Weighted Decision Aggregation for Dispersed Data in Unified and Diverse Coalitions
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel coalition-based approach for dispersed data classification with unified and diverse coalition formation strategies and their impact on accuracy.
- Integration of Pawlak’s conflict model to systematically identify compatible and diverse classifier groups.
- Evaluation of weighted vs. unweighted prediction aggregation, demonstrating how weighting schemes affect decision reliability.
- Introduction and evaluation of three strategies for coalition-based classification: single strongest coalition, two strongest coalitions, and all coalitions.
2. Related Works
3. Research Methods and Approach
| Algorithm 1: Creation of coalitions |
 |
| Algorithm 2: Weighted fusion of prediction vectors from selected coalitions |
 |
- without weights—aggregated vector , final decision ;
- with weights—aggregated vector , final decision .However, when considering diverse coalitions, the results will differ. For the single strongest coalition , we obtain
- without weights—aggregated vector , final decision ;
- with weights—aggregated vector , final decision .For the two strongest coalitions and all coalitions, we get
- without weights—aggregated vector , final decision ;
- with weights—aggregated vector , final decision .As demonstrated in the example, the choice of coalition type, the decision-making strategy, and the application of weights all play a crucial role in determining the final decision. This analysis underscores the necessity of selecting the appropriate coalition structure and weighting strategy based on the specific problem domain to improve classification accuracy and decision reliability.
4. Datasets and Experimental Design
- AL—prediction vectors from the abstract level;
- ML—prediction vectors from the measurement level;
- W—means that the weights for the prediction vectors were used;
- U—means that unified coalitions were used;
- D—means that diverse coalitions were used;
- 1—means that the final decision is made by one strongest coalition;
- 2—means that the final decision is made by two strongest coalitions;
- All—means that the final decision is taken by all coalitions.
- By systematically combining various approaches to explore all feasible and meaningful configurations, 4 baseline approaches without coalitions and 24 distinct approaches with coalitions and voting were obtained:
- AL—local classifiers generate predictions from the abstract level, and then the vectors are summed.
- AL-W—local classifiers generate predictions from the abstract level, and then the vectors are summed using weights proportional to the quality of the model evaluated on the validation set.
- U-AL-1—unified coalitions are created, local classifiers generate predictions from the abstract level, and, finally, the prediction vectors from only the one strongest coalition are summed.
- U-AL-All—unified coalitions are created, local classifiers generate predictions from the abstract level, and, finally, the prediction vectors from all coalitions are summed.
- U-AL-2—unified coalitions are created, local classifiers generate predictions from the abstract level, and, finally, the prediction vectors from only the two strongest coalitions are summed.
- U-AL-W-1—similar to U-AL-1 but, when summing prediction vectors, weights proportional to the quality of the local model are used.
- U-AL-W-All—similar to U-AL-All but, when summing prediction vectors, weights proportional to the quality of the local model are used.
- U-AL-W-2—similar to U-AL-2 but, when summing prediction vectors, weights proportional to the quality of the local model are used.
- D-AL-1—diverse coalitions are created, local classifiers generate predictions from the abstract level, and, finally, the prediction vectors from only the one strongest coalition are summed.
- D-AL-All—diverse coalitions are created, local classifiers generate predictions from the abstract level, and, finally, the prediction vectors from all coalitions are summed.
- D-AL-2—diverse coalitions are created, local classifiers generate predictions from the abstract level, and, finally, the prediction vectors from only the two strongest coalitions are summed.
- D-AL-W-1—similar to D-AL-1 but, when summing prediction vectors, weights proportional to the quality of the local model are used.
- D-AL-W-All—similar to D-AL-All but, when summing prediction vectors, weights proportional to the quality of the local model are used.
- D-AL-W-2—similar to D-AL-2 but, when summing prediction vectors, weights proportional to the quality of the local model are used.All the above approaches were also used in combination with prediction vectors from the measurement level. Thus, we obtained approaches ML, ML-W, U-ML-1, U-ML-All, U-ML-2, U-ML-W-1, U-ML-W-All, U-ML-W-2, D-ML-1, D-ML-All, D-ML-2, D-ML-W-1, D-ML-W-All, and D-ML-W-2.
- k-Nearest Neighbors (KNN);
- Decision Tree (DT);
- Gradient Boosting (GB);
- Random Forest (RF);
- Random Subspace (RS);
- AdaBoost.
- Various numbers of estimators were tested for Gradient Boosting, Random Forest, Random Subspace, and AdaBoost, specifically 20, 50, 100, 200, and 500. The tables present the best result achieved, along with the corresponding number of estimators that produced this outcome. For each dataset, the table indicates the best result obtained. The following parameter values were tested for the k-Nearest Neighbors classifier: 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5. The Decision Tree was built with defaults in the sklearn library in Python 3.13.0. The stages of building Random Subspace model from Decision Trees are presented in Algorithm 3. From all these parameters, the best results were selected and are included in Table A1, Table A2, Table A3, Table A4, Table A5, Table A6, Table A7, Table A8, Table A9, Table A10, Table A11, Table A12, Table A13, Table A14, Table A15, Table A16, Table A17, Table A18, Table A19, Table A20 and Table A21 in Appendix A. The values presented in the tables represent the average metrics calculated across all 10 evaluations. For each dataset, the best-performing score is highlighted in blue to indicate the top result.
| Algorithm 3: Creation of Random Subspace model |
 |
5. Experimental Results and Comparisons
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Detailed Experimental Results
| Method | K-Nearest Neighbors | Decision Tree | Gradient Boosting | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.673 | 0.62 | 0.194 | 0.62 | 0.712 | 0.66 | 0.312 | 0.66 | 0.646 | 0.609 | 0.31 | 0.609 |
| ML | 0.701 | 0.711 | 0.232 | 0.711 | 0.737 | 0.678 | 0.329 | 0.678 | 0.704 | 0.68 | 0.348 | 0.68 |
| AL-W | 0.716 | 0.696 | 0.263 | 0.696 | 0.719 | 0.671 | 0.308 | 0.671 | 0.688 | 0.66 | 0.26 | 0.66 |
| ML-W | 0.715 | 0.711 | 0.227 | 0.711 | 0.717 | 0.664 | 0.277 | 0.664 | 0.67 | 0.667 | 0.246 | 0.667 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.591 | 0.553 | 0.182 | 0.553 | 0.691 | 0.656 | 0.328 | 0.656 | 0.66 | 0.609 | 0.305 | 0.609 |
| U-AL-All | 0.65 | 0.629 | 0.197 | 0.629 | 0.732 | 0.678 | 0.329 | 0.678 | 0.683 | 0.629 | 0.328 | 0.629 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.659 | 0.66 | 0.217 | 0.66 | 0.712 | 0.66 | 0.312 | 0.66 | 0.646 | 0.609 | 0.31 | 0.609 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.655 | 0.631 | 0.212 | 0.631 | 0.717 | 0.671 | 0.307 | 0.671 | 0.688 | 0.66 | 0.26 | 0.66 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.701 | 0.707 | 0.254 | 0.707 | 0.717 | 0.671 | 0.307 | 0.671 | 0.688 | 0.66 | 0.26 | 0.66 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.702 | 0.707 | 0.254 | 0.707 | 0.716 | 0.664 | 0.304 | 0.664 | 0.688 | 0.66 | 0.26 | 0.66 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.6 | 0.551 | 0.186 | 0.551 | 0.699 | 0.658 | 0.317 | 0.658 | 0.658 | 0.611 | 0.311 | 0.611 |
| D-AL-All | 0.657 | 0.584 | 0.189 | 0.584 | 0.732 | 0.678 | 0.329 | 0.678 | 0.683 | 0.629 | 0.328 | 0.629 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.65 | 0.596 | 0.195 | 0.596 | 0.699 | 0.658 | 0.317 | 0.658 | 0.658 | 0.611 | 0.311 | 0.611 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.602 | 0.502 | 0.191 | 0.502 | 0.718 | 0.667 | 0.304 | 0.667 | 0.688 | 0.66 | 0.26 | 0.66 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.628 | 0.591 | 0.191 | 0.591 | 0.718 | 0.667 | 0.304 | 0.667 | 0.688 | 0.66 | 0.26 | 0.66 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.634 | 0.589 | 0.19 | 0.589 | 0.718 | 0.667 | 0.304 | 0.667 | 0.688 | 0.66 | 0.26 | 0.66 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.713 | 0.713 | 0.228 | 0.713 | 0.707 | 0.651 | 0.287 | 0.651 | 0.704 | 0.68 | 0.348 | 0.68 |
| U-ML-All | 0.717 | 0.713 | 0.228 | 0.713 | 0.704 | 0.653 | 0.292 | 0.653 | 0.704 | 0.68 | 0.348 | 0.68 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.717 | 0.713 | 0.228 | 0.713 | 0.704 | 0.653 | 0.292 | 0.653 | 0.704 | 0.68 | 0.348 | 0.68 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.714 | 0.713 | 0.228 | 0.713 | 0.713 | 0.656 | 0.273 | 0.656 | 0.67 | 0.667 | 0.246 | 0.667 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.72 | 0.713 | 0.228 | 0.713 | 0.713 | 0.656 | 0.273 | 0.656 | 0.67 | 0.667 | 0.246 | 0.667 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.72 | 0.713 | 0.228 | 0.713 | 0.713 | 0.656 | 0.273 | 0.656 | 0.67 | 0.667 | 0.246 | 0.667 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.642 | 0.678 | 0.211 | 0.678 | 0.69 | 0.656 | 0.321 | 0.656 | 0.704 | 0.68 | 0.348 | 0.68 |
| D-ML-All | 0.669 | 0.678 | 0.219 | 0.678 | 0.7 | 0.649 | 0.291 | 0.649 | 0.704 | 0.68 | 0.348 | 0.68 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.694 | 0.698 | 0.224 | 0.698 | 0.701 | 0.651 | 0.298 | 0.651 | 0.704 | 0.68 | 0.348 | 0.68 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.681 | 0.656 | 0.214 | 0.656 | 0.714 | 0.66 | 0.275 | 0.66 | 0.67 | 0.667 | 0.246 | 0.667 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.685 | 0.66 | 0.215 | 0.66 | 0.713 | 0.656 | 0.273 | 0.656 | 0.67 | 0.667 | 0.246 | 0.667 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.704 | 0.702 | 0.225 | 0.702 | 0.713 | 0.656 | 0.273 | 0.656 | 0.67 | 0.667 | 0.246 | 0.667 |
| Method | Random Forest | Random Subspace | AdaBoost | |||||||||
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.678 | 0.664 | 0.303 | 0.664 | 0.691 | 0.678 | 0.325 | 0.678 | 0.743 | 0.56 | 0.255 | 0.56 |
| ML | 0.803 | 0.767 | 0.35 | 0.767 | 0.756 | 0.729 | 0.348 | 0.729 | 0.714 | 0.689 | 0.227 | 0.689 |
| AL-W | 0.764 | 0.729 | 0.33 | 0.729 | 0.71 | 0.684 | 0.33 | 0.684 | 0.788 | 0.622 | 0.302 | 0.622 |
| ML-W | 0.777 | 0.74 | 0.301 | 0.74 | 0.732 | 0.724 | 0.34 | 0.724 | 0.758 | 0.689 | 0.23 | 0.689 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.667 | 0.656 | 0.298 | 0.656 | 0.706 | 0.673 | 0.332 | 0.673 | 0.698 | 0.558 | 0.264 | 0.558 |
| U-AL-All | 0.695 | 0.64 | 0.278 | 0.64 | 0.714 | 0.669 | 0.341 | 0.669 | 0.701 | 0.547 | 0.266 | 0.547 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.678 | 0.664 | 0.303 | 0.664 | 0.699 | 0.682 | 0.327 | 0.682 | 0.743 | 0.56 | 0.255 | 0.56 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.76 | 0.727 | 0.329 | 0.727 | 0.72 | 0.702 | 0.329 | 0.702 | 0.788 | 0.622 | 0.302 | 0.622 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.76 | 0.727 | 0.329 | 0.727 | 0.72 | 0.702 | 0.329 | 0.702 | 0.788 | 0.622 | 0.302 | 0.622 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.76 | 0.727 | 0.329 | 0.727 | 0.72 | 0.702 | 0.329 | 0.702 | 0.788 | 0.622 | 0.302 | 0.622 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.754 | 0.72 | 0.331 | 0.72 | 0.706 | 0.693 | 0.363 | 0.693 | 0.717 | 0.547 | 0.249 | 0.547 |
| D-AL-All | 0.74 | 0.7 | 0.312 | 0.7 | 0.738 | 0.72 | 0.373 | 0.72 | 0.701 | 0.547 | 0.266 | 0.547 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.759 | 0.724 | 0.332 | 0.724 | 0.75 | 0.733 | 0.368 | 0.733 | 0.717 | 0.547 | 0.249 | 0.547 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.785 | 0.749 | 0.342 | 0.749 | 0.71 | 0.696 | 0.358 | 0.696 | 0.788 | 0.622 | 0.302 | 0.622 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.79 | 0.751 | 0.343 | 0.751 | 0.768 | 0.744 | 0.358 | 0.744 | 0.788 | 0.622 | 0.302 | 0.622 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.79 | 0.751 | 0.343 | 0.751 | 0.768 | 0.744 | 0.358 | 0.744 | 0.788 | 0.622 | 0.302 | 0.622 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.803 | 0.767 | 0.35 | 0.767 | 0.753 | 0.729 | 0.345 | 0.729 | 0.714 | 0.689 | 0.227 | 0.689 |
| U-ML-All | 0.803 | 0.767 | 0.35 | 0.767 | 0.755 | 0.731 | 0.345 | 0.731 | 0.714 | 0.689 | 0.227 | 0.689 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.803 | 0.767 | 0.35 | 0.767 | 0.753 | 0.729 | 0.344 | 0.729 | 0.714 | 0.689 | 0.227 | 0.689 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.777 | 0.74 | 0.301 | 0.74 | 0.732 | 0.724 | 0.34 | 0.724 | 0.758 | 0.689 | 0.23 | 0.689 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.777 | 0.74 | 0.301 | 0.74 | 0.732 | 0.724 | 0.34 | 0.724 | 0.758 | 0.689 | 0.23 | 0.689 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.777 | 0.74 | 0.301 | 0.74 | 0.732 | 0.724 | 0.34 | 0.724 | 0.758 | 0.689 | 0.23 | 0.689 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.803 | 0.767 | 0.35 | 0.767 | 0.723 | 0.724 | 0.343 | 0.724 | 0.714 | 0.689 | 0.227 | 0.689 |
| D-ML-All | 0.803 | 0.767 | 0.35 | 0.767 | 0.726 | 0.729 | 0.344 | 0.729 | 0.714 | 0.689 | 0.227 | 0.689 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.803 | 0.767 | 0.35 | 0.767 | 0.741 | 0.729 | 0.352 | 0.729 | 0.714 | 0.689 | 0.227 | 0.689 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.778 | 0.738 | 0.3 | 0.738 | 0.725 | 0.724 | 0.343 | 0.724 | 0.758 | 0.689 | 0.23 | 0.689 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.777 | 0.74 | 0.301 | 0.74 | 0.726 | 0.729 | 0.344 | 0.729 | 0.758 | 0.689 | 0.23 | 0.689 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.777 | 0.74 | 0.301 | 0.74 | 0.736 | 0.727 | 0.351 | 0.727 | 0.758 | 0.689 | 0.23 | 0.689 |
| Method | K-Nearest Neighbors | Decision Tree | Gradient Boosting | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.778 | 0.784 | 0.466 | 0.784 | 0.939 | 0.937 | 0.864 | 0.937 | 0.963 | 0.962 | 0.836 | 0.962 |
| ML | 0.811 | 0.812 | 0.452 | 0.812 | 0.944 | 0.942 | 0.861 | 0.942 | 0.967 | 0.965 | 0.874 | 0.965 |
| AL-W | 0.784 | 0.785 | 0.459 | 0.785 | 0.936 | 0.935 | 0.859 | 0.935 | 0.962 | 0.961 | 0.831 | 0.961 |
