Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies of Sorption of Ammonium in the Soil-Water Environment in Agricultural Areas of Central Poland
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
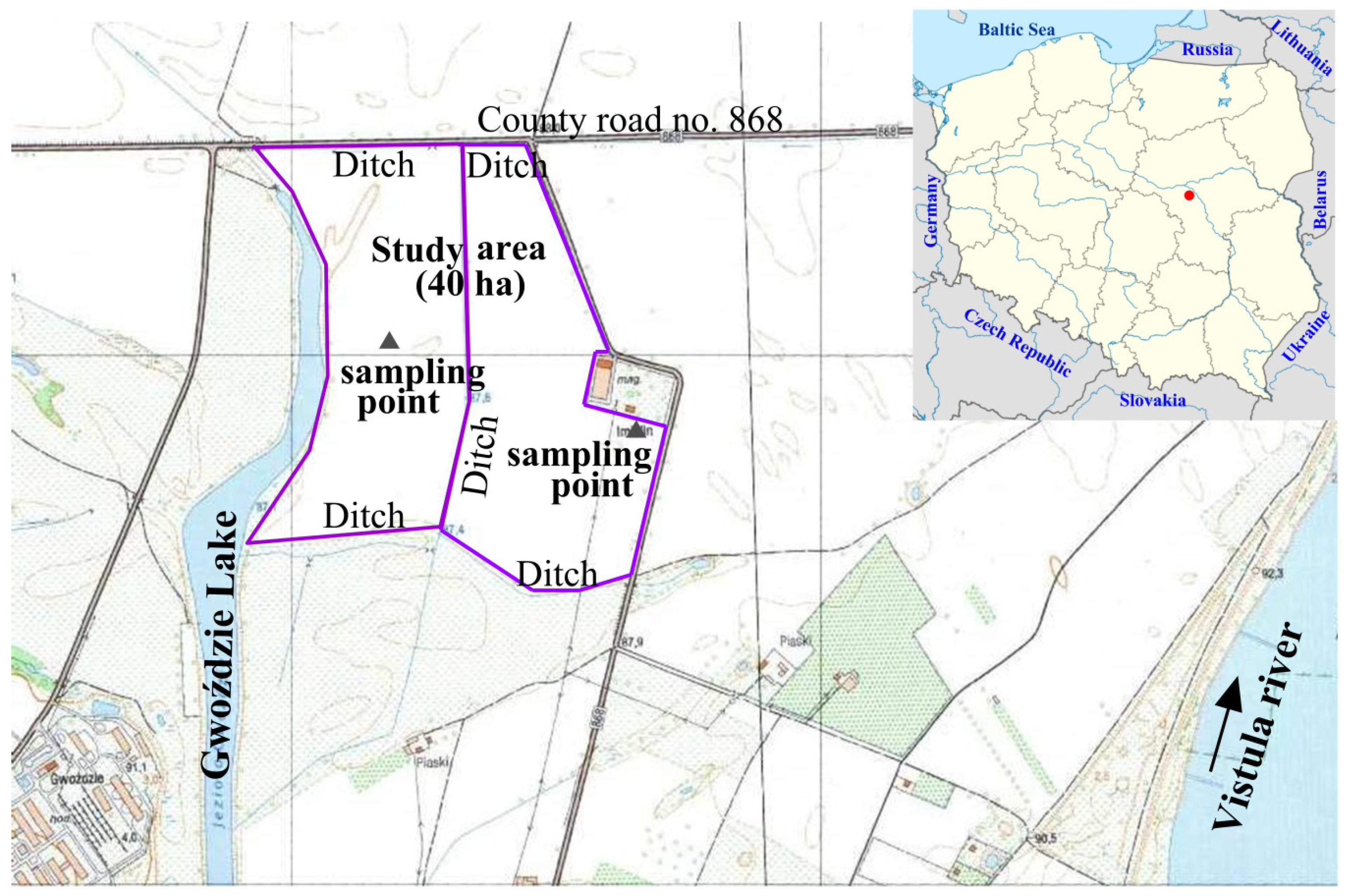
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Materials
2.3. Kinetic Tests
2.4. Equilibrium Studies
3. Results and Discussion
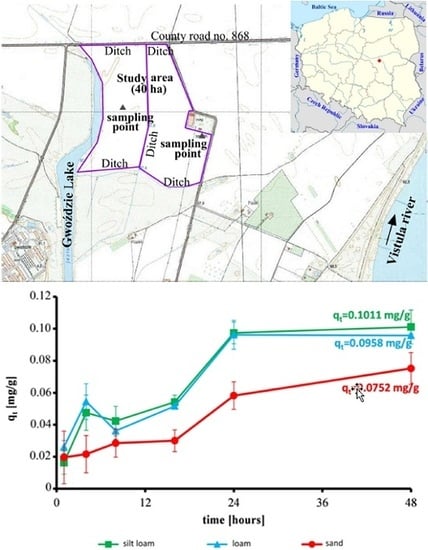
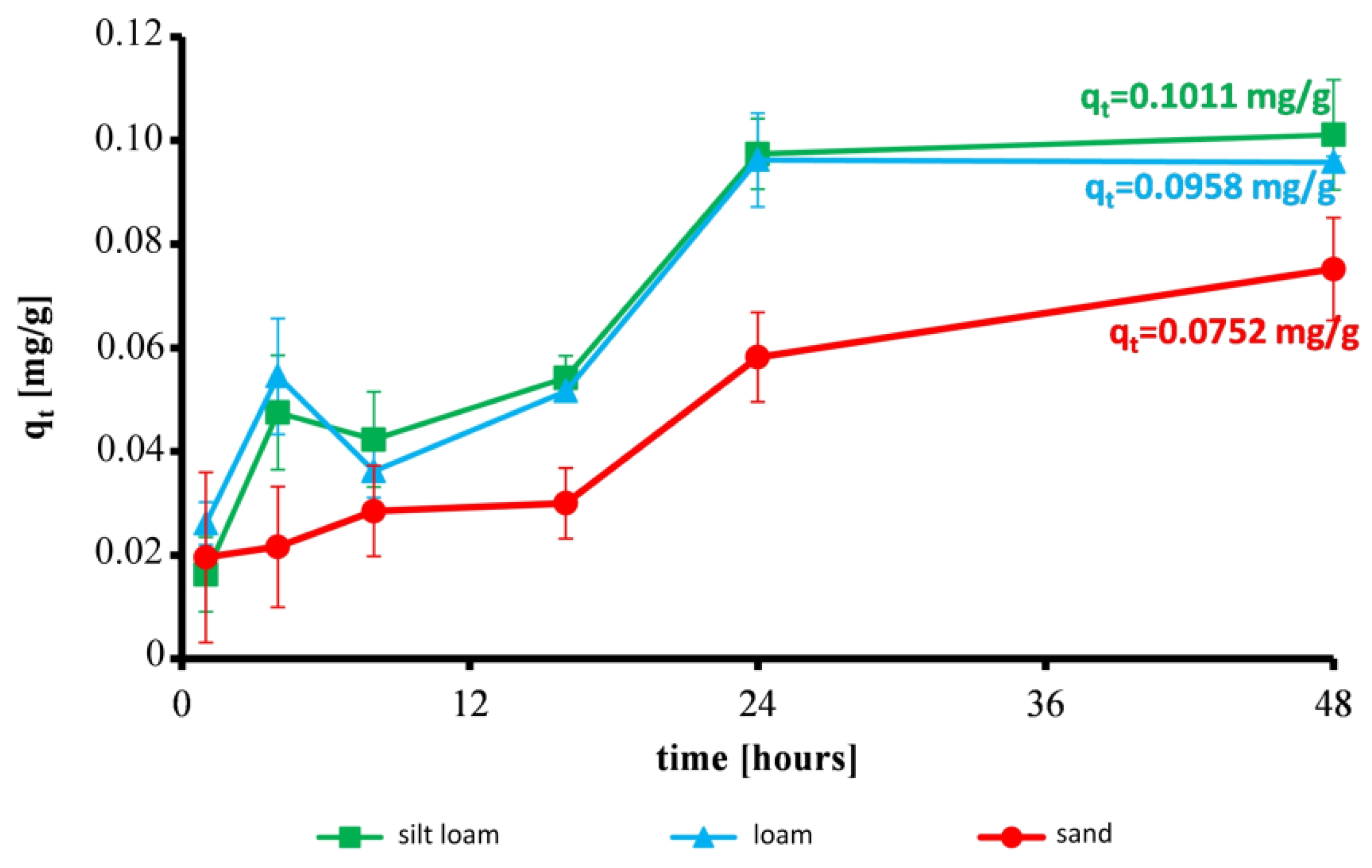
3.1. Effect of Contact Time on the Reduction of Ammonium and Sorption Capacity of Soils
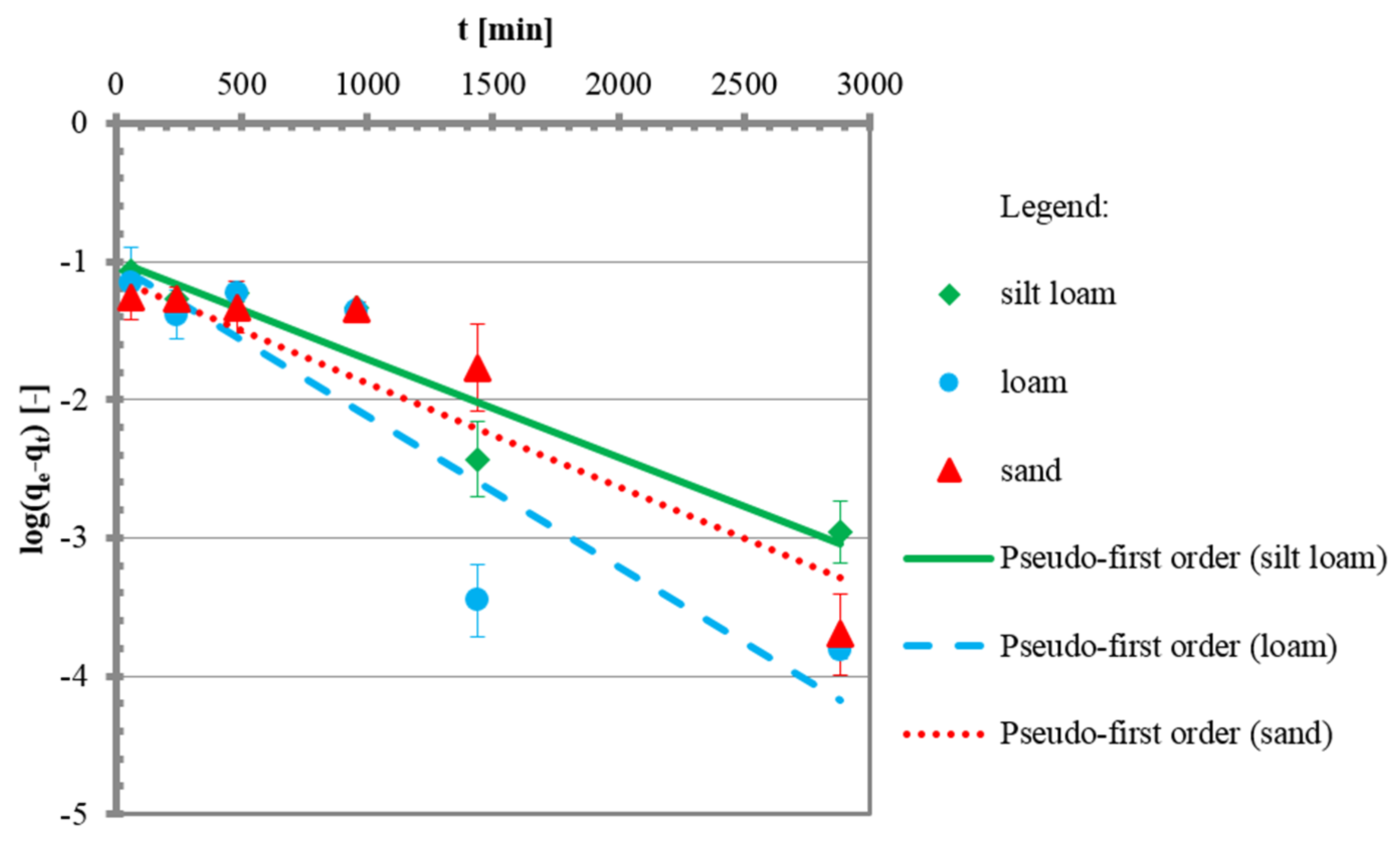
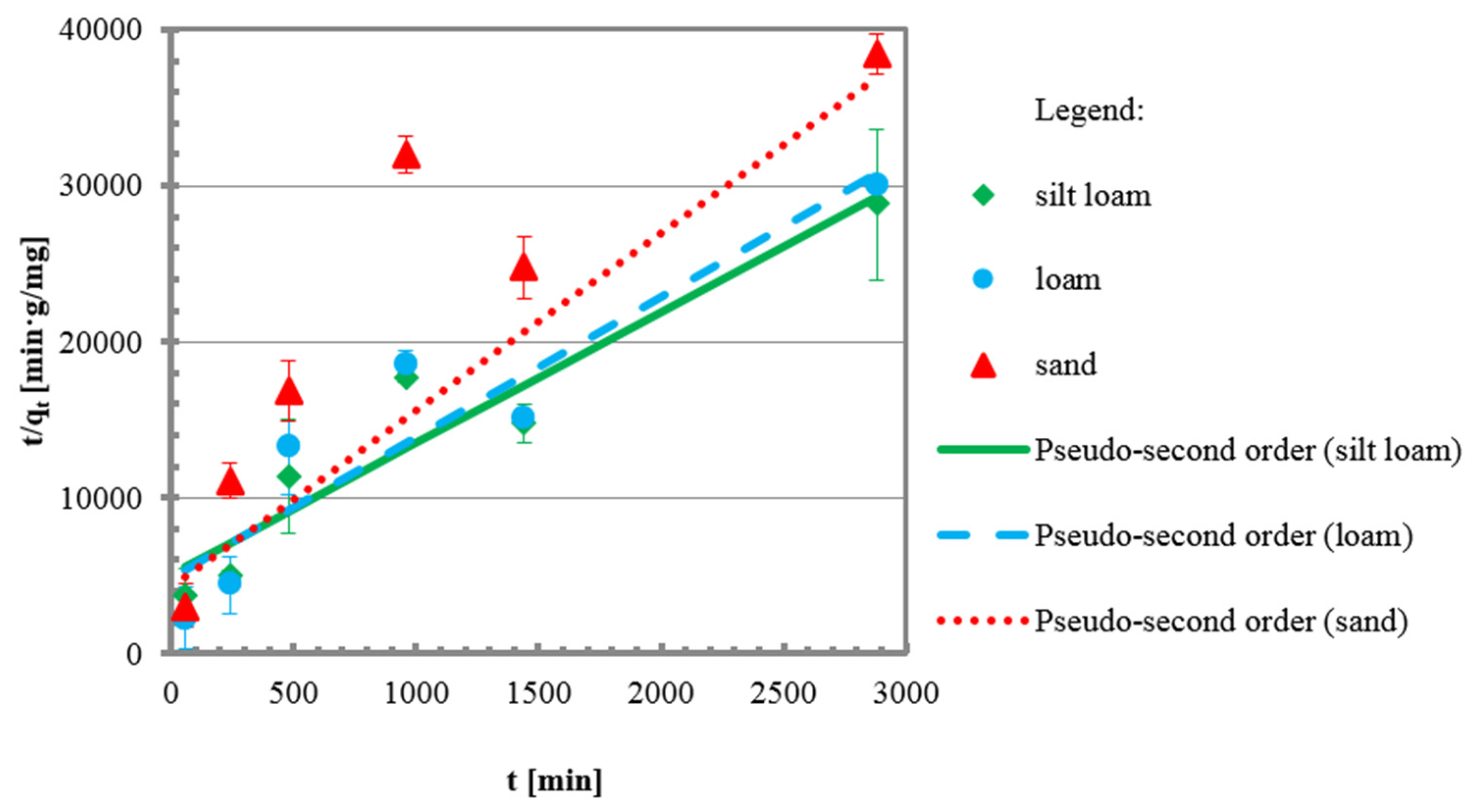
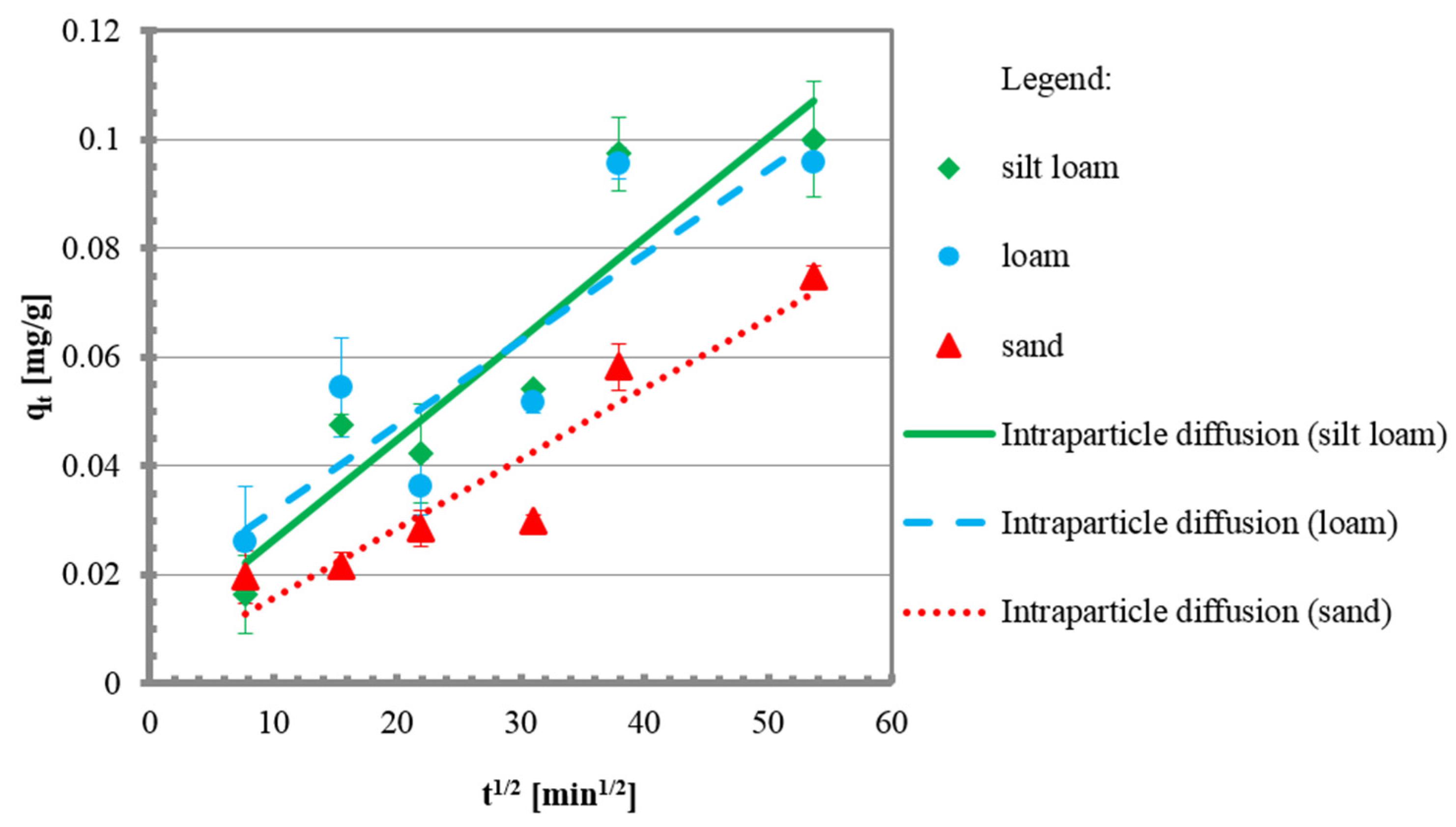
3.2. Kinetic Tests
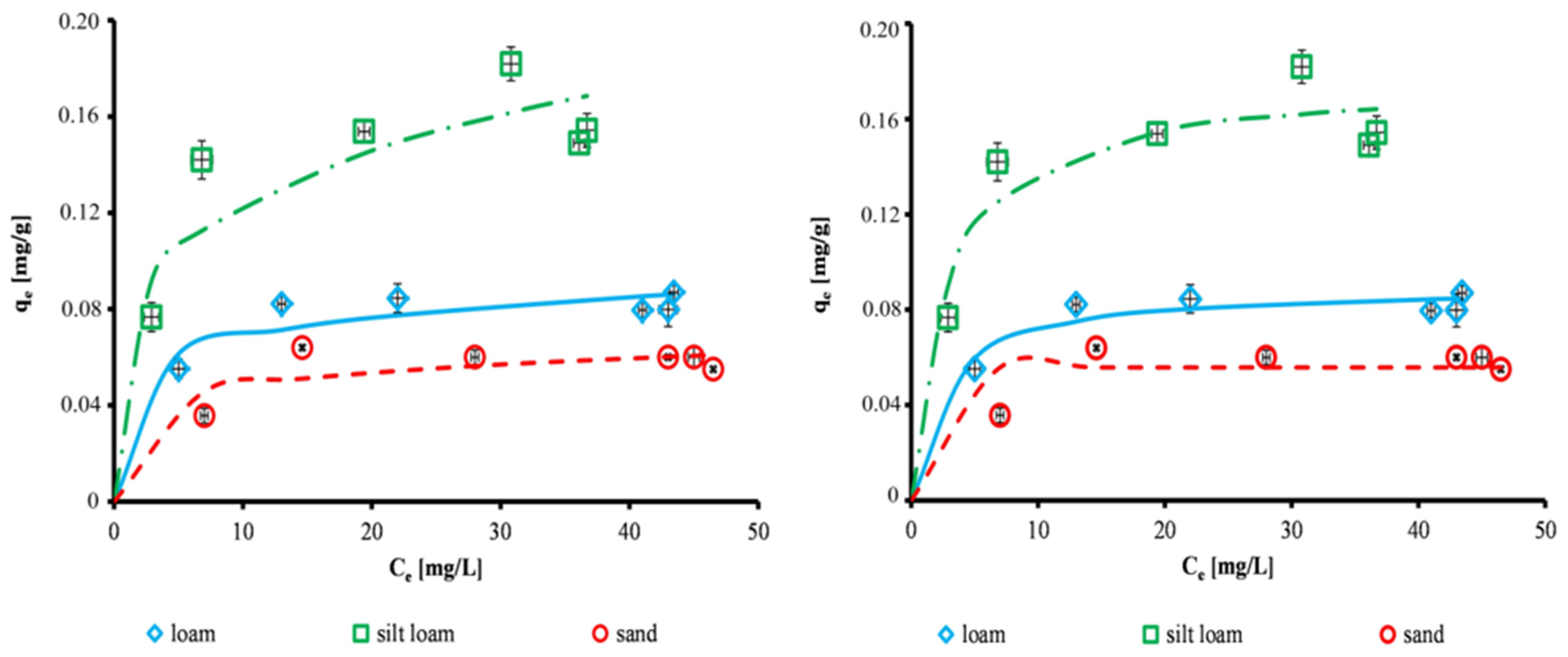
3.3. Equilibrium Studies
- for silt loam: Sips (R2 = 0.89) = Hill (R2 = 0.89) > Redlich-Peterson (R2 = 0.88) > Langmuir (R2 = 0.81) > Temkin (R2 = 0.72) > Freundlich (R2 = 0.66),
- for loam: Redlich-Peterson (R2 = 0.94) >Hill (R2 = 0.83) > Langmuir (R2 = 0.79) > Sips (R2 = 0.72) > Temkin (R2 = 0.63) > Freundlich (R2 = 0.59),
- for sand: Redlich-Peterson (R2 = 0.88) > Langmuir (R2 = 0.65) > Freundlich (R2 = 0.63) > Hill (R2 = 0.56) > Temkin (R2 = 0.43) > Sips (R2 = 0.39).
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schröder, J.J.; Scholefield, D.; Cabral, F.; Hofman, G. The effects of nutrient losses from agriculture on ground and surface water quality: The position of science in developing indicators for regulation. Environ. Sci. Policy 2004, 7, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, J.A.; Alonso, Á. Ecological and toxicological effects of inorganic nitrogen pollution in aquatic ecosystems: A global assessment. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 831–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Pan, Z.; Jin, M.; Li, F.; Wan, Y.; Gu, B. Determination of nitrate contamination sources using isotopic and chemical indicators in an agricultural region in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 155, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, K.; Heumesser, C.; Schmid, E. Groundwater nitrate contamination: Factors and indicators. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 111, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Perez, J.M.; Antiguedad, I.; Arrate, I.; Garcia-Linares, C.; Morell, I. The influence of nitrate leaching through unsaturated soil on ground water pollution in an agricultural area of the Basque country: A case of study. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 317, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epelde, A.M.; Cerro, I.; Sánchez-Pérez, J.M.; Sauvage, S.; Srinivasan, R.; Antigüedad, I. Application of the SWAT model to assess the impact of changes in agricultural management practices on water quality. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2015, 60, 825–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawniczak, A.E.; Zbierska, J.; Nowak, B.; Achtenberg, K.; Grześkowiak, A.; Kanas, K. Impact of agriculture and land use on nitrate contamination in groundwater and running waters in central-west Poland. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kučić, D.; Markić, M.; Briški, F. Ammonium Adsorption on the natural zeolite (Clinoptilolite): Adsorption isotherms and kinetics modeling. Holist. Approach Environ. 2012, 2, 145–158. [Google Scholar]
- Colombani, N.; Mastrocicco, M.; Di Giuseppe, D.; Faccini, B.; Coltorti, M. Batch and column experiments on nutrient leaching in soils amended with Italian natural zeolites. Catena 2015, 127, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fronczyk, J.; Sieczka, A.; Lech, M.; Radziemska, M.; Lechowicz, Z. Transport of nitrogen compounds through subsoils in agricultural areas: Column tests. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 25, 1505–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosier, A.R.; Syers, J.K.; Freney, J.R. Agriculture and the Nitrogen Cycle. Assessing the Impacts of Fertilizer Use on Food Production and the Environment; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.L.; Alva, A.K. Ammonium Adsorption and Desorption