Low-Frequency Noise Reduction by Earmuffs with Coir and Coir/Carbon Fibre-Reinforced Polypropylene Ear Cups
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Details and Materials
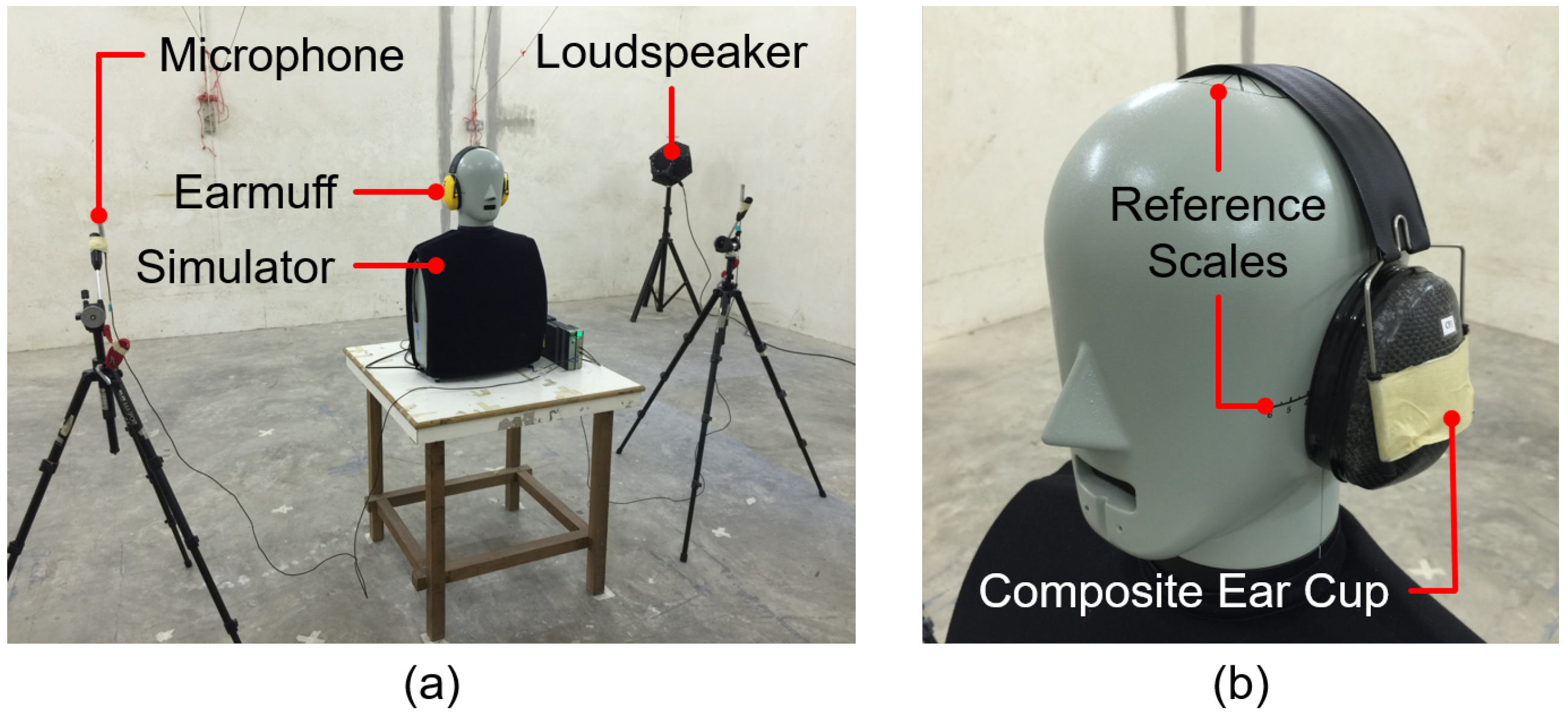
2.2. Experimental Details
3. Results
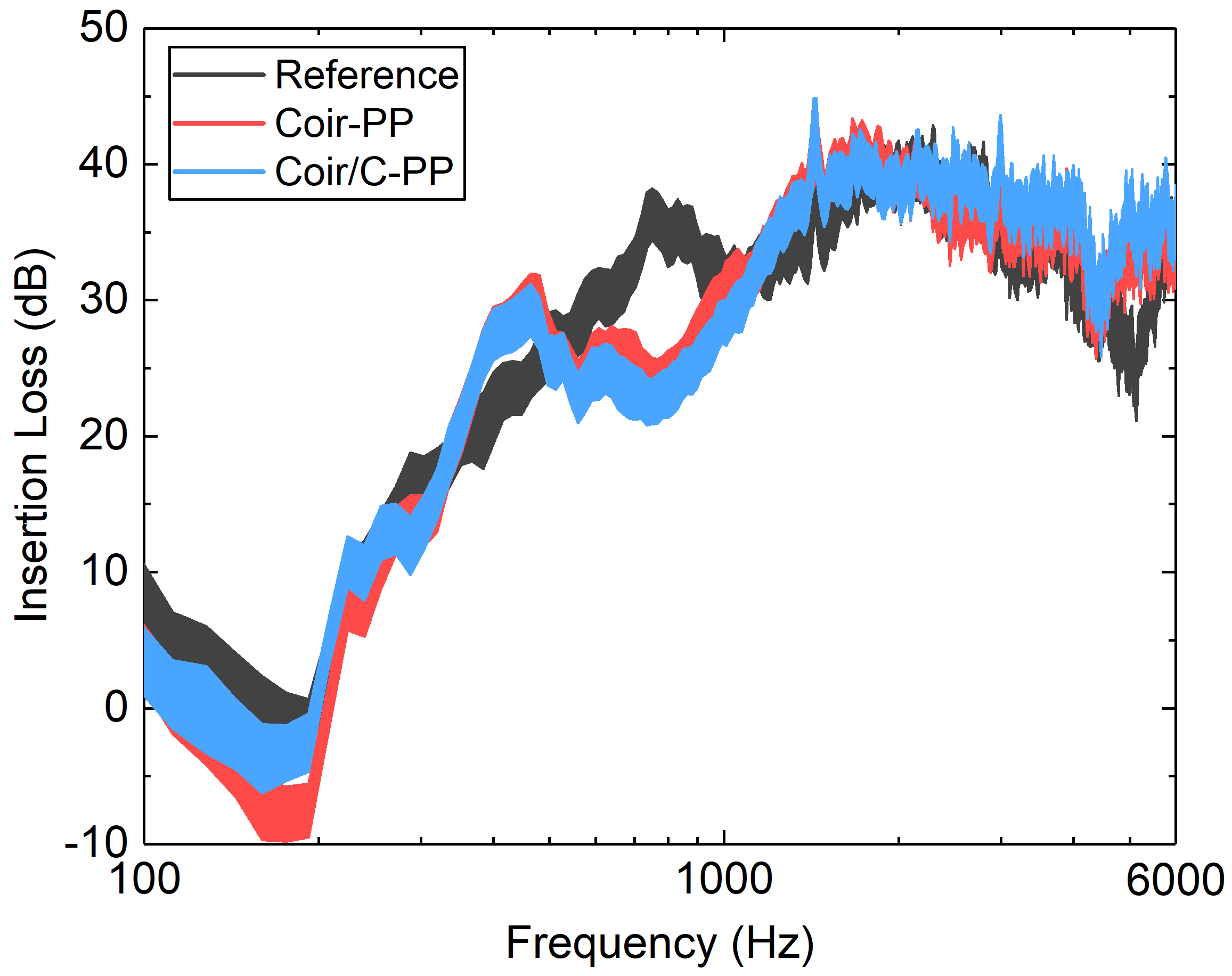
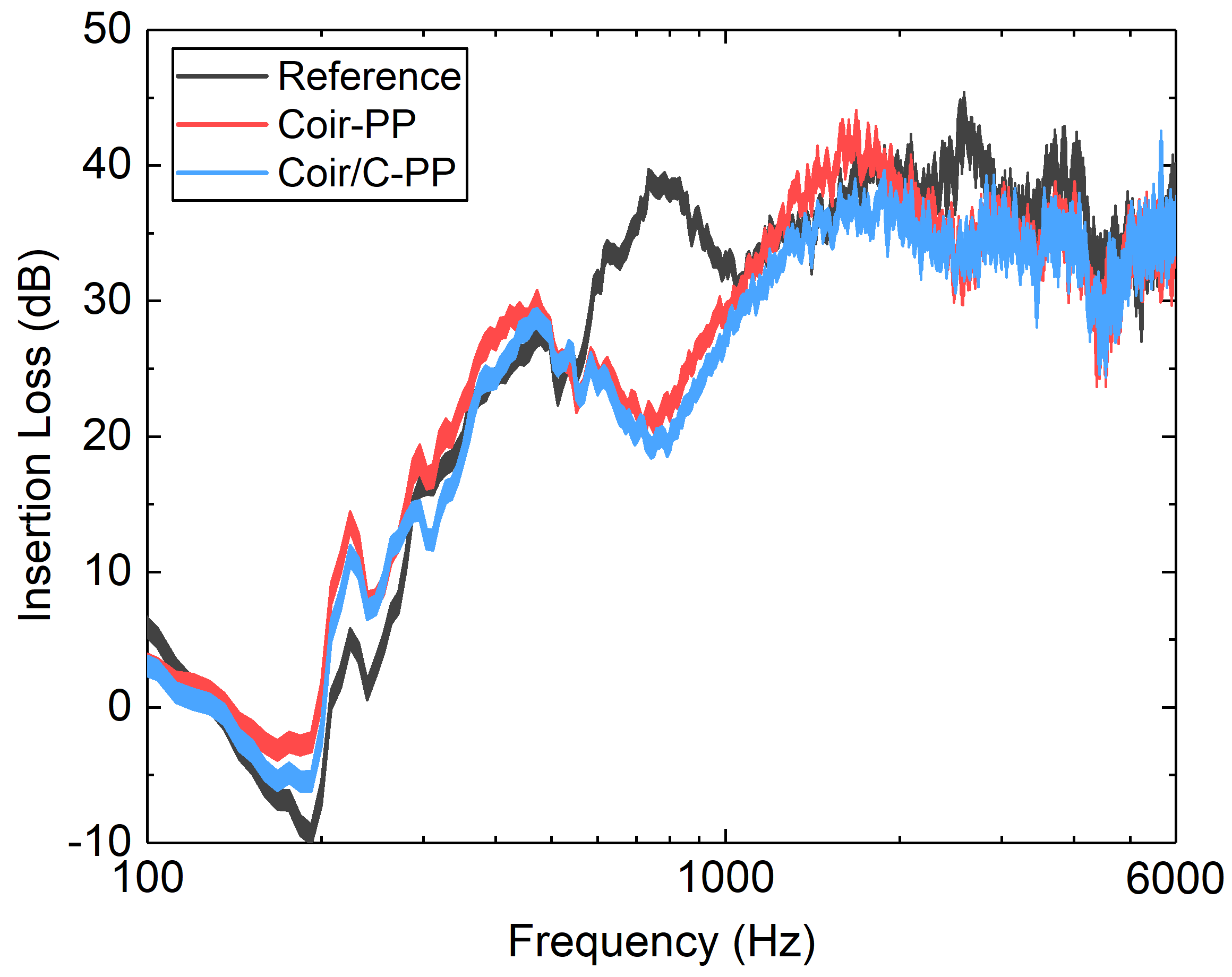
3.1. Acoustical Performance of the Earmuffs in Pink Noise
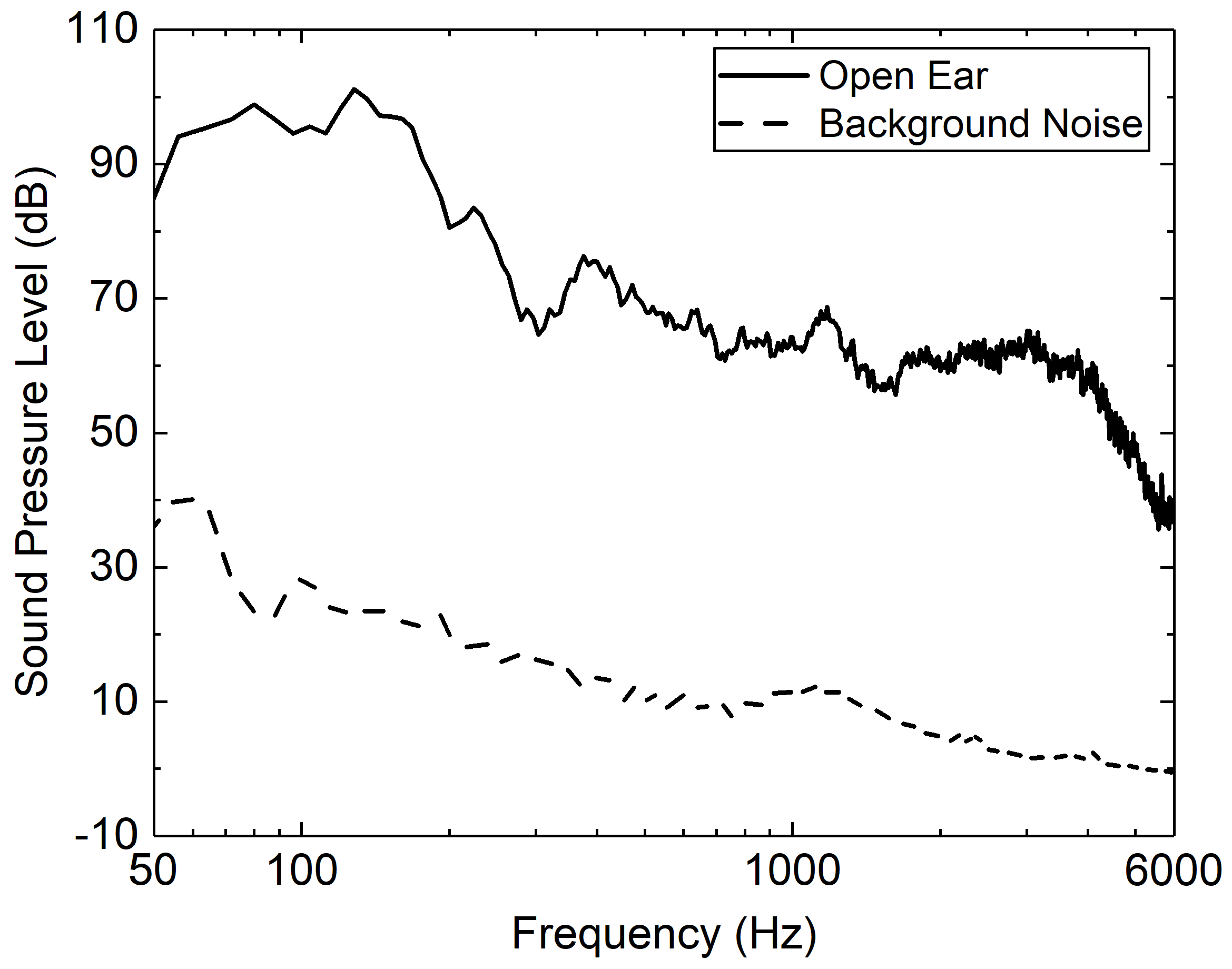
3.2. Acoustical Performance of the Earmuffs in Aircraft Take-Off Exterior Noise
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABS | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene |
| Coir-PP | Coir Fibre-Reinforced Polypropylene |
| Coir/C-PP | Coir/Carbon Fibre-Reinforced Polypropylene |
| HPDs | Hearing Protection Devices |
| IL | Insertion Loss |
| SPL | Sound Pressure Level |
References
- Arenas, J.P.; Crocker, M.J. Recent trends in porous sound-absorbing materials. Sound Vib. 2010, 44, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, S.V.; Drzal, L.T.; Mohanty, A.K.; Arora, S. Are natural fibre composites environmentally superior to glass fibre reinforced composites? Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2004, 35, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamtaz, H.; Fouladi, M.H.; Al-Atabi, M.; Namasivayam, S.N. Acoustic absorption of natural fibre composites. J. Eng. 2016, 2016, 5836107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitarresi, G.; Tumino, D.; Mancuso, A. Thermo-mechanical