Direct Electron Acceleration with Radially Polarized Laser Beams
Abstract
:1. Introduction
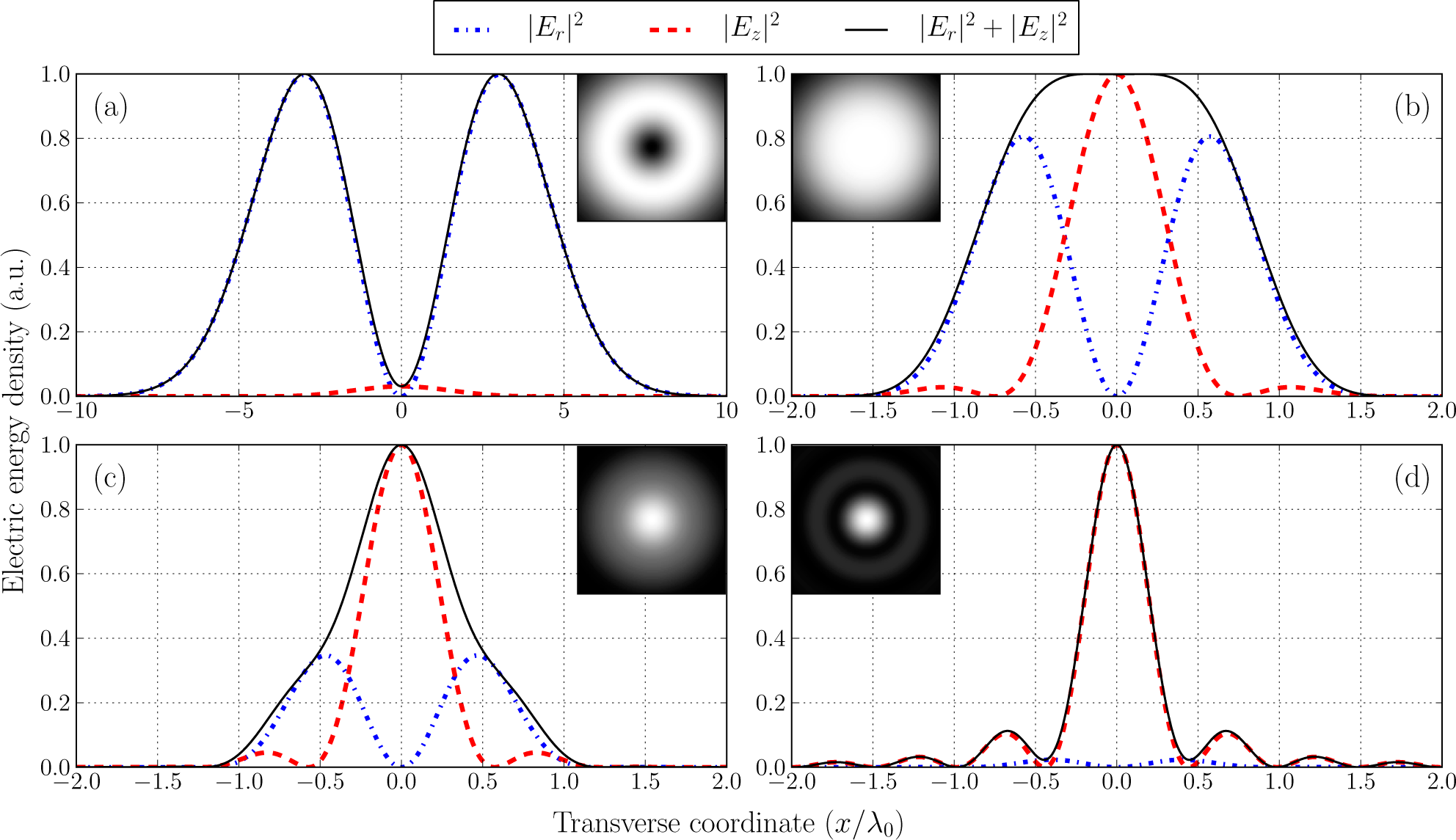
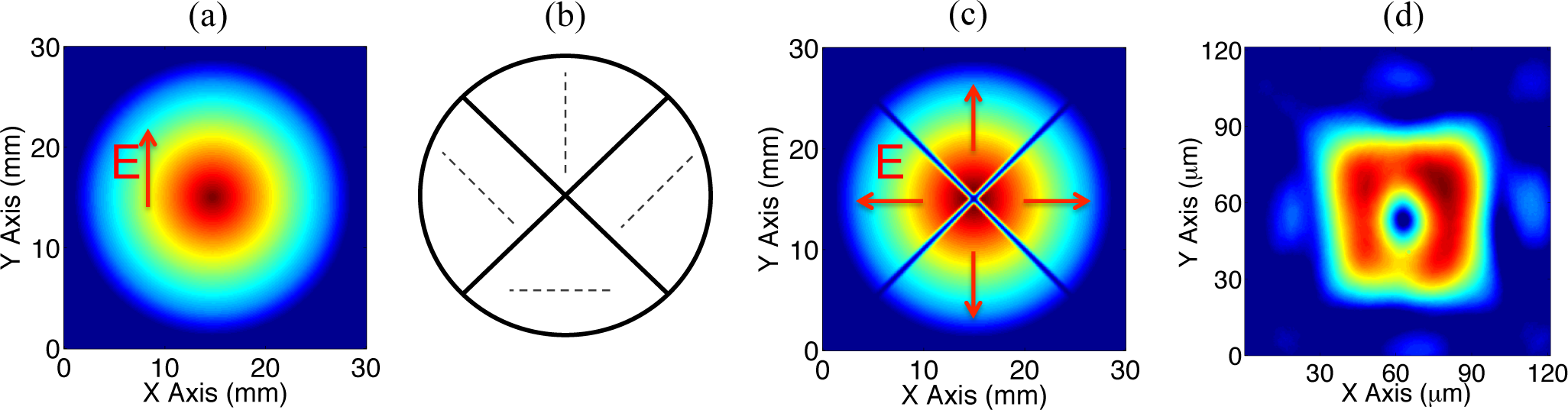
2. Radially Polarized Laser Beams
3. Electron Acceleration with Radially Polarized Laser Beams
3.1. Free-Space Electron Acceleration in Laser Beams
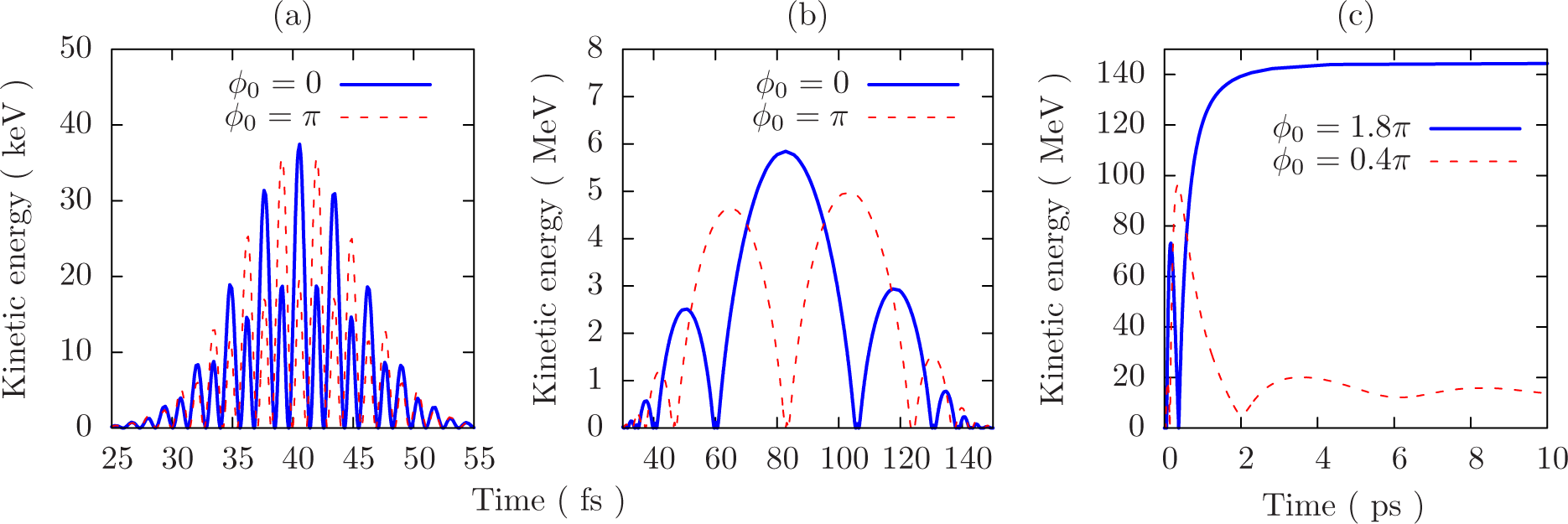
3.2. Direct Longitudinal Electron Acceleration with Radially Polarized Laser Beams
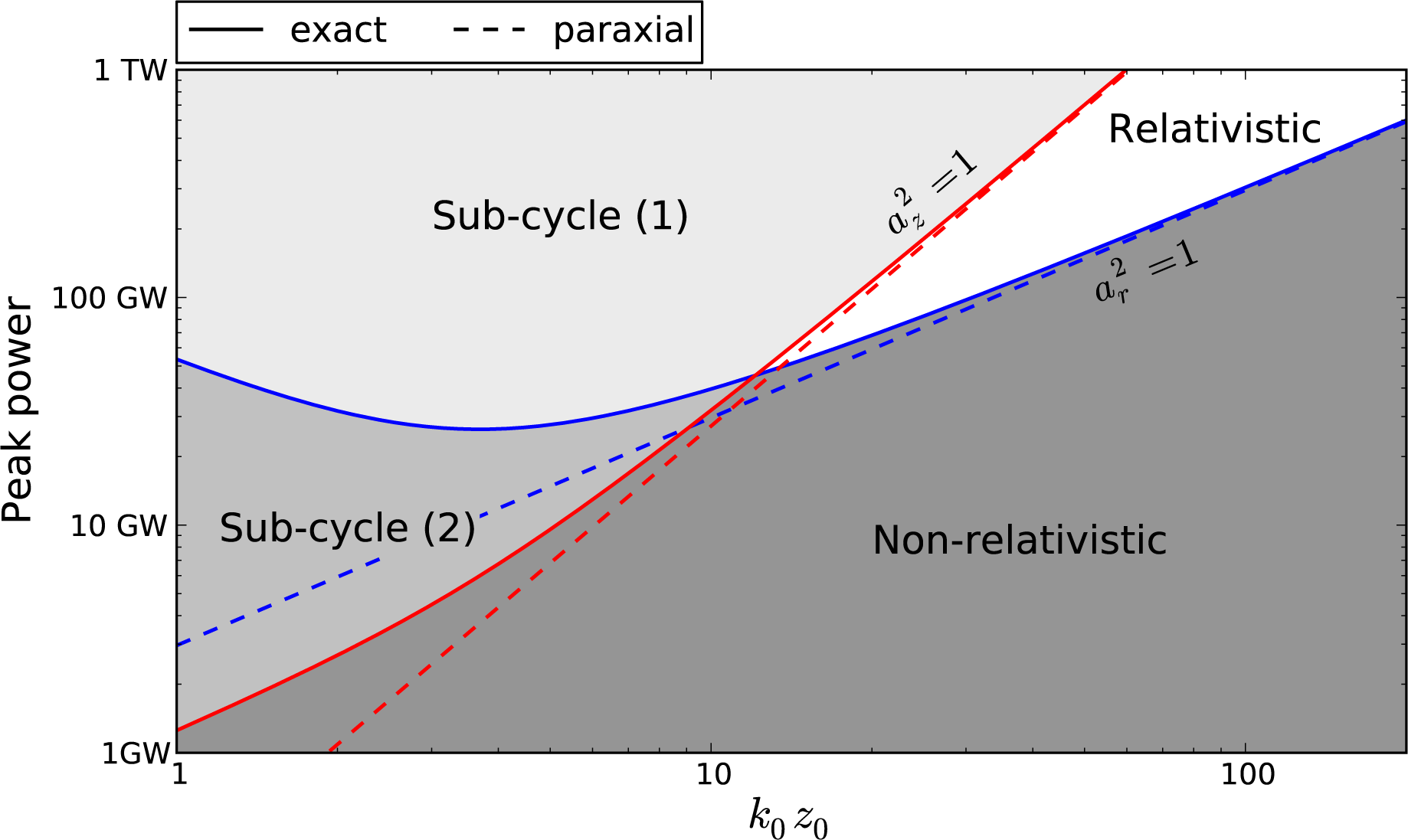
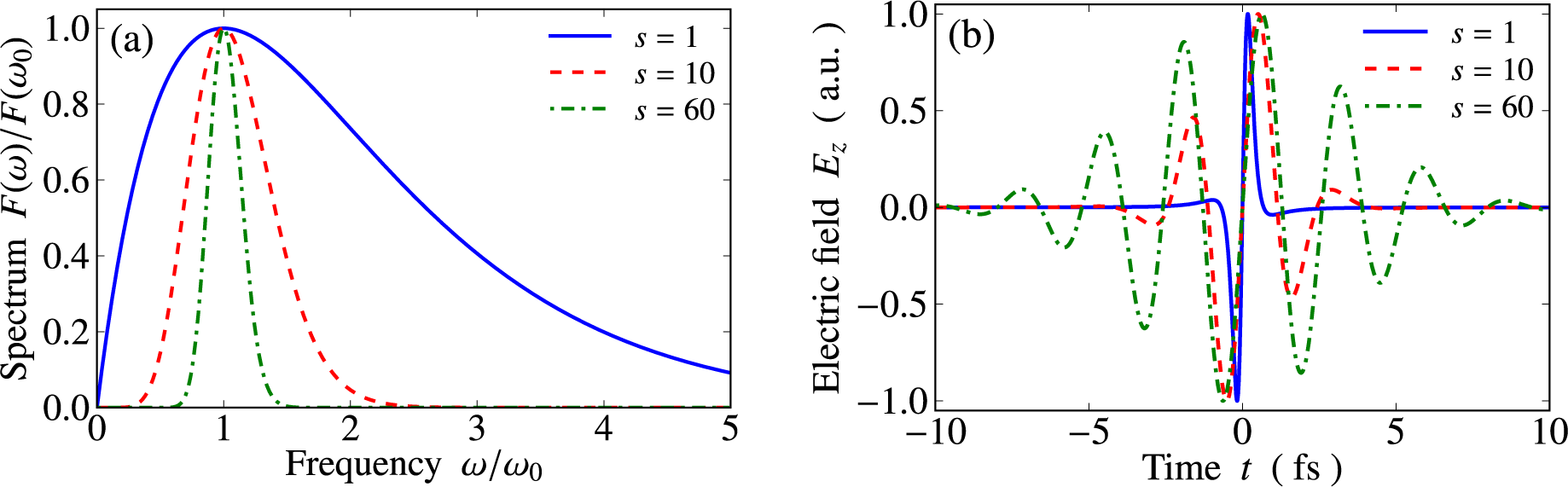
3.3. Threshold for Sub-Cycle Acceleration and Attosecond Bunching
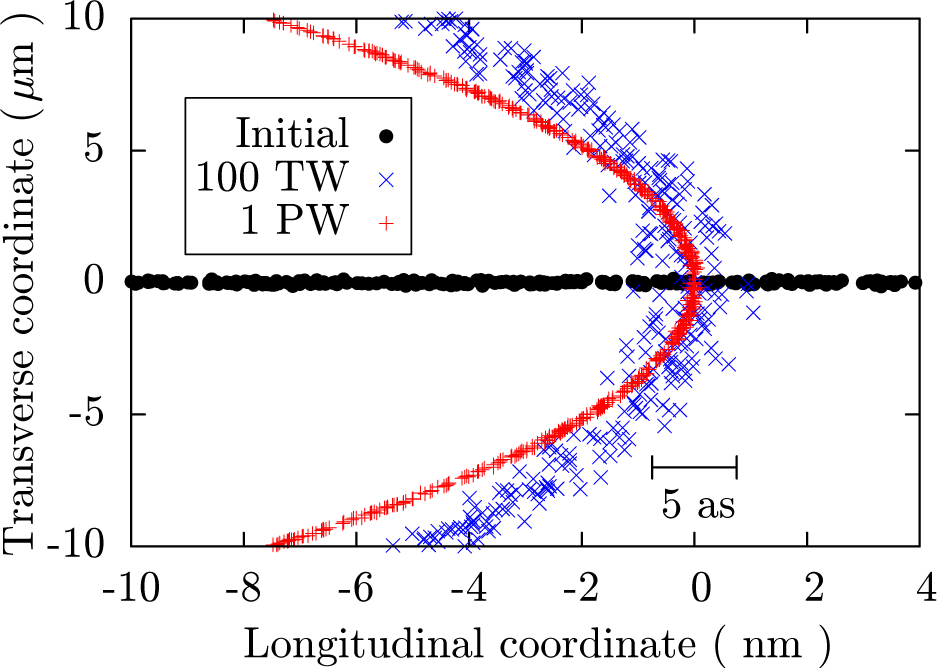
4. Acceleration by Ultrashort and Tightly Focused Radially Polarized Laser Pulses
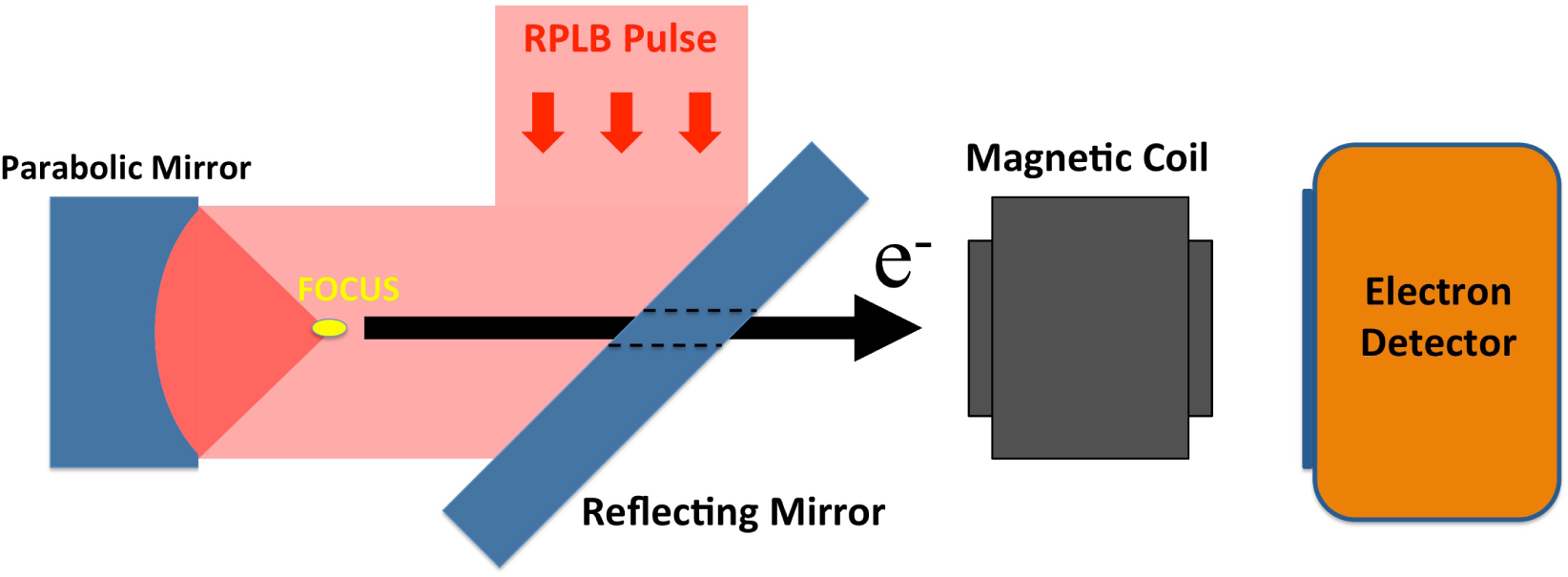
5. Experimental Observation of Electron Acceleration with Tightly Focused Radially Polarized Laser Beams
5.1. Method for Generating Tightly Focused Ultrashort RPLPs
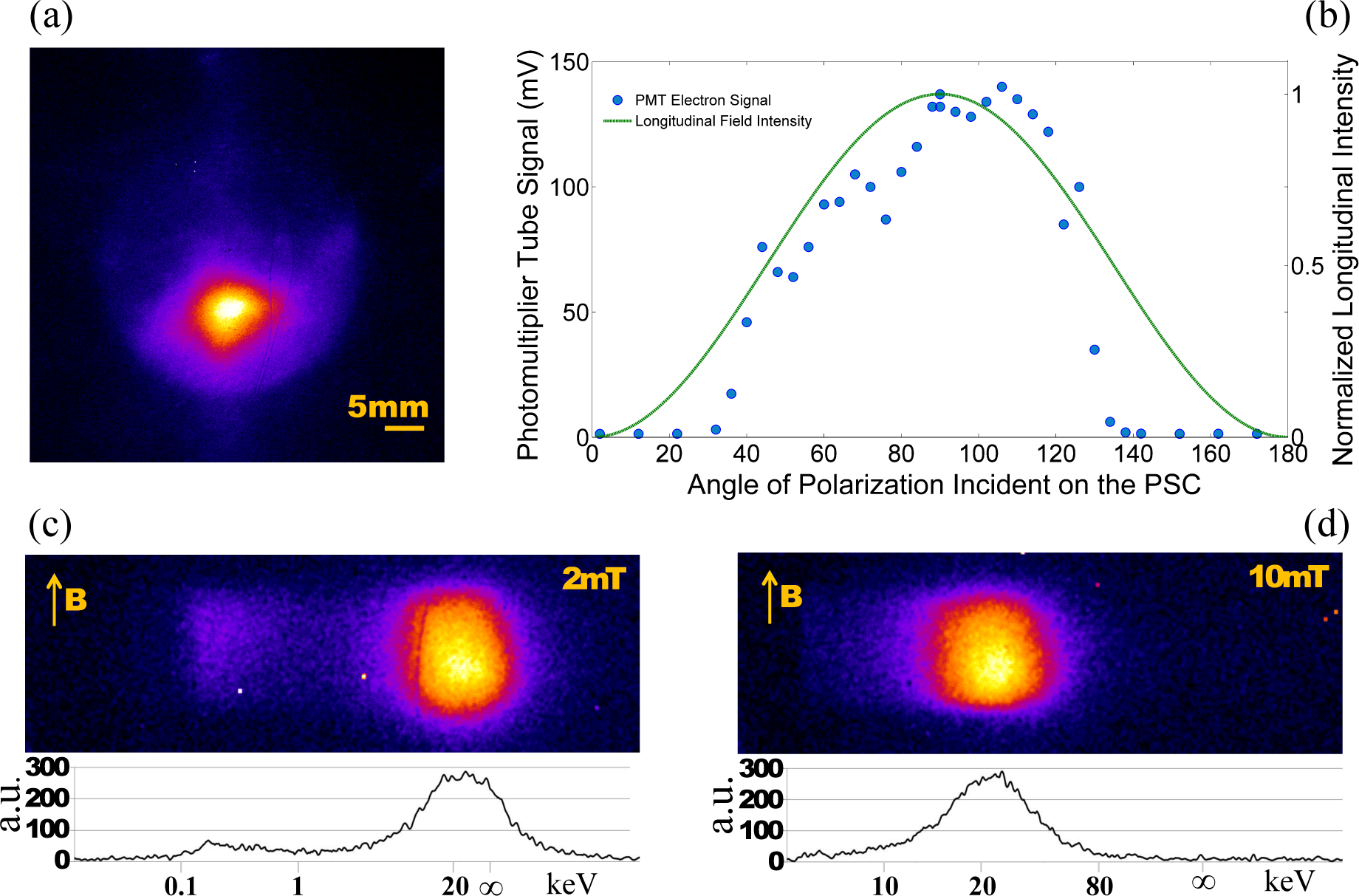
5.2. Electron Acceleration Measurements
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Appendix
A. Challenges for Producing High-Power Radially Polarized Laser Beams
B. Modelling Tightly Focused Ultrafast Laser Beams in Vacuum
Acknowledgments
References and Note
- Shimoda, K. Proposal for an electron accelerator using an optical maser. Appl. Opt. 1962, 1, 33–35. [Google Scholar]
- Malka, V.; Faure, J.; Gauduel, Y.A.; Lefebvre, E.; Rousse, A.; Phuoc, K.T. Principles and applications of compact laser-plasma accelerators. Nat. Phys. 2008, 4, 447–453. [Google Scholar]
- Esarey, E.; Schroeder, C.B.; Leemans, W.P. Physics of laser-driven plasma-based electron accelerators. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2009, 81, 1229–1285. [Google Scholar]
- Faure, J.; Glinec, Y.; Pukhov, A.; Kiselev, S.; Gordienko, S.; Lefebvre, E.; Rousseau, J.P.; Burgy, F.; Malka, V. A laser-plasma accelerator producing monoenergetic electron beams. Nature 2004, 431, 541–544. [Google Scholar]
- Geddes, C.G.R.; Toth, C.; van Tilborg, J.; Esarey, E.; Schroeder, C.B.; Bruhwiler, D.; Nieter, C.; Cary, J.; Leemans, W.P. High-quality electron beams from a laser wakefield accelerator using plasma-channel guiding. Nature 2004, 431, 538–541. [Google Scholar]
- Katsouleas, T. Accelerator physics: Electrons hang ten on laser wake. Nature 2004, 431, 515–516. [Google Scholar]
- Mangles, S.P.D.; Murphy, C.D.; Najmudin, Z.; Thomas, A.G.R.; Collier, J.L.; Dangor, A.E.; Divall, E.J.; Foster, P.S.; Gallacher, J.G.; Hooker, C.J.; et al. Monoenergetic beams of relativistic electrons from intense laser-plasma interactions. Nature 2004, 431, 535–538. [Google Scholar]
- Hogan, M.J.; Barnes, C.D.; Clayton, C.E.; Decker, F.J.; Deng, S.; Emma, P.; Huang, C.; Iverson, R.H.; Johnson, D.K.; Joshi, C.; et al. Multi-GeV energy gain in a plasma-wakefield accelerator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 054802. [Google Scholar]
