Human Emotion Recognition with Electroencephalographic Multidimensional Features by Hybrid Deep Neural Networks
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A new method is proposed to integrate the different EEG domain features. With the integration of multidimensional features, a sequence of two-dimensional images is constructed to express the variation in emotion.
- A hybrid deep learning neural network named CLRNN (Convolution Neural Networks (CNN) and Long-Short-Term-Memory Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN)) is built to undertake the recognition of human emotion from the EEG multidimensional feature image sequences.
- Empirical research is conducted with the open-source database DEAP [11] using our method, and the results demonstrate significant improvements over current state-of-the-art approaches in this field.
2. Related Work
2.1. EEG Feature Extraction
2.2. Emotion Classification Methods
3. Materials and Methods
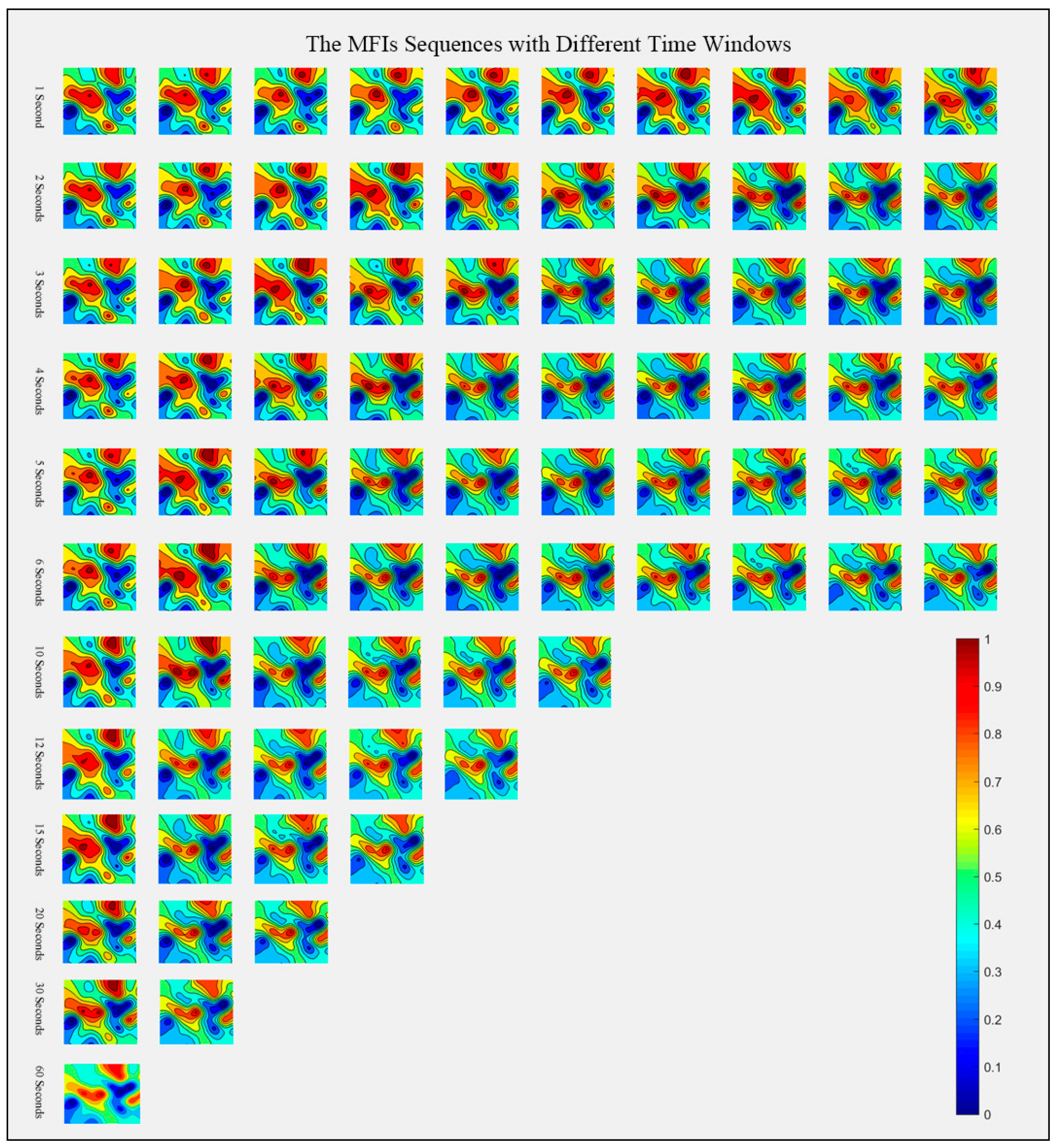
3.1. The Construction of EEG MFI Sequences
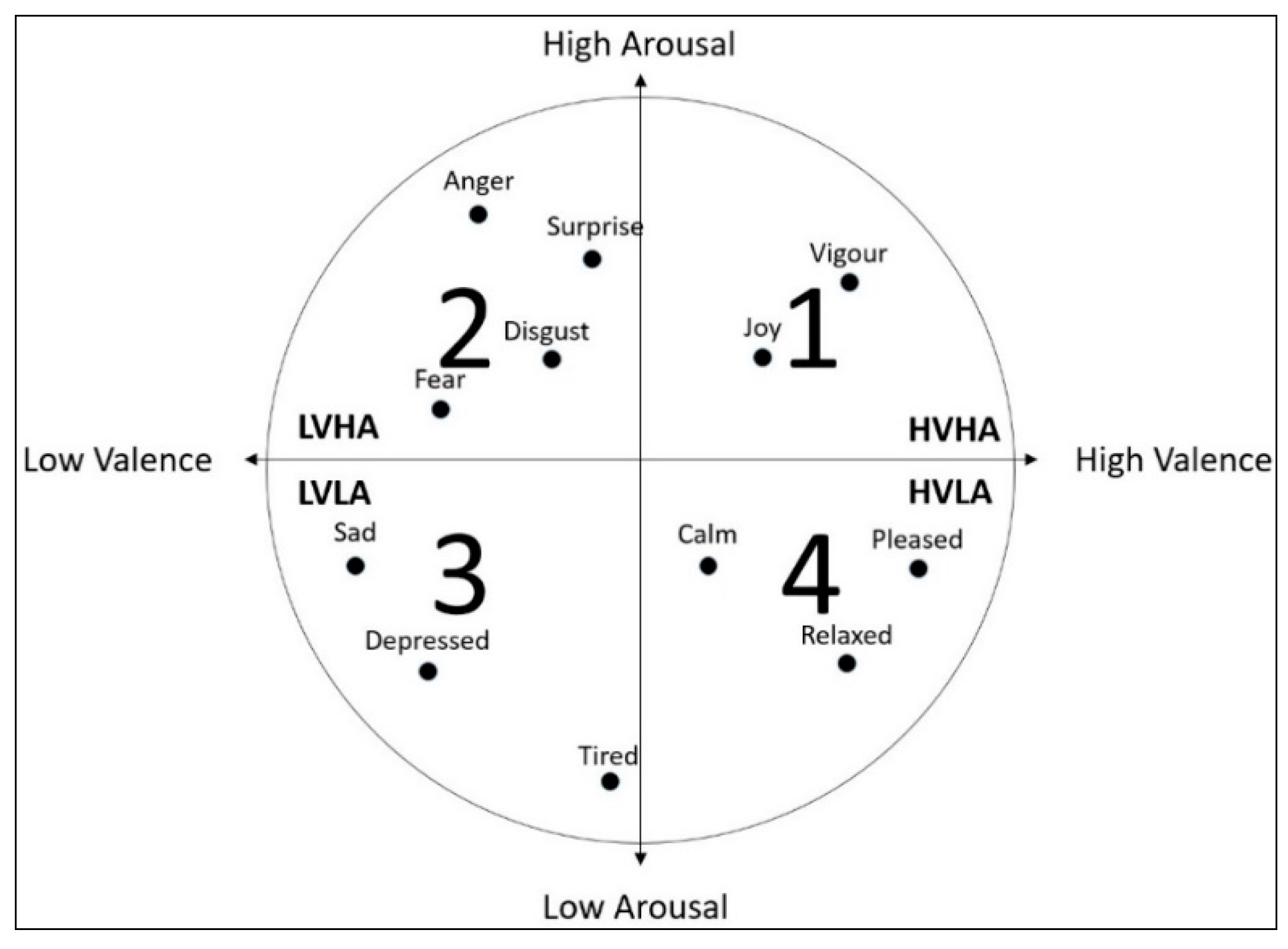
3.2. The Construction of the Emotion Classification Labels
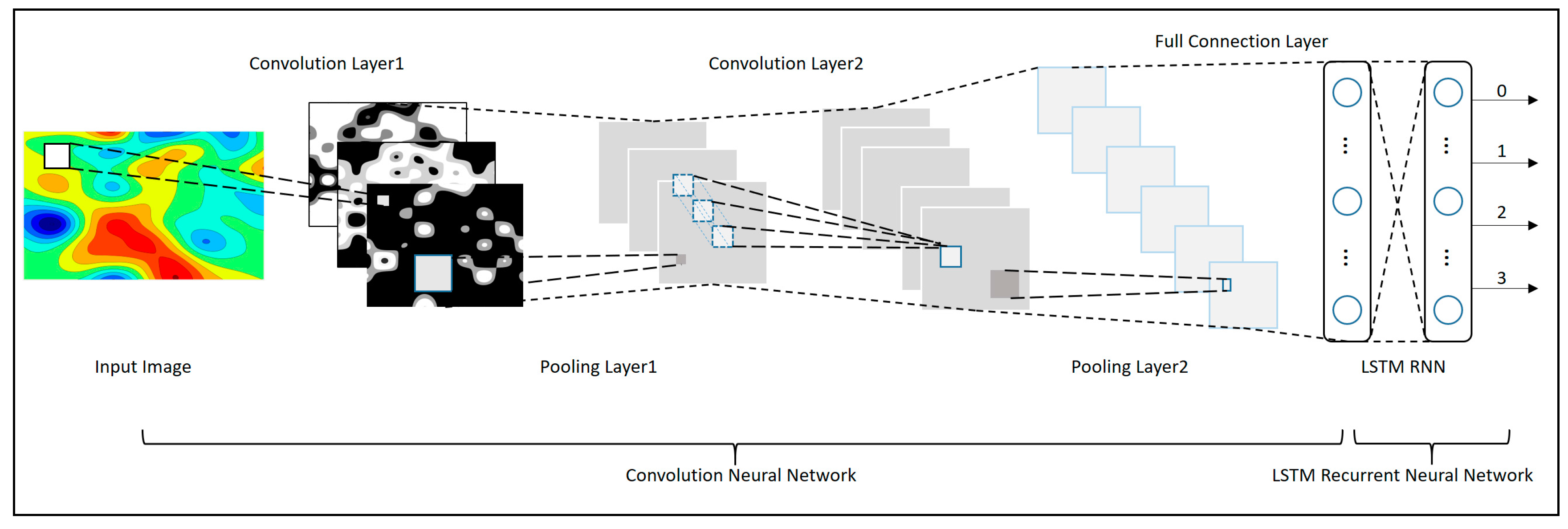
4. The Construction of the Hybrid Deep Neural Networks
4.1. The Construction of Convolutional Neural Networks
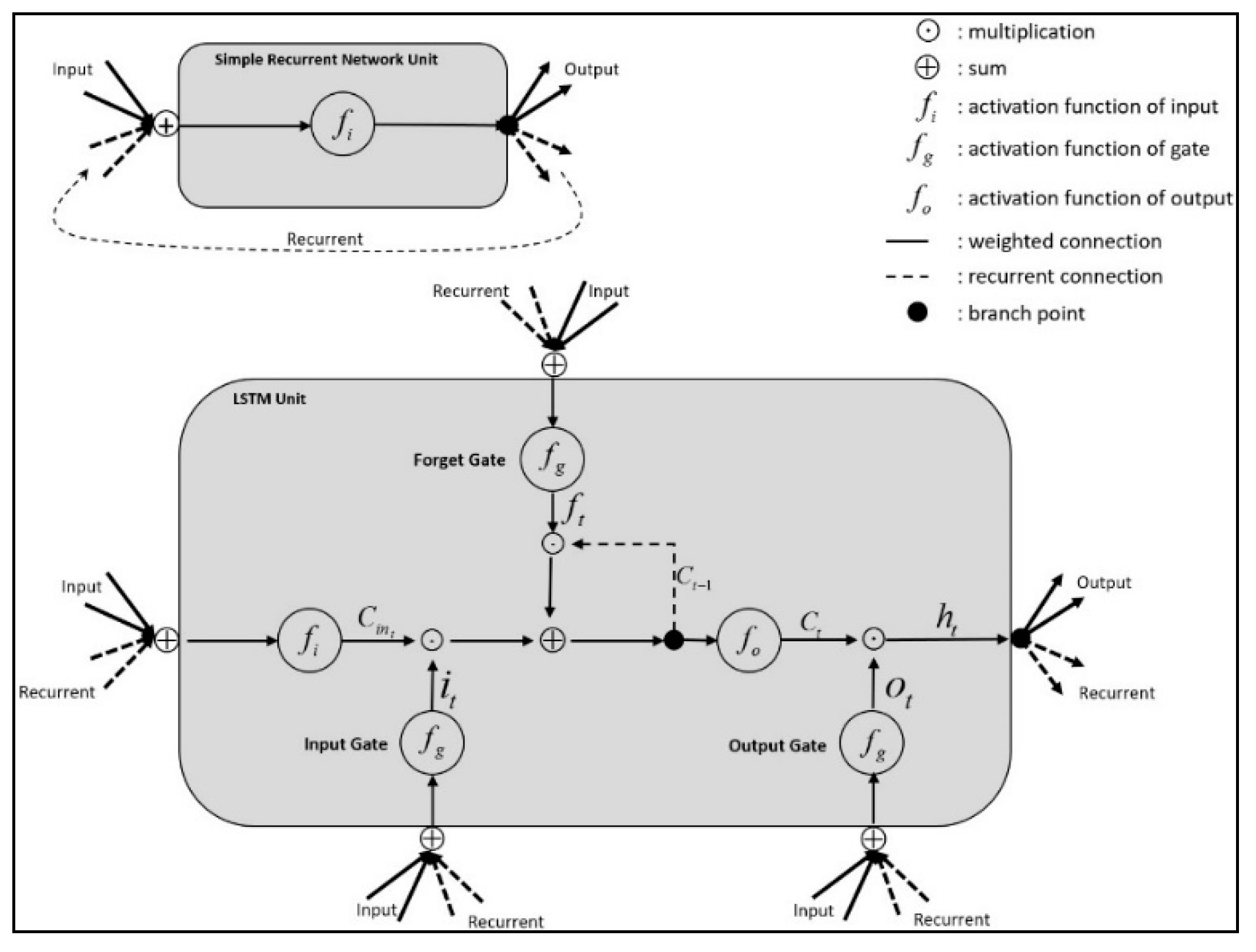
4.2. The Construction of LSTM Recurrent Neural Networks
4.3. The Construction of CLRNN with DL4J
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Experiment Dataset and Settings
5.2. Baseline Methods
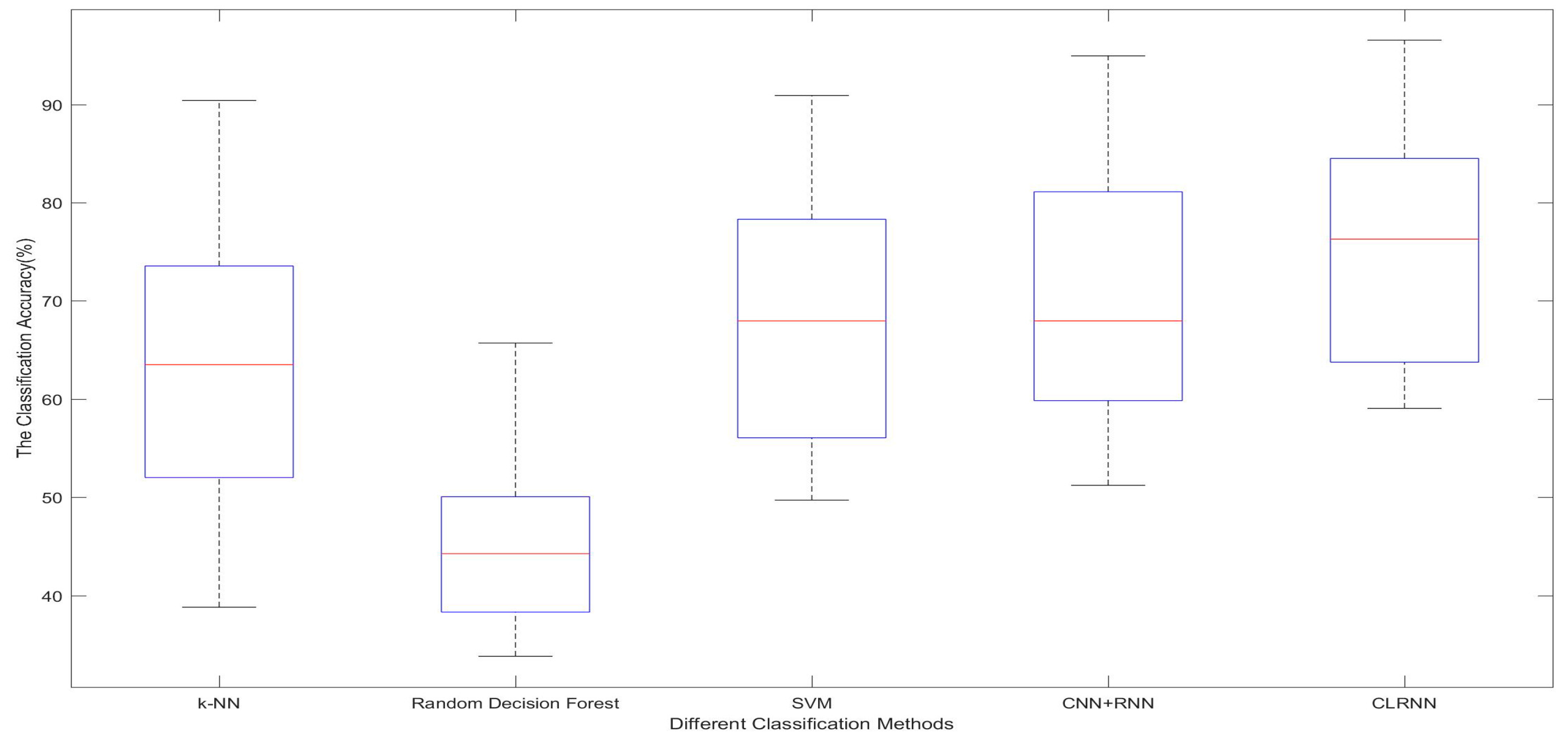
5.3. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
Appendix C
References
- Mandryk, R.L.; Inkpen, K.M.; Calvert, T.W. Using psychophysiological techniques to measure user experience with entertainment technologies. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2006, 25, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healey, J.A.; Picard, R.W. Detecting stress during real-world driving tasks using physiological sensors. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2005, 6, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsis, C.D.; Katertsidis, N.; Ganiatsas, G.; Fotiadis, D.I. Toward emotion recognition in car-racing drivers: A biosignal processing approach. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 2008, 38, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsis, C.D.; Katertsidis, N.S.; Fotiadis, D.I. An integrated system based on physiological signals for the assessment of affective states in patients with anxiety disorders. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2011, 6, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschuere, B.; Ben-Shakhar, G.; Meijer, E. Memory Detection: Theory and Application of the Concealed Information Test. In Psychopathy and the Detection of Concealed Information; Verschuere, B., Ben-Shakhar, G.M., Meijer, E., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 215–230. [Google Scholar]
