Abstract
With the development of higher-voltage power grids, the high- and low-voltage parallel loops are emerging, which lead to energy losses and even threaten the security and stability of power systems. The multi-infeed high-voltage direct current (HVDC) configurations widely appearing in AC/DC interconnected power systems make this situation even worse. Aimed at energy saving and system security, a decision optimization method for power grid operating conditions with high- and low-voltage parallel loops is proposed in this paper. Firstly, considering hub substation distribution and power grid structure, parallel loop opening schemes are generated with GN (Girvan-Newman) algorithms. Then, candidate opening schemes are preliminarily selected from all these generated schemes based on a filtering index. Finally, with the influence on power system security, stability and operation economy in consideration, an evaluation model for candidate opening schemes is founded based on analytic hierarchy process (AHP). And a fuzzy evaluation algorithm is used to find the optimal scheme. Simulation results of a New England 39-bus system and an actual power system validate the effectiveness and superiority of this proposed method.
1. Introduction
The high and low-voltage parallel loop is a kind of power grid structure, in which transmission lines of different voltage levels are looped by transformers at the sending and receiving ends. With the rapid development of higher-voltage power grids, parallel loops [1] have become more and more common. Parallel flow in a parallel loop would make unbalanced power flow in a power system, which leads to higher power losses. In some cases, parallel loop would even threaten the security and stability of a power system [2]. On the one hand, low-voltage transmission lines of parallel loops would bear a quite heavy load after faults on high-voltage transmission lines, which may cause cascading trips of low-voltage transmission lines [3]. On the other hand, parallel operation of high- and low-voltage transmission lines also leads to a high level of short circuit current, which may exceed the interrupting capacity of circuit breakers. Therefore, considering energy saving and system security and stability, some methods must be presented to solve these problems.
There are many studies that have tried to apply Flexible AC Transmission System (FACTS) technologies to eliminate parallel flow or control power flow in parallel loops [1,2,3,4]. These studies only improve the operational characteristics of power systems, however, they cannot solve the problems caused by parallel loops radically from the aspect of power grid structure. Especially for higher-voltage power grids, the use of FACTS is quite limited. Fortunately, it has been proved that switching specific transmission lines could make power flow more balanced [5], reduce power loss [6] and decrease short circuit current [7]. And some studies have been carried out to find the optimal line switching scheme [8,9]. Accordingly, the parallel loop problem mentioned above can be solved by switching specific low-voltage transmission lines at appropriate location and time. However, it is difficult to describe this problem as an accurate mathematical model [10]. It is actually a complicated mixed-integer programming problem, which is multi-objective, non-linear and discrete. In order to simplify the calculation complexity, the decision process of opening parallel loops is usually divided into two stages: scheme generation and scheme evaluation.
The generation of opening schemes used to only depend on engineering experiences. But things are changing gradually. There are studies employing linear programming algorithms to find the optimal line switching scheme with minimum power loss [11,12]. These studies only consider the branch active power flow constraint, and the bus voltage constraint is neglected. Simulation results in [13] show that the neglect of bus voltage constraint may cause the failure of optimization. A line switching optimization method considering bus voltage constraint is proposed in [14], which could effectively eliminate over-limited power flows. In [15], the Benders decomposition technology is applied to network reconfiguration, which could deal with the constraints of static security and transient stability simultaneously. But this method is barely able to be used in actual large-scale power systems, due to its high complexity.
The evaluation of opening schemes should consider static security, transient stability, short circuit current and operation economy of power systems. A comprehensive evaluation method for opening schemes is proposed in [16], which combines AHP (analytic hierarchy process) with fuzzy evaluation algorithms. The AHP is used to establish the hierarchical model to describe the operational characteristics of power systems. In this model, five performance indices and corresponding membership functions are presented. After detailed analysis and calculations for each opening scheme, the optimal one is obtained by two-level fuzzy evaluation.
All of the previous studies only discuss parallel loop opening issues in pure AC power grids. But things in AC/DC interconnected power grids would be quite different, usually more complicated indeed. The significant contributions of this paper are just at this area. Due to intensive loads in a relatively narrow region, several HVDC (high-voltage direct current) inverter stations would emerge in adjacent areas of the same AC power grid, called the multi-infeed HVDC configuration. In this situation, switching transmission lines, on the one hand, would decrease short circuit current, and, on the other hand, would stretch the electrical distance between different HVDC inverter stations. As a result, the multi-infeed short-circuit ratio (MISCR) may be increased or decreased under different conditions, which means the stability of power systems would be influenced [17]. Therefore, the decision for the optimal parallel loop opening scheme must consider the support ability for HVDCs, which is evaluated by MISCR. In this paper, a decision optimization method is proposed, which coordinates the relationship between parallel loop opening effect and support ability for multiple HVDC links. Thus, this method can be used to solve the parallel loop problem not only in pure AC power grids but also in AC/DC interconnected power grids, which distinguishes the proposed method from previous research.
