Effect of the Impact of Chemical and Environmental Factors on the Durability of the High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Geogrid in a Sanitary Landfill
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
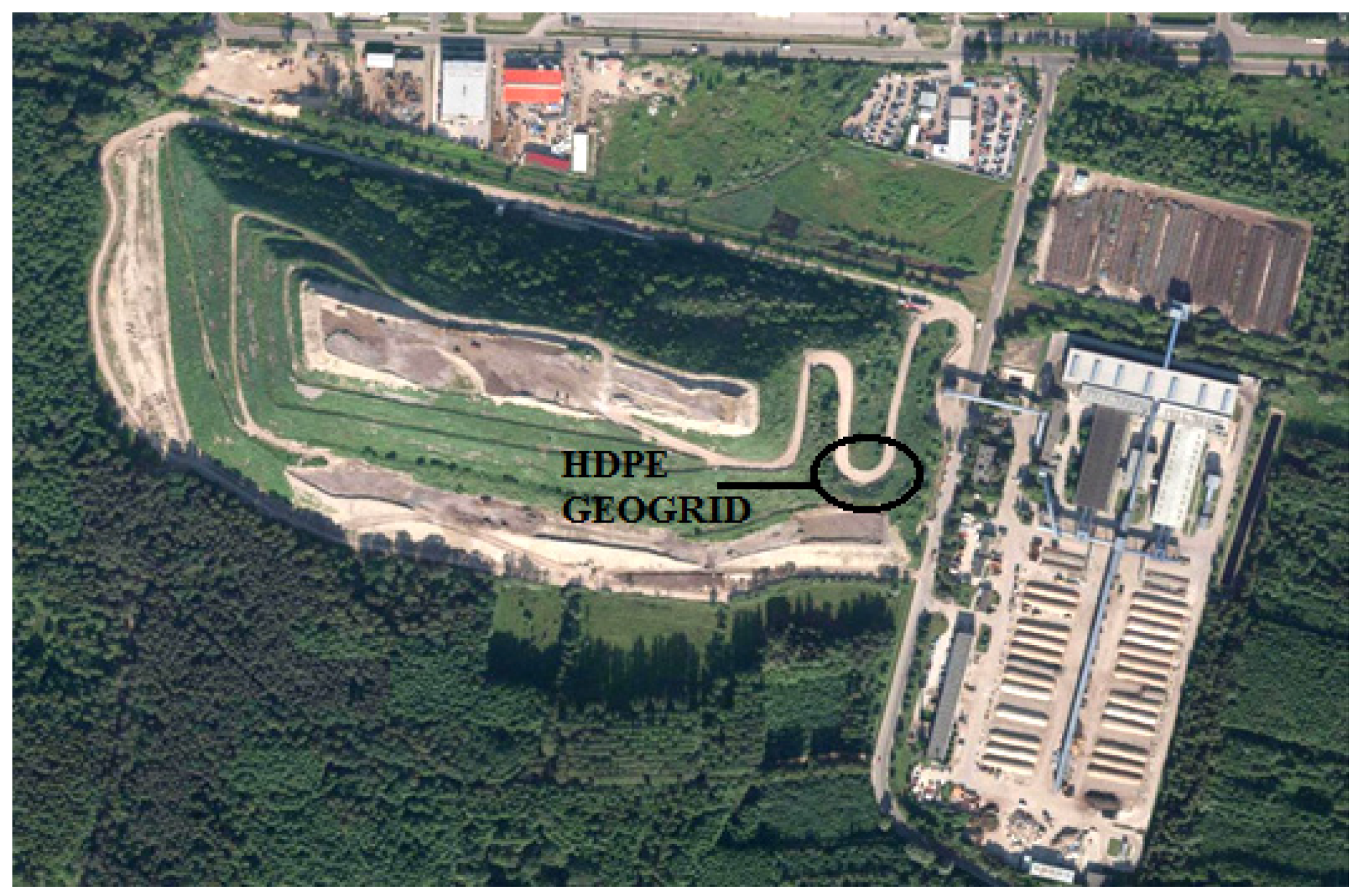
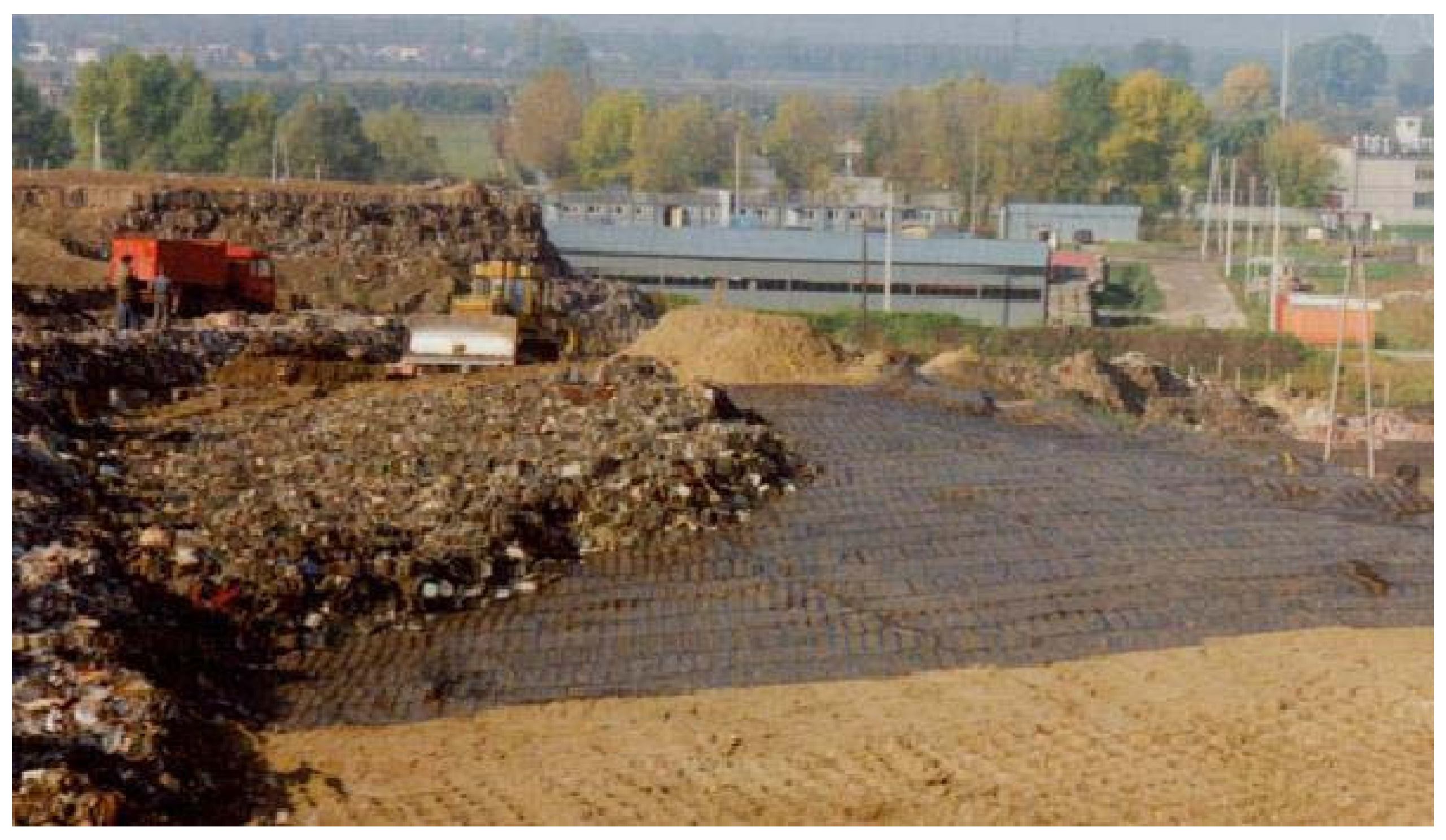
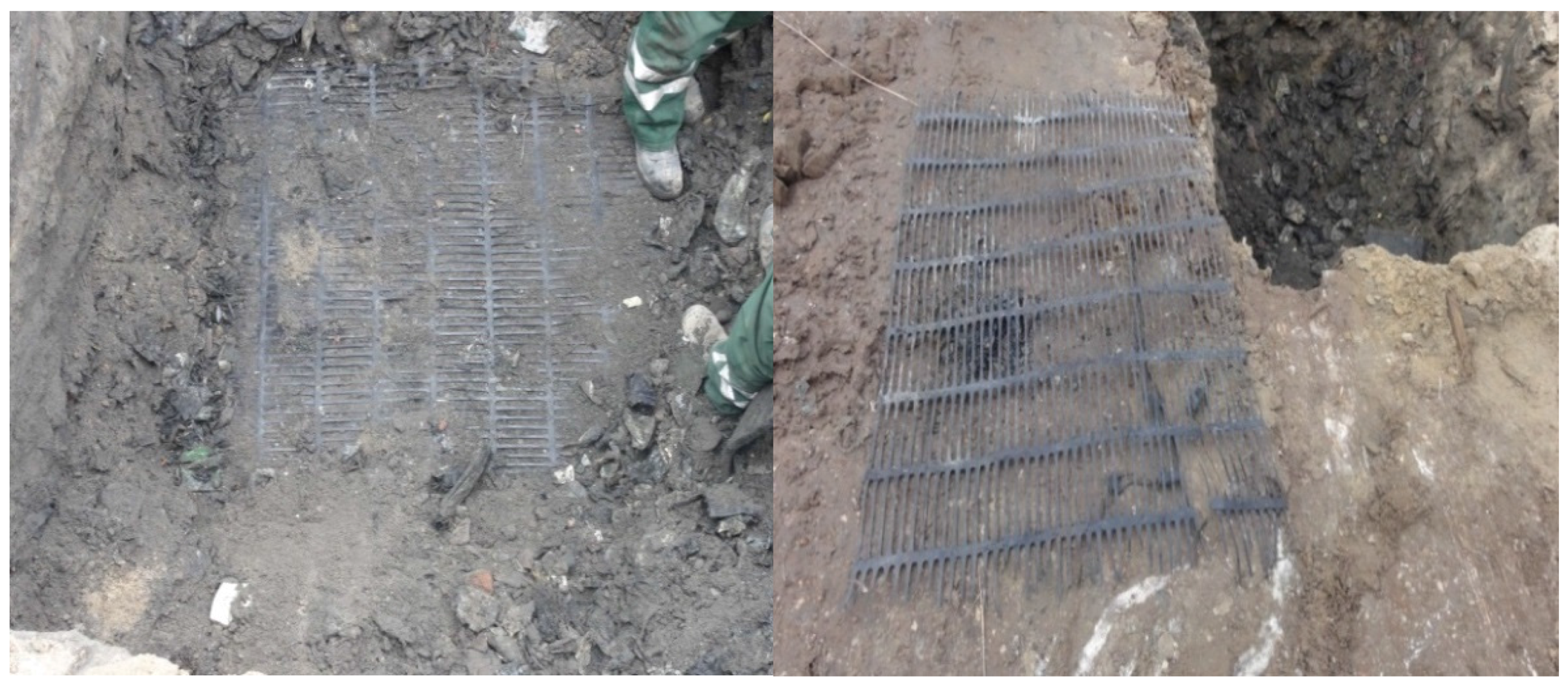
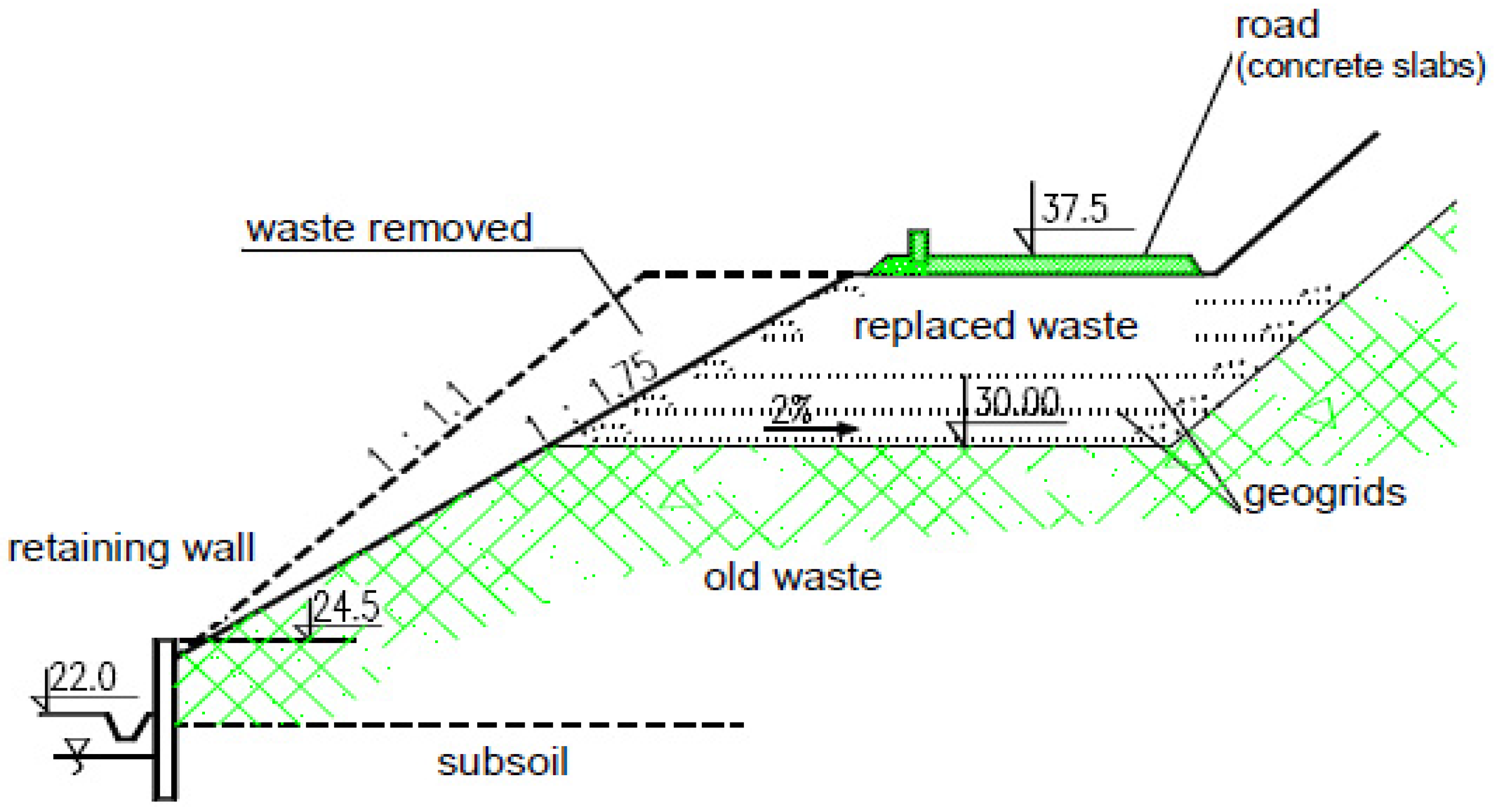
2.1. Location and Description of the Study Site
2.2. Materials
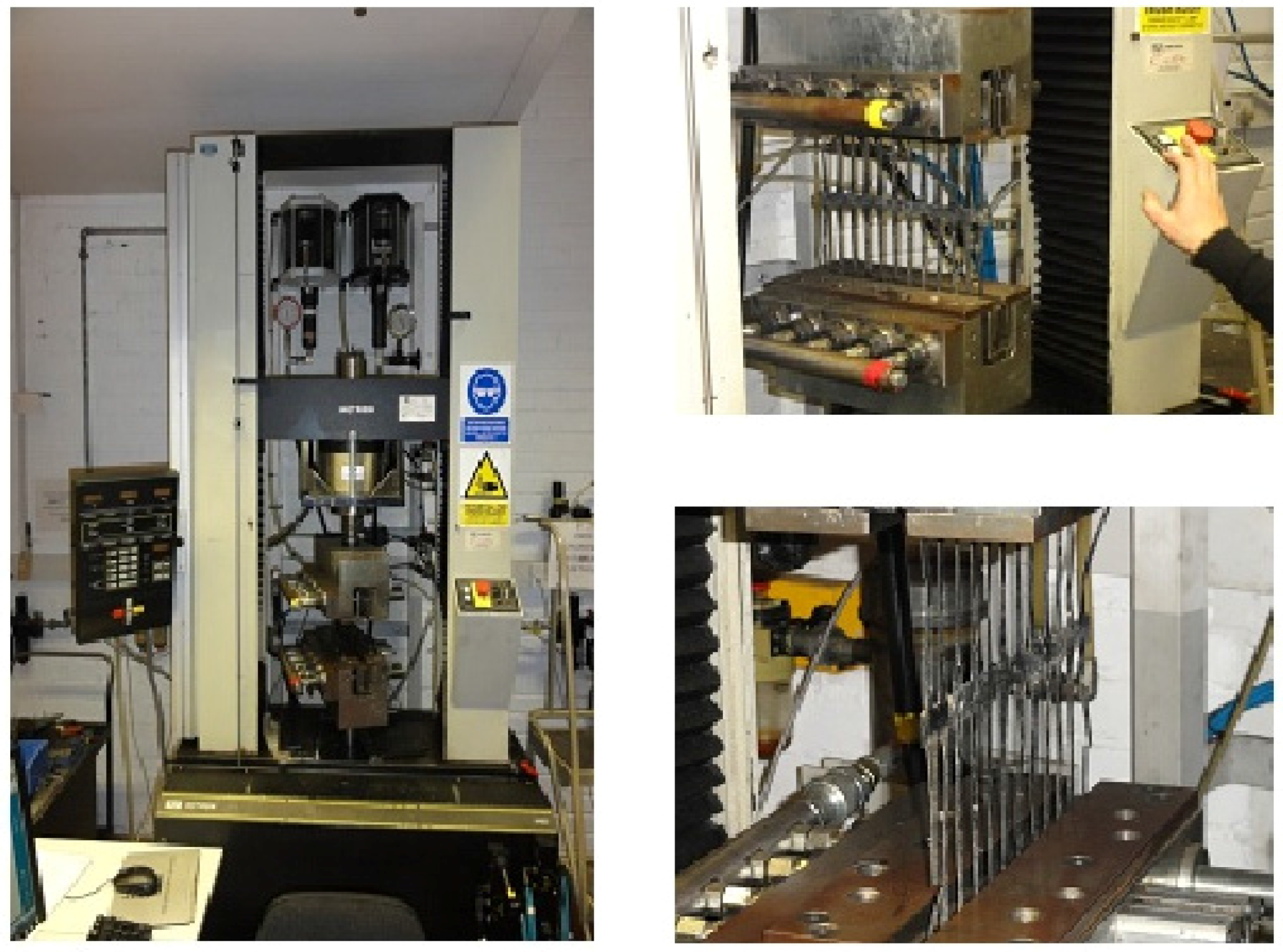
2.3. Tensile Strength Tests
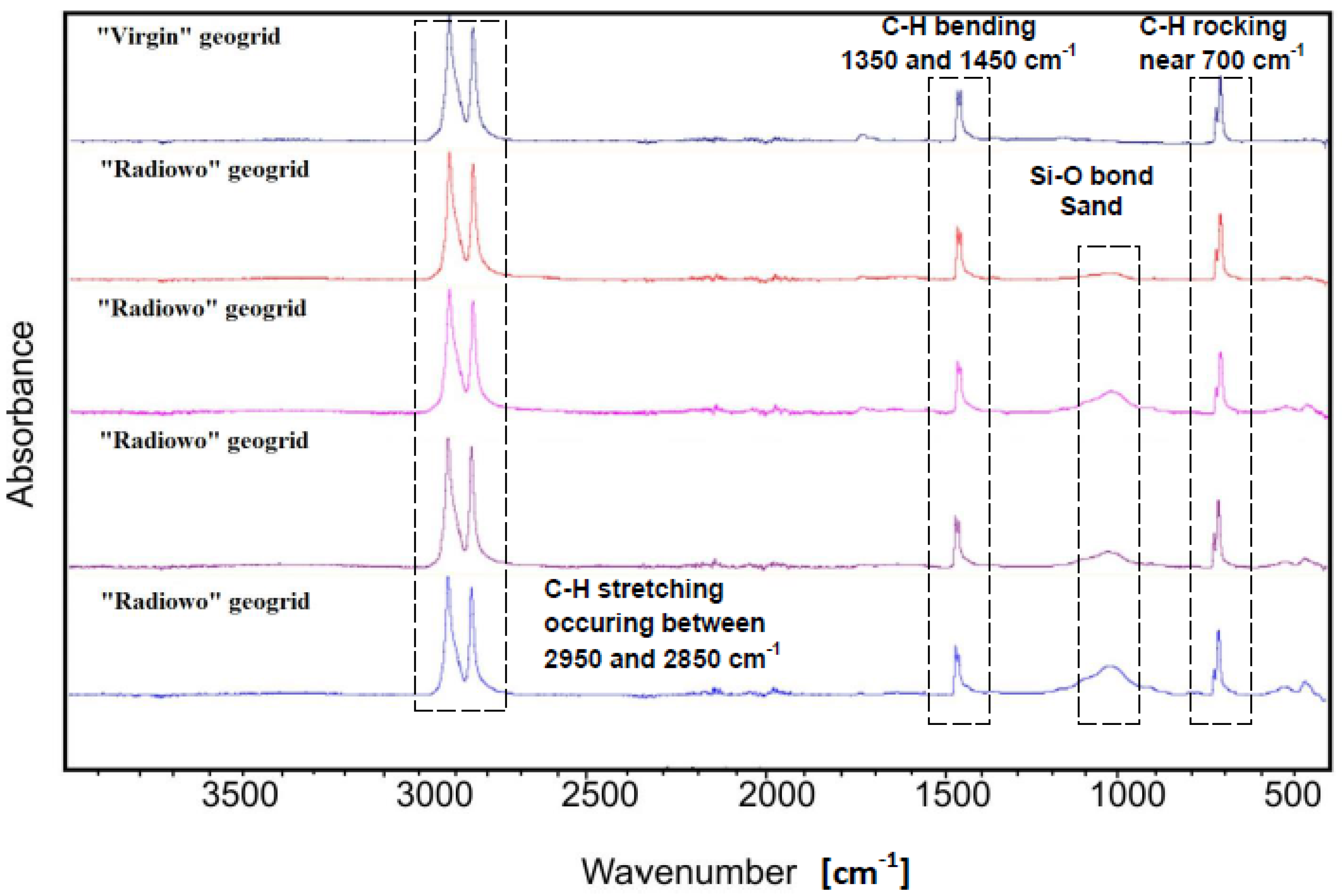
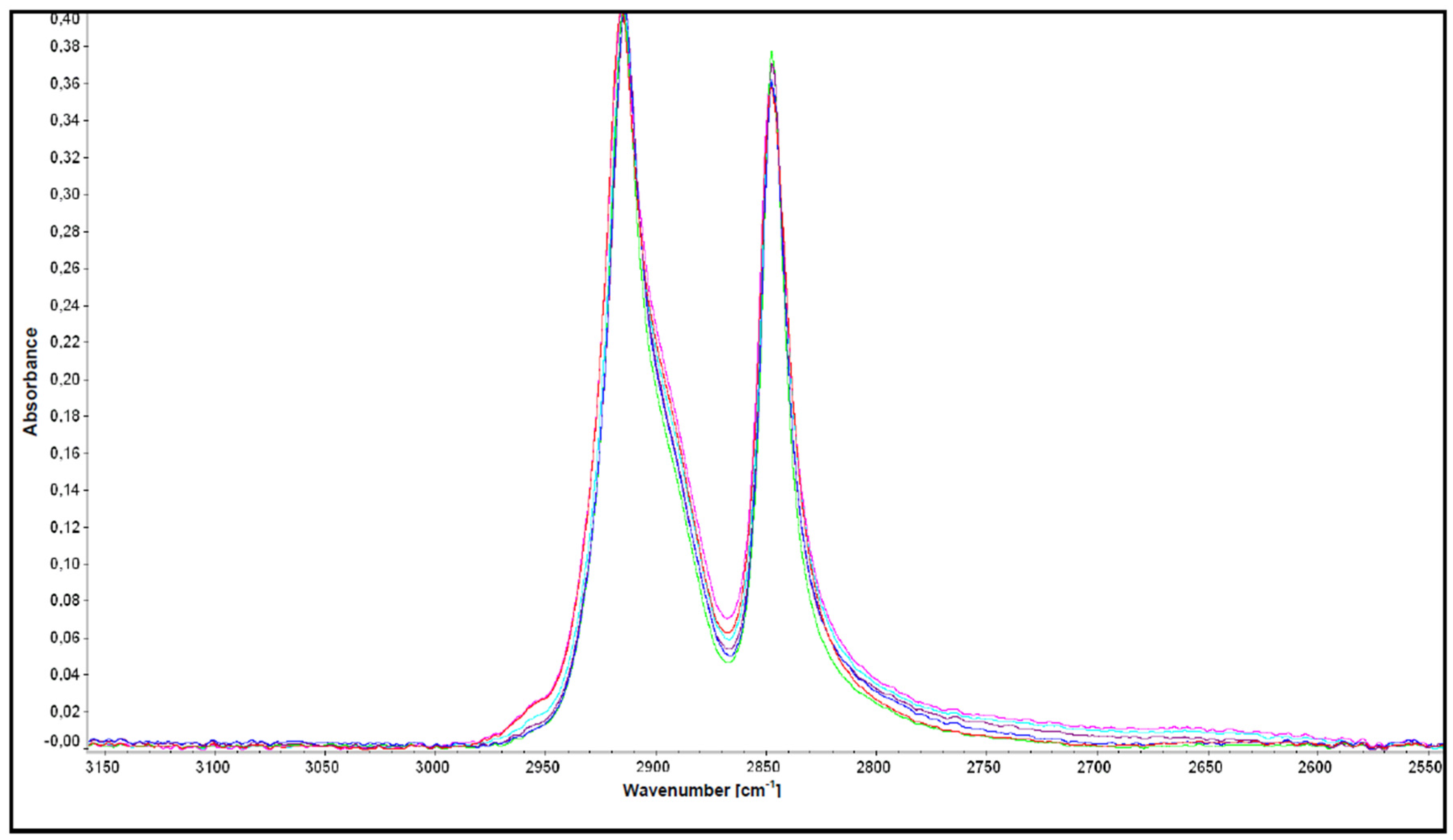
2.4. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy
2.5. Characteristics of Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.6. Electron Microscopy Analysis
3. Discussion
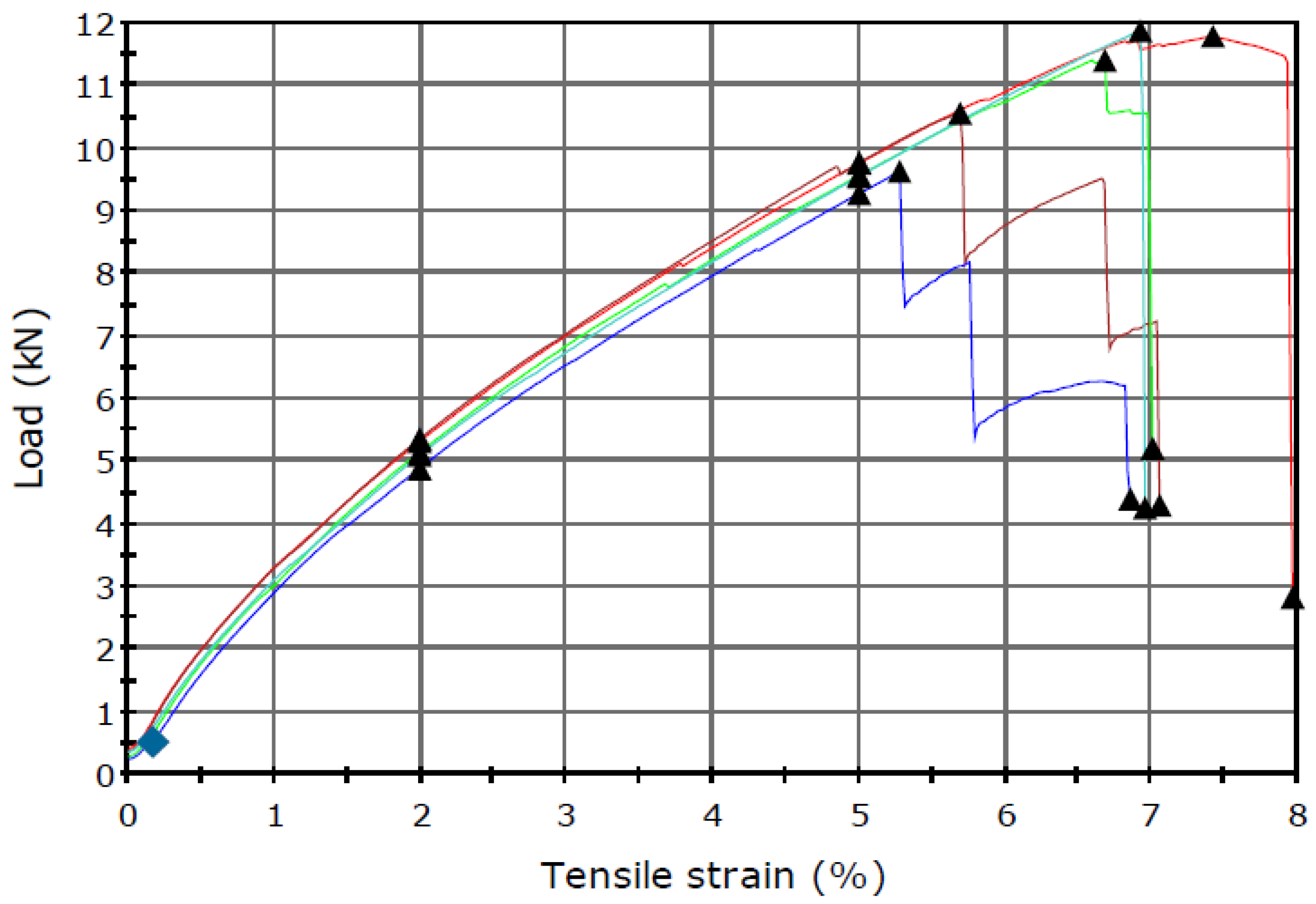
3.1. Tensile Strength Tests
3.2. FT-IR Spectroscopy