- Leemans, W.P.; Nagler, B.; Gonsalves, A.J.; Toth, C.; Nakamura, K.; Geddes, C.G.R.; Esarey, E.; Schroeder, C.B.; Hooker, S.M. GeV electron beams from a centimetre-scale accelerator. Nat. Phys. 2006, 2, 696–699. [Google Scholar]
- Blumenfeld, I.; Clayton, C.E.; Decker, F.J.; Hogan, M.J.; Huang, C.; Ischebeck, R.; Iverson, R.; Joshi, C.; Katsouleas, T.; Kirby, N.; et al. Energy doubling of 42-GeV electrons in a metre-scale plasma wakefield accelerator. Nature 2007, 445, 741–744. [Google Scholar]
- Baum, P.; Zewail, A.H. 4D attosecond imaging with free electrons: Diffraction methods and potential applications. Chem. Phys. 2009, 366, 2–8. [Google Scholar]
- Krausz, F.; Ivanov, M. Attosecond physics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2009, 81, 163–234. [Google Scholar]
- Zewail, A.H. Four-dimensional electron microscopy. Science 2010, 328, 187–193. [Google Scholar]
- Esarey, E.; Sprangle, P.; Krall, J. Laser acceleration of electrons in vacuum. Phys. Rev. E. 1995, 52, 5443–5453. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Cline, D.; He, P. Vacuum laser acceleration using a radially polarized CO2 laser beam. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A. 1999, 424, 296–303. [Google Scholar]
- Varin, C.; Piché, M.; Porras, M.A. Acceleration of electrons from rest to GeV energies by ultrashort transverse magnetic laser pulses in free space. Phys. Rev. E. 2005, 71, 026603. [Google Scholar]
- Salamin, Y.I.; Mono-energetic, GeV. electrons from ionization in a radially polarized laser beam. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 90–92. [Google Scholar]
- Varin, C.; Piché, M. Relativistic attosecond electron pulses from a free-space laser-acceleration scheme. Phys. Rev. E. 2006, 74, 045602. [Google Scholar]
- Karmakar, A.; Pukhov, A. Collimated attosecond GeV electron bunches from ionization of high-Z material by radially polarized ultra-relativistic laser pulses. Laser Part. Beams. 2007, 25, 371–377. [Google Scholar]
- Payeur, S.; Fourmaux, S.; Schmidt, B.E.; MacLean, J.P.; Tchervenkov, C.; Legare, F.; Piche, M.; Kieffer, J.C. Generation of a beam of fast electrons by tightly focusing a radially polarized ultrashort laser pulse. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 41105. [Google Scholar]
- Salamin, Y.I.; Harman, Z.; Keitel, C.H. Direct high-power laser acceleration of ions for medical applications. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 155004. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.X.; Salamin, Y.I.; Galow, B.J.; Keitel, C.H. Acceleration of proton bunches by petawatt chirped radially polarized laser pulses. Phys. Rev. A. 2012, 85, 063832. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.L.; Sheng, Z.M.; Zheng, J.; Liu, C.S.; Zhang, J. Proton acceleration by radially polarized chirped laser pulses. Phys. Rev. ST Accel. Beams. 2012, 15, 041301. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Lou, Q.; Zhou, J.; Dong, J.; Wei, Y. Focal shift in focused radially polarized ultrashort pulsed laser beams. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 6251–6255. [Google Scholar]