| ML-W | 0.798 | 0.802 | 0.46 | 0.802 | 0.936 | 0.935 | 0.859 | 0.935 | 0.966 | 0.964 | 0.869 | 0.964 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.779 | 0.786 | 0.48 | 0.786 | 0.938 | 0.937 | 0.862 | 0.937 | 0.962 | 0.961 | 0.831 | 0.961 |
| U-AL-All | 0.803 | 0.792 | 0.467 | 0.792 | 0.944 | 0.942 | 0.861 | 0.942 | 0.962 | 0.961 | 0.831 | 0.961 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.778 | 0.787 | 0.485 | 0.787 | 0.938 | 0.937 | 0.862 | 0.937 | 0.962 | 0.962 | 0.833 | 0.962 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.784 | 0.788 | 0.477 | 0.788 | 0.936 | 0.935 | 0.859 | 0.935 | 0.962 | 0.961 | 0.831 | 0.961 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.785 | 0.788 | 0.477 | 0.788 | 0.936 | 0.935 | 0.859 | 0.935 | 0.962 | 0.961 | 0.831 | 0.961 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.785 | 0.788 | 0.477 | 0.788 | 0.936 | 0.935 | 0.859 | 0.935 | 0.962 | 0.961 | 0.831 | 0.961 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.752 | 0.75 | 0.483 | 0.75 | 0.94 | 0.938 | 0.861 | 0.938 | 0.956 | 0.956 | 0.828 | 0.956 |
| D-AL-All | 0.78 | 0.772 | 0.44 | 0.772 | 0.944 | 0.942 | 0.861 | 0.942 | 0.958 | 0.957 | 0.818 | 0.957 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.76 | 0.778 | 0.475 | 0.778 | 0.938 | 0.937 | 0.86 | 0.937 | 0.956 | 0.956 | 0.819 | 0.956 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.754 | 0.759 | 0.489 | 0.759 | 0.936 | 0.935 | 0.859 | 0.935 | 0.952 | 0.952 | 0.812 | 0.952 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.768 | 0.786 | 0.489 | 0.786 | 0.936 | 0.935 | 0.859 | 0.935 | 0.962 | 0.958 | 0.822 | 0.958 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.768 | 0.786 | 0.489 | 0.786 | 0.936 | 0.935 | 0.859 | 0.935 | 0.962 | 0.958 | 0.822 | 0.958 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.789 | 0.803 | 0.462 | 0.803 | 0.937 | 0.936 | 0.856 | 0.936 | 0.967 | 0.965 | 0.874 | 0.965 |
| U-ML-All | 0.789 | 0.803 | 0.462 | 0.803 | 0.937 | 0.936 | 0.859 | 0.936 | 0.967 | 0.965 | 0.874 | 0.965 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.789 | 0.803 | 0.462 | 0.803 | 0.937 | 0.936 | 0.856 | 0.936 | 0.967 | 0.965 | 0.874 | 0.965 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.795 | 0.803 | 0.467 | 0.803 | 0.936 | 0.935 | 0.859 | 0.935 | 0.966 | 0.964 | 0.869 | 0.964 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.795 | 0.803 | 0.467 | 0.803 | 0.936 | 0.935 | 0.859 | 0.935 | 0.966 | 0.964 | 0.869 | 0.964 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.795 | 0.803 | 0.467 | 0.803 | 0.936 | 0.935 | 0.859 | 0.935 | 0.966 | 0.964 | 0.869 | 0.964 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.781 | 0.798 | 0.465 | 0.798 | 0.938 | 0.937 | 0.859 | 0.937 | 0.96 | 0.957 | 0.835 | 0.957 |
| D-ML-All | 0.78 | 0.798 | 0.464 | 0.798 | 0.938 | 0.937 | 0.859 | 0.937 | 0.962 | 0.959 | 0.837 | 0.959 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.784 | 0.801 | 0.468 | 0.801 | 0.937 | 0.936 | 0.854 | 0.936 | 0.962 | 0.959 | 0.837 | 0.959 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.784 | 0.796 | 0.467 | 0.796 | 0.936 | 0.935 | 0.859 | 0.935 | 0.96 | 0.957 | 0.835 | 0.957 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.783 | 0.796 | 0.466 | 0.796 | 0.936 | 0.935 | 0.859 | 0.935 | 0.962 | 0.959 | 0.837 | 0.959 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.787 | 0.799 | 0.467 | 0.799 | 0.936 | 0.935 | 0.859 | 0.935 | 0.962 | 0.959 | 0.837 | 0.959 |
| Method | Random Forest | Random Subspace | AdaBoost | |||||||||
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.904 | 0.903 | 0.727 | 0.903 | 0.756 | 0.763 | 0.343 | 0.763 | 0.842 | 0.852 | 0.606 | 0.852 |
| ML | 0.916 | 0.912 | 0.736 | 0.912 | 0.766 | 0.768 | 0.333 | 0.768 | 0.834 | 0.843 | 0.59 | 0.843 |
| AL-W | 0.905 | 0.905 | 0.739 | 0.905 | 0.763 | 0.766 | 0.361 | 0.766 | 0.845 | 0.854 | 0.609 | 0.854 |
| ML-W | 0.917 | 0.913 | 0.747 | 0.913 | 0.768 | 0.768 | 0.337 | 0.768 | 0.836 | 0.845 | 0.591 | 0.845 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.905 | 0.904 | 0.732 | 0.904 | 0.772 | 0.78 | 0.369 | 0.78 | 0.842 | 0.852 | 0.606 | 0.852 |
| U-AL-All | 0.903 | 0.901 | 0.714 | 0.901 | 0.764 | 0.777 | 0.349 | 0.777 | 0.846 | 0.855 | 0.61 | 0.855 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.904 | 0.904 | 0.729 | 0.904 | 0.772 | 0.78 | 0.366 | 0.78 | 0.842 | 0.852 | 0.606 | 0.852 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.905 | 0.905 | 0.739 | 0.905 | 0.774 | 0.781 | 0.376 | 0.781 | 0.845 | 0.854 | 0.609 | 0.854 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.905 | 0.905 | 0.739 | 0.905 | 0.774 | 0.781 | 0.376 | 0.781 | 0.845 | 0.854 | 0.609 | 0.854 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.905 | 0.905 | 0.739 | 0.905 | 0.774 | 0.781 | 0.376 | 0.781 | 0.845 | 0.854 | 0.609 | 0.854 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.892 | 0.896 | 0.71 | 0.896 | 0.765 | 0.778 | 0.368 | 0.778 | 0.825 | 0.832 | 0.589 | 0.832 |
| D-AL-All | 0.902 | 0.902 | 0.701 | 0.902 | 0.762 | 0.778 | 0.362 | 0.778 | 0.842 | 0.84 | 0.59 | 0.84 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.895 | 0.9 | 0.714 | 0.9 | 0.765 | 0.779 | 0.371 | 0.779 | 0.839 | 0.845 | 0.598 | 0.845 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.899 | 0.902 | 0.749 | 0.902 | 0.773 | 0.785 | 0.39 | 0.785 | 0.829 | 0.834 | 0.582 | 0.834 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.904 | 0.907 | 0.729 | 0.907 | 0.77 | 0.782 | 0.384 | 0.782 | 0.842 | 0.85 | 0.603 | 0.85 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.904 | 0.907 | 0.729 | 0.907 | 0.771 | 0.782 | 0.384 | 0.782 | 0.842 | 0.85 | 0.603 | 0.85 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.914 | 0.911 | 0.736 | 0.911 | 0.766 | 0.764 | 0.331 | 0.764 | 0.834 | 0.843 | 0.59 | 0.843 |
| U-ML-All | 0.915 | 0.912 | 0.743 | 0.912 | 0.762 | 0.763 | 0.329 | 0.763 | 0.834 | 0.843 | 0.59 | 0.843 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.915 | 0.912 | 0.739 | 0.912 | 0.766 | 0.764 | 0.331 | 0.764 | 0.834 | 0.843 | 0.59 | 0.843 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.916 | 0.913 | 0.747 | 0.913 | 0.768 | 0.768 | 0.337 | 0.768 | 0.836 | 0.845 | 0.591 | 0.845 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.916 | 0.913 | 0.747 | 0.913 | 0.768 | 0.768 | 0.337 | 0.768 | 0.836 | 0.845 | 0.591 | 0.845 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.918 | 0.914 | 0.752 | 0.914 | 0.768 | 0.768 | 0.337 | 0.768 | 0.836 | 0.845 | 0.591 | 0.845 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.914 | 0.912 | 0.744 | 0.912 | 0.76 | 0.765 | 0.335 | 0.765 | 0.837 | 0.841 | 0.587 | 0.841 |
| D-ML-All | 0.917 | 0.915 | 0.752 | 0.915 | 0.758 | 0.762 | 0.328 | 0.762 | 0.834 | 0.839 | 0.572 | 0.839 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.918 | 0.915 | 0.753 | 0.915 | 0.762 | 0.762 | 0.33 | 0.762 | 0.834 | 0.839 | 0.572 | 0.839 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.914 | 0.912 | 0.754 | 0.912 | 0.764 | 0.769 | 0.342 | 0.769 | 0.837 | 0.841 | 0.576 | 0.841 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.918 | 0.915 | 0.76 | 0.915 | 0.766 | 0.768 | 0.339 | 0.768 | 0.835 | 0.84 | 0.574 | 0.84 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.918 | 0.916 | 0.762 | 0.916 | 0.767 | 0.767 | 0.338 | 0.767 | 0.835 | 0.84 | 0.574 | 0.84 |
| Method | K-Nearest Neighbors | Decision Tree | Gradient Boosting | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.765 | 0.795 | 0.428 | 0.795 | 0.924 | 0.923 | 0.804 | 0.923 | 0.933 | 0.925 | 0.758 | 0.925 |
| ML | 0.738 | 0.77 | 0.393 | 0.77 | 0.932 | 0.927 | 0.796 | 0.927 | 0.937 | 0.929 | 0.75 | 0.929 |
| AL-W | 0.772 | 0.795 | 0.424 | 0.795 | 0.931 | 0.929 | 0.841 | 0.929 | 0.937 | 0.928 | 0.765 | 0.928 |
| ML-W | 0.751 | 0.779 | 0.407 | 0.779 | 0.931 | 0.929 | 0.843 | 0.929 | 0.937 | 0.929 | 0.751 | 0.929 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.766 | 0.795 | 0.422 | 0.795 | 0.926 | 0.924 | 0.81 | 0.924 | 0.933 | 0.926 | 0.759 | 0.926 |
| U-AL-All | 0.776 | 0.793 | 0.401 | 0.793 | 0.932 | 0.927 | 0.796 | 0.927 | 0.939 | 0.93 | 0.765 | 0.93 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.766 | 0.792 | 0.424 | 0.792 | 0.924 | 0.923 | 0.804 | 0.923 | 0.933 | 0.925 | 0.758 | 0.925 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.77 | 0.796 | 0.425 | 0.796 | 0.931 | 0.929 | 0.843 | 0.929 | 0.937 | 0.928 | 0.765 | 0.928 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.772 | 0.794 | 0.424 | 0.794 | 0.93 | 0.928 | 0.843 | 0.928 | 0.937 | 0.928 | 0.765 | 0.928 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.777 | 0.795 | 0.442 | 0.795 | 0.931 | 0.929 | 0.843 | 0.929 | 0.937 | 0.928 | 0.765 | 0.928 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.7 | 0.703 | 0.42 | 0.703 | 0.919 | 0.919 | 0.784 | 0.919 | 0.891 | 0.888 | 0.709 | 0.888 |
| D-AL-All | 0.764 | 0.741 | 0.409 | 0.741 | 0.932 | 0.927 | 0.796 | 0.927 | 0.895 | 0.901 | 0.644 | 0.901 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.736 | 0.715 | 0.41 | 0.715 | 0.925 | 0.923 | 0.799 | 0.923 | 0.901 | 0.898 | 0.729 | 0.898 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.708 | 0.702 | 0.436 | 0.702 | 0.931 | 0.929 | 0.843 | 0.929 | 0.906 | 0.904 | 0.758 | 0.904 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.747 | 0.755 | 0.423 | 0.755 | 0.931 | 0.929 | 0.843 | 0.929 | 0.902 | 0.904 | 0.699 | 0.904 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.737 | 0.707 | 0.409 | 0.707 | 0.931 | 0.929 | 0.843 | 0.929 | 0.911 | 0.909 | 0.765 | 0.909 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.736 | 0.768 | 0.387 | 0.768 | 0.926 | 0.924 | 0.814 | 0.924 | 0.937 | 0.929 | 0.75 | 0.929 |
| U-ML-All | 0.736 | 0.77 | 0.402 | 0.77 | 0.926 | 0.924 | 0.814 | 0.924 | 0.937 | 0.929 | 0.751 | 0.929 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.739 | 0.772 | 0.414 | 0.772 | 0.926 | 0.924 | 0.814 | 0.924 | 0.937 | 0.929 | 0.751 | 0.929 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.754 | 0.78 | 0.415 | 0.78 | 0.931 | 0.929 | 0.843 | 0.929 | 0.937 | 0.929 | 0.751 | 0.929 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.752 | 0.78 | 0.415 | 0.78 | 0.93 | 0.928 | 0.843 | 0.928 | 0.937 | 0.929 | 0.751 | 0.929 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.755 | 0.783 | 0.435 | 0.783 | 0.931 | 0.929 | 0.843 | 0.929 | 0.937 | 0.929 | 0.751 | 0.929 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.749 | 0.762 | 0.474 | 0.762 | 0.924 | 0.923 | 0.802 | 0.923 | 0.894 | 0.905 | 0.69 | 0.905 |
| D-ML-All | 0.743 | 0.76 | 0.456 | 0.76 | 0.925 | 0.923 | 0.807 | 0.923 | 0.896 | 0.909 | 0.686 | 0.909 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.75 | 0.765 | 0.473 | 0.765 | 0.925 | 0.923 | 0.805 | 0.923 | 0.895 | 0.905 | 0.692 | 0.905 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.742 | 0.761 | 0.476 | 0.761 | 0.931 | 0.929 | 0.843 | 0.929 | 0.893 | 0.903 | 0.688 | 0.903 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.74 | 0.762 | 0.452 | 0.762 | 0.931 | 0.929 | 0.843 | 0.929 | 0.897 | 0.909 | 0.686 | 0.909 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.727 | 0.756 | 0.454 | 0.756 | 0.931 | 0.929 | 0.843 | 0.929 | 0.895 | 0.905 | 0.693 | 0.905 |
| Method | Random Forest | Random Subspace | AdaBoost | |||||||||
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.886 | 0.883 | 0.639 | 0.883 | 0.741 | 0.744 | 0.311 | 0.744 | 0.836 | 0.83 | 0.446 | 0.83 |
| ML | 0.897 | 0.893 | 0.637 | 0.893 | 0.724 | 0.745 | 0.301 | 0.745 | 0.843 | 0.846 | 0.456 | 0.846 |
| AL-W | 0.887 | 0.884 | 0.641 | 0.884 | 0.737 | 0.746 | 0.319 | 0.746 | 0.846 | 0.837 | 0.452 | 0.837 |
| ML-W | 0.886 | 0.883 | 0.635 | 0.883 | 0.734 | 0.749 | 0.305 | 0.749 | 0.841 | 0.844 | 0.454 | 0.844 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.886 | 0.883 | 0.642 | 0.883 | 0.754 | 0.763 | 0.328 | 0.763 | 0.837 | 0.833 | 0.448 | 0.833 |
| U-AL-All | 0.887 | 0.883 | 0.626 | 0.883 | 0.755 | 0.764 | 0.33 | 0.764 | 0.854 | 0.841 | 0.459 | 0.841 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.884 | 0.88 | 0.642 | 0.88 | 0.755 | 0.763 | 0.327 | 0.763 | 0.836 | 0.83 | 0.446 | 0.83 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.884 | 0.881 | 0.642 | 0.881 | 0.753 | 0.763 | 0.329 | 0.763 | 0.846 | 0.837 | 0.452 | 0.837 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.887 | 0.884 | 0.641 | 0.884 | 0.753 | 0.763 | 0.329 | 0.763 | 0.846 | 0.837 | 0.452 | 0.837 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.887 | 0.884 | 0.641 | 0.884 | 0.755 | 0.763 | 0.329 | 0.763 | 0.846 | 0.837 | 0.452 | 0.837 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.844 | 0.855 | 0.607 | 0.855 | 0.718 | 0.754 | 0.356 | 0.754 | 0.791 | 0.785 | 0.51 | 0.785 |
| D-AL-All | 0.854 | 0.873 | 0.568 | 0.873 | 0.741 | 0.767 | 0.343 | 0.767 | 0.822 | 0.823 | 0.426 | 0.823 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.847 | 0.86 | 0.61 | 0.86 | 0.726 | 0.759 | 0.351 | 0.759 | 0.805 | 0.795 | 0.452 | 0.795 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.853 | 0.86 | 0.659 | 0.86 | 0.741 | 0.77 | 0.377 | 0.77 | 0.823 | 0.826 | 0.556 | 0.826 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.854 | 0.87 | 0.614 | 0.87 | 0.748 | 0.77 | 0.358 | 0.77 | 0.819 | 0.822 | 0.453 | 0.822 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.858 | 0.865 | 0.653 | 0.865 | 0.746 | 0.775 | 0.368 | 0.775 | 0.807 | 0.81 | 0.482 | 0.81 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.886 | 0.883 | 0.639 | 0.883 | 0.725 | 0.744 | 0.3 | 0.744 | 0.843 | 0.846 | 0.456 | 0.846 |
| U-ML-All | 0.897 | 0.893 | 0.639 | 0.893 | 0.727 | 0.745 | 0.3 | 0.745 | 0.843 | 0.846 | 0.456 | 0.846 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.897 | 0.893 | 0.64 | 0.893 | 0.725 | 0.744 | 0.3 | 0.744 | 0.843 | 0.846 | 0.456 | 0.846 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.887 | 0.883 | 0.638 | 0.883 | 0.734 | 0.749 | 0.305 | 0.749 | 0.841 | 0.844 | 0.454 | 0.844 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.897 | 0.893 | 0.637 | 0.893 | 0.733 | 0.749 | 0.305 | 0.749 | 0.841 | 0.844 | 0.454 | 0.844 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.897 | 0.893 | 0.637 | 0.893 | 0.733 | 0.749 | 0.305 | 0.749 | 0.841 | 0.844 | 0.454 | 0.844 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.861 | 0.863 | 0.623 | 0.863 | 0.718 | 0.745 | 0.303 | 0.745 | 0.847 | 0.85 | 0.477 | 0.85 |
| D-ML-All | 0.868 | 0.869 | 0.624 | 0.869 | 0.714 | 0.744 | 0.301 | 0.744 | 0.85 | 0.852 | 0.479 | 0.852 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.863 | 0.865 | 0.62 | 0.865 | 0.726 | 0.738 | 0.302 | 0.738 | 0.85 | 0.852 | 0.479 | 0.852 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.864 | 0.867 | 0.626 | 0.867 | 0.723 | 0.749 | 0.309 | 0.749 | 0.845 | 0.848 | 0.475 | 0.848 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.869 | 0.87 | 0.623 | 0.87 | 0.725 | 0.748 | 0.306 | 0.748 | 0.848 | 0.85 | 0.477 | 0.85 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.867 | 0.869 | 0.628 | 0.869 | 0.722 | 0.748 | 0.306 | 0.748 | 0.848 | 0.851 | 0.478 | 0.851 |
