Importance of Physical and Physiological Parameters in Simulated Particle Transport in the Alveolar Zone of the Human Lung
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Model Development and FSI Approach
2.2. Fluid-Structure Interaction Equations
2.3. Flow and Particle Transport Simulation
2.4. Boundary Condition
2.5. Analysis Description
3. Results and Discussion
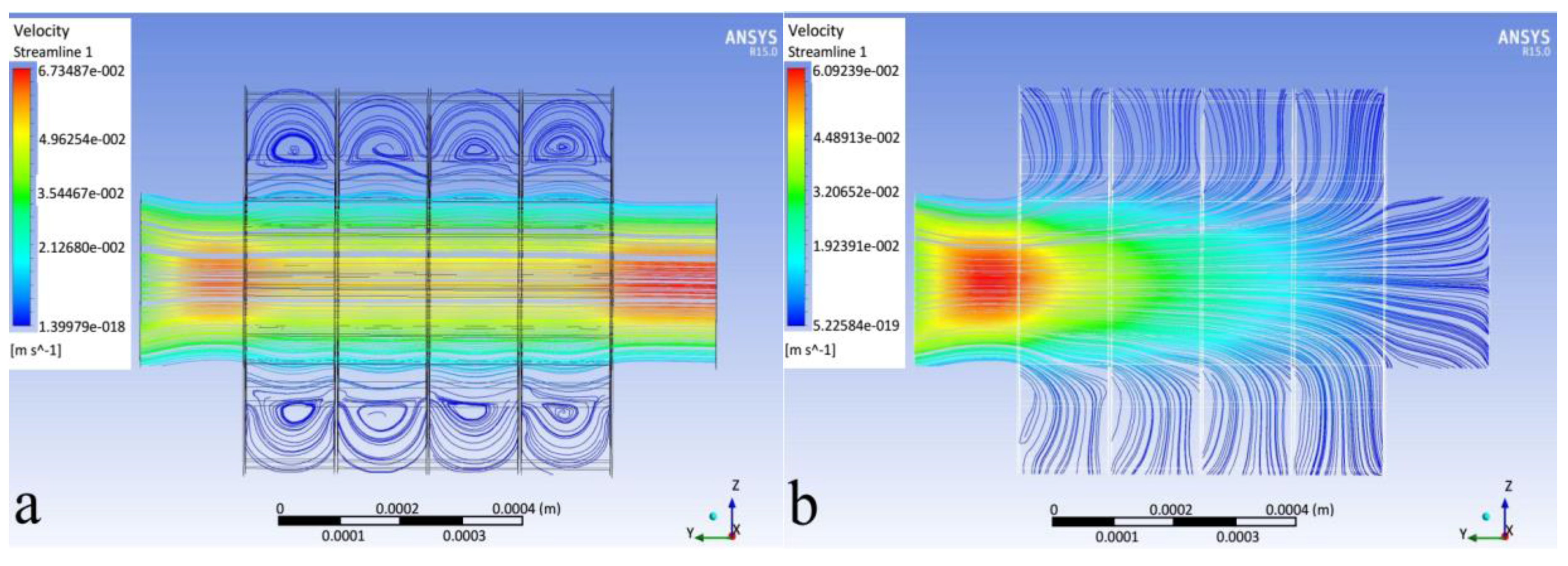
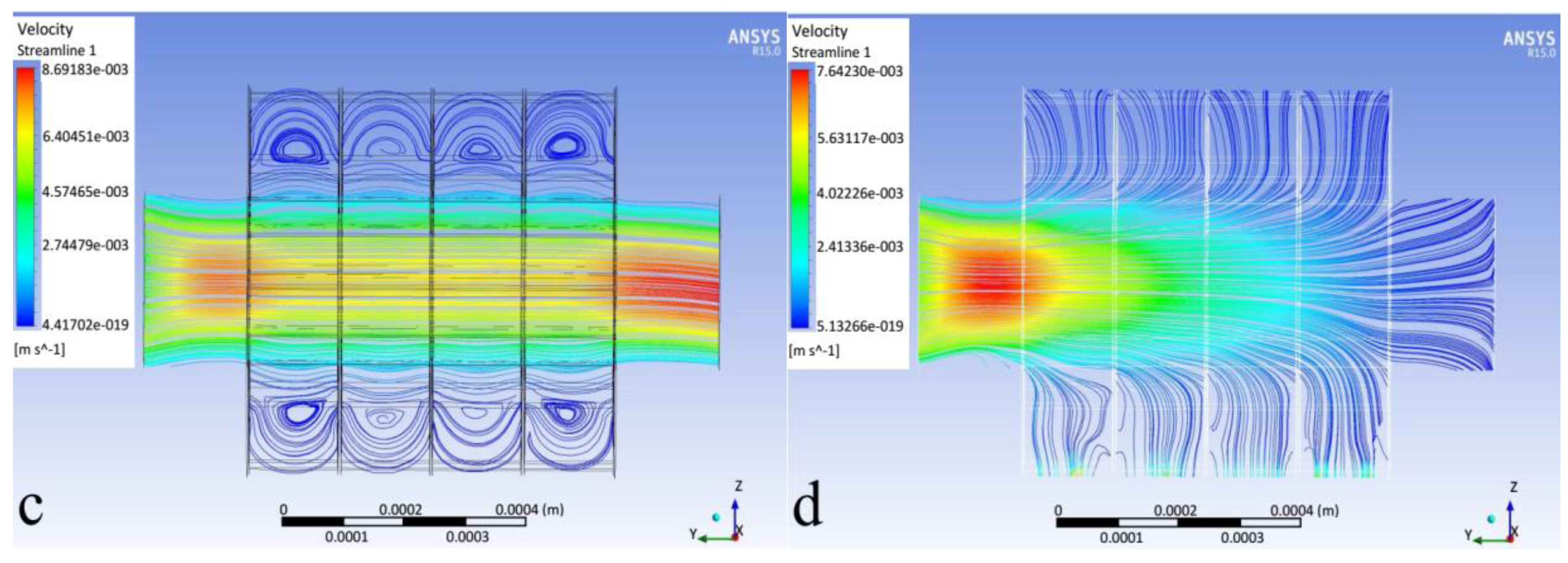
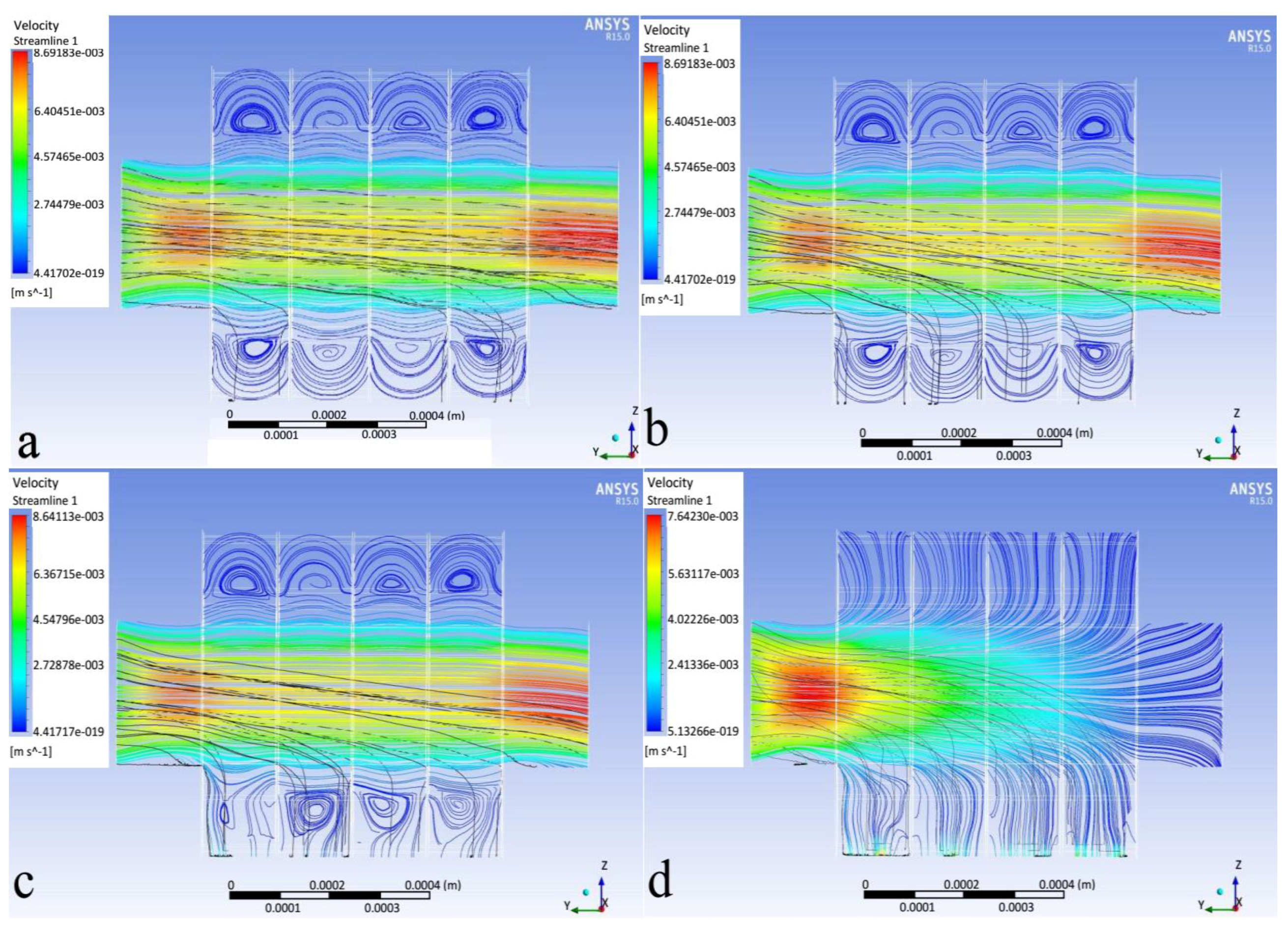
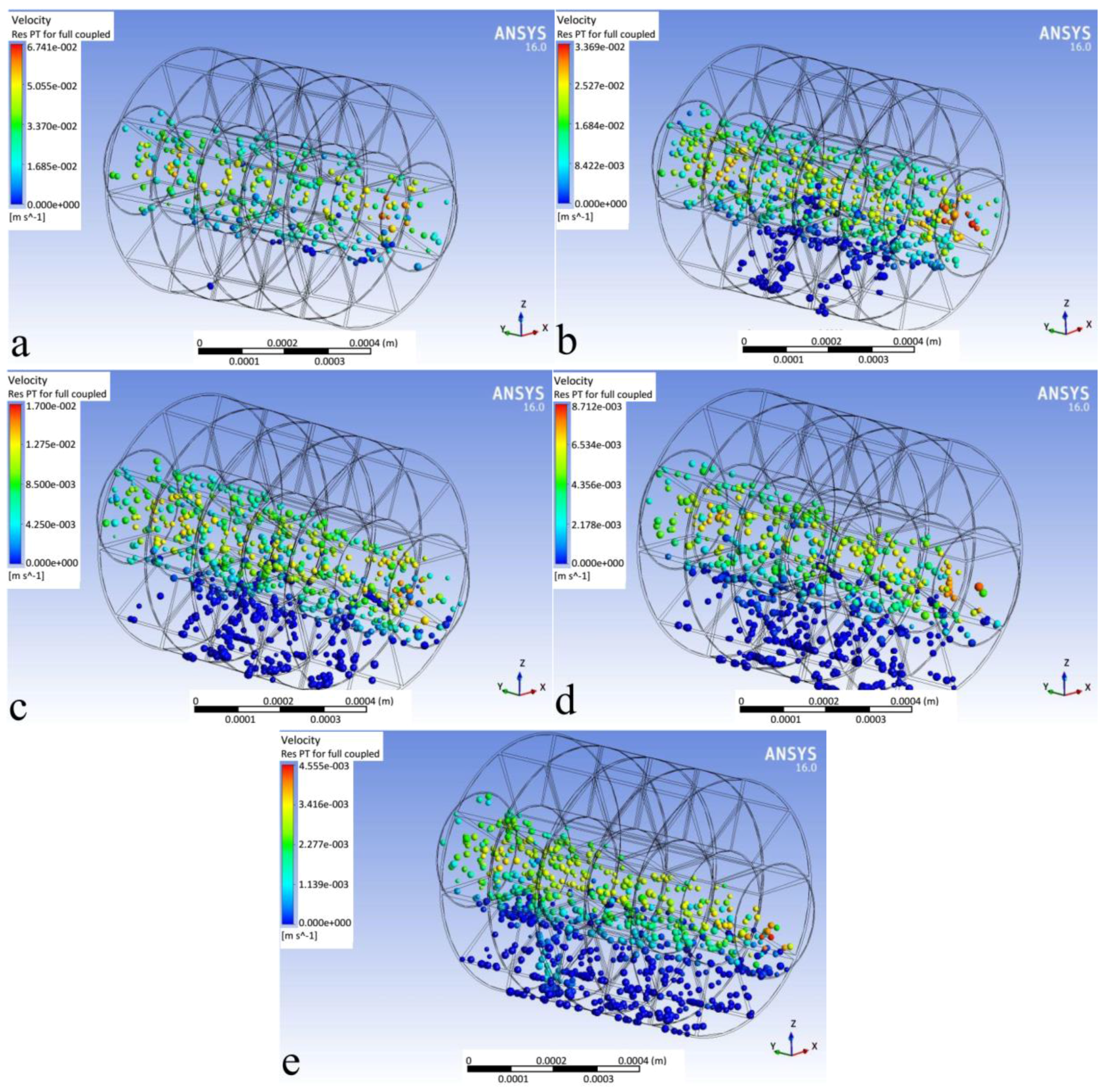