- April, A. Nonparaxial TM and TE beams in free space. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 1563–1565. [Google Scholar]
- Nesterov, A.V.; Niziev, V.G. Laser beams with axially symmetric polarization. J. Phys. D. 2000, 33, 1817–1822. [Google Scholar]
- Dorn, R.; Quabis, S.; Leuchs, G. Sharper focus for a radially polarized light beam. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 233901. [Google Scholar]
- Quabis, S.; Dorn, R.; Eberler, M.; Glockl, O.; Leuchs, G. Focusing light to a tighter spot. Opt. Commun. 2000, 179, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Youngworth, K.; Brown, T. Focusing of high numerical aperture cylindrical-vector beams. Opt. Express. 2000, 7, 77–87. [Google Scholar]
- Varin, C.; Piché, M.; Porras, M.A. Analytical calculation of the strong axial longitudinal electric field resulting from the tight focusing of an ultrafast transverse magnetic pulsed beam in free space. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A. 2006, 23, 2027–2038. [Google Scholar]
- April, A. Nonparaxial elegant Laguerre-Gaussian beams. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 1392–1394. [Google Scholar]
- Lax, M.; Louisell, W.H.; McKnight, W.B. From Maxwell to paraxial wave optics. Phys. Rev. A. 1975, 11, 1365–1370. [Google Scholar]
- Salamin, Y.I. Fields of a radially polarized Gaussian laser beam beyond the paraxial approximation. Opt. Lett. 2006, 31, 2619–2621. [Google Scholar]
- Siegman, A.E. Lasers; University Science: Mill Valley, CA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, J.D. Classical Electrodynamics, 3rd ed; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- April, A. Power carried by a nonparaxial TM beam. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A. 2010, 27, 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- Bokor, N.; Davidson, N. Toward a spherical spot distribution with 4π focusing of radially polarized light. Opt. Lett. 2004, 29, 1968–1970. [Google Scholar]
- April, A.; Piché, M. 4π Focusing of TM01 beams under nonparaxial conditions. Opt. Express. 2010, 18, 22128–22140. [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard, C.J.R.; Saghafi, S. Transverse-electric and transverse-magnetic beam modes beyond the paraxial approximation. Opt. Lett. 1999, 24, 1543–1545. [Google Scholar]
- Novotny, L.; Beversluis, M.R.; Youngworth, K.S.; Brown, T.G. Longitudinal field modes probed by single molecules. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 5251–5254. [Google Scholar]