- Picard, R.W.; Vyzas, E.; Healey, J. Toward machine emotional intelligence: Analysis of affective physiological state. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2001, 23, 1175–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ayadi, M.; Kamel, M.S.; Karray, F. Survey on speech emotion recognition: Features, classification schemes, and databases. Pattern Recognit. 2011, 44, 572–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, Y.V.; Kassim, A.A.; Yuan, J.; Nguyen, T.D. On the simultaneous recognition of identity and expression from BU-3DFE datasets. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2012, 33, 1785–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnrich, B.; Setz, C.; La Marca, R.; Troster, G.; Ehlert, U. What does your chair know about your stress level? IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2010, 14, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacioppo, J.T.; Berntson, G.G.; Larsen, J.T.; Poehlmann, K.M. The psychophysiology of emotion. In Handbook of Emotion; Lewis, M., Haviland-Jones, J.M., Eds.; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 173–191. [Google Scholar]
- Koelstra, S.; Muhl, C.; Soleymani, M.; Jong-Seok, L.; Yazdani, A.; Ebrahimi, T.; Pun, T.; Nijholt, A.; Patras, I. Deap: A database for emotion analysis ;using physiological signals. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2012, 3, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-K.; Kim, M.; Oh, E.; Kim, S.-P. A review on the computational methods for emotional state estimation from the human EEG. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2013, 2013, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari-Asl, K.; Chanel, G.; Pun, T. A channel selection method for EEG classification in emotion assessment based on synchronization likelihood. In Proceedings of the 15th European Signal Processing Conference, Poznan, Poland, 3–7 September 2007; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 1241–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Horlings, R.; Datcu, D.; Rothkrantz, L.J.M. Emotion recognition using brain activity. In Proceedings of the 9th international conference on computer systems and technologies and workshop for PhD students in computing, Gabrovo, Bulgaria, 12–13 June 2008; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Murugappan, M.; Ramachandran, N.; Sazali, Y. Classification of human emotion from EEG using discrete wavelet transform. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2010, 3, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrantonakis, P.C.; Hadjileontiadis, L.J. Emotion recognition from EEG using higher order crossings. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2010, 14, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrantonakis, P.C.; Hadjileontiadis, L.J. Emotion recognition from brain signals using hybrid adaptive filtering and higher order crossings analysis. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2010, 1, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, Z.; Moradi, M.H. Emotion detection using brain and peripheral signals. In Proceedings of the Biomedical Engineering Conference, Cairo, Egypt, 18–20 December 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 1223–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, L.; Lu, B.-L. Emotion classification based on gamma-band EEG. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 3–6 September 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 1223–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Sourina, O. EEG-based dominance level recognition for emotion-enabled interaction. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Melbourne, Australia, 9–13 July 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1039–1044. [Google Scholar]