| Method | K-Nearest Neighbors | Decision Tree | Gradient Boosting | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.723 | 0.746 | 0.341 | 0.746 | 0.902 | 0.902 | 0.737 | 0.902 | 0.955 | 0.949 | 0.766 | 0.949 |
| ML | 0.695 | 0.737 | 0.317 | 0.737 | 0.901 | 0.9 | 0.714 | 0.9 | 0.946 | 0.936 | 0.708 | 0.936 |
| AL-W | 0.736 | 0.755 | 0.35 | 0.755 | 0.901 | 0.902 | 0.748 | 0.902 | 0.955 | 0.949 | 0.771 | 0.949 |
| ML-W | 0.691 | 0.736 | 0.322 | 0.736 | 0.901 | 0.902 | 0.748 | 0.902 | 0.946 | 0.936 | 0.708 | 0.936 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.726 | 0.748 | 0.348 | 0.748 | 0.901 | 0.902 | 0.739 | 0.902 | 0.954 | 0.948 | 0.765 | 0.948 |
| U-AL-All | 0.731 | 0.75 | 0.348 | 0.75 | 0.901 | 0.9 | 0.714 | 0.9 | 0.955 | 0.948 | 0.755 | 0.948 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.709 | 0.74 | 0.326 | 0.74 | 0.902 | 0.903 | 0.738 | 0.903 | 0.955 | 0.949 | 0.766 | 0.949 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.733 | 0.754 | 0.347 | 0.754 | 0.901 | 0.902 | 0.748 | 0.902 | 0.955 | 0.949 | 0.771 | 0.949 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.726 | 0.749 | 0.34 | 0.749 | 0.901 | 0.902 | 0.748 | 0.902 | 0.955 | 0.949 | 0.771 | 0.949 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.718 | 0.747 | 0.332 | 0.747 | 0.901 | 0.902 | 0.748 | 0.902 | 0.955 | 0.949 | 0.771 | 0.949 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.714 | 0.659 | 0.388 | 0.659 | 0.9 | 0.901 | 0.739 | 0.901 | 0.86 | 0.854 | 0.644 | 0.854 |
| D-AL-All | 0.693 | 0.695 | 0.368 | 0.695 | 0.901 | 0.9 | 0.714 | 0.9 | 0.869 | 0.885 | 0.504 | 0.885 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.722 | 0.668 | 0.412 | 0.668 | 0.9 | 0.901 | 0.73 | 0.901 | 0.88 | 0.872 | 0.669 | 0.872 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.694 | 0.685 | 0.413 | 0.685 | 0.901 | 0.902 | 0.748 | 0.902 | 0.875 | 0.859 | 0.668 | 0.859 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.722 | 0.703 | 0.401 | 0.703 | 0.901 | 0.902 | 0.748 | 0.902 | 0.874 | 0.876 | 0.592 | 0.876 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.717 | 0.655 | 0.415 | 0.655 | 0.901 | 0.902 | 0.748 | 0.902 | 0.887 | 0.868 | 0.679 | 0.868 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.693 | 0.737 | 0.324 | 0.737 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.727 | 0.9 | 0.947 | 0.936 | 0.708 | 0.936 |
| U-ML-All | 0.688 | 0.735 | 0.319 | 0.735 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.727 | 0.9 | 0.946 | 0.936 | 0.708 | 0.936 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.679 | 0.731 | 0.315 | 0.731 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.727 | 0.9 | 0.946 | 0.936 | 0.708 | 0.936 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.701 | 0.741 | 0.328 | 0.741 | 0.901 | 0.902 | 0.748 | 0.902 | 0.947 | 0.936 | 0.708 | 0.936 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.69 | 0.737 | 0.321 | 0.737 | 0.901 | 0.902 | 0.748 | 0.902 | 0.946 | 0.936 | 0.708 | 0.936 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.69 | 0.737 | 0.321 | 0.737 | 0.901 | 0.902 | 0.748 | 0.902 | 0.946 | 0.936 | 0.708 | 0.936 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.712 | 0.737 | 0.39 | 0.737 | 0.902 | 0.902 | 0.74 | 0.902 | 0.838 | 0.847 | 0.494 | 0.847 |
| D-ML-All | 0.71 | 0.737 | 0.376 | 0.737 | 0.901 | 0.902 | 0.74 | 0.902 | 0.862 | 0.876 | 0.511 | 0.876 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.713 | 0.738 | 0.397 | 0.738 | 0.902 | 0.902 | 0.735 | 0.902 | 0.847 | 0.856 | 0.504 | 0.856 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.708 | 0.74 | 0.403 | 0.74 | 0.901 | 0.902 | 0.748 | 0.902 | 0.845 | 0.853 | 0.501 | 0.853 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.715 | 0.74 | 0.38 | 0.74 | 0.901 | 0.902 | 0.748 | 0.902 | 0.866 | 0.878 | 0.516 | 0.878 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.718 | 0.742 | 0.424 | 0.742 | 0.901 | 0.902 | 0.748 | 0.902 | 0.853 | 0.862 | 0.511 | 0.862 |
| Method | Random Forest | Random Subspace | AdaBoost | |||||||||
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.869 | 0.867 | 0.579 | 0.867 | 0.742 | 0.757 | 0.316 | 0.757 | 0.837 | 0.841 | 0.464 | 0.841 |
| ML | 0.868 | 0.867 | 0.556 | 0.867 | 0.742 | 0.749 | 0.306 | 0.749 | 0.846 | 0.844 | 0.459 | 0.844 |
| AL-W | 0.87 | 0.867 | 0.579 | 0.867 | 0.744 | 0.758 | 0.317 | 0.758 | 0.844 | 0.843 | 0.464 | 0.843 |
| ML-W | 0.87 | 0.868 | 0.56 | 0.868 | 0.741 | 0.75 | 0.307 | 0.75 | 0.846 | 0.844 | 0.459 | 0.844 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.869 | 0.866 | 0.576 | 0.866 | 0.766 | 0.777 | 0.341 | 0.777 | 0.836 | 0.84 | 0.461 | 0.84 |
| U-AL-All | 0.87 | 0.866 | 0.57 | 0.866 | 0.765 | 0.777 | 0.341 | 0.777 | 0.843 | 0.842 | 0.456 | 0.842 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.867 | 0.866 | 0.57 | 0.866 | 0.762 | 0.775 | 0.339 | 0.775 | 0.837 | 0.841 | 0.464 | 0.841 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.871 | 0.867 | 0.581 | 0.867 | 0.767 | 0.778 | 0.344 | 0.778 | 0.844 | 0.843 | 0.464 | 0.843 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.87 | 0.866 | 0.574 | 0.866 | 0.765 | 0.777 | 0.341 | 0.777 | 0.844 | 0.843 | 0.464 | 0.843 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.868 | 0.866 | 0.574 | 0.866 | 0.765 | 0.777 | 0.341 | 0.777 | 0.844 | 0.843 | 0.464 | 0.843 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.81 | 0.822 | 0.59 | 0.822 | 0.745 | 0.772 | 0.407 | 0.772 | 0.783 | 0.766 | 0.522 | 0.766 |
| D-AL-All | 0.832 | 0.845 | 0.482 | 0.845 | 0.751 | 0.781 | 0.385 | 0.781 | 0.825 | 0.821 | 0.454 | 0.821 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.811 | 0.825 | 0.571 | 0.825 | 0.737 | 0.772 | 0.396 | 0.772 | 0.797 | 0.798 | 0.487 | 0.798 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.842 | 0.847 | 0.677 | 0.847 | 0.776 | 0.796 | 0.452 | 0.796 | 0.8 | 0.788 | 0.59 | 0.788 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.833 | 0.844 | 0.543 | 0.844 | 0.752 | 0.782 | 0.396 | 0.782 | 0.806 | 0.799 | 0.475 | 0.799 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.847 | 0.852 | 0.678 | 0.852 | 0.782 | 0.802 | 0.439 | 0.802 | 0.801 | 0.793 | 0.552 | 0.793 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.87 | 0.868 | 0.557 | 0.868 | 0.739 | 0.748 | 0.305 | 0.748 | 0.846 | 0.844 | 0.459 | 0.844 |
| U-ML-All | 0.877 | 0.871 | 0.56 | 0.871 | 0.743 | 0.748 | 0.305 | 0.748 | 0.846 | 0.844 | 0.459 | 0.844 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.876 | 0.87 | 0.556 | 0.87 | 0.738 | 0.748 | 0.304 | 0.748 | 0.846 | 0.844 | 0.459 | 0.844 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.871 | 0.869 | 0.56 | 0.869 | 0.739 | 0.75 | 0.307 | 0.75 | 0.846 | 0.844 | 0.459 | 0.844 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.878 | 0.872 | 0.564 | 0.872 | 0.741 | 0.75 | 0.306 | 0.75 | 0.846 | 0.844 | 0.459 | 0.844 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.876 | 0.87 | 0.555 | 0.87 | 0.739 | 0.75 | 0.306 | 0.75 | 0.846 | 0.844 | 0.459 | 0.844 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.858 | 0.859 | 0.524 | 0.859 | 0.732 | 0.75 | 0.309 | 0.75 | 0.823 | 0.838 | 0.455 | 0.838 |
| D-ML-All | 0.853 | 0.855 | 0.506 | 0.855 | 0.717 | 0.742 | 0.301 | 0.742 | 0.816 | 0.83 | 0.457 | 0.83 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.858 | 0.859 | 0.524 | 0.859 | 0.725 | 0.748 | 0.307 | 0.748 | 0.823 | 0.838 | 0.455 | 0.838 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.859 | 0.86 | 0.527 | 0.86 | 0.729 | 0.751 | 0.31 | 0.751 | 0.827 | 0.839 | 0.456 | 0.839 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.841 | 0.85 | 0.515 | 0.85 | 0.715 | 0.745 | 0.303 | 0.745 | 0.816 | 0.83 | 0.457 | 0.83 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.859 | 0.861 | 0.53 | 0.861 | 0.724 | 0.75 | 0.309 | 0.75 | 0.827 | 0.839 | 0.456 | 0.839 |
| Method | K-Nearest Neighbors | Decision Tree | Gradient Boosting | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.718 | 0.742 | 0.331 | 0.742 | 0.887 | 0.89 | 0.727 | 0.89 | 0.933 | 0.917 | 0.67 | 0.917 |
| ML | 0.67 | 0.723 | 0.289 | 0.723 | 0.894 | 0.893 | 0.72 | 0.893 | 0.935 | 0.919 | 0.654 | 0.919 |
| AL-W | 0.726 | 0.748 | 0.335 | 0.748 | 0.892 | 0.893 | 0.747 | 0.893 | 0.932 | 0.919 | 0.676 | 0.919 |
| ML-W | 0.659 | 0.72 | 0.292 | 0.72 | 0.892 | 0.893 | 0.747 | 0.893 | 0.935 | 0.919 | 0.654 | 0.919 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.719 | 0.748 | 0.327 | 0.748 | 0.888 | 0.891 | 0.726 | 0.891 | 0.932 | 0.917 | 0.673 | 0.917 |
| U-AL-All | 0.722 | 0.748 | 0.326 | 0.748 | 0.894 | 0.893 | 0.72 | 0.893 | 0.935 | 0.917 | 0.675 | 0.917 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.719 | 0.745 | 0.328 | 0.745 | 0.887 | 0.89 | 0.732 | 0.89 | 0.933 | 0.917 | 0.675 | 0.917 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.72 | 0.751 | 0.333 | 0.751 | 0.892 | 0.893 | 0.747 | 0.893 | 0.932 | 0.919 | 0.676 | 0.919 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.723 | 0.748 | 0.331 | 0.748 | 0.892 | 0.893 | 0.747 | 0.893 | 0.932 | 0.919 | 0.676 | 0.919 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.725 | 0.75 | 0.332 | 0.75 | 0.892 | 0.893 | 0.747 | 0.893 | 0.932 | 0.919 | 0.676 | 0.919 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.717 | 0.625 | 0.381 | 0.625 | 0.886 | 0.889 | 0.726 | 0.889 | 0.817 | 0.8 | 0.584 | 0.8 |
| D-AL-All | 0.756 | 0.657 | 0.376 | 0.657 | 0.894 | 0.893 | 0.72 | 0.893 | 0.836 | 0.84 | 0.46 | 0.84 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.73 | 0.632 | 0.395 | 0.632 | 0.888 | 0.89 | 0.723 | 0.89 | 0.835 | 0.818 | 0.586 | 0.818 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.728 | 0.653 | 0.396 | 0.653 | 0.892 | 0.893 | 0.747 | 0.893 | 0.869 | 0.85 | 0.702 | 0.85 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.716 | 0.683 | 0.378 | 0.683 | 0.892 | 0.893 | 0.747 | 0.893 | 0.843 | 0.844 | 0.533 | 0.844 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.725 | 0.654 | 0.392 | 0.654 | 0.892 | 0.893 | 0.747 | 0.893 | 0.877 | 0.859 | 0.708 | 0.859 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.67 | 0.723 | 0.288 | 0.723 | 0.889 | 0.891 | 0.733 | 0.891 | 0.935 | 0.919 | 0.654 | 0.919 |
| U-ML-All | 0.669 | 0.722 | 0.292 | 0.722 | 0.889 | 0.891 | 0.733 | 0.891 | 0.935 | 0.919 | 0.654 | 0.919 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.671 | 0.723 | 0.289 | 0.723 | 0.889 | 0.891 | 0.733 | 0.891 | 0.935 | 0.919 | 0.654 | 0.919 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.663 | 0.722 | 0.292 | 0.722 | 0.892 | 0.893 | 0.747 | 0.893 | 0.935 | 0.919 | 0.654 | 0.919 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.666 | 0.722 | 0.293 | 0.722 | 0.892 | 0.893 | 0.747 | 0.893 | 0.935 | 0.919 | 0.654 | 0.919 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.666 | 0.722 | 0.293 | 0.722 | 0.892 | 0.893 | 0.747 | 0.893 | 0.935 | 0.919 | 0.654 | 0.919 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.63 | 0.669 | 0.325 | 0.669 | 0.889 | 0.891 | 0.733 | 0.891 | 0.839 | 0.855 | 0.521 | 0.855 |
| D-ML-All | 0.661 | 0.688 | 0.322 | 0.688 | 0.889 | 0.891 | 0.733 | 0.891 | 0.851 | 0.858 | 0.523 | 0.858 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.626 | 0.668 | 0.319 | 0.668 | 0.887 | 0.889 | 0.728 | 0.889 | 0.844 | 0.859 | 0.526 | 0.859 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.631 | 0.672 | 0.332 | 0.672 | 0.892 | 0.893 | 0.747 | 0.893 | 0.845 | 0.858 | 0.529 | 0.858 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.655 | 0.688 | 0.324 | 0.688 | 0.892 | 0.893 | 0.747 | 0.893 | 0.848 | 0.859 | 0.52 | 0.859 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.629 | 0.672 | 0.325 | 0.672 | 0.892 | 0.893 | 0.747 | 0.893 | 0.85 | 0.862 | 0.533 | 0.862 |
| Method | Random Forest | Random Subspace | AdaBoost | |||||||||
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.862 | 0.859 | 0.55 | 0.859 | 0.747 | 0.76 | 0.318 | 0.76 | 0.874 | 0.828 | 0.451 | 0.828 |
| ML | 0.855 | 0.856 | 0.545 | 0.856 | 0.749 | 0.754 | 0.311 | 0.754 | 0.83 | 0.821 | 0.446 | 0.821 |
| AL-W | 0.859 | 0.858 | 0.553 | 0.858 | 0.746 | 0.762 | 0.322 | 0.762 | 0.841 | 0.838 | 0.452 | 0.838 |
| ML-W | 0.856 | 0.857 | 0.543 | 0.857 | 0.753 | 0.758 | 0.316 | 0.758 | 0.829 | 0.821 | 0.444 | 0.821 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.862 | 0.859 | 0.547 | 0.859 | 0.751 | 0.767 | 0.329 | 0.767 | 0.874 | 0.828 | 0.452 | 0.828 |
| U-AL-All | 0.856 | 0.855 | 0.541 | 0.855 | 0.752 | 0.769 | 0.331 | 0.769 | 0.855 | 0.837 | 0.455 | 0.837 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.861 | 0.858 | 0.545 | 0.858 | 0.754 | 0.769 | 0.329 | 0.769 | 0.873 | 0.827 | 0.451 | 0.827 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.859 | 0.857 | 0.55 | 0.857 | 0.753 | 0.772 | 0.331 | 0.772 | 0.841 | 0.838 | 0.452 | 0.838 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.857 | 0.855 | 0.547 | 0.855 | 0.752 | 0.77 | 0.33 | 0.77 | 0.841 | 0.838 | 0.452 | 0.838 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.857 | 0.856 | 0.547 | 0.856 | 0.752 | 0.77 | 0.33 | 0.77 | 0.841 | 0.838 | 0.452 | 0.838 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.793 | 0.807 | 0.544 | 0.807 | 0.733 | 0.758 | 0.391 | 0.758 | 0.771 | 0.736 | 0.5 | 0.736 |
| D-AL-All | 0.809 | 0.826 | 0.477 | 0.826 | 0.741 | 0.773 | 0.372 | 0.773 | 0.827 | 0.808 | 0.441 | 0.808 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.797 | 0.813 | 0.548 | 0.813 | 0.742 | 0.768 | 0.403 | 0.768 | 0.776 | 0.749 | 0.489 | 0.749 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.824 | 0.835 | 0.624 | 0.835 | 0.784 | 0.789 | 0.469 | 0.789 | 0.772 | 0.768 | 0.526 | 0.768 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.818 | 0.832 | 0.564 | 0.832 | 0.746 | 0.774 | 0.391 | 0.774 | 0.809 | 0.8 | 0.457 | 0.8 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.833 | 0.844 | 0.635 | 0.844 | 0.783 | 0.796 | 0.456 | 0.796 | 0.779 | 0.778 | 0.53 | 0.778 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.854 | 0.855 | 0.535 | 0.855 | 0.748 | 0.754 | 0.311 | 0.754 | 0.83 | 0.821 | 0.446 | 0.821 |