- Stadler, J.; Stanciu, C.; Stupperich, C.; Meixner, A.J. Tighter focusing with a parabolic mirror. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 681–683. [Google Scholar]
- Imai, R.; Kanda, N.; Higuchi, T.; Zheng, Z.; Konishi, K.; Kuwata-Gonokami, M. Terahertz vector beam generation using segmented nonlinear optical crystals with threefold rotational symmetry. Opt. Express. 2012, 20, 21896–21904. [Google Scholar]
- Winnerl, S.; Hubrich, R.; Mittendorff, M.; Schneider, H.; Helm, M. Universal phase relation between longitudinal and transverse fields observed in focused terahertz beams. New J. Phys. 2012, 14, 103049. [Google Scholar]
- Boot, H.A.H.; Harvie, R.B.R.S. Charged particles in a non-uniform radio-frequency field. Nature (London) 1957, 180, 1187. [Google Scholar]
- Kibble, T.W.B. Mutual refraction of electrons and photons. Phys. Rev. 1966, 150, 1060–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Kibble, T.W.B. Refraction of electron beams by intense electromagnetic waves. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1966, 16, 1054–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Quesnel, B.; Mora, P. Theory and simulation of the interaction of ultraintense laser pulses with electrons in vacuum. Phys. Rev. E. 1998, 58, 3719–3732. [Google Scholar]
- Startsev, E.A.; McKinstrie, C.J. Multiple scale derivation of the relativistic ponderomotive force. Phys. Rev. E. 1997, 55, 7527–7535. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, D.; Mulser, P.; Steeb, W.H. Relativistic ponderomotive force, uphill acceleration, and transition to chaos. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 75, 4622–4625. [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre, E.; Malka, G.; Miquel, J.L. Reply to comment on ‘Experimental observation of electrons accelerated in vacuum to relativistic energies by a high-intensity laser’. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 1352. [Google Scholar]
- Malka, G.; Lefebvre, E.; Miquel, J.L. Experimental observation of electrons accelerated in vacuum to relativistic energies by a high-intensity laser. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 3314–3317. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, K.T. Comment on ‘experimental observation of electrons accelerated in vacuum to relativistic energies by a high-intensity laser’. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 1350. [Google Scholar]
- Mora, P.; Quesnel, B. Comment on ‘experimental observation of electrons accelerated in vacuum to relativistic energies by a high-intensity laser’. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 1351. [Google Scholar]
- Hora, H.; Hoelss, M.; Scheid, W.; Wang, J.W.; Ho, Y.K.; Osman, F.; Castillo, R. Principle of high accuracy for the nonlinear theory of the acceleration of electrons in a vacuum by lasers at relativistic intensities. Laser Part. Beams. 2000, 18, 135. [Google Scholar]