3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry Results (DSC)
3.4. Electron Microscopy Analysis
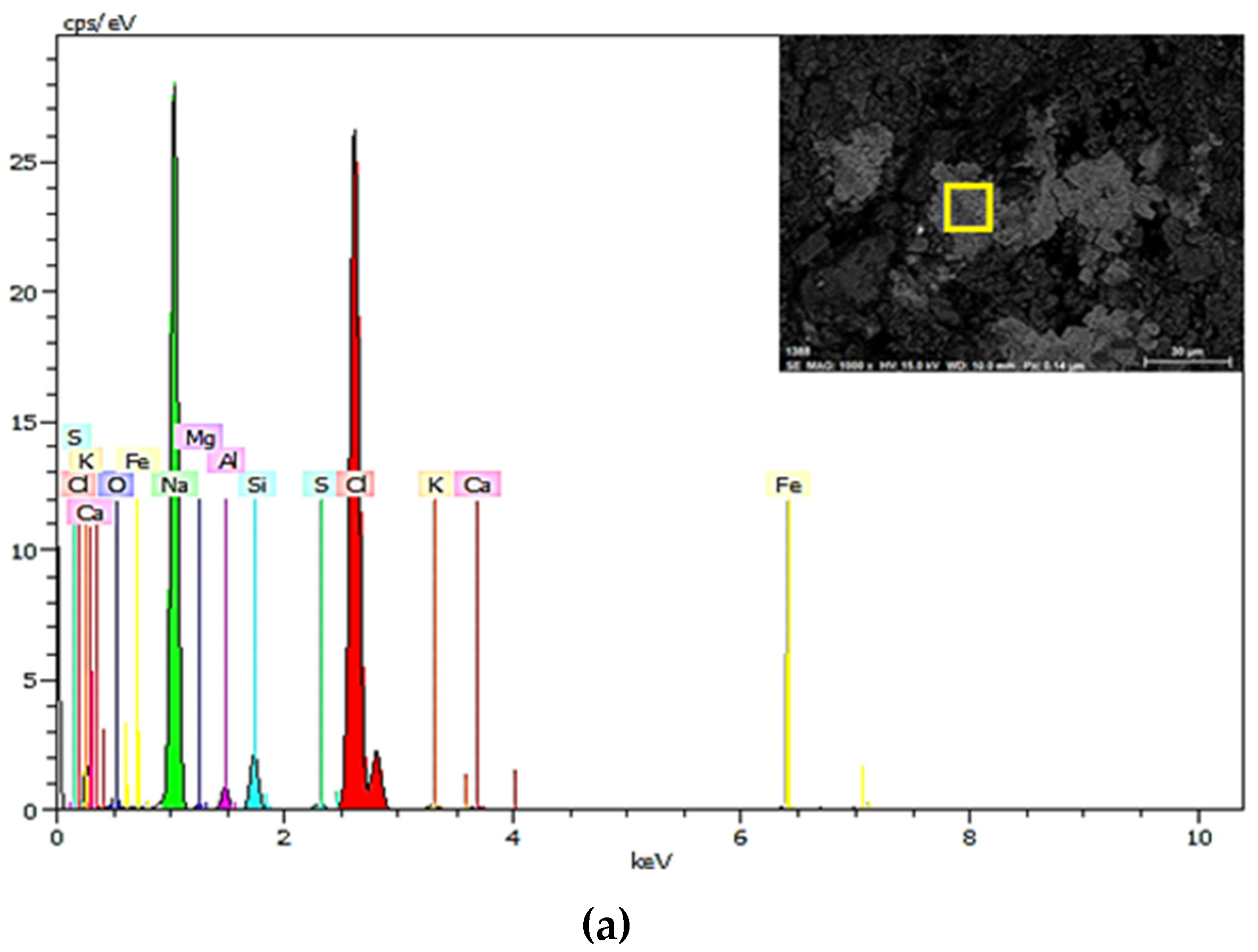
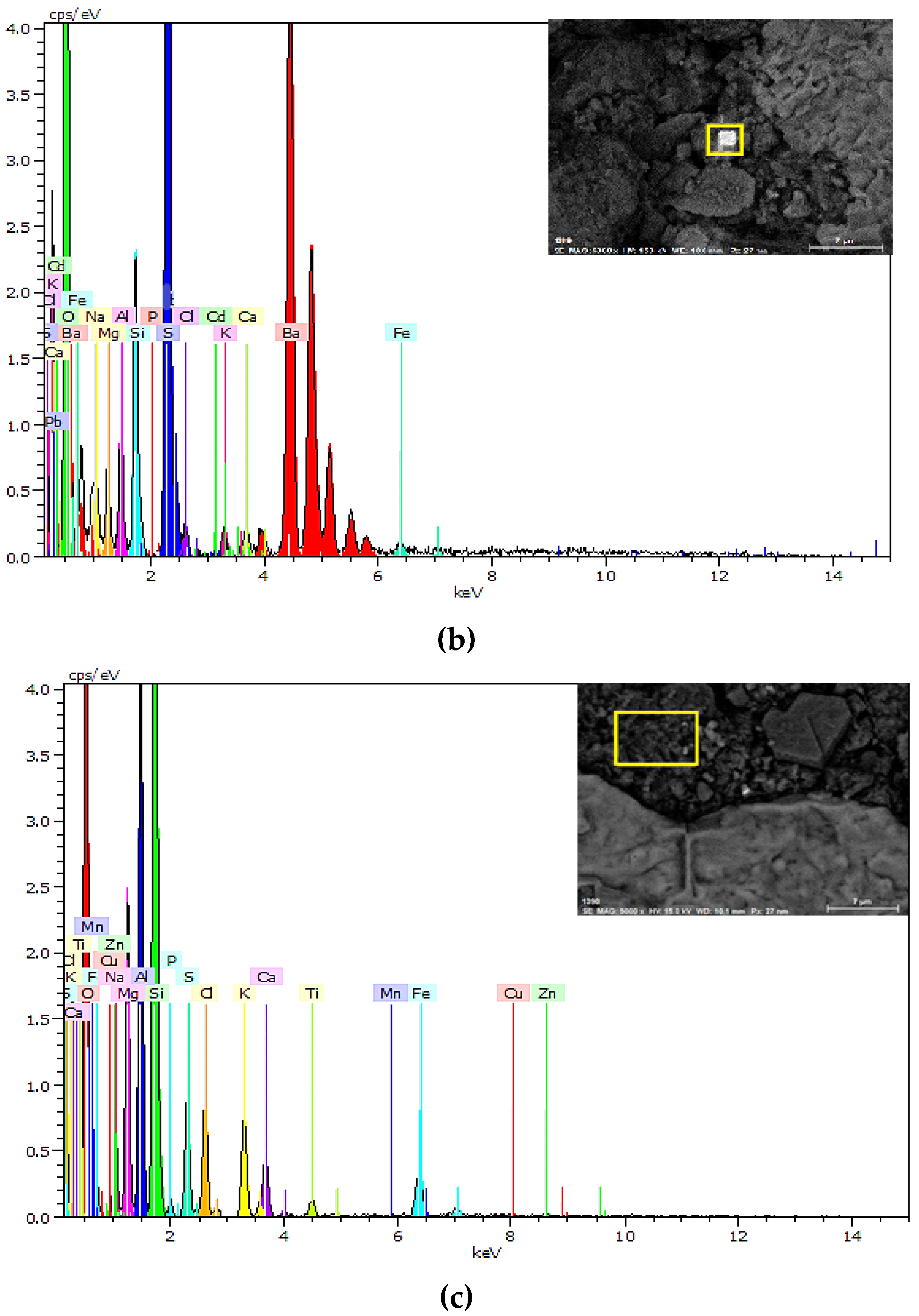
3.4.1. SEM-EDS Observations of Geogrids
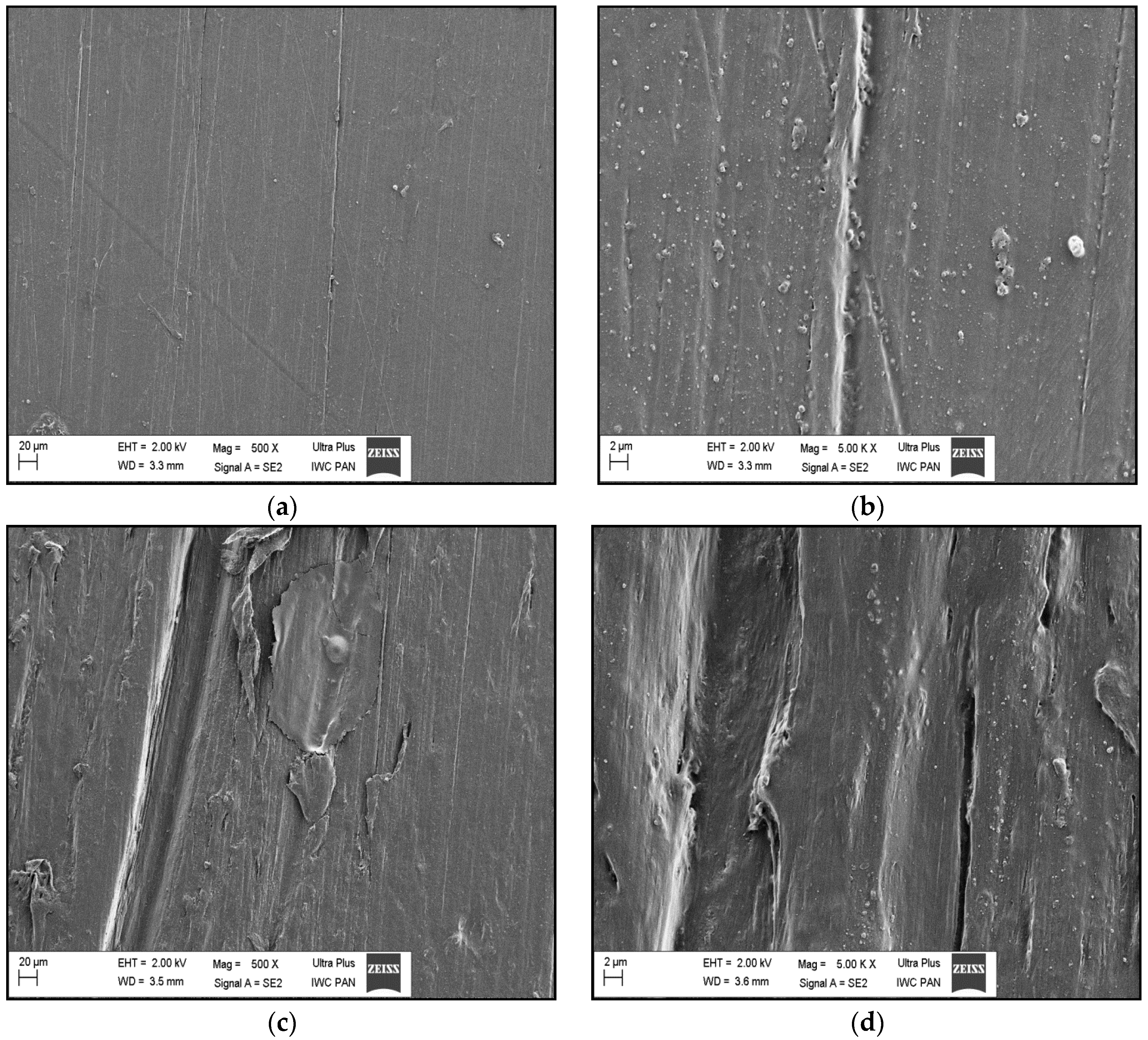
3.4.2. SEM Observations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koerner, R.M. Designing with Geosynthetics, 5th ed.; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hsuan, Y.G.; Li, M. Temperature and pressure effects on the oxidation of high-density polyethylene geogrids. Geotext. Geomembr. 2005, 23, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Ha, S. Effects of Particle Size on the Shear Behavior of Coarse Grained Soils Reinforced with Geogrid. Materials 2014, 7, 963–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, S.L. Geogrid Reinforcement Base Courses for Flexible Pavements for Light