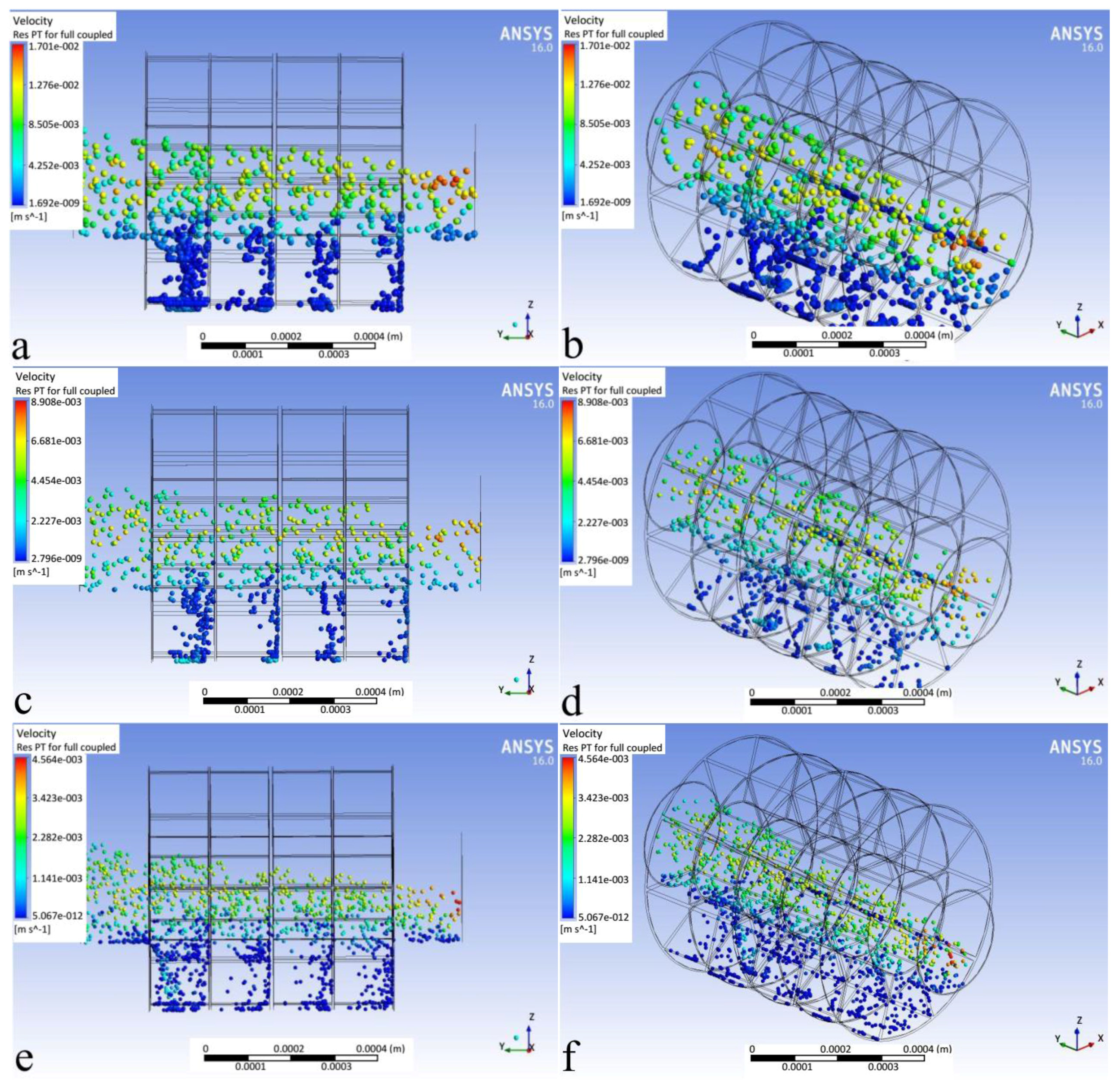
3.1. Flow Field and Particle Trajectories
- (a)
- The direct inertial impaction causes deposition in the first rows.
- (b)
- The 3-D secondary flow effects cause wall deposition.
- (c)
- Particle–particle (elastic) contact forces cause wall deposition.