| U-ML-All | 0.855 | 0.855 | 0.534 | 0.855 | 0.747 | 0.754 | 0.311 | 0.754 | 0.83 | 0.821 | 0.446 | 0.821 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.854 | 0.855 | 0.537 | 0.855 | 0.748 | 0.754 | 0.311 | 0.754 | 0.83 | 0.821 | 0.446 | 0.821 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.856 | 0.856 | 0.538 | 0.856 | 0.752 | 0.758 | 0.316 | 0.758 | 0.829 | 0.821 | 0.444 | 0.821 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.856 | 0.857 | 0.541 | 0.857 | 0.752 | 0.758 | 0.316 | 0.758 | 0.829 | 0.821 | 0.444 | 0.821 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.856 | 0.856 | 0.538 | 0.856 | 0.752 | 0.758 | 0.316 | 0.758 | 0.829 | 0.821 | 0.444 | 0.821 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.829 | 0.831 | 0.504 | 0.831 | 0.728 | 0.749 | 0.312 | 0.749 | 0.824 | 0.818 | 0.45 | 0.818 |
| D-ML-All | 0.827 | 0.829 | 0.49 | 0.829 | 0.722 | 0.746 | 0.306 | 0.746 | 0.799 | 0.803 | 0.44 | 0.803 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.83 | 0.832 | 0.502 | 0.832 | 0.726 | 0.748 | 0.312 | 0.748 | 0.823 | 0.816 | 0.44 | 0.816 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.831 | 0.833 | 0.505 | 0.833 | 0.729 | 0.751 | 0.318 | 0.751 | 0.819 | 0.807 | 0.446 | 0.807 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.826 | 0.83 | 0.491 | 0.83 | 0.733 | 0.751 | 0.311 | 0.751 | 0.799 | 0.803 | 0.44 | 0.803 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.831 | 0.833 | 0.504 | 0.833 | 0.727 | 0.75 | 0.318 | 0.75 | 0.821 | 0.813 | 0.439 | 0.813 |
| Method | K-Nearest Neighbors | Decision Tree | Gradient Boosting | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.716 | 0.746 | 0.32 | 0.746 | 0.878 | 0.873 | 0.638 | 0.873 | 0.917 | 0.907 | 0.648 | 0.907 |
| ML | 0.656 | 0.719 | 0.273 | 0.719 | 0.878 | 0.87 | 0.617 | 0.87 | 0.918 | 0.908 | 0.635 | 0.908 |
| AL-W | 0.717 | 0.747 | 0.322 | 0.747 | 0.88 | 0.877 | 0.651 | 0.877 | 0.915 | 0.906 | 0.641 | 0.906 |
| ML-W | 0.65 | 0.718 | 0.271 | 0.718 | 0.872 | 0.871 | 0.631 | 0.871 | 0.918 | 0.908 | 0.635 | 0.908 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.72 | 0.748 | 0.324 | 0.748 | 0.876 | 0.87 | 0.63 | 0.87 | 0.916 | 0.907 | 0.644 | 0.907 |
| U-AL-All | 0.697 | 0.728 | 0.309 | 0.728 | 0.878 | 0.87 | 0.617 | 0.87 | 0.916 | 0.907 | 0.651 | 0.907 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.701 | 0.729 | 0.314 | 0.729 | 0.878 | 0.872 | 0.636 | 0.872 | 0.916 | 0.906 | 0.65 | 0.906 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.715 | 0.746 | 0.323 | 0.746 | 0.872 | 0.871 | 0.631 | 0.871 | 0.915 | 0.91 | 0.646 | 0.91 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.697 | 0.728 | 0.309 | 0.728 | 0.872 | 0.87 | 0.631 | 0.87 | 0.915 | 0.908 | 0.652 | 0.908 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.705 | 0.73 | 0.323 | 0.73 | 0.872 | 0.871 | 0.631 | 0.871 | 0.913 | 0.906 | 0.649 | 0.906 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.688 | 0.66 | 0.377 | 0.66 | 0.871 | 0.871 | 0.636 | 0.871 | 0.792 | 0.757 | 0.57 | 0.757 |
| D-AL-All | 0.766 | 0.642 | 0.372 | 0.642 | 0.878 | 0.87 | 0.617 | 0.87 | 0.802 | 0.802 | 0.425 | 0.802 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.738 | 0.625 | 0.375 | 0.625 | 0.882 | 0.873 | 0.634 | 0.873 | 0.796 | 0.762 | 0.57 | 0.762 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.754 | 0.64 | 0.396 | 0.64 | 0.872 | 0.87 | 0.631 | 0.87 | 0.804 | 0.762 | 0.588 | 0.762 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.739 | 0.67 | 0.379 | 0.67 | 0.872 | 0.87 | 0.631 | 0.87 | 0.809 | 0.79 | 0.521 | 0.79 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.754 | 0.64 | 0.396 | 0.64 | 0.872 | 0.87 | 0.631 | 0.87 | 0.806 | 0.766 | 0.594 | 0.766 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.664 | 0.721 | 0.276 | 0.721 | 0.878 | 0.872 | 0.636 | 0.872 | 0.918 | 0.909 | 0.637 | 0.909 |
| U-ML-All | 0.652 | 0.717 | 0.271 | 0.717 | 0.878 | 0.872 | 0.636 | 0.872 | 0.917 | 0.909 | 0.64 | 0.909 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.655 | 0.717 | 0.272 | 0.717 | 0.878 | 0.872 | 0.636 | 0.872 | 0.918 | 0.909 | 0.639 | 0.909 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.659 | 0.721 | 0.274 | 0.721 | 0.872 | 0.871 | 0.631 | 0.871 | 0.918 | 0.909 | 0.637 | 0.909 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.652 | 0.718 | 0.271 | 0.718 | 0.872 | 0.87 | 0.631 | 0.87 | 0.917 | 0.909 | 0.64 | 0.909 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.653 | 0.717 | 0.271 | 0.717 | 0.872 | 0.871 | 0.631 | 0.871 | 0.918 | 0.909 | 0.64 | 0.909 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.607 | 0.671 | 0.292 | 0.671 | 0.874 | 0.872 | 0.637 | 0.872 | 0.837 | 0.843 | 0.507 | 0.843 |
| D-ML-All | 0.655 | 0.692 | 0.299 | 0.692 | 0.878 | 0.872 | 0.636 | 0.872 | 0.841 | 0.852 | 0.512 | 0.852 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.623 | 0.671 | 0.316 | 0.671 | 0.871 | 0.872 | 0.634 | 0.872 | 0.836 | 0.842 | 0.508 | 0.842 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.63 | 0.68 | 0.312 | 0.68 | 0.872 | 0.87 | 0.631 | 0.87 | 0.839 | 0.844 | 0.507 | 0.844 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.66 | 0.694 | 0.315 | 0.694 | 0.872 | 0.87 | 0.631 | 0.87 | 0.84 | 0.85 | 0.511 | 0.85 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.635 | 0.677 | 0.324 | 0.677 | 0.872 | 0.87 | 0.631 | 0.87 | 0.837 | 0.843 | 0.507 | 0.843 |
| Method | Random Forest | Random Subspace | AdaBoost | |||||||||
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.839 | 0.831 | 0.462 | 0.831 | 0.738 | 0.762 | 0.323 | 0.762 | 0.844 | 0.845 | 0.455 | 0.845 |
| ML | 0.838 | 0.838 | 0.452 | 0.838 | 0.727 | 0.756 | 0.314 | 0.756 | 0.864 | 0.828 | 0.455 | 0.828 |
| AL-W | 0.843 | 0.835 | 0.47 | 0.835 | 0.738 | 0.764 | 0.322 | 0.764 | 0.842 | 0.845 | 0.453 | 0.845 |
| ML-W | 0.837 | 0.837 | 0.451 | 0.837 | 0.726 | 0.755 | 0.312 | 0.755 | 0.863 | 0.827 | 0.454 | 0.827 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.83 | 0.827 | 0.459 | 0.827 | 0.769 | 0.786 | 0.353 | 0.786 | 0.836 | 0.844 | 0.461 | 0.844 |
| U-AL-All | 0.844 | 0.835 | 0.46 | 0.835 | 0.769 | 0.786 | 0.351 | 0.786 | 0.85 | 0.848 | 0.46 | 0.848 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.842 | 0.834 | 0.475 | 0.834 | 0.767 | 0.784 | 0.349 | 0.784 | 0.843 | 0.844 | 0.454 | 0.844 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.836 | 0.83 | 0.464 | 0.83 | 0.762 | 0.782 | 0.347 | 0.782 | 0.843 | 0.848 | 0.47 | 0.848 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.841 | 0.833 | 0.463 | 0.833 | 0.766 | 0.783 | 0.348 | 0.783 | 0.847 | 0.85 | 0.457 | 0.85 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.843 | 0.835 | 0.473 | 0.835 | 0.765 | 0.783 | 0.348 | 0.783 | 0.847 | 0.85 | 0.457 | 0.85 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.766 | 0.785 | 0.508 | 0.785 | 0.763 | 0.786 | 0.427 | 0.786 | 0.718 | 0.675 | 0.456 | 0.675 |
| D-AL-All | 0.803 | 0.823 | 0.496 | 0.823 | 0.746 | 0.784 | 0.388 | 0.784 | 0.816 | 0.793 | 0.442 | 0.793 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.776 | 0.79 | 0.522 | 0.79 | 0.765 | 0.787 | 0.425 | 0.787 | 0.72 | 0.69 | 0.461 | 0.69 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.781 | 0.792 | 0.543 | 0.792 | 0.777 | 0.792 | 0.427 | 0.792 | 0.682 | 0.685 | 0.495 | 0.685 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.783 | 0.8 | 0.526 | 0.8 | 0.745 | 0.78 | 0.395 | 0.78 | 0.807 | 0.787 | 0.546 | 0.787 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.786 | 0.795 | 0.543 | 0.795 | 0.779 | 0.792 | 0.423 | 0.792 | 0.689 | 0.692 | 0.499 | 0.692 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.838 | 0.84 | 0.462 | 0.84 | 0.725 | 0.755 | 0.312 | 0.755 | 0.864 | 0.828 | 0.455 | 0.828 |
| U-ML-All | 0.838 | 0.837 | 0.451 | 0.837 | 0.727 | 0.757 | 0.314 | 0.757 | 0.864 | 0.828 | 0.455 | 0.828 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.837 | 0.838 | 0.461 | 0.838 | 0.725 | 0.755 | 0.312 | 0.755 | 0.864 | 0.828 | 0.455 | 0.828 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.464 | 0.84 | 0.726 | 0.755 | 0.312 | 0.755 | 0.863 | 0.827 | 0.454 | 0.827 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.842 | 0.84 | 0.451 | 0.84 | 0.727 | 0.755 | 0.313 | 0.755 | 0.863 | 0.827 | 0.454 | 0.827 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.839 | 0.839 | 0.465 | 0.839 | 0.727 | 0.755 | 0.313 | 0.755 | 0.863 | 0.827 | 0.454 | 0.827 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.795 | 0.813 | 0.493 | 0.813 | 0.725 | 0.753 | 0.322 | 0.753 | 0.81 | 0.794 | 0.471 | 0.794 |
| D-ML-All | 0.801 | 0.814 | 0.477 | 0.814 | 0.726 | 0.753 | 0.313 | 0.753 | 0.822 | 0.805 | 0.481 | 0.805 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.796 | 0.814 | 0.491 | 0.814 | 0.727 | 0.753 | 0.322 | 0.753 | 0.81 | 0.794 | 0.471 | 0.794 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.793 | 0.815 | 0.489 | 0.815 | 0.727 | 0.754 | 0.323 | 0.754 | 0.806 | 0.791 | 0.468 | 0.791 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.8 | 0.814 | 0.48 | 0.814 | 0.727 | 0.753 | 0.314 | 0.753 | 0.822 | 0.805 | 0.481 | 0.805 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.791 | 0.813 | 0.483 | 0.813 | 0.726 | 0.753 | 0.322 | 0.753 | 0.806 | 0.791 | 0.468 | 0.791 |
| Method | K-Nearest Neighbors | Decision Tree | Gradient Boosting | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.535 | 0.297 | 0.255 | 0.297 | 0.587 | 0.319 | 0.316 | 0.319 | 0.577 | 0.314 | 0.28 | 0.314 |
| ML | 0.674 | 0.348 | 0.281 | 0.348 | 0.647 | 0.51 | 0.497 | 0.51 | 0.623 | 0.324 | 0.245 | 0.324 |
| AL-W | 0.607 | 0.591 | 0.548 | 0.591 | 0.68 | 0.666 | 0.709 | 0.666 | 0.691 | 0.685 | 0.692 | 0.685 |
| ML-W | 0.595 | 0.593 | 0.555 | 0.593 | 0.68 | 0.666 | 0.709 | 0.666 | 0.694 | 0.687 | 0.693 | 0.687 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.544 | 0.297 | 0.254 | 0.297 | 0.581 | 0.322 | 0.319 | 0.322 | 0.589 | 0.31 | 0.273 | 0.31 |
| U-AL-All | 0.449 | 0.277 | 0.166 | 0.277 | 0.42 | 0.269 | 0.223 | 0.269 | 0.654 | 0.27 | 0.185 | 0.27 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.544 | 0.297 | 0.254 | 0.297 | 0.581 | 0.322 | 0.319 | 0.322 | 0.589 | 0.31 | 0.273 | 0.31 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.607 | 0.591 | 0.548 | 0.591 | 0.68 | 0.666 | 0.709 | 0.666 | 0.691 | 0.685 | 0.692 | 0.685 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.607 | 0.591 | 0.548 | 0.591 | 0.68 | 0.666 | 0.709 | 0.666 | 0.691 | 0.685 | 0.692 | 0.685 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.607 | 0.591 | 0.548 | 0.591 | 0.68 | 0.666 | 0.709 | 0.666 | 0.691 | 0.685 | 0.692 | 0.685 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.531 | 0.331 | 0.289 | 0.331 | 0.146 | 0.102 | 0.063 | 0.102 | 0.586 | 0.307 | 0.262 | 0.307 |
| D-AL-All | 0.455 | 0.32 | 0.245 | 0.32 | 0.178 | 0.147 | 0.076 | 0.147 | 0.654 | 0.27 | 0.185 | 0.27 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.535 | 0.351 | 0.302 | 0.351 | 0.199 | 0.145 | 0.074 | 0.145 | 0.598 | 0.305 | 0.269 | 0.305 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.607 | 0.591 | 0.548 | 0.591 | 0.68 | 0.666 | 0.709 | 0.666 | 0.691 | 0.685 | 0.692 | 0.685 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.607 | 0.591 | 0.548 | 0.591 | 0.68 | 0.666 | 0.709 | 0.666 | 0.691 | 0.685 | 0.692 | 0.685 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.607 | 0.591 | 0.548 | 0.591 | 0.68 | 0.666 | 0.709 | 0.666 | 0.691 | 0.685 | 0.692 | 0.685 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.621 | 0.252 | 0.212 | 0.252 | 0.675 | 0.477 | 0.439 | 0.477 | 0.623 | 0.324 | 0.245 | 0.324 |
| U-ML-All | 0.621 | 0.252 | 0.212 | 0.252 | 0.675 | 0.477 | 0.439 | 0.477 | 0.623 | 0.324 | 0.245 | 0.324 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.621 | 0.252 | 0.212 | 0.252 | 0.675 | 0.477 | 0.439 | 0.477 | 0.623 | 0.324 | 0.245 | 0.324 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.584 | 0.581 | 0.542 | 0.581 | 0.68 | 0.666 | 0.709 | 0.666 | 0.694 | 0.687 | 0.693 | 0.687 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.584 | 0.581 | 0.542 | 0.581 | 0.68 | 0.666 | 0.709 | 0.666 | 0.694 | 0.687 | 0.693 | 0.687 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.584 | 0.581 | 0.542 | 0.581 | 0.68 | 0.666 | 0.709 | 0.666 | 0.694 | 0.687 | 0.693 | 0.687 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.552 | 0.291 | 0.275 | 0.291 | 0.668 | 0.385 | 0.403 | 0.385 | 0.623 | 0.324 | 0.245 | 0.324 |
| D-ML-All | 0.571 | 0.334 | 0.3 | 0.334 | 0.668 | 0.384 | 0.404 | 0.384 | 0.623 | 0.324 | 0.245 | 0.324 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.575 | 0.331 | 0.298 | 0.331 | 0.675 | 0.477 | 0.439 | 0.477 | 0.623 | 0.324 | 0.245 | 0.324 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.583 | 0.58 | 0.54 | 0.58 | 0.669 | 0.593 | 0.681 | 0.593 | 0.694 | 0.687 | 0.693 | 0.687 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.583 | 0.58 | 0.54 | 0.58 | 0.68 | 0.666 | 0.709 | 0.666 | 0.694 | 0.687 | 0.693 | 0.687 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.583 | 0.58 | 0.54 | 0.58 | 0.68 | 0.666 | 0.709 | 0.666 | 0.694 | 0.687 | 0.693 | 0.687 |
| Method | Random Forest | Random Subspace | AdaBoost | |||||||||
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.638 | 0.345 | 0.303 | 0.345 | 0.634 | 0.395 | 0.319 | 0.395 | 0.241 | 0.206 | 0.12 | 0.206 |
| ML | 0.756 | 0.606 | 0.581 | 0.606 | 0.676 | 0.445 | 0.358 | 0.445 | 0.189 | 0.224 | 0.148 | 0.224 |
| AL-W | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.713 | 0.713 | 0.725 | 0.713 | 0.346 | 0.376 | 0.228 | 0.376 |
| ML-W | 0.734 | 0.726 | 0.736 | 0.726 | 0.71 | 0.708 | 0.704 | 0.708 | 0.207 | 0.27 | 0.165 | 0.27 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.638 | 0.345 | 0.303 | 0.345 | 0.608 | 0.398 | 0.321 | 0.398 | 0.262 | 0.215 | 0.126 | 0.215 |
| U-AL-All | 0.691 | 0.28 | 0.2 | 0.28 | 0.593 | 0.343 | 0.213 | 0.343 | 0.16 | 0.213 | 0.139 | 0.213 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.638 | 0.345 | 0.303 | 0.345 | 0.614 | 0.392 | 0.321 | 0.392 | 0.262 | 0.215 | 0.126 | 0.215 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.717 | 0.717 | 0.722 | 0.717 | 0.346 | 0.376 | 0.228 | 0.376 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.717 | 0.717 | 0.722 | 0.717 | 0.346 | 0.376 | 0.228 | 0.376 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.717 | 0.717 | 0.722 | 0.717 | 0.346 | 0.376 | 0.228 | 0.376 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.67 | 0.392 | 0.35 | 0.392 | 0.609 | 0.412 | 0.348 | 0.412 | 0.304 | 0.221 | 0.128 | 0.221 |
| D-AL-All | 0.734 | 0.341 | 0.225 | 0.341 | 0.566 | 0.36 | 0.245 | 0.36 | 0.16 | 0.213 | 0.139 | 0.213 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.633 | 0.358 | 0.324 | 0.358 | 0.623 | 0.412 | 0.342 | 0.412 | 0.297 | 0.215 | 0.124 | 0.215 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.717 | 0.717 | 0.722 | 0.717 | 0.346 | 0.376 | 0.228 | 0.376 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.717 | 0.717 | 0.722 | 0.717 | 0.346 | 0.376 | 0.228 | 0.376 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.717 | 0.717 | 0.722 | 0.717 | 0.346 | 0.376 | 0.228 | 0.376 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.756 | 0.606 | 0.581 | 0.606 | 0.678 | 0.447 | 0.364 | 0.447 | 0.189 | 0.224 | 0.148 | 0.224 |
