An Improved Geospatial Object Detection Framework for Complex Urban and Environmental Remote Sensing Scenes
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Scale-adaptive feature extraction: Dynamic Convolution adjusts receptive fields via learnable attention, enabling fine-grained representation for small objects and global context for large ones.
- Context-aware multi-path attention: Selective Kernel Attention (SKAttention) fuses multi-branch features with channel-wise attention, enhancing relevant spatial-semantic cues while suppressing background noise.
- Geometry-aware localization loss: Multi-Polar Distance Intersection over Unio (MPDIoU) jointly optimizes center distance, scale, aspect ratio, and vertex alignment, reducing orientation-induced localization errors.
2. YOLOv11 Object Detection Network and Improvements
2.1. YOLOv11 Algorithm
2.2. RS-YOLO Within the GeoAI Framework
- Scale Adaptation: Remote sensing images present significant scale variation challenges, with objects ranging from sub-meter vehicles to kilometer-level ports. To enhance RS-YOLO’s multi-scale adaptation capabilities, a Dynamic Convolution module is innovatively embedded into the feature transmission path from the Backbone to the Neck, enabling better handling of such diverse scale scenarios.
- Use of Geographical Context: Remote sensing scenes exhibit strong spatial structures, such as vehicles clustering in parking areas and vessels appearing near ports. To leverage these spatial co-occurrence patterns, the SKAttention module is inserted into the feature fusion pathway of the Neck region, enabling the model to capture multi-scale contextual information and improve detection accuracy.
- Geometry-Aware Localization: Many geospatial entities are direction-sensitive, such as roads, bridges, and runways. RS-YOLO adopts MPDIoU as the regression loss to provide orientation-aware bounding box prediction, which benefits accurate mapping and GIS integration.
2.3. Enhancing Model Representation with Dynamic Convolution
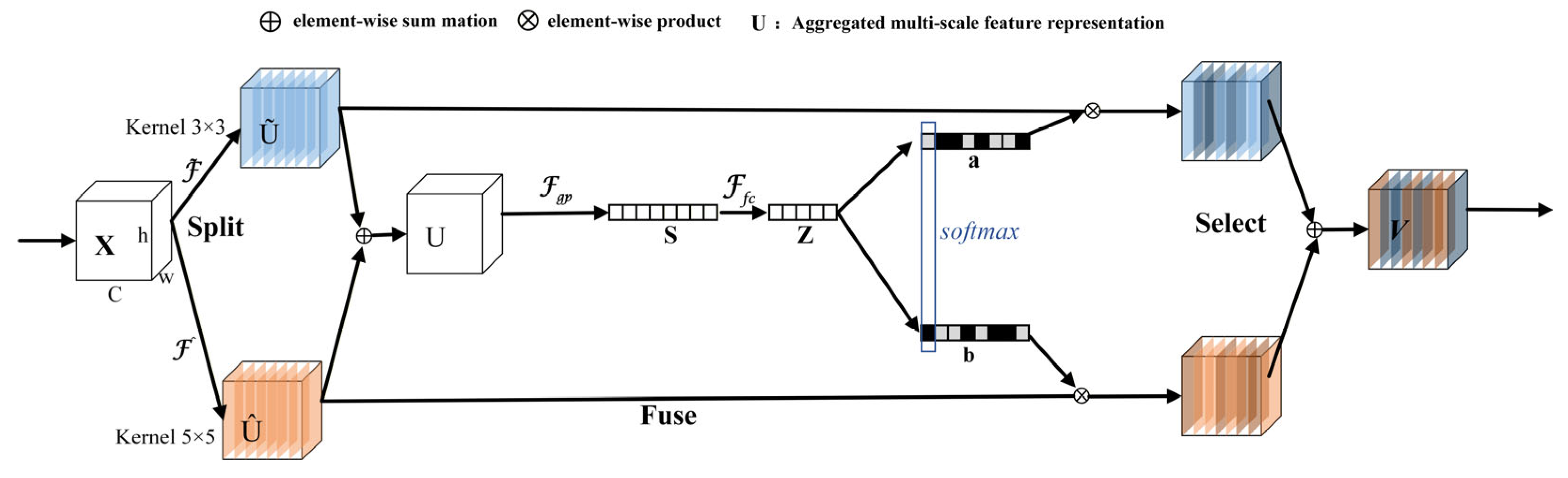
2.4. Feature Refinement with Selective Kernel Attention
2.5. Efficient and Accurate Bounding Box Regression Loss
- The input consists of two convex shapes , within an image of width w and height ;
- Define the coordinates of the top-left and bottom-right corners of shapes and . and represent the top-left and bottom-right corners of shape , while and represent those of shape ;
- Compute the squared distance between the top-left corners of and , . Compute the squared distance between the bottom-right corners of and , ;
- Calculate and output the value, Based on the definition of , the loss function derived from is shown in Equation (1).