in Sandy Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 64, 1669–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieling, K.; Kage, H. N balance as an indicator of N leaching in an oilseed rape—Winter wheat—Winter barley rotation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 115, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruijter, F.J.; Boumans, L.J.M.; Smit, A.L.; van den Berg, M. Nitrate in upper groundwater on farms under tillage as affected by fertilizer use, soil type and groundwater table. Nutri. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2007, 77, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyllmar, K.; Bechmann, M.; Deelstra, J.; Iital, A.; Blicher-Mathiesen, G.; Jansons, V.; Koskiaho, J.; Povilaitis, A. Long-term monitoring of nutrient losses from agricultural catchments in the Nordic-Baltic region: A discussion of methods, uncertainties and future needs. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 198, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radziemska, M.; Fronczyk, J.; Lech, M.; Sieczka, A.; Lechowicz, Z. Selected monitoring properties of agricultural soil from the Imielin experimental site. Sci. Rev. Eng. Environ. Sci. 2016, 72, 105–115. [Google Scholar]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koda, E. Influence of Vertical Barrier Surrounding Old Sanitary Landfill on Eliminating Transport of Pollutants on the Basis of Numerical Modeling and Monitoring Results. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2012, 21, 929–935. [Google Scholar]
- Iital, A.; Klõga, M.; Pihlak, M.; Pachel, K.; Zahharov, A.; Loigu, E. Nitrogen content and trends in agricultural catchments in Estonia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 198, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koda, E.; Osiński, P.; Sieczka, A.; Wychowaniak, D. Areal Distribution of Ammonium Nitrogen Contamination of Soil-Water Environment in the Vicinity of Old Municipal Landfill Site with Vertical Barrier. Water 2015, 7, 2656–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wychowaniak, D.; Zawadzki, Ł.; Lech, M. Application of column tests and electrical resistivity methods for leachate transport monitoring. Ann. Wars. Univ. Life Sci. SGGW Land Reclam. 