The decision optimization method is expounded in this paper. In Section 2 the complex network theory used for opening parallel loops is discussed in detail. GN algorithm and modularity indicators are introduced. In Section 3 the generation process of candidate opening schemes is proposed. The weighted modularity indicator and weighted MISCR are defined respectively, and combined to filter generated opening schemes. In Section 4 an evaluation model for candidate schemes is founded based on AHP, which considers the relationship between stability and short circuit current level of a power system. A fuzzy evaluation algorithm is used to find the optimal opening scheme. In Section 5 a New England 39-bus system and an actual power system are analyzed. Simulation results validate the effectiveness and superiority of this proposed method.
2. Complex Network Theory Used for Opening Parallel Loops
2.1. Complex Network Complexity
A power grid is a typical kind of complex network. High complexity is the significant characteristic shared by all kinds of complex networks, which mainly lies on three aspects:
(a) Structural complexity
The amount of nodes in a complex network is quite large, which leads to complex connection relationships between nodes. Furthermore, the network structure may keep changing, and the connections between nodes may even have different weights or directions.
(b) Node complexity
There may be many different types of nodes in a complex network. Moreover, the nodes in a complex network may be dynamical systems which have complex nonlinear behaviors like bifurcation, chaos, etc.
(c) Interaction among various complexity factors
The characteristics of an actual complex network can be influenced by various factors. For example, the long-term planning of power system networks should take many factors including generation capacity, electricity demand, network evolution, etc., into consideration.
2.2. Complex Network Indices
The high complexity of a complex network can be described by a group of basic statistical indices. Some typical indices are listed below:
(a) Node degree
Node degree of a node is defined as the number of other nodes connected to it, which has different practical meanings in different complex networks. In general, node degree indicates the importance of a node in a complex network.
(b) Shortest path
The shortest path is defined as the path from the specified beginning node to the specified end node with shortest length. The distance between two nodes in a complex network is defined as the length of the shortest path between them. The average shortest path length is defined as the average distance between any two nodes in complex network.
(c) Edge betweenness
Edge is the line connecting two nodes in a complex network. Edge betweenness of an edge is defined as the number of shortest paths passing it in a complex network. Edge betweenness is usually used to reflect the importance of an edge.
2.3. Floyd-Warshall Algorithm
As shown above, shortest path is the key index to describe a complex network. In general, the calculation for shortest path should search the whole network. It would consume a lot of time if an inappropriate algorithm is employed. Considering the loop structure of power grid networks, the Floyd-Warshall algorithm is employed. The Floyd-Warshall algorithm is a dynamic programming algorithm, the key idea of which is to calculate the shortest path matrix between any two nodes by the correlation matrix of network. The details of Floyd-Warshall algorithm can be found in [18].
2.4. GN Algorithm
GN (Girvan-Newman) algorithm [19], which was proposed by Girvan and Newman, has been a standard algorithm to analyze community structure of complex networks. A community is a set of nodes and edges, which is the subset of a complex network. If a network contains several communities, these communities must be connected by a small number of interconnected edges, and the shortest paths between these communities are bound through these interconnected edges. As a result, these interconnected edges have high edge betweenness. Then, communities contained in the network can be distinguished and separated by removing these edges. The basic steps of GN algorithm are as shown below:
- (a)
- Calculate the betweenness of all edges in the complex network;
- (b)
- Find the edge with the largest betweenness and remove it from the current network; and
- (c)
- Return to step (a) until every node degenerates into a community.
2.5. Modularity Indicator
The GN algorithm can effectively find the communities contained in complex networks, however, it cannot estimate the practical significance of the communities obtained from the original network. To solve this problem, Newman introduced an index, called modularity indicator, to evaluate the community separating result [20]. And Fortunato proved that reasonable results can be obtained using this indicator when the scales of obtained communities differ in a relatively small range [21].
