Subsidence Evolution of the Leizhou Peninsula, China, Based on InSAR Observation from 1992 to 2010
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Hydrogeological Setting
3. Data Coverage and Method
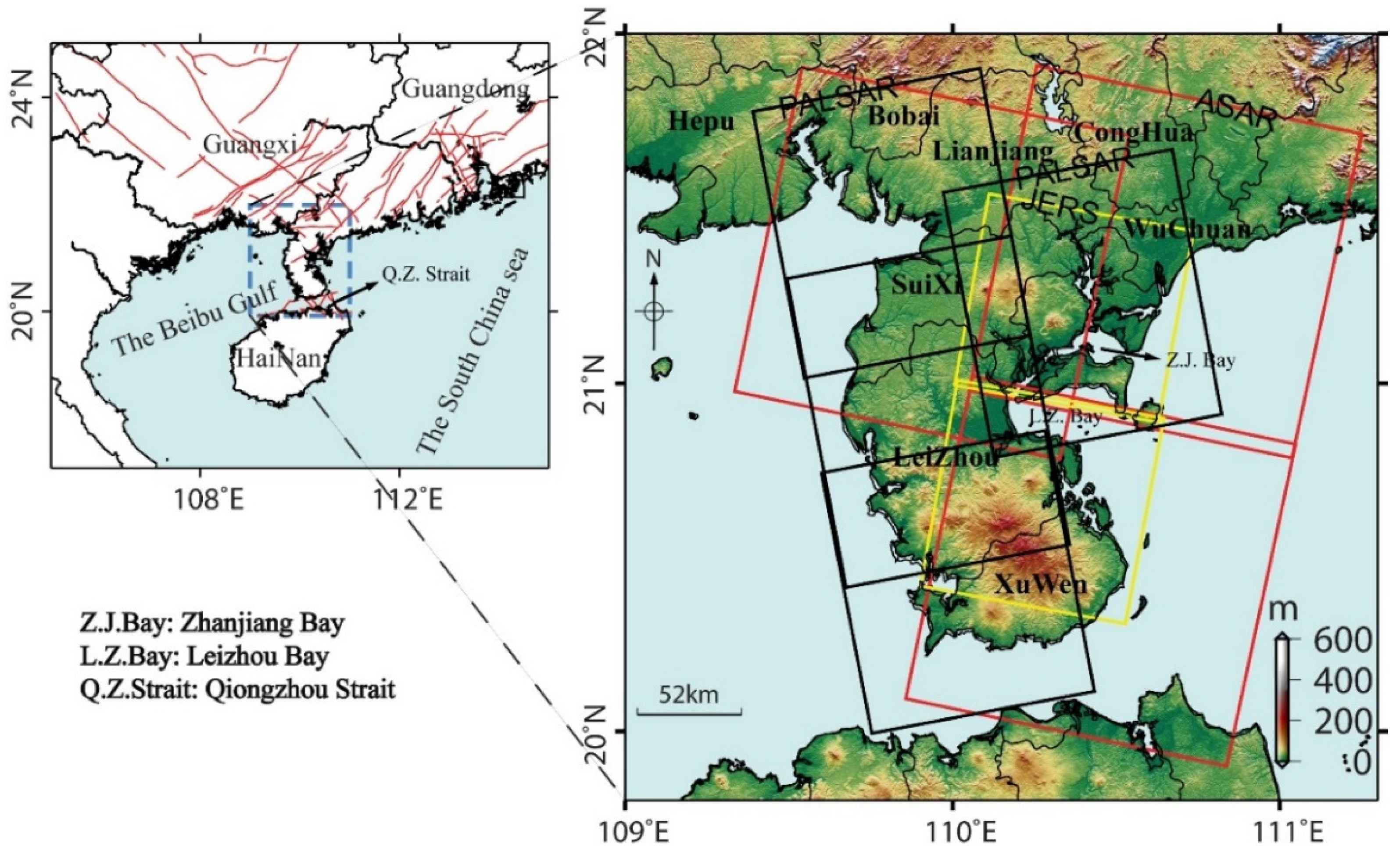
3.1. Data Coverage and InSAR Processing