| U-ML-All | 0.756 | 0.606 | 0.581 | 0.606 | 0.682 | 0.448 | 0.366 | 0.448 | 0.189 | 0.224 | 0.148 | 0.224 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.756 | 0.606 | 0.581 | 0.606 | 0.678 | 0.447 | 0.364 | 0.447 | 0.189 | 0.224 | 0.148 | 0.224 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.734 | 0.726 | 0.736 | 0.726 | 0.71 | 0.708 | 0.704 | 0.708 | 0.207 | 0.27 | 0.165 | 0.27 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.734 | 0.726 | 0.736 | 0.726 | 0.71 | 0.708 | 0.704 | 0.708 | 0.207 | 0.27 | 0.165 | 0.27 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.734 | 0.726 | 0.736 | 0.726 | 0.71 | 0.708 | 0.704 | 0.708 | 0.207 | 0.27 | 0.165 | 0.27 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.756 | 0.606 | 0.581 | 0.606 | 0.679 | 0.448 | 0.367 | 0.448 | 0.189 | 0.224 | 0.148 | 0.224 |
| D-ML-All | 0.756 | 0.606 | 0.581 | 0.606 | 0.678 | 0.447 | 0.364 | 0.447 | 0.189 | 0.224 | 0.148 | 0.224 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.756 | 0.606 | 0.581 | 0.606 | 0.678 | 0.447 | 0.364 | 0.447 | 0.189 | 0.224 | 0.148 | 0.224 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.734 | 0.726 | 0.736 | 0.726 | 0.71 | 0.708 | 0.704 | 0.708 | 0.207 | 0.27 | 0.165 | 0.27 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.734 | 0.726 | 0.736 | 0.726 | 0.71 | 0.708 | 0.704 | 0.708 | 0.207 | 0.27 | 0.165 | 0.27 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.734 | 0.726 | 0.736 | 0.726 | 0.71 | 0.708 | 0.704 | 0.708 | 0.207 | 0.27 | 0.165 | 0.27 |
| Method | K-Nearest Neighbors | Decision Tree | Gradient Boosting | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.473 | 0.331 | 0.252 | 0.331 | 0.515 | 0.235 | 0.106 | 0.235 | 0.465 | 0.199 | 0.084 | 0.199 |
| ML | 0.61 | 0.366 | 0.326 | 0.366 | 0.607 | 0.547 | 0.543 | 0.547 | 0.683 | 0.514 | 0.461 | 0.514 |
| AL-W | 0.607 | 0.591 | 0.548 | 0.591 | 0.69 | 0.679 | 0.729 | 0.679 | 0.691 | 0.685 | 0.692 | 0.685 |
| ML-W | 0.594 | 0.58 | 0.549 | 0.58 | 0.69 | 0.679 | 0.729 | 0.679 | 0.693 | 0.686 | 0.692 | 0.686 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.532 | 0.348 | 0.248 | 0.348 | 0.505 | 0.225 | 0.1 | 0.225 | 0.47 | 0.2 | 0.086 | 0.2 |
| U-AL-All | 0.558 | 0.409 | 0.246 | 0.409 | 0.353 | 0.189 | 0.08 | 0.189 | 0.38 | 0.201 | 0.084 | 0.201 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.532 | 0.348 | 0.248 | 0.348 | 0.505 | 0.225 | 0.1 | 0.225 | 0.47 | 0.2 | 0.086 | 0.2 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.607 | 0.591 | 0.548 | 0.591 | 0.69 | 0.679 | 0.729 | 0.679 | 0.691 | 0.685 | 0.692 | 0.685 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.607 | 0.591 | 0.548 | 0.591 | 0.69 | 0.679 | 0.729 | 0.679 | 0.691 | 0.685 | 0.692 | 0.685 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.607 | 0.591 | 0.548 | 0.591 | 0.69 | 0.679 | 0.729 | 0.679 | 0.691 | 0.685 | 0.692 | 0.685 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.536 | 0.442 | 0.316 | 0.442 | 0.645 | 0.526 | 0.562 | 0.526 | 0.497 | 0.216 | 0.094 | 0.216 |
| D-AL-All | 0.548 | 0.451 | 0.297 | 0.451 | 0.694 | 0.507 | 0.438 | 0.507 | 0.38 | 0.201 | 0.084 | 0.201 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.536 | 0.442 | 0.316 | 0.442 | 0.645 | 0.526 | 0.562 | 0.526 | 0.497 | 0.216 | 0.094 | 0.216 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.6 | 0.578 | 0.527 | 0.578 | 0.69 | 0.679 | 0.729 | 0.679 | 0.691 | 0.685 | 0.692 | 0.685 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.6 | 0.578 | 0.527 | 0.578 | 0.69 | 0.679 | 0.729 | 0.679 | 0.691 | 0.685 | 0.692 | 0.685 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.6 | 0.578 | 0.527 | 0.578 | 0.69 | 0.679 | 0.729 | 0.679 | 0.691 | 0.685 | 0.692 | 0.685 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.561 | 0.356 | 0.326 | 0.356 | 0.611 | 0.547 | 0.538 | 0.547 | 0.683 | 0.514 | 0.461 | 0.514 |
| U-ML-All | 0.561 | 0.356 | 0.326 | 0.356 | 0.611 | 0.547 | 0.538 | 0.547 | 0.683 | 0.514 | 0.461 | 0.514 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.561 | 0.356 | 0.326 | 0.356 | 0.611 | 0.547 | 0.538 | 0.547 | 0.683 | 0.514 | 0.461 | 0.514 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.579 | 0.581 | 0.526 | 0.581 | 0.69 | 0.679 | 0.729 | 0.679 | 0.693 | 0.686 | 0.692 | 0.686 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.579 | 0.581 | 0.526 | 0.581 | 0.69 | 0.679 | 0.729 | 0.679 | 0.693 | 0.686 | 0.692 | 0.686 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.579 | 0.581 | 0.526 | 0.581 | 0.69 | 0.679 | 0.729 | 0.679 | 0.693 | 0.686 | 0.692 | 0.686 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.572 | 0.421 | 0.347 | 0.421 | 0.69 | 0.585 | 0.696 | 0.585 | 0.683 | 0.514 | 0.461 | 0.514 |
| D-ML-All | 0.576 | 0.424 | 0.348 | 0.424 | 0.69 | 0.585 | 0.696 | 0.585 | 0.683 | 0.514 | 0.461 | 0.514 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.572 | 0.421 | 0.347 | 0.421 | 0.69 | 0.585 | 0.696 | 0.585 | 0.683 | 0.514 | 0.461 | 0.514 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.588 | 0.566 | 0.527 | 0.566 | 0.69 | 0.679 | 0.729 | 0.679 | 0.693 | 0.686 | 0.692 | 0.686 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.588 | 0.566 | 0.527 | 0.566 | 0.69 | 0.679 | 0.729 | 0.679 | 0.693 | 0.686 | 0.692 | 0.686 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.588 | 0.566 | 0.527 | 0.566 | 0.69 | 0.679 | 0.729 | 0.679 | 0.693 | 0.686 | 0.692 | 0.686 |
| Method | Random Forest | Random Subspace | AdaBoost | |||||||||
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.369 | 0.193 | 0.087 | 0.193 | 0.509 | 0.263 | 0.108 | 0.263 | 0.368 | 0.209 | 0.082 | 0.209 |
| ML | 0.723 | 0.546 | 0.455 | 0.546 | 0.555 | 0.189 | 0.072 | 0.189 | 0.16 | 0.266 | 0.105 | 0.266 |
| AL-W | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.721 | 0.72 | 0.727 | 0.72 | 0.441 | 0.376 | 0.228 | 0.376 |
| ML-W | 0.727 | 0.722 | 0.731 | 0.722 | 0.757 | 0.66 | 0.621 | 0.66 | 0.22 | 0.296 | 0.13 | 0.296 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.373 | 0.193 | 0.087 | 0.193 | 0.529 | 0.291 | 0.145 | 0.291 | 0.379 | 0.211 | 0.083 | 0.211 |
| U-AL-All | 0.302 | 0.194 | 0.082 | 0.194 | 0.324 | 0.212 | 0.09 | 0.212 | 0.061 | 0.138 | 0.053 | 0.138 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.366 | 0.193 | 0.087 | 0.193 | 0.581 | 0.254 | 0.106 | 0.254 | 0.379 | 0.211 | 0.083 | 0.211 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.717 | 0.717 | 0.724 | 0.717 | 0.441 | 0.376 | 0.228 | 0.376 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.717 | 0.717 | 0.724 | 0.717 | 0.441 | 0.376 | 0.228 | 0.376 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.717 | 0.717 | 0.724 | 0.717 | 0.441 | 0.376 | 0.228 | 0.376 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.651 | 0.214 | 0.199 | 0.214 | 0.464 | 0.205 | 0.101 | 0.205 | 0.365 | 0.206 | 0.08 | 0.206 |
| D-AL-All | 0.611 | 0.215 | 0.193 | 0.215 | 0.548 | 0.219 | 0.094 | 0.219 | 0.061 | 0.138 | 0.053 | 0.138 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.651 | 0.214 | 0.199 | 0.214 | 0.486 | 0.211 | 0.103 | 0.211 | 0.365 | 0.206 | 0.08 | 0.206 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.727 | 0.716 | 0.724 | 0.716 | 0.707 | 0.689 | 0.702 | 0.689 | 0.441 | 0.376 | 0.228 | 0.376 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.73 | 0.719 | 0.715 | 0.712 | 0.714 | 0.712 | 0.441 | 0.376 | 0.228 | 0.376 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.727 | 0.716 | 0.724 | 0.716 | 0.707 | 0.689 | 0.702 | 0.689 | 0.441 | 0.376 | 0.228 | 0.376 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.723 | 0.546 | 0.455 | 0.546 | 0.6 | 0.197 | 0.076 | 0.197 | 0.16 | 0.266 | 0.105 | 0.266 |
| U-ML-All | 0.723 | 0.546 | 0.455 | 0.546 | 0.556 | 0.19 | 0.072 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.266 | 0.105 | 0.266 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.723 | 0.546 | 0.455 | 0.546 | 0.556 | 0.19 | 0.072 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.266 | 0.105 | 0.266 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.727 | 0.722 | 0.731 | 0.722 | 0.751 | 0.665 | 0.632 | 0.665 | 0.22 | 0.296 | 0.13 | 0.296 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.727 | 0.722 | 0.731 | 0.722 | 0.731 | 0.657 | 0.617 | 0.657 | 0.22 | 0.296 | 0.13 | 0.296 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.727 | 0.722 | 0.731 | 0.722 | 0.731 | 0.657 | 0.617 | 0.657 | 0.22 | 0.296 | 0.13 | 0.296 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.69 | 0.449 | 0.418 | 0.449 | 0.412 | 0.187 | 0.1 | 0.187 | 0.16 | 0.266 | 0.105 | 0.266 |
| D-ML-All | 0.69 | 0.449 | 0.418 | 0.449 | 0.461 | 0.189 | 0.101 | 0.189 | 0.16 | 0.266 | 0.105 | 0.266 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.69 | 0.449 | 0.418 | 0.449 | 0.422 | 0.19 | 0.102 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.266 | 0.105 | 0.266 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.724 | 0.716 | 0.725 | 0.716 | 0.736 | 0.446 | 0.395 | 0.446 | 0.22 | 0.296 | 0.13 | 0.296 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.728 | 0.723 | 0.732 | 0.723 | 0.738 | 0.461 | 0.396 | 0.461 | 0.22 | 0.296 | 0.13 | 0.296 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.724 | 0.716 | 0.725 | 0.716 | 0.726 | 0.466 | 0.417 | 0.466 | 0.22 | 0.296 | 0.13 | 0.296 |
| Method | K-Nearest Neighbors | Decision Tree | Gradient Boosting | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.589 | 0.143 | 0.104 | 0.143 | 0.352 | 0.18 | 0.069 | 0.18 | 0.348 | 0.168 | 0.064 | 0.168 |
| ML | 0.696 | 0.079 | 0.072 | 0.079 | 0.337 | 0.216 | 0.104 | 0.216 | 0.38 | 0.237 | 0.11 | 0.237 |
| AL-W | 0.498 | 0.494 | 0.468 | 0.494 | 0.519 | 0.498 | 0.496 | 0.498 | 0.576 | 0.561 | 0.564 | 0.561 |
| ML-W | 0.491 | 0.492 | 0.463 | 0.492 | 0.515 | 0.493 | 0.493 | 0.493 | 0.563 | 0.567 | 0.556 | 0.567 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.589 | 0.143 | 0.104 | 0.143 | 0.341 | 0.172 | 0.065 | 0.172 | 0.348 | 0.168 | 0.064 | 0.168 |
| U-AL-All | 0.474 | 0.135 | 0.103 | 0.135 | 0.338 | 0.209 | 0.079 | 0.209 | 0.345 | 0.201 | 0.076 | 0.201 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.589 | 0.143 | 0.104 | 0.143 | 0.334 | 0.182 | 0.069 | 0.182 | 0.348 | 0.168 | 0.064 | 0.168 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.498 | 0.494 | 0.468 | 0.494 | 0.497 | 0.479 | 0.485 | 0.479 | 0.576 | 0.561 | 0.564 | 0.561 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.498 | 0.494 | 0.468 | 0.494 | 0.509 | 0.489 | 0.489 | 0.489 | 0.576 | 0.561 | 0.564 | 0.561 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.498 | 0.494 | 0.468 | 0.494 | 0.516 | 0.495 | 0.493 | 0.495 | 0.576 | 0.561 | 0.564 | 0.561 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.471 | 0.275 | 0.269 | 0.275 | 0.524 | 0.491 | 0.491 | 0.491 | 0.348 | 0.168 | 0.064 | 0.168 |
| D-AL-All | 0.401 | 0.255 | 0.273 | 0.255 | 0.524 | 0.491 | 0.491 | 0.491 | 0.345 | 0.201 | 0.076 | 0.201 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.471 | 0.275 | 0.269 | 0.275 | 0.524 | 0.491 | 0.491 | 0.491 | 0.348 | 0.168 | 0.064 | 0.168 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.498 | 0.494 | 0.468 | 0.494 | 0.519 | 0.498 | 0.496 | 0.498 | 0.576 | 0.561 | 0.564 | 0.561 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.498 | 0.494 | 0.468 | 0.494 | 0.519 | 0.498 | 0.496 | 0.498 | 0.576 | 0.561 | 0.564 | 0.561 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.498 | 0.494 | 0.468 | 0.494 | 0.519 | 0.498 | 0.496 | 0.498 | 0.576 | 0.561 | 0.564 | 0.561 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.833 | 0.111 | 0.087 | 0.111 | 0.341 | 0.216 | 0.103 | 0.216 | 0.38 | 0.237 | 0.11 | 0.237 |
| U-ML-All | 0.833 | 0.111 | 0.087 | 0.111 | 0.34 | 0.216 | 0.103 | 0.216 | 0.38 | 0.237 | 0.11 | 0.237 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.833 | 0.111 | 0.087 | 0.111 | 0.34 | 0.216 | 0.103 | 0.216 | 0.38 | 0.237 | 0.11 | 0.237 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.484 | 0.494 | 0.473 | 0.494 | 0.511 | 0.489 | 0.488 | 0.489 | 0.563 | 0.567 | 0.556 | 0.567 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.484 | 0.494 | 0.473 | 0.494 | 0.511 | 0.489 | 0.489 | 0.489 | 0.563 | 0.567 | 0.556 | 0.567 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.484 | 0.494 | 0.473 | 0.494 | 0.515 | 0.493 | 0.493 | 0.493 | 0.563 | 0.567 | 0.556 | 0.567 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.506 | 0.278 | 0.276 | 0.278 | 0.507 | 0.422 | 0.467 | 0.422 | 0.38 | 0.237 | 0.11 | 0.237 |
| D-ML-All | 0.506 | 0.278 | 0.276 | 0.278 | 0.507 | 0.422 | 0.467 | 0.422 | 0.38 | 0.237 | 0.11 | 0.237 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.506 | 0.278 | 0.276 | 0.278 | 0.507 | 0.422 | 0.467 | 0.422 | 0.38 | 0.237 | 0.11 | 0.237 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.484 | 0.494 | 0.473 | 0.494 | 0.516 | 0.493 | 0.493 | 0.493 | 0.563 | 0.567 | 0.556 | 0.567 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.484 | 0.494 | 0.473 | 0.494 | 0.516 | 0.493 | 0.493 | 0.493 | 0.563 | 0.567 | 0.556 | 0.567 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.484 | 0.494 | 0.473 | 0.494 | 0.516 | 0.493 | 0.493 | 0.493 | 0.563 | 0.567 | 0.556 | 0.567 |
| Method | Random Forest | Random Subspace | AdaBoost | |||||||||
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.329 | 0.184 | 0.078 | 0.184 | 0.317 | 0.187 | 0.071 | 0.187 | 0.203 | 0.231 | 0.088 | 0.231 |
| ML | 0.501 | 0.219 | 0.097 | 0.219 | 0.138 | 0.138 | 0.053 | 0.138 | 0.256 | 0.255 | 0.097 | 0.255 |
| AL-W | 0.566 | 0.549 | 0.542 | 0.549 | 0.576 | 0.569 | 0.528 | 0.569 | 0.379 | 0.325 | 0.155 | 0.325 |
| ML-W | 0.57 | 0.554 | 0.513 | 0.554 | 0.682 | 0.334 | 0.192 | 0.334 | 0.256 | 0.255 | 0.097 | 0.255 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.329 | 0.184 | 0.078 | 0.184 | 0.308 | 0.193 | 0.076 | 0.193 | 0.203 | 0.231 | 0.088 | 0.231 |
| U-AL-All | 0.355 | 0.202 | 0.077 | 0.202 | 0.254 | 0.198 | 0.075 | 0.198 | 0.271 | 0.212 | 0.081 | 0.212 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.329 | 0.184 | 0.078 | 0.184 | 0.316 | 0.189 | 0.072 | 0.189 | 0.203 | 0.231 | 0.088 | 0.231 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.566 | 0.549 | 0.542 | 0.549 | 0.578 | 0.568 | 0.527 | 0.568 | 0.379 | 0.325 | 0.155 | 0.325 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.566 | 0.549 | 0.542 | 0.549 | 0.573 | 0.565 | 0.52 | 0.565 | 0.379 | 0.325 | 0.155 | 0.325 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.566 | 0.549 | 0.542 | 0.549 | 0.573 | 0.565 | 0.52 | 0.565 | 0.379 | 0.325 | 0.155 | 0.325 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.565 | 0.299 | 0.171 | 0.299 | 0.286 | 0.156 | 0.077 | 0.156 | 0.207 | 0.233 | 0.089 | 0.233 |
