Experimental Study on Vortex-Induced Vibration of Risers Considering the Effects of Different Design Parameters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
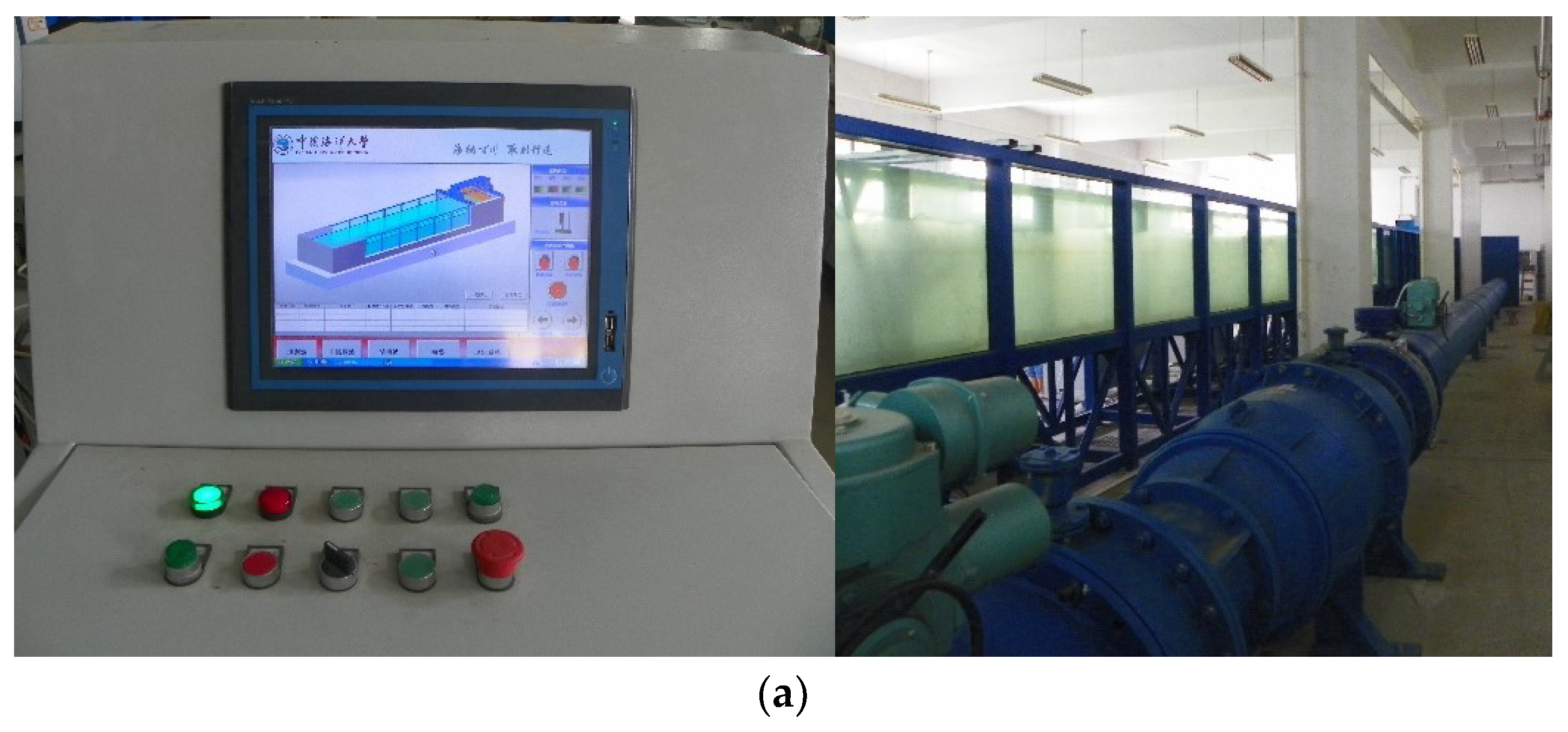
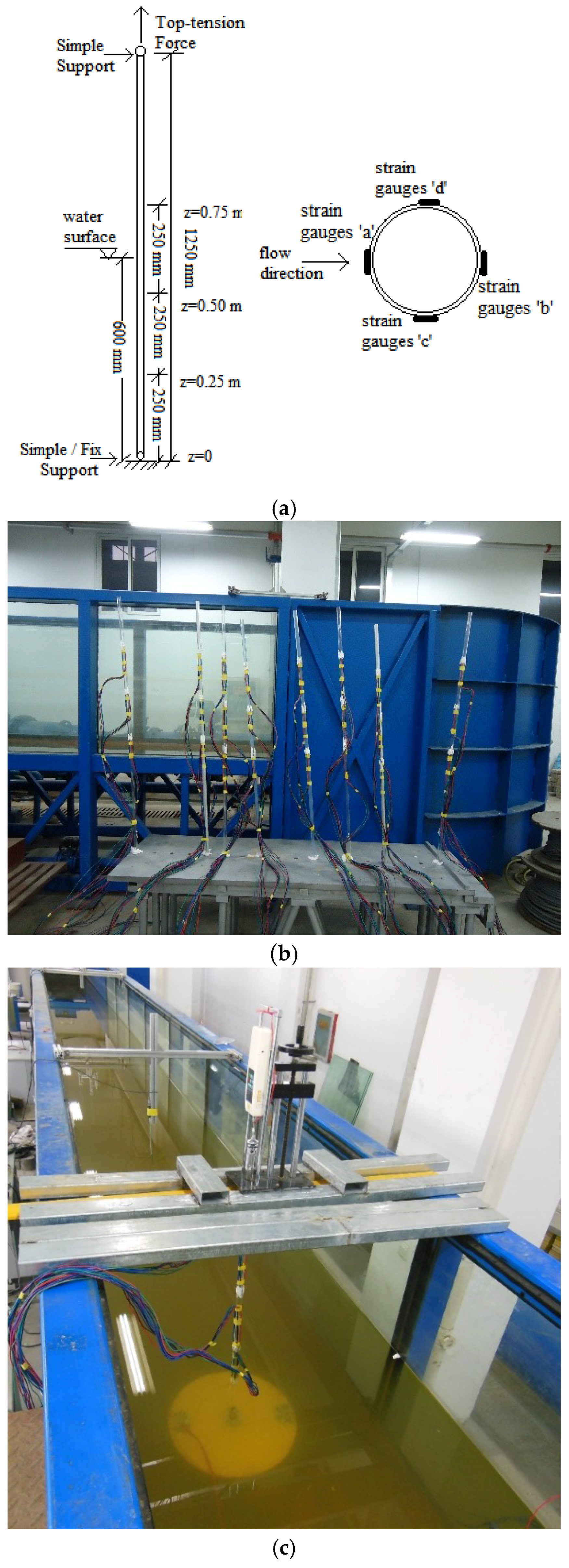
2. Setup of Experiment
2.1. Instrumentation
2.2. Experimental Model of Risers
2.3. Experiment Cases
