A New Approach to Fall Detection Based on the Human Torso Motion Model
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
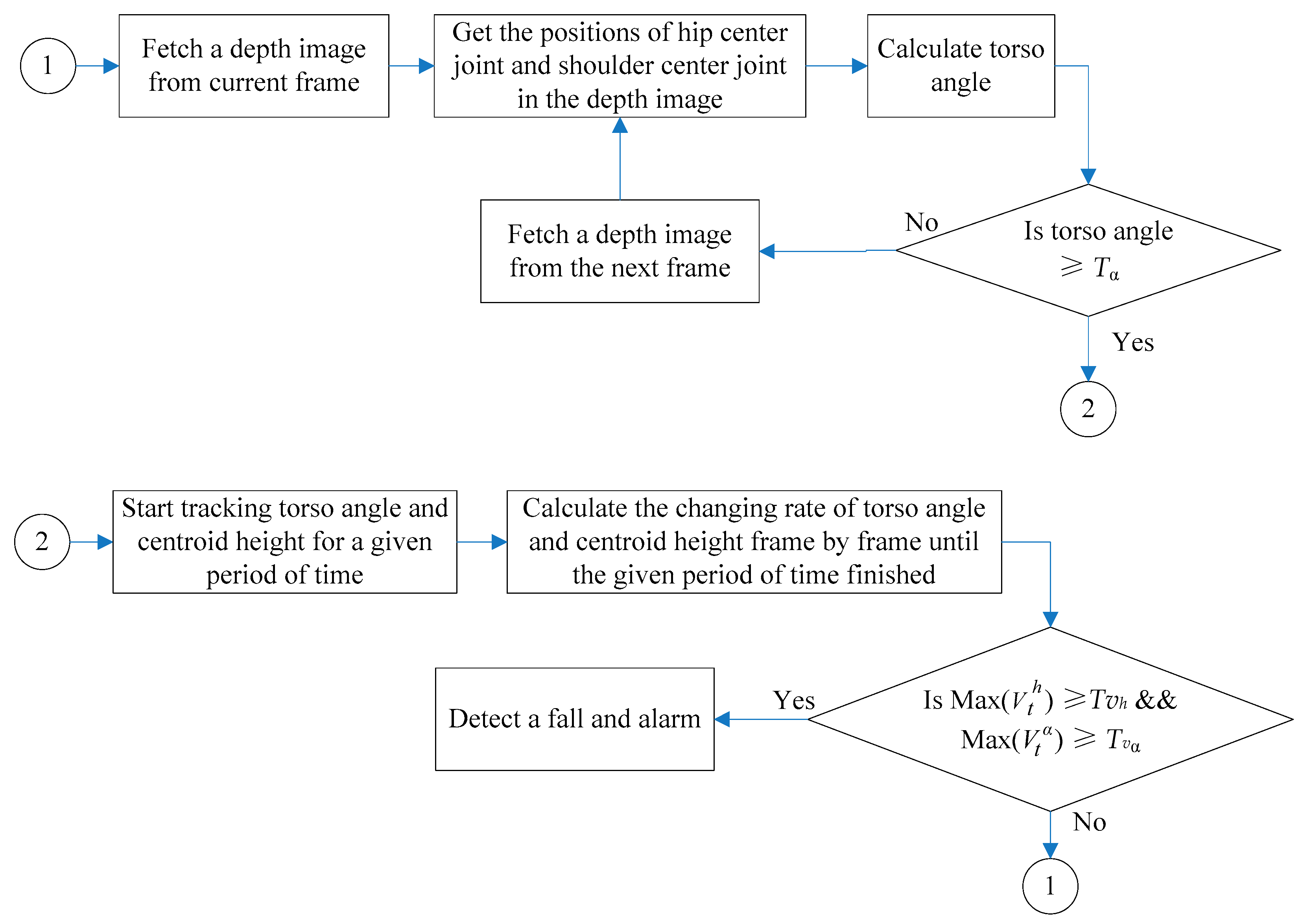
3. Our Approach for Fall Detection
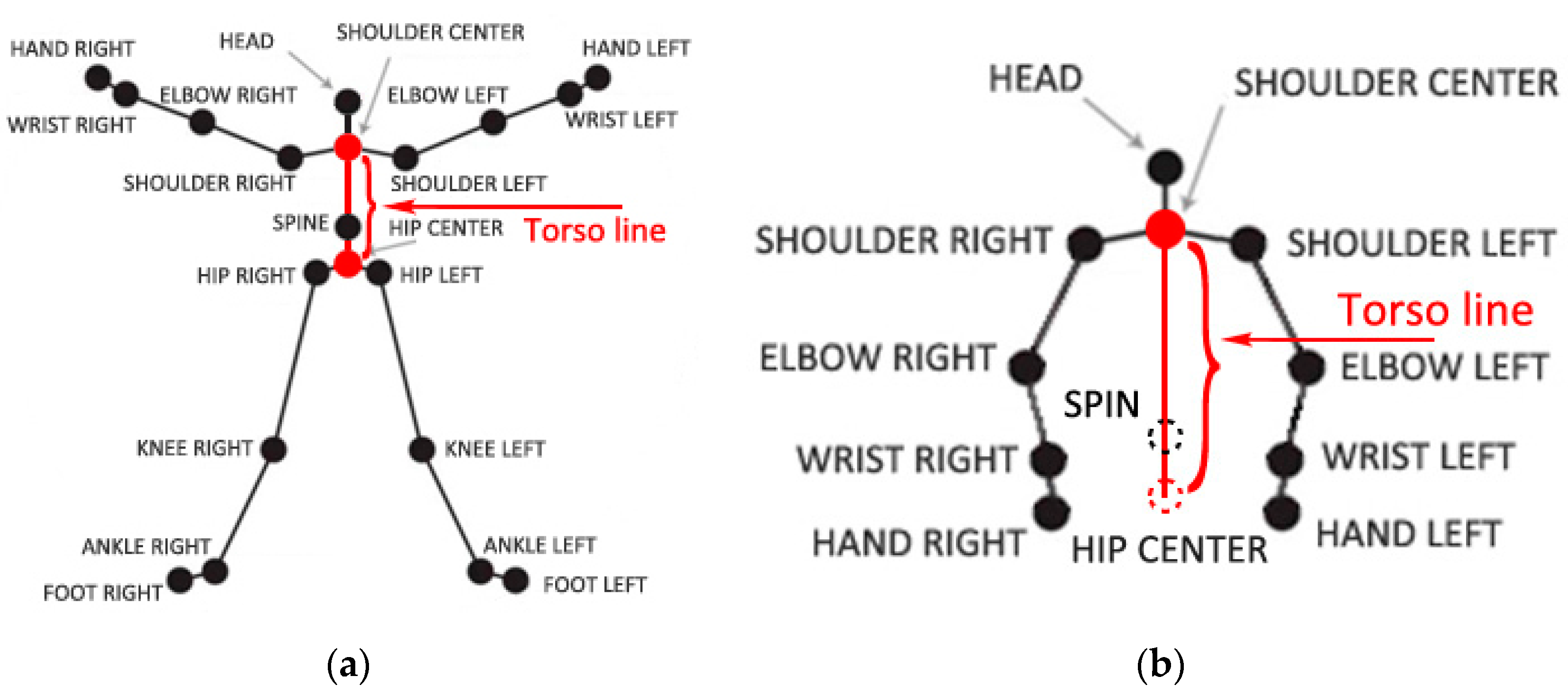
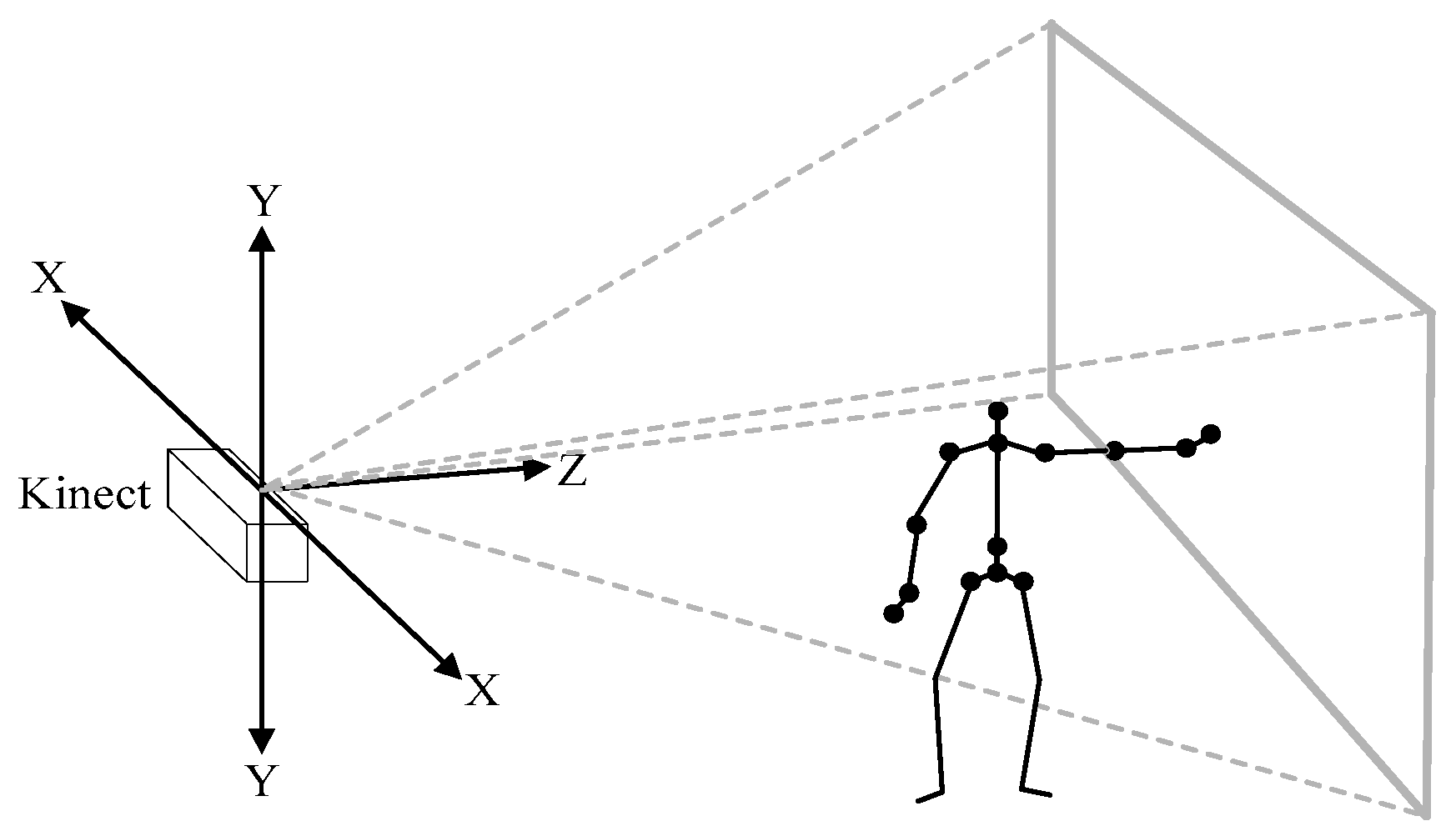
3.1. The Key Concepts and Definitions in HTMM
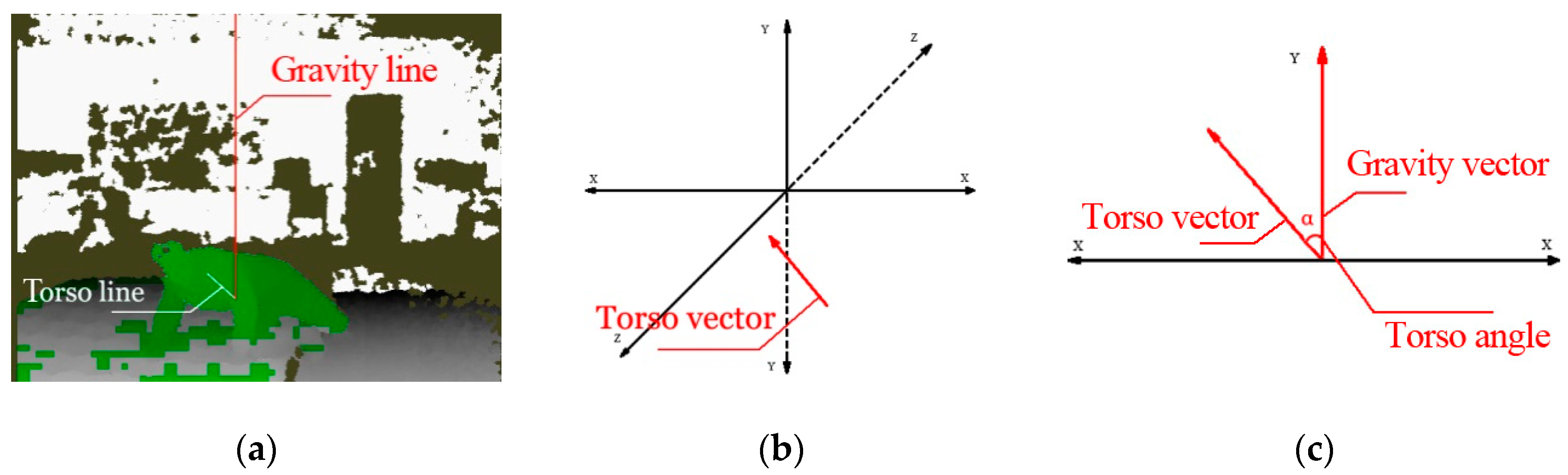
3.1.1. Torso Line and Torso Vector
3.1.2. Gravity Vector and Torso Angle
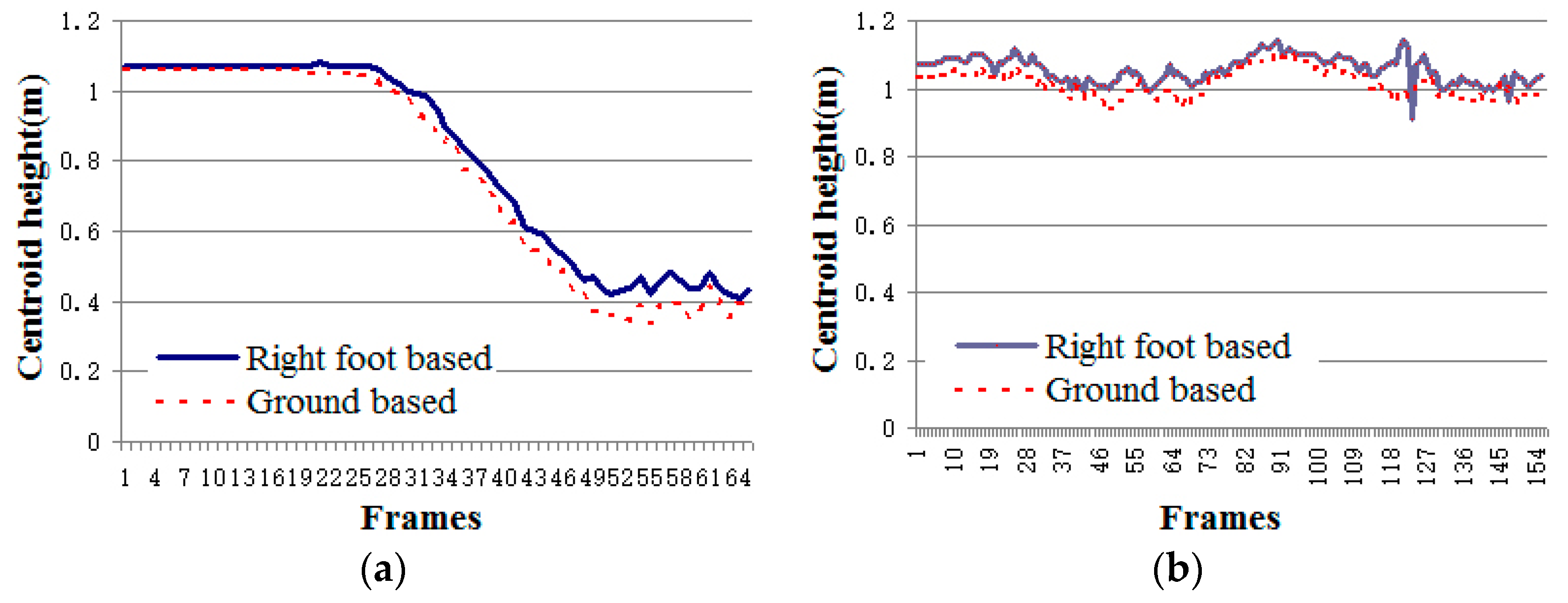
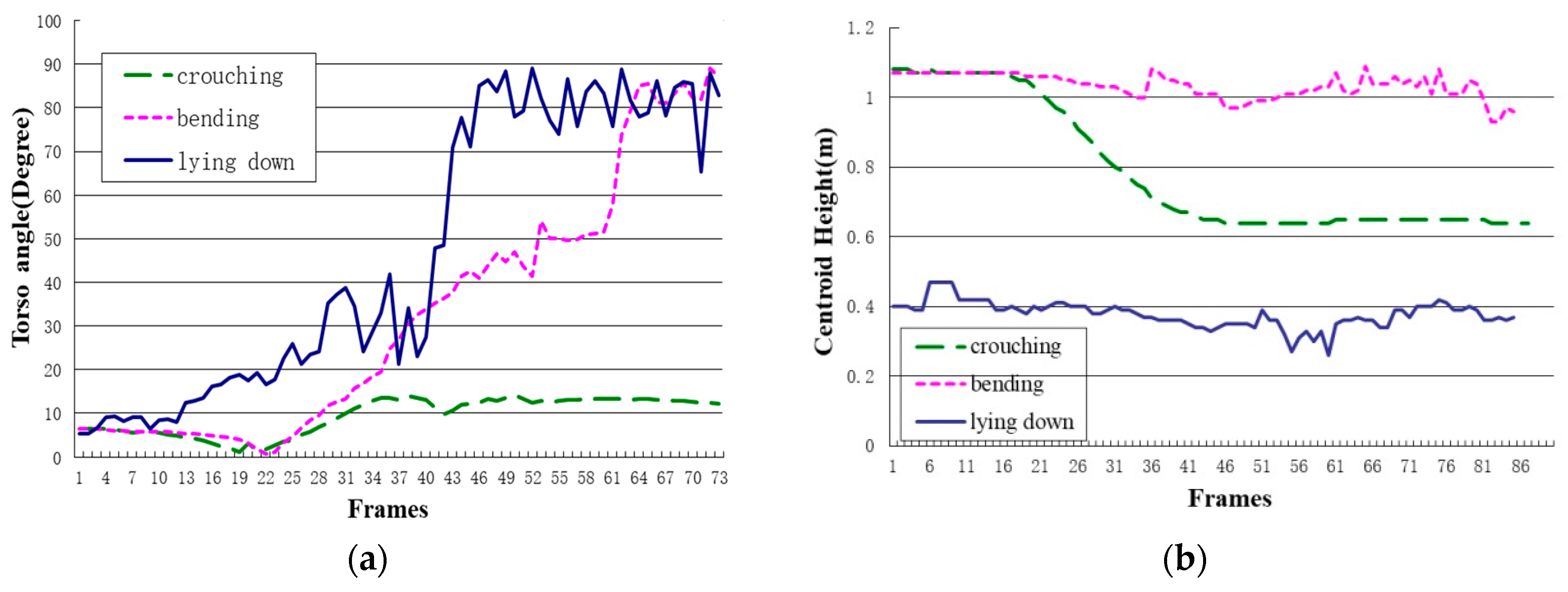
3.1.3. Centroid Height
3.2. Human Torso Motion Model
| Algorithm 1: Pseudocode of our proposed method for fall detection. |
| Input: Sequence of the skeleton frames captured by Kinect sensor |
| Output: bool bFallIsDetected |
| Loop 1: |
| while (torsoAngle < Tα) |
| { |
| joint_shoulderCenter ← fetch shoulder center 3D position from current skeleton frame; |
| joint_hipCenter ← fetch hip center 3D position from current skeleton frame; |
| torsoAngle ← calculate torso angle of current skeleton frame; |
| } |
| Loop 2: |
| While (trackingTime < Ŧ) |
| { |
| V_torsoAngle ← calculate the current torso angle changing rate by current frame; |
| MaxV_torsoAngle ← update its value if V_torsoAngle is larger |
| V_CentroidHeight ← calculate the current centroid height changing rate by current frame; |
| MaxV_CentroidHeight ← update its value if V_ CentroidHeight is larger |
| If (MaxV_torsoAngle > Tvα && MaxV_CentroidHeight > Tvh) |
| { |
| bFallIsDetected = TRUE; |
| fallAlarm(); |
| } |
| } |
| goto Loop 1; |
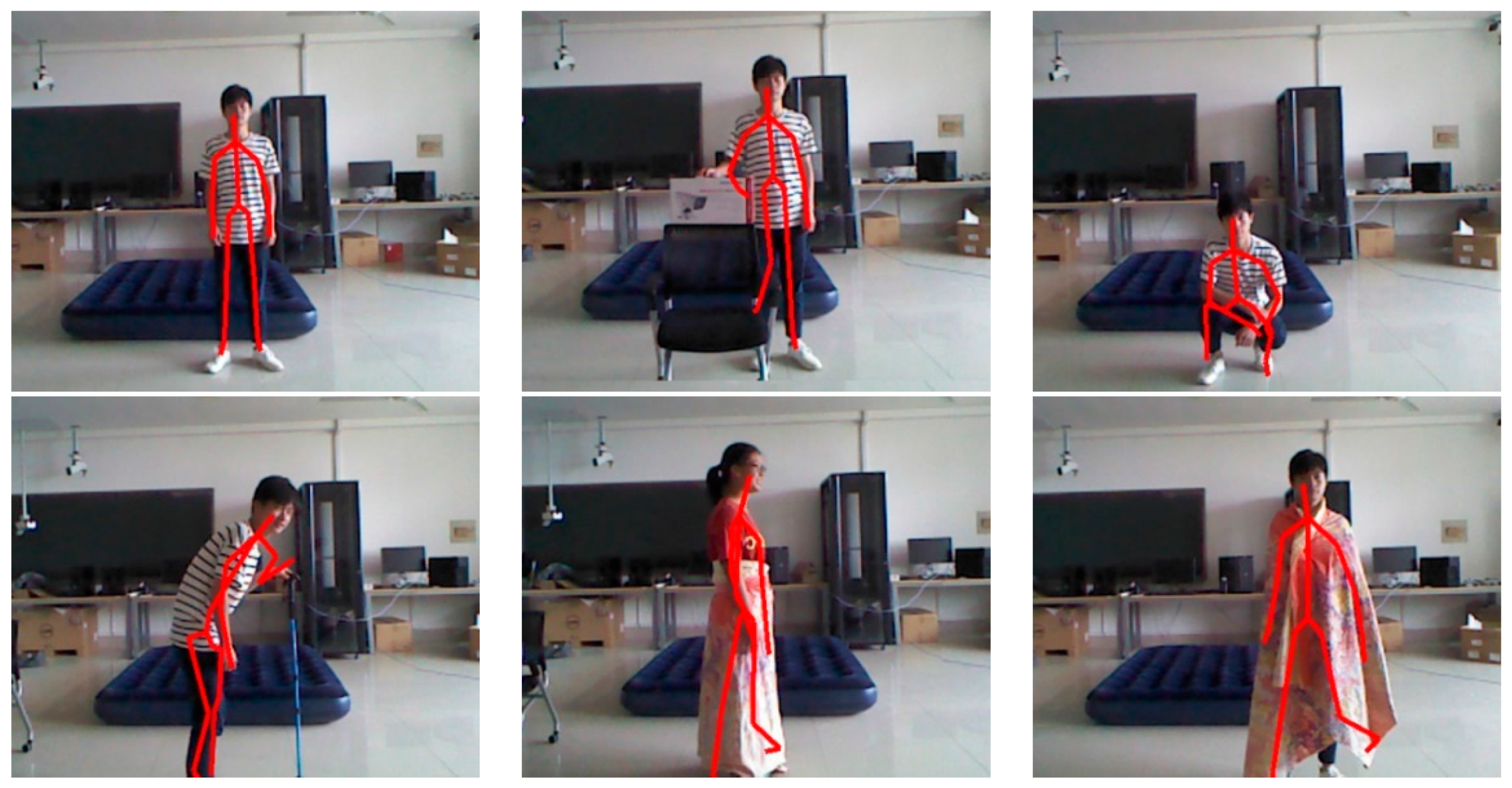