3.2. Modified Stacking Method
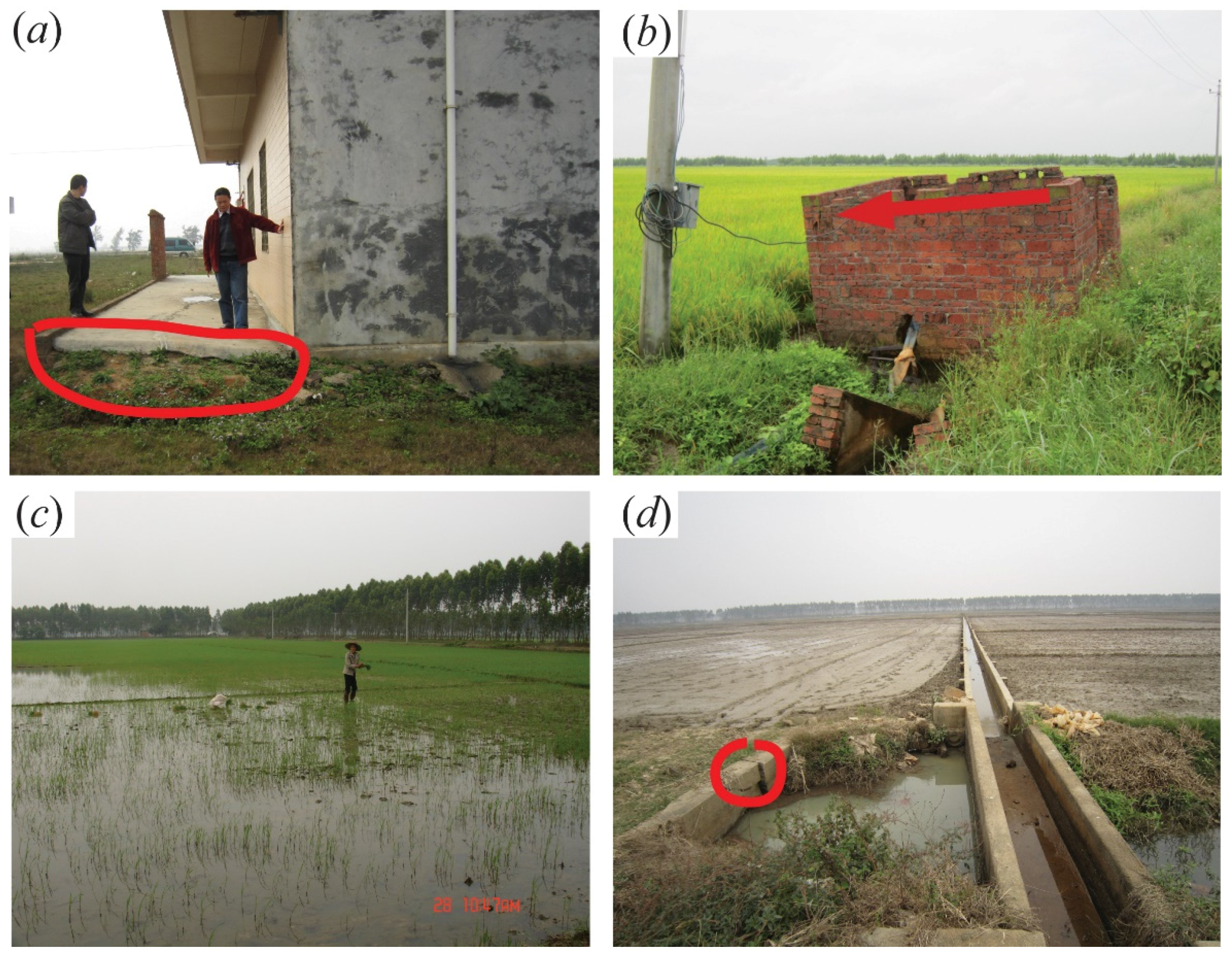
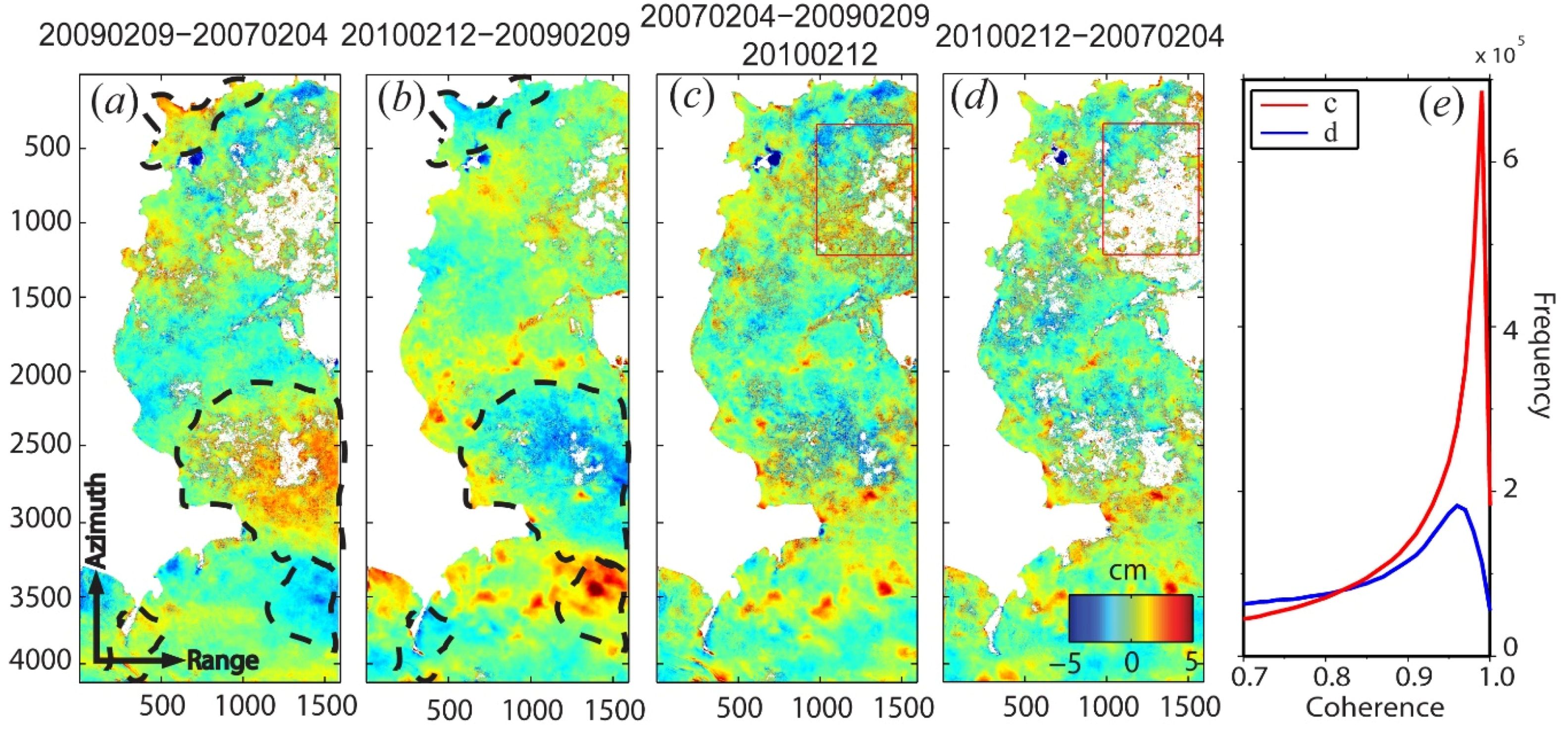
3.3. Uncertainty Estimation
4. Results: Spatial—Temporal Evolution of Subsidence
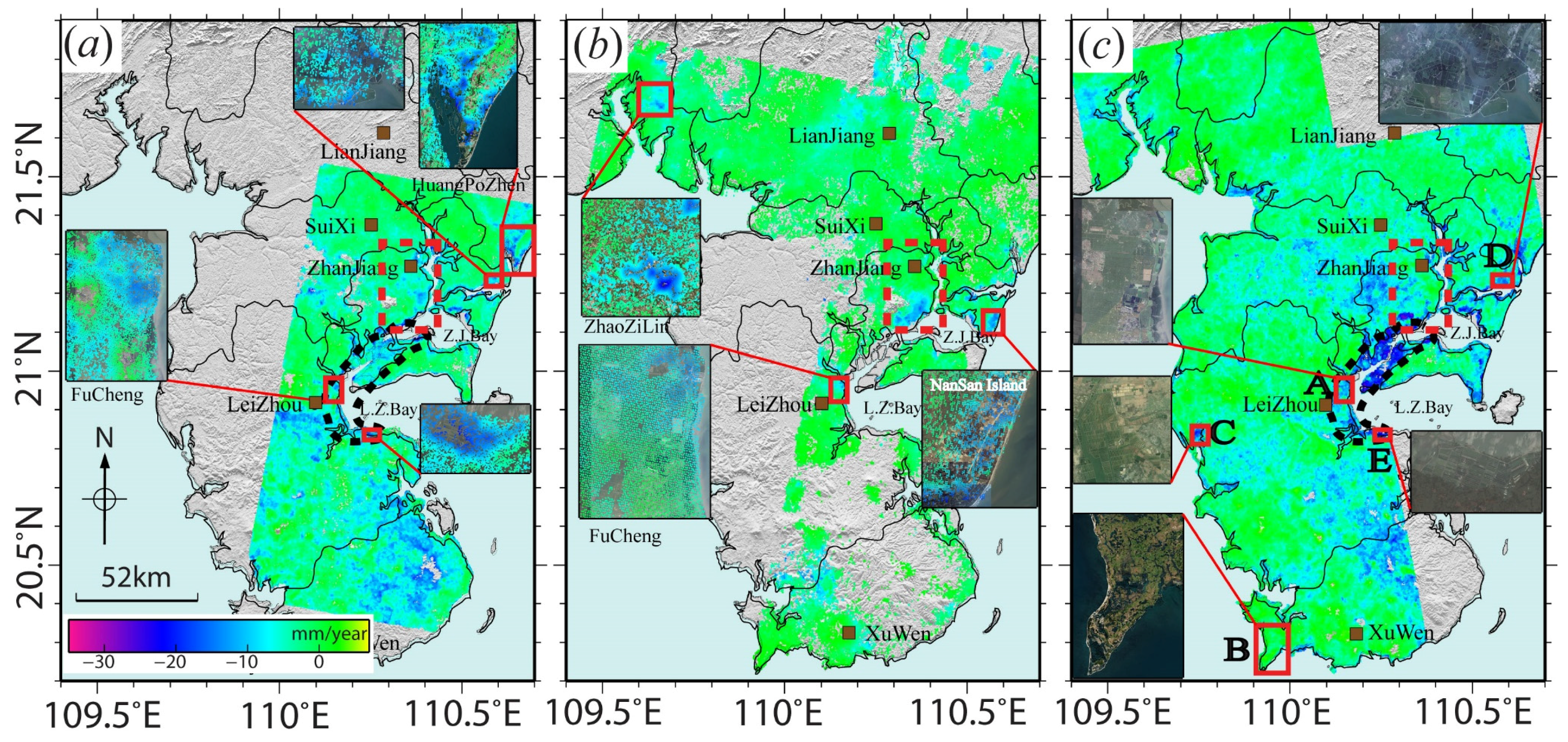
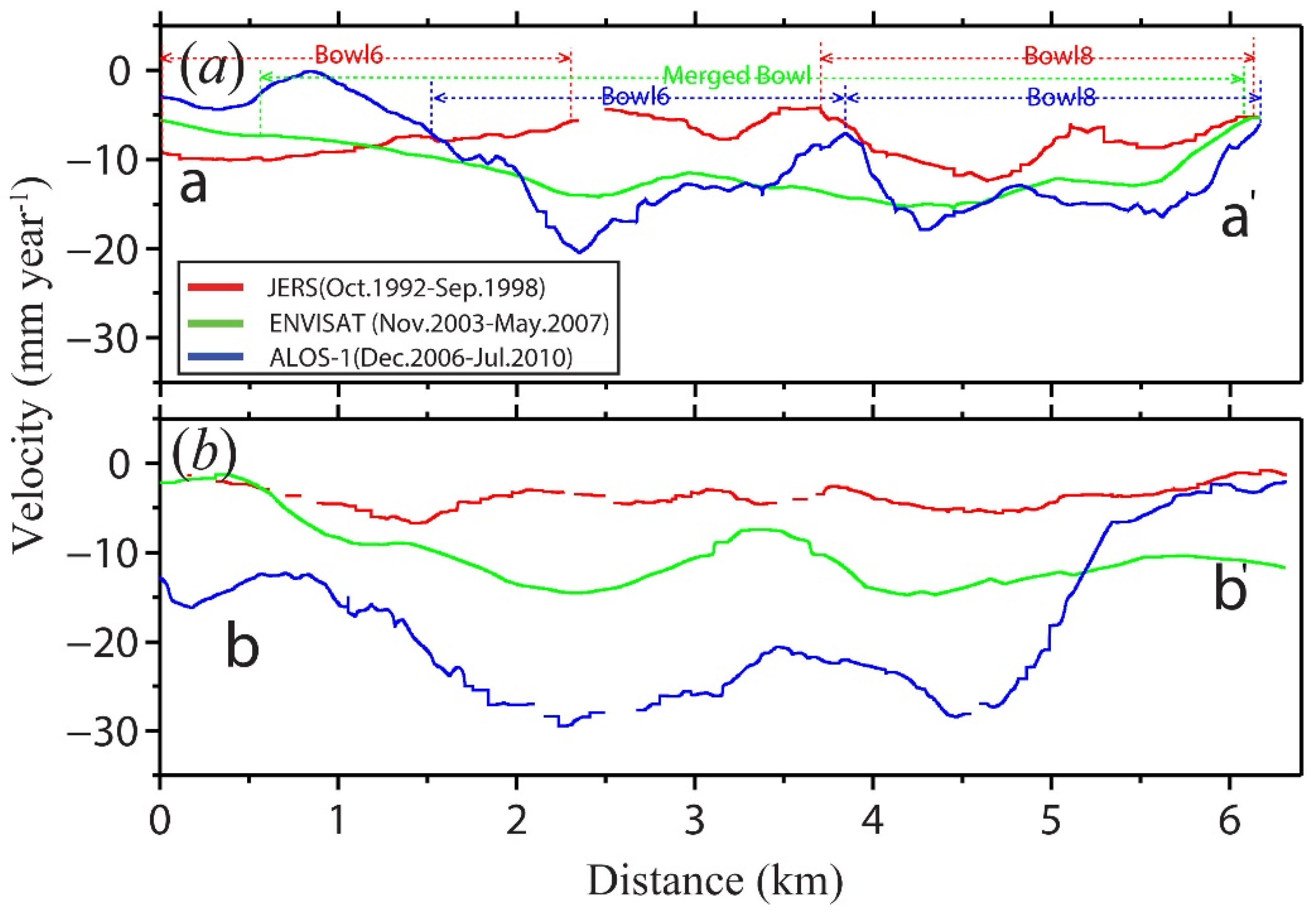