- Rozgic, V.; Vitaladevuni, S.N.; Prasad, R. Robust EEG emotion classification using segment level decision fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–31 May 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 1286–1290. [Google Scholar]
- Daunizeau, J.; Lee, Y.-Y.; Hsieh, S. Classifying different emotional states by means of EEG-based functional connectivity patterns. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95415. [Google Scholar]
- Bashivan, P.; Rish, I.; Yeasin, M.; Codella, N. Learning representations from EEG with deep recurrent-convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations 2016, San Juan, PR, USA, 2–4 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J. Cross-subject EEG feature selection for emotion recognition using transfer recursive feature elimination. Front. Neurorobot. 2017, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanel, G.; Karim, A.-A.; Thierry, P. Valence-arousal evaluation using physiological signals in an emotion recall paradigm. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–10 October 2007; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 2662–2667. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, D.; Wang, X.-W.; Shi, L.-C.; Lu, B.-L. EEG-based emotion recognition during watching movies. In Proceedings of the 5th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering, Cancun, Mexico, 27 April–1 May 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 667–670. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.L.; Dong, B.N.; Lu, B.-L. Multimodal emotion recognition using EEG and eye tracking data. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 26–30 August 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 5040–5043. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.-L.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Lu, B.-L. Identifying stable patterns over time for emotion recognition from EEG. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2017, PP, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thammasan, N.; Moriyama, K.; Fukui, K.; Numao, M. Continuous music-emotion recognition based on electroencephalogram. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 2016, 99, 1234–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugappan, M.; Rizon, M.; Nagarajan, R.; Yaacob, S. Inferring of human emotional states using multichannel EEG. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2010, 48, 281–299. [Google Scholar]
- Kroupi, E.; Yazdani, A.; Ebrahimi, T. EEG correlates of different emotional states elicited during watching music videos. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction, Memphis, TN, USA, 9–12 October 2011; Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction (ACII): Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 457–466. [Google Scholar]
- Hadjidimitriou, S.K.; Hadjileontiadis, L.J. Toward an EEG-based recognition of music liking using time-frequency analysis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 3498–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuderink, B.; Mühl, C.; Poel, M. Valence, arousal and dominance in the EEG during game play. Int. J. Auton. Adapt. Commun. Syst. 2013, 6, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahane, P.; Sangaiah, A.K. An approach to EEG based emotion recognition and classification using kernel density estimation. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 48, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Mazumder, A.; Ghosh, P.; Tibarewala, D.N.; Vimalarani, G. EEG based emotion recognition system using MFDFA as feature extractor. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics, Automation, Control and Embedded Systems (RACE), Chennai, India, 18–20 February 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Qi, X.Y.; Sun, X.Q.; Xie, J.L.; Fan, M.D.; Kang, J.N. An improved multi-scale entropy algorithm in emotion EEG features extraction. J. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 2017, 7, 436–439. [Google Scholar]
- Soleymani, M.; Koelstra, S.; Patras, I.; Pun, T. Continuous emotion detection in response to music videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition and Workshops, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 21–25 March 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 803–808. [Google Scholar]
- Klem, G.H.; Luders, H.O.; Jasper, H.H.; Elger, C. The ten-twenty electrode system of the international federation. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. Suppl. 1999, 52, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, L.; Grundlehner, B.; Penders, J. Towards wireless emotional valence detection from EEG. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 2188–2191. [Google Scholar]
- Frantzidis, C.A.; Bratsas, C.; Papadelis, C.L.; Konstantinidis, E.; Pappas, C.; Bamidis, P.D. Toward emotion aware computing: An integrated approach using multichannel neurophysiological recordings and affective visual stimuli. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2010, 14, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaaff, K.; Schultz, T. Towards emotion recognition from electroencephalographic signals. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction and Workshops, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 10–12 September 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, S.A.; Khalilzadeh, M.A.; Naghibi-Sistani, M.B.; Niazmand, V. Higher order spectra analysis of EEG signals in emotional stress states. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Information Technology and Computer Science, Kiev, Ukraine, 24–25 July 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 60–63. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, S.Y.; Yoon, H.J. Affective classification using Bayesian classifier and supervised learning. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems, JeJu Island, Korea, 17–21 October 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1768–1771. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Song, D.; Zhang, P.; Yu, G.; Hou, Y.; Hu, B. Emotion recognition from multi-channel EEG data through convolutional recurrent neural network. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Shenzhen, China, 15–18 December 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 352–359. [Google Scholar]
- Candra, H.; Yuwono, M.; Rifai, C.; Handojoseno, A.; Elamvazuthi, I.; Nguyen, H.T.; Su, S. Investigation of window size in classification of EEG-emotion signal with wavelet entropy and support vector machine. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 7250–7253. [Google Scholar]
- 10–20 System (EEG). Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/10-20_system_(EEG) (accessed on 10 September 2017).