4. Experiment and Results
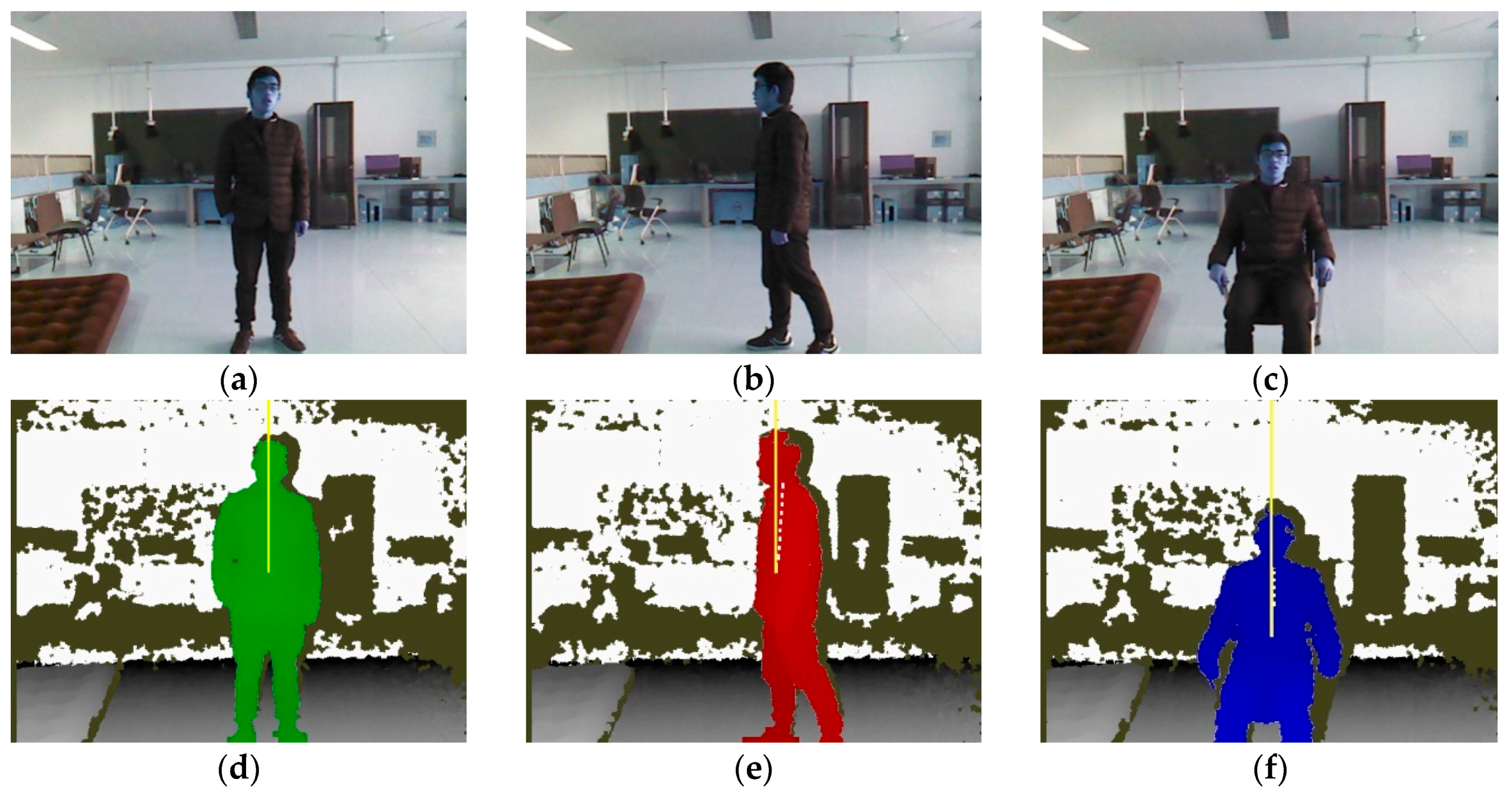
4.1. Experimental Setup and Dataset
4.2. Result and Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ozcan, A.; Donat, H.; Gelecek, N.; Ozdirenc, M.; Karadibak, D. The relationship between risk factors for falling and the quality of life in older adults. BMC Public Health 2005, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yardley, L.; Smith, H. A prospective study of the relationship between feared consequences of falling and avoidance of activity in community-living older people. Gerontologist 2002, 42, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvà, A.; Bolíbar, I.; Pera, G.; Arias, C. Incidence and consequences of falls among elderly people living in the community. Med. Clín. 2004, 122, 172–176. [Google Scholar]
- Doughty, K.; Lewis, R.; Mcintosh, A. The design of a practical and reliable fall detector for community and institutional telecare. J. Telemed. Telecare 2000, 6, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chiang, C.; Chen, G. Fall detection system for healthcare quality improvement in residential care facilities. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2010, 30, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubashir, M.; Shao, L.; Seed, L. A survey on fall detection: Principles and approaches. Neurocomputing 2013, 100, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathie, M.J.; Coster, A.C.F.; Lovell, N.H.; Celler, B.G. Accelerometry: Providing an integrated, practical method for long-term, ambulatory monitoring of human movement. Physiol. Meas. 