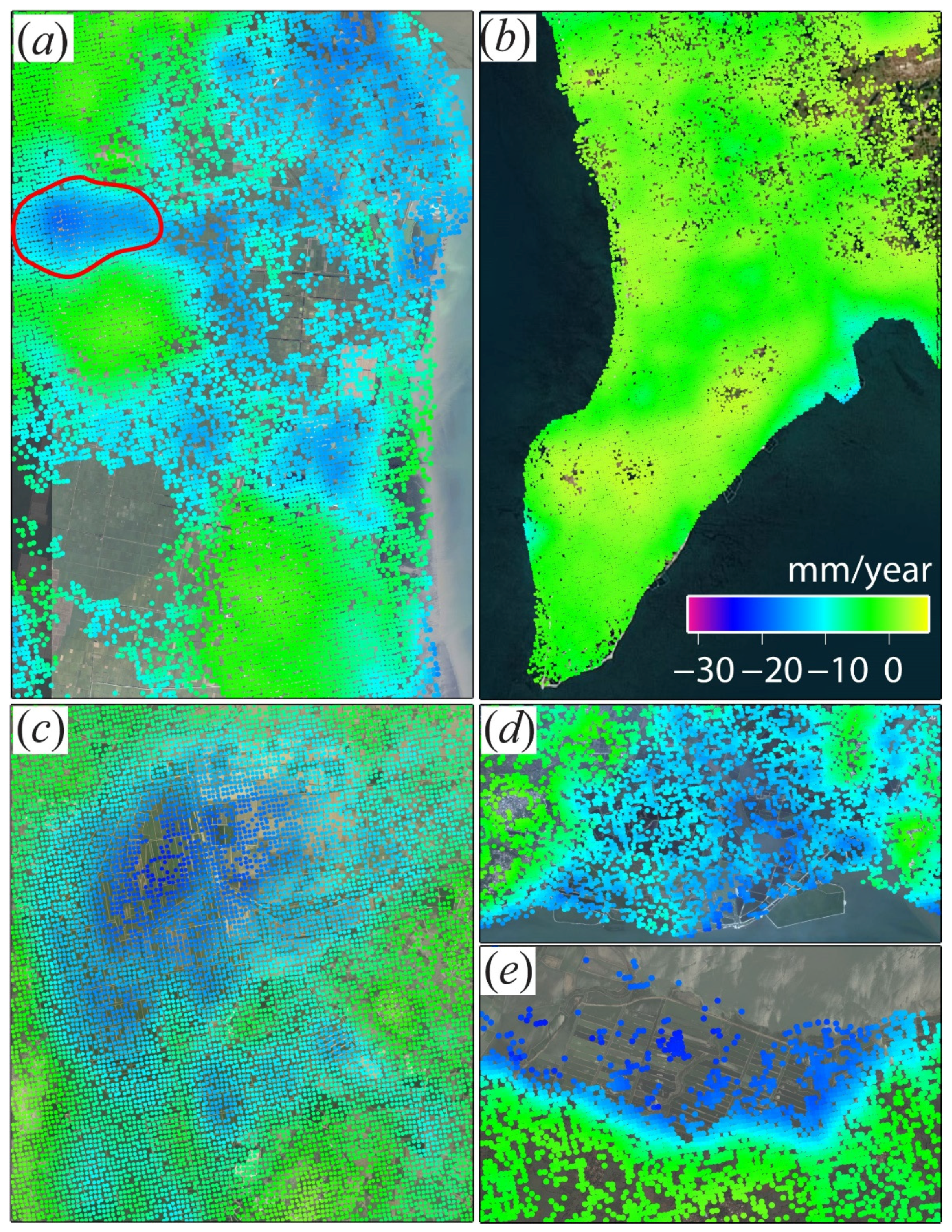
4.1. Rates of Land Subsidence
4.2. Land Subsidence in the Urban Areas
4.3. Land Subsidence in Agriculture Areas
4.4. Validations
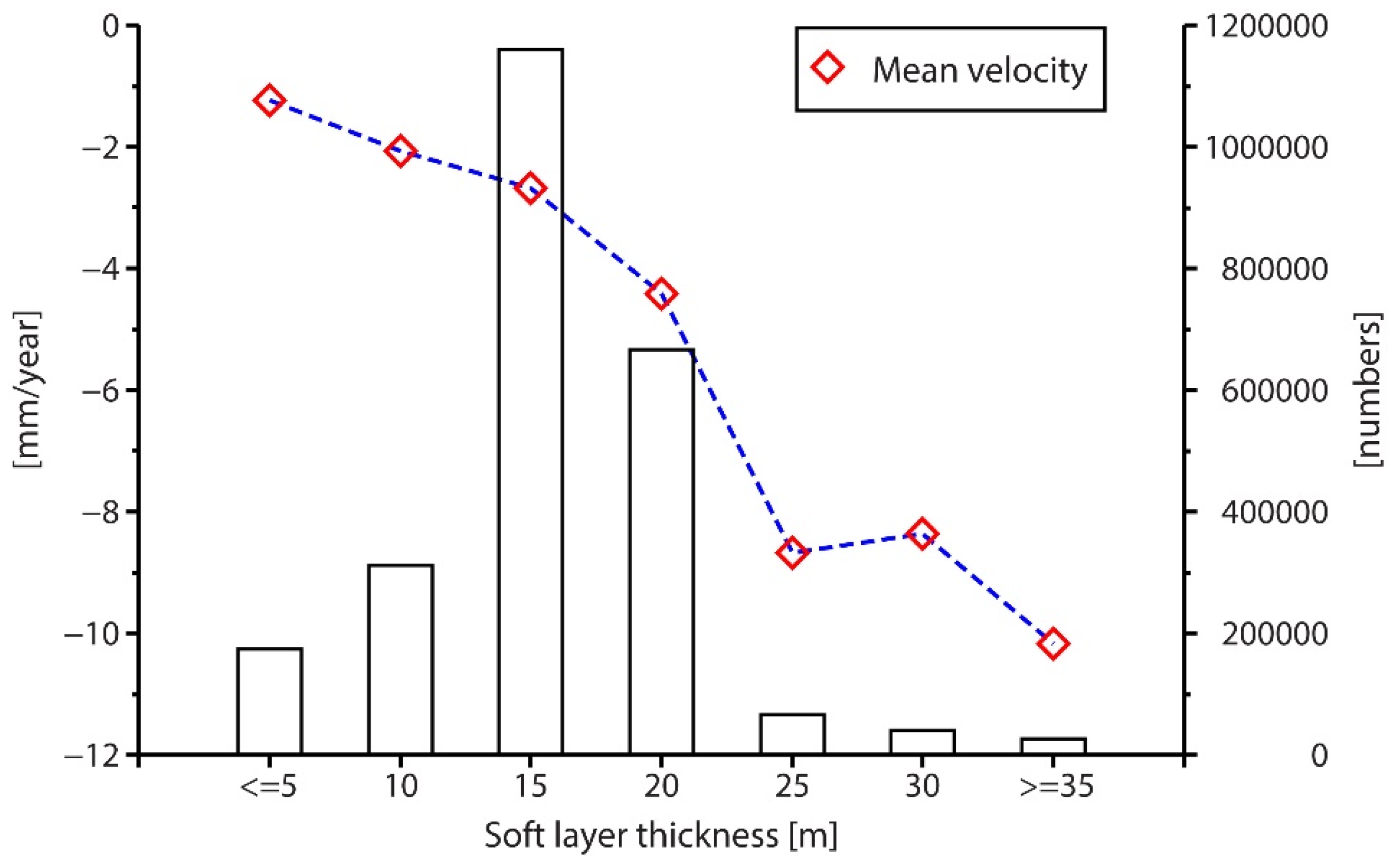
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.Q. Vulnerability of Ecological Environment in Leizhou Peninsula Coastal Zone and Counterneasures. In Proceedings of the 2012 2nd International Conference on IEEE Remote Sensing, Environment and Transportation Engineering (RSETE), Nanjing, China, 1–3 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.Q. Analysis of regional subsidence of Zhanjiang city. West-China Explor. Eng. 2009, 12, 108–110. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhanjiang Municipal Bureau of Land and Resources (ZMBLR). Available online: http://www.zjlr.gov.cn/newDetail-2000-20111204.htm (accessed on 17 January 2013).
