Effects of Fine Particles on Thermal Conductivity of Mixed Silica Sands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
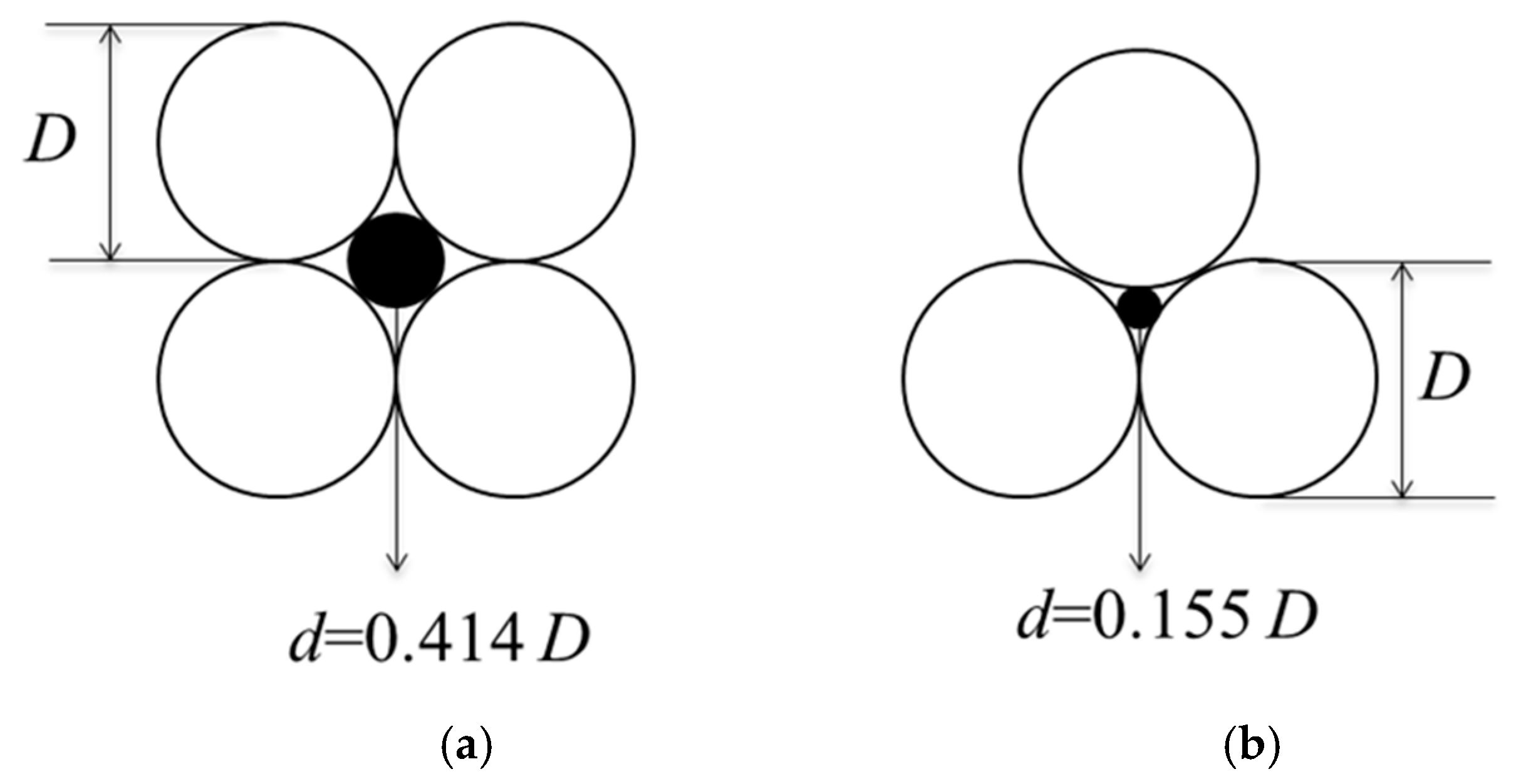
2. Thermal Properties
3. Experimental Study
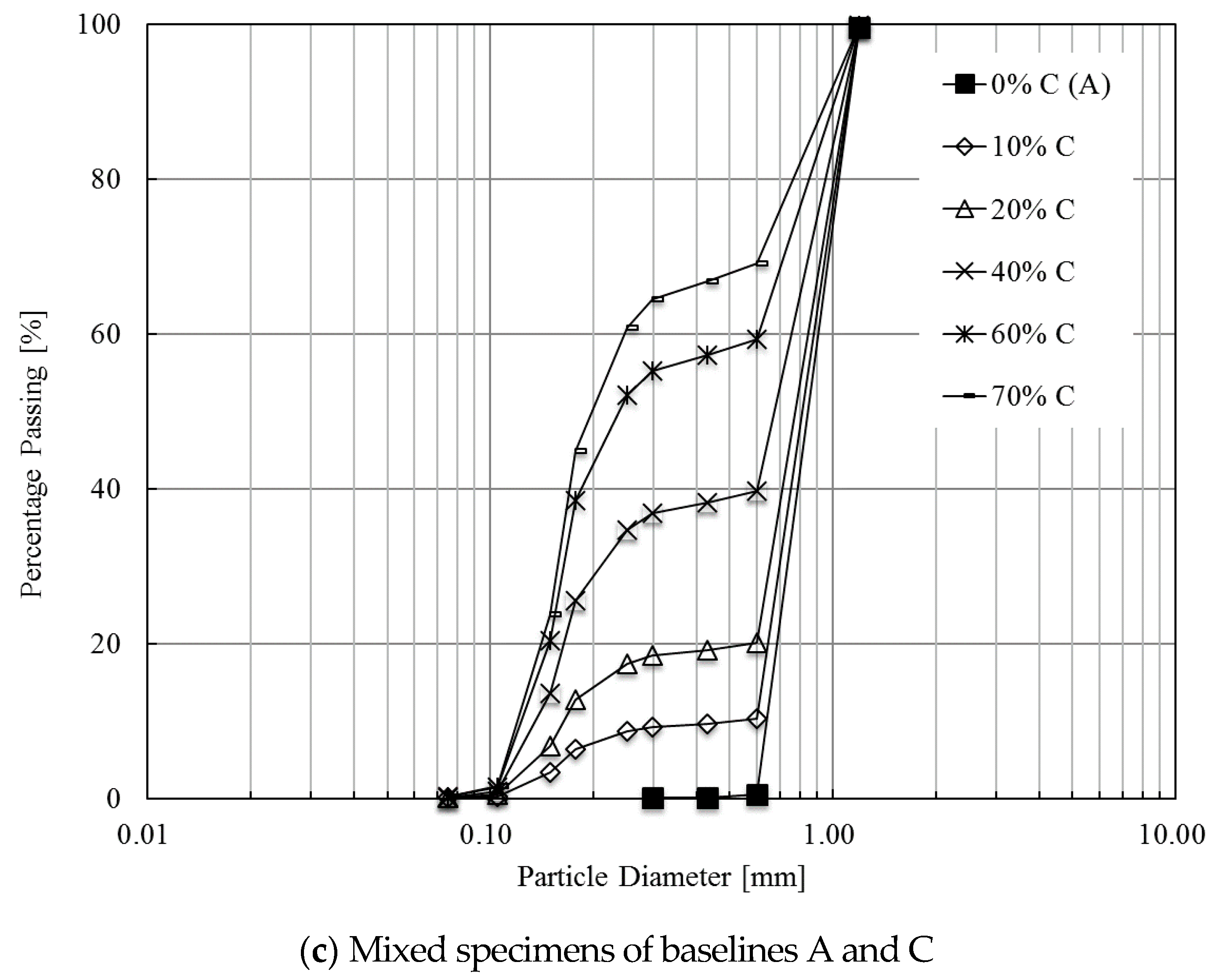
3.1. Materials
3.2. Experiment Procedure
4. Results and Discussion
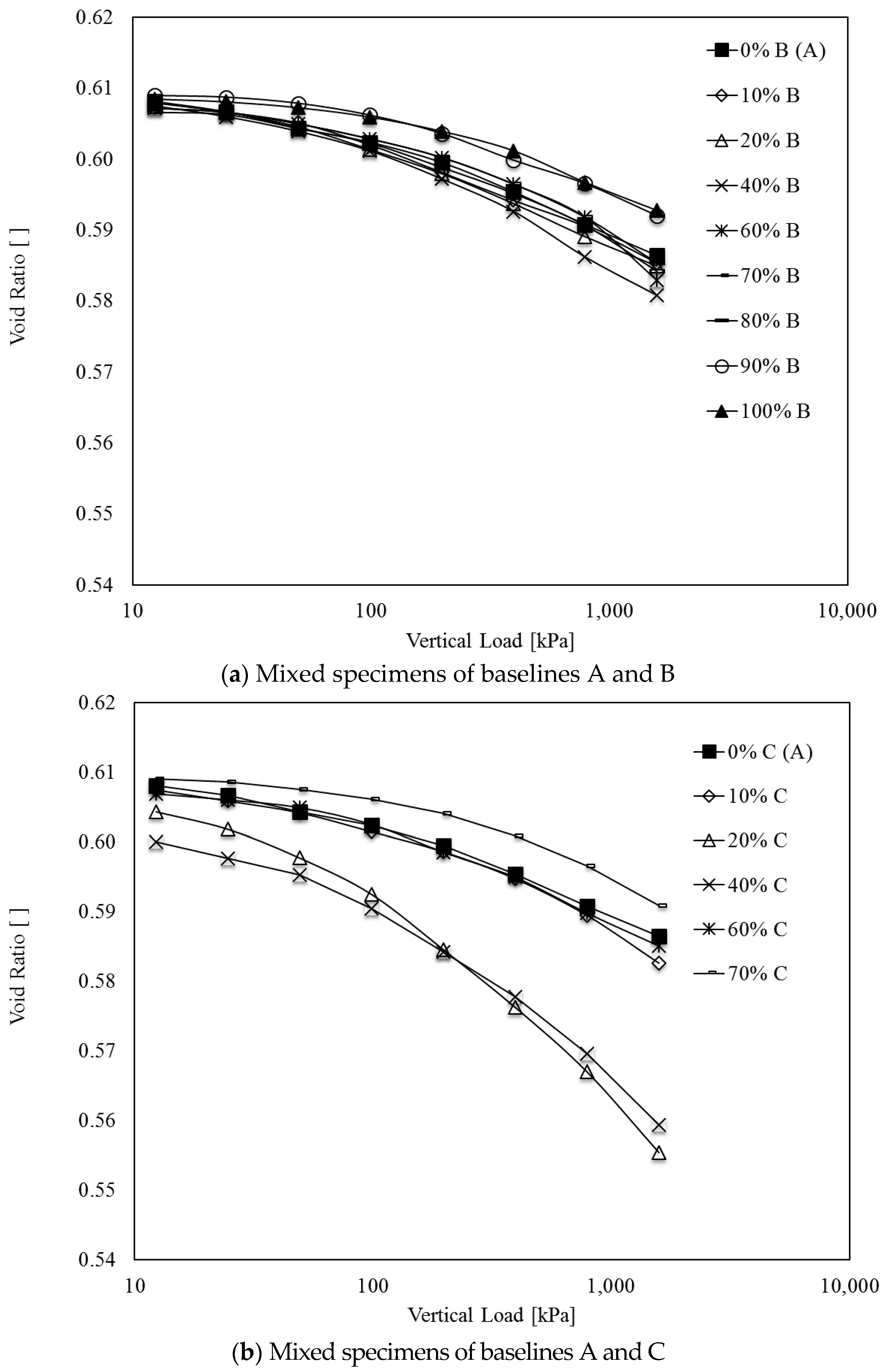
4.1. Void Ratio with Change in Vertical Effective Stress
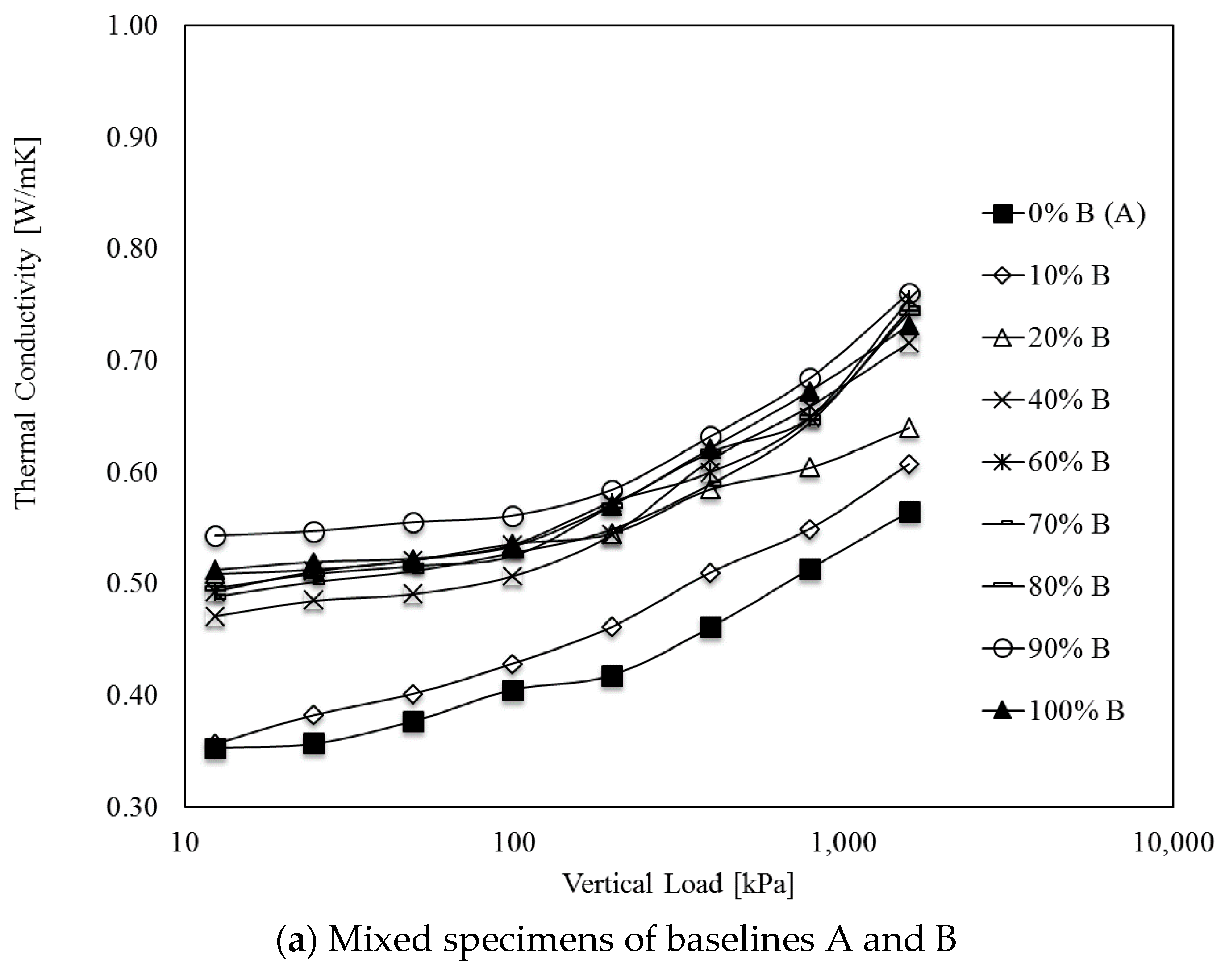
4.2. Thermal Conductivity with Change in Vertical Effective Stress
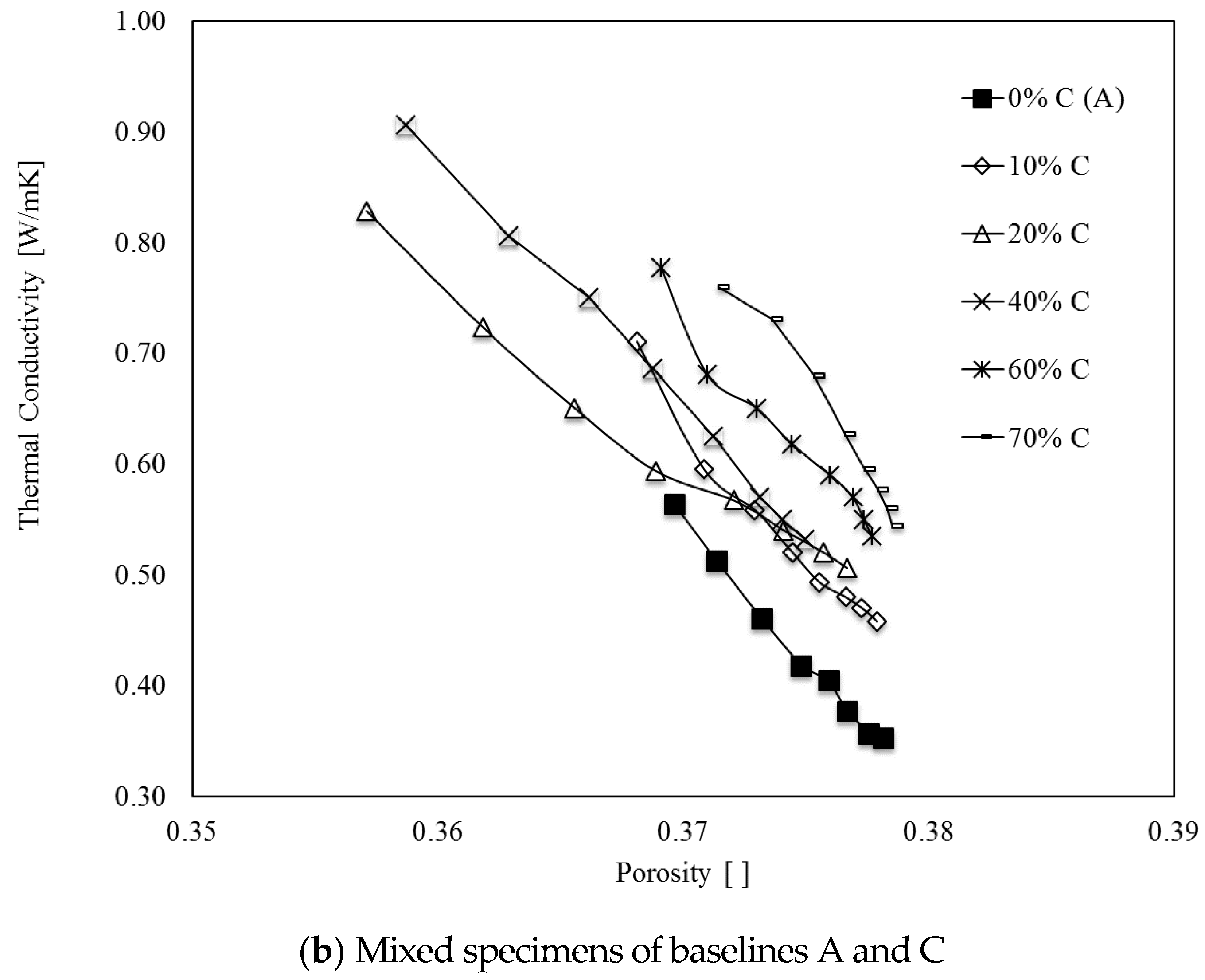
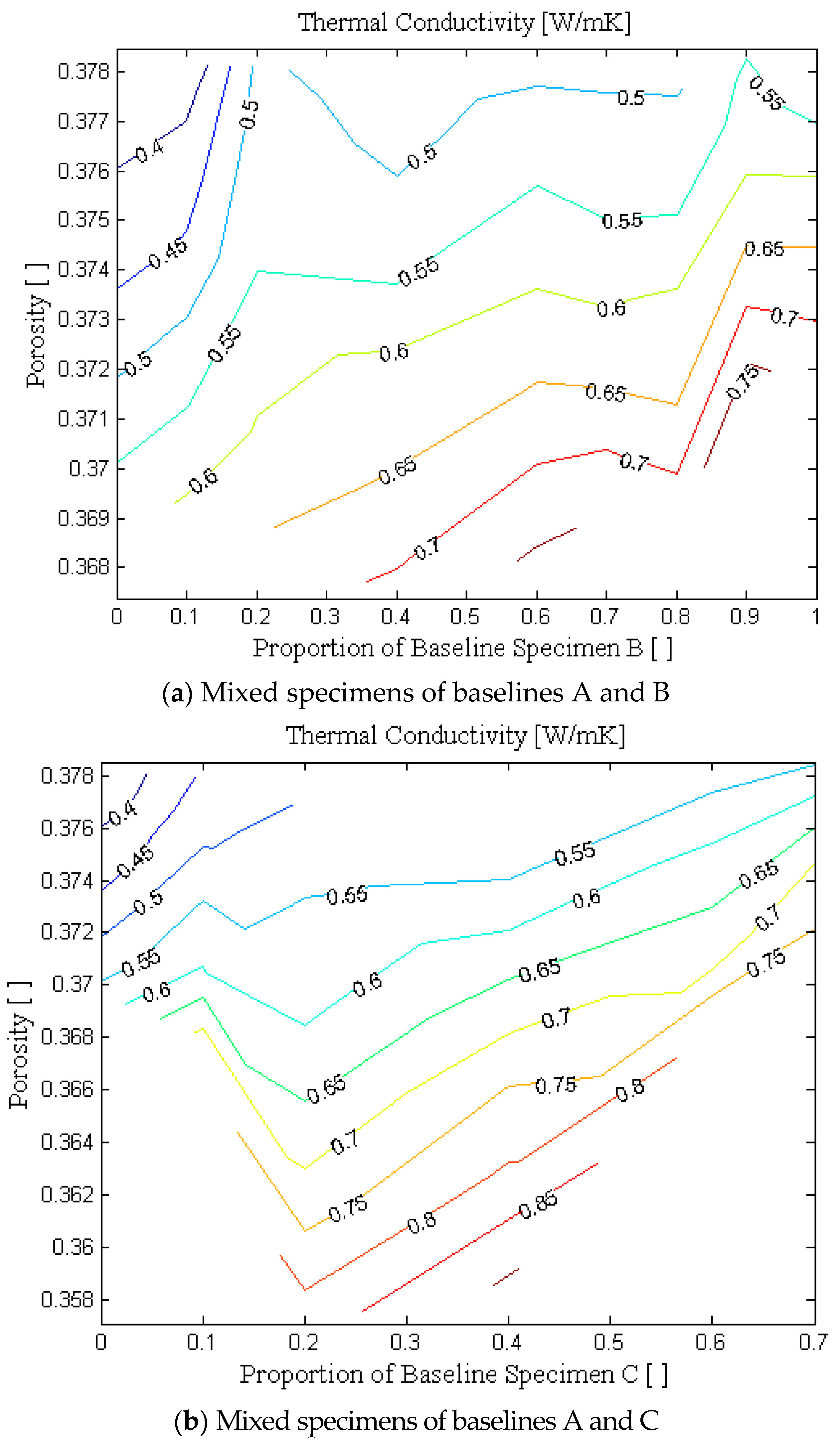
4.3. Thermal Conductivity with Change in Porosity and Fine Particle Contents
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simms, R.B.; Haslam, S.R.; Craig, J.R. Impact of soil heterogeneity on the functioning of horizontal ground heat exchangers. Geothermics 2014, 50, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, N.-W.; Lai, C.-H.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Chiang, Y.-C.; Chang, C.-C.; Chen, S.