Fracture Toughness of Hybrid Components with Selective Laser Melting 18Ni300 Steel Parts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
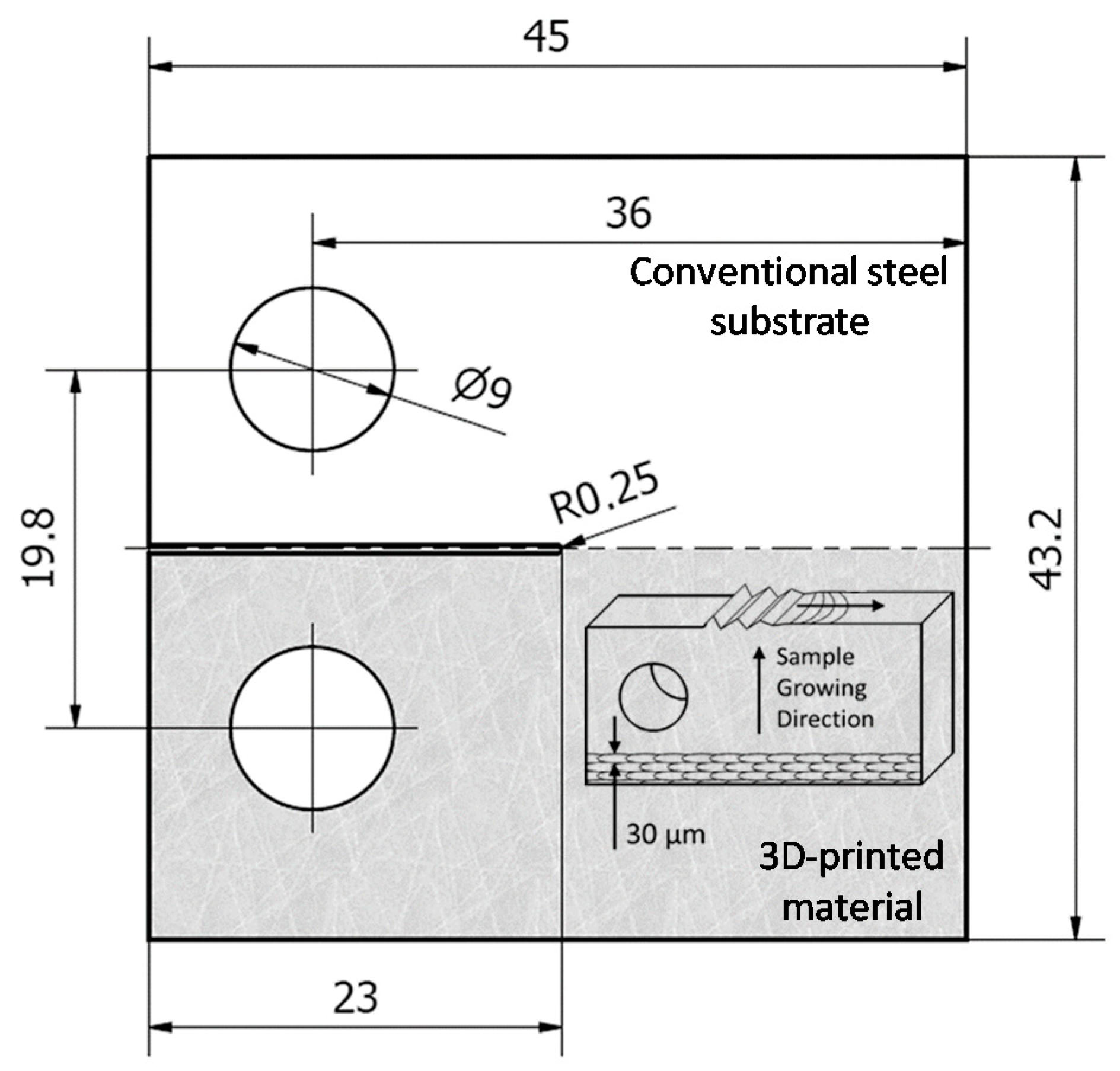
2.1. Materials and Specimens Manufacturing
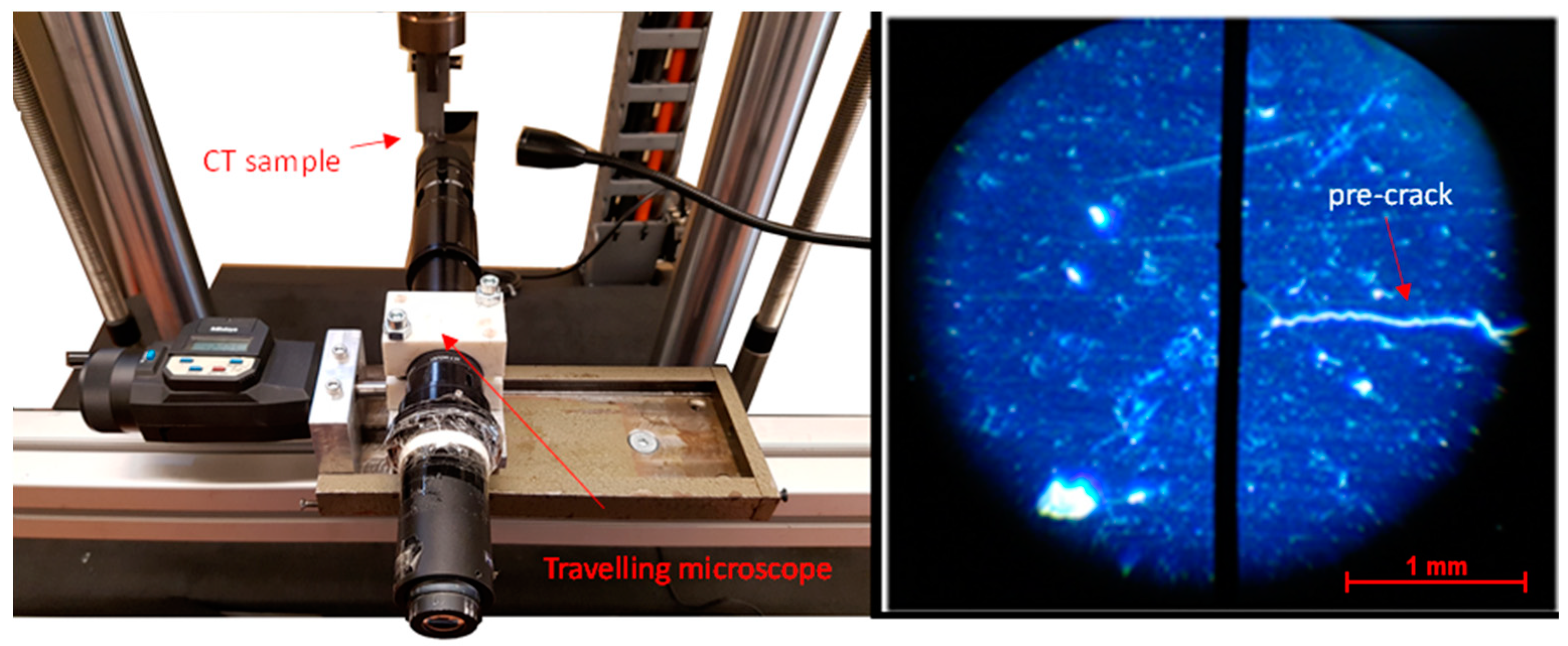
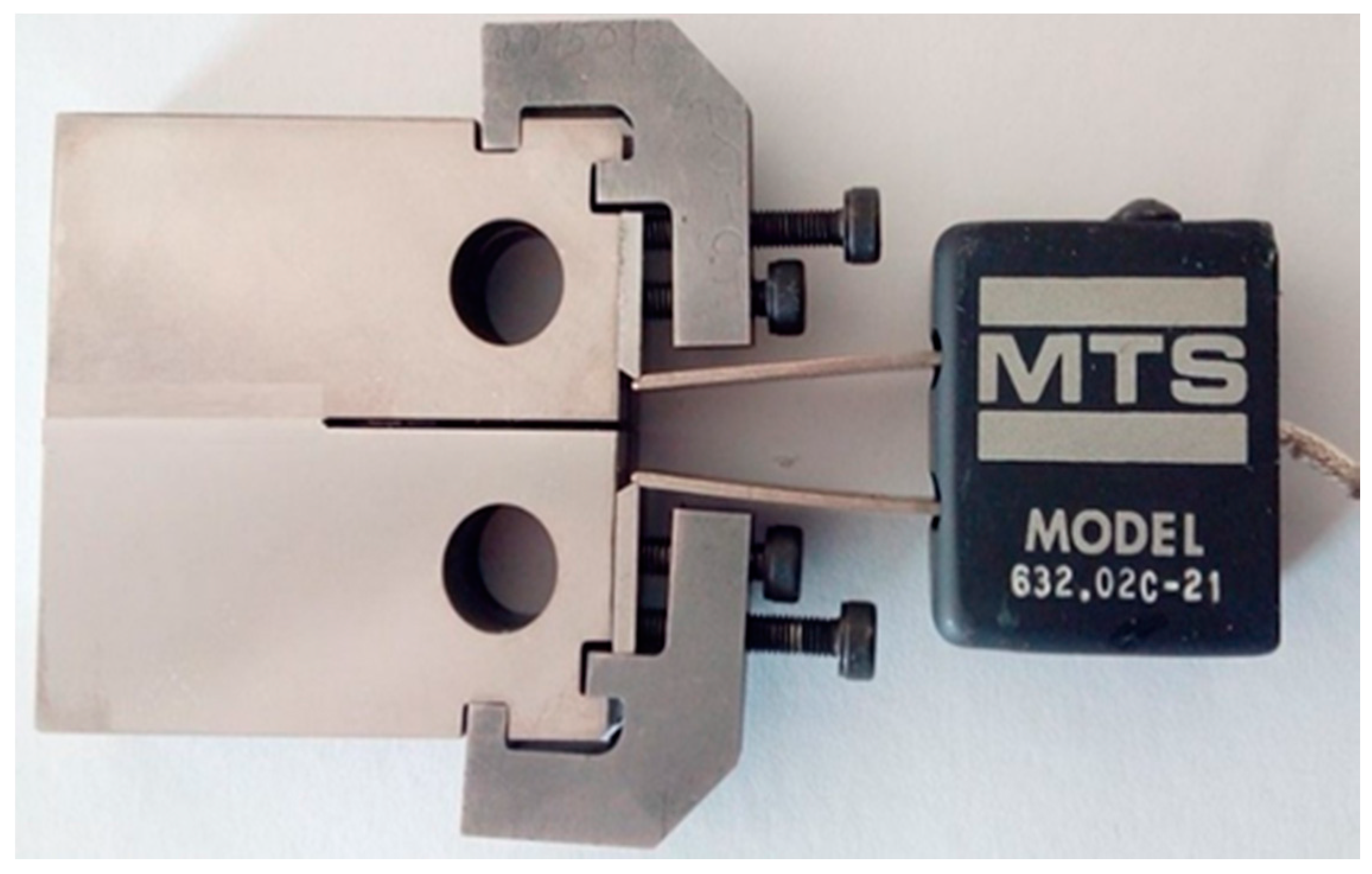
2.2. Fracture Toughness Tests
3. Results and Discussion
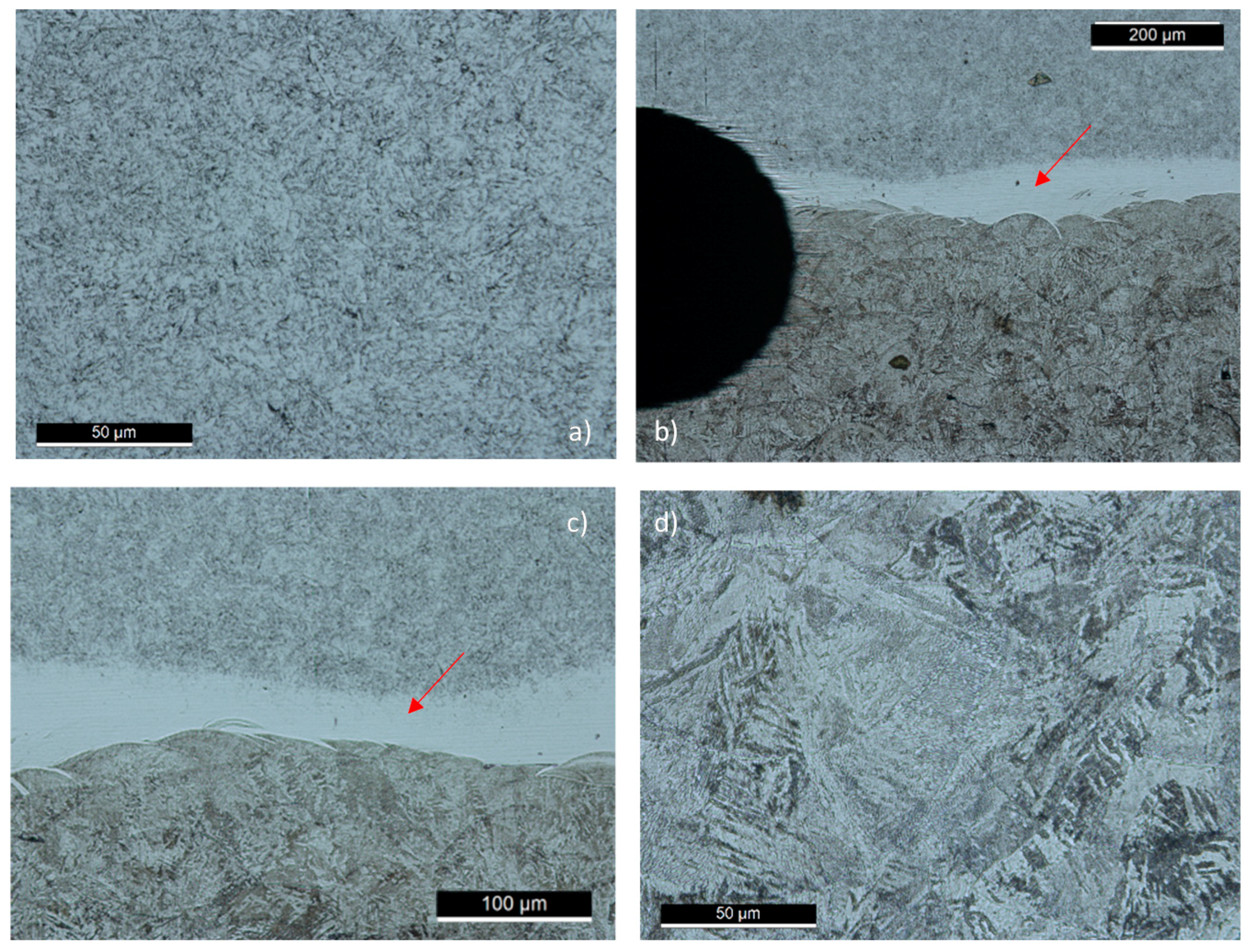
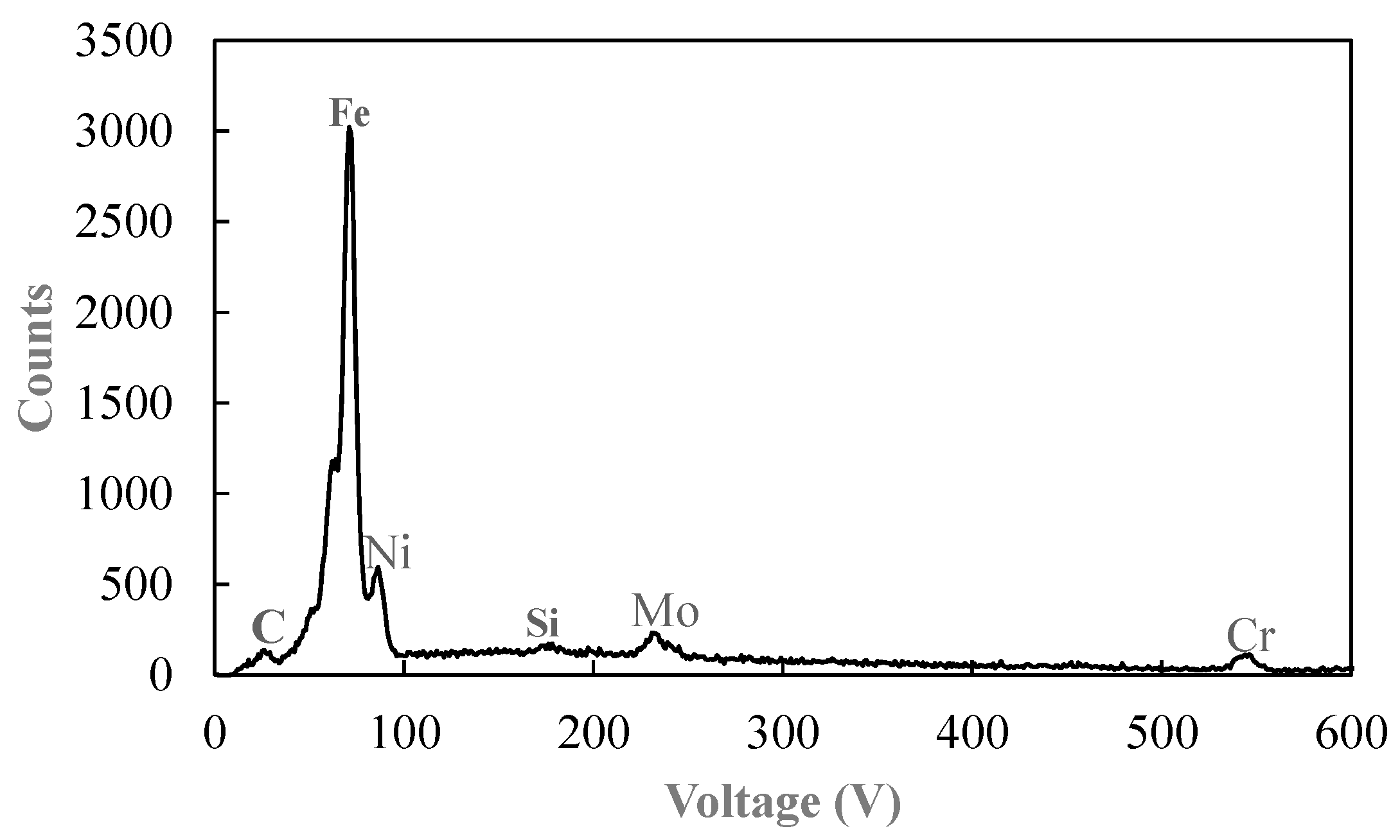
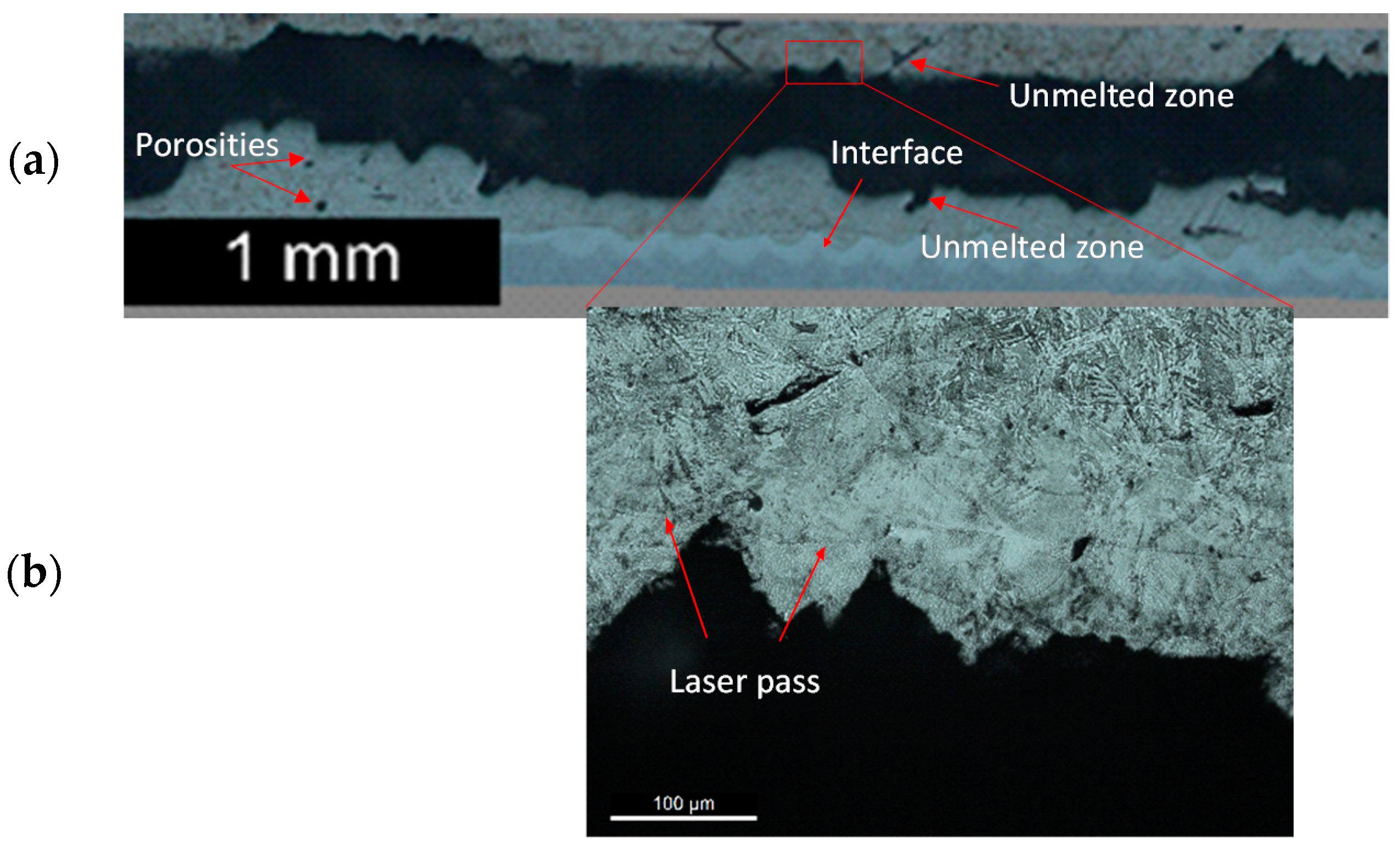
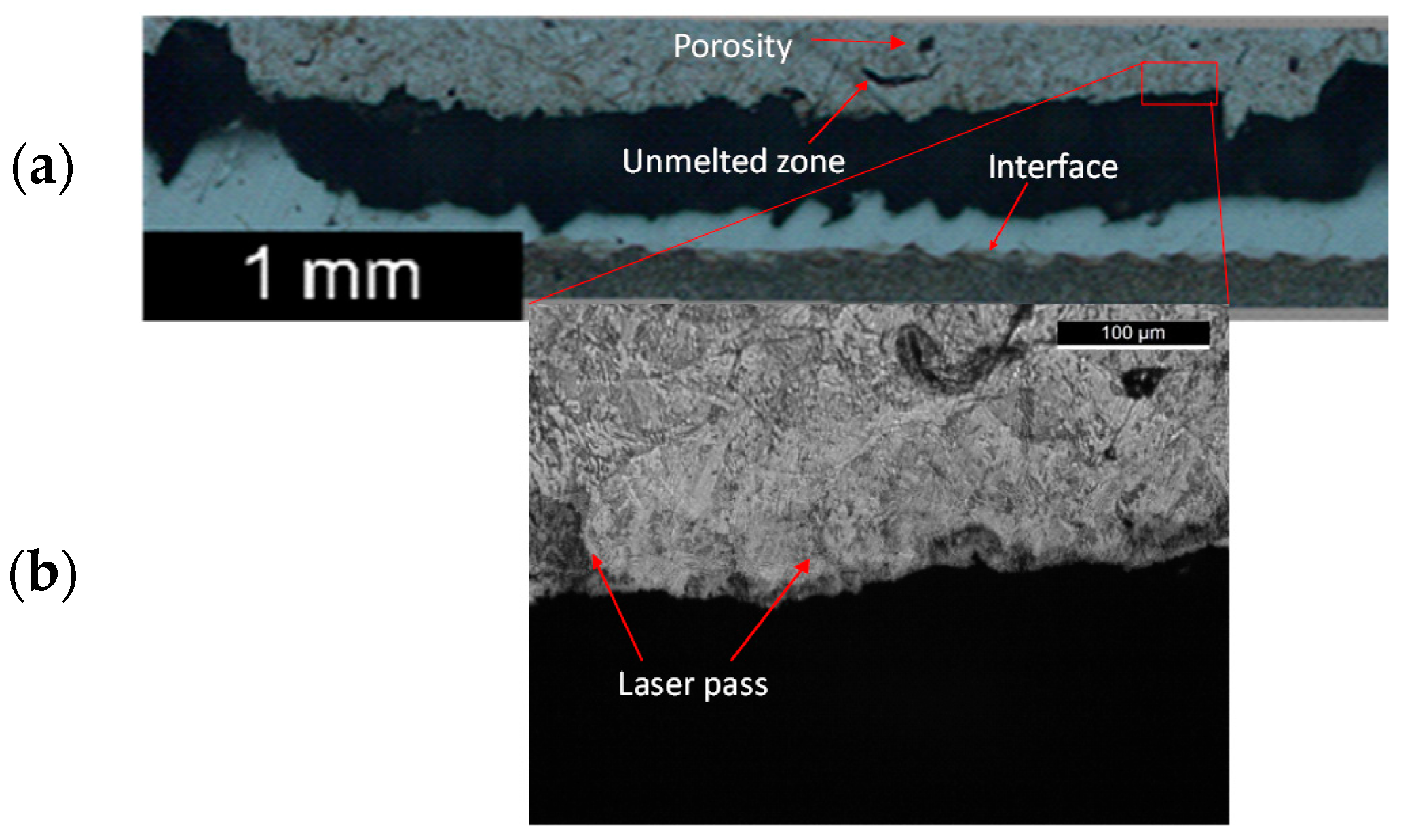
3.1. Metallographic Analysis
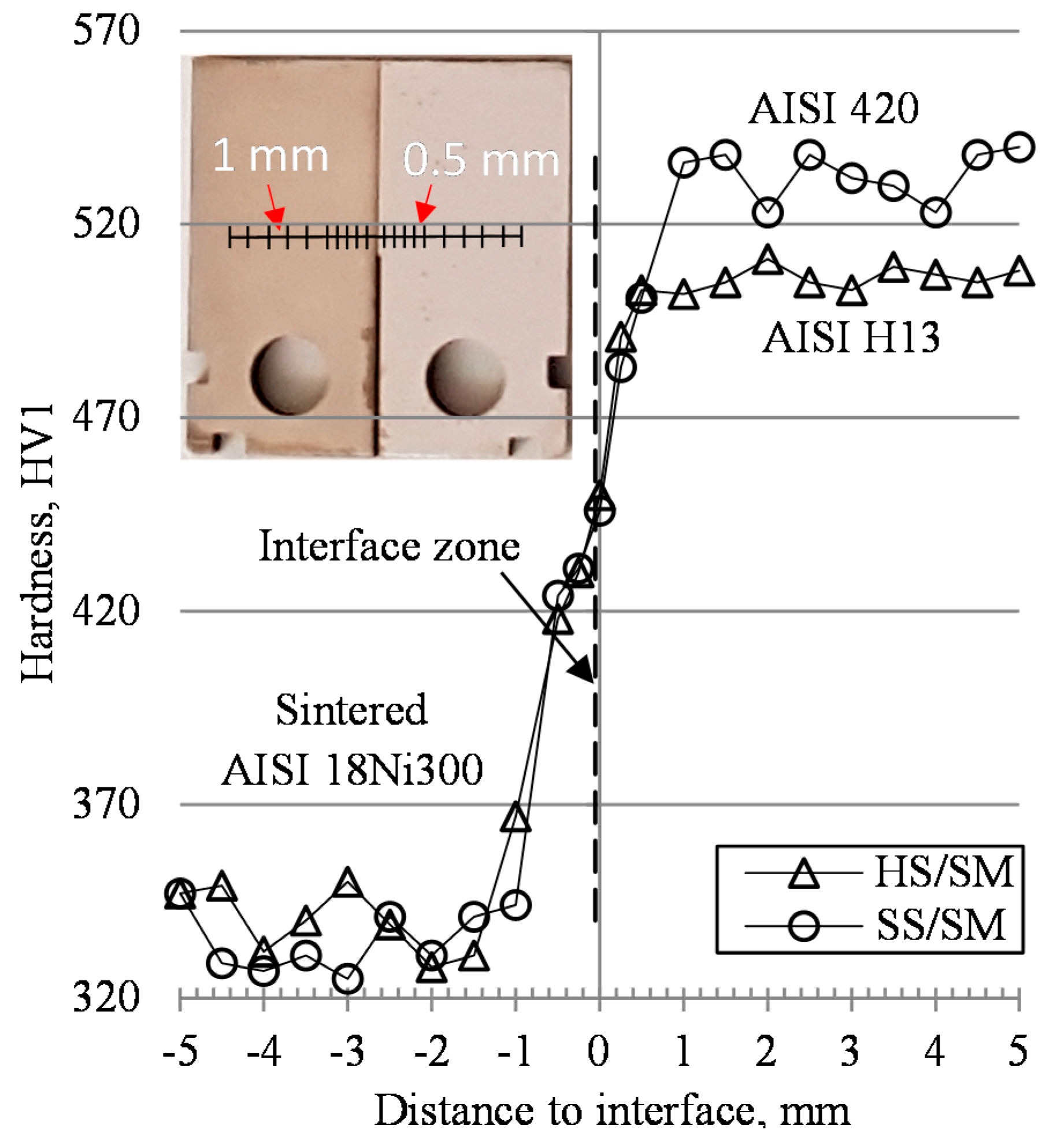
3.2. Microhardness
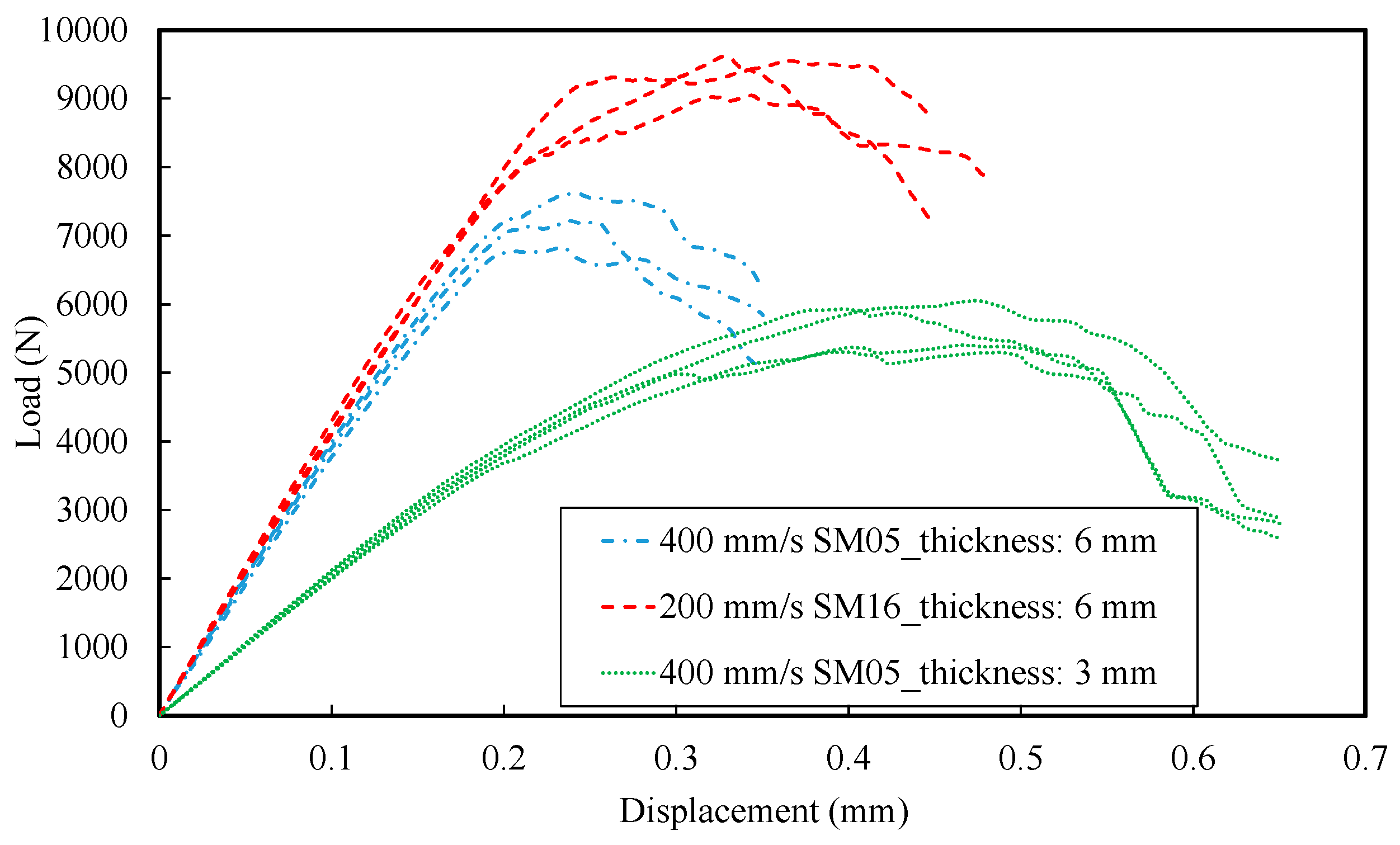
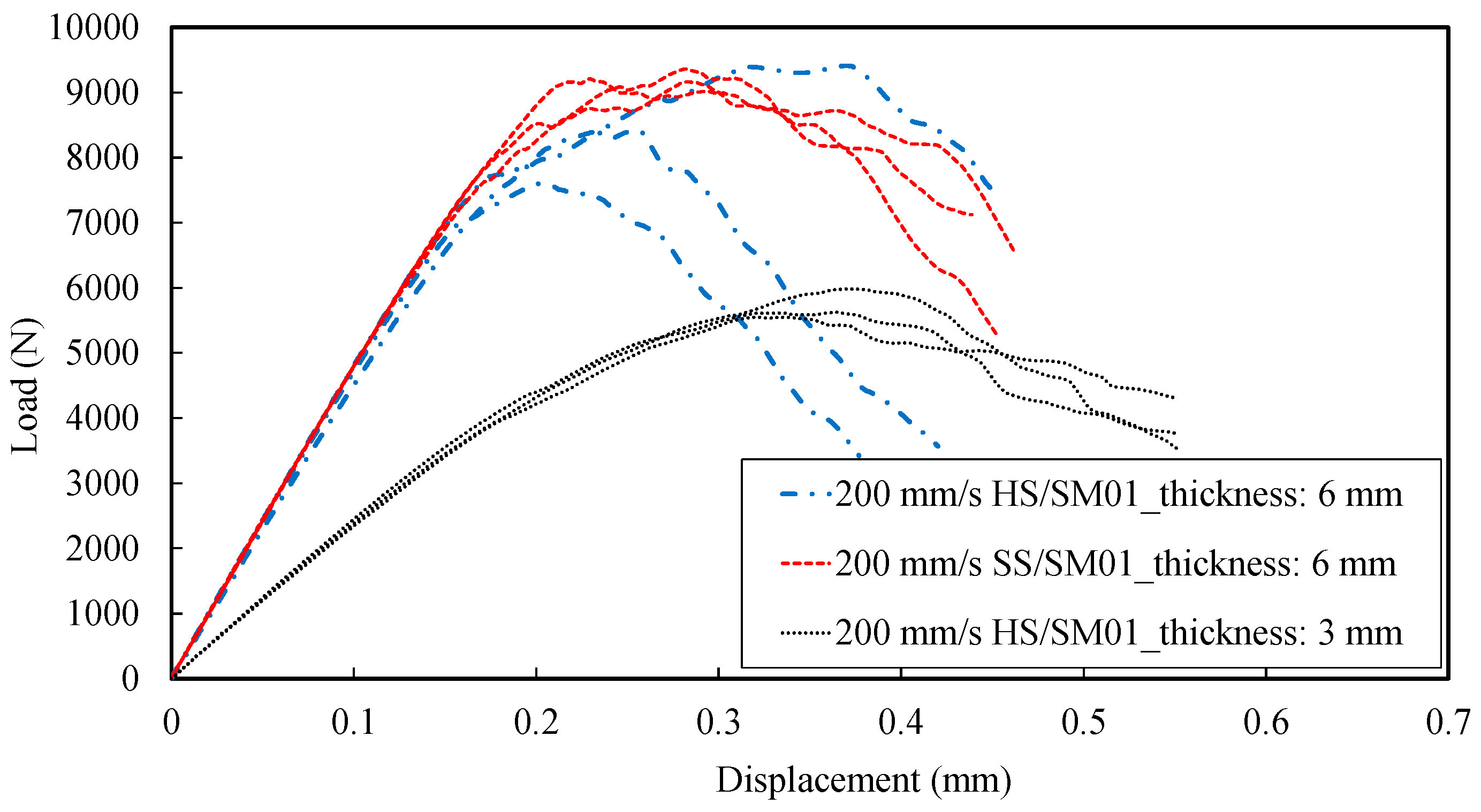
3.3. Fracture Tests: Load vs. Displacement Curves
3.4. Fracture Toughness
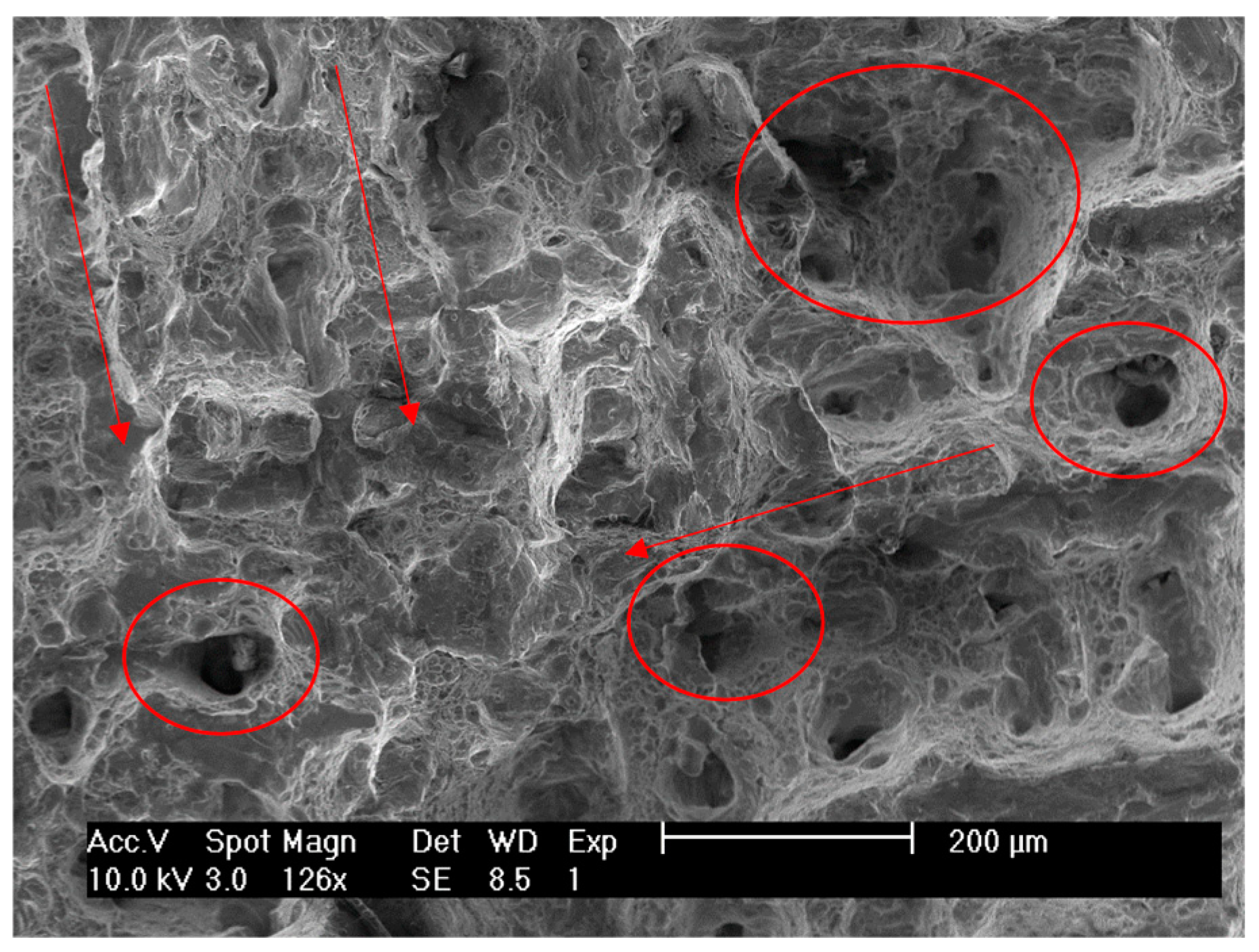
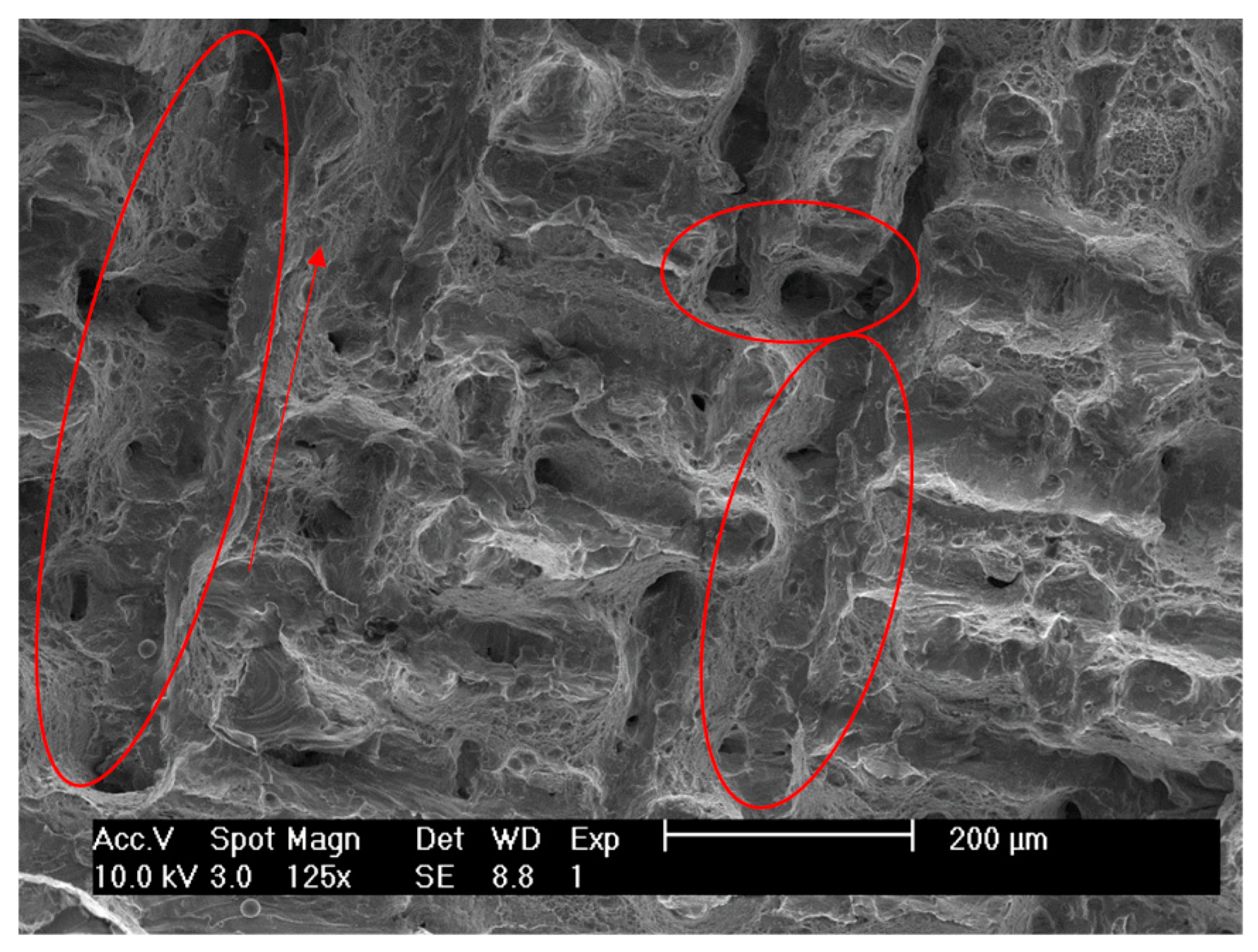
3.5. Fracture Surface Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fayazfar, H.; Salarian, M.; Rogalsky, A.; Sarker, D.; Russo, P.; Paserin, V.; Toyserkan, E. A critical review of powder-based additive manufacturing of ferrous alloys: Process parameters, microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Des. 2018, 144, 98–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balc, N.C.; Berce, P.; Pacurar, R. Comparison between SLM and SLS in producing complex metal parts. In Annals of DAAAM for 2010 & Proceeding of the 21st