- Zhou, X.; Yan, X.; Li, J.; Yao, J.M.; Dai, W.Y. Evolution of the groundwater environment under a long-term exploitation in the coastal area near Zhanjiang, China. Environ. Geol. 2007, 51, 847–856. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Lu, Z.; Ding, X.L.; Jung, H.S.; Feng, G.C.; Lee, C.W. Mapping ground surface deformation using temporarily coherent point SAR interferometry: Application to Los Angeles Basin. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yi, H.; Hu, J.; Feng, G. Deriving dynamic subsidence of coal mining areas using InSAR and logistic model. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.N.; Zhang, L.; Feng, G.C.; Lu, Z.; Sun, Q. On the Accuracy of Topographic Residuals Retrieved by MTInSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussard, E.; Wdowins, S.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Amelung, F. Land subsidence in central Mexico detected by ALOS InSAR time-series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, J.C.; Zhang, L.N.; Zou, G.X.; Liu, G.X.; Zhang, R.; Yu, B. Deformation Trend Extraction Based on Multi-Temporal InSAR in Shanghai. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 1774–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussard, E.; Amelung, F.; Abidin, H.; Hong, S.H. Sinking cities in Indonesia: ALOS PALSAR detects rapid subsidence due to groundwater and gas extraction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 128, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansoto, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Feng, G.C.; Li, Z.W.; Wang, Q.J.; Wang, C.C.; Xie, R.A. Coastal Subsidence Monitoring Associated with Land Reclamation Using the Point Target Based SBAS-InSAR Method: A Case Study of Shenzhen, China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.H. Study on Circulation Pattern and Numerical Modeling of Groundwater Flow in Leizhou Peninsula. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2013. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, M.; Liang, C. Optimal schemes of groundwater exploitation for prevention of seawater intrusion in the Leizhou Peninsula in southern China. Environ. Geol. 2003, 43, 978–985. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.H.; Wang, R.; Zhu, C.Q. Research on spatial distribution law of gray clays of Zhanjiang Formation. Rock Soil Mech. 2013, 34, 331–339. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wegmuller, U.; Werner, C.L. Gamma SAR processor and interferometry software. In Proceedings of the 3rd ERS Symposium Europe Space Agency Special, Florence, Italy, 14–21 March 1997; ESA SP-414: Auckland, New Zealand; pp. 1686–1692. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, C.; Feng, G.C.; Li, Z.W.; Shan, X.J.; Du, Y.N.; Wang, H.Q. Spatio-Temporal Error Sources Analysis and Accuracy Improvement in Landsat 8 Image Ground Displacement Measurements. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.N.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Feng, G.C.; Li, Z.W.; Chen, R.F.; Lin, C.W. Recent Landslide Movement in Tsaoling, Taiwan Tracked by TerraSAR-X/TanDEM-X DEM Time Series. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.C.; Li, Z.W.; Xu, B.; Shan, X.J.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, J.J. Coseismic Deformation of the 2015 Mw 6.4 Pishan, China, Earthquake, Estimated from Sentinel1 and ALOS2 Data. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2016, 87, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.C.; Li, Z.W.; Shan, X.J. Geodetic Model of the April 25, 2015 Mw 7.8 Gorkha Nepal Earthquake and Mw 7.3 Aftershock Estimated from InSAR and GPS Data. Geophys. J. Int. 2015, 203, 896–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, T.J.; Parsons, B.E.; Lu, Z. Toward mapping surface deformation in three dimensions using InSAR. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L07607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.H. A ground crack long itudinally penetrating the holocene sand dyke in Gangzi, Leizhou Peninsula is discovered. Quaty. Sci. 2008, 28, 712–720. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Strozzi, T.; Wegmuller, U.; Werner, C.; Wiesmann, A. Measurement of slow uniform surface displacement with mm/year accuracy. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2000 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 24–28 July 2000; pp. 2239–2241. [Google Scholar]