2015, 47, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, S.R.; Herbert, A.W.; Morgan, P.; Thornton, S.F.; Smith, J.W.N. A review of ammonium attenuation in soil and groundwater. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 2004, 37, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackin, T.E.; Aller, R.C. Ammonium Adsorption in Marine Sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1984, 29, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, M.S.; Ozdemir, B.; Turan, M.; Koyuncu, I.; Ateok, G.; Sarikaya, H.Z. Removal of ammonia by natural clay materials using fixed and fluidised bed column reactors. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply. 2001, 1, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Balci, S.; Dince, Y. Ammonium ion adsorption with sepiolite: Use of transient uptake method. Chem. Eng. Process. 2002, 41, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikołajków, J. Laboratory methods of estimating the retardation factor of migrating mineral nitrogen compounds in shallow groundwater. Geol. Q. 2003, 47, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulgawad, F.; Bockelmann-Evans, B.; Sapsford, D.; Williams, K.P.; Falconer, R. Ammonium Ion Adsorption on Clays and Sand Under Freshwater and Seawater Conditions. In Advances in Water Resources and Hydraulic Engineering, Proceedings of 16th IAHR-APD Congress and 3rd Symposium of IAHR-ISHS(II), Nanjing, China, 20–23 October 2008; Zhang, C., Tang, H., Eds.; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2009; pp. 656–661. [Google Scholar]
- Tosun, İ. Ammonium Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Clinoptilolite: Determination of Isotherm and Thermodynamic Parameters and Comparison of Kinetics by the Double Exponential Model and Conventional Kinetic Models. Int. J. Environ. Res. Publ. Health 2012, 9, 970–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buragohain, P.; Sredeep, S.; Saiyouri, N. A study on the adsorption of ammonium in bentonite and kaolinite. Int. J. Chem. Environ. Biol. Sci. 2013, 1, 157–160. [Google Scholar]