2004, 25, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Cho, M.C.; Lee, T.S. Automatic fall detection using wearable biomedical signal measurement terminal. In Proceedings of the International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society, Cheongju, Korea, 3–6 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sixsmith, A.; Johnson, N. A smart sensor to detect the falls of the elderly. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2004, 3, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangas, M.; Vikman, I.; Wiklander, J.; Lindgren, P.; Nyberg, L.; Jämsä, T. Sensitivity and specificity of fall detection in people aged 40 years and over. Gait Posture 2009, 29, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, X.; Huang, J.; Potamianos, G.; Hasegawa-Johnson, M. Acoustic fall detection using Gaussian mixture models and GMM super vectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Taipei, Taiwan, 19–24 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Alwan, M.; Rajendran, P.J.; Kell, S.; Mack, D. A Smart and Passive Floor-Vibration Based Fall Detector for Elderly. Inf. Commun. Technol. 2006, 1, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, G.; Mai, J.; Ban, Z.; Guo, X.; Wang, G. Floor pressure imaging for fall detection with fiber-optic sensors. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2016, 15, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpoot, Q.M.; Jensen, C.D. Security and Privacy in Video Surveillance: Requirements and Challenges. In Proceedings of the 29th IFIP International Information Security and Privacy Conference, Marrakech, Morocco, 2–4 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chaaraoui, A.A.; Padillalópez, J.R.; Ferrándezpastor, F.J.; Nietohidalgo, M.; Flórezrevuelta, F. A vision-based system for intelligent monitoring: Human behaviour analysis and privacy by context. Sensors 2014, 14, 8895–8925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rougier, C.; Meunier, J.; St-Arnaud, A.; Rousseau, J. Robust video surveillance for fall detection based on human shape deformation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2011, 21, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.H. Fall alarm and inactivity detection system design and implementation on Raspberry Pi. In Proceedings of the 17th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Communications Technology, Pyeonhchang, South Africa, 1–3 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kwolek, B.; Kepski, M. Fuzzy inference-based fall detection using Kinect and body-worn accelerometer. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 40, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.J.; Habib, H.A. Video analytic for fall detection from shape features and motion gradients. Lect. Notes Eng. Comput. Sci. 2009, 1, 1311–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, A.; Ganesan, D.; Hanson, A. Aging in place: Fall detection and localization in a distributed smart camera network. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Multimedia, Augsburg, Germany, 24–29 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.; Yu, Y.; Rhuma, A.; Naqvi, S.M.; Wang, L.; Chambers, J.A. An online one class support vector machine-based person-specific fall detection system for monitoring an elderly individual in a room environment. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2013, 17, 1002–1014. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rougier, C.; Meunier, J.; St-Arnaud, A.; Rousseau, J. 3D head tracking for fall detection using a single calibrated camera. Image Vis. Comput. 2013, 31, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, D.N.; Mez Conde, I.; Vila Sobrino, X. Eigenspace-based fall detection and activity recognition from motion templates and machine learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 5935–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ren, Y.; Hu, H.; Tian, B. New fast fall detection method based on spatio-temporal context tracking of head by using depth images. Sensors 2015, 15, 23004–23019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rougier, C.; Auvinet, E.; Rousseau, J.; Mignotte, M.; Meunier, J. Fall detection from depth map video sequences. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Smart Homes and Health Telematics, Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–22 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gasparrini, S.; Cippitelli, E.; Spinsante, S.; Gambi, E. A depth-based fall detection system using a Kinect® sensor. Sensors 2014, 14, 2756–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibañez, R.; Soria, Á.; Teyseyre, A.; Rodriguez, G.; Campo, M. Approximate string matching: A lightweight approach to recognize gestures with Kinect. Pattern Recognit. 