- Bengio, Y.; Simard, P.; Frasconi, P. Learning long-term dependencies with gradient descent is difficult. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1994, 5, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DEEPLEARNING4J. Available online: https://deeplearning4j.org/ (accessed on 10 September 2017).
- Panksepp, J. A role for affective neuroscience in understanding stress: The case of separation distress circuitry. Psychobiol. Stress 1990, 54, 41–57. [Google Scholar]
- Papez, J.W. A proposed mechanism of emotion. Arch. Neurol. Psychiatry 1937, 38, 725–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, R.J.; Sutton, S.K. Affective neuroscience: The emergence of a discipline. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1995, 5, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
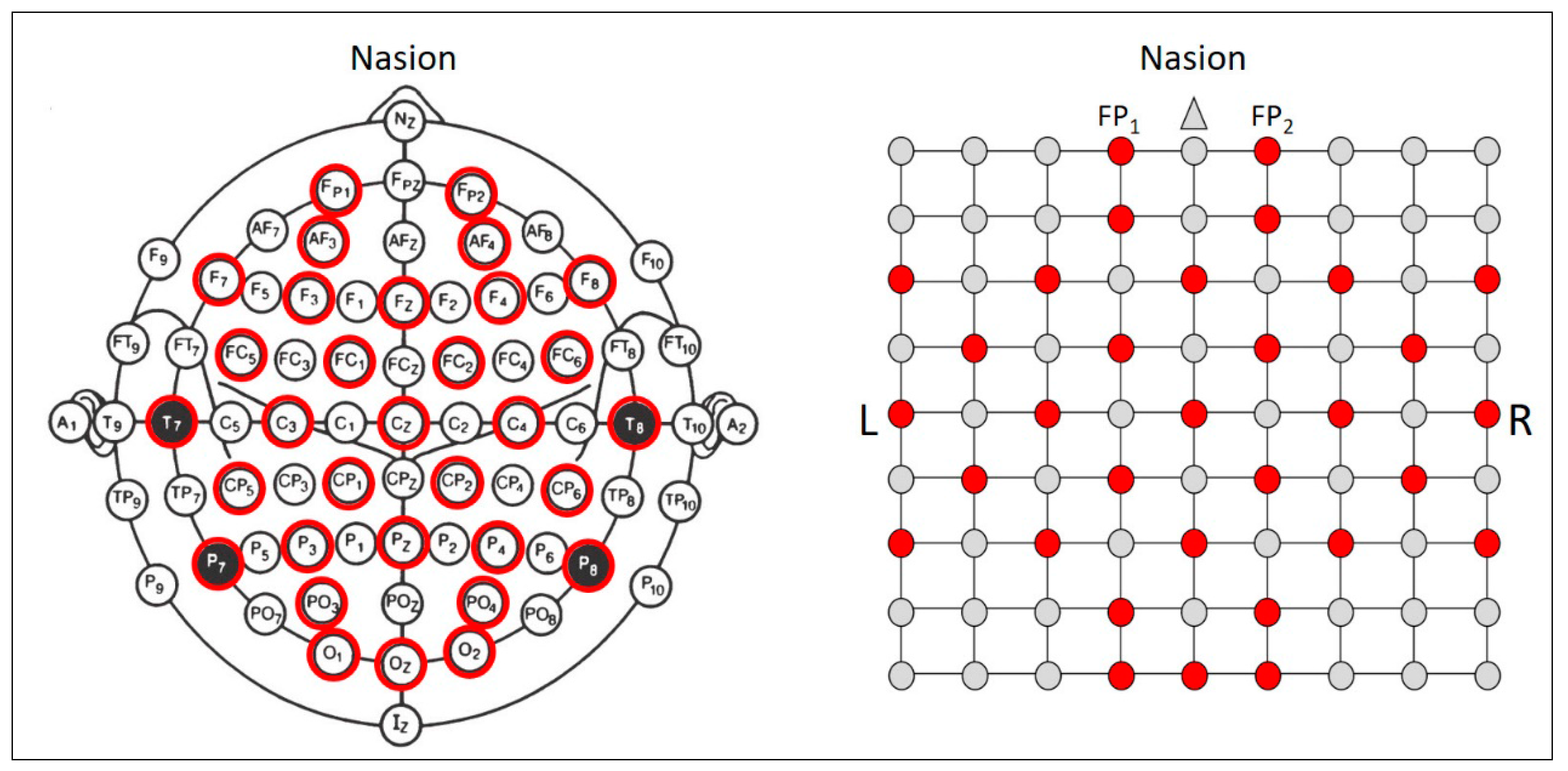
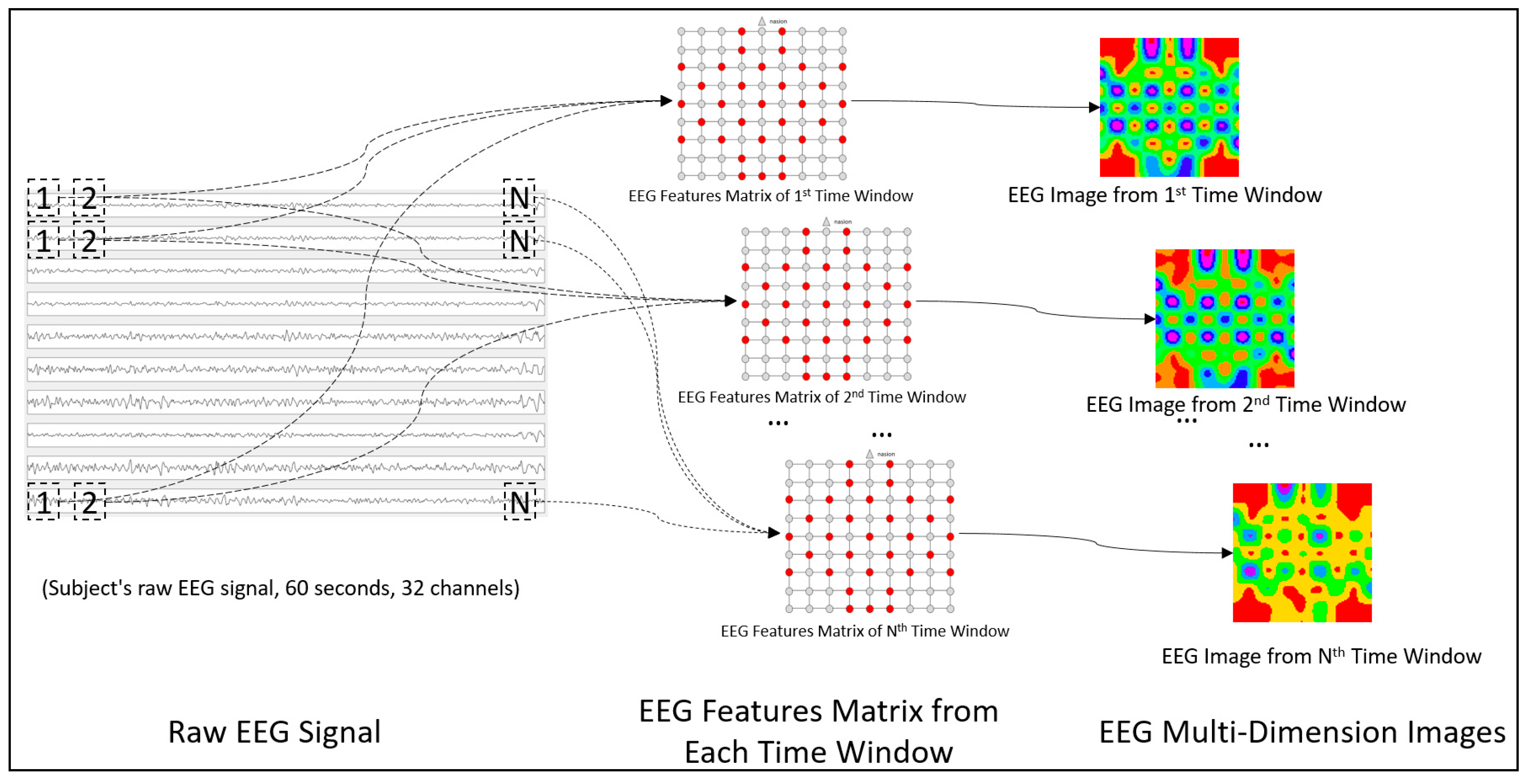
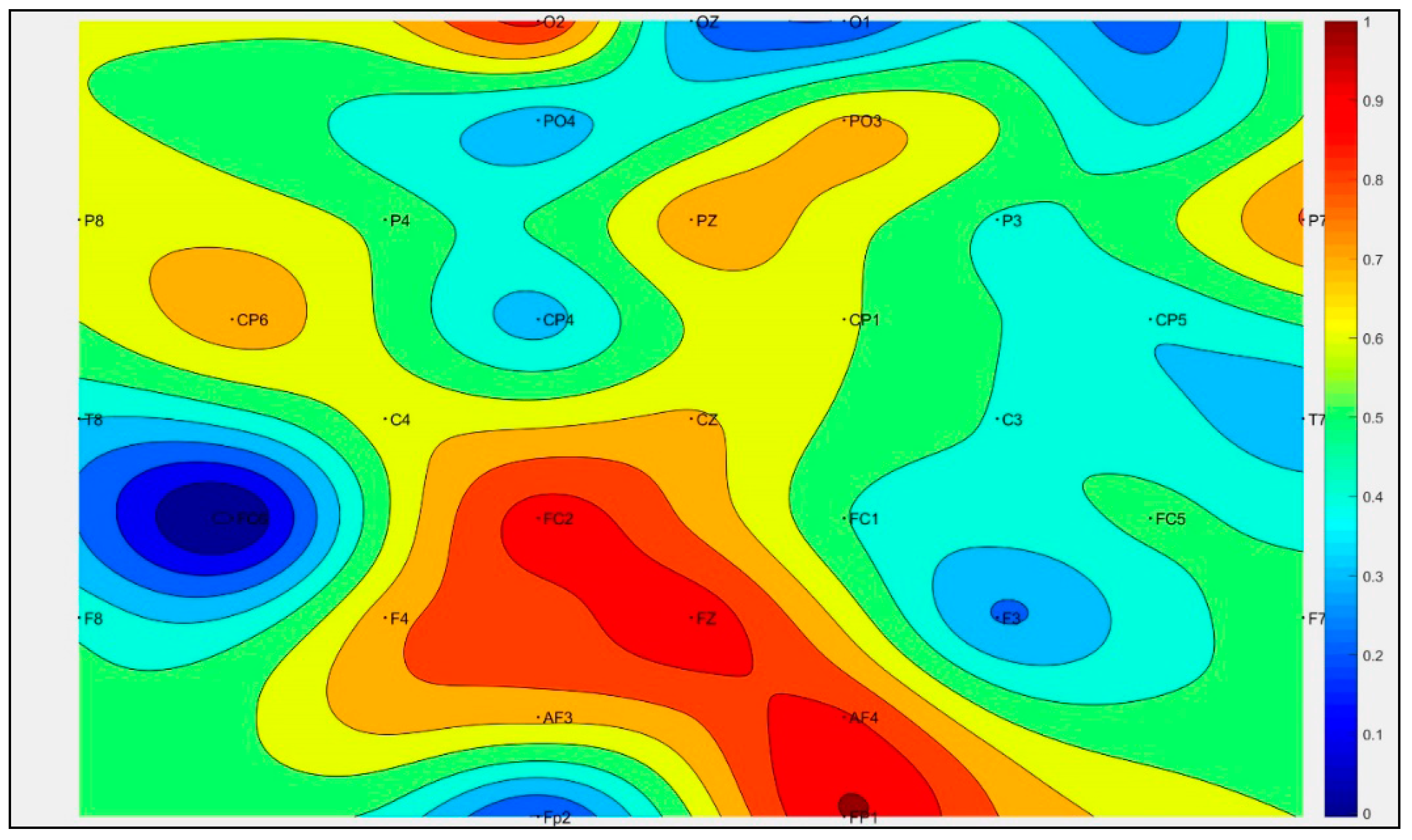
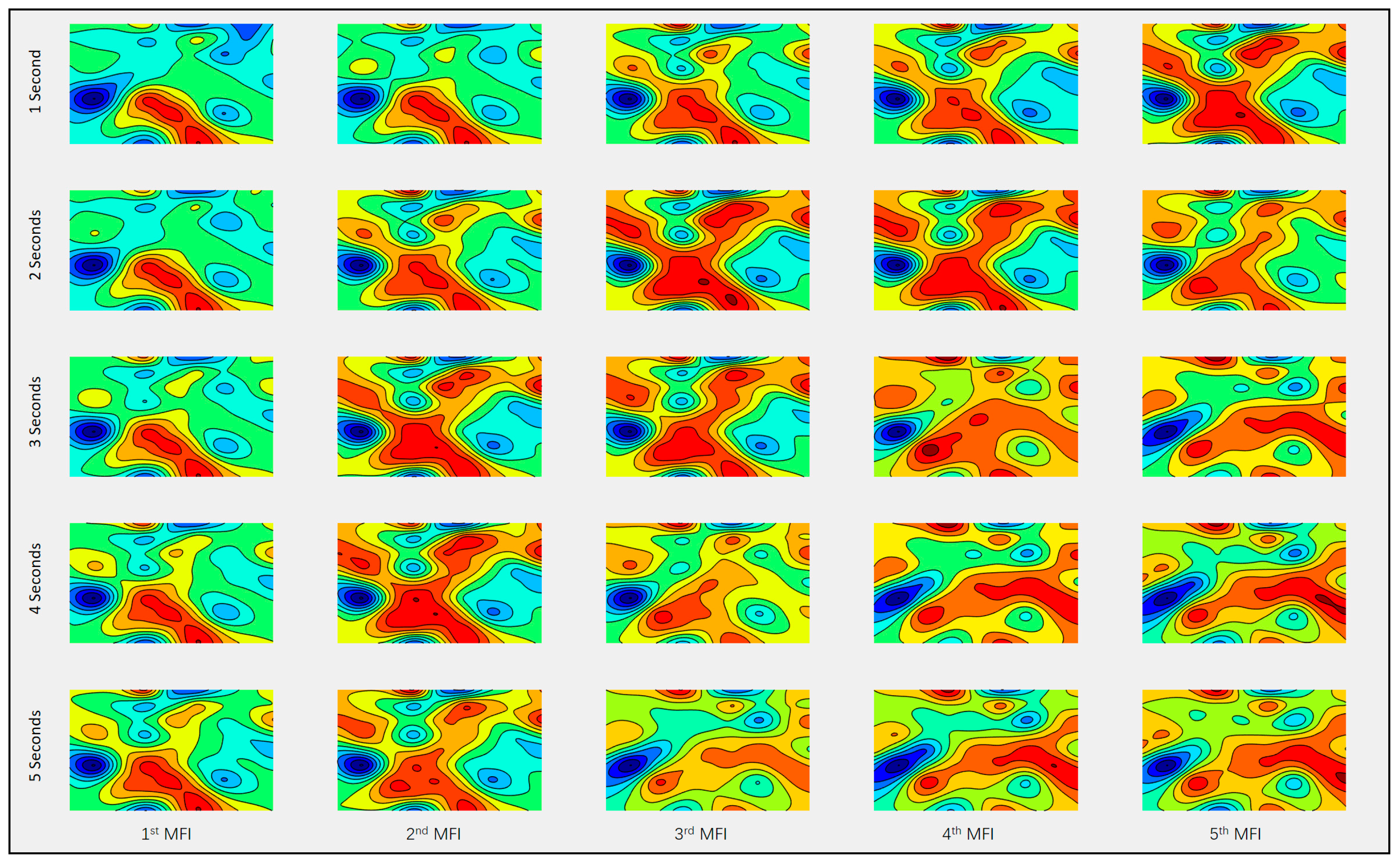
| Author and Study | Year | EEG Features | Extraction Method | Dimension |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ansari et al. [13] | 2007 | Activity, Mobility, and Complexity | Sevcik’s method | Time |
| Chanel et al. [25] | 2007 | 9 sub-bands of the EEG (4–20 Hz) | STFT | Frequency |
| Horlings [14] | 2008 | Activity, Mobility, and Complexity | Welch’s Method | Time |
| Khalili and Moradi [18] | 2008 | Sub-band: θ, α, β, γ | FFT | Frequency |
| Li and Lu [19] | 2009 | EEG γ band (30–100 Hz) | FFT | Frequency |
| Petrantonakis and Hadjileontiadis [16,17] | 2010 | Higher Order Crossing | DWT | Time |
