Evaluation of Anti-Wear Properties of Metalworking Fluids Enhanced with Halloysite Nanotubes
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
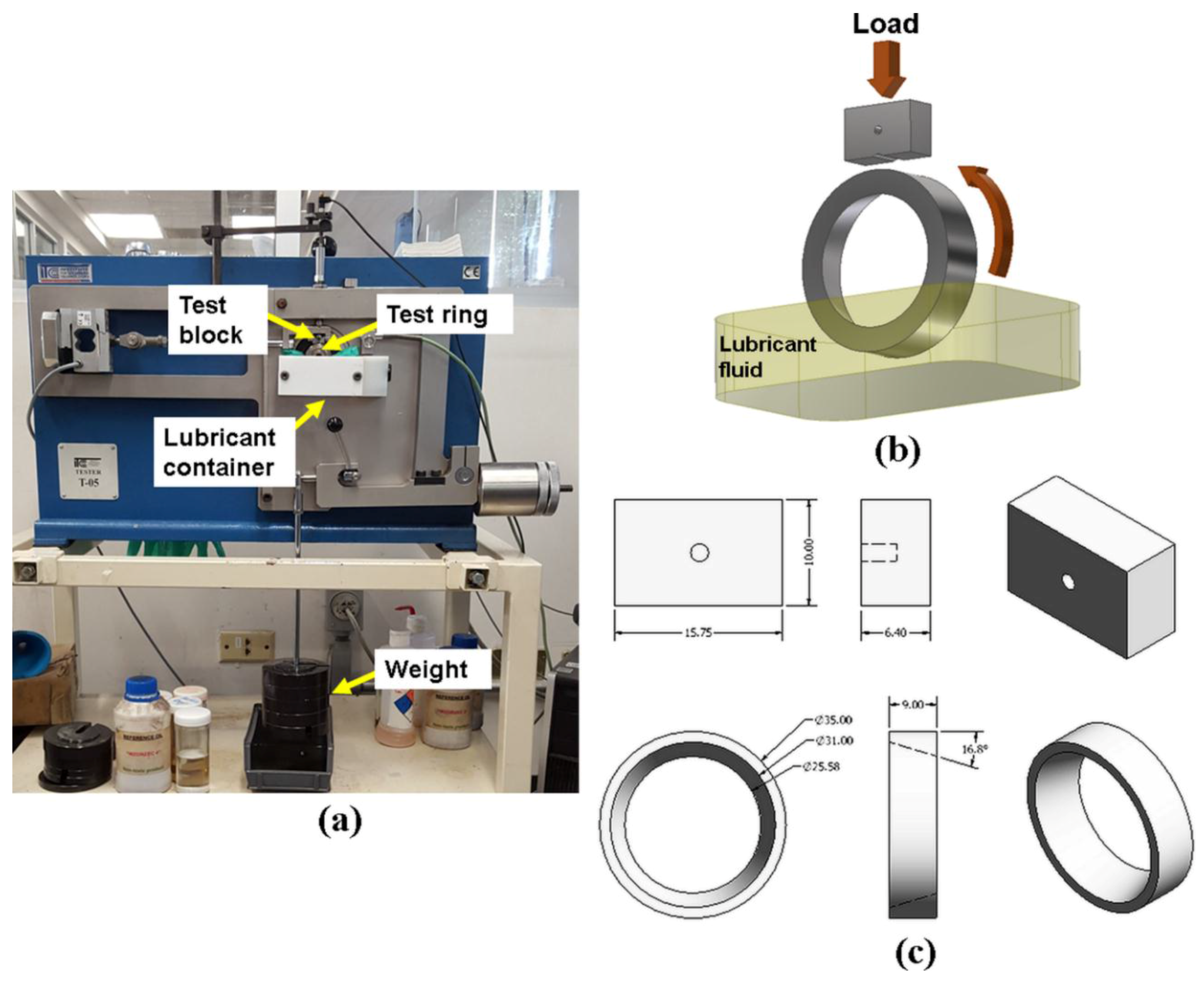
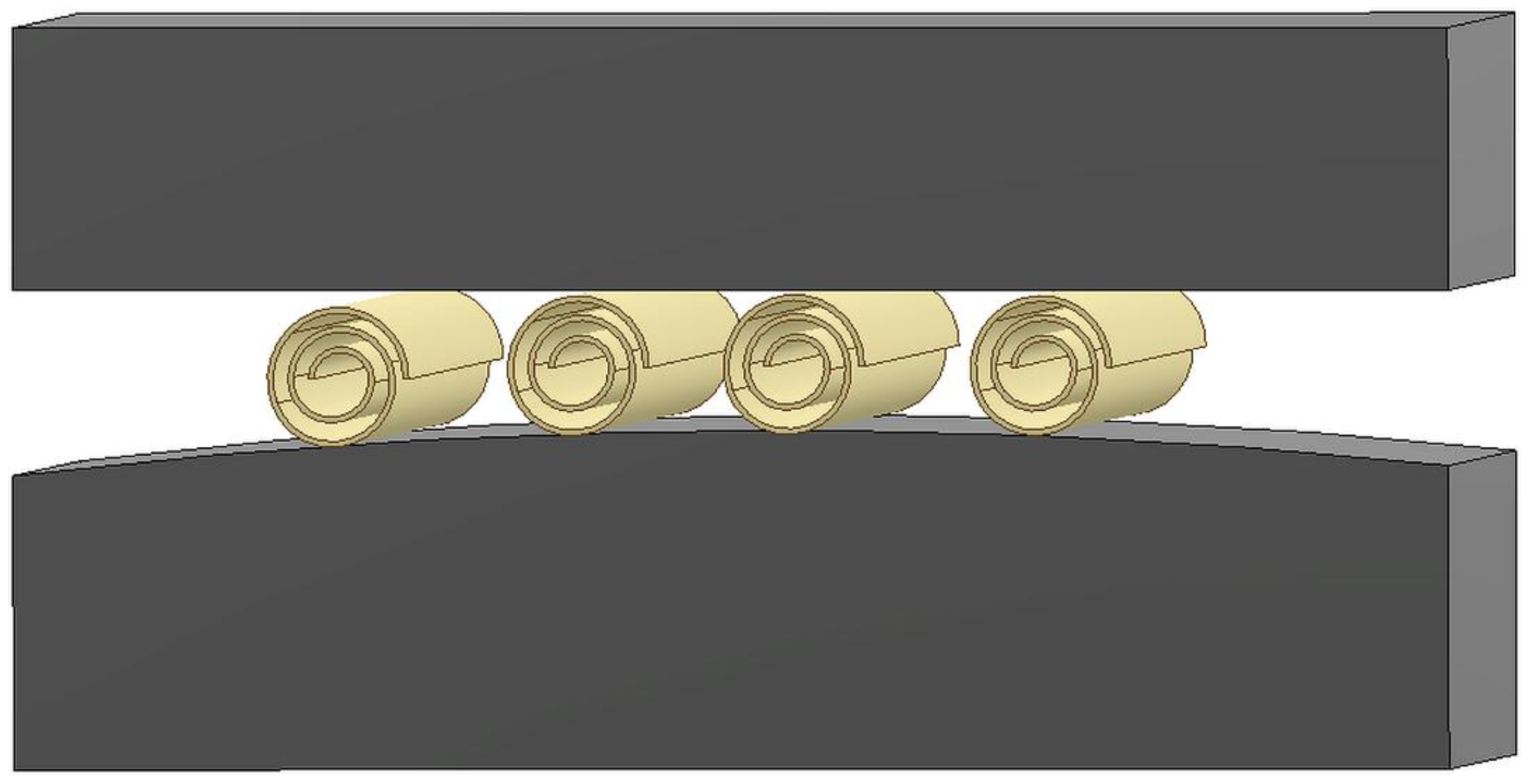
2.2. Tribological Tests
2.3. Surface Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
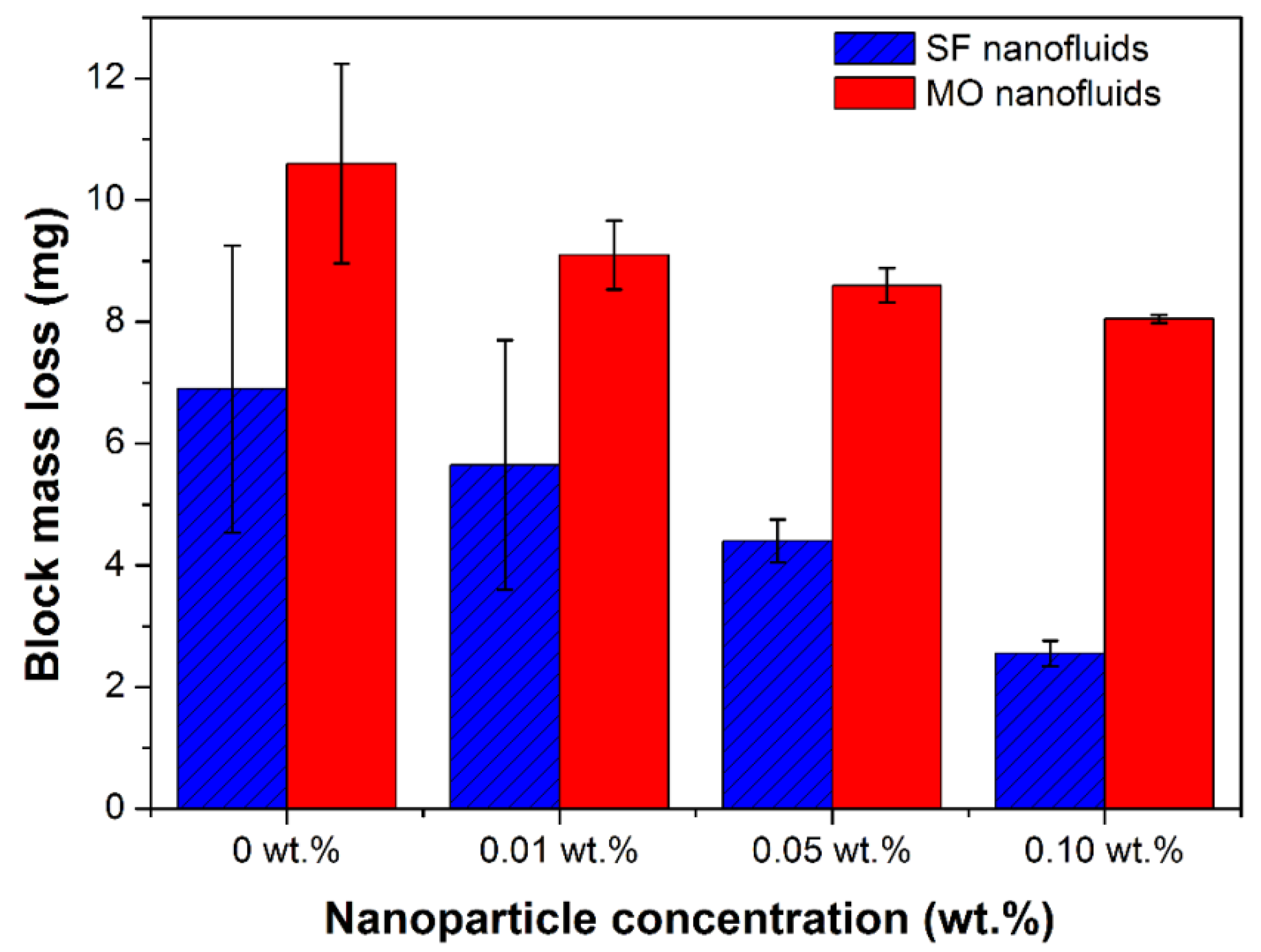
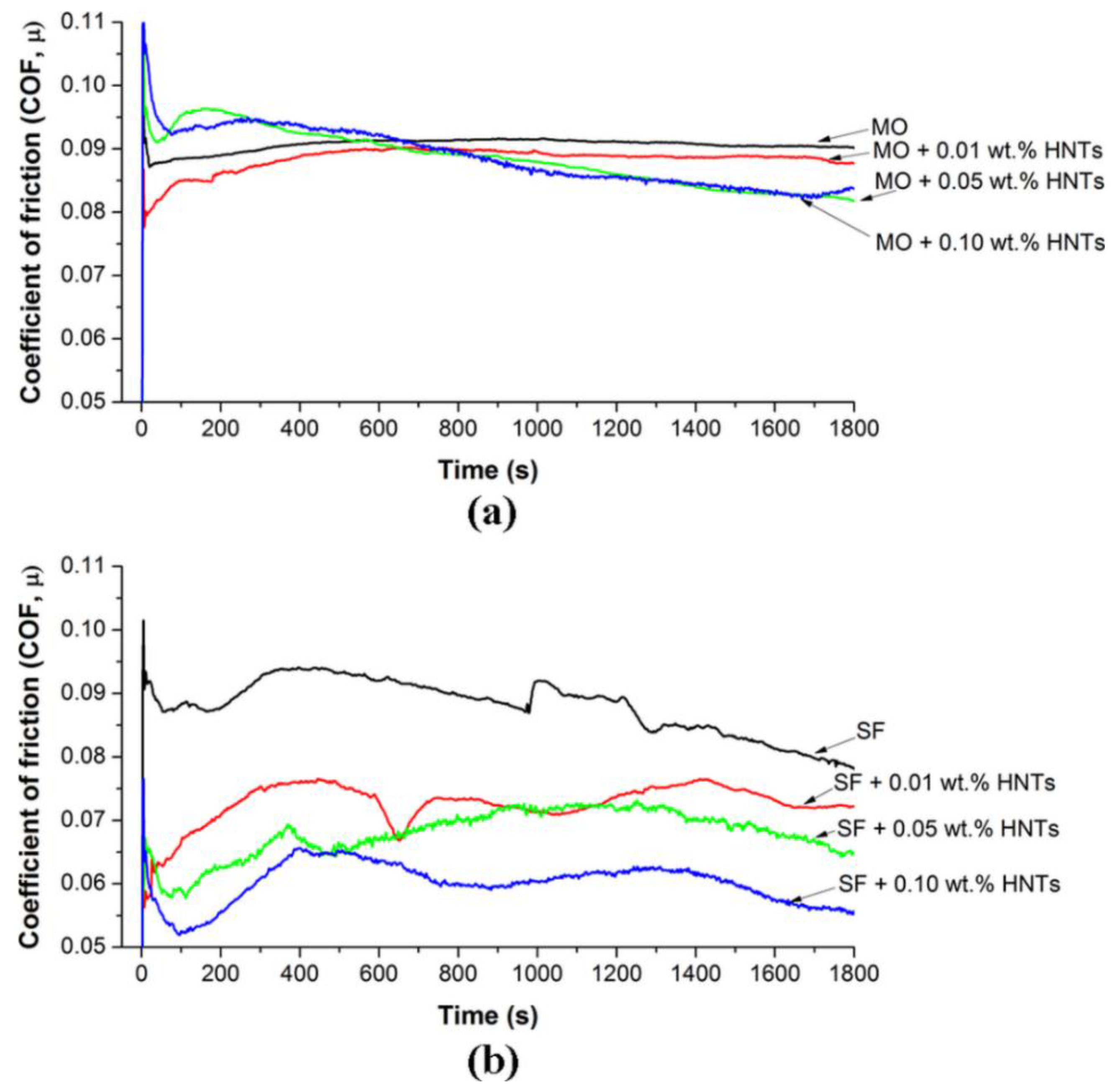
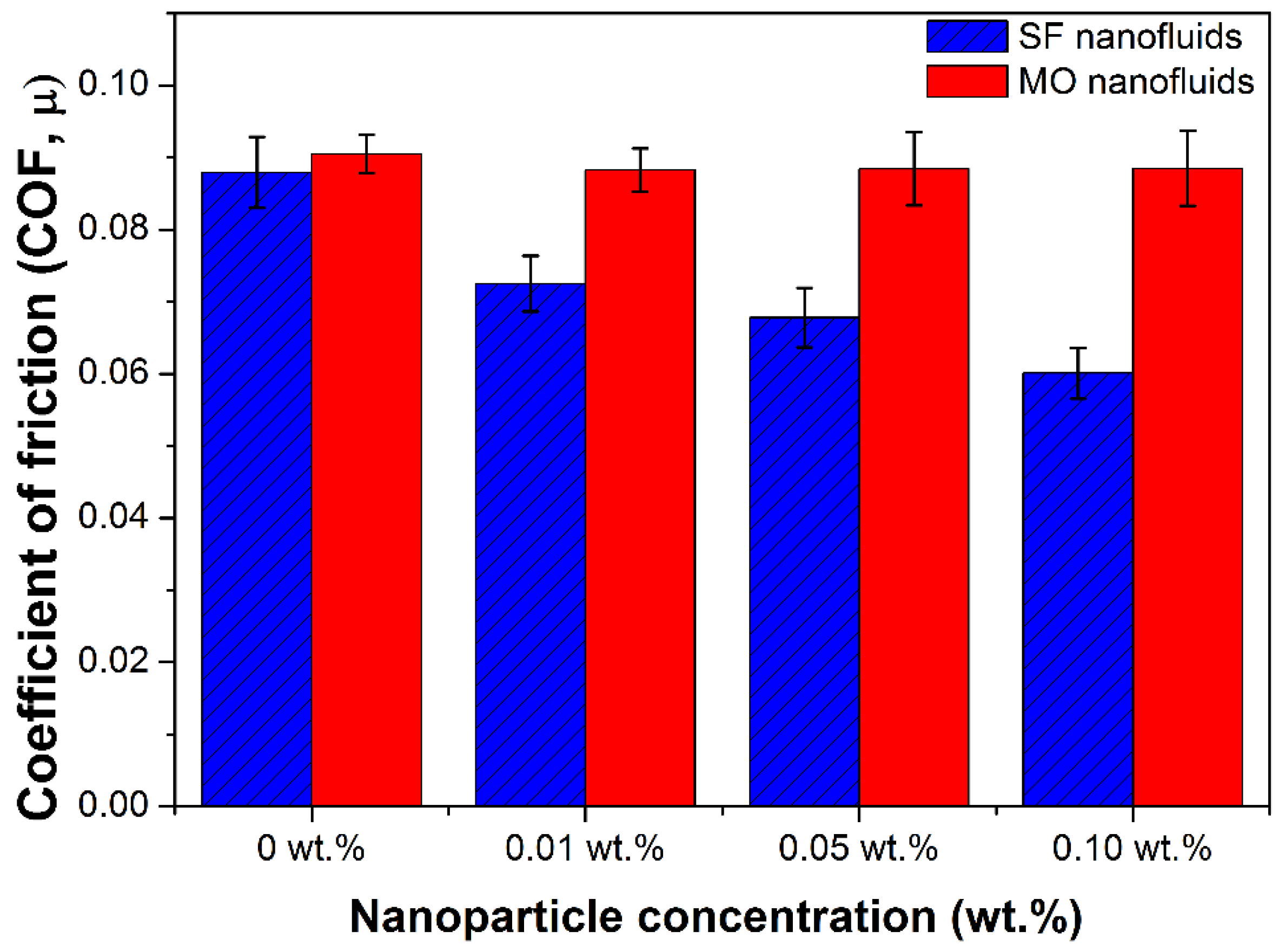
3.1. Tribological Results
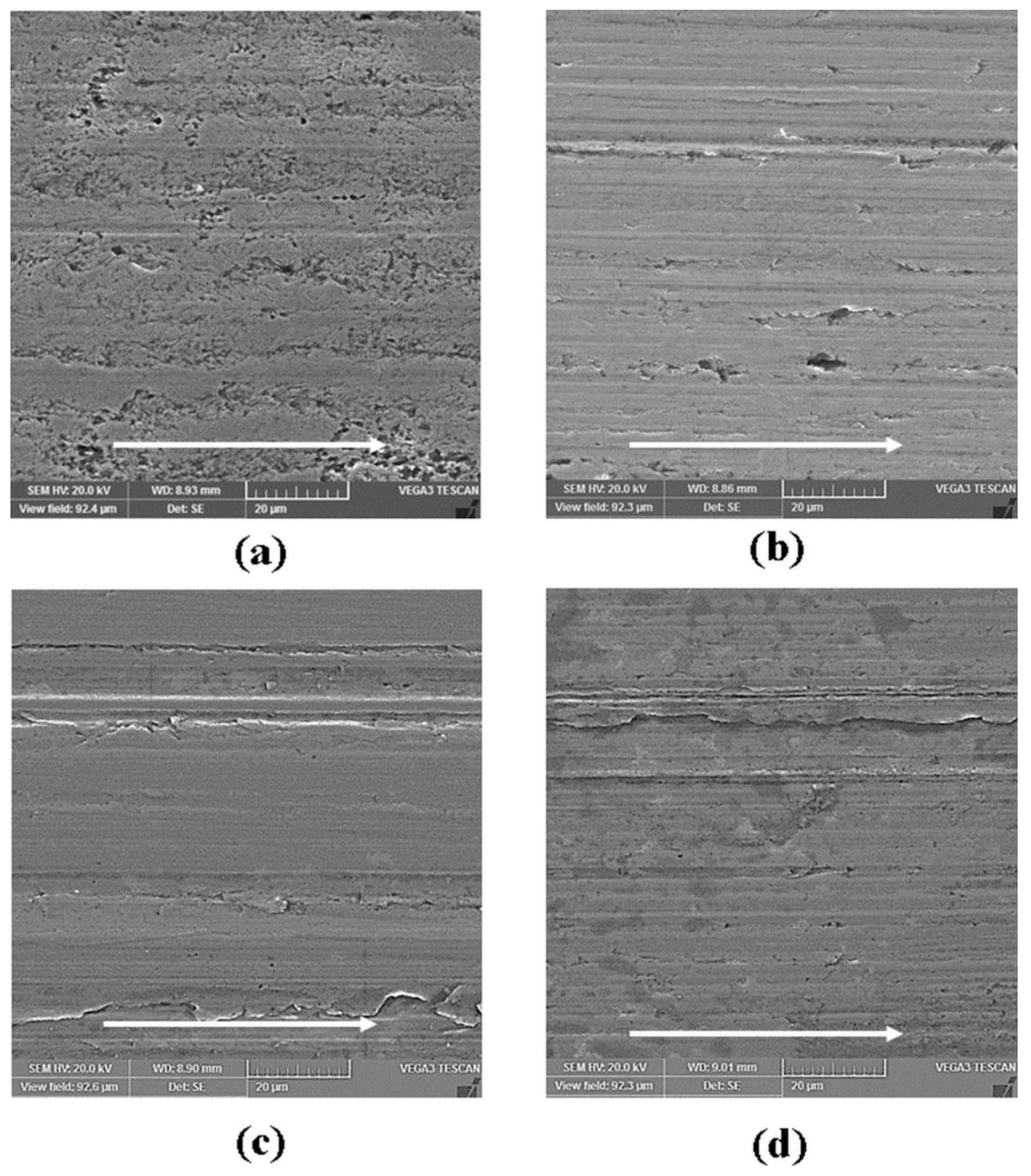
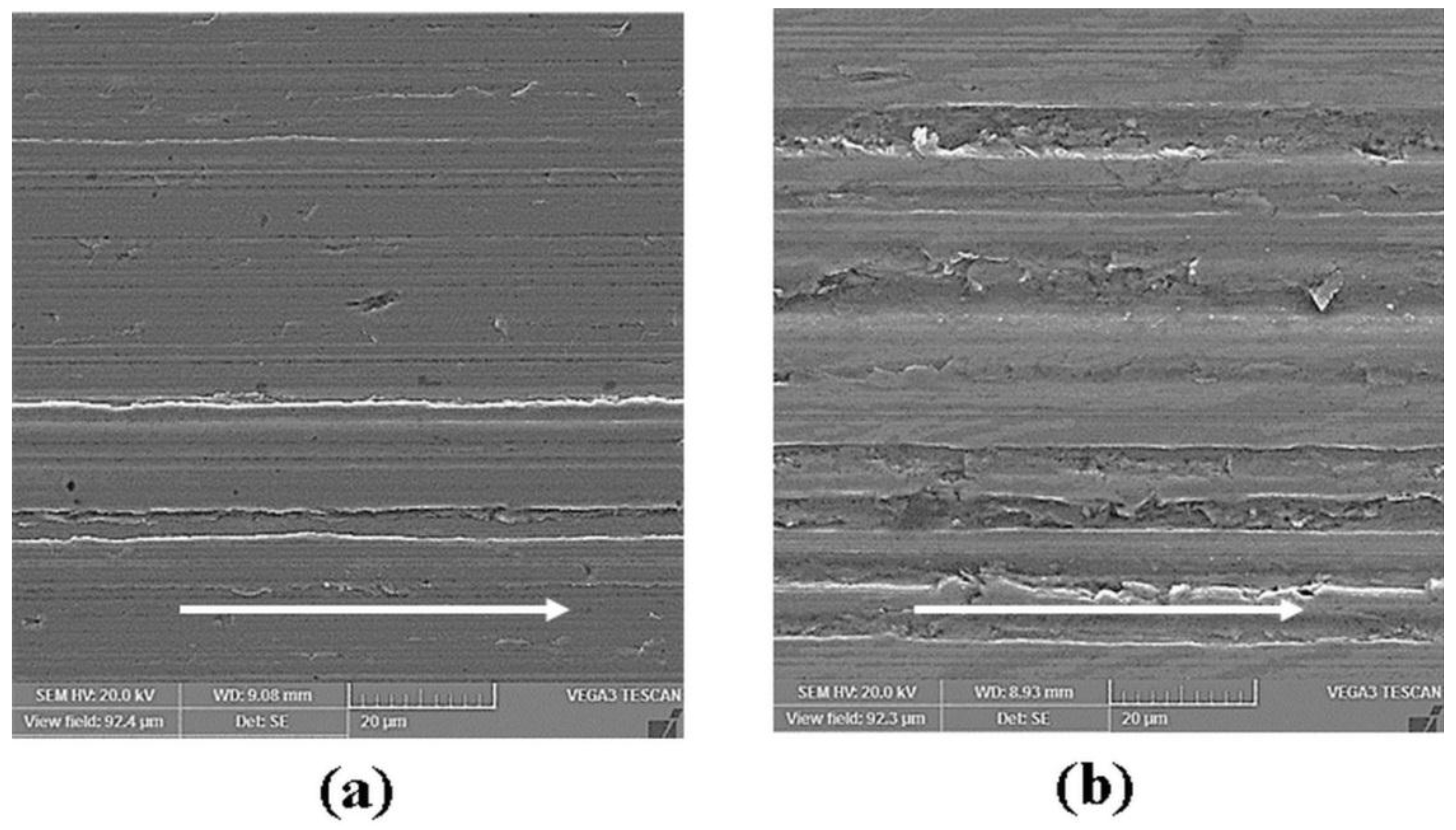
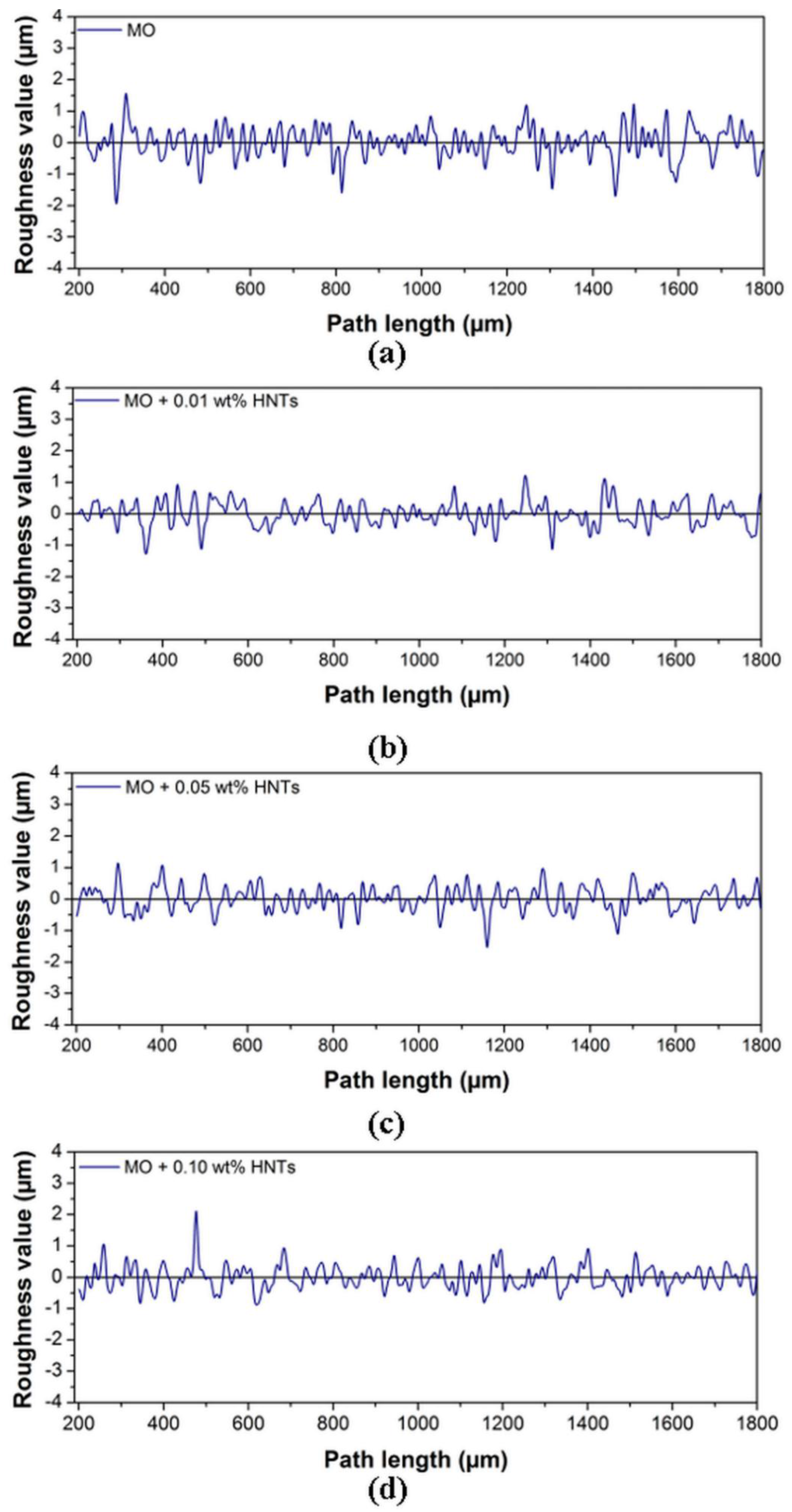
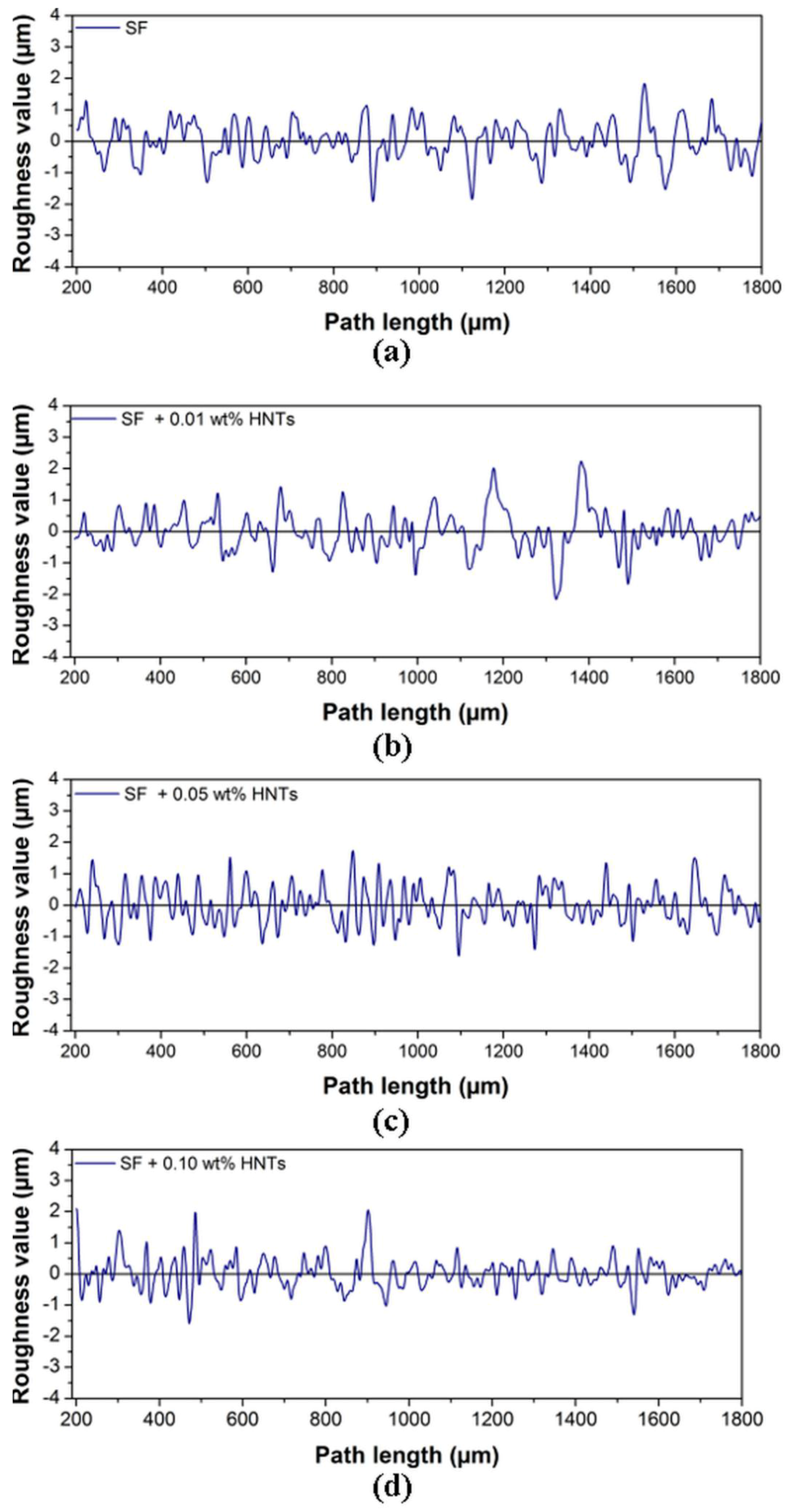
3.2. Surface Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brinksmeier, E.; Meyer, D.; Huesmann-Cordes, A.G.; Herrmann, C. Metalworking fluids—Mechanisms and performance. CIRP Ann. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, M.; Dado, M.; Hnilica, R.; Veverkoná, D. Environmental and health aspects of metalworking fluid use. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Do, T.-V.; Hsu, Q.-C. Optimization of Minimum Quantity Lubricant Conditions and Cutting Parameters in Hard Milling of AISI H13 Steel. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gariani, S.; Shyha, I.; Inam, F.; Huo, D. Evaluation of a Novel Controlled Cutting Fluid Impinging Supply System When Machining Titanium Alloys. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Tsui, W.C.; Liu, T.C. Experimental analysis of tribological properties of lubricating oils with nanoparticle additives. Wear 2007, 262, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gara, L.; Zou, Q. Friction and Wear Characteristics of Water-Based ZnO and Al2O3 Nanofluids. Tribol. Trans. 2012, 55, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.V.; De Leon, O. Applications of nanofluids: Current and future. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Xie, H. A review on nanofluids: Preparation, stability mechanisms, and applications. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thottackkad, M.V.; Rajendrakumar, P.K.; Prabhakaran Nair, K.P. Experimental studies on the tribological behaviour of engine oil (SAE15W40) with the addition of CuO nanoparticles. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2014, 66, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Parás, L.; Taha-Tijerina, J.; García, A.; Maldonado, D.; González, J.A.; Molina, D.; Palacios, E.; Cantú, P. Antiwear and Extreme Pressure Properties of Nanofluids for Industrial Applications. Tribol. Trans. 2014, 57, 1072–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, K.D.; Cantú, D.S.; Segura, A.F.; Araiz, F.; Peña-Parás, L.; Maldonado, D. Application of Nanofluids to improve tool life in machining processes. In Proceedings of the LUBMAT 2014, Manchester, UK, 25–27 June 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mosleh, M.; Ghaderi, M. Deagglomeration of Transfer Film in Metal Contacts Using Nanolubricants. Tribol. Trans. 