International DAAAM Symposium, Volume 21, No. 1, ISSN 1726-9679; DAAAM International: Vienna, Austria, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, J.M.; Ferreira, J.M.; Capela, C. Fracture toughness of the heat affected zone on Nd-YAG laser welded joints. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2009, 16, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempena, K.; Yasaa, E.; Thijsb, L.; Krutha, J.-P.; Van Humbeeckb, J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Selective Laser Melted 18Ni-300 steel. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 725, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalino, G.; Campanelli, S.L.; Contuzzi, N.; Ludovico, A.D. Experimental investigation and statistical optimization of the selective laser melting process of a maraging steel. Opt. Laser Technol. 2015, 65, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, M. Influence mechanism of parameters process and mechanical properties evolution mechanism of maraging steel 300 by selective laser melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 703, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casatia, R.; Codurib, M.; Lecisa, N.; Andrianopolic, C.; Vedania, M. Microstructure and mechanical behavior of hot-work tool steels processed by Selective Laser Melting. Mater. Charact. 2018, 137, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsaei, N.; Yadollahi, A.; Bian, L.; Thompson, S.M. An overview of direct laser deposition for additive manufacturing; Part II: Mechanical behavior, process parameter optimization and control. Addit. Manuf. 2015, 8, 12–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.S.; Koike, M.; Mason, R.L.; Okabe, T. Fatigue life of titanium alloys fabricated by additive layer manufacturing techniques for dental implants. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 1010–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wycisk, E.; Emmelmann, C.; Siddique, S.; Walther, F. High cycle fatigue (HCF) performance of Ti-6Al-4V alloy processed by selective laser melting. Adv. Mater. Res. 2016, 816, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.J.; Zheng, D.L.; Li, H.X.; Jia, X.; Sun, J.F.; Li, Y.L.; Qian, M.; Yan, M. Selective laser melting of H13: Microstructure and residual stress. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 12476–12485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.M.S.; Ferreira, J.A.M.; Jesus, J.S.; Costa, J.M.; Capela, C. Fatigue behaviour of selective laser melting steel components. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2016, 85, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryawanshi, J.; Prashanth, K.G.; Ramamurty, U. Tensile, fracture, and fatigue crack growth properties of a 3D printed maraging steel through selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 725, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, M.; Brincat, P.; Leary, M.; Brandt, M. Numerical and experimental evaluation of a conformally cooled H13 steel injection mould manufactured with selective laser melting. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 93, 881–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, M.; Šafka, J.; Voleský, L.; Bobek, J. Impact Testing of H13 Tool Steel Processed with Use of Selective Laser Melting Technology. Mater. Sci. Forum 2018, 919, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyr, E.; Asgari, H.; Shamsdini, S.; Purdy, M.; Hosseinkhani, K.; Mohammadi, M. Fracture behaviour of additively manufactured MS1-H13 hybrid hard steels. Mater. Lett. 2018, 212, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.A.M.; Santos, L.M.S.; Jesus, J.S.; Costa, J.M.; Capela, C. Assessment of the fatigue life on functional hybrid laser sintering steel components. Proc. Struct. Integr. 2016, 1, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanelli, S.L.; Angelastro, A.; Signorile, C.G.; Casalino, G. Investigation on direct laser powder deposition of 18 Ni (300) marage steel using mathematical model and experimental characterization. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 89, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E8/E8M-16a. Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- BS 7448-3:1991. Fracture Mechanics Toughness tests, Part 1. Method for Determination of K1c, Critical CTOD and Critical J Values of Metallic Materials; British Standards Institution: London, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM Standard E3, 2011. Standard Guide for Preparation of Metallographic Specimens; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM Standard E384, 2011e1. Standard Test Method for Knoop and Vickers Hardness of Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isfahany, A.N.; Saghafian, H.; Borhani, G. The effect of heat treatment on mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of AISI420 martensitic stainless steel. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 3931–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, R.; Costa, J.D.M.; Berto, F.; Mohammad, S.; Ferreira, J.A.M.; Capela, C.; Santos, L.; Antunes, F. Low-Cycle Fatigue Behaviour of AISI 18Ni300 Maraging Steel Produced by Selective Laser Melting. Metals 2018, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marashi, J.; Yakushina, E.; Xirouchakis, P.; Zante, R.; Foster, J. An evaluation of H13 tool steel deformation in hot forging conditions. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 246, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolovich, S.D.; Risbeck, T.R.; Saxena, A.; Kawabe, Y. The effect of microstructure on the fracture toughness of 300 and 350 grade maraging steels. Eng. Fract. Mech. 1980, 13, 717–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Steel | C | Ni | Co | V | Mo | Ti | Al | Cr | P | Si | Mn | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18Ni300 (powder) | 0.01 | 18.2 | 9.0 | - | 5.0 | 0.6 | 0.05 | 0.3 | 0.01 | 0.1 | 0.04 | Balance |
| AISI H13 (CM) | 0.4 | - | - | 0.94 | 1.30 | - | - | 5.29 | 0.017 | 1.05 | 0.036 | Balance |
| AISI 420 (CM) | 0.37 | - | - | 0.17 | - | - | - | 14.22 | 0.021 | 0.64 | 0.037 | Balance |
| Specimen | SM | SS/SM | HS/SM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scan rate (mm/s) | 200 | 400 | 200 | 400 | 200 | 400 |
| Ultimate Tensile Stress [MPa] | 1147 | 1032 | 1135 | 1000 | 1146 | 1000 |
| Yield stress [MPa] | 1000 | 910 | 1115 | 900 | 1125 | 900 |
| Extension at break [%] | 6 | 2.2 | 3.6 | 1.5 | 4.2 | 1.7 |
| Young‘s modulus [GPa] | 180 | 180 | 190 | 180 | 190 | 180 |
| Sample Reference | Valid KQ = KIc | KQ (MPa.m1/2) | Average KQ (MPa.m1/2) | Jc (N/mm) | Average Jc (N/mm) | Critical Crack, ac (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2SM01_3 | No | 72.99 | 80.17 ± 6.71 | 59.23 | 65.68 ± 5.35 | 31.26 |
| 2SM02_3 | No | 80.44 | 67.86 | 31.31 | ||
| 2SM03_3 | Yes | 90.85 | 73.26 | 31.11 | ||
| 2SM04_3 | No | 76.40 | 62.4 | 31.96 | ||
| 2SM13_6 | No | 76.38 | 72.85 ± 4.26 | 42.9 | 42.4 ± 2.5 | 29.39 |