| Murugappan et al. [15,30] | 2010 | Power | DWT | Time |
| Nie et al. [26] | 2011 | Sub-band: δ, θ, α (8–13 Hz), β (1–30 Hz), γ (36–40 Hz) | STFT | Frequency |
| Kroupi et al. [31] | 2011 | Sub-band: θ, α, β, γ, NLD, NSI | Welch’s Method | Frequency |
| Liu and Sourina [20] | 2012 | β/α, Sub-band: β | FFT | Frequency |
| Hadjidimitriou et al. [32] | 2012 | HHS-based Feature Vectors | HHS | Time and Frequency |
| Reuderink et al. [33] | 2013 | The change and asymmetry in Sub-band of α | Welch’s Method | Frequency and Spatial |
| Rozgic et al. [21] | 2013 | Spectral Power and Spectral Power Differences | FFT | Frequency and Spatial |
| Lee and Hsieh [22] | 2014 | Correlation, Coherence, and Phase Synchronization | FFT | Frequency |
| Zheng et al. [27] | 2014 | PSD, DE, DASM and RASM | STFT | Frequency |
| Lahane and Sangaiah [34] | 2015 | Density Estimate | Kernel Density Estimation | Frequency |
| Paul et al. [35] | 2015 | Sub-band: α, β, θ | MFDFA | Frequency |
| Bashivan et al. [23] | 2015 | Sum of squared absolute values of the Sub-band: α, β, θ | FFT | Frequency Spatial |
| Thammasan et al. [29] | 2016 | Fractal Dimension (FD) and Power Spectral Density (PSD) | Welch’s Method | Frequency |
| Zheng et al. [28] | 2016 | PSD, DE, DASM, RASM, ASM, and DCAU | STFT | Frequency |
| Li et al. [36] | 2017 | Multi-scale entropy | HHT | Time and Frequency |
| Yin et al. [24] | 2017 | Frequency Features and Time-Frequency Features | FFT | Time and Frequency |