Aircraft; Technical Report GL-93-6; U.S. Army Engineers Water-Ways Experiment Station: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Kawalec, J. Stabilisation of the subsoil with geogrids (in Polish). Inżynieria Morska Geotech. 2010, 4, 522–530. [Google Scholar]
- Moraci, N.; Cardile, G. Influence of cyclic tensile loading on pullout resistance of geogrids embedded in a compacted granular soil. Geotext. Geomembr. 2009, 27, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.L.; Li, F.L.; Tan, Y.; Kongkitkul, W. Effects of Loading Rate on Viscoplastic Properties of Polymer Geosynthetics and Its Constitutive Modeling. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2010, 50, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongkitkul, W.; Hirakawa, D.; Tatsuoka, F.; Uchimura, T. Viscous deformation of geosynthetic reinforcement under cyclic loading conditions and its model simulation. Geosinthetic Int. 2004, 11, 73–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraci, N.; Cardile, G. Deformative behaviour of different geogrids embedded in a granular soil under monotonic and cyclic pullout loads. Geotext. Geomembr. 2012, 32, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathurst, R.J.; Cai, Z. In-isolation cyclic load-extensionbehavior of two geogrids. Geosinthetic Int. 1994, 1, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki, A.; Kazimierowicz-Frankowska, K. Influence of strain rate on the load-strain characteristics of geosynthetics. Geosinthetic Int. 2002, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmeira, E.M. Soil geosynthetic interaction. Modeling and analysis. Geotext. Geomembr. 2009, 27, 368–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geosynthetics—Guidelines for the Assessment of Durability; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; ISO/TS 13434:2008.
