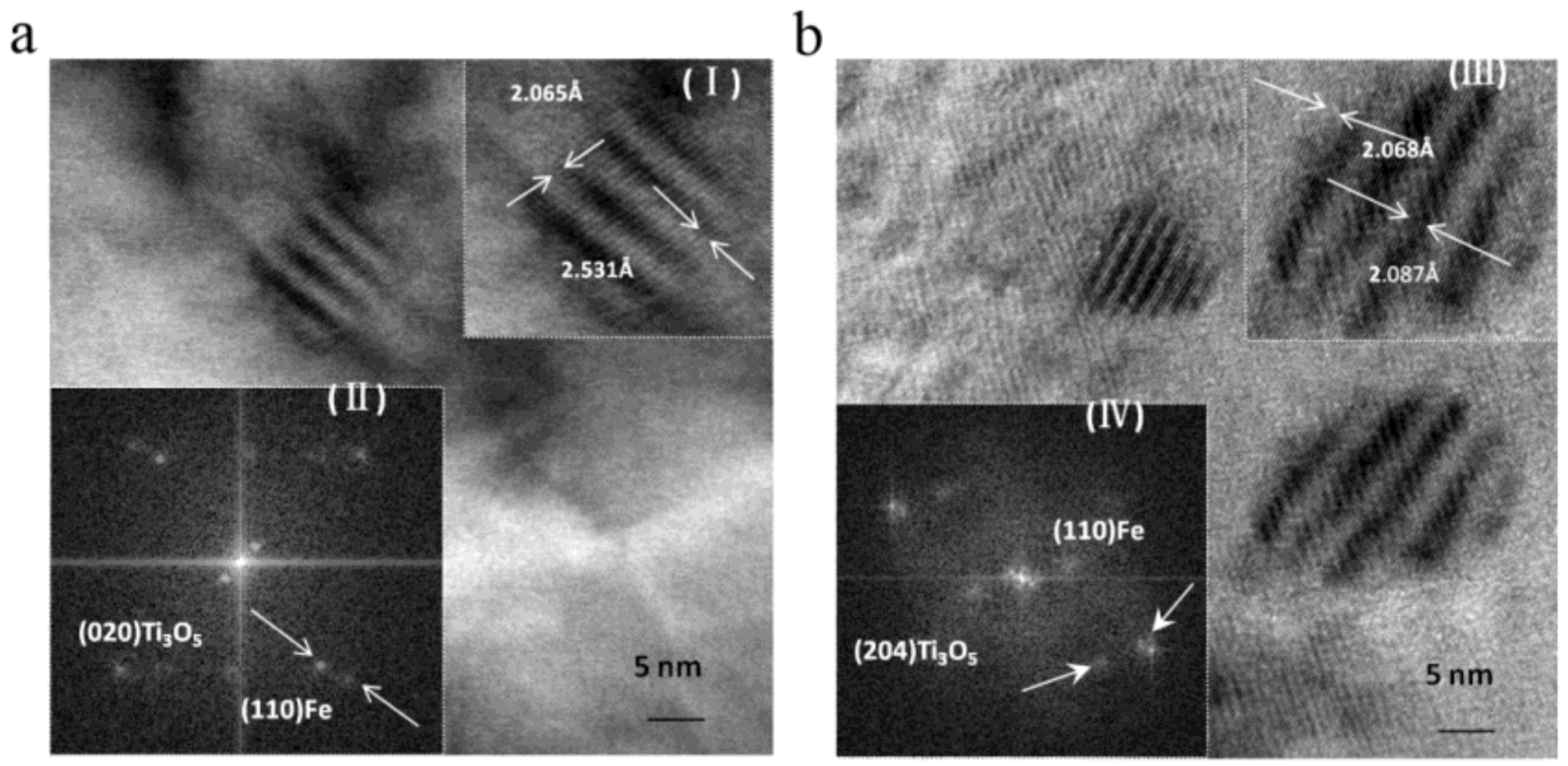
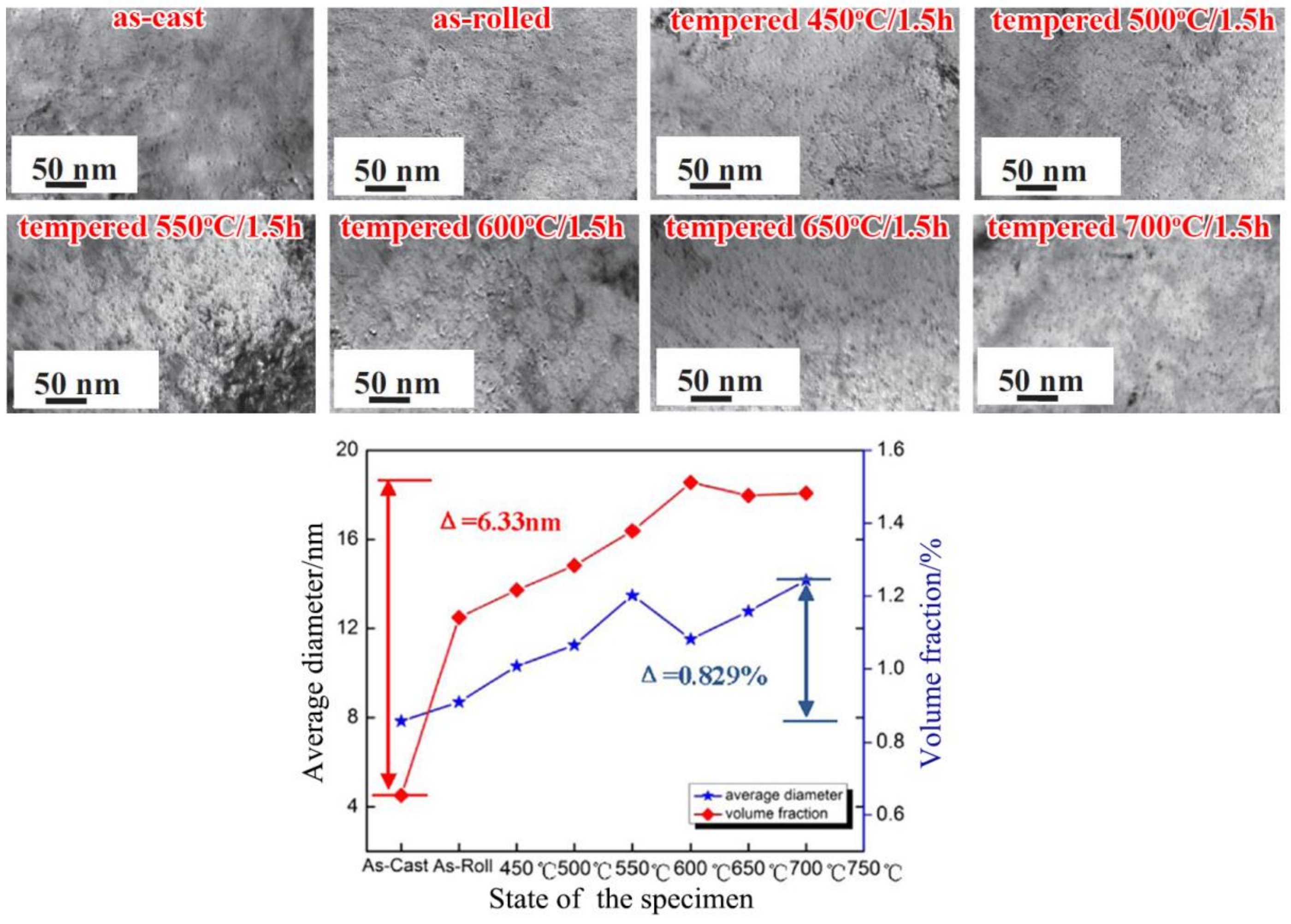
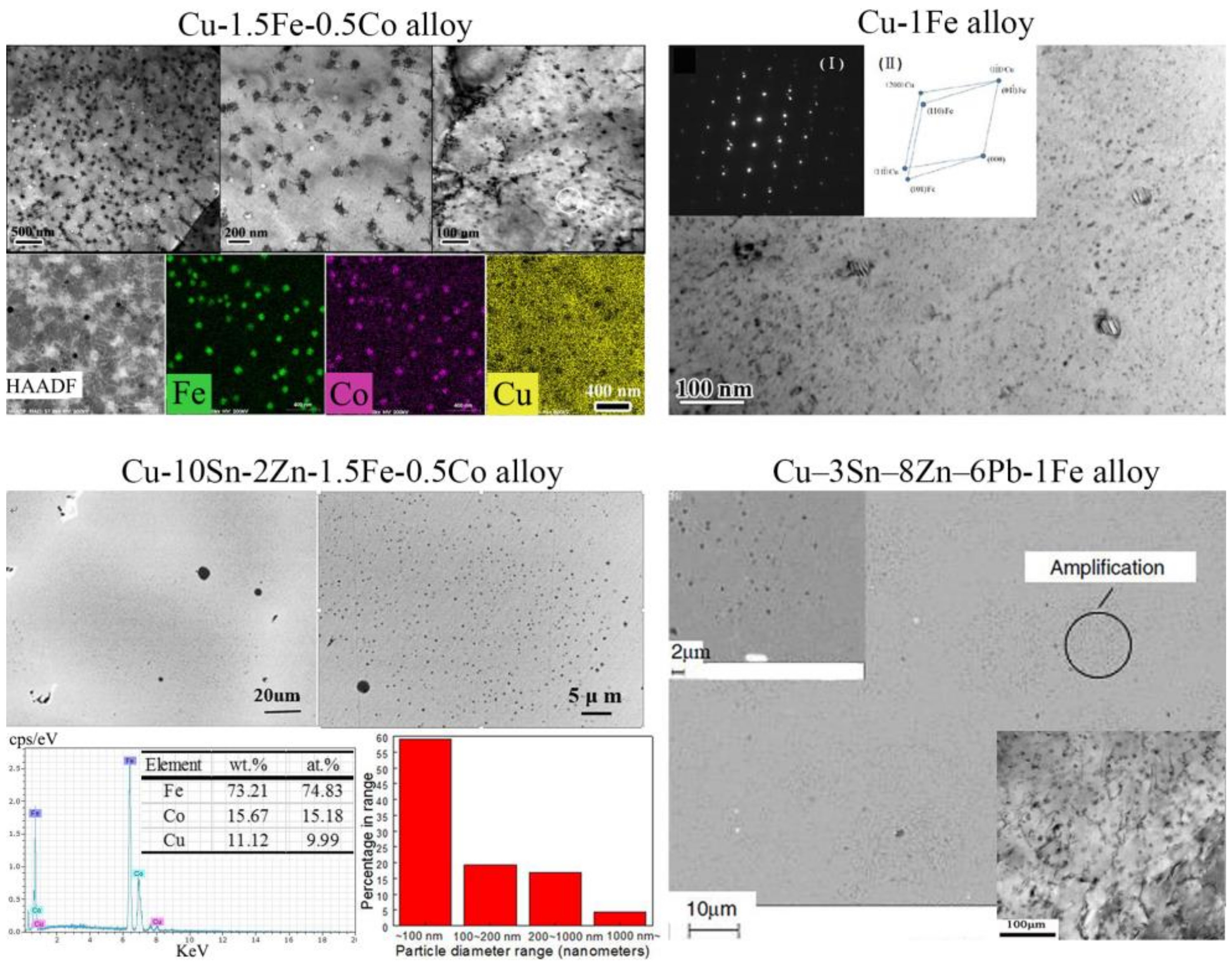
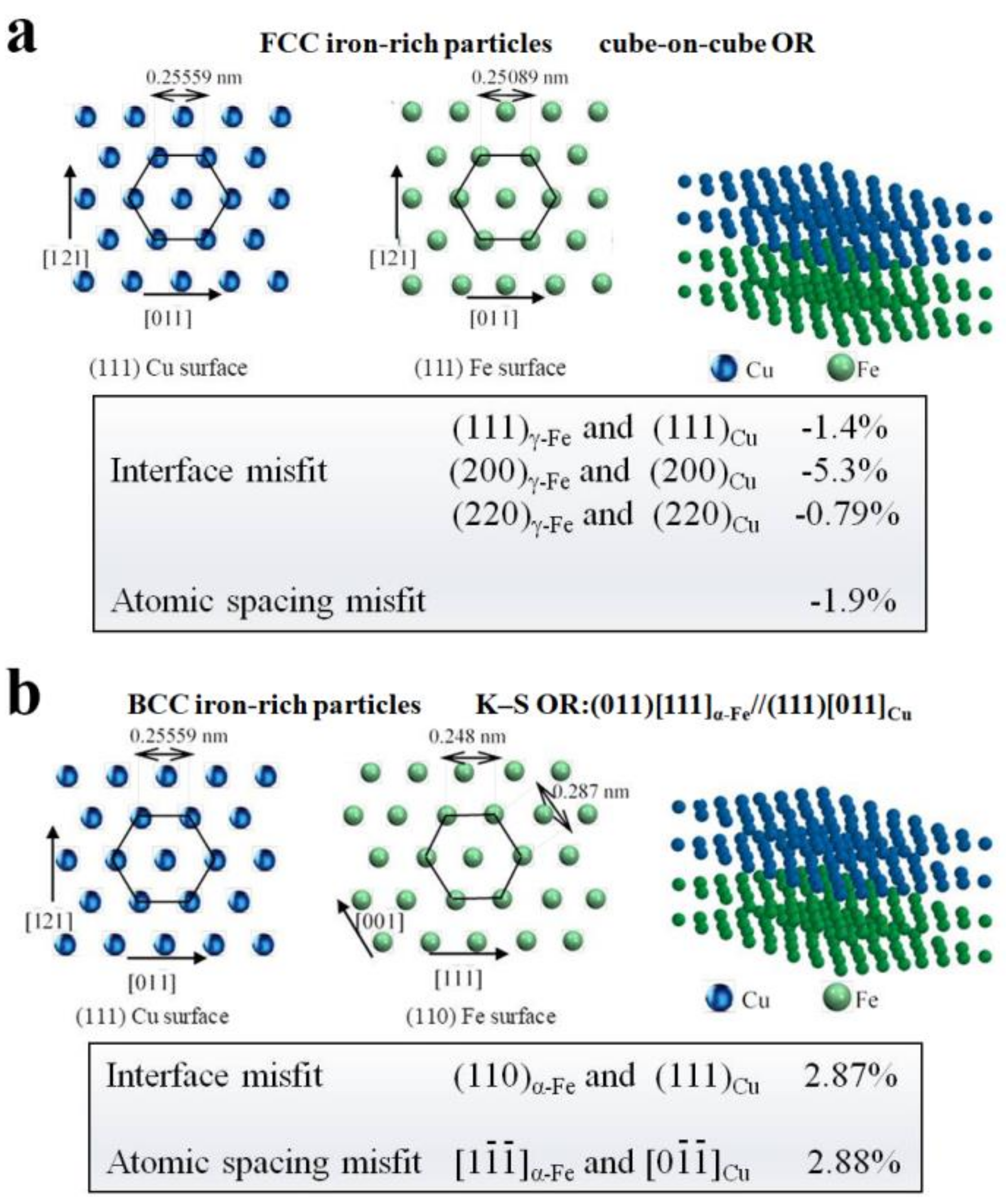


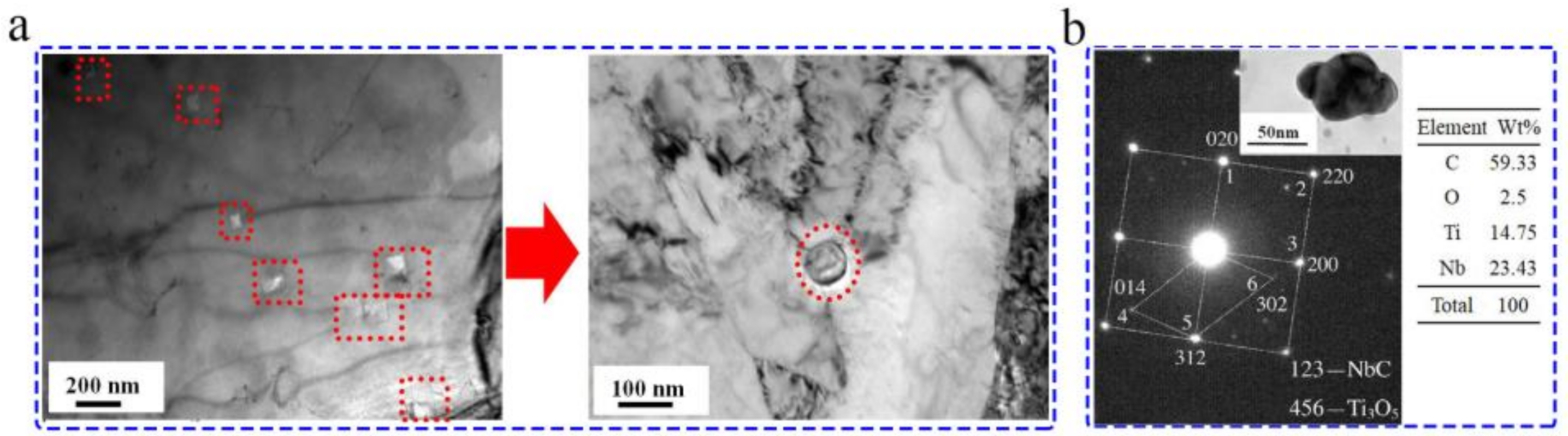
| Temperature/K | Phase | Phase Compositions/wt. % | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | Co | Cu | Zn | Sn | ||
| 1300 | FCC_L12 | 68.389 | 23.671 | 7.782 | 0.089 | 0.070 |
| 1200 | FCC_L12 | 72.802 | 21.575 | 5.398 | 0.141 | 0.084 |
| 1000 | BCC_B2 | 76.113 | 23.545 | 1.258 | 0.196 | 0.023 |