- Hartemann, F.V.; van Meter, J.R.; Troha, A.L.; Landahl, E.C.; Luhmann, N.C., Jr.; Baldis, H.A.; Gupta, A.; Kerman, A.K. Three-dimensional relativistic electron scattering in an ultrahigh-intensity laser focus. Phys. Rev. E. 1998, 58, 5001–5012. [Google Scholar]
- Hartemann, F.V.; Fochs, S.N.; Le Sage, G.P.; Luhmann, N.C.; Woodworth, J.G.; Perry, M.D.; Chen, Y.J.; Kerman, A.K. Nonlinear ponderomotive scattering of relativistic electrons by an intense laser field at focus. Phys. Rev. E. 1995, 51, 4833–4843. [Google Scholar]
- Cicchitelli, L.; Hora, H.; Postle, R. Longitudinal field components for laser beams in vacuum. Phys. Rev. A. 1990, 41, 3727–3732. [Google Scholar]
- Maltsev, A.; Ditmire, T. Above threshold ionization in tightly focused, strongly relativistic laser fields. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 053002. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, C.I.; Knauer, J.P.; Meyerhofer, D.D. Observation of the transition from Thomson to Compton scattering in multiphoton interactions with low-energy electrons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 74, 2439–2442. [Google Scholar]
- Stupakov, G.V.; Zolotorev, M.S. Ponderomotive laser acceleration and focusing in vacuum for generation of attosecond electron bunches. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 5274–5277. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Q.; Miyazaki, S.; Kawata, S.; Miyauchi, K.; Nakajima, K.; Masuda, S.; Miyanaga, N.; Ho, Y.K. Electron bunch acceleration and trapping by the ponderomotive force of an intense short-pulse laser. Phys. Plasmas. 2003, 10, 4605–4608. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Q.; Miyazaki, S.; Kawata, S.; Miyauchi, K.; Sakai, K.; Ho, Y.K.; Nakajima, K.; Miyanaga, N.; Limpouch, J.; Andreev, A.A. Electron bunch trapping and compression by an intense focused pulse laser. Phys. Rev. E. 2004, 69, 056502. [Google Scholar]
- Varin, C.; Piché, M. Acceleration of ultra-relativistic electrons using high-intensity TM01 laser beams. Appl. Phys. B. 2002, 74, S83–S88. [Google Scholar]
- Salamin, Y.I. Electron acceleration from rest in vacuum by an axicon Gaussian laser beam. Phys. Rev. A. 2006, 73, 043402. [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard, C.J.R.; Saghafi, S. Electromagnetic Gaussian beams beyond the paraxial approximation. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A. 1999, 16, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar]
- Freiberg, R.J.; Halsted, A.S. Properties of low order transverse modes in argon ion lasers. Appl. Opt. 1969, 8, 355–362. [Google Scholar]