Assuming the complex network can be divided into l communities, a symmetric matrix E = (eij)l×l with l × l order can be defined, and eij represents the proportion of edges connecting community i and community j. The summation of elements on the diagonal is taken as T, which represents the proportion of edges connecting internal nodes of communities. The summation of elements in each row (column) is defined as ai, representing the proportion of edges connecting nodes of community i. Then, the modularity indicator can be defined as:
The definition of (1) is the expectation value of the proportion of the edges connecting community internal nodes in original network minus its corresponding proportion in another random network. The random network can be constructed by connecting different nodes randomly with the community property and node degree of each node unchanged. It indicates that the community separating result of original network is better if Q is closer to 1, which is the upper limit. If the proportion of the edges connecting community internal nodes in original network is smaller than its corresponding value of random network, Q = 0. In an actual network, the value of Q is usually between 0.3 and 0.7.
In order to simplify the calculation, the equivalent equation of Equation (1) is derived as below [22]:
where n is number of nodes, m is number of edges, and kv and kw are the node degrees of node v and w, respectively.
3. Generation of Parallel Loop Opening Schemes
3.1. Weighted Network and Weighted Modularity Indicator
The original GN algorithm can only be applied in unweighted networks. In an unweighted network, the existence of an edge only means that the nodes on the two ends of the edge are connected. No more information is contained in the edge. However, most of actual networks, especially power grids, are weighted networks, where weights of network edges have practical significance. The edges in weighted networks can contain information about how the nodes on the two ends of the edge are connected or how closely they are connected. This information is represented by edge weights. If a weighted network is analyzed as an unweighted network, the information contained in weights will be lost, which will influence the reasonableness of analysis results. To solve this problem, Newman found a way to convert the weighted network to multigraph, which makes GN algorithms applicable in weighted networks [23].
For a power grid network, better community separating results can be derived if the edge weights are considered in the separating process. Considering the length and physical parameters of transmission lines in power grid networks, the modulus value of branch admittance is defined as the edge weight. The weight of an edge in a complex network usually represents the connection tightness of the two nodes connected by this edge. Thus, the larger the admittance modulus value of a branch, the shorter the electrical distance between two substations connected by this branch.
In a weighted complex network, the weighted edge betweenness can be defined as the ratio of the edge betweenness obtained from the corresponding unweighted network and the weight of this edge. Thus, a larger edge betweenness and a smaller weight value would jointly make a larger weighted edge betweenness of this edge, whose possibility of being removed from the network in community separating process would be larger.
Based on the edge weight defined above, the weighted modularity indicator can be derived from (2) as:
where Svw is the weight of the edge connecting node v and w.
3.2. Weighted Multi-Infeed Short Circuit Ratio
With the development of HVDC transmission systems, parallel loops might emerge in typical multi-infeed HVDC configurations. MISCR can represent the interactions between AC and DC systems and among different DC links in AC/DC interconnected power systems [24]. A practical definition of MISCR based on impedance matrix can be derived as [25]:
where Uaci is the inverter bus voltage of the i-th DC; and Zeqij is the element of the equivalent impedance matrix Zeq, which can be obtained by multi-port Thevenin equivalent method. It should be noted that the value of Zeqij is equal to the voltage of node i when unit current is only being injected to node j.
It is obvious that opening parallel loops would change the elements of the equivalent impedance matrix Zeq. Thus, it can be deduced from (8) that opening parallel loops would influence the MISCR of each DC link, which indicates system stability would be influenced by any parallel loops opening scheme. In general, system stability should not descend a lot after opening parallel loops. In order to evaluate the influence of opening schemes on system stability in multi-infeed HVDC configurations, the evaluation index must be defined based on MISCR.
Although the stability of multi-infeed HVDC systems is determined by all of the infeed DC links, the contribution of each DC link is different. Based on this evidence, the system stability evaluation index can be defined as the weighted MISCR, which is derived as:
where n is the number of DCs; MISCRi is the multi-infeed short-circuit ratio of the i-th DC; and ωi is the weighted factor of the i-th DC, which represents the importance of the i-th DC. A larger value of ωi indicates greater importance of i-th DC and greater influence on other DCs.
Obviously, the weighted factor ωi is quite essential to define the weighted MISCR, which must meet three requirements:
- (a)
- The weighted factor should not be assigned a value manually;
- (b)
- The weighted factor should represent the interaction between different DC links; and
- (c)
- The weighted factor should represent the contribution to system stability of the specific DC link.
To define the weighted factor ωi, the definition of MISCR should be analyzed firstly. Equation (8) can be transformed as:
where μi is a penalty factor. It should be noted that Saci/Pdi is the definition of single-infeed short circuit ratio (SISCR) without considering the interaction between different DC links. Based on the physical meaning of SISCR, a small μi indicates the i-th DC can be influenced by other DCs easily, which means a smaller contribution to system stability. Thus, this penalty factor can represent the importance of the i-th DC in multi-infeed DC systems.