- Biggs, J.; Wright, T.; Lu, Z.; Parsons, B. Multi-interferogram method for measuring interseismic deformation: Denali Fault, Alaska. Geophys. J. Int. 2007, 170, 1165–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.N.; Feng, G.C.; Li, Z.W.; Zhu, J.J.; Peng, X. Generation of high precision DEM from TerraSAR-X/TanDEM-X. Chin. J. Geophys. 2015, 58, 1634–1644. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, B.; Wright, T.; Rowe, P.; Andrews, J.; Jackson, J. The 1994 Sefidabeh (eastern Iran) earthquake revisited: New evidence from satellite radar interferometry and carbonatedating about the growth of an active fold above a blind thrust fault. Geophys. J. Int. 2006, 164, 202–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Osmanoğlu, B.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Dixon, T.H.; Ávila-Olivera, J.A.; Garduño-Monroy, V.H.; Wdowinski, S. Monitoring land subsidence and its induced geological hazard with Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry: A case study in Morelia, Mexico. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonì, R.; Herrera, G.; Meisina, C.; Notti, D.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Zucca, F.; Fernández-Merodo, J.A. Twenty-year advanced DInSAR analysis of severe land subsidence: The Alto Guadalentín Basin (Spain) case study. Eng. Geol. 2015, 198, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, G.; Fernández, J.A.; Tomás, R.; Cooksley, G.; Mulas, J. Advanced interpretation of subsidence in Murcia (SE Spain) using A-DInSAR data-modelling and validation. Nat. Hazard. Earth Sys. 2009, 9, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ding, L.G.; Li, W.H.; Lu, W.F.; Cai, L.X. Characteristics of the evolution of groundwater flow field in Zhanjiang. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2006, 33, 95–98. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Q.; Su, Z.H. The characteristic analysis and the prevention and control methods from the sea water invasion in Naozhou island. J. Geol. Hazards Environ. Preserv. 2007, 18, 28–32. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi, K. Erdbaumechanik auf Bodenphysikalischer Grundlage; Franz Deuticke: Wien, Austria, 1925; p. 399. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, J.; Howard, A.Z. Seasonal subsidence and rebound in Las Vegas Valley, Nevada, observed by synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 1551–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.H. Causes and prevention of ground subsidence in Shaoshan village, Leizhou city. West-China Explor. Eng. 2011, 5, 121–124. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.P.; Li, G.M.; Li, M.; Dong, Y.H. Numerical modeling of tidal effects on groundwater in the coastal aquifer of Donghai Island. New Front. Eng. Geol. Environ. Springer Geol. 2013, 9, 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, S.; Overeem, I.; Tanaka, A.; Syvitski, J.P.M. Land subsidence at aquaculture facilities in the Yellow River delta, China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 3898–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.Q.; Xue, Y.Q.; Wu, J.C.; Ye, S.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Z.X.; Yu, J. Characterization of regional land subsidence in Yangtze delta, China: The example of Su-Xi-Chang area and the city of Shanghai. Hydrogeol. J. 2008, 16, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syvitski James, P.M. Sinking deltas due to human activities. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera-Hernandez, J.J.; Gaskin, S.J. The basin of Mexico aquifer system: Regional groundwater level dynamics and database development. Hydrogol. J. 2007, 15, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, H.Z.; Andreas, H.; Gumilar, I.; Fukuda, Y.; Pohan, Y.E.; Deguchi, T. Land subsidence of Jakarta (Indonesia) and its relation with urban development. Nat. Hazards 2011, 59, 1753–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Guerrero, A.; Rudolph, D.L.; Cherry, J.A. Analysis of long-term land subsidence near Mexico City: Field investigations and predictive modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 35, 3327–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


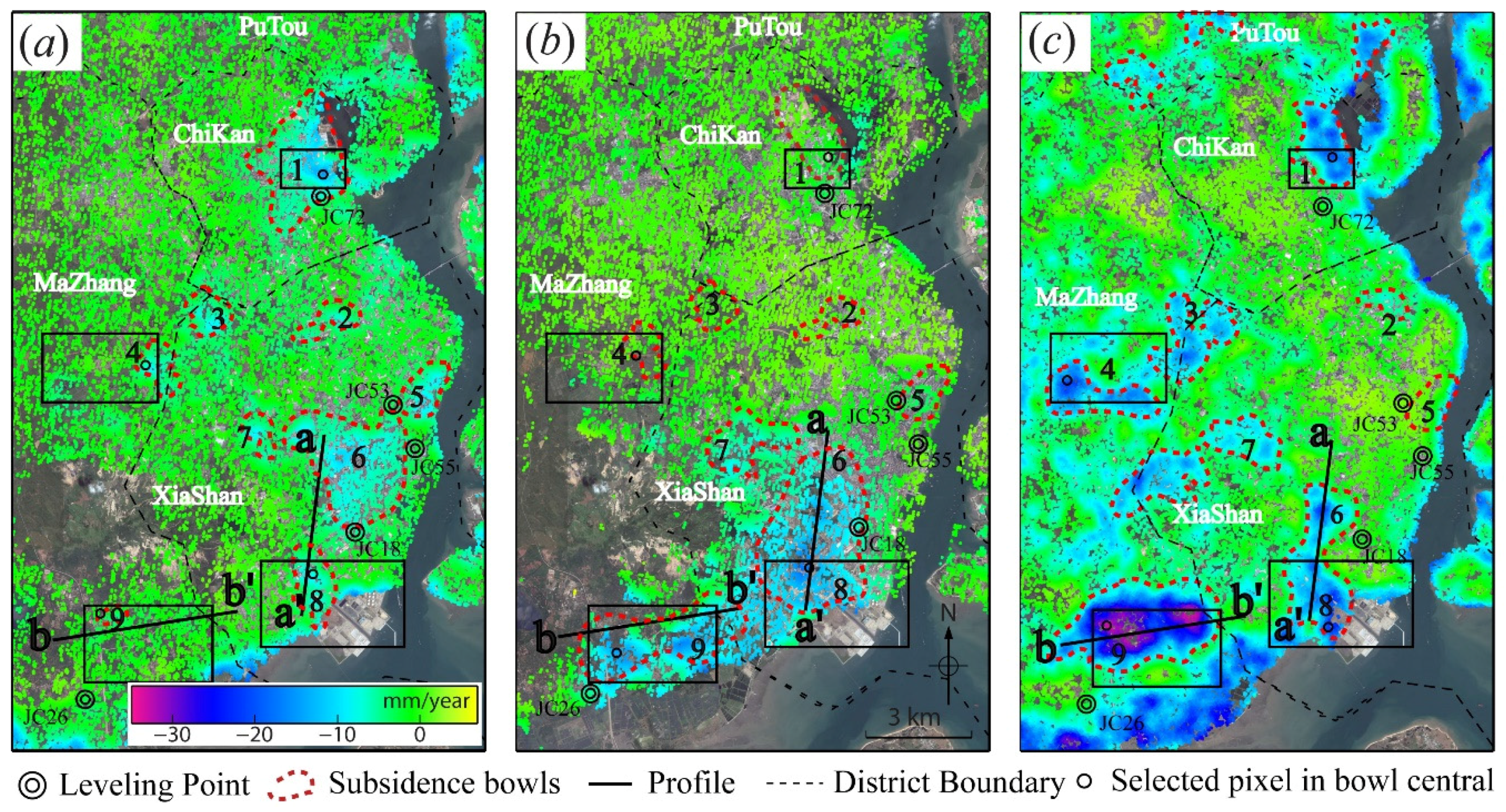
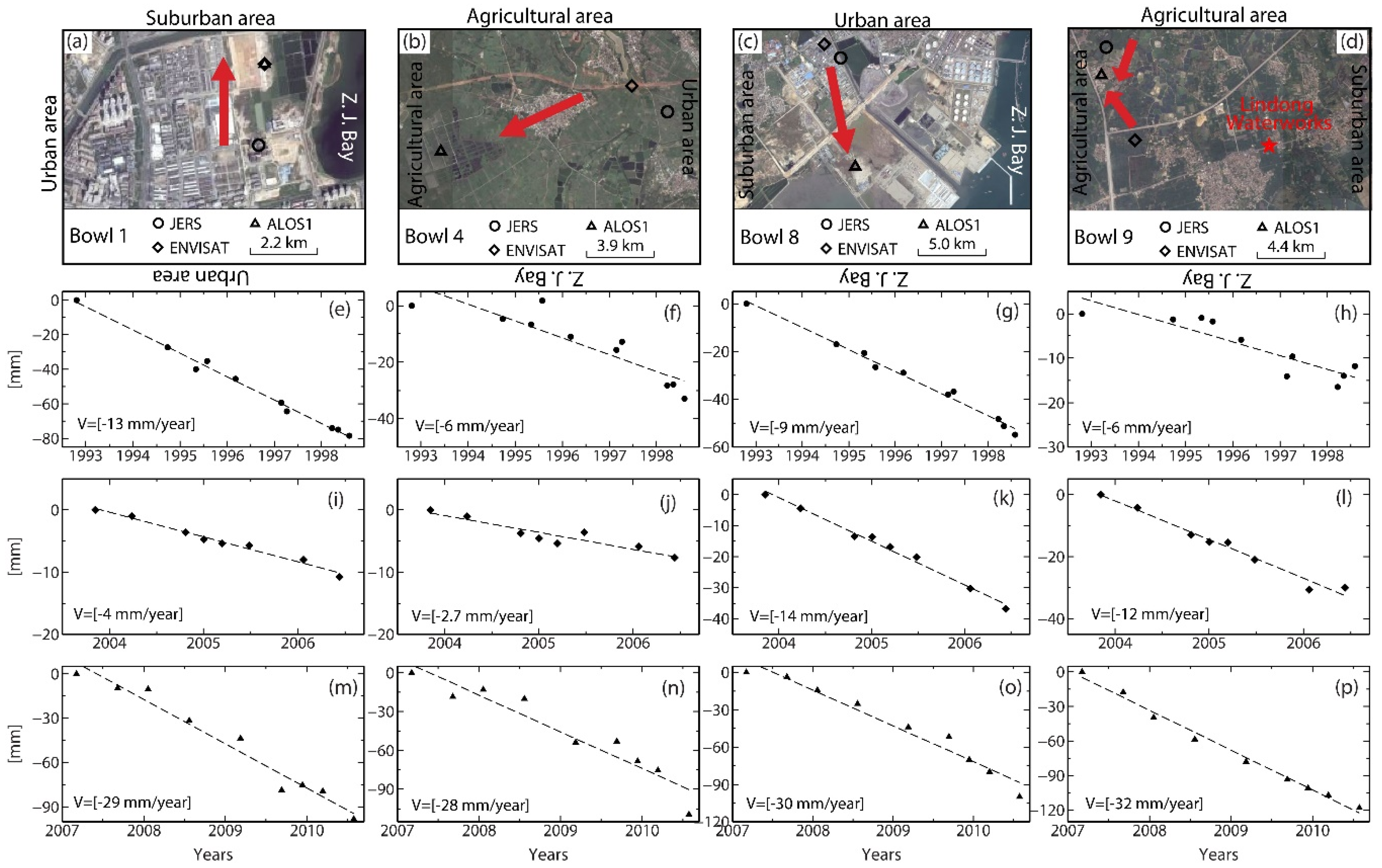

| Data | B1 (U) | B2 (U) | B3 (A) | B4 (A) | B5 (U) | B6 (U) | B7 (U) | B8 (U) | B9 (S) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Areas: km² (Bowl: B, Urban area: U, Agricultural area: A, Suburban area; S) | |||||||||
| JERS | 3.3 | 1.9 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 2.3 | 9.7 | 1.4 | 2.1 | 0.9 |
| ENVISAT | - | - | - | - | - | 10.7 | 2.8 | 10.8 | 4.3 |
| ALOS1 | 3.0 | 0.8 | 4.8 | 6.1 | 2.0 | 6.1 | 2.7 | 6.1 | 12.2 |
| Comparison (mm/year) | JC18 | JC72 | JC53 | JC26 | JC55 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leveling1989~1999 | −5 | −3.2 | −3.6 | −2.5 | −3.1 |
| InSAR_JERS1992~1998 | −7 | −5 | −6 | −4 | −5 |
| Difference | 2 | 1.8 | 2.4 | 1.5 | 1.9 |
| Urban areas | Mexico City (Chalco) | Jakarta of Indonesia | LZP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aquifers | Lacustrine aquitard Granular aquifer Volcanic aquitard (0 < d < 300m) | Upper aquifer (<40 m) Middle aquifer (40 < d < 140 m) Lower aquifer (140 < d < 250 m) | Shallow aquifer (<30 m) Middle aquifer (30 < d < 200 m) Deep aquifer (200 < d < 500 m) |
| Sediments | Lacustrine deposits and Alluvial deposits of Quaternary | Quaternary sediments overlying Tertiary sediments | Unconsolidated alluvial and lacustrine overlaying the basement rocks of Neogene and Quaternary age. |
| Ava. extraction speed | 1990s: 7.8 m³/s | 1995: 1.5 m³/s | Until 2001: 6.7 m³/s |
| Max. velocity | <40 cm/year | <22 cm/year | <3.2 cm/year |
| Water level decline speed | 1.5 m/year | 0.1–1.9 m/year | 0.1–0.8 m/year |
| Correlation with surface geology | Thickness of deposits | Land use | Thickness of soft soil/Land use |
| Agricultural areas | Mexico City(Chalco) | Jakarta of Indonesia | LZP |
| Max. velocity | <18.4 cm/year | 15.1 cm/year | <2.5 cm/year |
| Surface geology | Compressible deposits | Surficial deposits | Volcanic basalt |
| Correlation with geology | Type of compressible deposits | Correlate with land use | Thickness of soft soil |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, Y.; Feng, G.; Peng, X.; Li, Z. Subsidence Evolution of the Leizhou Peninsula, China, Based on InSAR Observation from 1992 to 2010. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7050466
Du Y, Feng G, Peng X, Li Z. Subsidence Evolution of the Leizhou Peninsula, China, Based on InSAR Observation from 1992 to 2010. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(5):466. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7050466
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Yanan, Guangcai Feng, Xing Peng, and Zhiwei Li. 2017. "Subsidence Evolution of the Leizhou Peninsula, China, Based on InSAR Observation from 1992 to 2010" Applied Sciences 7, no. 5: 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7050466
APA StyleDu, Y., Feng, G., Peng, X., & Li, Z. (2017). Subsidence Evolution of the Leizhou Peninsula, China, Based on InSAR Observation from 1992 to 2010. Applied Sciences, 7(5), 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7050466