| 2SM14_6 | No | 68.93 | 40.1 | 30.62 | ||
| 2SM15_6 | No | 77.77 | 46.3 | 31.03 | ||
| 2SM16_6 | No | 68.32 | 40.3 | 29.11 | ||
| 4SM05_6 | No | 49.22 | 55.42 ± 4.71 | 19.71 | 18.65 ± 4.10 | 29.65 |
| 4SM06_6 | No | 52.56 | 12.27 | 28.89 | ||
| 4SM07_6 | No | 60.71 | 23.71 | 30.23 | ||
| 4SM08_6 | No | 59.18 | 18.93 | 30.06 |
| Sample Reference | Valid KQ = KIc | KQ (MPa.m1/2) | Average KQ (MPa.m1/2) | Jc (N/mm) | Average Jc (N/mm) | Crack to Fracture, ac (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2SS/SM01_3 | No | 83.22 | 83.9 ± 1.1 | 48.9 | 55.82 ± 7.13 | 32.03 |
| 2SS/SM02_3 | No | 82.46 | 48.5 | 31.98 | ||
| 2SS/SM03_3 | No | 85.15 | 62.7 | 31.45 | ||
| 2SS/SM04_3 | No | 84.75 | 63.21 | 31.67 | ||
| 2SS/SM01_6 | No | 67.71 | 70.97 ± 2.55 | 41.14 | 39.02 ± 1.52 | 30.58 |
| 2SS/SM03_6 | No | 71.24 | 37.59 | 29.91 | ||
| 2SS/SM04_6 | No | 73.95 | 38.33 | 31.06 | ||
| 4SS/SM01_6 | No | 54.76 | 56.47 ± 2.36 | 17.08 | 19.56 ± 2.5 | 28.98 |
| 4SS/SM02_6 | No | 57.84 | 19.53 | 29.05 | ||
| 4SS/SM03_6 | No | 59.59 | 23.64 | 29.86 | ||
| 4SS/SM04_6 | No | 53.69 | 18.02 | 30.14 |
| Sample Reference | Valid KQ = KIc | KQ (MPa.m1/2) | Average KQ (MPa.m1/2) | Jc (N/mm) | Average Jc (N/mm) | Crack to Fracture, ac (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2HS/SM01_3 | No | 73.93 | 73.66 ± 5.77 | 40.7 | 44.78 ± 16.17 | 32.13 |
| 2HS/SM02_3 | No | 81.7 | 71.55 | 32.98 | ||