behaviour of flax-fibre reinforced epoxy laminates for industrial applications. Materials 2015, 8, 7371–7388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoof, D.; Pickering, K.; Yuanji, Z. Fused deposition modelling of natural fibre/polylactic acid composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2017, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swolfs, Y.; Gorbatikh, L.; Verpoest, I. Fibre hybridisation in polymer composites: A review. Compos. Part A 2014, 67, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.; Gope, P.C.; Shandilya, A.; Gupta, A.; Maheshwari, M.K. Coir fibre reinforcement and application in polymer composites: A review. J. Mater. Environ. Sci 2013, 4, 263–276. [Google Scholar]
- Wambua, P.; Ivens, J.; Verpoest, I. Natural fibres: Can they replace glass in fibre reinforced plastics? Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McReynolds, M.C. Noise-induced hearing loss. Air Med. J. 2005, 24, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, D.; Bielefeld, E.C.; Harris, K.C.; Hu, B.H. The role of oxidative stress in noise-induced hearing loss. Ear Hear. 2006, 27, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Prell, C.G.; Yamashita, D.; Minami, S.B.; Yamasoba, T.; Miller, J.M. Mechanisms of noise-induced hearing loss indicate multiple methods of prevention. Hear. Res. 2007, 226, 22–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralli, M.; Balla, M.P.; Greco, A.; Altissimi, G.; Ricci, P.; Turchetta, R.; de Virgilio, A.; de Vincentiis, M. Work-related noise exposure in a cohor of patients with chronic tinnitus: Analysis of demographic and audiological characteristics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masterson, E.A.; Bushnell, P.T.; Themann, C.L.; Morata, T.C. Hearing impairment among noise-exposed workers—United States, 2003–2012. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2016, 65, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosler, G. Progression of hearing loss caused by occupational noise. Scand. Audiol. 1994, 23, 13–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colucci, D.A. Fit for hearing protection with earplug testing. Hear. J. 2014, 67, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivonen, M.; Paakkonen, R.; Savolainen, S.; Lehtomaki, K. Noise attenuation and proper insertion of earplugs into ear canals. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2002, 46, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nelisse, H.; Gaudreau, M.A.; Boutin, J.; Voix, J.; Laville, F. Measurement of hearing protection devices performance in the workplace during full-shift working operations. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2012, 56, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berger, E.H.; Casali, J.G. Hearing protection devices. In Handbook of Acoustics, 3rd ed.; Crocker, M.J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998; pp. 799–813. [Google Scholar]