Thus, the weighted factor of the i-th DC can be defined as:
where Zeqij is the equivalent mutual-impedance between the i-th DC and the j-th DC; Zeqii is the equivalent self-impedance of the i-th DC; and Pdi and Pdj are the rated transmission powers of the i-th DC and the j-th DC, respectively. The definition of (11) considers not only the electrical distance, but also the transmission capacity of a DC link, which fulfills the three requirements above.
3.3. Generation Process
For parallel loop opening issues, the situation that a lower-voltage isolated power grid partition is separated from the main grid should be avoided. Thus, power substations in higher-voltage power grids are usually selected as hub substations. And each power grid partition consists of at least one hub substation. The maximum possible number of partitions is determined by the number of hub substations. The parallel loop opening process should be stopped when all hub substations are divided into different partitions by GN algorithm.
The generated partitions, each of which contains one hub substation, can be defined as basic partitions. Neighboring basic partitions can be combined in different ways to generate different parallel loop opening schemes. An actual AC/DC interconnected power grid contains many higher voltage substations, which usually leads to a huge number of candidate opening schemes. It is usually not necessary to evaluate each of these generated schemes using comprehensive evaluation models because of huge computation times. Thus, a filtering strategy is needed.
According to the analysis above, the weighted modularity indicator can be used to filter the generated opening schemes preliminarily in pure AC power grids. But in AC/DC interconnected power grids, where the influence on MISCR of generated opening schemes must be considered, it is obviously not appropriate to filter opening schemes only based on weighted modularity indicator. Thus, a new filtering index is defined as:
where λ1 and λ2 are the weighted coefficients, respectively. There exists the relationship λ1 + λ2 = 1. It should be noted that λ1 and λ2 are normalized values, not the real algebraic values. The new filtering index is applicable to not only AC/DC interconnected power grids, but also pure AC power grids with λ1 = 1, λ2 = 0.
All of the generated opening schemes are sorted in descending order according to the filtering index defined in (12) and the first M schemes are selected as candidate schemes to find the optimal one. The generation process of parallel loop opening schemes is shown in Figure 1, where the shortest-path matrix can be used to judge whether each hub substation is divided into different partitions.
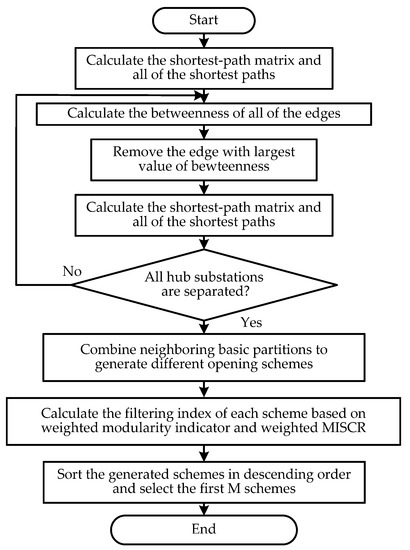
Figure 1.
Generation process of parallel loop opening schemes.
4. Evaluation for Parallel Loop Opening Schemes
4.1. Comprehensive Evaluation Model
There are many factors that should be considered to evaluate the candidate parallel loop opening schemes. The most principal one is the contradictory relationship between system stability and short-circuit current. In this paper, a comprehensive evaluation model is established based on AHP, which can reflect all of the principal factors. The model is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2.
Comprehensive evaluation model for candidate opening schemes.
The details of this evaluation model are discussed below:
(a) Static security
Static security should be analyzed with the premise that the system is transferred from a steady state before the fault to another steady state after the fault immediately. The transient process during the fault is not considered. Static security is used to examine whether the operation constraints are satisfied after faults. Operation statuses of key components after specified faults, including line overload, transformer overload and bus voltage limit violation, can be used to evaluate the static security. Thus, two indicators are defined, which are shown below:
Indicator C11: over load indicator of line or transformer.
where γ is the set of specified faults; α is the set of key transmission lines and transformers; ωP,l is the weighted factor; Sl is the power flow of branch l; Slmax is the upper limit of power flow of branch l; and n is a positive integer.
Indicator C12: bus voltage limit violation indicator.
where γ is the set of specified faults; β is the set of buses; ωU,i is the weighted factor; Ui is voltage of bus i; Uimax and Uimin are the upper and lower limits of voltage of bus i; and n is a positive integer.