- Ismadji, S.; Soetaredjo, F.E.; Ayucitra, A. Clay Materials for Environmental Remediation; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- McKay, G. Solution to the homogeneous surface diffusion model for batch adsorption systems using orthogonal collocation. Chem. Eng. J. 2001, 81, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mon, J.; Flury, M.; Harsh, J.B. Sorption of four triarylmethane dyes in a sandy soil determined by batch and column experiments. Geoderma 2006, 133, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Dong, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Adsorption behavior of ammonium by a bioadsorbent—Boston ivy leaf powder. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1513–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, A.M.; Keat, L.K.; Ibrahim, Z.; Majid, Z.A.; Nizam, N.A. Kinetic and equilibrium studies of the removal of ammonium ions from aqueous solution by rice husk ash-synthesized zeolite Y and powdered and granulated forms of mordenite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, M.M.; Kiedryńska, L. Modelling equlibrium data for manganese (II) sorption onto manganese modified chalcedonite using the non-linear regression method. Ann. Wars. Univ. of Life Sci. SGGW Land Reclam. 2011, 43, 155–163. [Google Scholar]
- Boopathy, R.; Karthikeyan, S.; Mandal, A.B.; Sekaran, G. Adsorption of ammonium ion by coconut shell-activated carbon from aqueous solution: Kinetic, isotherm, and thermodynamic studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiecak, A.; Kret, E.; Malina, G. Ocena opóźnienia migracji TCE w ośrodku porowatym na podstawie testów statycznych (Estimation of ratardation of TCE migration in a porous medium using batch tests). Prz. Geol. 2013, 61, 62–66. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Olgun, A.; Atar, N.; Wang, S. Batch and column studies of phosphate and nitrate adsorption on waste solids containing boron impurity. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 222, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbeig, H.; Bagheri, N.; Ghorbanian, S.A.; Hallajisani, A.; Poorkarimi, S. A new adsorption isotherm model of aqueous solutions on granular activated carbon. WJMS 2013, 9, 243–254. [Google Scholar]
- Kalenik, M. Sewage Treatment Efficacy of Sandy Soil Bed with Natural Clinoptilolite Assist Layer. Ochr. Środowiska 2014, 36, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Moradzadeh, M.; Moazed, H.; Sayyad, G.; Khaledian, M. Transport of nitrate and ammonium ions in a sandy loam soil treated with potassium zeolite—Evaluating equilibrium and non-equilibrium equations. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Agriculture. Soil Conservation Service. Soil Survey Staff. Soil Survey Manual; Agricultural Handbook No. 18; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1951.
- Özcan, A.S.; Erdem, B.; Özcan, A. Adsorption of Acid Blue 193 from aqueous solutions onto BTMA-bentonite. Colloids Surf. A 2005, 266, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S. Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruíz-Baltazar, A.; Pérez, R. Kinetic Adsorption Study of Silver Nanoparticles on Natural Zeolite: Experimental and Theoretical Models. Appl. Sci. 2015, 5, 1869–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption geloster stoffe. Kungliga Svenska Vetnskapsakademiens. Handlingar 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S. Adsorption of Heavy Metals from Waste Streams by Peat. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK, January 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, W.J.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1963, 89, 31–59. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Batch—Type Procedures for Estimating Soil Adsorption of Chemicals; US EPA/530/SW-87/006-F; United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA): Washington, DC, USA, 1992.