2012, 55, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Xia, Y.; Shu, Z.; Zhao, X. Conductive grease synthesized using nanometer ATO as an additive. Friction 2015, 3, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.; Lin, J.-W. Tribological Properties of Aluminum Nanoparticles as Additives in an Aqueous Glycerol Solution. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosleh, M.; Atnafu, N.D.; Belk, J.H.; Nobles, O.M. Modification of sheet metal forming fluids with dispersed nanoparticles for improved lubrication. Wear 2009, 267, 1220–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Fu, X.; Xia, Y. Performance and anti-wear mechanism of CaCO3 nanoparticles as a green additive in poly-alpha-olefin. Tribol. Int. 2009, 42, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalin, M.; Kogovšek, J.; Remškar, M. Nanoparticles as novel lubricating additives in a green, physically based lubrication technology for DLC coatings. Wear 2013, 303, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-H.; Ewald, B.; Kwon, P.Y. Effect of Nano-Enhanced Lubricant in Minimum Quantity Lubrication Balling Milling. J. Tribol. 2011, 133, 31803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sia, S.Y.; Sarhan, A.A.D. Morphology investigation of worn bearing surfaces using SiO2 nanolubrication system. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 70, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sia, S.Y.; Bassyony, E.Z.; Sarhan, A.A.D. Development of SiO2 nanolubrication system to be used in sliding bearings. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 71, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, B.; Sarhan, A.A.D.; Sayuti, M. Morphology of surface generated by end milling AL6061-T6 using molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanolubrication in end milling machining. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 66, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Jia, Z.; Jia, D.; Zhou, C. Recent advance in research on halloysite nanotubes-polymer nanocomposite. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1498–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawtani, D.; Agrawal, Y.K. Multifarious applications of halloysite nano tubes: A review. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2012, 30, 282–295. [Google Scholar]
- Pasbakhsh, P.; Churchman, G.J.; Keeling, J.L. Characterisation of properties of various halloysites relevant to their use as nanotubes and microfibre fillers. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 74, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makaremi, M.