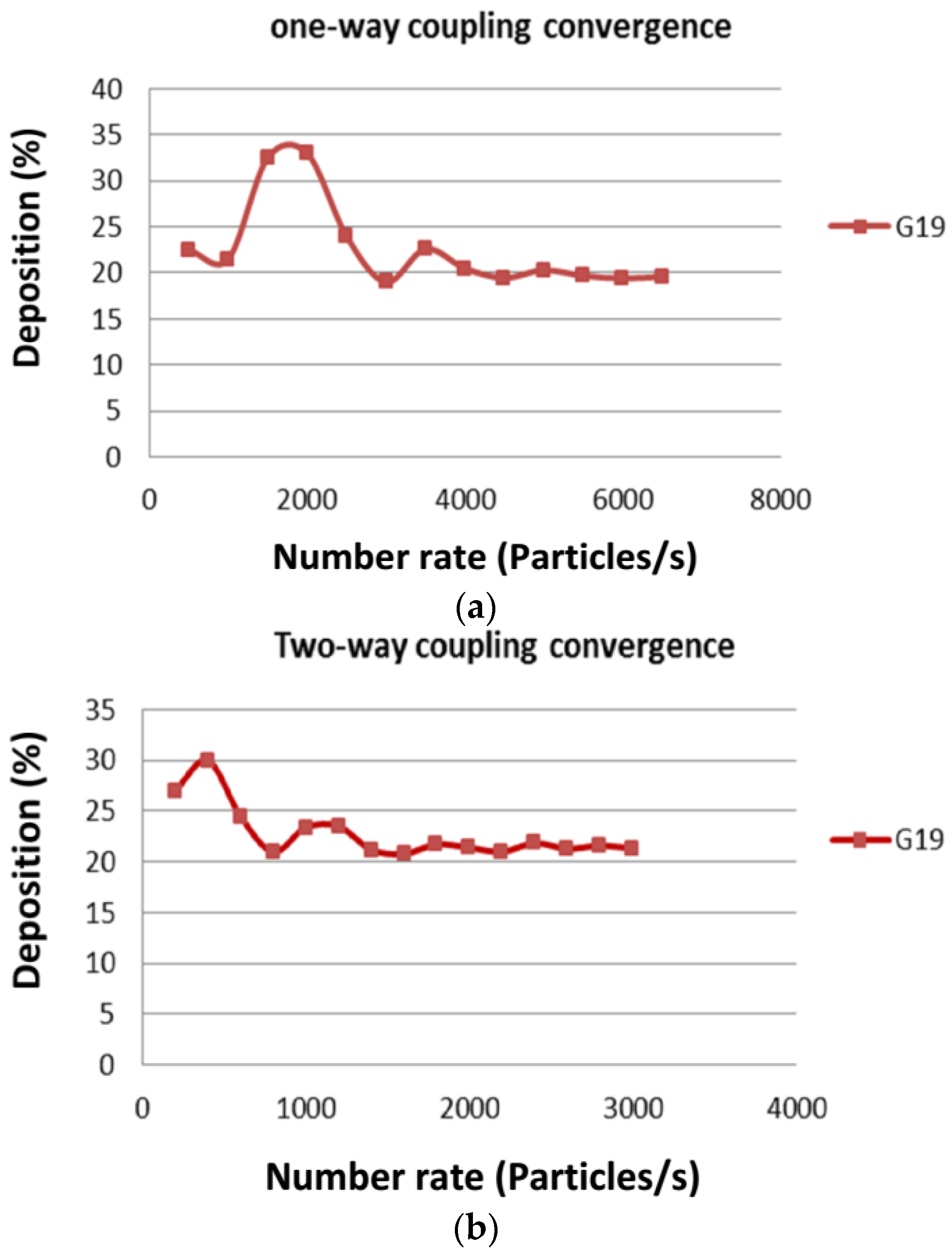
3.2. Comparisons of Deposition Efficiency Predictions Using DPM Approach
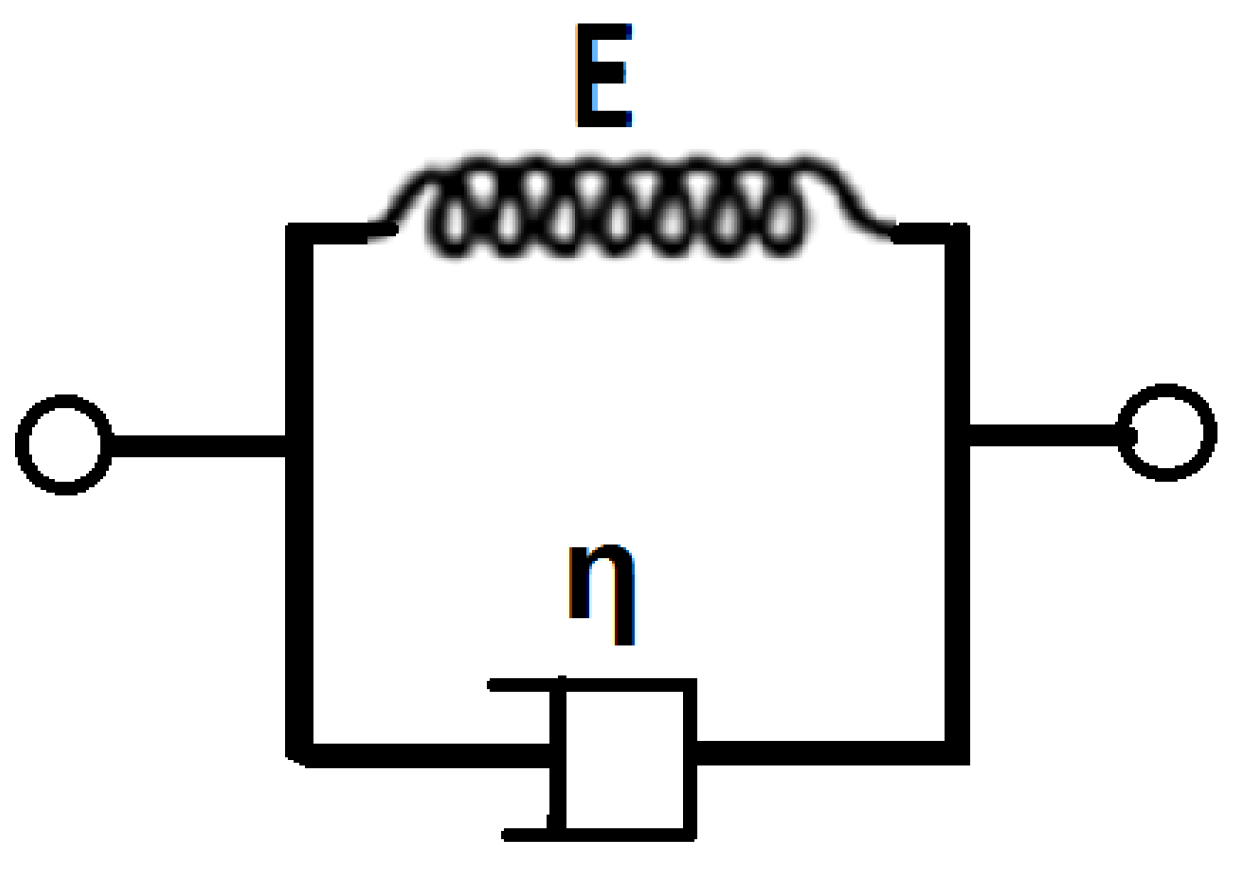
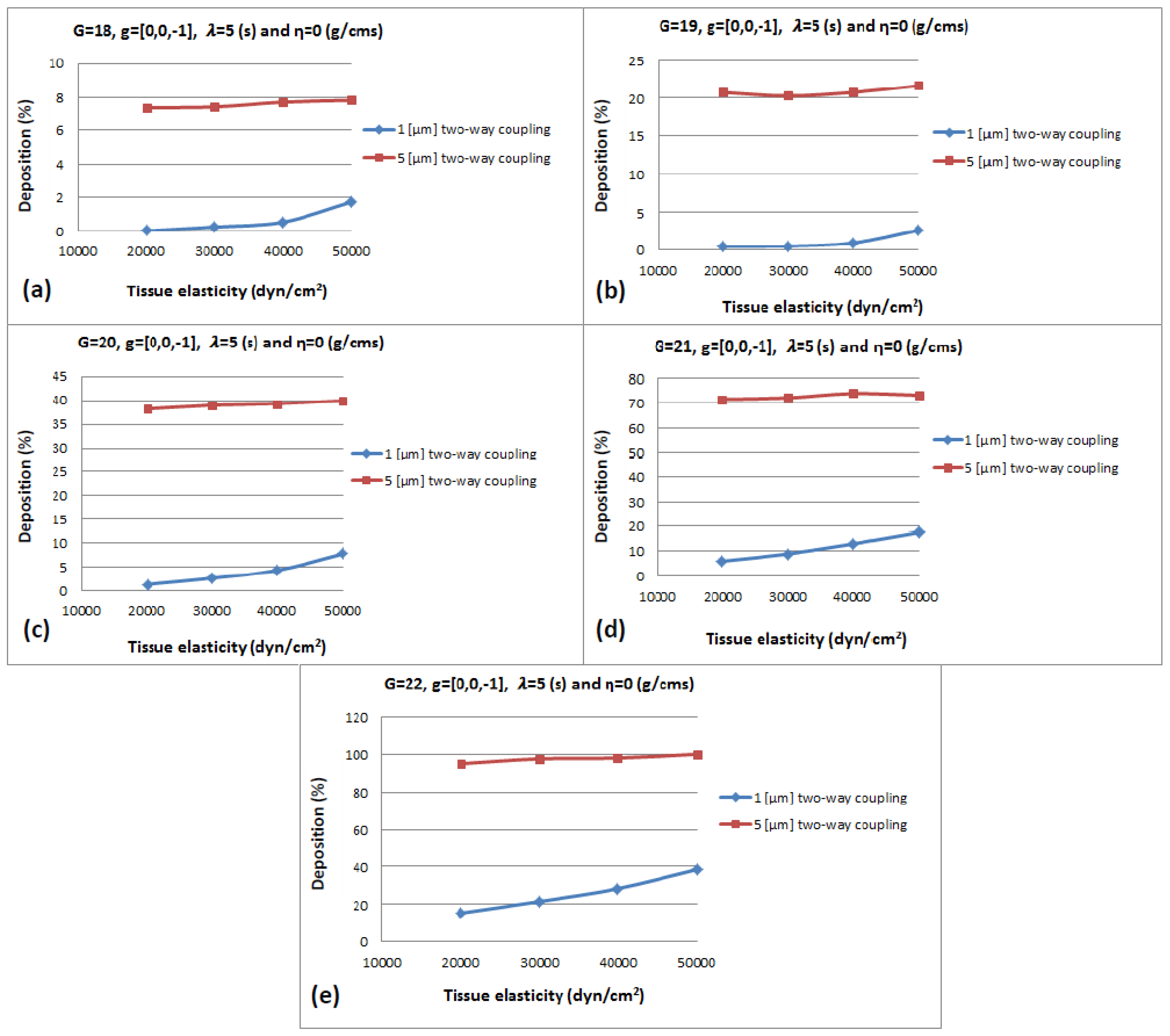
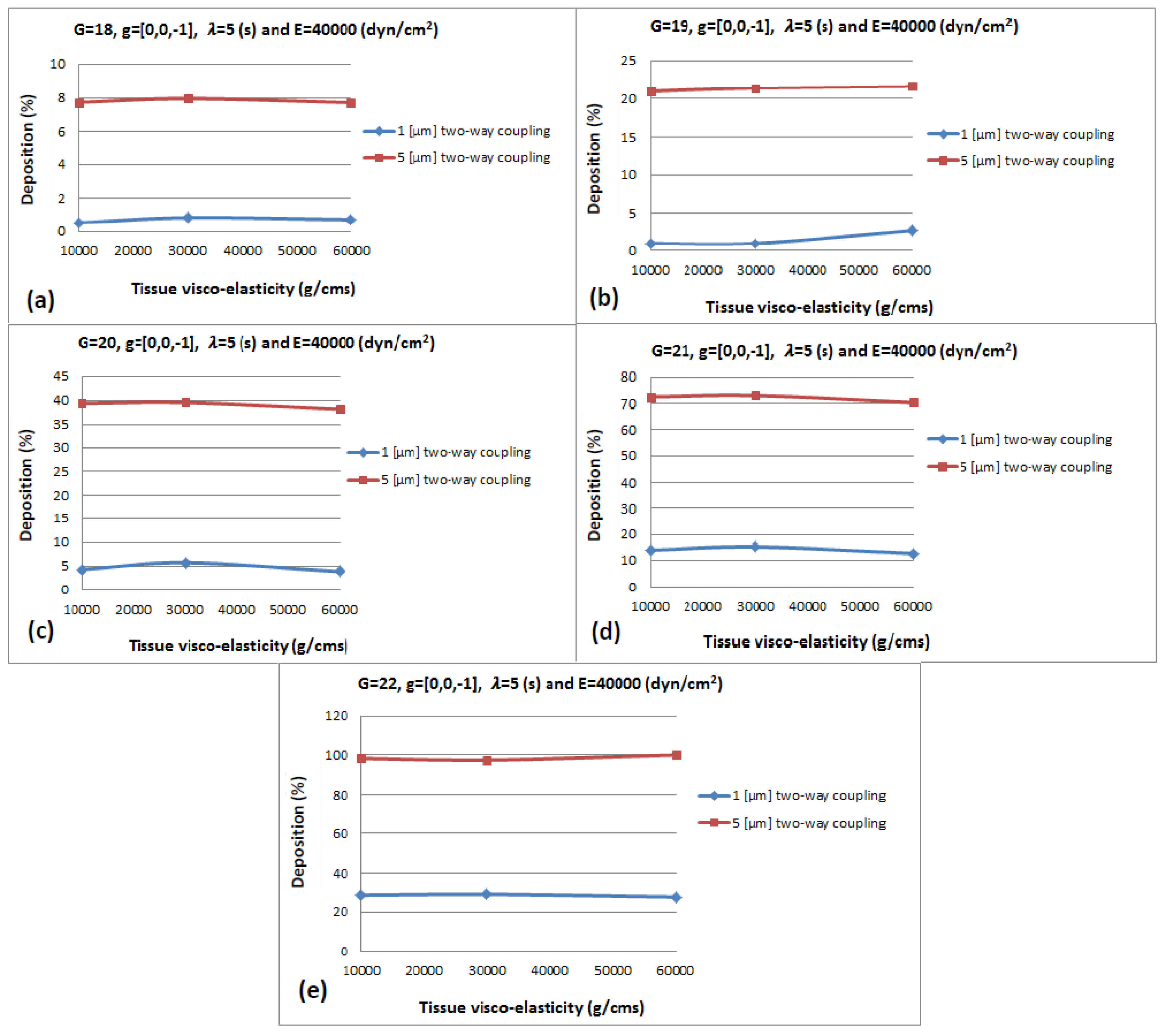
3.2.1. Tissue Visco-Elasticity
3.2.2. Tidal Breathing
3.2.3. Particle Diameter
3.2.4. Gravity Orientation
4. Comparison with Previous Studies
5. Conclusions
Limitations of the Model
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| ATS | American Thoracic Society |
| Ap | Cross sectional area of particles |
| CVM | coefficients of virtual force |
| HPIVs | Human par influenza viruses |
| The fluid nodal displacements | |
| The solid nodal displacements | |
| E | Young’s modulus |
| FD | Drag force |
| FBr | Force resulting from Brownian motion |
| FC,ij | Inter-particle contact forces resulting from DEM approach |
| FVM | Virtual mass force |
| MF | Coefficients of virtual force |
| mg | Gravitational force |
| nj | The interface normal vector |
| K | Boltzmann constant |
| p | Pressure of fluid |
| ∆P | The pressure gradient |
| RMS | Root mean square |
| RSV | Respiratory Syncytial Virus |
| Sn | Normal stiffness |
| S0 | Amplitude of the white noise process |
| t | Time |
| t | The local vector of fluid |
| T | Temperature of air |
| u | Velocity of fluid |
| up | Velocity of particles |
| ν | Poisson ratio |
| Breathing period | |
| η | Tissue viscosity |
| ρ | Density of fluid |
| µ | Viscosity of fluid |
| υ | Kinematic viscosity of air |