- Waste and Waste Water. Test For Nitrogen Compounds Contents. Determination of Ammonium Nitrogen in Water by Direct Nesslerization Method; PN-C-04576-4; Polish Committee for Standarization: Warsaw, Poland, 1994. (In Polish)
- Water Analysis Handbook, 7th ed.; Nitrate Cadmium Reduction Method 8171; Hach Company: Loveland, CO, USA, 2012.
- Kumar, P.; Kirthika, K. Equilibrium and kinetic study of adsorption of nickel from aqueous solution onto bael tree leaf powder. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2009, 4, 351–363. [Google Scholar]
- Freundlich, H.M.F. Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–471. [Google Scholar]
- Langmuir, I. The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1916, 38, 2221–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temkin, M.I.; Pyzhev, V. Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalyst. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 1940, 12, 327–356. [Google Scholar]
- Redlich, O.J.; Peterson, D.L. A useful adsorption isotherm. J. Phys. Chem. 1959, 63, 1024–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sips, R. On the structure of a catalyst surface. J. Chem. Phys. 1948, 16, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, T.L. Theory of physical adsorption. Adv. Catal. 1952, 4, 211–258. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifnia, S.; Khadivi, M.A.; Shojaeimehr, T.; Shavisi, Y. Characterization, isotherm and kinetic studies for ammonium ion adsorption by light expanded clay aggregate (LECA). J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olu-Owolabi, B.I.; Diagboya, P.N.; Adebowale, K.O. Evaluation of pyrene sorption-desorption on tropical soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 137, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desta, M.B. Batch Sorption Experiments: Langmuir and Freundlich Isotherm Studies for the Adsorption of Textile Metal Ions onto Teff Straw (Eragrostis tef) Agricultural Waste. J. Thermodyn. 2013, 2013, 375830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, T.W.; Chakkravorti, R.K. Pore and solid diffusion models for fixed-bed adsorbers. J. Am. Inst. Chem. Eng. 1974, 20, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadag, D.; Koc, Y.; Turan, M.; Ozturk, M. A comparative study of linear and nonlinear regression analysis for ammonium exchange by clinoptilolite zeolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 144, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmesh, T.V.N.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Sekaran, G.; Velan, M. Application of Two-and Three-Parameter Isotherm Models: Biosorption of Acid Red 88 onto Azolla microphylla. Bioremediation J. 2006, 10, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdaoui, O.; Naffrechoux, E. Modeling of adsorption isotherms of phenol and chlorophenols onto granular activated carbon. Part II. Models with more than two parameters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belhachemi, M.; Addoun, F. Comparative adsorption isotherms and modeling of methylene blue onto activated carbons. Appl. Water Sci. 2011, 3, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
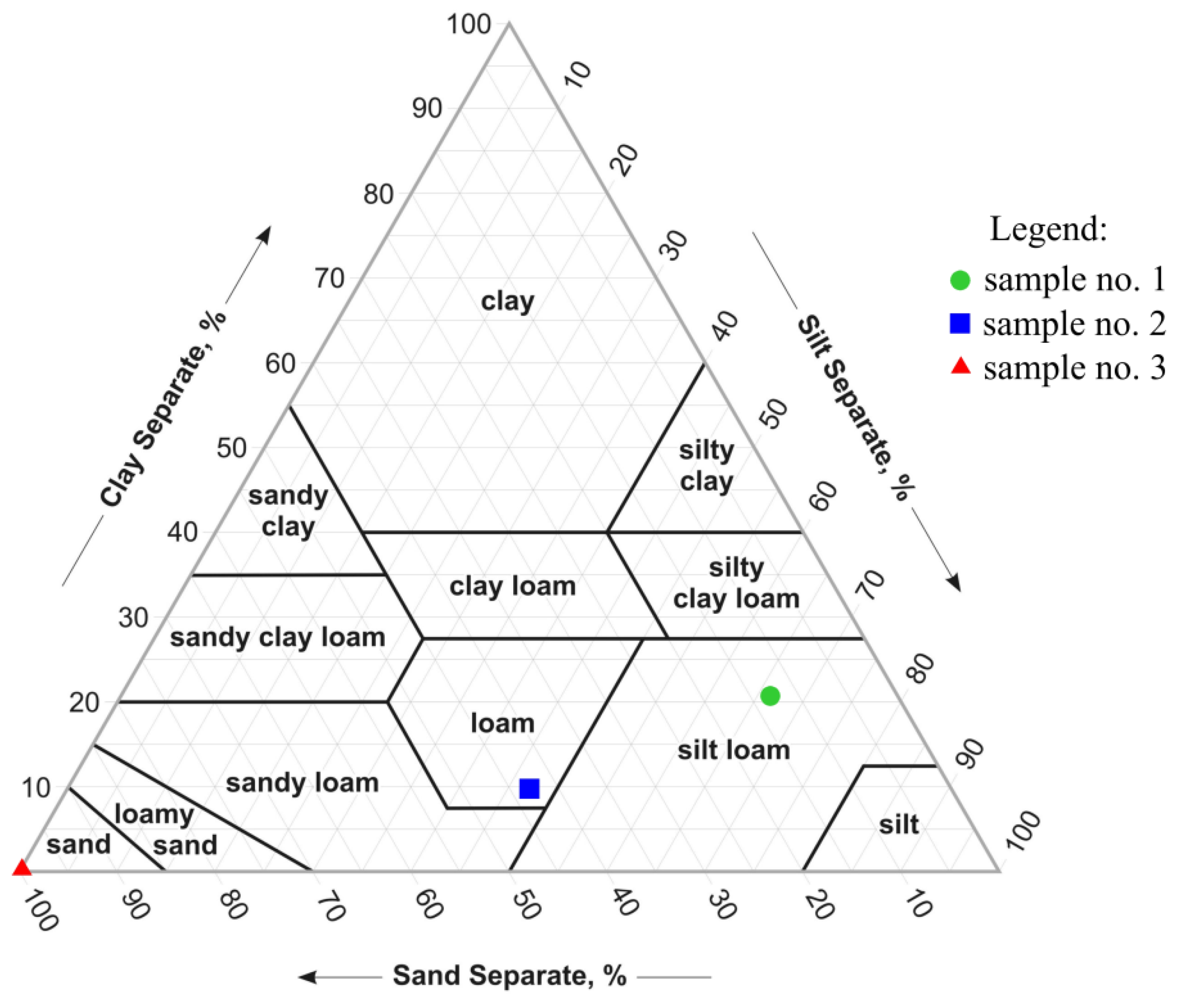

| Adsorbent | Bulk Density | Porosity | pH | Electrical Conductivity | Organic Matter | Hydraulic Conductivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [Mg/m3] | [-] | [-] | [μS/cm] | [%] | [m/s] | |
| Silt loam | 1.63 | 0.40 | 7.4 | 363 | 3.1 | 1.9 × 10−8 |