-L. A conformal-mapping method for predicting the thermal properties of U-shaped borehole heat-exchangers. Geothermics 2014, 50, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.L.; Singh, R.M.; Bouazza, A.; Bui, H.H. Determining Soil Thermal Conductivity through Numerical Simulation of a Heating Test on a Heat Exchanger Pile. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2015, 33, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, C.; Ghasemi-Fare, O.; Basu, P. Laboratory Thermal Performance Tests on a Model Heat Exchanger Pile in Sand. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2015, 33, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perpar, M.; Rek, Z.; Bajric, S.; Zun, I. Soil thermal conductivity prediction for district heating pre-insulated pipeline in operation. Energy 2012, 44, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Rosa, A.; Li, H.; Svendsen, S. Method for optimal design of pipes for low-energy district heating, with focus on heat losses. Energy 2011, 36, 2407–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Kim, K.-Y.; Choi, J.-C.; Kwon, T.-H. Experimental investigation on the variation of thermal conductivity of soils with effective stress, porosity, and water saturation. Geomechanics and Engineering 2016, 11, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, W.; Yu, W.; Li, S.; Zhou, J. A new method to model the thermal conductivity of soil–rock media in cold regions: An example from permafrost regions tunnel. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2013, 95, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrianov, I.V.; Starushenko, G.A.; Danishevskii, V.V. Asymptotic determination of the effective thermal conductivity of a pile field. Soil. Mech. Found. Eng. 1999, 36, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, H.; Lee, W.; Lee, C. Compressibility and small strain stiffness of kaolin clay mixed with varying amounts of sand. KSCE J. Civil Eng. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, W.; Lee, C. Relationship between hydraulic conductivity and formation factor of coarse-grained soils as a function of particle size. J. Appl. Geophys. 2016, 127, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, B.J. Thermal expansion. Mem.—Geol. Soc. Am. 1966, 97, 75–96. [Google Scholar]