| v | Velocity vector of fluid |
| The Kronecker delta function | |
| The solid stress tensors | |
| The fluid stress tensors | |
| Zero-mean, unit-variance Gaussian random vector |
References
- Heyder, J.; Rudolf, G. Mathematical-models of particle deposition in the human respiratory-tract. J. Aerosol Sci. 1984, 15, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koblinger, L.; Hofmann, W. Monte-Carlo modeling of aerosol deposition in human lungs. 1. Simulation of particle-transport in a stochastic lung structure. J. Aerosol Sci. 1990, 21, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharian, B.; Wood, R.; Schlesinger, R.B. Empirical modeling of particle deposition in the alveolar region of the lungs: a basis for interspecies extrapolation. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1995, 27, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martonen, T.B. Analytical model of hygroscopic particle behavior in human airways. Bull. Math. Biol. 1982, 44, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsakou, C.; Helmis, C.; Housiadas, C. Eulerian modeling of lung deposition with sectional representation of aerosol dynamics. J. Aerosol Sci. 2005, 36, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, W.; Asgharian, B.; Winkler-Heil, R. Modeling intersubject variability of particle deposition in human lungs. J. Aerosol Sci. 2002, 33, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comer, J.K.; Kleinstreuer, C.; Zhang, Z. Flow structures