3. Results and Discussion
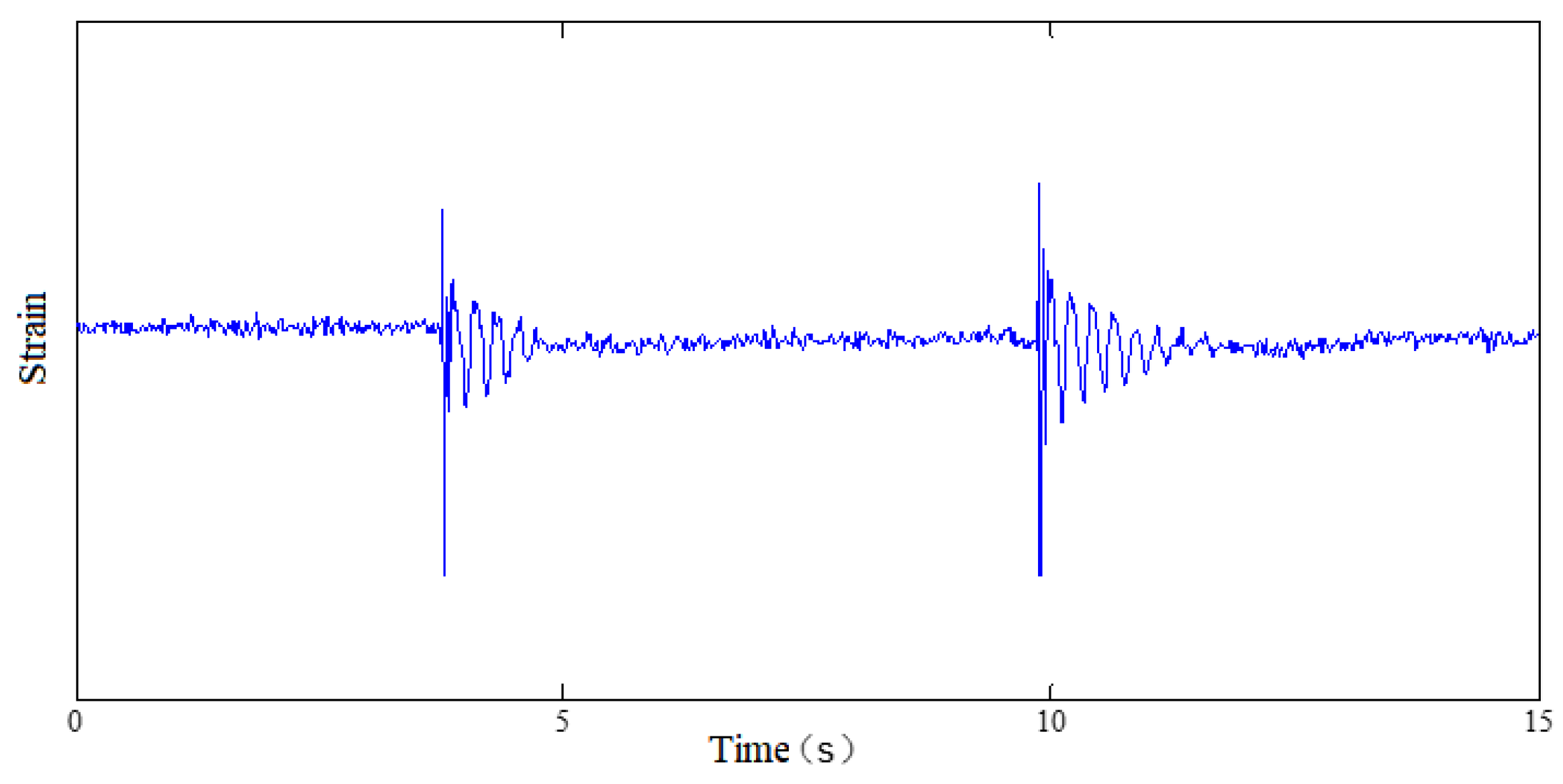
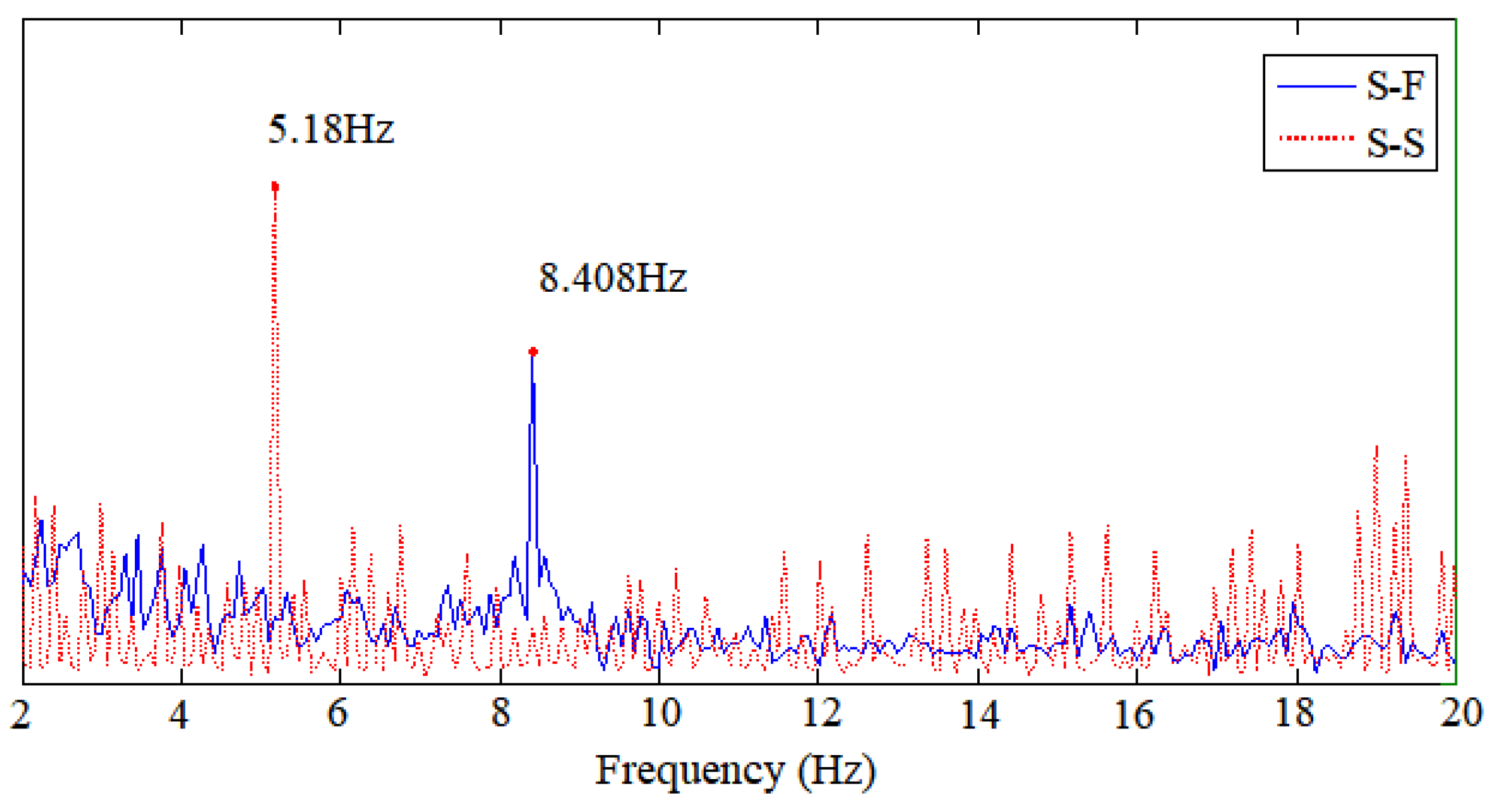
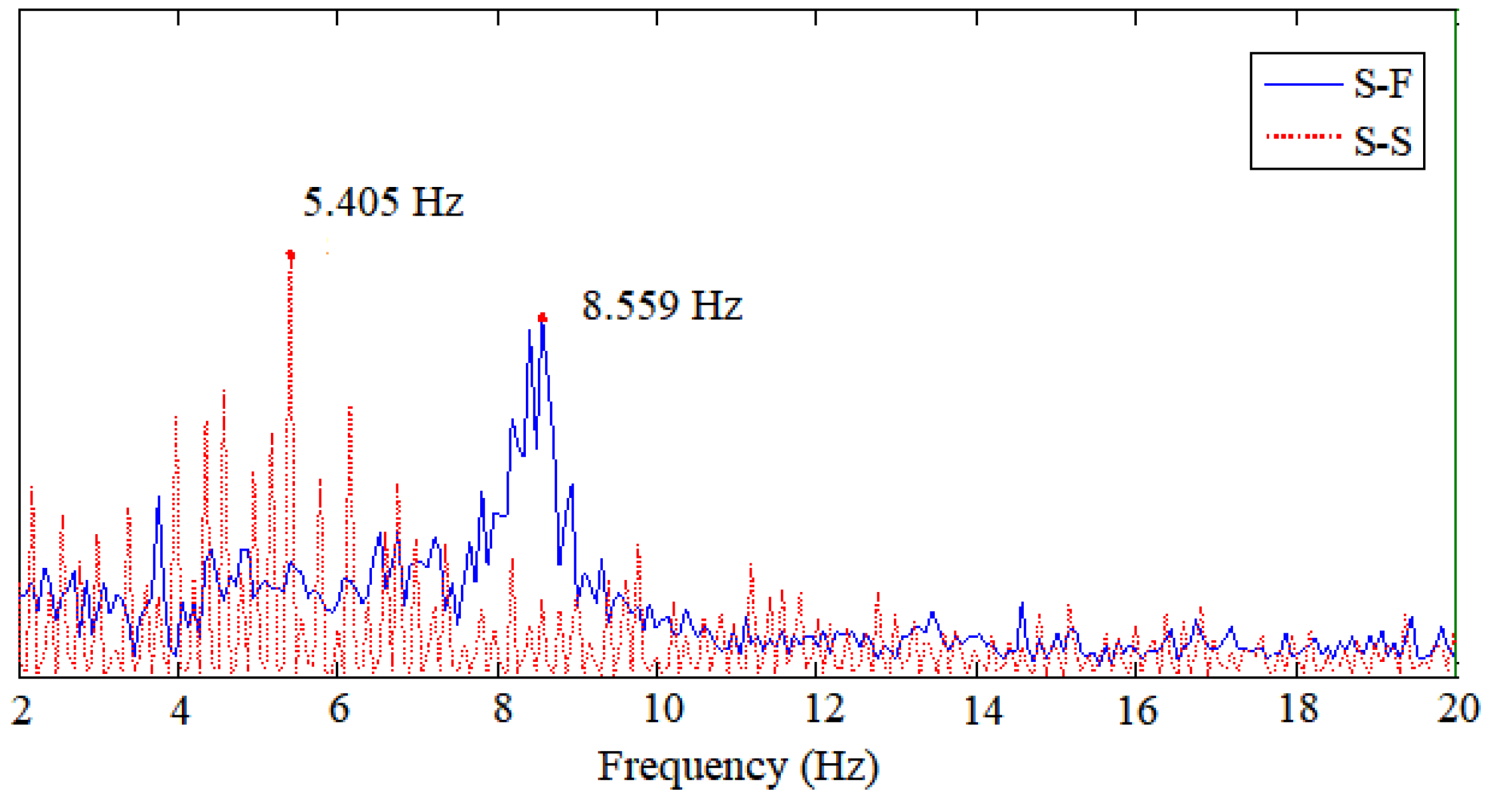
3.1. Natural Vibration Frequency in Water