- Eppelbaum, L.; Kutasov, I.; Pilchin, A. Thermal Properties of Rocks and Density of Fluids. Appl. Geotherm. 2014, 99–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, T.S.; Santamarina, J.C. Fundamental study of thermal conduction in dry soils. Granul. Matter 2008, 10, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry-Macaulay, D.; Bouazza, A.; Singh, R.M.; Wang, B.; Ranjith, P.G. Thermal conductivity of soils and rocks from the Melbourne (Australia) region. Eng. Geol. 2013, 164, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, J.; Konrad, J.-M. Thermal conductivity of base-course materials. Can. Geotech. J. 2005, 42, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Lu, S.; Horton, R.; Ren, T. An Empirical Model for Estimating Soil Thermal Conductivity from Texture, Water Content, and Bulk Density. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 1859–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kömle, N.; Hütter, E.; Feng, W. Thermal conductivity measurements of coarse-grained gravel materials using a hollow cylindrical sensor. Acta Geotech. 2010, 5, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuel-Naga, H.M.; Bergado, D.T.; Bouazza, A.; Pender, M.J. Thermal conductivity of soft Bangkok clay from laboratory and field measurements. Eng. Geol. 2009, 105, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochsner, T.E.; Horton, R.; Ren, T. A New Perspective on Soil Thermal Properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wahed, R.M.; Pfender, E.; Eckert, E.R.G. A Transient Method for Measuring Thermal Properties of Soils. Wärme Stoffübertrag. 1987, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, M.; Jung, J. Thermal properties of fly ashes and biomass ashes including wood- and sugarcane ashes. J. Mater. Civil Eng. (ASCE) 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashin, Z.; Shtrikman, S. A variational approach to the theory of the effective magnetic permeability of multiphase materials. J. Appl. Phys. 1962, 33, 