and particle deposition patterns in double-bifurcation airways models. Part 1. Air flow fields. J. Fluid Mech. 2001, 435, 25–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, F.; Butler, J.; Tsuda, A. Kinematically irreversible acinar flow: A departure from classical dispersive aerosol transport theories. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dailey, H.L.; Ghadiali, S.N. Fluid-structure analysis of micro-particle transport in deformable pulmonary alveoli. J. Aerosol Sci. 2007, 38, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, S.; Butler, J.P.; Brenner, H.; Emanuel, I.; Tsuda, A. Shear flow over a self-similar expanding pulmonary alveolus during rhythmical breathing. J. Fluid Mech. 2000, 405, 243–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haefeli-Bleuer, B.; Weibel, E. Morphometry of the human pulmonary acinus. Anat. Rec. 1988, 220, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, L.; Kim Prisk, G.; Darquenne, C. Importance of the bifurcation zone and branch orientation in simulated aerosol deposition in the alveolar zone of the human lung. J. Aerosol Sci. 2006, 37, 37–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussmann, B.; Pfitzner, M.; Esch, T.; Frank, T.A. stochastic particle-particle collision model for dense gas-particle flows implemented in the Lagrangian solver of ANSYS CFX and its validation. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Multiphase Flows (ICMF), Leipzig, Germany, 23–27 July 2007; pp. 9–13.