(b) Transient stability
Transient stability considers the ability of a system to remain stable during the transient process from a steady state before the fault to another steady state after the fault. The transient stability of a power system is composed of voltage stability and power angle stability. Voltage stability is mainly determined by load distribution and load characteristics, which can be measured by transient voltage safety margin. Power angle stability is used to evaluate the interaction between generators with long electrical distance, which can be represented by transient angle deviation. These two indicators are defined as below:
Indicator C21: transient voltage safety margin indicator.
where γ is the set of specified faults; η is the set of voltage curves of monitored buses; ωTV,k is the weighted factor; and εk is the transient voltage dip acceptable margin of bus voltage curve k.
Indicator C22: transient angle deviation indicator.
where γ is the set of specified faults; ωθ,m is the weighted factor; θi and θj are the power angles of two generators in the transient process of a specified fault, respectively.
(c) Short circuit current
Short circuit current should be limited to not exceed the interrupting capacity of electrical equipment, such as circuit breakers. It can be represented by short circuit current limit violation.
Indicator C31: short circuit current limit violation indicator.
where β is the set of buses; ωI,i is the weighted factor; Ii is actual short circuit current of bus i; Iimax is the maximum interrupting current of circuit breaker of bus i; and n is a positive integer.
(d) Operation economy
In this paper, power loss is used to represent the operation economy.
Indicator C41: power loss indicator.
It should be noted that the values of weighted factors used in these indicators above depend on the importance of the corresponding indicators. The weighted factor is defined based on the principle that tries to highlight limit violations and avoid overshadowing them. It should also be noted that the value of positive integer n is usually defined as 1. With n = 1, not only the computation speed for these indicators can meet requirements, but also the indicator values can vary in a large enough range to reflect the difference of limit violation clearly.
4.2. Fuzzy Evaluation Algorithm
The comprehensive evaluation model founded above considers almost all of the important factors to evaluate candidate opening schemes. A powerful evaluation algorithm, however, is still needed to find the optimal opening scheme based on the founded model.
Fuzzy evaluation algorithm is based on AHP and fuzzy mathematics [26], which not only includes engineering experience from experts, but also combines the advantages of qualitative analysis and quantitative calculation. Thus, use of fuzzy evaluation algorithms could avoid the disadvantages of expert systems, including uneasy knowledge representation and long computation time [27], which guarantees an effective and fast way to find the optimal opening scheme.
The priority index P of any parallel loop opening scheme can be obtained by fuzzy evaluation algorithm, and the scheme with the largest priority index in the M-dimensional candidate opening scheme set is selected as the optimal one.
5. Case Study
In this section, a New England 39-bus system and an actual AC/DC interconnected power system are used as examples to validate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method.
5.1. New England 39-Bus System
The New England 39-bus system is a pure AC system, which is shown in Figure 3. Many parallel loops would emerge if a higher-voltage power grid is connected to this system via node 5, 16 and 26. With node 5, 16 and 26 as hub substations, this power grid can be divided into three basic partitions at most after switching off several specific lines.
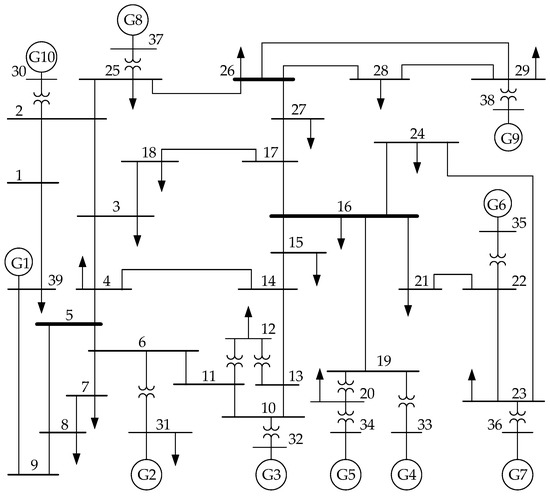
Figure 3.
New England 39-bus system.
According to the complex network theory in Section 2, edge betweenness of each branch should be calculated before switching off any line. The calculation results are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Edge Betweenness of Each Branch.
In the original power grid network, the maximum edge betweenness is 2.0273 of line 3–4, which is between bus 3 and bus 4. According to GN algorithm, line 3–4 should be switched off firstly. No new partition emerges after line 3–4 is switched off. Then, the edge betweenness of the modified network without the line 3–4 is calculated. The calculation results are shown in Table 1 as well. In this round, the maximum edge betweenness is 2.8089 of line 14–15. No new partition emerges after line 14–15 is switched off. During the third round, line 1–39 has the largest edge betweenness, with a value of 4.9039. After line 1–39 is switched off, the original network would be divided into two partitions. Since there are still two hub substations in the same partition, the line switching process should be continued until all of the hub substations are divided into different partitions. It should be noted that the edge betweenness of some specific branches in a subsequent line switching process might be larger than their corresponding values in the previous process, which is due to the change of network connectivity and the branch number along with the line switching process.