- Recommendations for Design and Analysis of Earth Structures Using Geosynthetic Reinforcements; Ernst & Sohn Verlag, EBGEO: Berlin, Germany, 2011.
- Code of Practice for Strengthened/Reinforced Soils and Other Fills; British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2010; BS8006-1:2010.
- Geogrids for Reinforced Soil Retaining Wall and Bridge Abutment System; British Board Agreement Technical Approval: Blackburn, UK, 2010; BBA 99/R109.
- Hufenus, R.; Rüegger, R.; Flum, D.; Sterba, I.J. Strength reduction factors due to installation damage of reinforcing geosynthetics. Geotext. Geomembr. 2005, 23, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsuan, Y.G.; Koerner, R.M. Antioxidant depletion lifetime in high density polyethylene geomembranes. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. ASCE 1998, 124, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, R.K.; Sangam, H. Durability of HDPE geomembranes. Geotext. Geomembr. 2002, 20, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, J.R.; Almeida, P.J.; Lopes, M.L. Resistance of high-density polyethylene geonets against chemical ageing. In Proceedings of the 6th International Congress on Environmental Geotechnics, New Delhi, India, 7–12 November 2010.
- Rowe, K.; Islam, M.Z.; Hsuan, Y.G. Leachate chemical composition effects on OIT depletion in an HDPE geomembrane. Geosinthetics Int. 2008, 15, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, D.; Blond, E.; Mlynarek, J. Geosynthetics durability: A polymer chemistry. In Proceedings of the 57th Canadian Geotechnical Conference, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 24–26 October 2004.
- Petermann, J.; Miles, M.; Gleiter, H. Growth of polymer crystals during annealing. J. Macromol. Sci. Phys. 1976, 12, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, A.; Netravali, A.N.; O′Rourke, T.D. Chemical aging effect on the physico–mechanical properties of polyester and polypropylene geotextiles. Geotext. Geomembr. 1994, 13, 591–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerner, R.M.; Hsuan, Y.D.; Lord, A.E. Remaining Technical Barriers to Obtain General Acceptance of Geosynthetics. In ASCE Geotechnical Special Publication; The American Society of Civil Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Elias, V.; Kenneth, P.E.; Fishman, L.; Christopher, B.R.; Berg, R.R. Corrosion/Degradation of Soil Reinforcements for Mechanically Stabilized Earth Walls and Reinforced Soil Slopes; U.S. Department of Transportation Federal Highway Administration: Woodbury, MN, USA, 2009; Publication No. FHWA-NHI-09-087.