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Aw, Y.K.; Lee, S.M.; Milioto, S. Effect of Morphology and Size of Halloysite Nanotubes on Functional Pectin Bionanocomposites for Food Packaging Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 17476–17488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Fernández, A.; Peña-Parás, L.; Vidaltamayo, R.; Cué-Sampedro, R.; Mendoza-Martínez, A.; Zomosa-Signoret, V.; Rivas-Estilla, A.; Riojas, P. Synthesization, Characterization, and in Vitro Evaluation of Cytotoxicity of Biomaterials Based on Halloysite Nanotubes. Materials 2014, 7, 7770–7780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lvov, Y.; Abdullayev, E. Functional polymer—Clay nanotube composites with sustained release of chemical agents. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1690–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Noto, R.; Riela, S. Covalently modified halloysite clay nanotubes: Synthesis, properties, biological and medical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolino, V.; Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F. Biopolymer-Targeted Adsorption onto Halloysite Nanotubes in Aqueous Media. Langmuir 2017, 33, 3317–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallaro, G.; Danilushkina, A.; Evtugyn, V.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F.; Rozhina, E.; Fakhrullin, R. Halloysite Nanotubes: Controlled Access and Release by Smart Gates. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F. Hydrophobically Modified Halloysite Nanotubes as Reverse Micelles for Water-in-Oil Emulsion. Langmuir 2015, 31, 7472–7478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F.; Sanzillo, V. Modified halloysite nanotubes: Nanoarchitectures for enhancing the capture of oils from vapor and liquid phases. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña-Parás, L.; Maldonado-Cortés, D.; García, P.; Irigoyen, M.; Taha-Tijerina, J.; Guerra, J. Tribological performance of halloysite clay nanotubes as green lubricant additives. Wear 2017, 376–377, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecouvet, B.; Horion, J.; D’haese, C.; Bailly, C.; Nysten, B.; D’Haese, C.; Bailly, C.; Nysten, B. Elastic modulus of halloysite nanotubes. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 105704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahouij, I.; Dassenoy, F.; Vacher, B.; Martin, J.-M. Real Time TEM Imaging of Compression and Shear of Single Fullerene-Like MoS2 Nanoparticle. Tribol. Lett. 2012, 45, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaednia, H.; Jackson, R.L. The Effect of Nanoparticles on the Real Area of Contact, Friction, and Wear. J. Tribol. 2013, 135, 41603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