3125–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau, F.; Choo, H.; Hu, J.W.; Jung, J. Engineering behavior and characteristics of wood ash and sugarcane bagasse ash. Materials 2015, 8, 6962–6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, B.K. Basic Soils Engineering; The Ronald Press Company: New York, NY, USA, 1957; p. 513. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, D.D.; Martin, A.I.; Yun, T.S.; Francisca, F.M.; Santamarina, J.C.; Ruppel, C. Thermal conductivity of hydrate-bearing sediments. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narsilio, G.A.; Yun, T.S.; Kress, J.; Evans, T.M. Hydraulic and thermal conduction phenomena in soils at the particle-scale: Towards realistic FEM simulations. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2010, 10, 012086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Yun, T.; Choi, S.-U. The Effect of Particle Size on Thermal Conduction in Granular Mixtures. Materials 2015, 8, 3975–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Hamdeh, N.H. Thermal Properties of Soils as affected by Density and Water Content. Biosyst. Eng. 2003, 86, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, T.S.; Evans, T.M. Three-dimensional random network model for thermal conductivity in particulate materials. Comput. Geotech. 2010, 37, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahn, J.; Jung, J. Effects of Fine Particles on Thermal Conductivity of Mixed Silica Sands. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7070650
Ahn J, Jung J. Effects of Fine Particles on Thermal Conductivity of Mixed Silica Sands. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(7):650. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7070650
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhn, Jaehun, and Jongwon Jung. 2017. "Effects of Fine Particles on Thermal Conductivity of Mixed Silica Sands" Applied Sciences 7, no. 7: 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7070650
APA StyleAhn, J., & Jung, J. (2017). Effects of Fine Particles on Thermal Conductivity of Mixed Silica Sands. Applied Sciences, 7(7), 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7070650