| D-AL-All | 0.657 | 0.3 | 0.169 | 0.3 | 0.288 | 0.155 | 0.064 | 0.155 | 0.271 | 0.212 | 0.081 | 0.212 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.565 | 0.299 | 0.171 | 0.299 | 0.308 | 0.155 | 0.075 | 0.155 | 0.207 | 0.233 | 0.089 | 0.233 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.566 | 0.549 | 0.542 | 0.549 | 0.531 | 0.449 | 0.39 | 0.449 | 0.379 | 0.325 | 0.155 | 0.325 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.566 | 0.549 | 0.542 | 0.549 | 0.519 | 0.403 | 0.32 | 0.403 | 0.379 | 0.325 | 0.155 | 0.325 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.566 | 0.549 | 0.542 | 0.549 | 0.517 | 0.447 | 0.392 | 0.447 | 0.379 | 0.325 | 0.155 | 0.325 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.501 | 0.219 | 0.097 | 0.219 | 0.138 | 0.138 | 0.053 | 0.138 | 0.256 | 0.255 | 0.097 | 0.255 |
| U-ML-All | 0.501 | 0.219 | 0.097 | 0.219 | 0.138 | 0.138 | 0.053 | 0.138 | 0.256 | 0.255 | 0.097 | 0.255 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.502 | 0.22 | 0.1 | 0.22 | 0.138 | 0.138 | 0.053 | 0.138 | 0.256 | 0.255 | 0.097 | 0.255 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.57 | 0.554 | 0.513 | 0.554 | 0.688 | 0.343 | 0.209 | 0.343 | 0.256 | 0.255 | 0.097 | 0.255 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.57 | 0.554 | 0.513 | 0.554 | 0.684 | 0.334 | 0.188 | 0.334 | 0.256 | 0.255 | 0.097 | 0.255 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.57 | 0.554 | 0.513 | 0.554 | 0.684 | 0.334 | 0.188 | 0.334 | 0.256 | 0.255 | 0.097 | 0.255 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.632 | 0.328 | 0.181 | 0.328 | 0.477 | 0.174 | 0.081 | 0.174 | 0.256 | 0.255 | 0.097 | 0.255 |
| D-ML-All | 0.646 | 0.329 | 0.184 | 0.329 | 0.486 | 0.173 | 0.078 | 0.173 | 0.256 | 0.255 | 0.097 | 0.255 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.632 | 0.328 | 0.181 | 0.328 | 0.498 | 0.176 | 0.082 | 0.176 | 0.256 | 0.255 | 0.097 | 0.255 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.57 | 0.554 | 0.513 | 0.554 | 0.546 | 0.334 | 0.242 | 0.334 | 0.256 | 0.255 | 0.097 | 0.255 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.57 | 0.554 | 0.513 | 0.554 | 0.64 | 0.321 | 0.223 | 0.321 | 0.256 | 0.255 | 0.097 | 0.255 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.57 | 0.554 | 0.513 | 0.554 | 0.552 | 0.338 | 0.243 | 0.338 | 0.256 | 0.255 | 0.097 | 0.255 |
| Method | K-Nearest Neighbors | Decision Tree | Gradient Boosting | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.496 | 0.166 | 0.122 | 0.166 | 0.276 | 0.151 | 0.075 | 0.151 | 0.398 | 0.186 | 0.072 | 0.186 |
| ML | 0.064 | 0.064 | 0.053 | 0.064 | 0.354 | 0.234 | 0.179 | 0.234 | 0.397 | 0.212 | 0.127 | 0.212 |
| AL-W | 0.591 | 0.504 | 0.513 | 0.504 | 0.546 | 0.528 | 0.475 | 0.528 | 0.561 | 0.547 | 0.511 | 0.547 |
| ML-W | 0.553 | 0.497 | 0.504 | 0.497 | 0.552 | 0.502 | 0.468 | 0.502 | 0.542 | 0.531 | 0.497 | 0.531 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.519 | 0.138 | 0.098 | 0.138 | 0.38 | 0.186 | 0.088 | 0.186 | 0.398 | 0.186 | 0.072 | 0.186 |
| U-AL-All | 0.576 | 0.13 | 0.084 | 0.13 | 0.358 | 0.161 | 0.089 | 0.161 | 0.138 | 0.138 | 0.053 | 0.138 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.556 | 0.104 | 0.078 | 0.104 | 0.348 | 0.204 | 0.157 | 0.204 | 0.398 | 0.186 | 0.072 | 0.186 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.591 | 0.504 | 0.513 | 0.504 | 0.54 | 0.516 | 0.459 | 0.516 | 0.561 | 0.547 | 0.511 | 0.547 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.591 | 0.504 | 0.513 | 0.504 | 0.544 | 0.525 | 0.467 | 0.525 | 0.561 | 0.547 | 0.511 | 0.547 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.591 | 0.504 | 0.513 | 0.504 | 0.55 | 0.534 | 0.48 | 0.534 | 0.561 | 0.547 | 0.511 | 0.547 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.434 | 0.286 | 0.265 | 0.286 | 0.242 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.369 | 0.186 | 0.072 | 0.186 |
| D-AL-All | 0.431 | 0.282 | 0.259 | 0.282 | 0.259 | 0.14 | 0.058 | 0.14 | 0.138 | 0.138 | 0.053 | 0.138 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.434 | 0.286 | 0.265 | 0.286 | 0.242 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.369 | 0.186 | 0.072 | 0.186 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.588 | 0.501 | 0.507 | 0.501 | 0.546 | 0.498 | 0.463 | 0.498 | 0.561 | 0.547 | 0.511 | 0.547 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.588 | 0.501 | 0.507 | 0.501 | 0.541 | 0.497 | 0.463 | 0.497 | 0.561 | 0.547 | 0.511 | 0.547 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.588 | 0.501 | 0.507 | 0.501 | 0.546 | 0.498 | 0.463 | 0.498 | 0.561 | 0.547 | 0.511 | 0.547 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.147 | 0.065 | 0.056 | 0.065 | 0.372 | 0.227 | 0.163 | 0.227 | 0.397 | 0.212 | 0.127 | 0.212 |
| U-ML-All | 0.064 | 0.064 | 0.053 | 0.064 | 0.413 | 0.277 | 0.248 | 0.277 | 0.397 | 0.212 | 0.127 | 0.212 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.064 | 0.064 | 0.053 | 0.064 | 0.398 | 0.22 | 0.221 | 0.22 | 0.397 | 0.212 | 0.127 | 0.212 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.53 | 0.498 | 0.473 | 0.498 | 0.541 | 0.481 | 0.443 | 0.481 | 0.542 | 0.531 | 0.497 | 0.531 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.514 | 0.485 | 0.447 | 0.485 | 0.542 | 0.509 | 0.465 | 0.509 | 0.542 | 0.531 | 0.497 | 0.531 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.513 | 0.488 | 0.448 | 0.488 | 0.551 | 0.519 | 0.473 | 0.519 | 0.542 | 0.531 | 0.497 | 0.531 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.446 | 0.164 | 0.213 | 0.164 | 0.533 | 0.353 | 0.359 | 0.353 | 0.397 | 0.212 | 0.127 | 0.212 |
| D-ML-All | 0.446 | 0.164 | 0.213 | 0.164 | 0.533 | 0.353 | 0.359 | 0.353 | 0.397 | 0.212 | 0.127 | 0.212 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.446 | 0.164 | 0.213 | 0.164 | 0.533 | 0.353 | 0.359 | 0.353 | 0.397 | 0.212 | 0.127 | 0.212 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.555 | 0.477 | 0.489 | 0.477 | 0.542 | 0.483 | 0.464 | 0.483 | 0.542 | 0.531 | 0.497 | 0.531 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.555 | 0.477 | 0.489 | 0.477 | 0.542 | 0.483 | 0.464 | 0.483 | 0.542 | 0.531 | 0.497 | 0.531 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.555 | 0.477 | 0.489 | 0.477 | 0.542 | 0.483 | 0.464 | 0.483 | 0.542 | 0.531 | 0.497 | 0.531 |
| Method | Random Forest | Random Subspace | AdaBoost | |||||||||
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.386 | 0.177 | 0.069 | 0.177 | 0.249 | 0.149 | 0.06 | 0.149 | 0.361 | 0.282 | 0.11 | 0.282 |
| ML | 0.464 | 0.237 | 0.121 | 0.237 | 0.138 | 0.138 | 0.053 | 0.138 | 0.134 | 0.132 | 0.084 | 0.132 |
| AL-W | 0.566 | 0.54 | 0.514 | 0.54 | 0.497 | 0.442 | 0.368 | 0.442 | 0.418 | 0.389 | 0.203 | 0.389 |
| ML-W | 0.581 | 0.539 | 0.504 | 0.539 | 0.496 | 0.215 | 0.121 | 0.215 | 0.101 | 0.137 | 0.093 | 0.137 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.386 | 0.177 | 0.069 | 0.177 | 0.218 | 0.149 | 0.06 | 0.149 | 0.36 | 0.281 | 0.11 | 0.281 |
| U-AL-All | 0.138 | 0.138 | 0.053 | 0.138 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.054 | 0.14 | 0.389 | 0.337 | 0.131 | 0.337 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.386 | 0.177 | 0.069 | 0.177 | 0.226 | 0.151 | 0.06 | 0.151 | 0.36 | 0.281 | 0.11 | 0.281 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.566 | 0.54 | 0.514 | 0.54 | 0.497 | 0.44 | 0.367 | 0.44 | 0.419 | 0.389 | 0.203 | 0.389 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.566 | 0.54 | 0.514 | 0.54 | 0.497 | 0.44 | 0.367 | 0.44 | 0.419 | 0.389 | 0.203 | 0.389 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.566 | 0.54 | 0.514 | 0.54 | 0.497 | 0.44 | 0.367 | 0.44 | 0.419 | 0.389 | 0.203 | 0.389 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.651 | 0.312 | 0.206 | 0.312 | 0.22 | 0.158 | 0.061 | 0.158 | 0.374 | 0.279 | 0.109 | 0.279 |
| D-AL-All | 0.688 | 0.303 | 0.202 | 0.303 | 0.197 | 0.146 | 0.056 | 0.146 | 0.389 | 0.337 | 0.131 | 0.337 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.651 | 0.312 | 0.206 | 0.312 | 0.22 | 0.158 | 0.061 | 0.158 | 0.374 | 0.279 | 0.109 | 0.279 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.566 | 0.54 | 0.514 | 0.54 | 0.524 | 0.518 | 0.417 | 0.518 | 0.419 | 0.389 | 0.203 | 0.389 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.566 | 0.54 | 0.514 | 0.54 | 0.518 | 0.504 | 0.419 | 0.504 | 0.419 | 0.389 | 0.203 | 0.389 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.566 | 0.54 | 0.514 | 0.54 | 0.524 | 0.518 | 0.417 | 0.518 | 0.419 | 0.389 | 0.203 | 0.389 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.464 | 0.237 | 0.12 | 0.237 | 0.138 | 0.138 | 0.053 | 0.138 | 0.134 | 0.132 | 0.084 | 0.132 |
| U-ML-All | 0.464 | 0.237 | 0.12 | 0.237 | 0.138 | 0.138 | 0.053 | 0.138 | 0.134 | 0.132 | 0.084 | 0.132 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.465 | 0.238 | 0.122 | 0.238 | 0.138 | 0.138 | 0.053 | 0.138 | 0.134 | 0.132 | 0.084 | 0.132 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.581 | 0.539 | 0.504 | 0.539 | 0.496 | 0.215 | 0.121 | 0.215 | 0.101 | 0.137 | 0.093 | 0.137 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.581 | 0.539 | 0.504 | 0.539 | 0.496 | 0.215 | 0.121 | 0.215 | 0.101 | 0.137 | 0.093 | 0.137 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.581 | 0.539 | 0.504 | 0.539 | 0.496 | 0.215 | 0.121 | 0.215 | 0.101 | 0.137 | 0.093 | 0.137 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.575 | 0.345 | 0.237 | 0.345 | 0.209 | 0.152 | 0.067 | 0.152 | 0.134 | 0.132 | 0.084 | 0.132 |
| D-ML-All | 0.575 | 0.345 | 0.237 | 0.345 | 0.209 | 0.152 | 0.067 | 0.152 | 0.134 | 0.132 | 0.084 | 0.132 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.575 | 0.345 | 0.237 | 0.345 | 0.209 | 0.152 | 0.067 | 0.152 | 0.134 | 0.132 | 0.084 | 0.132 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.581 | 0.539 | 0.504 | 0.539 | 0.535 | 0.268 | 0.155 | 0.268 | 0.101 | 0.137 | 0.093 | 0.137 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.581 | 0.539 | 0.504 | 0.539 | 0.519 | 0.244 | 0.142 | 0.244 | 0.101 | 0.137 | 0.093 | 0.137 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.581 | 0.539 | 0.504 | 0.539 | 0.535 | 0.268 | 0.155 | 0.268 | 0.101 | 0.137 | 0.093 | 0.137 |
| Method | K-Nearest Neighbors | Decision Tree | Gradient Boosting | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.488 | 0.14 | 0.158 | 0.14 | 0.147 | 0.145 | 0.056 | 0.145 | 0.198 | 0.146 | 0.055 | 0.146 |
| ML | 0.43 | 0.091 | 0.097 | 0.091 | 0.327 | 0.26 | 0.177 | 0.26 | 0.309 | 0.263 | 0.195 | 0.263 |
| AL-W | 0.435 | 0.402 | 0.411 | 0.402 | 0.454 | 0.406 | 0.369 | 0.406 | 0.458 | 0.437 | 0.42 | 0.437 |
| ML-W | 0.419 | 0.38 | 0.39 | 0.38 | 0.515 | 0.428 | 0.41 | 0.428 | 0.498 | 0.438 | 0.425 | 0.438 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.539 | 0.141 | 0.154 | 0.141 | 0.158 | 0.145 | 0.056 | 0.145 | 0.156 | 0.144 | 0.055 | 0.144 |
| U-AL-All | 0.287 | 0.16 | 0.121 | 0.16 | 0.143 | 0.154 | 0.075 | 0.154 | 0.138 | 0.138 | 0.053 | 0.138 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.34 | 0.135 | 0.138 | 0.135 | 0.267 | 0.214 | 0.125 | 0.214 | 0.176 | 0.145 | 0.055 | 0.145 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.417 | 0.399 | 0.406 | 0.399 | 0.475 | 0.409 | 0.363 | 0.409 | 0.484 | 0.462 | 0.438 | 0.462 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.419 | 0.388 | 0.393 | 0.388 | 0.488 | 0.446 | 0.393 | 0.446 | 0.484 | 0.462 | 0.438 | 0.462 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.43 | 0.386 | 0.385 | 0.386 | 0.478 | 0.447 | 0.394 | 0.447 | 0.484 | 0.462 | 0.438 | 0.462 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.323 | 0.182 | 0.185 | 0.182 | 0.288 | 0.084 | 0.066 | 0.084 | 0.182 | 0.145 | 0.055 | 0.145 |
| D-AL-All | 0.291 | 0.179 | 0.182 | 0.179 | 0.318 | 0.086 | 0.066 | 0.086 | 0.138 | 0.138 | 0.053 | 0.138 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.323 | 0.182 | 0.185 | 0.182 | 0.288 | 0.084 | 0.066 | 0.084 | 0.182 | 0.145 | 0.055 | 0.145 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.435 | 0.402 | 0.411 | 0.402 | 0.479 | 0.417 | 0.375 | 0.417 | 0.486 | 0.463 | 0.438 | 0.463 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.435 | 0.402 | 0.411 | 0.402 | 0.478 | 0.423 | 0.378 | 0.423 | 0.486 | 0.463 | 0.438 | 0.463 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.435 | 0.402 | 0.411 | 0.402 | 0.479 | 0.417 | 0.375 | 0.417 | 0.486 | 0.463 | 0.438 | 0.463 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.536 | 0.098 | 0.116 | 0.098 | 0.316 | 0.257 | 0.171 | 0.257 | 0.309 | 0.263 | 0.195 | 0.263 |
| U-ML-All | 0.624 | 0.092 | 0.109 | 0.092 | 0.402 | 0.301 | 0.246 | 0.301 | 0.309 | 0.263 | 0.195 | 0.263 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.628 | 0.093 | 0.11 | 0.093 | 0.449 | 0.251 | 0.283 | 0.251 | 0.309 | 0.263 | 0.195 | 0.263 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.421 | 0.383 | 0.392 | 0.383 | 0.521 | 0.407 | 0.368 | 0.407 | 0.498 | 0.438 | 0.425 | 0.438 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.482 | 0.301 | 0.314 | 0.301 | 0.502 | 0.436 | 0.414 | 0.436 | 0.498 | 0.438 | 0.425 | 0.438 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.475 | 0.285 | 0.286 | 0.285 | 0.496 | 0.449 | 0.413 | 0.449 | 0.498 | 0.438 | 0.425 | 0.438 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.317 | 0.139 | 0.131 | 0.139 | 0.323 | 0.158 | 0.31 | 0.158 | 0.309 | 0.263 | 0.195 | 0.263 |
| D-ML-All | 0.317 | 0.139 | 0.131 | 0.139 | 0.323 | 0.158 | 0.31 | 0.158 | 0.309 | 0.263 | 0.195 | 0.263 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.317 | 0.139 | 0.131 | 0.139 | 0.323 | 0.158 | 0.31 | 0.158 | 0.309 | 0.263 | 0.195 | 0.263 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.404 | 0.382 | 0.409 | 0.382 | 0.508 | 0.419 | 0.386 | 0.419 | 0.498 | 0.438 | 0.425 | 0.438 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.404 | 0.382 | 0.409 | 0.382 | 0.508 | 0.419 | 0.386 | 0.419 | 0.498 | 0.438 | 0.425 | 0.438 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.404 | 0.382 | 0.409 | 0.382 | 0.508 | 0.419 | 0.386 | 0.419 | 0.498 | 0.438 | 0.425 | 0.438 |
| Method | Random Forest | Random Subspace | AdaBoost | |||||||||
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.198 | 0.167 | 0.078 | 0.167 | 0.129 | 0.145 | 0.055 | 0.145 | 0.202 | 0.183 | 0.075 | 0.183 |