| Author and Study | Emotion Classification Basis | Subjects | Accuracy | Classification Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horlings [14] | Valence and Arousal (2 classes) | 10 | 81% | SVM |
| Schaaff [41] | Valence and Arousal (3 classes) | 30 | 66.7% | SVM |
| Frantzidis [40] | Valence and Arousal (2 classes, respectively) | 28 | 81.3% | SVM |
| Murugappan [15] | Valence(2 classes) | 12 | 71.3% | k-NN |
| Brown [39] | Valence (2 classes) | 9 | 82% | SVM, k-NN |
| Hosseini [42] | Valence and Arousal (2 classes) | 15 | 82% | SVM |
| Chung [43] | Valence and Arousal (2/3 classes respectively) | 32 | 66.6%, 66.4% (2) 53.4%, 51.0% (3) | Bayes neural network |
| Li [44] | Valence and Arousal (2 classes, respectively) | 32 | 74.12% | C-RNN |
| Our Method | Valence and Arousal (4 classes) | 32 | 75.21% | CLRNN |
| Emotion Labels | Number of the Samples |
|---|---|
| HVHA | 348 |
| HVLA | 298 |
| LVLA | 282 |
| LVHA | 352 |
| Total | 1280 |
| Input Data | Convolutional Layer 1 | Max Pooling Layer 1 | Convolutional Layer 2 | Max Pooling Layer 2 | Dense Layer | LSTM RNN | RNN Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <200 × 200> × 3 | <2 × 2> × 30 | <2 × 2> | <2 × 2> × 10 | <2 × 2> | 6250:625 | 625:625 | 4 |
| <5 × 5> × 30 | <2 × 2> | <2 × 2> × 10 | <2 × 2> | 4000:400 | 400:400 | ||
| <10 × 10> × 30 | <2 × 2> | <2 × 2> × 10 | <2 × 2> | 1000:100 | 100:100 |
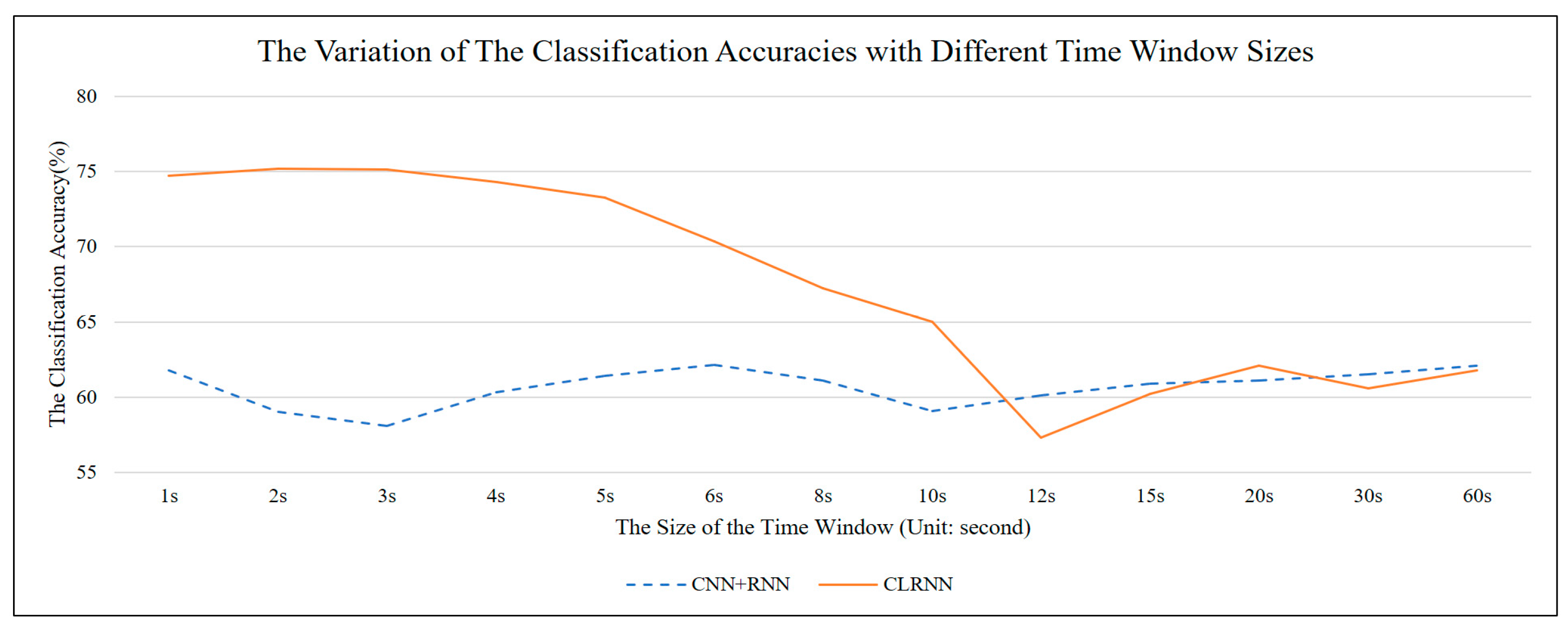
| Classification Methods | 1 s | 2 s | 3 s | 4 s | 5 s | 6 s | 8 s | 10 s | 12 s | 15 s | 20 s | 30 s | 60 s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k-NN | 46.09 | 52.49 | 57.29 | 59.49 | 61.69 | 61.39 | 61.49 | 61.89 | 61.79 | 62.19 | 62.59 | 62.19 | 62.39 |