The basic partitions of the New England 39-bus system is shown in Figure 4 After three branches are switched off, the network is divided into two partitions. And three partitions would emerge with four branches switched off.

Figure 4.
Basic partitions of New England 39-bus system.
There are three basic partitions illustrated in Figure 4, which can be combined to generate four different opening schemes in total according to Combinatorics and actual neighboring relationships. Because the number of generated opening schemes is quite small, it is not necessary to filter them using the filtering index. The filtering index (only weighted modularity indicator is considered in this example with λ2 = 0) and priority index of these four generated opening schemes (No. 1–4) as well as two experiential schemes (No. 5–6), are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Filtering Index and Priority Index of Candidate Schemes.
It is obvious in Table 2 that the filtering index and priority index of the first four opening schemes generated by proposed method are overall larger than two experiential schemes. For New England 39-bus system, which is a pure AC power system, a larger filtering index indicates a better network structure after specific lines are switched off. And a larger priority index indicates better operational characteristics if the opening scheme is employed. By comprehensively considering the filtering index and priority index, scheme 1 should be selected as the optimal opening scheme. Based on the analysis above, it is easy to recognize the effectiveness of the proposed method to find optimal opening schemes, as well as its superiority over experiential method. The simulation results show that the proposed opening method can successfully be applied in a pure AC power system.
5.2. Actual AC/DC Interconnected Power System
In many modern power systems with intensive load, the AC power system and DC transmission systems are usually operating together and interacting in a complicated way. An actual AC/DC interconnected power system is shown in Figure 5. With the development of 1000 kV transmission systems, 1000 kV/500 kV parallel loops would emerge, which can be recognized in Figure 5.
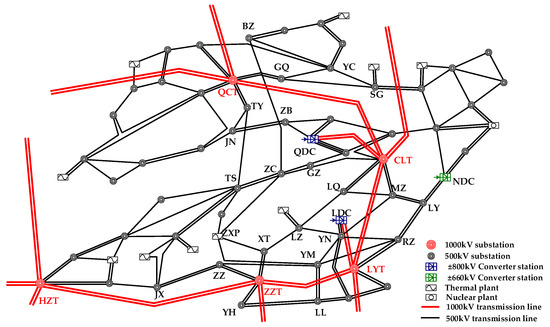
Figure 5.
Actual AC/DC interconnected power system.
Substation QCT, CLT, LYT, ZZT and HZT are 1000 kV substations, which are also hub substations in this power grid network. The number of hub substations decides the number of basic partitions. Thus, the power grid network can be divided into five basic partitions at most. During the line switching process, the edge betweenness of each branch is dynamically calculated until all of the five basic partitions are separated. Because of the huge amount of branches, it is not appropriate to list the edge betweenness of all of the branches at each line switching round. The switched-off branches and their edge betweenness are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Computation Results of Edge Betweenness.
In this AC/DC interconnected power system, there are three inverter stations: QDC, NDC and LDC. It should be noted that the inverter stations QDC and LDC are hierarchically interconnected to the receiving-end power grid [28,29]. Thus, each of them is equivalent to two inverter stations (One is in 1000 kV power grid and another is in 500 kV power grid), respectively. The MISCR calculation results are shown in Table 4. QDC-L and LDC-L are equivalent inverter stations in a 500 kV power grid. QDC-H and LDC-H are equivalent inverter stations in a 1000 kV power grid.

Table 4.
MISCR of Each Inverter Station before Optimization.
The basic partitions of this actual power system are shown in Figure 6. After six branches are switched off, the power system is divided into two partitions. And three partitions would emerge with nine branches switched off. Then, there are four partitions with twelve switched-off branches and five partitions with fifteen switched-off branches. These five partitions are basic partitions and can be combined to generate different opening schemes.
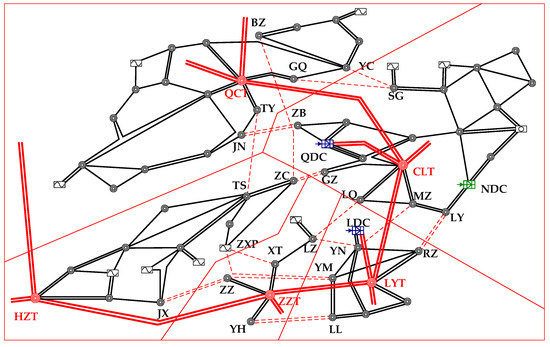
Figure 6.