- Leflaive, E. Durability of geotextiles: The French experience. Geotext. Geomembr. 1988, 7, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouig, J.; Blivet, J.C.; Pasquet, P. Earth reinforced fill with synthetic fabric. In Proceedings of the International Conference on use of fabrics in Geotechniques, Paris, France, 20–22 April 1977.
- Bell, J.R.; Steward, J.E. Construction and observations of fabric soil walls. In Proceedings of the International Conference on use of fabrics in Geotechniques, Paris, France, 20–22 April 1977.
- Bell, J.R.; Szymoniak, T.; Thommen, G.R. Construction of a steep sided geogrid retaining wall for an Oregon Coastal Highway. In Proceedings of the Polymer Grid Reinforcement Conference, London, UK, 22–23 March 1984.
- Koda, E. Stability conditions improvement of the old sanitary landfills. In Proceedings of the 3th Internatonal Congress on Environment Geotechnics, Lisboa, Portugal, 7–11 September 1998.
- Koda, E.; Osiński, P. Application of alternative methods of slope stability improvements on landfills. In Proceedings of the XVI European Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering “Geotechnical Engineering for Infrastructure and Development”, Edinburgh, UK, 13–17 September 2015.
- Koda, E.; Szymański, A.; Wolski, W. Field and laboratory experience with the use of strip drains in organic soils. Can. Geotech. J. 1993, 30, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koda, E. Anthropogenic waste products utilization for old landfills rehabilitation. Ann. Wars. Univ. Life Sci. Land Reclam. 2012, 44, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tensar. The Long-Term Performance of Tensar Geogrids; Tensar/Nelton LTD: Blackburn, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Geosynthetics—Wide-Width Tensile Test; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; ISO 10319:2010.
- Pinter, G.; Haager, M.; Wolf, C.; Lang, R.W. Thermo-oxidative degradation during creep crack growth of PE-HD grades as assessed by FT-IR spectroscopy. Macromol. Symp. 2004, 217, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, R.K.; Rimal, S.; Sangam, H. Ageing of HDPE geomembrane exposed to air, water and leachate at different temperatures. Geotext. Geomembr. 2009, 27, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Hay, J.N. The measurement of the crystallinity of polymers by DSC. Polymer 2002, 43, 3873–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, B. Reversible crystallization and the rigid–amorphous phase in semicrystalline macromolecules. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2003, 28, 3383–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Geometry | |
| Aperture size (mm × mm) | 16 × 140 |
| Rib thickness (mm) | 0.95 |
| CMD bar thickness (mm) | 2.5 ÷ 2.7 |
| Rib width (mm) | 6.7 |
| CMD bar width (mm) | 16 |
| Weight (g/m2) | 500 |
| Mechanical Properties | |
| Tensile strength at 2% strain (kN/m) | 19.0 |
| Tensile strength at 5% strain (kN/m) | 33.5 |
| Peak tensile strength (kN/m) | 55 |
| Yield point elongation (%) | 11.2 |
| Sample Number | Sample before Installing (Virgin) (Declared Strength 55 kN/m) | Samples 20 Years after Installation (Aged) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Tensile Strength (kN/m) | Mean Strain at Maximum Load (%) | Mean Tensile Strength (kN/m) | Mean Strain at Maximum Load (%) | |
| 1 | 60.77 | 9.55 | 52.18 | 7.41 |
| 2 | 61.68 | 9.80 | 46.74 | 5.69 |
| 3 | 60.79 | 9.32 | 50.48 | 6.68 |
| 4 | 61.45 | 10.07 | 52.55 | 6.92 |
| 5 | 60.28 | 9.66 | 42.63 | 5.28 |
| Mean | 60.99 | 9.68 | 48.92 | 6.40 |
| Standard Deviation | 0.57 | 0.28 | 4.20 | 0.89 |
| Coefficient of Variation (%) | 0.93 | 2.89 | 8.58 | 13.86 |
| Sample | ΔH (J/g) | Tm (°C) | ΔHo (J/g) | Wk (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDPEV1 | 153.3 | 131.15 | 293 | 52 |
| HDPEV2 | 154.1 | 130.13 | 293 | 52 |
| HDPER1 | 178.8 | 129.77 | 293 | 60 |
| HDPER2 | 184.1 | 130.22 | 293 | 62 |
| HDPER3 | 174.7 | 129.70 | 293 | 59 |
| HDPER4 | 185.0 | 129.60 | 293 | 62 |
| Characteristic Elements | Elemental Percentage (%) (a) | Elemental Percentage (%) (b) | Elemental Percentage (%) (c) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ba | - | 50.31 | |
| O | 3.69 | 28.01 | 44.37 |
| Na | 38.10 | 1.27 | 1.92 |
| Mg | 0.32 | 1.08 | 5.12 |
| Al | 1.31 | 1.57 | 8.77 |
| Si | 3.13 | 2.97 | 18.40 |
| P | - | 0.07 | 0.29 |
| S | 0.31 | 11.68 | 2.44 |
| Cl | 51.55 | 0.41 | 2.80 |
| K | 0.46 | 0.43 | 2.91 |
| Ca | 0.27 | 0.64 | 2.17 |
| Ti | - | - | 1.04 |
| Mn | - | - | 0.27 |
| Fe | 0.86 | 1.49 | 6.60 |
| Cu | - | - | 1.11 |
| Zn | - | - | 1.78 |
| Cd | - | 0.06 | - |
| TOTAL | 100 | 100 | 100 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kiersnowska, A.; Koda, E.; Fabianowski, W.; Kawalec, J. Effect of the Impact of Chemical and Environmental Factors on the Durability of the High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Geogrid in a Sanitary Landfill. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7010022
Kiersnowska A, Koda E, Fabianowski W, Kawalec J. Effect of the Impact of Chemical and Environmental Factors on the Durability of the High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Geogrid in a Sanitary Landfill. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiersnowska, Agnieszka, Eugeniusz Koda, Wojciech Fabianowski, and Jacek Kawalec. 2017. "Effect of the Impact of Chemical and Environmental Factors on the Durability of the High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Geogrid in a Sanitary Landfill" Applied Sciences 7, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7010022
APA StyleKiersnowska, A., Koda, E., Fabianowski, W., & Kawalec, J. (2017). Effect of the Impact of Chemical and Environmental Factors on the Durability of the High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Geogrid in a Sanitary Landfill. Applied Sciences, 7(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7010022