| ML | 0.341 | 0.251 | 0.183 | 0.251 | 0.138 | 0.138 | 0.053 | 0.138 | 0.107 | 0.143 | 0.062 | 0.143 |
| AL-W | 0.47 | 0.423 | 0.419 | 0.423 | 0.259 | 0.238 | 0.159 | 0.238 | 0.268 | 0.292 | 0.145 | 0.292 |
| ML-W | 0.528 | 0.438 | 0.403 | 0.438 | 0.208 | 0.148 | 0.056 | 0.148 | 0.112 | 0.154 | 0.084 | 0.154 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.198 | 0.167 | 0.078 | 0.167 | 0.125 | 0.145 | 0.055 | 0.145 | 0.196 | 0.184 | 0.073 | 0.184 |
| U-AL-All | 0.168 | 0.164 | 0.062 | 0.164 | 0.138 | 0.138 | 0.053 | 0.138 | 0.119 | 0.141 | 0.054 | 0.141 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.198 | 0.167 | 0.078 | 0.167 | 0.144 | 0.143 | 0.054 | 0.143 | 0.243 | 0.192 | 0.073 | 0.192 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.485 | 0.447 | 0.422 | 0.447 | 0.299 | 0.269 | 0.143 | 0.269 | 0.331 | 0.316 | 0.168 | 0.316 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.49 | 0.45 | 0.423 | 0.45 | 0.299 | 0.269 | 0.143 | 0.269 | 0.331 | 0.316 | 0.168 | 0.316 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.485 | 0.447 | 0.422 | 0.447 | 0.299 | 0.269 | 0.143 | 0.269 | 0.331 | 0.316 | 0.168 | 0.316 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.252 | 0.189 | 0.135 | 0.189 | 0.221 | 0.147 | 0.061 | 0.147 | 0.211 | 0.194 | 0.079 | 0.194 |
| D-AL-All | 0.267 | 0.172 | 0.114 | 0.172 | 0.139 | 0.14 | 0.058 | 0.14 | 0.119 | 0.141 | 0.054 | 0.141 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.252 | 0.189 | 0.135 | 0.189 | 0.221 | 0.147 | 0.061 | 0.147 | 0.211 | 0.194 | 0.079 | 0.194 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.481 | 0.446 | 0.421 | 0.446 | 0.378 | 0.302 | 0.202 | 0.302 | 0.331 | 0.316 | 0.168 | 0.316 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.481 | 0.446 | 0.421 | 0.446 | 0.375 | 0.306 | 0.198 | 0.306 | 0.331 | 0.316 | 0.168 | 0.316 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.481 | 0.446 | 0.421 | 0.446 | 0.378 | 0.302 | 0.202 | 0.302 | 0.331 | 0.316 | 0.168 | 0.316 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.341 | 0.251 | 0.183 | 0.251 | 0.138 | 0.138 | 0.053 | 0.138 | 0.107 | 0.143 | 0.062 | 0.143 |
| U-ML-All | 0.341 | 0.251 | 0.183 | 0.251 | 0.138 | 0.138 | 0.053 | 0.138 | 0.107 | 0.143 | 0.062 | 0.143 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.341 | 0.251 | 0.183 | 0.251 | 0.138 | 0.138 | 0.053 | 0.138 | 0.107 | 0.143 | 0.062 | 0.143 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.528 | 0.438 | 0.403 | 0.438 | 0.202 | 0.149 | 0.057 | 0.149 | 0.112 | 0.154 | 0.084 | 0.154 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.528 | 0.438 | 0.403 | 0.438 | 0.202 | 0.149 | 0.057 | 0.149 | 0.112 | 0.154 | 0.084 | 0.154 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.528 | 0.438 | 0.403 | 0.438 | 0.202 | 0.149 | 0.057 | 0.149 | 0.112 | 0.154 | 0.084 | 0.154 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.347 | 0.258 | 0.201 | 0.258 | 0.205 | 0.146 | 0.06 | 0.146 | 0.107 | 0.143 | 0.062 | 0.143 |
| D-ML-All | 0.347 | 0.258 | 0.201 | 0.258 | 0.205 | 0.146 | 0.06 | 0.146 | 0.107 | 0.143 | 0.062 | 0.143 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.347 | 0.258 | 0.201 | 0.258 | 0.205 | 0.146 | 0.06 | 0.146 | 0.107 | 0.143 | 0.062 | 0.143 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.528 | 0.438 | 0.403 | 0.438 | 0.369 | 0.198 | 0.121 | 0.198 | 0.112 | 0.154 | 0.084 | 0.154 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.528 | 0.438 | 0.403 | 0.438 | 0.416 | 0.207 | 0.12 | 0.207 | 0.112 | 0.154 | 0.084 | 0.154 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.528 | 0.438 | 0.403 | 0.438 | 0.369 | 0.198 | 0.121 | 0.198 | 0.112 | 0.154 | 0.084 | 0.154 |
| Method | K-Nearest Neighbors | Decision Tree | Gradient Boosting | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.64 | 0.64 | 0.627 | 0.64 | 0.72 | 0.709 | 0.69 | 0.709 | 0.747 | 0.731 | 0.718 | 0.731 |
| ML | 0.609 | 0.621 | 0.601 | 0.621 | 0.738 | 0.722 | 0.705 | 0.722 | 0.756 | 0.742 | 0.73 | 0.742 |
| AL-W | 0.62 | 0.626 | 0.609 | 0.626 | 0.721 | 0.709 | 0.691 | 0.709 | 0.75 | 0.732 | 0.72 | 0.732 |
| ML-W | 0.63 | 0.635 | 0.614 | 0.635 | 0.732 | 0.72 | 0.702 | 0.72 | 0.758 | 0.744 | 0.732 | 0.744 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.639 | 0.64 | 0.628 | 0.64 | 0.722 | 0.708 | 0.69 | 0.708 | 0.752 | 0.734 | 0.722 | 0.734 |
| U-AL-All | 0.637 | 0.624 | 0.617 | 0.624 | 0.738 | 0.722 | 0.705 | 0.722 | 0.752 | 0.728 | 0.717 | 0.728 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.642 | 0.643 | 0.631 | 0.643 | 0.72 | 0.707 | 0.689 | 0.707 | 0.754 | 0.735 | 0.723 | 0.735 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.621 | 0.619 | 0.608 | 0.619 | 0.726 | 0.714 | 0.698 | 0.714 | 0.749 | 0.728 | 0.716 | 0.728 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.621 | 0.619 | 0.608 | 0.619 | 0.726 | 0.714 | 0.698 | 0.714 | 0.749 | 0.728 | 0.716 | 0.728 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.622 | 0.619 | 0.608 | 0.619 | 0.726 | 0.714 | 0.698 | 0.714 | 0.749 | 0.728 | 0.716 | 0.728 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.594 | 0.579 | 0.568 | 0.579 | 0.72 | 0.705 | 0.687 | 0.705 | 0.708 | 0.694 | 0.683 | 0.694 |
| D-AL-All | 0.593 | 0.583 | 0.569 | 0.583 | 0.738 | 0.722 | 0.705 | 0.722 | 0.707 | 0.692 | 0.68 | 0.692 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.613 | 0.592 | 0.583 | 0.592 | 0.734 | 0.719 | 0.702 | 0.719 | 0.708 | 0.694 | 0.683 | 0.694 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.603 | 0.587 | 0.577 | 0.587 | 0.726 | 0.714 | 0.698 | 0.714 | 0.695 | 0.668 | 0.658 | 0.668 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.609 | 0.592 | 0.581 | 0.592 | 0.726 | 0.714 | 0.698 | 0.714 | 0.705 | 0.69 | 0.678 | 0.69 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.614 | 0.597 | 0.589 | 0.597 | 0.726 | 0.714 | 0.698 | 0.714 | 0.705 | 0.69 | 0.678 | 0.69 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.631 | 0.637 | 0.617 | 0.637 | 0.721 | 0.706 | 0.687 | 0.706 | 0.755 | 0.739 | 0.728 | 0.739 |
| U-ML-All | 0.631 | 0.636 | 0.616 | 0.636 | 0.728 | 0.713 | 0.694 | 0.713 | 0.755 | 0.739 | 0.728 | 0.739 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.632 | 0.638 | 0.617 | 0.638 | 0.721 | 0.706 | 0.687 | 0.706 | 0.755 | 0.739 | 0.728 | 0.739 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.63 | 0.637 | 0.616 | 0.637 | 0.726 | 0.714 | 0.698 | 0.714 | 0.756 | 0.741 | 0.729 | 0.741 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.629 | 0.635 | 0.615 | 0.635 | 0.726 | 0.714 | 0.698 | 0.714 | 0.756 | 0.741 | 0.729 | 0.741 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.632 | 0.639 | 0.618 | 0.639 | 0.726 | 0.714 | 0.698 | 0.714 | 0.756 | 0.741 | 0.729 | 0.741 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.629 | 0.622 | 0.607 | 0.622 | 0.727 | 0.711 | 0.692 | 0.711 | 0.748 | 0.742 | 0.726 | 0.742 |
| D-ML-All | 0.634 | 0.628 | 0.612 | 0.628 | 0.727 | 0.711 | 0.692 | 0.711 | 0.748 | 0.743 | 0.727 | 0.743 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.629 | 0.628 | 0.61 | 0.628 | 0.721 | 0.706 | 0.687 | 0.706 | 0.752 | 0.749 | 0.732 | 0.749 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.629 | 0.622 | 0.607 | 0.622 | 0.726 | 0.714 | 0.698 | 0.714 | 0.746 | 0.74 | 0.724 | 0.74 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.63 | 0.633 | 0.613 | 0.633 | 0.726 | 0.714 | 0.698 | 0.714 | 0.747 | 0.741 | 0.725 | 0.741 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.632 | 0.632 | 0.613 | 0.632 | 0.726 | 0.714 | 0.698 | 0.714 | 0.751 | 0.748 | 0.732 | 0.748 |
| Method | Random Forest | Random Subspace | AdaBoost | |||||||||
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.752 | 0.762 | 0.741 | 0.762 | 0.748 | 0.76 | 0.734 | 0.76 | 0.669 | 0.628 | 0.621 | 0.628 |
| ML | 0.765 | 0.777 | 0.752 | 0.777 | 0.771 | 0.783 | 0.757 | 0.783 | 0.694 | 0.667 | 0.654 | 0.667 |
| AL-W | 0.752 | 0.761 | 0.74 | 0.761 | 0.751 | 0.761 | 0.736 | 0.761 | 0.659 | 0.625 | 0.617 | 0.625 |
| ML-W | 0.767 | 0.78 | 0.753 | 0.78 | 0.768 | 0.78 | 0.754 | 0.78 | 0.694 | 0.666 | 0.653 | 0.666 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.753 | 0.762 | 0.741 | 0.762 | 0.752 | 0.756 | 0.734 | 0.756 | 0.675 | 0.619 | 0.617 | 0.619 |
| U-AL-All | 0.755 | 0.76 | 0.742 | 0.76 | 0.751 | 0.75 | 0.734 | 0.75 | 0.649 | 0.63 | 0.619 | 0.63 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.753 | 0.762 | 0.741 | 0.762 | 0.748 | 0.761 | 0.735 | 0.761 | 0.66 | 0.62 | 0.611 | 0.62 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.753 | 0.761 | 0.74 | 0.761 | 0.752 | 0.756 | 0.734 | 0.756 | 0.654 | 0.618 | 0.61 | 0.618 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.753 | 0.761 | 0.74 | 0.761 | 0.752 | 0.756 | 0.734 | 0.756 | 0.654 | 0.618 | 0.61 | 0.618 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.752 | 0.76 | 0.739 | 0.76 | 0.752 | 0.756 | 0.734 | 0.756 | 0.656 | 0.62 | 0.613 | 0.62 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.741 | 0.745 | 0.726 | 0.745 | 0.718 | 0.717 | 0.697 | 0.717 | 0.649 | 0.609 | 0.597 | 0.609 |
| D-AL-All | 0.743 | 0.748 | 0.729 | 0.748 | 0.734 | 0.735 | 0.713 | 0.735 | 0.675 | 0.643 | 0.633 | 0.643 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.744 | 0.752 | 0.731 | 0.752 | 0.738 | 0.748 | 0.723 | 0.748 | 0.651 | 0.619 | 0.61 | 0.619 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.726 | 0.724 | 0.705 | 0.724 | 0.709 | 0.705 | 0.687 | 0.705 | 0.654 | 0.609 | 0.596 | 0.609 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.746 | 0.752 | 0.731 | 0.752 | 0.733 | 0.73 | 0.713 | 0.73 | 0.647 | 0.606 | 0.599 | 0.606 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.744 | 0.75 | 0.73 | 0.75 | 0.734 | 0.731 | 0.714 | 0.731 | 0.647 | 0.606 | 0.599 | 0.606 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.763 | 0.776 | 0.749 | 0.776 | 0.77 | 0.782 | 0.756 | 0.782 | 0.694 | 0.668 | 0.655 | 0.668 |
| U-ML-All | 0.763 | 0.776 | 0.75 | 0.776 | 0.77 | 0.782 | 0.756 | 0.782 | 0.694 | 0.668 | 0.655 | 0.668 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.763 | 0.776 | 0.749 | 0.776 | 0.77 | 0.782 | 0.756 | 0.782 | 0.694 | 0.668 | 0.655 | 0.668 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.766 | 0.779 | 0.752 | 0.779 | 0.768 | 0.78 | 0.754 | 0.78 | 0.695 | 0.668 | 0.655 | 0.668 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.766 | 0.779 | 0.752 | 0.779 | 0.768 | 0.78 | 0.754 | 0.78 | 0.695 | 0.668 | 0.655 | 0.668 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.766 | 0.779 | 0.752 | 0.779 | 0.768 | 0.78 | 0.754 | 0.78 | 0.695 | 0.668 | 0.655 | 0.668 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.757 | 0.769 | 0.744 | 0.769 | 0.761 | 0.773 | 0.75 | 0.773 | 0.672 | 0.634 | 0.627 | 0.634 |
| D-ML-All | 0.758 | 0.771 | 0.745 | 0.771 | 0.768 | 0.78 | 0.756 | 0.78 | 0.686 | 0.647 | 0.643 | 0.647 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.759 | 0.772 | 0.746 | 0.772 | 0.766 | 0.78 | 0.755 | 0.78 | 0.687 | 0.647 | 0.643 | 0.647 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.758 | 0.77 | 0.745 | 0.77 | 0.761 | 0.773 | 0.75 | 0.773 | 0.671 | 0.632 | 0.626 | 0.632 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.759 | 0.771 | 0.746 | 0.771 | 0.768 | 0.78 | 0.757 | 0.78 | 0.682 | 0.643 | 0.638 | 0.643 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.761 | 0.773 | 0.748 | 0.773 | 0.769 | 0.779 | 0.754 | 0.779 | 0.684 | 0.643 | 0.639 | 0.643 |
| Method | K-Nearest Neighbors | Decision Tree | Gradient Boosting | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.596 | 0.592 | 0.577 | 0.592 | 0.738 | 0.737 | 0.717 | 0.737 | 0.738 | 0.745 | 0.721 | 0.745 |
| ML | 0.603 | 0.614 | 0.591 | 0.614 | 0.736 | 0.732 | 0.715 | 0.732 | 0.714 | 0.724 | 0.7 | 0.724 |
| AL-W | 0.593 | 0.588 | 0.574 | 0.588 | 0.733 | 0.727 | 0.708 | 0.727 | 0.728 | 0.735 | 0.711 | 0.735 |
| ML-W | 0.599 | 0.613 | 0.587 | 0.613 | 0.733 | 0.727 | 0.708 | 0.727 | 0.715 | 0.724 | 0.701 | 0.724 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.596 | 0.59 | 0.577 | 0.59 | 0.74 | 0.739 | 0.719 | 0.739 | 0.73 | 0.738 | 0.714 | 0.738 |
| U-AL-All | 0.606 | 0.595 | 0.585 | 0.595 | 0.736 | 0.732 | 0.715 | 0.732 | 0.739 | 0.742 | 0.719 | 0.742 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.597 | 0.594 | 0.58 | 0.594 | 0.736 | 0.735 | 0.716 | 0.735 | 0.732 | 0.739 | 0.717 | 0.739 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.587 | 0.582 | 0.568 | 0.582 | 0.733 | 0.727 | 0.708 | 0.727 | 0.728 | 0.736 | 0.712 | 0.736 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.592 | 0.587 | 0.574 | 0.587 | 0.733 | 0.727 | 0.708 | 0.727 | 0.727 | 0.737 | 0.712 | 0.737 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.591 | 0.587 | 0.574 | 0.587 | 0.733 | 0.727 | 0.708 | 0.727 | 0.727 | 0.736 | 0.711 | 0.736 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.582 | 0.552 | 0.541 | 0.552 | 0.73 | 0.73 | 0.71 | 0.73 | 0.647 | 0.635 | 0.617 | 0.635 |
| D-AL-All | 0.592 | 0.561 | 0.548 | 0.561 | 0.736 | 0.732 | 0.715 | 0.732 | 0.683 | 0.674 | 0.654 | 0.674 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.596 | 0.564 | 0.554 | 0.564 | 0.737 | 0.735 | 0.715 | 0.735 | 0.654 | 0.647 | 0.627 | 0.647 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.58 | 0.543 | 0.533 | 0.543 | 0.733 | 0.727 | 0.708 | 0.727 | 0.632 | 0.621 | 0.601 | 0.621 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.592 | 0.572 | 0.56 | 0.572 | 0.733 | 0.727 | 0.708 | 0.727 | 0.668 | 0.669 | 0.649 | 0.669 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.592 | 0.561 | 0.553 | 0.561 | 0.733 | 0.727 | 0.708 | 0.727 | 0.642 | 0.635 | 0.615 | 0.635 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.618 | 0.624 | 0.601 | 0.624 | 0.742 | 0.74 | 0.721 | 0.74 | 0.714 | 0.723 | 0.699 | 0.723 |
| U-ML-All | 0.608 | 0.617 | 0.592 | 0.617 | 0.742 | 0.74 | 0.721 | 0.74 | 0.715 | 0.726 | 0.702 | 0.726 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.608 | 0.617 | 0.592 | 0.617 | 0.742 | 0.74 | 0.721 | 0.74 | 0.715 | 0.727 | 0.703 | 0.727 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.621 | 0.626 | 0.603 | 0.626 | 0.733 | 0.727 | 0.708 | 0.727 | 0.714 | 0.724 | 0.7 | 0.724 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.612 | 0.619 | 0.594 | 0.619 | 0.733 | 0.727 | 0.708 | 0.727 | 0.715 | 0.727 | 0.703 | 0.727 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.611 | 0.619 | 0.594 | 0.619 | 0.733 | 0.727 | 0.708 | 0.727 | 0.716 | 0.728 | 0.703 | 0.728 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.642 | 0.631 | 0.619 | 0.631 | 0.738 | 0.735 | 0.716 | 0.735 | 0.666 | 0.672 | 0.65 | 0.672 |