- Fortin, P.L.; Piché, M.; Varin, C. Direct-field electron acceleration with ultrafast radially polarized laser beams: scaling laws and optimization. J. Phys. B. 2010, 43, 025401. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, L.J.; Kärtner, F.X. Direct acceleration of an electron in infinite vacuum by a pulsed radially-polarized laser beam. Opt. Express. 2010, 18, 25035–25051. [Google Scholar]
- Scully, M.O.; Zubairy, M.S. Simple laser accelerator: Optics and particle dynamics. Phys. Rev. A. 1991, 44, 2656–2663. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K.P.; Kumar, M. Electron acceleration by a radially polarized laser pulse during ionization of low density gases. Phys. Rev. ST Accel. Beams. 2011, 14, 30401. [Google Scholar]
- The idea was initially proposed by Moore et al. [103] and by Hu and Starace [104] for ponderomotive acceleration in Gaussian beams.
- Bochkarev, S.G.; Popov, K.I.; Bychenkov, V.Y. Vacuum electron acceleration by a tightly focused, radially polarized, relativistically strong laser pulse. Plasma Phys. Rep. 2011, 37, 603–614. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, L.J.; Kärtner, F.X. Two-color-laser-driven direct electron acceleration in infinite vacuum. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 957–959. [Google Scholar]
- Malav, H.; Maheshwari, K.P.; Senecha, V. Analytical and numerical investigation of the effect of pulse shape of intense, few-cycles TM01 laser on the acceleration of charged particles. Ind. J. Pure & Appl. Phys. 2011, 49, 251–256. [Google Scholar]
- Marceau, V.; April, A.; Piché, M. Electron acceleration driven by ultrashort and nonparaxial radially polarized laser pulses. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 2442–2444. [Google Scholar]
- Mourou, G.A.; Tajima, T.; Bulanov, S.V. Optics in the relativistic regime. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2006, 78, 309–371. [Google Scholar]
- April, A. Ultrashort Strongly Focused Laser Pulses in Free Space. In Coherence and Ultrashort Pulse Laser Emission; Duarte, F.J., Ed.; InTech: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 355–382. [Google Scholar]
- Caron, C.F.R.; Potvliege, R.M. Free-space propagation of ultrashort pulses: Space-time couplings in Gaussian pulse beams. J. Mod. Opt. 1999, 46, 1881–1891. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.; Winful, H.G. Spatiotemporal structure of isodiffracting ultrashort electromagnetic pulses. Phys. Rev. E. 2000, 61, 862–873. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, B.E.; Shiner, A.D.; Lassonde, P.; Kieffer, J.C.; Corkum, P.B.; Villeneuve, D.M.; Légaré, F. CEP stable 1.6 cycle laser pulses at 1.8 μm. Opt. Express. 2011, 19, 6858–6864. [Google Scholar]
- Augst, S.; Meyerhofer, D.D.; Strickland, D.; Chin, S.L. Laser ionization of noble gases by Coulomb-barrier suppression. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B. 1991, 8, 858–867. [Google Scholar]