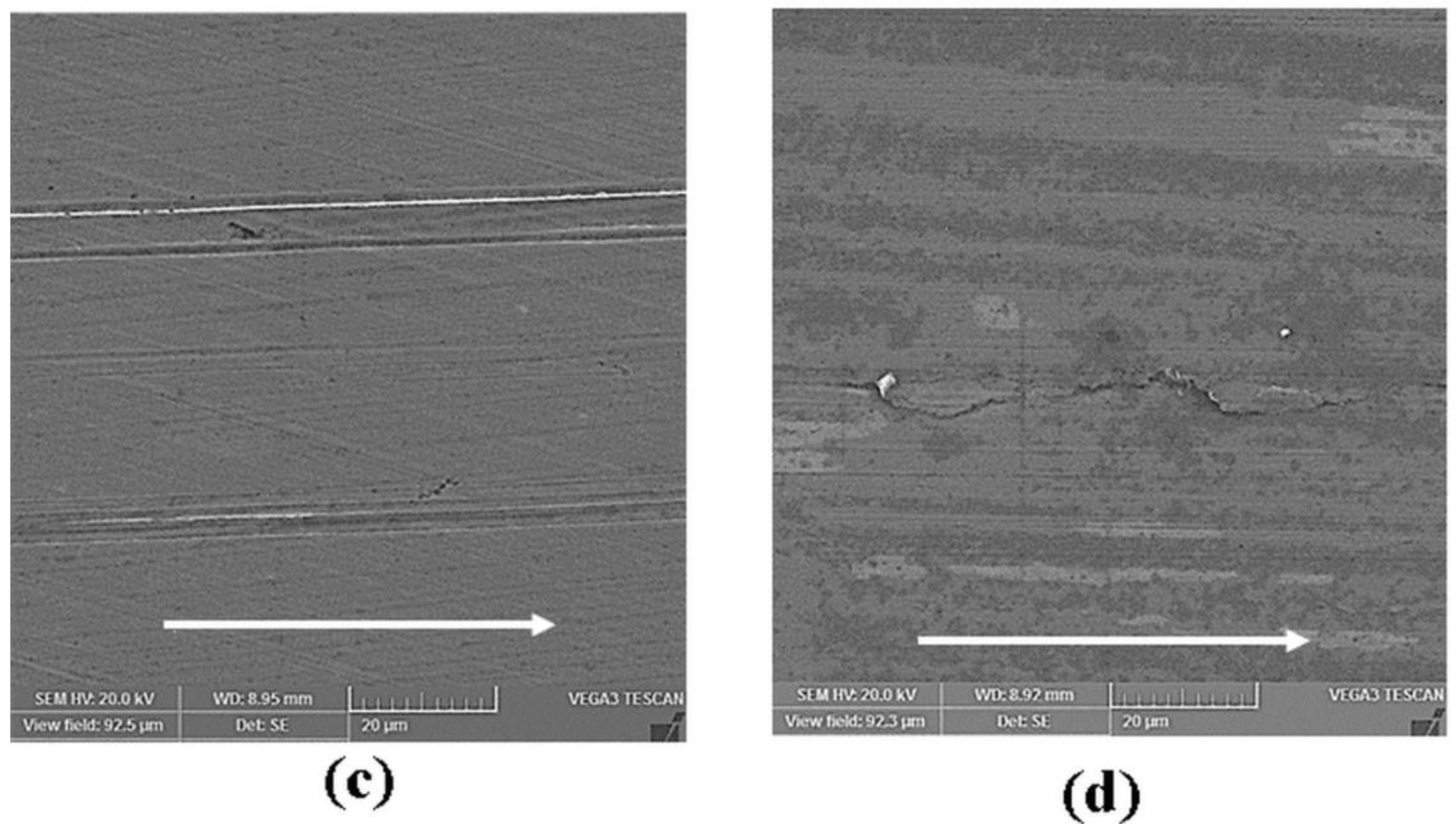
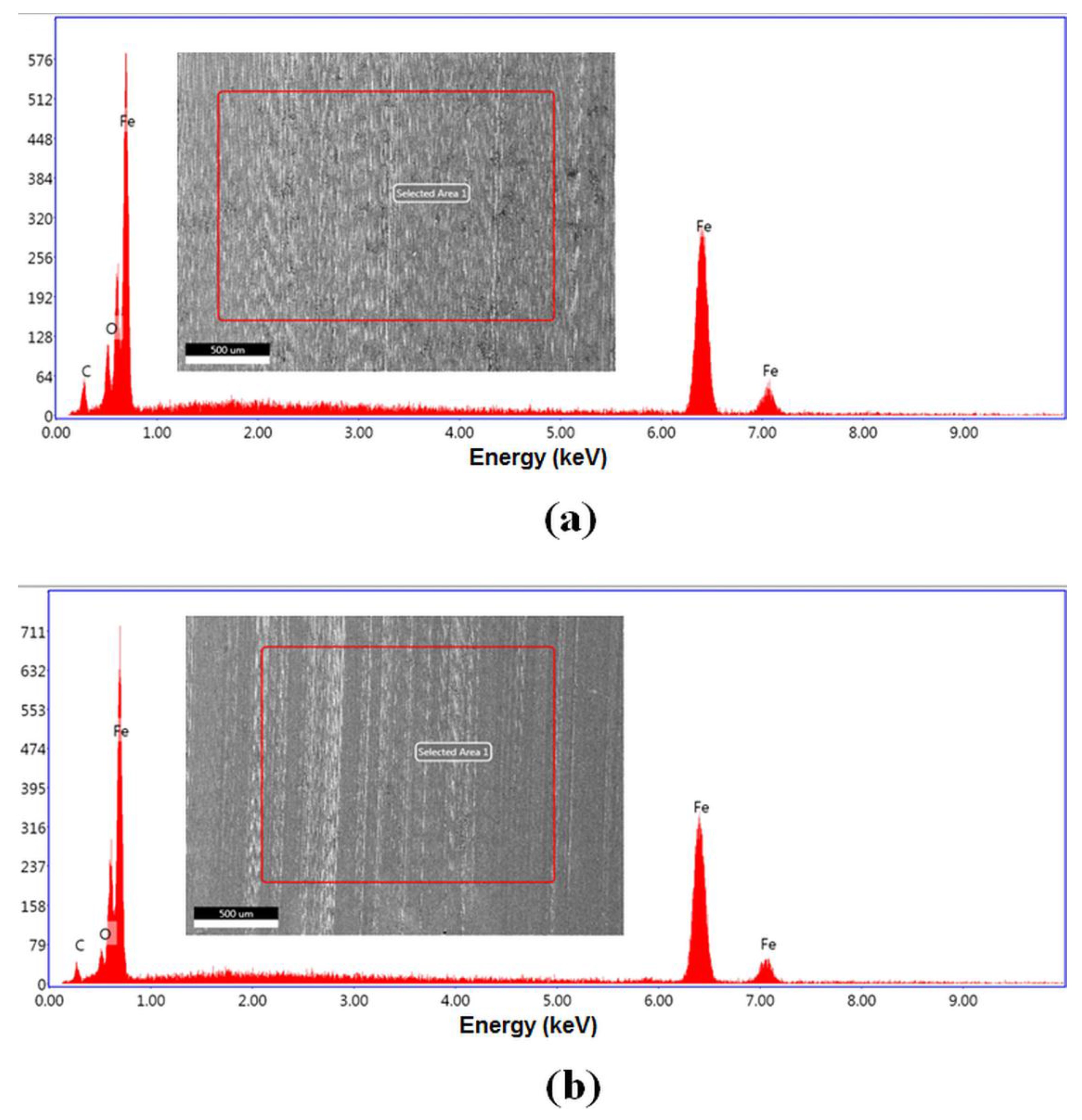
| Materials | Properties | |
|---|---|---|
| Metalworking fluids | Density (15 °C) | Viscosity (40 °C) |
| Semi-synthetic fluid (SF) | 0.970 g/cm3 | 75.0 mm2/s |
| Mineral oil (MO) | 0.871 g/cm3 | 33.2 mm2/s |
| Nanoparticle | ||
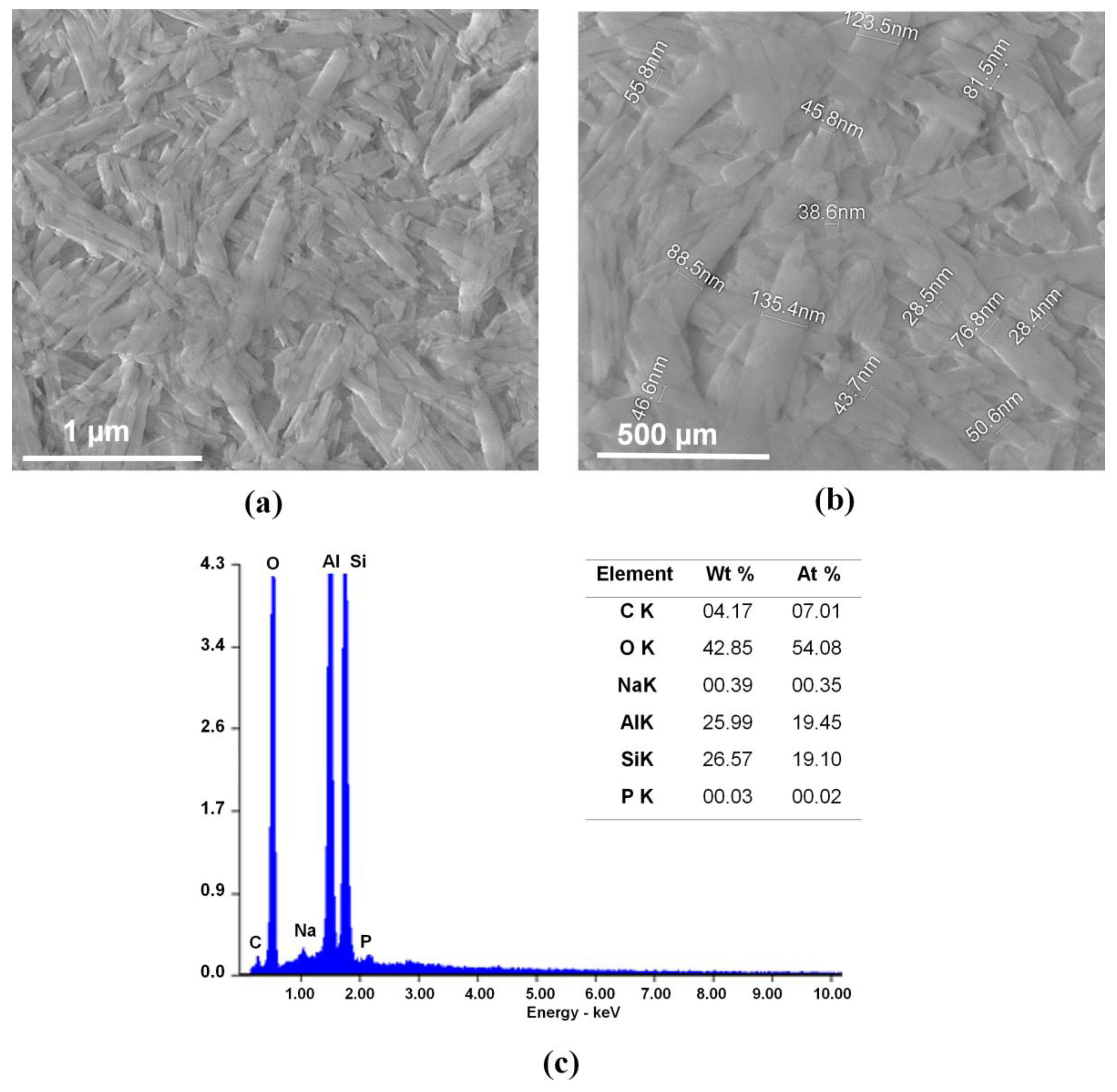
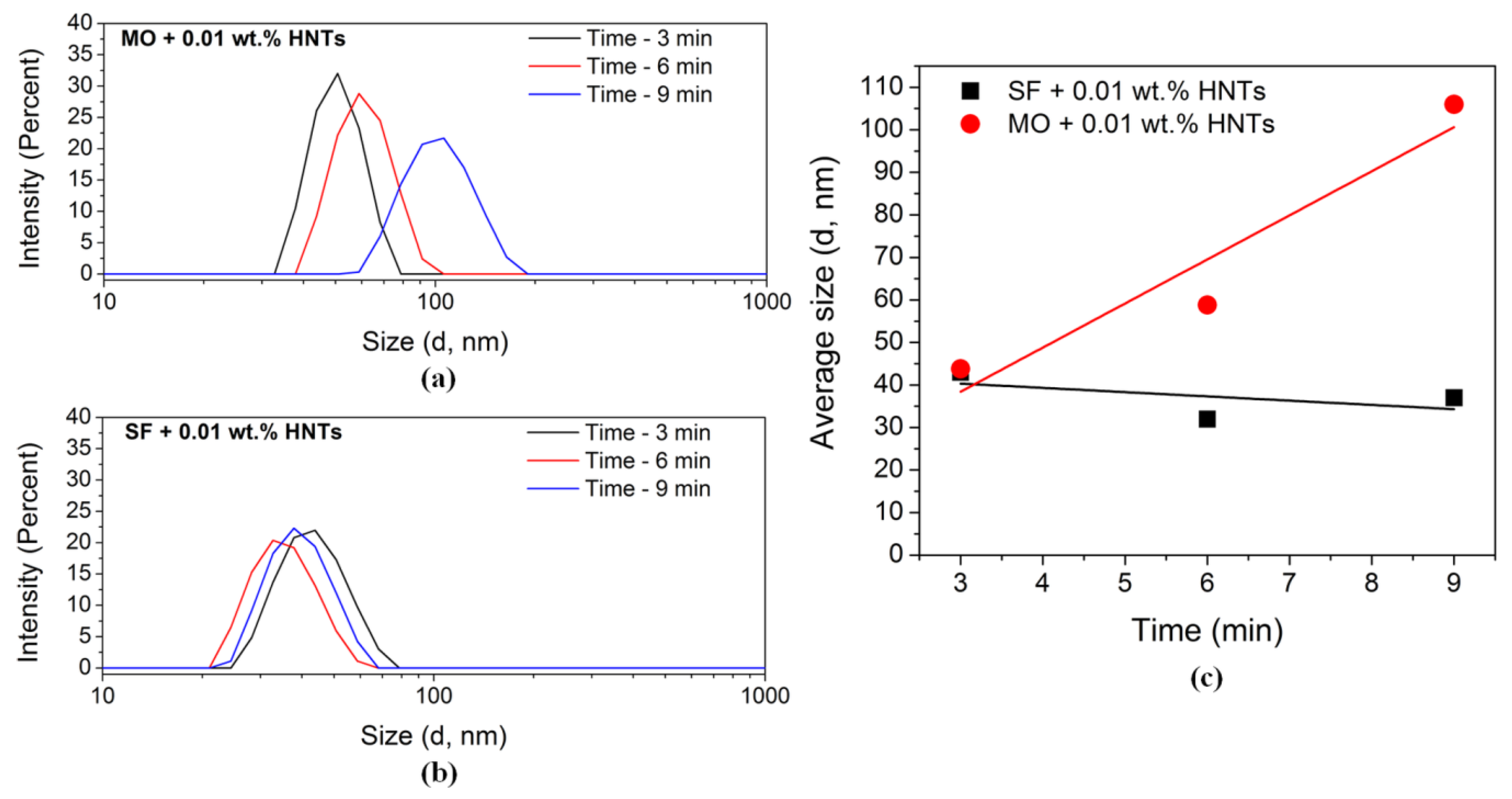
| Halloysite clay nanotubes (HNTs) | Morphology: tubular; diameter: 28.5–135 nm × length: 1–3 μm | |
| Test blocks | ||
| AISI 1018 | Dimensions: 6.35 × 10 × 15.75 mm, 71 HRB, Ra = 0.45 μm Chemical composition: 0.14–0.20% C, 0.60–0.90% Mn, <0.04% P, 0.05% S, Fe Balance | |
| Test rings | ||
| AISI D2 | Diameter: 35 mm, 58 HRC, Ra = 0.65 μm Chemical composition: 1.5511.5% Cr, 0.90% Mo, 0.80% V, Fe Balance | |
| Average Roughness, Ra (µm) | Root Mean Square, Rq (µm) | Mean Roughness Depth, Rz (µm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MO | 0.53 | 0.80 | 4.47 |
| MO + 0.01 wt. % | 0.44 | 0.58 | 2.92 |
| MO + 0.05 wt. % | 0.37 | 0.52 | 3.15 |
| MO + 0.10 wt. % | 0.34 | 0.46 | 2.75 |
| SF | 0.53 | 0.68 | 3.29 |
| SF + 0.01 wt. % | 0.47 | 0.63 | 2.83 |
| SF + 0.05 wt. % | 0.42 | 0.61 | 2.94 |