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
3.1. Experimental Setup and Data
3.2. Performance Comparison of Different Improvement Modules
3.3. Comparison of Different Object Detection Algorithms
3.4. Geospatial Application Perspective
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASFF | Adaptively Spatial Feature Fusion |
| SPP | Spatial Pyramid Pooling |
| MFAF | Multi-scale Feature Adaptive Fusion |
| FI | Feature Integration |
| SAW | Spatial Attention Weight |
| DE | Detail Enhancement |
| SE | Squeeze-and-Excitation |
| CSP | Cross Stage Partial |
| SPPNet | Spatial Pyramid Pooling Network |
| CSPNet | Cross Stage Partial Network |
| ECA | Efficient Channel Attention |
| VFL | Varifocal Loss |
| SAHI | Slicing Aided Hyper Inference |
| SGFT | Structure-Guided Feature Transform |
| HR | Hybrid Residual |
| DConv | Dynamic Convolution |
| LocalAttn | Local Attention |
| FRPN | Feature Residual Pyramid Network |
| OLCN | Optimized Low-Coupling Network |
| LCRR | Low-Coupling Robust Regression |
| RFOL | Receptive Field Optimization Layer |
| MSSA | Multi-Scale Split Attention |
| MSDPA | Multi-Scale Deformable Prescreening Attention |
| NACAD | Noise-Adaptive Context-Aware Detector |
| NAM | Noise-Adaptive Module |
| CAM | Context-Aware Module |
| PRM | Position-Refined Module |
| DConvTrans-LGA | Dynamic Convolution Transformer with Local-Global Attention |
| LGA | Local-Global Attention |
| SKAttention | Selective Kernel Attention |
| GAP | Global Average Pooling |
| SGD | Stochastic Gradient Descent |
| VHR RSI | Very High Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery |
| GeoAI | Geospatial Artificial Intelligence |
| GIS | Geographic Information Systems |
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
| Faster R-CNN | Faster Region-based Convolutional Neural Network |
References
- Jiang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Miao, S.; Jin, X.; Lee, S.J.; Wozniak, M.; Yao, S. SR_ColorNet: Multi-path attention aggregated and mask enhanced network for the super resolution and colorization of panchromatic image. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 276, 127091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Fan, X.; Wang, X.; Nava, L.; Zhong, H.; Dong, X.; Qi, J.; Catani, F. A globally distributed dataset of coseismic landslide mapping via multi-source high-resolution remote sensing images. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2024, 16, 4817–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Li, Y.; Xie, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, T. Monitoring vessel deadweight tonnage for maritime transportation surveillance using high resolution satellite image. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 239, 106607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, N.; Zhu, R. A novel transformer-based object detection method with geometric and object co-occurrence prior knowledge for remote sensing images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2024, 18, 2383–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Pi, D.; Qin, S. An efficient single shot detector with weight-based feature fusion for small object detection. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, T.; Han, W.; Xu, S. Yolo-rs: A more accurate and faster object detection method for remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Qian, W.; Chen, T.; Yang, H.; Zhou, X. Multiscale feature adaptive fusion for object detection in optical remote sensing images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 6511005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, G.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z. M-YOLO: Traffic sign detection algorithm applicable to complex scenarios. Symmetry 2022, 14, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yuan, G.; Zhou, H.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Wu, H. RS-YOLOX: A high-precision detector for object detection in satellite remote sensing images. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Song, R.; Xie, W.; Li, Y.; Du, Q. Structure-guided feature transform hybrid residual network for remote sensing object detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5610713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Jiao, D.; Huang, X.; Tang, T.; Gui, G. A hybrid CNN-transformer network for object detection in optical remote sensing images: Integrating local and global feature fusion. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2024, 18, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Y. OLCN: An optimized low coupling network for small objects detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 8022005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cao, C.; Feng, Z.; Xu, X.; Wu, Z.; Ye, S.; Yong, J. Remote sensing object detection based on strong feature extraction and prescreening network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 8000505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, D. NACAD: A noise-adaptive context-aware detector for remote sensing small objects. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1001413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M.; Wu, Y.H.; Chen, P.Y.; Hsieh, J.W.; Yeh, I.H. CSPNet: A new backbone that can enhance learning capability of CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 390–391. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8759–8768. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Dai, X.; Liu, M.; Chen, D.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Z. Dynamic convolution: Attention over convolution kernels. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11030–11039. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Xu, Y. Mpdiou: A loss for efficient and accurate bounding box regression. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.07662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Feng, Y.; Lu, X. Hierarchical and robust convolutional neural network for very high-resolution remote sensing object detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 5535–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.S.; Bai, X.; Ding, J.; Zhu, Z.; Belongie, S.; Luo, J.; Datcu, M.; Pelillo, M.; Zhang, L. DOTA: A large-scale dataset for object detection in aerial images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3974–3983. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Wan, G.; Cheng, G.; Meng, L.; Han, J. Object detection in optical remote sensing images: A survey and a new benchmark. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 159, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, T.; Xu, D. Object detection in remote sensing images based on improved YOLOv8 algorithm. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2024, 61, 1028001. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Wang, J.; Li, K.; Xie, X.; Lang, C.; Yao, Y.; Han, J. Anchor-free oriented proposal generator for object detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5625411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Module | Function |
|---|---|
| Conv | Basic convolution with BN and SiLU activation |
| C2f | CSP bottleneck with residual connections |
| C3k2 | Dynamic kernel feature extraction |
| SPPF | Multi-scale spatial pooling for context |
| Upsample | Resolution enhancement for feature fusion |
| Concat | Feature concatenation along the channel dimension |
| Category | Number of Samples | Typical Size | Rotation Range | Scene Type | Background Complexity | Scale Group | Boundary Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Airplane | 757 | 50–200 | 0–360° | Urban | Medium | Medium | Medium |
| Baseball diamond | 390 | 100–300 | 0°, 180° | Urban | Medium | Medium | High |
| Basketball court | 159 | 80–250 | 0°, 180° | Urban | Medium | Medium | Low |
| Bridge | 124 | 150–500 | 0–90° | River/canyon and Urban overpasses | High and medium | Medium | High |
| Cross road | 5401 | 200–800 | 0–90° | Urban | High | Large | High |
| Ground track field | 163 | 300–600 | 0–45° | Urban | Medium | Medium | Low |
| Harbor | 224 | 500–2000 | 0–180° | Coastline | High | Large | Medium |
| Parking | 5417 | 400–1500 | 0–90° | Urban | High | Large | Low |
| Ship | 302 | 100–500 | 0–360° | Coastline | High | Medium | Medium |
| Storage tank | 655 | 100–400 | 0° | Industrial zone | Low | Medium | Low |
| T junction | 543 | 150–400 | 0–90° | Urban | High | Medium | High |
| Tennis court | 524 | 100–300 | 0°, 90° | Urban | Medium | Medium | Low |
| Vehicle | 4961 | 20–100 | 0–360° | Urban | High | Small | Medium |
| YOLOv11n | (+) SKAttention | (+) Dynamic | (+) MPDIoU | RS-YOLO (Ours) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP | 87.0% | 89.8% | 88.7% | 87.0% | 89.0% |
| Bridge | 90.9% | 88.8% | 91.4% | 91.9% | 94.4% |
| Airplane | 99.3% | 99.3% | 99.4% | 99.2% | 99.3% |
| Ground track field | 96.7% | 97.5% | 97.8% | 97% | 98% |
| Vehicle | 93.1% | 94.5% | 95.5% | 91% | 95.1% |
| Parking | 67.7% | 67.0% | 66.7% | 64% | 71.8% |
| T junction | 71.6% | 71.0% | 72.5% | 72.4% | 81.0% |
| Baseball diamond | 79.2% | 79.2% | 78.4% | 82.9% | 78.8% |
| Tennis court | 91.7% | 91.7% | 91.5% | 89.7% | 91.2% |
| Basketball court | 67% | 65.5% | 69.7% | 63% | 66.6% |
| Ship | 89.1% | 89.8% | 86.9% | 88.2% | 93.0% |
| Cross road | 88.3% | 89.1% | 89.5% | 88.9% | 91.4% |
| Harbor | 97.9% | 99.0% | 96.8% | 96.5% | 99.2% |
| Storage tank | 98.2% | 98.2% | 97.9% | 97.8% | 98.2% |
| Model | mAP (%) | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|
| Swin Transformer [23] | 82.00 | 63.10 |
| YOLOv5 | 84.40 | 85.00 |
| YOLOv8n | 85.70 | 83.00 |
| YOLOv11n | 87.00 | 85.00 |
| Faster R-CNN [24] | 81.40 | 64.90 |
| Xie’s [6] | 88.39 | / |
| MFAF [7] | 86.90 | / |
| Liu’s [8] | 85.50 | / |
| SGFTHR [10] | 86.38 | / |
| DConvTrans-LGA [11] | 82.10 | 63.88 |
| OLCN [12] | 60.00 | / |
| Li’s [13] | 86.30 | / |
| NACAD [14] | 88.60 | / |
| RS-YOLO (Ours) | 89.00 | 87.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Chen, A.; Li, X.; Pan, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, N.; Chen, W.; Huang, J.; Cai, J.; Fu, H. An Improved Geospatial Object Detection Framework for Complex Urban and Environmental Remote Sensing Scenes. Appl. Sci. 2026, 16, 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16031288
Zhu Y, Chen A, Li X, Pan Y, Yuan Y, Yang N, Chen W, Huang J, Cai J, Fu H. An Improved Geospatial Object Detection Framework for Complex Urban and Environmental Remote Sensing Scenes. Applied Sciences. 2026; 16(3):1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16031288
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yueying, Aidong Chen, Xiang Li, Yu Pan, Yanwei Yuan, Ning Yang, Wenwen Chen, Jiawang Huang, Jun Cai, and Hui Fu. 2026. "An Improved Geospatial Object Detection Framework for Complex Urban and Environmental Remote Sensing Scenes" Applied Sciences 16, no. 3: 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16031288
APA StyleZhu, Y., Chen, A., Li, X., Pan, Y., Yuan, Y., Yang, N., Chen, W., Huang, J., Cai, J., & Fu, H. (2026). An Improved Geospatial Object Detection Framework for Complex Urban and Environmental Remote Sensing Scenes. Applied Sciences, 16(3), 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16031288