Basic partitions of actual power system.
According to Combinatorics and the neighboring relationships among basic partitions, 46 different opening schemes can be generated. It is not necessary to have all of these opening schemes evaluated by the comprehensive evaluation model and fuzzy evaluation algorithm, which usually costs a lot of computation time. Thus, the generated opening schemes should be filtered first using the filtering index defined in (11) in Section 3 The weighted factors of filtering index are assigned as λ1 = 0.5, λ2 = 0.5. Four generated opening schemes (No. 1–4) with the largest filtering index as well as two experiential opening schemes (No. 5–6) are selected as the candidate opening schemes, whose filtering indices and priority indices are shown in Table 5. In addition, the original network with no branch being switched off acts as the control group (No. 7) to highlight the effect of optimal opening scheme.

Table 5.
Filtering Index and Priority Index of Candidate Schemes.
In Table 5 the filtering index and priority index of the first four opening schemes generated by proposed method are overall larger than two experiential schemes and original network. Based on the analysis above and results in Table 5, it can be concluded that the proposed parallel loop opening method can effectively find optimal opening schemes in AC/DC interconnected power systems, which is usually more effective than the method based on engineering experience. Additionally, the comparison between scheme 6 and scheme 7 indicates that the experiential method cannot always guarantee a better opening scheme. According to the priority index in Table 5, scheme 1 should be the optimal opening scheme, with the original network divided into two partitions.
As an AC/DC interconnected power system, the system stability (evaluated by MISCR) should be checked after any opening scheme is employed. The MISCR calculation results after scheme 1 is employed, are shown in Table 6.

Table 6.
MISCR (Multi-Infeed Short Circuit Ratio) of Each Inverter Station with the Optimal Scheme.
Compared with the MISCR results in Table 4, it can be concluded from Table 6 that system stability is high enough after scheme 1 is employed. From the perspective of time-domain simulation, transient voltage curves of inverter buses of QDC and LDC inverter stations also validate this conclusion, which are shown in Figure 7. The assumed fault is that QCT-CLT double lines are disconnected abruptly. After the optimal scheme is employed, the voltage curves of all of four inverter buses are able to recover to stable state faster, which indicates a more stable power system.
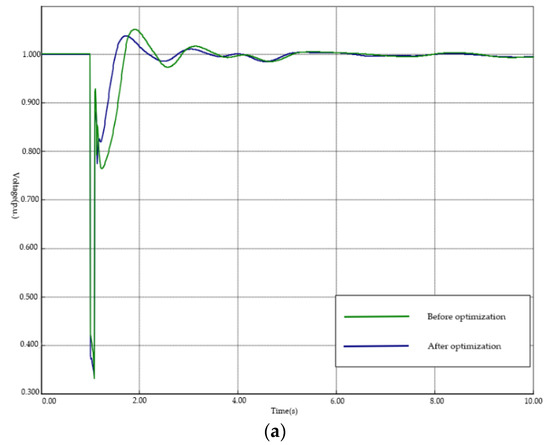
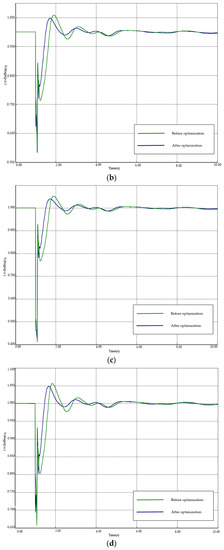
Figure 7.
Transient voltage curves of inverter buses: (a) QDC-L; (b) QDC-H; (c) LDC-L; (d) LDC-H.
All of the above simulation results in this actual power system case show that the proposed method can effectively be applied in AC/DC interconnected power systems and successfully finds the optimal opening scheme. The derived optimal scheme has good parallel loop opening effects and strong support ability for multiple HVDC links.
6. Conclusions
With the development of higher-voltage power grids, the high- and low-voltage parallel loops are emerging, which lead to energy losses and even threaten the security and stability of power systems. To solve this problem not only in pure AC power grids but also in AC/DC interconnected power grids, a decision optimization method is proposed. With this method, parallel loop opening schemes are generated firstly and evaluated secondly. According to simulation results, this proposed method can be used to find the optimal opening scheme in pure AC power systems, which is based on complex network theory and has obvious superiority over experiential methods. In addition, this method can be employed in AC/DC interconnected power systems successfully. The derived optimal scheme can effectively coordinate the relationship between parallel loop opening effect and support ability for multiple HVDC links.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by State Grid Corporation of China, Major Projects under Grant SGCC-MPLG020-2012 and SGSDDK00KJJS1600149.