- Varin, C.; Peltz, C.; Brabec, T.; Fennel, T. Attosecond plasma wave dynamics in laser-driven cluster nanoplasmas. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 175007. [Google Scholar]
- Tovar, A.A. Production and propagation of cylindrically polarized Laguerre-Gaussian laser beams. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A. 1998, 15, 2705–2711. [Google Scholar]
- Pohl, D. Operation of a ruby laser in the purely transverse electric mode TE01. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1972, 20, 266–267. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, M.; Romano, V.; Feurer, T. Material processing with pulsed radially and azimuthally polarized laser radiation. Appl. Phys. A. 2007, 86, 329–334. [Google Scholar]
- Moshe, I.; Jackel, S.; Meir, A. Production of radially or azimuthally polarized beams in solid-state lasers and the elimination of thermally induced birefringence effects. Opt. Lett. 2003, 28, 807–809. [Google Scholar]
- Nesterov, A.V.; Niziev, V.G.; Yakunin, V.P. Generation of high-power radially polarized beam. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 1999, 32, 2871–2875. [Google Scholar]
- Niziev, V.G.; Nesterov, A.V. Influence of beam polarization on laser cutting efficiency. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 1999, 32, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar]
- Kawauchi, H.; Kozawa, Y.; Sato, S. Generation of radially polarized Ti:sapphire laser beam using a c-cut crystal. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 1984–1986. [Google Scholar]
- Tidwell, S.; Ford, D.H.; Kimura, D. Generating radially polarized beams interferometrically. Appl. Opt. 1990, 29, 2234–2239. [Google Scholar]
- Youngworth, K.S.; Brown, T.G. Inhomogenous polarization in scanning optical microscopy. Proc. SPIE. 2000, 3919, 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Churin, E.; Hofeld, J.; Tschudi, T. Polarization configurations with singular point formed by computer generated holograms. Opt. Commun. 1993, 99, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, C.H.; Gu, B.Y.; Dong, B.Z.; Zhang, Y. A new method for generating axially symmetric and radially polarized beams. J. Phys. D. 2005, 38, 827–832. [Google Scholar]
- Machavariani, G.; Lumer, Y.; Moshe, I.; Meir, A.; Jackel, S. Efficient extracavity generation of radially and azimuthally polarized beams. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 1468–1470. [Google Scholar]
- Bomzon, Z.; Biener, G.; Kleiner, V.; Hasman, E. Radially and azimuthally polarized beams generated by space-variant dielectric subwavelength gratings. Opt. Lett. 2002, 27, 285–287. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, L.W. Theory of electromagnetic beams. Phys. Rev. A. 1979, 19, 1177–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, G.P.; Lax, M. Free-space wave propagation beyond the paraxial approximation. Phys. Rev. A. 1983, 27, 1693–1695. [Google Scholar]