2016, 62, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastorakis, G.; Makris, D. Fall detection system using Kinect’s infrared sensor. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2014, 9, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, W.; Morales, S. 3D environment mapping using the Kinect v2 and path planning based on RRT algorithms. Electronics 2016, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazrai, R.; Momani, M.; Daoud, M.I. Fall detection for elderly from partially observed depth-map video sequences based on view-invariant human activity representation. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Zuo, C. An improved algorithm of automatic fall detection. AASRI Procedia 2012, 1, 353–358. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Li, M.; Ji, H.; Gong, Z. A novel modeling approach to fall detection and experimental validation using motion capture system. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Shenzhen, China, 12–14 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bosch-Jorge, M.; Sánchez-Salmerón, A.J.; Valera, Á.; Ricolfe-Viala, C. Fall detection based on the gravity vector using a wide-angle camera. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 7980–7986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Yu, M.; Naqvi, S.M.; Chambers, J.A. Deep learning for posture analysis in fall detection. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, Milan, Italy, 19–21 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Melzer, I.; Benjuya, N.; Kaplanski, J. Association between ankle muscle strength and limit of stability in older adults. Age Ageing 2009, 38, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.; Ponce, C.; Selman, B.; Saxena, A. Unstructured human activity detection from RGBD images. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, St. Paul, MN, USA, 14–18 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, J.; Abdulrazak, L.; Mokhtari, M. Inclusive society: Health and wellbeing in the community, and care at home. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Smart Homes and Health Telematics, Singapore, 19–21 June 2013. [Google Scholar]

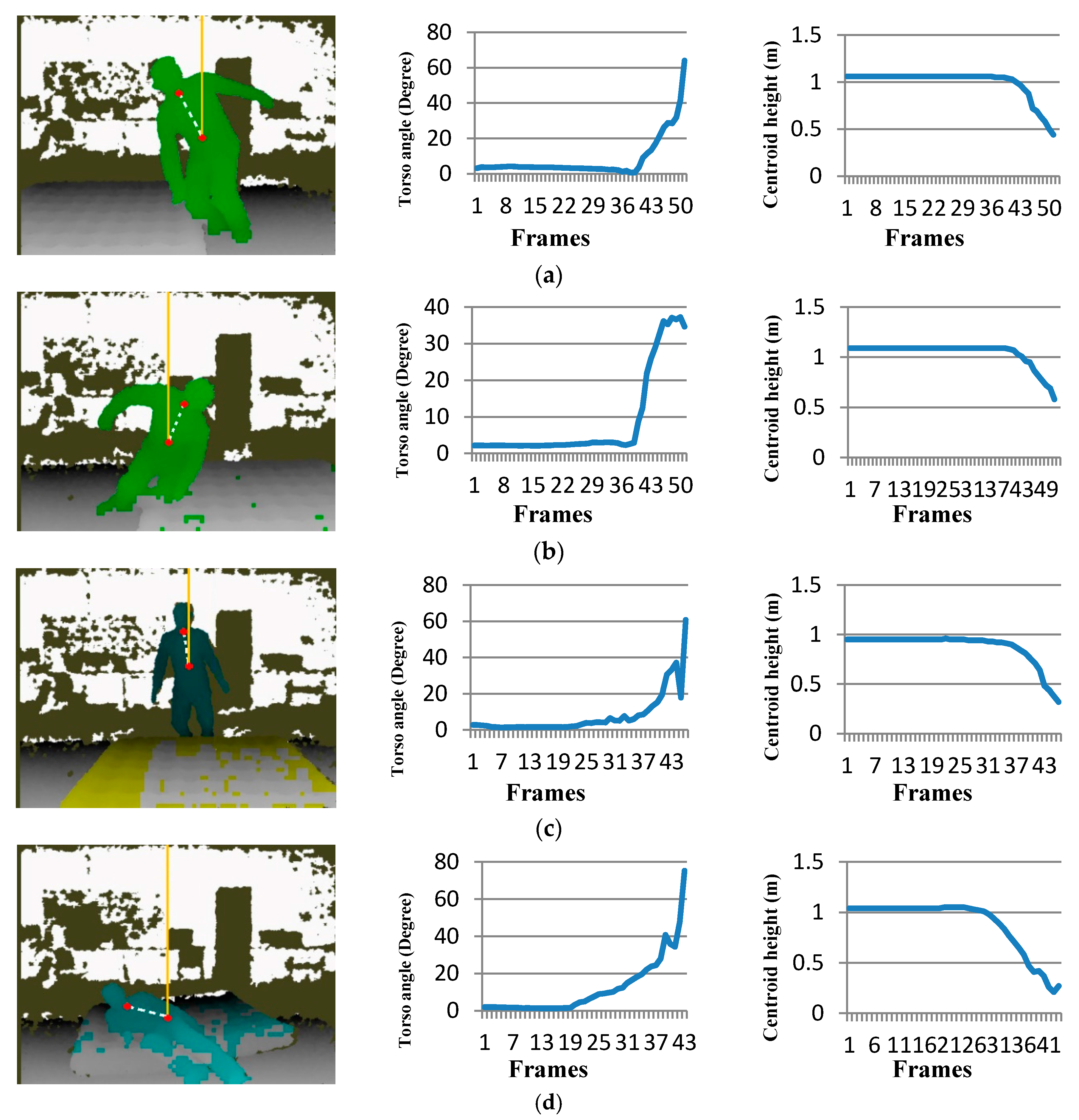
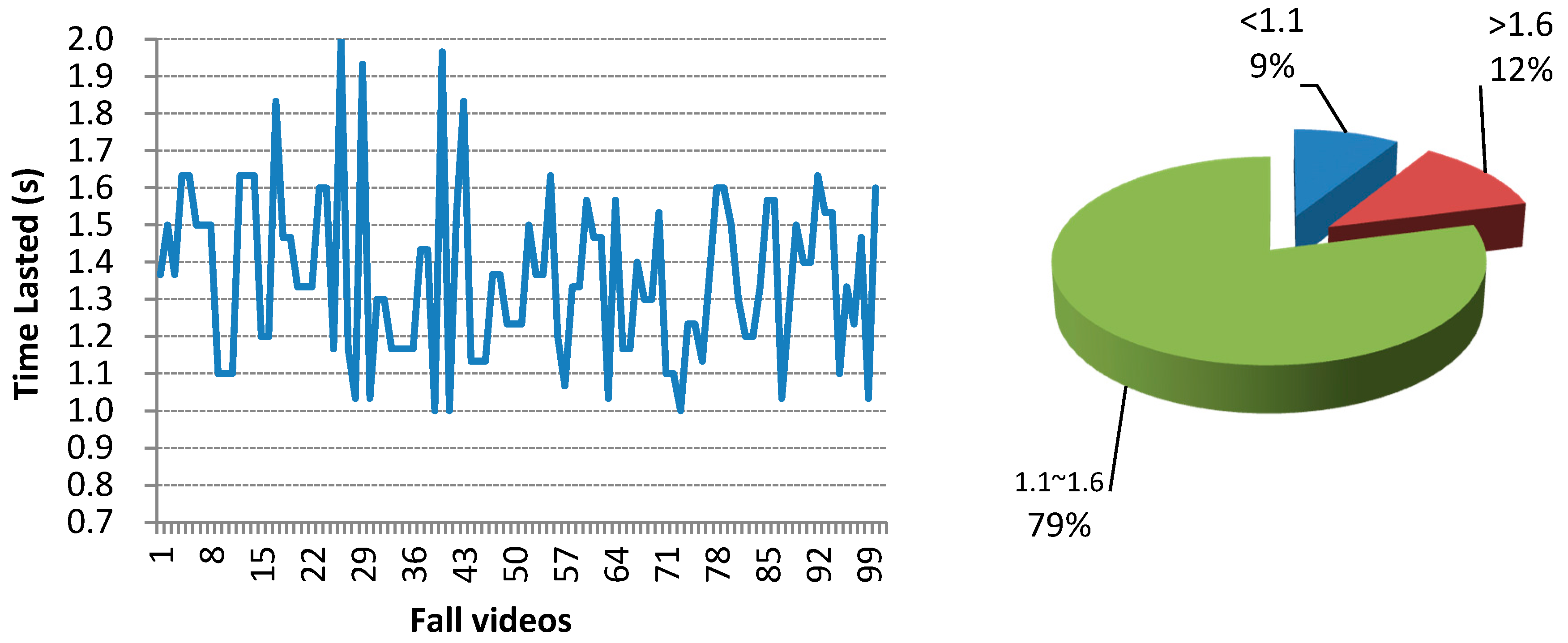
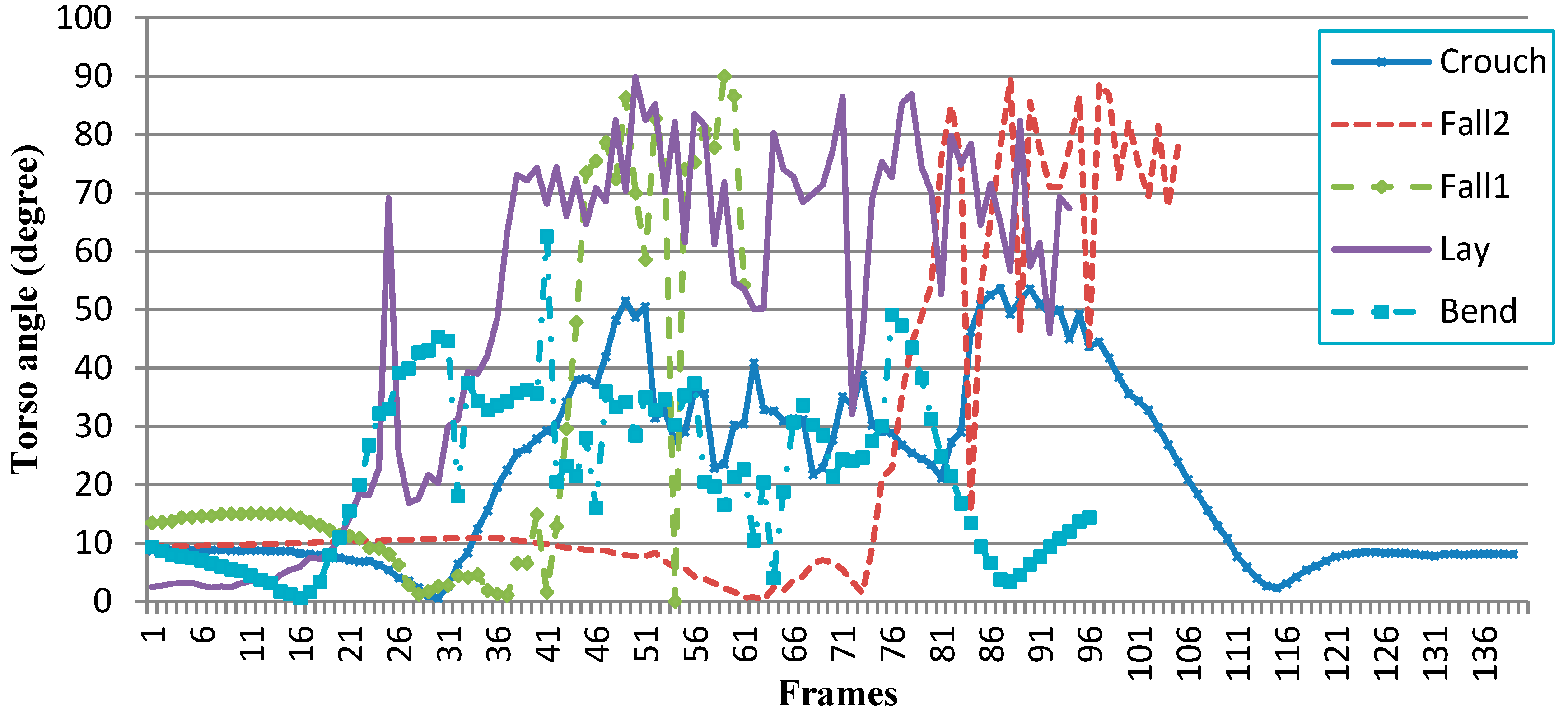
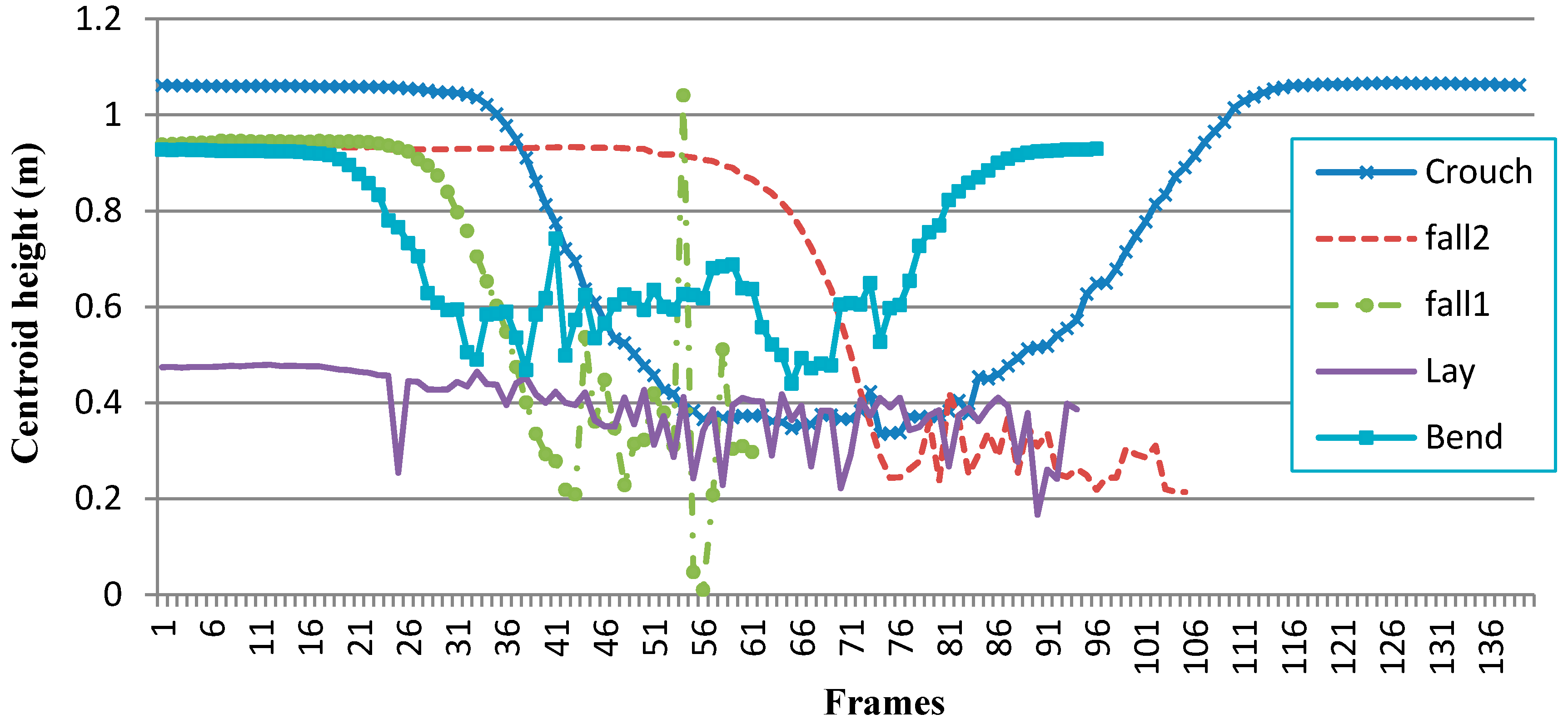
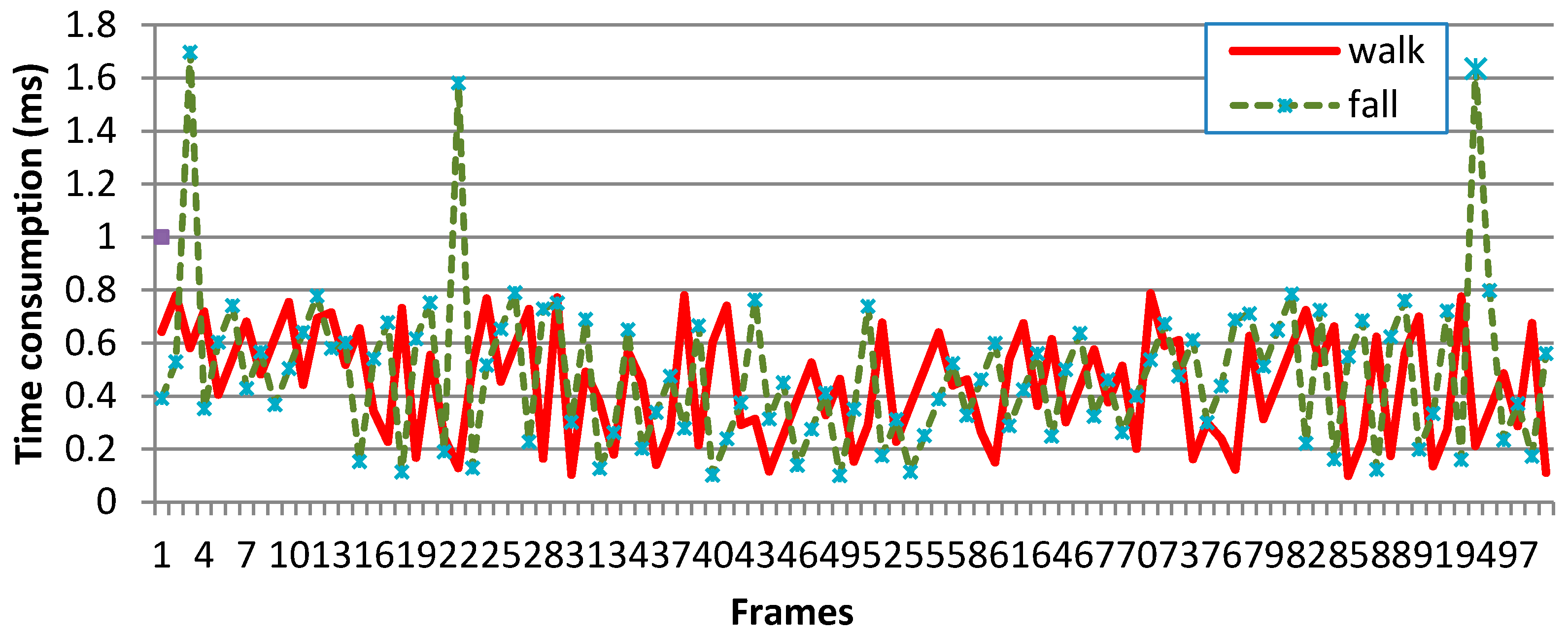
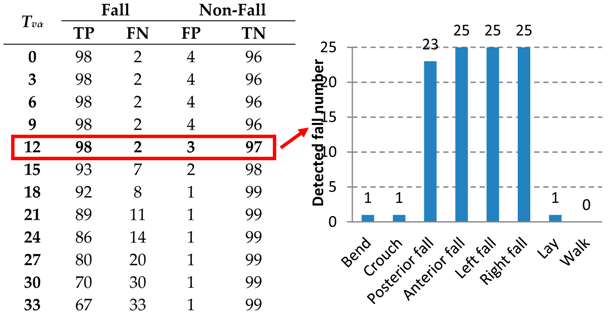 |
| Activity Type | The Number of Sample Videos | The Number of Detected as Fall Videos | 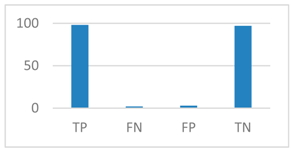 |
| Fall | 100 | 98 | |
| Lay | 25 | 1 | |
| Crouch | 25 | 1 | 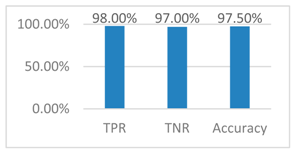 |
| Bend | 25 | 1 | |
| Walk | 25 | 0 |
| Approach | Fall | Crouch | Bend | Walk | Lay | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | Backward | Left | Right | |||||
| Rougier, C. et al. [22] | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 11 | 20 | 0 | 1 |
| Yang, L. et al. [24] | 10 | 15 | 23 | 18 | 2 | 8 | 0 | 25 |
| Gasparrini, S. et al. [26] | 23 | 22 | 25 | 25 | 12 | 25 | 0 | 25 |
| Mastorakis, G. et al. [28] | 8 | 22 | 21 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Our proposed method | 25 | 23 | 25 | 25 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Approach | Capability of Detecting Falls | Capability of Discriminating Controlled Lying Down | Capability of Discriminating ADLs with Changing slightly in Height | Capability of Discriminating Fall-Like Activities with Changing Sharply in Height |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height based method | High | Poor | High | Poor |
| Height velocity based method | High | High | High | Poor |
| Bounding box/ratio of the height and width based methods | Medium | High | High | High |
| Our proposed method | High | High | High | High |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, L.; Min, W.; Lu, K. A New Approach to Fall Detection Based on the Human Torso Motion Model. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7100993
Yao L, Min W, Lu K. A New Approach to Fall Detection Based on the Human Torso Motion Model. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(10):993. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7100993
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Leiyue, Weidong Min, and Keqiang Lu. 2017. "A New Approach to Fall Detection Based on the Human Torso Motion Model" Applied Sciences 7, no. 10: 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7100993
APA StyleYao, L., Min, W., & Lu, K. (2017). A New Approach to Fall Detection Based on the Human Torso Motion Model. Applied Sciences, 7(10), 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7100993