Author Contributions
Dong Yang conceived and proposed the method; Kang Zhao and Hao Tian performed the simulations and analyzed the data; Yutian Liu contributed academic ideas and paper framework; Dong Yang and Kang Zhao wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Miller, J.; Balmat, B. Operating problems with parallel flows. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1991, 6, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.; Shu, Y.; Ruan, J.; Hu, Y. Ultra high voltage transmission in china: Developments, current status and future prospects. Proc. IEEE. 2009, 97, 555–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, R.; Terzija, V. Power system restoration: A literature review from 2006 to 2016. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2016, 4, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granelli, G.; Montagna, M.; Zanellini, F.; Bresesti, P.; Vailati, R. A genetic algorithm-based procedure to optimize system topology against parallel flows. IEEE Trans Power Syst. 2006, 21, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makela, O.; Warrington, J.; Morari, M.; Andersson, G. Optimal transmission line switching for large-scale power systems using the alternating direction method of multipliers. In Proceedings of the Power Systems Computation Conference, Wrocław, Poland, 18–22 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, L.R.; Chiang, H.D. Toward online line switching method for reducing transmission loss in power systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Boston, MA, USA, 17–21 July 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Zeng, B. Vulnerability analysis of power grids with line switching. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2013, 28, 2727–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, J.D.; Ramasra, R.; Cha, A. Fast heuristics for transmission-line switching. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2012, 27, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Luh, P.B.; Michel, L.D.; Zhao, Q.; Luo, X. Corrective line switching with security constraints for the base and contingency cases. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2012, 27, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cheung, K.W. On selection of transmission line candidates for optimal transmission switching in large power networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 21–25 July 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Bacher, R.; Glavitsch, H. Network topology optimization with security constraints. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1986, 1, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacher, R.; Glavitsch, H. Loss reduction by network switching. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1988, 3, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Vittal, V. A new algorithm for relieving overloads and voltage violations by transmission line and bus-bar switching. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE PES Power Systems Conference and Exposition, NewYork, NY, USA, 10–13 October 2004; pp. 322–327. [Google Scholar]
- Arya, L.D.; Choube, S.C.; Kotharib, D.P. Line switching for alleviating overloads under line outage condition taking bus voltage limits into account. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2000, 22, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tozyo, H.; Tada, Y.; Okamoto, H.; Tanabe, R. Reconfiguration of transmission systems with transient stability constraints. Proceeding of the 2000 IEEE Power Engineering Society Winter Meeting, Singapore, 23–27 January 2000; pp. 1320–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Ye, H.; Liu, Y. Decision support for choosing optimal electromagnetic loop circuit opening scheme based on analytic hierarchy process and multi-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation. Eng. Intell. Syst. Electr. Eng. Commun. 2008, 16, 183–191. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Zhao, K.; Liu, Y. Coordinated optimization for controlling short circuit current and multi-infeed dc interaction. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2014, 2, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormen, T.H.; Leiserson, C.E.; Rivest, R.L.; Stein, C. Introduction to Algorithms; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Girvan, M.; Newman, M.E.J. Community structure in social and biological networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7821–7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, M.E.J.; Girvan, M. Finding and evaluating community structure in networks. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2004, 69, 026113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santo, F.; Marc, B. Resolution limit in community detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Clauset, A.; Newman, M.E.J.; Moore, C. Finding community structure in very large networks. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2004, 70, 066111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, M.E.J. Analysis of weighted networks. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2004, 70, 056131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CIGRE. Working Group B4.41. In Systems with Multiple dc Infeed; CIGRE: Paris, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.; Tang, Y.; Bu, G.; Shao, Y. Voltage stability analysis of multi-infeed ac/dc power system based on multi-infeed short circuit ratio. Proceeding of the 2010 Power System Technology International Conference (POWERCON), Hangzhou, China, 24–28 October 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Y. Multi-objective reactive power and voltage control based on fuzzy optimization strategy and fuzzy adaptive particle swarm. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2008, 30, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Yang, K.; Sun, Y.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z. Decision support for choice optimal power generation projects: Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model based on the electricity market. Energy Policy 2006, 34, 3359–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Global Energy Interconnection; Academic Press: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, N.; Kang, C.; Ge, Y.; Xie, Z.; Huang, J. Techno-economic analysis of contingency reserve allocation scheme for combined UHV DC and AC recieving -end power system. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2016, 2, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).