| Random Decision Forest | 39.03 | 38.17 | 39.38 | 40.19 | 38.53 | 36.43 | 44.53 | 45.38 | 45.88 | 46.58 | 46.68 | 46.78 | 46.98 |
| SVM | 65.11 | 65.11 | 66.11 | 64.21 | 63.01 | 64.31 | 61.01 | 63.01 | 62.61 | 62.41 | 63.01 | 63.41 | 63.21 |
| CNN + RNN | 61.76 | 59.02 | 58.07 | 60.34 | 61.43 | 62.13 | 61.13 | 59.1 | 60.1 | 60.9 | 61.1 | 61.5 | 62.1 |
| CLRNN | 74.73 | 75.21 | 75.13 | 74.32 | 73.25 | 70.37 | 67.23 | 65.01 | 57.3 | 60.2 | 62.1 | 60.6 | 61.8 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhong, N. Human Emotion Recognition with Electroencephalographic Multidimensional Features by Hybrid Deep Neural Networks. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7101060
Li Y, Huang J, Zhou H, Zhong N. Human Emotion Recognition with Electroencephalographic Multidimensional Features by Hybrid Deep Neural Networks. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(10):1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7101060
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Youjun, Jiajin Huang, Haiyan Zhou, and Ning Zhong. 2017. "Human Emotion Recognition with Electroencephalographic Multidimensional Features by Hybrid Deep Neural Networks" Applied Sciences 7, no. 10: 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7101060
APA StyleLi, Y., Huang, J., Zhou, H., & Zhong, N. (2017). Human Emotion Recognition with Electroencephalographic Multidimensional Features by Hybrid Deep Neural Networks. Applied Sciences, 7(10), 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7101060