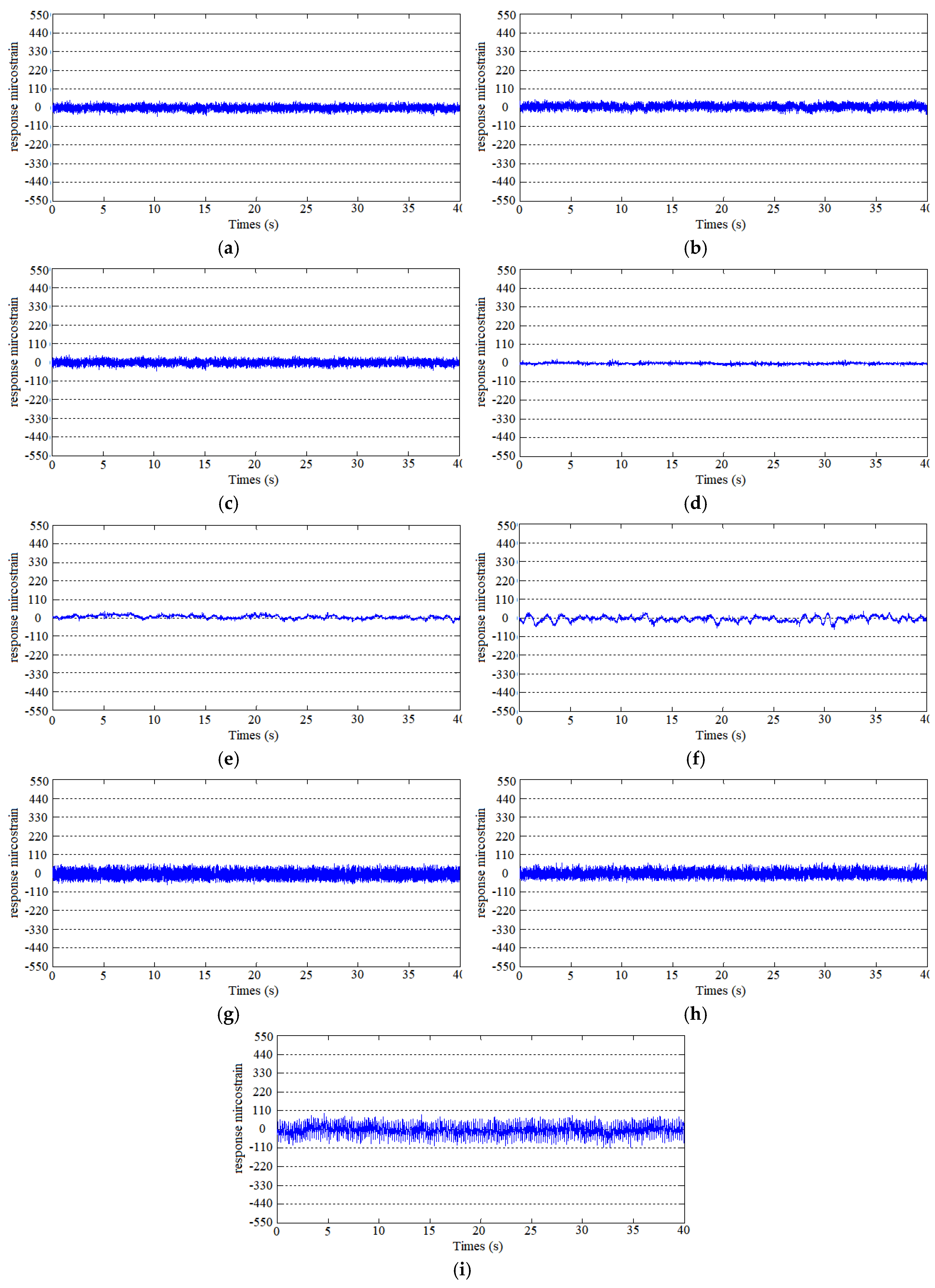
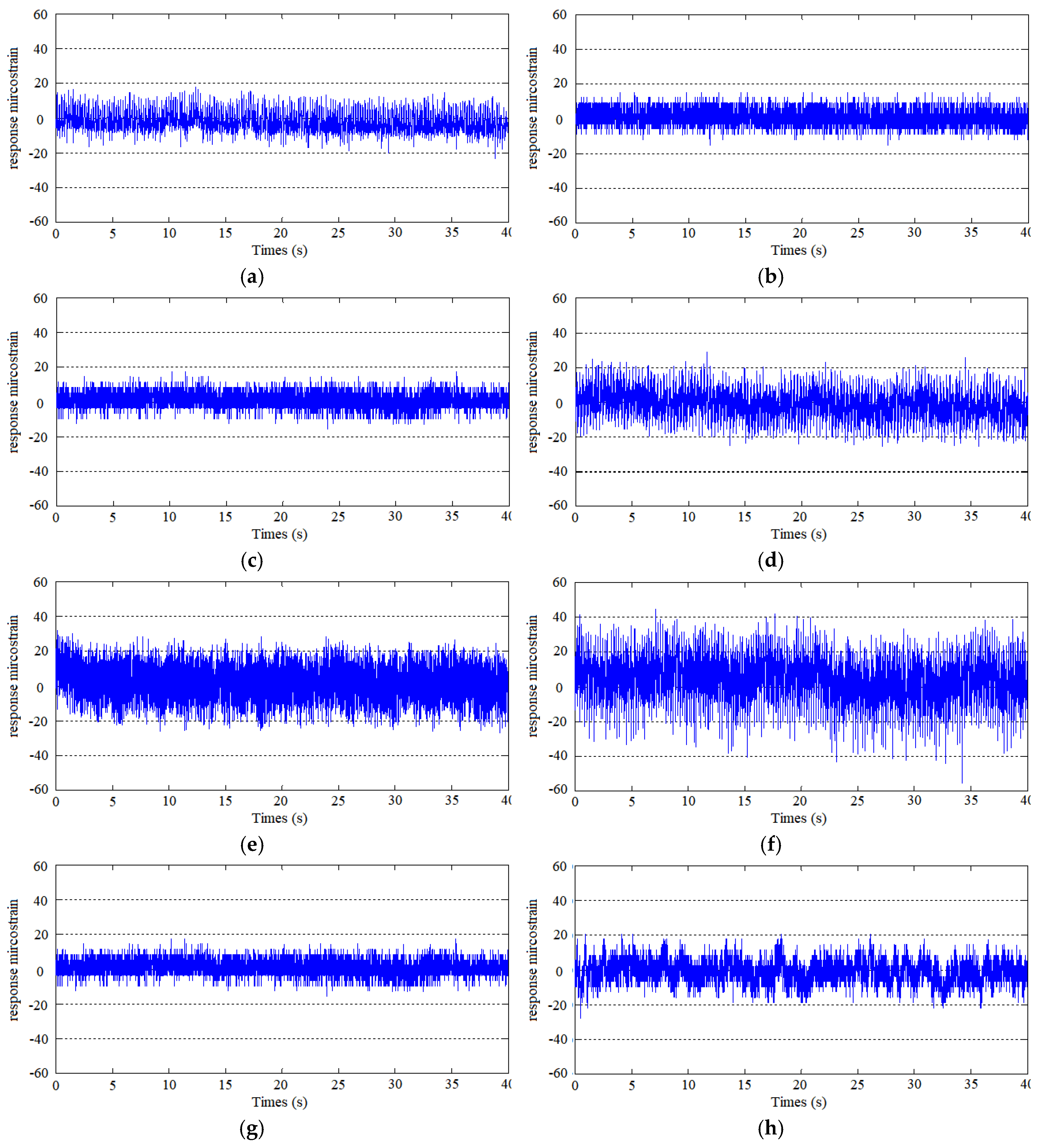
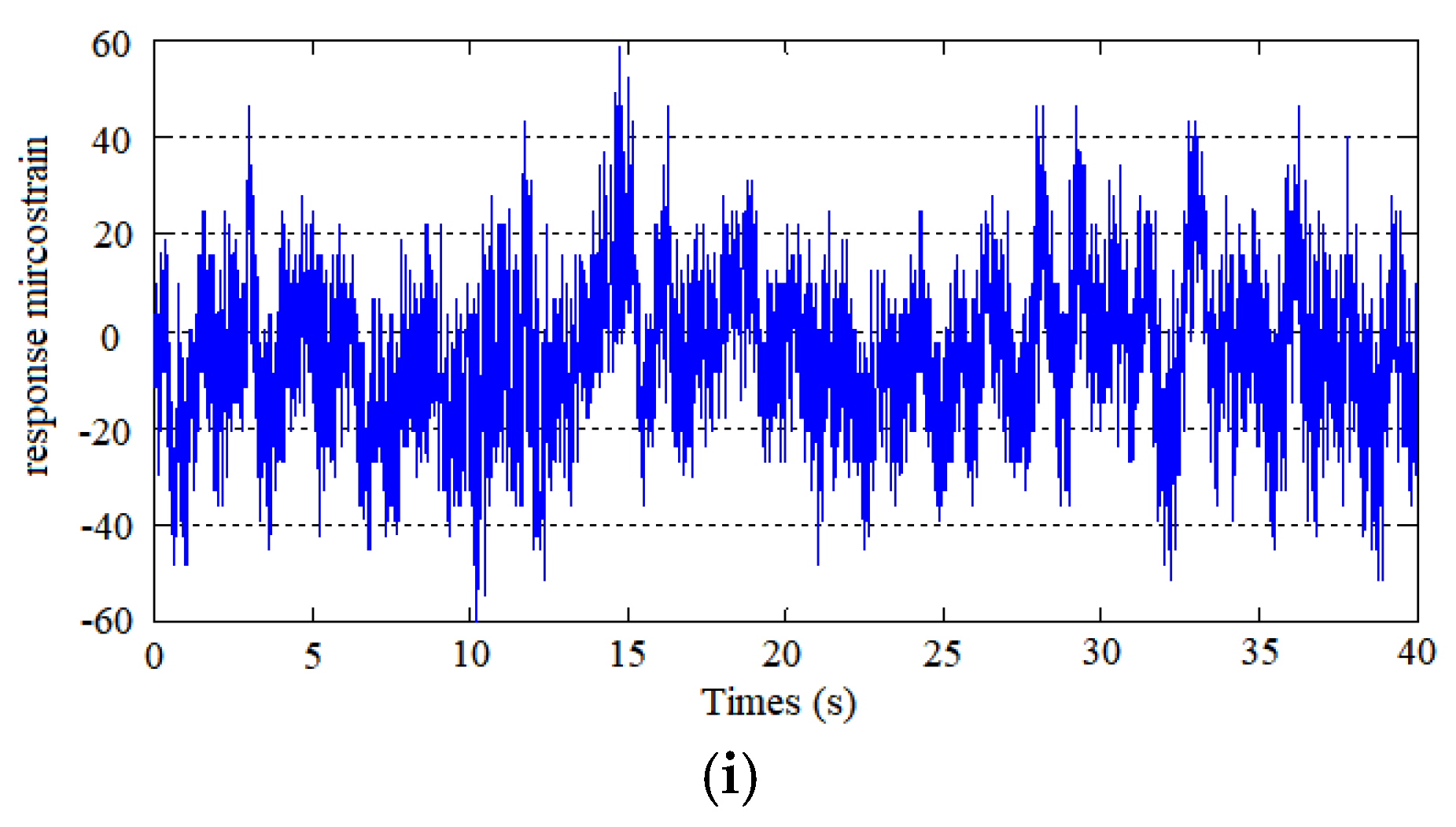
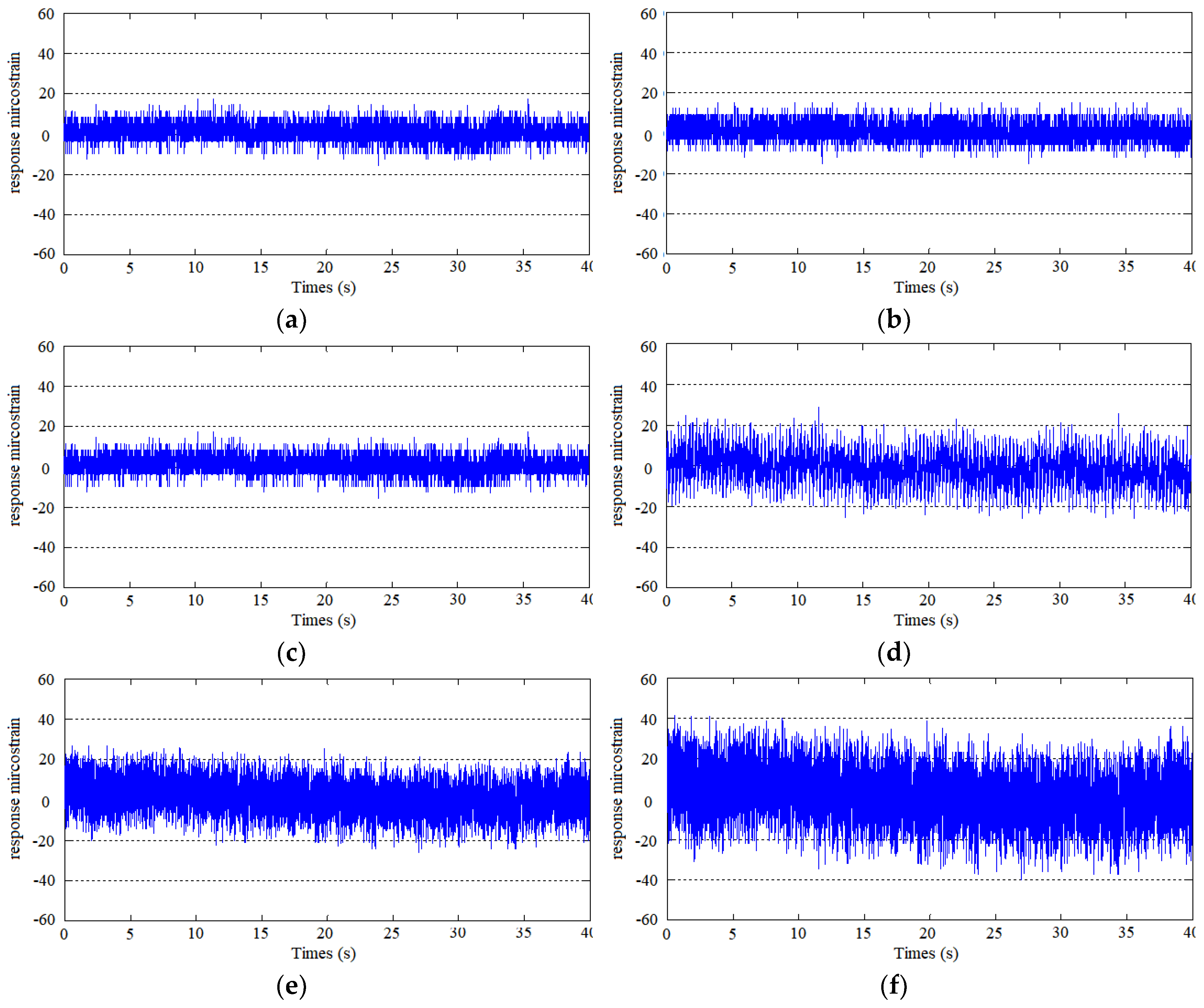