| 600 | BCC_B2 | 74.953 | 24.975 | 0.067 | 0.004 | 7.17 × 10−6 |
| 298 | / | 62.01 | 17.03 | 19.69 | 0.32 | 0.94 |
| Alloys | Morphology 1 | Nv (m−3) | rmean/rr (nm) | f (vol. %) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu-1.0Fe-0.5Co | spherical | 1.4 × 1020 | 21.8 | 0.6 | [69,71] |
| Cu-1.5Fe-0.5Co | spherical | 1.1 × 1020 | 28.2 | 1.0 | |
| Cu-2.0Fe-0.5Co | spherical + petal-like | 5.0 × 1019 | 44.3 | 1.8 | |
| Cu-3.0Fe-0.5Co | spherical + petal-like | 2.7 × 1019 | 59.1 | 2.3 | |
| Cu-1.5Fe-0.1Sn | spherical | 5.0 × 1019 | 27.7 | 0.4 | |
| Cu-10Sn-2Zn-1.5Fe | spherical + petal-like | - | 6 | 1.6 | [41] |
| Cu-10Sn-2Zn-1.5Fe-0.5Co | spherical + petal-like | 2.01 × 1024 | 20–40 | - | [64] |
| Cu-3Sn-8Zn-6Pb-1Fe | spherical | - | 2–20 | - | [40] |
| Cu-1Fe | spherical + petal-like | - | 5–50 | - | [38] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, S.; Zhou, X.; Chen, K.; Yang, M.; Cao, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z. In-Situ Nanoparticles: A New Strengthening Method for Metallic Structural Material. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122479
Pan S, Zhou X, Chen K, Yang M, Cao Y, Chen X, Wang Z. In-Situ Nanoparticles: A New Strengthening Method for Metallic Structural Material. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(12):2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122479
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Shiwei, Xianglin Zhou, Kaixuan Chen, Ming Yang, Yudong Cao, Xiaohua Chen, and Zidong Wang. 2018. "In-Situ Nanoparticles: A New Strengthening Method for Metallic Structural Material" Applied Sciences 8, no. 12: 2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122479
APA StylePan, S., Zhou, X., Chen, K., Yang, M., Cao, Y., Chen, X., & Wang, Z. (2018). In-Situ Nanoparticles: A New Strengthening Method for Metallic Structural Material. Applied Sciences, 8(12), 2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122479