- Baoshun, M.; Ruwetb, V.; Corierib, P.; Theunissenb, R.; Riethmullerb, M.; Darquenne, C. CFD simulation and experimental validation of fluid flow and particle transport in a model of alveolated airways. J. Aerosol Sci. 2009, 40, 403–414. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.; Ahmadi, G. Dispersion and deposition of spherical particles from point sources in a turbulent channel flow. J. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1992, 16, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Zhong, W.; Jin, B.; Yuan, Z.; Lu, Y. Modeling of gas–particle turbulent flow in spout-fluid bed by computational fluid dynamics with Discrete Element Method. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2011, 34, 2059–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, C.T.; Schwarzkopf, J.D.; Sommerfeld, M.; Tsuji, Y. Multiphase Flows with Droplets and Particles, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Darquenne, C.; Paiva, M. Two-and three-dimensional simulations of aerosol transport and deposition in alveolar zone of human lung. J. Appl. Physiol. 1996, 80, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Darquenne, C.; Harrington, L.; Prisk, G.K. Alveolar duct expansion greatly enhances aerosol deposition: A three-dimensional computational fluid dynamics study. J. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2009, 367, 2333–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Kleinstreuer, C. Micron-particle transport, interactions and deposition in triple lung-airway bifurcations using a novel modeling approach. J. Aerosol Sci. 2014, 71, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhong, W.; Zhou, X.; Jin, B.; Sun, B. CFD-DEM simulation of particle transport and deposition in pulmonary airway. Powder Technol. 2012, 228, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darquenne, C. A realistic two-dimensional model of aerosol transport and deposition in the alveolar zone of the human lung. J. Aerosol Sci. 2001, 32, 1161–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darquenne, C.; Prisk, G.K. Effect of gravitational sedimentation on simulated aerosol dispersion in the human acinus. J. Aerosol Sci. 2002, 34, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darquenne, C.; Brand, P.; Heyder, J.; Paiva, M. Aerosol dispersion in human lung: Comparison between numerical simulations and experiments for bolus test. J. Appl. Physiol. 1997, 83, 974–996. [Google Scholar]