- Boyer, S.W.; Doutres, O.; Sgard, F.; Laville, F.; Boutin, J. Objective assessment of the sound paths through earmuff components. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 83, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, L.; Berger, E.H.; Kieper, R. Attenuation characteristics of fit-compromised earmuffs and various non-standard hearing protectors. Proc. Meet. Acoust. 2013, 19, 040003. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, W.; Seeto, M.; Dillon, H. The mechanical properties of earmuffs. Noise Control Eng. J. 2012, 60, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Zannin, P.H.T.; Gerges, S.N.Y. Effects of cup, cushion, headband force, and foam lining on the attenuation of an earmuff. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2006, 36, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, S.C. Sound Attenuation Performance of Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Composite Circumaural Hearing Protection Devices. Master’s Thesis, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fouladi, M.H.; Nor, M.J.M.; Ayub, M.; Leman, Z.A. Utilisation of coir fibre in multilayer acoustic absorption panel. Appl. Acoust. 2010, 71, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkifli, R.; Nor, M.J.M.; Mat Tahir, M.F.; Ismail, A.R.; Nuawi, M.Z. Acoustic properties of multi-layer coir fibres sound absorption panel. J. Appl. Sci. 2008, 8, 3709–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor, M.J.M.; Ayub, M.; Zulkifli, R.; Amin, N.; Fouladi, M.H. Effect of different factors on the acoustic absorption of coir fibre. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 10, 2887–2892. [Google Scholar]
- Fouladi, M.H.; Ayub, M.; Nor, M.J.M. Analysis of coir fibre acoustical characteristics. Appl. Acoust. 2011, 72, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Z.Y.; Putra, A.; Nor, M.J.M.; Muhammad, N.; Yaakob, M.Y. Sound absorption of multilayer natural coir and kenaf fibres. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Congress on Sound and Vibration (ICSV23), Athens, Greece, 10–14 July 2016; International Institute of Acoustics and Vibration: Athens, Greece, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fatima, S.; Mohanty, A.R. Acoustical characterisation of bulk natural fibrous material using flow resistivity. In Proceedings of the 45th International Congress and Exposition of Noise Control Engineering (INTER-NOISE 2016), Hamburg, Germany, 21–24 August 2016; Kropp, W., Ed.; Deutsche Gesellschaft Fuer Akustik: Hamburg, Germany, 2016; pp. 2813–2821. [Google Scholar]