| 2HS/SM03_3 | No | 73.03 | 38.71 | 30.47 | ||
| 2HS/SM04_3 | No | 65.99 | 28.17 | 30.51 | ||
| 2HS/SM01_6 | No | 61.54 | 65.41 ± 3.45 | 21.05 | 22.84 ± 4.1 | 28.58 |
| 2HS/SM03_6 | No | 64.77 | 24.9 | 29.71 | ||
| 2HS/SM04_6 | No | 69.91 | 17.24 | 30.03 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos, L.M.S.; De Jesus, J.; Ferreira, J.M.; Costa, J.D.; Capela, C. Fracture Toughness of Hybrid Components with Selective Laser Melting 18Ni300 Steel Parts. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101879
Santos LMS, De Jesus J, Ferreira JM, Costa JD, Capela C. Fracture Toughness of Hybrid Components with Selective Laser Melting 18Ni300 Steel Parts. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(10):1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101879
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, Luis M. S., Joel De Jesus, José M. Ferreira, José D. Costa, and Carlos Capela. 2018. "Fracture Toughness of Hybrid Components with Selective Laser Melting 18Ni300 Steel Parts" Applied Sciences 8, no. 10: 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101879
APA StyleSantos, L. M. S., De Jesus, J., Ferreira, J. M., Costa, J. D., & Capela, C. (2018). Fracture Toughness of Hybrid Components with Selective Laser Melting 18Ni300 Steel Parts. Applied Sciences, 8(10), 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101879