- Porras, M.A. Pulse correction to monochromatic light-beam propagation. Opt. Lett. 2001, 26, 44–46. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, W.H. Anomalies in the field of a gaussian beam near focus. Opt. Commun. 1973, 7, 211–218. [Google Scholar]
- Novotny, L.; Hecht, B. Principles of Nano-Optics; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, D.; Guo, Q. Analytical vectorial structure of radially polarized light beams. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 2711–2713. [Google Scholar]
- An der Brügge, D.; Pukhov, A. Ultrashort focused electromagnetic pulses. Phys. Rev. E. 2009, 79, 016603. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, C. I.; Ting, A.; McNaught, S. J.; Qiu, J.; Burris, H. R.; Sprangle;, P. A laser-accelerator injector based on laser ionization and ponderomotive acceleration of electrons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 1688–1691. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S. X.; Starace, A. F. GeV electrons from ultraintense laser interaction with highly charged ions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 245003. [Google Scholar]

| Regime | |
|---|---|
| Non-relativistic | ≪ 1 |
| Relativistic | ~ 1 |
| Ultra-relativistic | ≫ 1 |
| [zi, zf] | Scenario | |
|---|---|---|
| [−∞, ∞] | 0 | Lawson-Woodward [14] |
| [−zR, zR] | ΔWlim | Limited interaction [14,15,69] |
| [0, ∞] | ΔWlim | Single pulse [19,64,72] |
| [zR, ∞] | ΔWlim/2 | Pump-probe [16,18,67] |
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Varin, C.; Payeur, S.; Marceau, V.; Fourmaux, S.; April, A.; Schmidt, B.; Fortin, P.-L.; Thiré, N.; Brabec, T.; Légaré, F.; et al. Direct Electron Acceleration with Radially Polarized Laser Beams. Appl. Sci. 2013, 3, 70-93. https://doi.org/10.3390/app3010070
Varin C, Payeur S, Marceau V, Fourmaux S, April A, Schmidt B, Fortin P-L, Thiré N, Brabec T, Légaré F, et al. Direct Electron Acceleration with Radially Polarized Laser Beams. Applied Sciences. 2013; 3(1):70-93. https://doi.org/10.3390/app3010070
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarin, Charles, Stéphane Payeur, Vincent Marceau, Sylvain Fourmaux, Alexandre April, Bruno Schmidt, Pierre-Louis Fortin, Nicolas Thiré, Thomas Brabec, François Légaré, and et al. 2013. "Direct Electron Acceleration with Radially Polarized Laser Beams" Applied Sciences 3, no. 1: 70-93. https://doi.org/10.3390/app3010070
APA StyleVarin, C., Payeur, S., Marceau, V., Fourmaux, S., April, A., Schmidt, B., Fortin, P.-L., Thiré, N., Brabec, T., Légaré, F., Kieffer, J.-C., & Piché, M. (2013). Direct Electron Acceleration with Radially Polarized Laser Beams. Applied Sciences, 3(1), 70-93. https://doi.org/10.3390/app3010070