- Ang, L.Y.L.; Koh, Y.K.; Lee, H.P. Acoustic metamaterials: A potential for cabin noise control in automobiles and armoured vehicles. Int. J. Appl. Mech. 2016, 8, 1650072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.P.; Wang, Z.; Lim, K.M. Assessment of noise from equipment and processes at construction sites. Build. Acoust. 2016, 24, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardarelli, F. Materials Handbook: A Concise Desktop Reference, 2nd ed.; Springer-Verlag: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- American National Standards Institute (ANSI). ANSI/ASA S12.42-2010 Methods for the Measurement of Insertion Loss of Hearing Protection Devices in Continuous or Impulsive Noise Using Microphone-in-Real-Ear or Acoustic Test Fixture Procedures; American National Standards Institute: Melville, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO). BS EN ISO 4869-3:2007 Acoustics—Hearing Protectors—Part 3: Measurement of Insertion Loss of Earmuff Type Protectors Using an Acoustic Test Fixture; International Organisation for Standardisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bruel & Kjaer (B&K). Sound Quality Head and Torso Simulator Type 4100 and 4100D User Manual; Bruel & Kjaer: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ang, L.Y.L.; Koh, Y.K.; Lee, H.P. The performance of active noise-cancelling headphones in different noise environments. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 122, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.L.; Huang, C.C.; Yo, C.Y.; Chen, C.J.; Lien, C.M. Comfort evaluation of hearing protection. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2004, 33, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO). BS EN ISO 354:2003 Acoustics—Measurement of Sound Absorption in a Reverberation Room; International Organisation for Standardisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. ASTM E90-09: Standard Test Method for Laboratory Measurement Of Airborne Sound Transmission Loss of Building Partitions and Elements; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, H.W.; Steele, W.G. Errors and Uncertainties in a Measured Variable. In Experimentation, Validation, and Uncertainty Analysis for Engineers, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 29–60. [Google Scholar]
- Paurobally, M.R.; Pan, J. The mechanisms of passive ear defenders. Appl. Acoust. 2000, 60, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, S.W.; Doutres, O.; Sgard, F.; Laville, F.; Boutin, J. Low frequency finite element models of the acoustical behavior of earmuffs. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 137, 2602–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
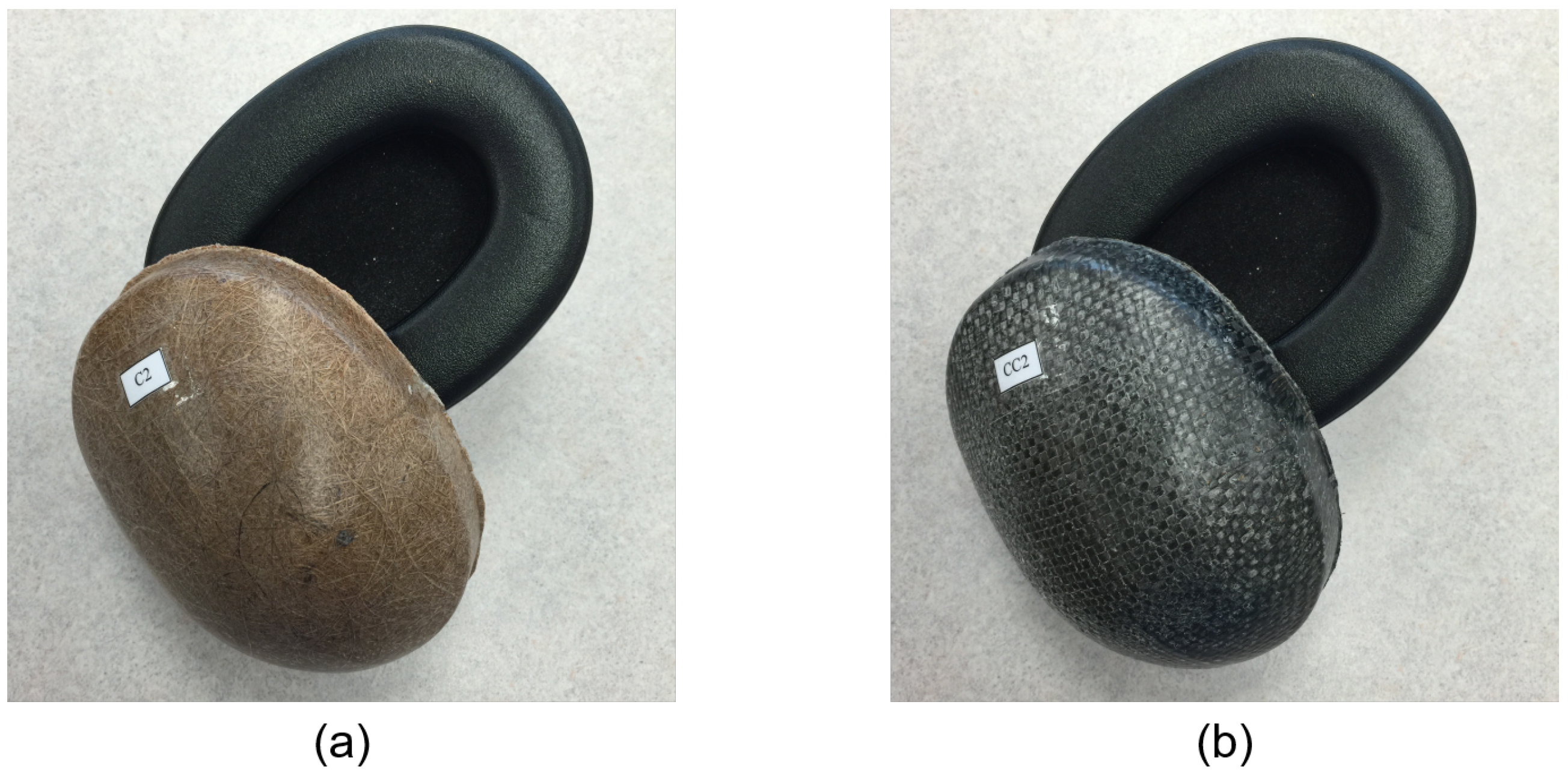

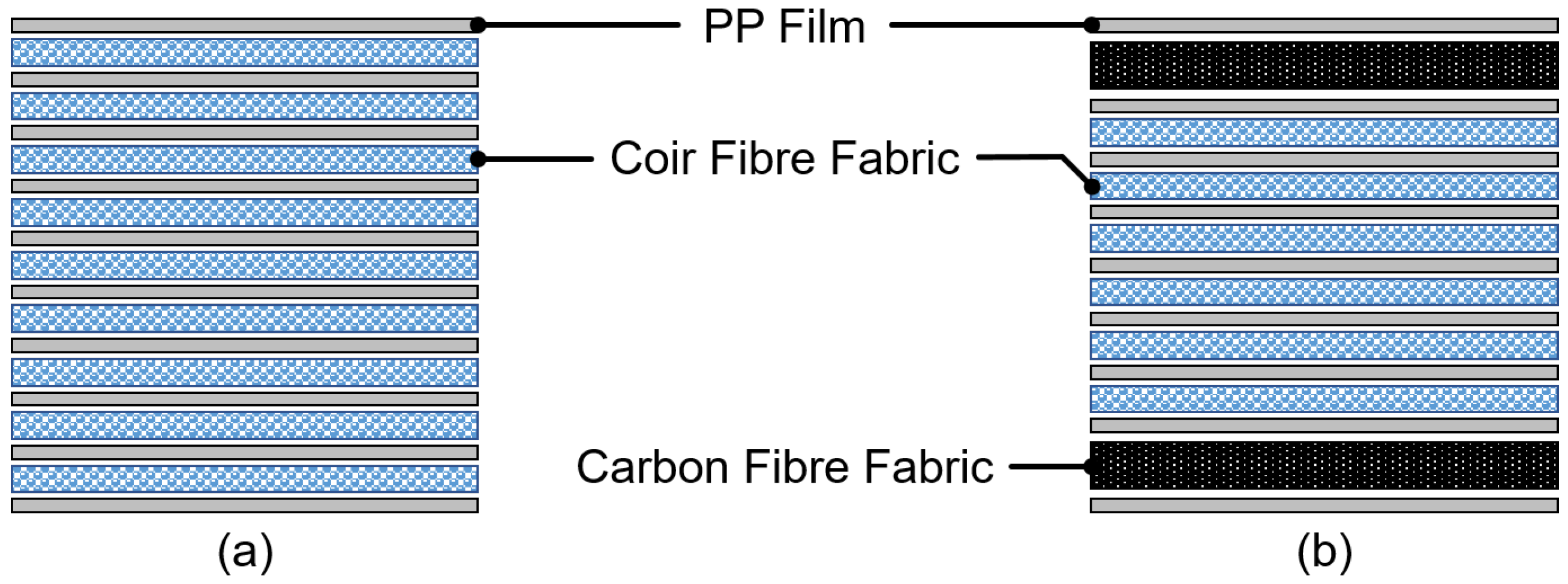
| Ear Cup | Mass (g) | Estimated Cost ($/kg) * |
|---|---|---|
| Reference | 39.0 | 5.00 |
| Coir Fibre-Reinforced Polypropylene | 27.6 | 3.00 |
| Coir/Carbon Fibre-Reinforced Polypropylene | 28.1 | 8.00 |