| SF + 0.10 wt. % | 0.35 | 0.46 | 2.48 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peña-Parás, L.; Sánchez-Fernández, J.A.; Martínez, C.R.; Ontiveros, J.A.; Saldívar, K.I.; Urbina, L.M.; Arias, M.J.; García-Pineda, P.; Castaños, B. Evaluation of Anti-Wear Properties of Metalworking Fluids Enhanced with Halloysite Nanotubes. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7101019
Peña-Parás L, Sánchez-Fernández JA, Martínez CR, Ontiveros JA, Saldívar KI, Urbina LM, Arias MJ, García-Pineda P, Castaños B. Evaluation of Anti-Wear Properties of Metalworking Fluids Enhanced with Halloysite Nanotubes. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(10):1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7101019
Chicago/Turabian StylePeña-Parás, Laura, José Antonio Sánchez-Fernández, Carlos Rafael Martínez, José Abraham Ontiveros, Karla Itzel Saldívar, Luis Manuel Urbina, Moisés Jair Arias, Patricio García-Pineda, and Brenda Castaños. 2017. "Evaluation of Anti-Wear Properties of Metalworking Fluids Enhanced with Halloysite Nanotubes" Applied Sciences 7, no. 10: 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7101019
APA StylePeña-Parás, L., Sánchez-Fernández, J. A., Martínez, C. R., Ontiveros, J. A., Saldívar, K. I., Urbina, L. M., Arias, M. J., García-Pineda, P., & Castaños, B. (2017). Evaluation of Anti-Wear Properties of Metalworking Fluids Enhanced with Halloysite Nanotubes. Applied Sciences, 7(10), 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7101019