| Loam | 1.60 | 0.40 | 7.5 | 160 | 2.3 | 3.6 × 10−6 |
| Sand | 1.70 | 0.34 | 7.2 | 155 | 0.1 | 3.0 × 10−5 |
| Kinetic Model | Equation | Plot | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first order | [47] | ||
| Pseudo-second order | [47,48] | ||
| Intraparticle diffusion | qt vs. t0.5 | [49] |
| Isotherm | Equation | Model Parameters | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Two-parameter models | |||
| Freundlich | KF, n | [54] | |
| Langmuir | qmax, KL | [55] | |
| Temkin | B, A | [56] | |
| Three-parameter models | |||
| Redlich-Peterson | KR, br, g | [57] | |
| Sips | qmax, m, b | [58] | |
| Hill | qH, KD, nH | [59] | |
| Soil | Contact Time [h] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 24 | 48 | |
| Reduction of ammonium [%] | ||||||
| Silt loam | 3.1 | 8.1 | 9.1 | 10.4 | 18.7 | 19.4 |
| Loam | 5.0 | 6.9 | 10.5 | 11.3 | 18.4 | 18.5 |
| Sand | 3.8 | 4.2 | 5.5 | 5.8 | 11.2 | 14.4 |
| Parameter | Soil | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silt Loam | Loam | Sand | ||
| Pseudo-first order kinetic model | ||||
| qe | mg/g | 0.1011 | 0.0960 | 0.0752 |
| k1 | 1/min | 0.0016 | 0.0024 | 0.0016 |
| R2 | - | 0.89 | 0.80 | 0.89 |
| Pseudo-second order kinetic model | ||||
| qe | mg/g | 0.1189 | 0.1110 | 0.0880 |
| k2 | mg/g min | 0.0140 | 0.0167 | 0.0306 |
| v0 | mg/g min | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 |
| R2 | - | 0.91 | 0.87 | 0.94 |
| Intra-particle diffusion | ||||
| kint | mg/g min1/2 | 0.0018 | 0.0016 | 0.0013 |
| Ci | mg/g | 0.0080 | 0.0161 | 0.0029 |
| R2 | - | 0.86 | 0.77 | 0.89 |
| Soil | Freundlich | Langmuir | Temkin | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KF | n | R2 | qmax | KL | R2 | A | B | R2 | |
| Silt loam | 0.071 | 4.17 | 0.66 | 0.18 | 0.36 | 0.81 | 9.50 | 0.029 | 0.72 |
| Loam | 0.048 | 6.41 | 0.59 | 0.09 | 0.40 | 0.79 | 2.31 | 0.019 | 0.63 |
| Sand | 0.034 | 6.59 | 0.63 | 0.06 | 0.79 | 0.65 | 0.18 | 0.030 | 0.43 |
| Soil | Redlich-Peterson | Sips | Hill | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR | bR | g | R2 | qmax | n | b | R2 | qmax | Kd | m | R2 | |
| Silt loam | 0.035 | 0.062 | 1.32 | 0.88 | 0.16 | 0.40 | 0.07 | 0.89 | 0.16 | 15.25 | 2.48 | 0.89 |
| Loam | 0.017 | 0.064 | 1.27 | 0.94 | 0.09 | 1.88 | 1.27 | 0.72 | 0.09 | 2.59 | 1.17 | 0.83 |
| Sand | 0.006 | 0.006 | 1.71 | 0.88 | 0.50 | 5.57 | 0.02 | 0.39 | 0.07 | 2.58 | 0.89 | 0.56 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sieczka, A.; Koda, E. Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies of Sorption of Ammonium in the Soil-Water Environment in Agricultural Areas of Central Poland. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6100269
Sieczka A, Koda E. Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies of Sorption of Ammonium in the Soil-Water Environment in Agricultural Areas of Central Poland. Applied Sciences. 2016; 6(10):269. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6100269
Chicago/Turabian StyleSieczka, Anna, and Eugeniusz Koda. 2016. "Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies of Sorption of Ammonium in the Soil-Water Environment in Agricultural Areas of Central Poland" Applied Sciences 6, no. 10: 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6100269
APA StyleSieczka, A., & Koda, E. (2016). Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies of Sorption of Ammonium in the Soil-Water Environment in Agricultural Areas of Central Poland. Applied Sciences, 6(10), 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6100269