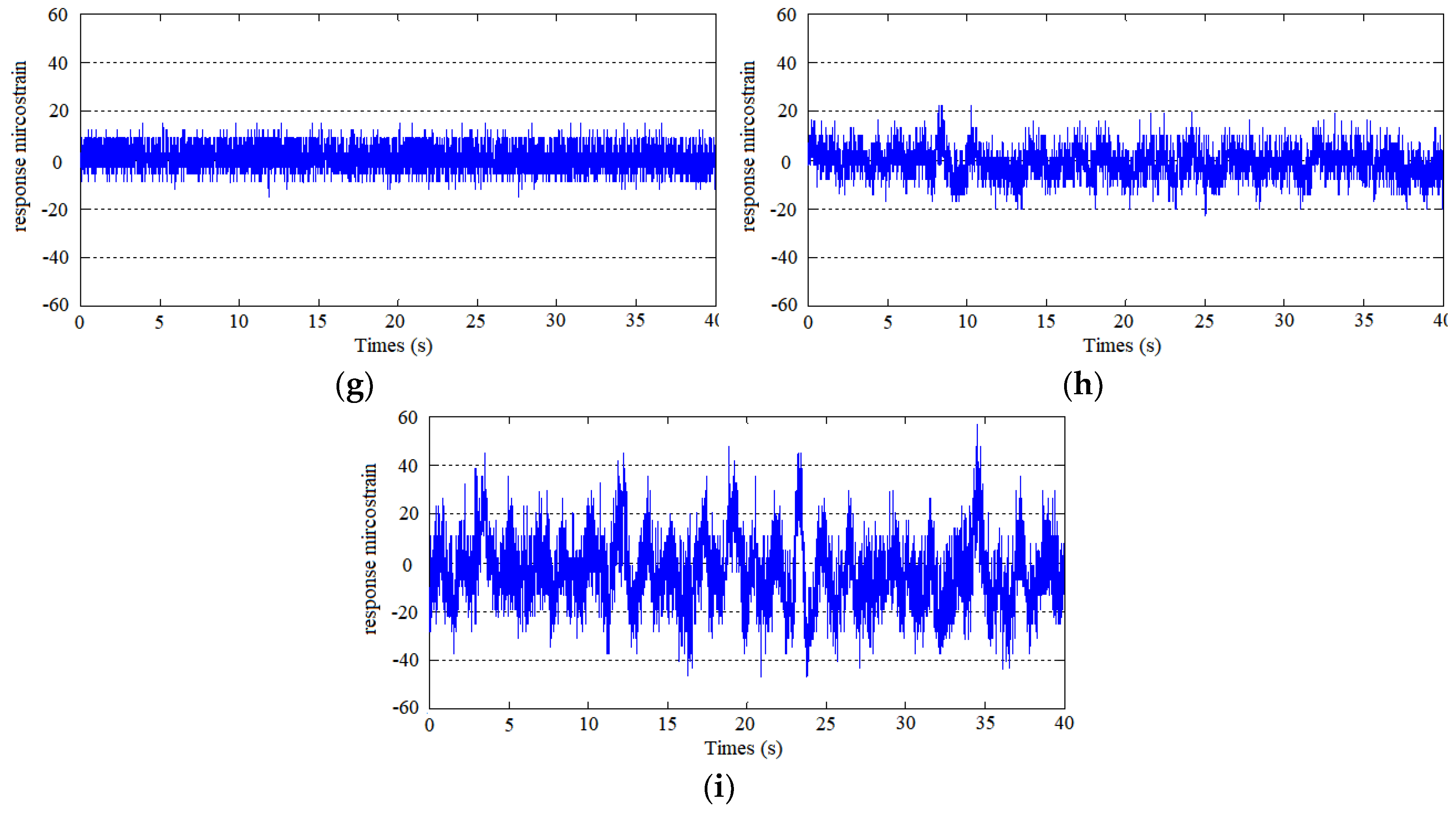
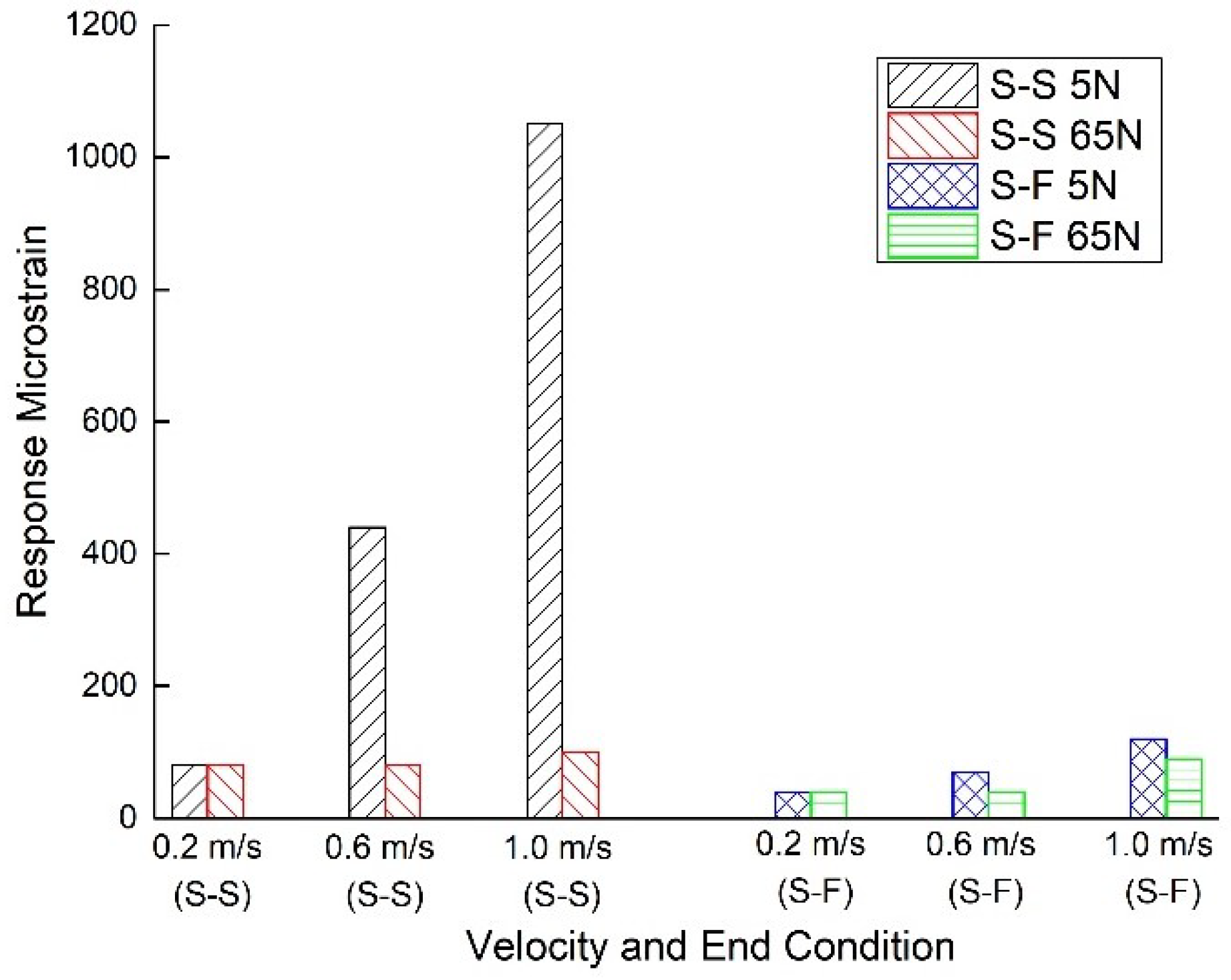
3.2. Vortex-Induced Vibration of the Risers
3.3. Grey Relational Analysis of Multiple Parameters
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The modulus of the riser, number of constraints and the top tension force is positively correlated with the natural vibration frequency.