| Material | Type | Density (g/m2) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coir Fibre Fabric | Non-Woven | 120 | Can Tho University, Can Tho, Vietnam |
| Carbon Fibre Fabric (282 3K) | Plain Woven | 197 | Hexcel, Stamford, CT, USA |
| PP Film (Cosmoplene Y101E) | Unmodified | 90 | The Polyolefin Company, Singapore |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ang, L.Y.L.; Tran, L.Q.N.; Phillips, S.; Koh, Y.K.; Lee, H.P. Low-Frequency Noise Reduction by Earmuffs with Coir and Coir/Carbon Fibre-Reinforced Polypropylene Ear Cups. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7111121
Ang LYL, Tran LQN, Phillips S, Koh YK, Lee HP. Low-Frequency Noise Reduction by Earmuffs with Coir and Coir/Carbon Fibre-Reinforced Polypropylene Ear Cups. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(11):1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7111121
Chicago/Turabian StyleAng, Linus Yinn Leng, Le Quan Ngoc Tran, Steve Phillips, Yong Khiang Koh, and Heow Pueh Lee. 2017. "Low-Frequency Noise Reduction by Earmuffs with Coir and Coir/Carbon Fibre-Reinforced Polypropylene Ear Cups" Applied Sciences 7, no. 11: 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7111121
APA StyleAng, L. Y. L., Tran, L. Q. N., Phillips, S., Koh, Y. K., & Lee, H. P. (2017). Low-Frequency Noise Reduction by Earmuffs with Coir and Coir/Carbon Fibre-Reinforced Polypropylene Ear Cups. Applied Sciences, 7(11), 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7111121