- Darquenne, C.; Paiva, M.; West, J.B.; Prisk, G. Effect of microgravity and hyper gravity on deposition of 0.5 µm to 3 µm diameter aerosol in the human lung. J. Appl. Physiol. 1997, 83, 2029–2036. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.S.; Hu, S.C.; DeWitt, P.; Gerrity, T.R. Assessment of regional deposition of inhaled particles in human lungs by serial bolus delivery method. J. Appl. Physiol. 1996, 81, 2203–2213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

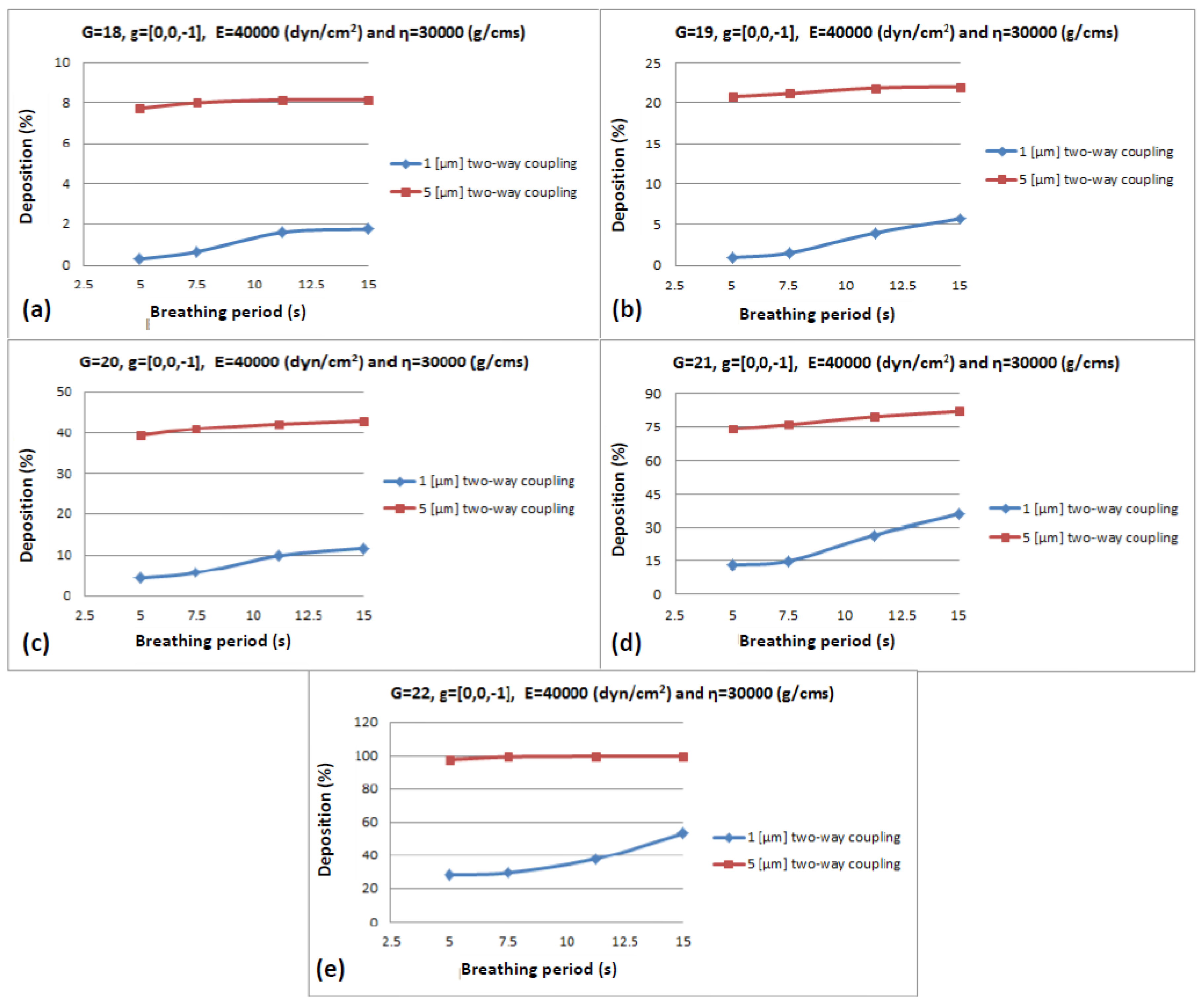
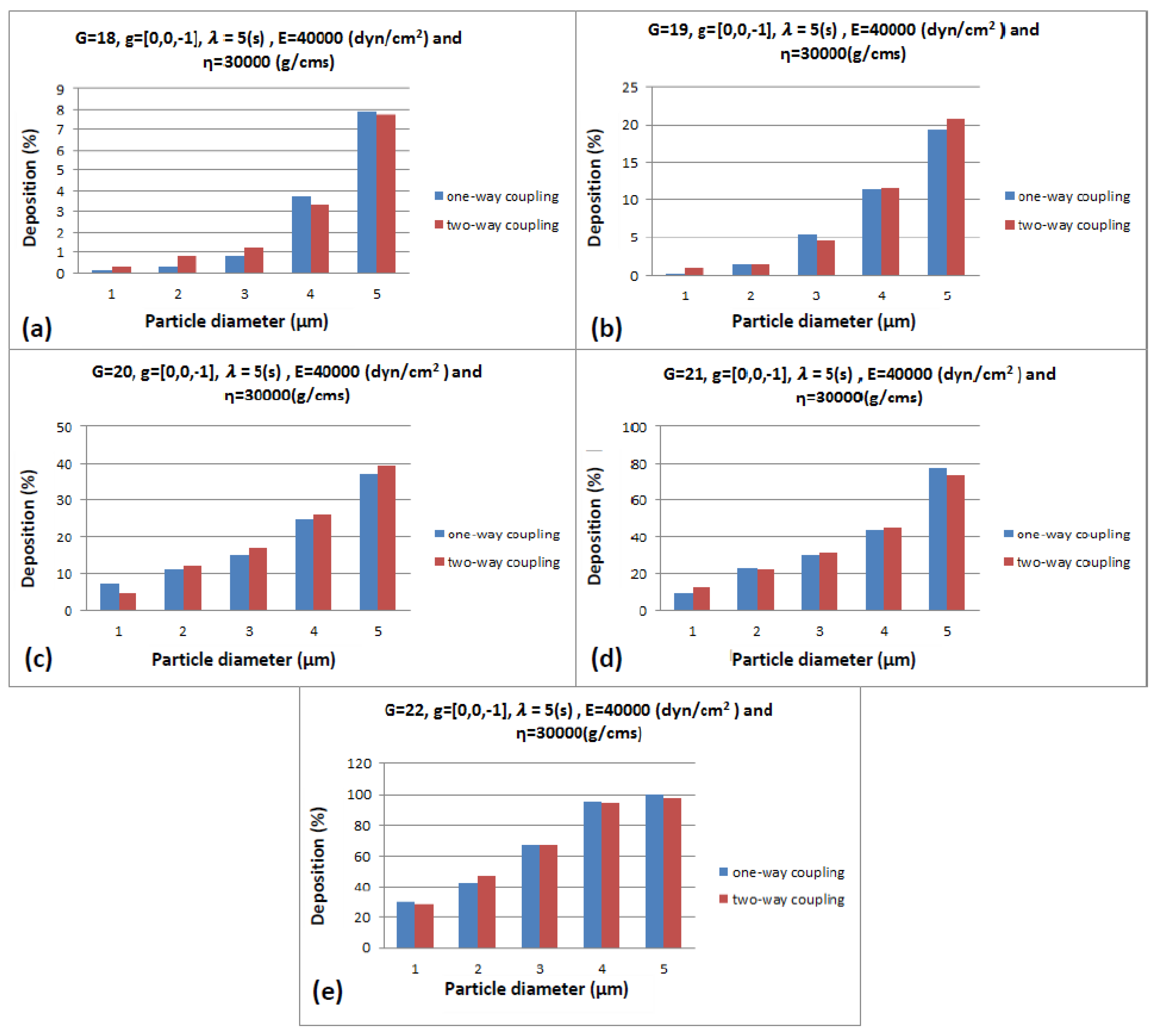

| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter | One-Way | Two-Way | Diameter | One-Way | Two-Way | Diameter | One-Way | Two-Way | Diameter | One-Way | Two-Way | Diameter | One-Way | Two-Way |
| 1 | 1.171 | 0.3 | 1 | 2.522 | 0.94 | 1 | 6.33 | 4.32 | 1 | 15 | 13 | 1 | 30 | 28.4 |
| 2 | 1.73 | 0.8 | 2 | 3.6095 | 1.41 | 2 | 14.23 | 12 | 2 | 23 | 22 | 2 | 43 | 47.1 |
| 3 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 3 | 6.15 | 4.6 | 3 | 17.5 | 16.93 | 3 | 30 | 31.2 | 3 | 67.6 | 67.1 |
| 4 | 3.975 | 3.33 | 4 | 12.835 | 11.6 | 4 | 26.95 | 26 | 4 | 44.16 | 45.4 | 4 | 91.51 | 94.91 |
| 5 | 8.49 | 7.73 | 5 | 22 | 20.75 | 5 | 41 | 39.33 | 5 | 67.6 | 74 | 5 | 94 | 98 |
| Condition | Deposition Efficiency (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Generation Number | Particle Size (µm) | Reported [19] | Computed Here |
| 18 | 1 | 2.7 | 3 |
| 2 | 11 | 14.37 | |
| 3 | 20 | 25.94 | |
| 5 | 47.7 | 52.2 | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciloglu, D.; Athari, H.; Bolukbasi, A.; Rosen, M.A. Importance of Physical and Physiological Parameters in Simulated Particle Transport in the Alveolar Zone of the Human Lung. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7020113
Ciloglu D, Athari H, Bolukbasi A, Rosen MA. Importance of Physical and Physiological Parameters in Simulated Particle Transport in the Alveolar Zone of the Human Lung. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(2):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7020113
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiloglu, Dogan, Hassan Athari, Abdurrahim Bolukbasi, and Marc A. Rosen. 2017. "Importance of Physical and Physiological Parameters in Simulated Particle Transport in the Alveolar Zone of the Human Lung" Applied Sciences 7, no. 2: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7020113
APA StyleCiloglu, D., Athari, H., Bolukbasi, A., & Rosen, M. A. (2017). Importance of Physical and Physiological Parameters in Simulated Particle Transport in the Alveolar Zone of the Human Lung. Applied Sciences, 7(2), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7020113