- (2)
- The increase of modulus, number of constraints and top tension force and the reduction of velocity lead to a decrease in the amplitude of VIV for riser.
- (3)
- The lock-in phenomenon does not happen for Al riser under all experiment cases, while for the PMMA riser and the UPVC riser, the lock-in phenomenon occurs in specific experiment cases.
- (4)
- The S-F end condition leads to higher frequencies of VIV for the risers.
- (5)
- The grey relational grade of the influence on the amplitude of VIV for riser are: .
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, C.; Shankar, K.; Morozov, E.V. Tailored local design of deep sea frp composite risers. Adv. Compos. Mater. 2015, 24, 375–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shankar, K.; Morozov, E.V. Global design and analysis of deep sea frp composite risers under combined environmental loads. Adv. Compos. Mater. 2017, 26, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.K.; Frampton, R.E. Review of riser analysis techniques. Appl. Ocean Res. 1982, 4, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, C.P. Lightweight composite production risers for a deep water tension leg platform. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering (OMAE) Symposium, Tokyo, Japan, 13–18 April 1986; pp. 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Sparks, C.P.; Odru, P.; Bono, H.; Metivaud, G. Mechanical testing of high-performance composite tubes for tlp production risers. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 2–5 May 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Salama, M.M.; Johnson, D.B.; Long, J.R. Composite production riser-testing and qualification. SPE Prod. Facil. 1998, 13, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.L.; Leveque, M.E. Ultra-Deepwater Production Systems Technical-Progress Report; ConocoPhillips Company: Houston, TX, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, K.L.; Leveque, M.E. Ultra-Deepwater Production Systems-Final Report; ConocoPhillips Company: Houston, TX, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Picard, D.; Hudson, W.; Bouquier, L.; Dupupet, G.; Zivanovic, I. Composite carbon thermoplastic tubes for deepwater application. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 30 April–3 May 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Shankar, K.; Ashraf, M.A.; Morozov, E.V.; Ray, T. Surrogate-assisted optimisation design of composite riser. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2016, 230, 18–34. [Google Scholar]
- Smits, A.; Neto, T.B.; Boer, H.D. Thermoplastic composite riser development for ultradeep water. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 30 April–3 May 2018; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Shankar, K.; Morozov, E.V. Tailored design of top-tensioned composite risers for deep-water applications using three different approaches. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 1687814016684271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarpkaya, T. Fluid forces on oscillating cylinders. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Div. 1978, 104, 275–290. [Google Scholar]
- Gopalkrishnan, R. Vortex Induced Forces on Oscillating Bluff Cylinders; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Khalak, A.; Williamson, C.H.K. Motions, forces and mode transitions in vortex-induced vibrations at low mass-damping. JFS 1999, 13, 813–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govardhan, R.; Williamson, C.H.K. Resonance forever: Existence of a critical mass and an infinite regime of resonance in vortex-induced vibration. J. Fluid Mech. 2002, 473, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B. Prediction model and influence factors on vortex-induced vibration of deepwater risers. J. Harbin Eng. Univ. 2017, 38, 338–343. [Google Scholar]
- Tsahalis, D.; Jones, W. The effect of the sea-bottom proximity of the fatigue life of suspended spans of offshore pipelines undergoing vortex-induced vibrations. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 3–6 May 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Tsahalis, D.T. Vortex-induced vibrations due to steady and wave-induced currents of a flexible cylinder near a plane boundary. J. Offshore Mech. Arct. Eng. 1987, 109, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsahalis, D. Vortex-induced vibrations of a flexible cylinder near a plane boundary exposed to steady and wave-induced currents. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 1984, 106, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsahalis, D.; Jones, T.W. Vortex-induced vibrations of a flexible cylinder near a plane boundary in steady flow. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 4–7 May 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Hartlen, R.T.; Currie, I.G. Lift-oscillator model of vortex-induced vibration. J. Eng. Mech. Div. 1970, 96, 577–591. [Google Scholar]
- Skop, R.A.; Griffin, O.M. On a theory for the vortex-excited oscillations of flexible cylindrical structures. J. Sound Vib. 1975, 41, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.J.; Perkins, N.C. Two-dimensional vortex-induced vibration of cable suspensions. JFS 2002, 16, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchinetti, M.L.; de Langre, E.; Biolley, F. Coupling of structure and wake oscillators in vortex-induced vibrations. JFS 2004, 19, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.M.; Huang, W.P. A New Model for Predicting Vortex-Induced Vibration of a Long Flexible Riser with Large Deformation. J. Vib. Shock 2013, 32, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, F. Experimental investigation of the effect of internal flow on top tension of the riser. Period. Ocean Univ. China 2015, 45, 102–109. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, M.; Yu, C. Dynamic responses of a riser under combined excitation of internal waves and background currents. Int. J. Nav. Arch. Ocean Eng. 2014, 6, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.G.; Shao, W.D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.Y.; Gui, L. Dynamic Response Analysis for Coupled Parametric Vibration and Vortex-Induced Vibration of Top-Tensioned riser in Deep-Sea. Eng. Mech. 2013, 30, 282–286. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Guo, H.; Zhao, J. Numerical simulaiton of flow around two tandem circular cylinder of equal dimeter. Period. Ocean Univ. China 2013, 43, 92–97. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, C.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. Numerical investigation on vortex-induced vibration of an elastically mounted circular cylinder at low reynolds number using the fictitious domain method. IJCFD 2011, 25, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.B.; Chen, Y.; Jaiman, R.K.; Sun, X.; Tan, V.B.C.; Tay, T.E. Coupled fluid–structure simulations for evaluating a performance of full-scale deepwater composite riser. Ocean Eng. 2015, 94, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.Z. Composite ttr design for an ultradeepwater tlp. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 2–5 May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Tan, L.B.; Jaiman, R.K.; Sun, X.; Tay, T.E.; Tan, V.B.C. Global-local analysis of a full-scale composite riser during vortex-induced vibration. In Proceedings of the ASME 2013 32nd International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering, Nantes, France, 9–14 June 2013; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Sun, M.; Shankar, K.; Xing, S.; Zhang, L. Cfd simulation of vortex induced vibration for frp composite riser with different modeling methods. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán, J.; Granada, E.; Míguez, J.L.; Porteiro, J. Use of grey relational analysis to assess and optimize small biomass boilers. Fuel Process. Technol. 2006, 87, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju-Long, D. Control problems of grey systems. Syst. Control Lett. 1982, 1, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.L. Introduction to grey system theory. J. Grey Syst. 1989, 1, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, M.F.; Lu, H.C. Evaluating weapon systems based on grey relational analysis and fuzzy arithmetic operations. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. 2000, 23, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-C.; Yeh, M.-F. Robot path planning based on modified grey relational analysis. CySys 2002, 33, 129–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.; Yeh, M. Grey relational analysis based approach for data clustering. IEE Proc. Vis. Image Signal Process. 2005, 152, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blevins, R.D. Flow-Induced Vibratin, 2nd ed.; Krieger Publishing Company: Malabar, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B.C.; Szu-Lang, T.; Chien-Chih, W. Machine vision-based gray relational theory applied to ic marking inspection. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 2002, 15, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.J.; Lu, I.J.; Lewis, C. Grey relation performance correlations among economics, energy use and carbon dioxide emission in taiwan. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 1948–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, C.-P. Manufacturing process optimization for wear property of fiber-reinforced polybutylene terephthalate composites with grey relational analysis. Wear 2003, 254, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. | Materials | O.D. (m) | I.D. (m) | Length (m) | Density (kg/m−3) | Modulus (Pa) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Al | 0.02 | 0.016 | 1.25 | 3043.17 | 70 × 109 | |
| 2 | PMMA | 0.02 | 0.016 | 1.25 | 1549.89 | 3.5 × 109 | |
| 3 | UPVC | 0.02 | 0.016 | 1.25 | 1153.57 | 2.0 × 109 |
| Materials | Top Tension Force (N) | End Conditions | Velocities (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al/PMMA/UPVC | 5/65 | S-S/S-F | 0.2/0.6/1.0 |
| No. | Parameters | No. | Parameters | No. | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Al, 5 N, S-S, 0.2 m/s | 2 | Al, 5 N, S-S, 0.6 m/s | 3 | Al, 5 N, S-S, 1.0 m/s |
| 4 | Al, 5 N, S-F, 0.2 m/s | 5 | Al, 5 N, S-F, 0.6 m/s | 6 | Al, 5 N, S-F, 1.0 m/s |
| 7 | Al, 65 N, S-S, 0.2 m/s | 8 | Al, 65 N, S-S, 0.6 m/s | 9 | Al, 65 N, S-S, 1.0 m/s |
| 10 | Al, 65 N, S-F, 0.2 m/s | 11 | Al, 65 N, S-F, 0.6 m/s | 12 | Al, 65 N, S-F, 1.0 m/s |
| 13 | PMMA, 5 N, S-S, 0.2 m/s | 14 | PMMA, 5 N, S-S, 0.6 m/s | 15 | PMMA, 5 N, S-S, 1.0 m/s |
| 16 | PMMA, 5 N, S-F, 0.2 m/s | 17 | PMMA, 5 N, S-F, 0.6 m/s | 18 | PMMA, 5 N, S-F, 1.0 m/s |
| 19 | PMMA, 65 N, S-S, 0.2 m/s | 20 | PMMA, 65 N, S-S, 0.6 m/s | 21 | PMMA, 65 N, S-S, 1.0 m/s |
| 22 | PMMA, 65 N, S-F, 0.2 m/s | 23 | PMMA, 65 N, S-F, 0.6 m/s | 24 | PMMA, 65 N, S-F, 1.0 m/s |
| 25 | UPVC, 5 N, S-S, 0.2 m/s | 26 | UPVC, 5 N, S-S, 0.6 m/s | 27 | UPVC, 5 N, S-S, 1.0 m/s |
| 28 | UPVC, 5 N, S-F, 0.2 m/s | 29 | UPVC, 5 N, S-F, 0.6 m/s | 30 | UPVC, 5 N, S-F, 1.0 m/s |
| 31 | UPVC, 65 N, S-S, 0.2 m/s | 32 | UPVC, 65 N, S-S, 0.6 m/s | 33 | UPVC, 65 N, S-S, 1.0 m/s |
| 34 | UPVC, 65 N, S-F, 0.2 m/s | 35 | UPVC, 65 N, S-F, 0.6 m/s | 36 | UPVC, 65 N, S-F, 1.0 m/s |
| S-S | S-F | |
|---|---|---|
| Al | 18.302 (T = 5 N) | 22.019 (T = 5 N) |
| 20.551 (T = 65 N) | 25.7911 (T = 65 N) | |
| PMMA | 6.251 (T = 5 N) | 8.096 (T = 5 N) |
| 7.582 (T = 65 N) | 9.395 (T = 65 N) | |
| UPVC | 4.429 (T = 5 N) | 6.006 (T = 5 N) |
| 5.521 (T = 65 N) | 6.456 (T = 65 N) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Cui, Y.; Ge, S.; Sun, M.; Jia, Z. Experimental Study on Vortex-Induced Vibration of Risers Considering the Effects of Different Design Parameters. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2411. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122411
Wang C, Cui Y, Ge S, Sun M, Jia Z. Experimental Study on Vortex-Induced Vibration of Risers Considering the Effects of Different Design Parameters. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(12):2411. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122411
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chunguang, Yangyang Cui, Shiquan Ge, Mingyu Sun, and Zhirong Jia. 2018. "Experimental Study on Vortex-Induced Vibration of Risers Considering the Effects of Different Design Parameters" Applied Sciences 8, no. 12: 2411. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122411
APA StyleWang, C., Cui, Y., Ge, S., Sun, M., & Jia, Z. (2018). Experimental Study on Vortex-Induced Vibration of Risers Considering the Effects of Different Design Parameters. Applied Sciences, 8(12), 2411. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122411