| D-ML-All | 0.647 | 0.638 | 0.625 | 0.638 | 0.74 | 0.737 | 0.718 | 0.737 | 0.693 | 0.7 | 0.678 | 0.7 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.649 | 0.638 | 0.626 | 0.638 | 0.738 | 0.735 | 0.715 | 0.735 | 0.679 | 0.687 | 0.664 | 0.687 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.63 | 0.618 | 0.606 | 0.618 | 0.733 | 0.727 | 0.708 | 0.727 | 0.662 | 0.669 | 0.647 | 0.669 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.638 | 0.629 | 0.615 | 0.629 | 0.733 | 0.727 | 0.708 | 0.727 | 0.688 | 0.695 | 0.673 | 0.695 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.637 | 0.626 | 0.613 | 0.626 | 0.733 | 0.727 | 0.708 | 0.727 | 0.678 | 0.685 | 0.662 | 0.685 |
| Method | Random Forest | Random Subspace | AdaBoost | |||||||||
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.763 | 0.772 | 0.748 | 0.772 | 0.767 | 0.773 | 0.753 | 0.773 | 0.657 | 0.668 | 0.643 | 0.668 |
| ML | 0.757 | 0.769 | 0.742 | 0.769 | 0.775 | 0.783 | 0.763 | 0.783 | 0.666 | 0.647 | 0.638 | 0.647 |
| AL-W | 0.76 | 0.766 | 0.743 | 0.766 | 0.76 | 0.769 | 0.748 | 0.769 | 0.666 | 0.672 | 0.646 | 0.672 |
| ML-W | 0.76 | 0.771 | 0.744 | 0.771 | 0.775 | 0.784 | 0.763 | 0.784 | 0.664 | 0.645 | 0.635 | 0.645 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.762 | 0.771 | 0.747 | 0.771 | 0.769 | 0.776 | 0.757 | 0.776 | 0.659 | 0.668 | 0.642 | 0.668 |
| U-AL-All | 0.763 | 0.772 | 0.749 | 0.772 | 0.772 | 0.776 | 0.758 | 0.776 | 0.647 | 0.664 | 0.638 | 0.664 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.761 | 0.77 | 0.746 | 0.77 | 0.769 | 0.776 | 0.757 | 0.776 | 0.653 | 0.662 | 0.637 | 0.662 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.757 | 0.764 | 0.741 | 0.764 | 0.76 | 0.768 | 0.749 | 0.768 | 0.666 | 0.672 | 0.644 | 0.672 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.757 | 0.764 | 0.741 | 0.764 | 0.76 | 0.768 | 0.748 | 0.768 | 0.659 | 0.666 | 0.64 | 0.666 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.756 | 0.763 | 0.74 | 0.763 | 0.762 | 0.769 | 0.75 | 0.769 | 0.657 | 0.664 | 0.638 | 0.664 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.714 | 0.711 | 0.693 | 0.711 | 0.683 | 0.67 | 0.656 | 0.67 | 0.566 | 0.532 | 0.52 | 0.532 |
| D-AL-All | 0.748 | 0.74 | 0.726 | 0.74 | 0.753 | 0.755 | 0.736 | 0.755 | 0.655 | 0.583 | 0.571 | 0.583 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.735 | 0.737 | 0.716 | 0.737 | 0.708 | 0.7 | 0.685 | 0.7 | 0.598 | 0.559 | 0.546 | 0.559 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.742 | 0.728 | 0.714 | 0.728 | 0.678 | 0.665 | 0.649 | 0.665 | 0.606 | 0.559 | 0.543 | 0.559 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.747 | 0.741 | 0.727 | 0.741 | 0.722 | 0.729 | 0.71 | 0.729 | 0.61 | 0.579 | 0.567 | 0.579 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.752 | 0.746 | 0.731 | 0.746 | 0.695 | 0.691 | 0.671 | 0.691 | 0.608 | 0.568 | 0.556 | 0.568 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.76 | 0.771 | 0.744 | 0.771 | 0.773 | 0.781 | 0.761 | 0.781 | 0.647 | 0.631 | 0.619 | 0.631 |
| U-ML-All | 0.758 | 0.769 | 0.743 | 0.769 | 0.774 | 0.781 | 0.761 | 0.781 | 0.662 | 0.644 | 0.632 | 0.644 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.755 | 0.768 | 0.74 | 0.768 | 0.776 | 0.783 | 0.763 | 0.783 | 0.667 | 0.649 | 0.638 | 0.649 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.764 | 0.774 | 0.748 | 0.774 | 0.774 | 0.783 | 0.762 | 0.783 | 0.642 | 0.651 | 0.622 | 0.651 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.762 | 0.772 | 0.746 | 0.772 | 0.774 | 0.783 | 0.762 | 0.783 | 0.655 | 0.638 | 0.626 | 0.638 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.761 | 0.772 | 0.745 | 0.772 | 0.776 | 0.785 | 0.764 | 0.785 | 0.657 | 0.639 | 0.629 | 0.639 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.753 | 0.765 | 0.74 | 0.765 | 0.77 | 0.775 | 0.75 | 0.775 | 0.643 | 0.587 | 0.583 | 0.587 |
| D-ML-All | 0.758 | 0.769 | 0.743 | 0.769 | 0.774 | 0.781 | 0.756 | 0.781 | 0.659 | 0.606 | 0.602 | 0.606 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.757 | 0.769 | 0.743 | 0.769 | 0.771 | 0.778 | 0.753 | 0.778 | 0.656 | 0.602 | 0.597 | 0.602 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.753 | 0.763 | 0.739 | 0.763 | 0.766 | 0.774 | 0.751 | 0.774 | 0.634 | 0.591 | 0.587 | 0.591 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.756 | 0.765 | 0.74 | 0.765 | 0.777 | 0.783 | 0.759 | 0.783 | 0.649 | 0.606 | 0.601 | 0.606 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.757 | 0.767 | 0.742 | 0.767 | 0.771 | 0.779 | 0.754 | 0.779 | 0.646 | 0.603 | 0.598 | 0.603 |
| Method | K-Nearest Neighbors | Decision Tree | Gradient Boosting | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.612 | 0.62 | 0.605 | 0.62 | 0.715 | 0.712 | 0.695 | 0.712 | 0.744 | 0.742 | 0.729 | 0.742 |
| ML | 0.598 | 0.613 | 0.589 | 0.613 | 0.711 | 0.707 | 0.693 | 0.707 | 0.758 | 0.754 | 0.743 | 0.754 |
| AL-W | 0.613 | 0.62 | 0.606 | 0.62 | 0.715 | 0.713 | 0.697 | 0.713 | 0.745 | 0.743 | 0.73 | 0.743 |
| ML-W | 0.588 | 0.602 | 0.578 | 0.602 | 0.718 | 0.715 | 0.699 | 0.715 | 0.758 | 0.754 | 0.742 | 0.754 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.605 | 0.613 | 0.596 | 0.613 | 0.724 | 0.72 | 0.705 | 0.72 | 0.749 | 0.747 | 0.734 | 0.747 |
| U-AL-All | 0.616 | 0.623 | 0.609 | 0.623 | 0.711 | 0.707 | 0.693 | 0.707 | 0.745 | 0.739 | 0.727 | 0.739 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.621 | 0.628 | 0.615 | 0.628 | 0.724 | 0.722 | 0.706 | 0.722 | 0.746 | 0.742 | 0.729 | 0.742 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.611 | 0.617 | 0.603 | 0.617 | 0.716 | 0.713 | 0.698 | 0.713 | 0.749 | 0.746 | 0.734 | 0.746 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.613 | 0.62 | 0.607 | 0.62 | 0.716 | 0.713 | 0.698 | 0.713 | 0.746 | 0.741 | 0.729 | 0.741 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.618 | 0.624 | 0.611 | 0.624 | 0.716 | 0.713 | 0.698 | 0.713 | 0.748 | 0.742 | 0.729 | 0.742 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.532 | 0.507 | 0.498 | 0.507 | 0.709 | 0.704 | 0.69 | 0.704 | 0.631 | 0.604 | 0.602 | 0.604 |
| D-AL-All | 0.611 | 0.568 | 0.567 | 0.568 | 0.711 | 0.707 | 0.693 | 0.707 | 0.628 | 0.616 | 0.607 | 0.616 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.561 | 0.538 | 0.533 | 0.538 | 0.715 | 0.711 | 0.696 | 0.711 | 0.639 | 0.619 | 0.613 | 0.619 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.552 | 0.54 | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.716 | 0.713 | 0.698 | 0.713 | 0.644 | 0.621 | 0.618 | 0.621 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.588 | 0.6 | 0.716 | 0.713 | 0.698 | 0.713 | 0.652 | 0.637 | 0.629 | 0.637 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.57 | 0.558 | 0.551 | 0.558 | 0.716 | 0.713 | 0.698 | 0.713 | 0.642 | 0.62 | 0.615 | 0.62 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.608 | 0.622 | 0.597 | 0.622 | 0.724 | 0.72 | 0.705 | 0.72 | 0.757 | 0.755 | 0.743 | 0.755 |
| U-ML-All | 0.598 | 0.61 | 0.586 | 0.61 | 0.718 | 0.717 | 0.701 | 0.717 | 0.754 | 0.75 | 0.738 | 0.75 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.601 | 0.614 | 0.59 | 0.614 | 0.724 | 0.72 | 0.705 | 0.72 | 0.759 | 0.751 | 0.74 | 0.751 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.602 | 0.614 | 0.589 | 0.614 | 0.716 | 0.713 | 0.698 | 0.713 | 0.758 | 0.755 | 0.743 | 0.755 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.594 | 0.607 | 0.583 | 0.607 | 0.716 | 0.713 | 0.698 | 0.713 | 0.757 | 0.751 | 0.74 | 0.751 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.595 | 0.608 | 0.584 | 0.608 | 0.716 | 0.713 | 0.698 | 0.713 | 0.76 | 0.752 | 0.74 | 0.752 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.591 | 0.594 | 0.574 | 0.594 | 0.714 | 0.712 | 0.695 | 0.712 | 0.693 | 0.687 | 0.677 | 0.687 |
| D-ML-All | 0.604 | 0.604 | 0.591 | 0.604 | 0.719 | 0.717 | 0.702 | 0.717 | 0.692 | 0.687 | 0.676 | 0.687 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.592 | 0.595 | 0.582 | 0.595 | 0.714 | 0.712 | 0.695 | 0.712 | 0.691 | 0.686 | 0.675 | 0.686 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.598 | 0.587 | 0.574 | 0.587 | 0.716 | 0.713 | 0.698 | 0.713 | 0.694 | 0.688 | 0.677 | 0.688 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.61 | 0.614 | 0.601 | 0.614 | 0.716 | 0.713 | 0.698 | 0.713 | 0.692 | 0.687 | 0.676 | 0.687 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.59 | 0.594 | 0.578 | 0.594 | 0.716 | 0.713 | 0.698 | 0.713 | 0.692 | 0.687 | 0.676 | 0.687 |
| Method | Random Forest | Random Subspace | AdaBoost | |||||||||
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.744 | 0.751 | 0.731 | 0.751 | 0.752 | 0.756 | 0.739 | 0.756 | 0.703 | 0.672 | 0.667 | 0.672 |
| ML | 0.732 | 0.75 | 0.722 | 0.75 | 0.756 | 0.768 | 0.745 | 0.768 | 0.701 | 0.698 | 0.68 | 0.698 |
| AL-W | 0.735 | 0.744 | 0.724 | 0.744 | 0.75 | 0.754 | 0.737 | 0.754 | 0.712 | 0.675 | 0.67 | 0.675 |
| ML-W | 0.736 | 0.754 | 0.726 | 0.754 | 0.757 | 0.767 | 0.745 | 0.767 | 0.7 | 0.697 | 0.678 | 0.697 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.74 | 0.748 | 0.728 | 0.748 | 0.755 | 0.759 | 0.741 | 0.759 | 0.692 | 0.666 | 0.653 | 0.666 |
| U-AL-All | 0.741 | 0.75 | 0.73 | 0.75 | 0.758 | 0.76 | 0.743 | 0.76 | 0.723 | 0.679 | 0.678 | 0.679 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.739 | 0.747 | 0.727 | 0.747 | 0.758 | 0.758 | 0.742 | 0.758 | 0.714 | 0.674 | 0.67 | 0.674 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.738 | 0.747 | 0.727 | 0.747 | 0.753 | 0.755 | 0.738 | 0.755 | 0.689 | 0.665 | 0.652 | 0.665 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.739 | 0.747 | 0.727 | 0.747 | 0.752 | 0.756 | 0.739 | 0.756 | 0.714 | 0.673 | 0.67 | 0.673 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.739 | 0.748 | 0.728 | 0.748 | 0.75 | 0.754 | 0.736 | 0.754 | 0.717 | 0.676 | 0.672 | 0.676 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.666 | 0.654 | 0.638 | 0.654 | 0.656 | 0.631 | 0.62 | 0.631 | 0.556 | 0.498 | 0.504 | 0.498 |
| D-AL-All | 0.709 | 0.698 | 0.682 | 0.698 | 0.697 | 0.682 | 0.667 | 0.682 | 0.638 | 0.605 | 0.602 | 0.605 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.695 | 0.675 | 0.66 | 0.675 | 0.662 | 0.63 | 0.619 | 0.63 | 0.556 | 0.498 | 0.502 | 0.498 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.68 | 0.654 | 0.643 | 0.654 | 0.646 | 0.602 | 0.598 | 0.602 | 0.552 | 0.538 | 0.533 | 0.538 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.716 | 0.703 | 0.687 | 0.703 | 0.692 | 0.68 | 0.668 | 0.68 | 0.614 | 0.602 | 0.602 | 0.602 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.693 | 0.666 | 0.654 | 0.666 | 0.653 | 0.609 | 0.606 | 0.609 | 0.561 | 0.548 | 0.544 | 0.548 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.737 | 0.753 | 0.726 | 0.753 | 0.755 | 0.765 | 0.743 | 0.765 | 0.695 | 0.687 | 0.671 | 0.687 |
| U-ML-All | 0.737 | 0.754 | 0.727 | 0.754 | 0.751 | 0.762 | 0.739 | 0.762 | 0.705 | 0.695 | 0.681 | 0.695 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.737 | 0.753 | 0.726 | 0.753 | 0.749 | 0.76 | 0.737 | 0.76 | 0.701 | 0.689 | 0.676 | 0.689 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.74 | 0.756 | 0.729 | 0.756 | 0.754 | 0.761 | 0.74 | 0.761 | 0.694 | 0.687 | 0.669 | 0.687 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.738 | 0.755 | 0.728 | 0.755 | 0.752 | 0.761 | 0.74 | 0.761 | 0.702 | 0.693 | 0.678 | 0.693 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.741 | 0.757 | 0.73 | 0.757 | 0.751 | 0.759 | 0.737 | 0.759 | 0.701 | 0.69 | 0.676 | 0.69 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.704 | 0.72 | 0.693 | 0.72 | 0.717 | 0.72 | 0.695 | 0.72 | 0.659 | 0.65 | 0.639 | 0.65 |
| D-ML-All | 0.713 | 0.728 | 0.701 | 0.728 | 0.721 | 0.735 | 0.707 | 0.735 | 0.668 | 0.657 | 0.645 | 0.657 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.701 | 0.717 | 0.689 | 0.717 | 0.716 | 0.722 | 0.697 | 0.722 | 0.66 | 0.65 | 0.637 | 0.65 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.711 | 0.726 | 0.7 | 0.726 | 0.71 | 0.714 | 0.69 | 0.714 | 0.66 | 0.653 | 0.64 | 0.653 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.72 | 0.735 | 0.708 | 0.735 | 0.721 | 0.736 | 0.708 | 0.736 | 0.671 | 0.659 | 0.646 | 0.659 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.707 | 0.722 | 0.696 | 0.722 | 0.711 | 0.719 | 0.695 | 0.719 | 0.662 | 0.652 | 0.639 | 0.652 |
| Method | K-Nearest Neighbors | Decision Tree | Gradient Boosting | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.601 | 0.608 | 0.584 | 0.608 | 0.68 | 0.677 | 0.659 | 0.677 | 0.722 | 0.737 | 0.71 | 0.737 |
| ML | 0.627 | 0.634 | 0.61 | 0.634 | 0.698 | 0.689 | 0.674 | 0.689 | 0.73 | 0.746 | 0.718 | 0.746 |
| AL-W | 0.597 | 0.607 | 0.58 | 0.607 | 0.687 | 0.684 | 0.666 | 0.684 | 0.725 | 0.741 | 0.714 | 0.741 |
| ML-W | 0.63 | 0.639 | 0.614 | 0.639 | 0.686 | 0.683 | 0.665 | 0.683 | 0.742 | 0.758 | 0.73 | 0.758 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.599 | 0.612 | 0.586 | 0.612 | 0.697 | 0.691 | 0.674 | 0.691 | 0.727 | 0.742 | 0.715 | 0.742 |
| U-AL-All | 0.604 | 0.609 | 0.584 | 0.609 | 0.698 | 0.689 | 0.674 | 0.689 | 0.722 | 0.735 | 0.71 | 0.735 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.606 | 0.615 | 0.59 | 0.615 | 0.697 | 0.69 | 0.673 | 0.69 | 0.725 | 0.739 | 0.713 | 0.739 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.596 | 0.61 | 0.583 | 0.61 | 0.686 | 0.683 | 0.665 | 0.683 | 0.727 | 0.743 | 0.715 | 0.743 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.599 | 0.612 | 0.585 | 0.612 | 0.685 | 0.683 | 0.664 | 0.683 | 0.729 | 0.743 | 0.717 | 0.743 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.599 | 0.612 | 0.585 | 0.612 | 0.686 | 0.683 | 0.665 | 0.683 | 0.72 | 0.734 | 0.708 | 0.734 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.494 | 0.454 | 0.45 | 0.454 | 0.691 | 0.684 | 0.666 | 0.684 | 0.523 | 0.502 | 0.495 | 0.502 |
| D-AL-All | 0.621 | 0.554 | 0.549 | 0.554 | 0.698 | 0.689 | 0.674 | 0.689 | 0.611 | 0.569 | 0.55 | 0.569 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.511 | 0.487 | 0.483 | 0.487 | 0.687 | 0.682 | 0.664 | 0.682 | 0.534 | 0.505 | 0.496 | 0.505 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.493 | 0.444 | 0.43 | 0.444 | 0.686 | 0.683 | 0.665 | 0.683 | 0.569 | 0.528 | 0.517 | 0.528 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.589 | 0.546 | 0.543 | 0.546 | 0.686 | 0.683 | 0.665 | 0.683 | 0.595 | 0.576 | 0.561 | 0.576 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.494 | 0.469 | 0.462 | 0.469 | 0.686 | 0.683 | 0.665 | 0.683 | 0.572 | 0.535 | 0.524 | 0.535 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.635 | 0.643 | 0.619 | 0.643 | 0.684 | 0.681 | 0.663 | 0.681 | 0.727 | 0.744 | 0.715 | 0.744 |
| U-ML-All | 0.626 | 0.634 | 0.609 | 0.634 | 0.684 | 0.681 | 0.663 | 0.681 | 0.734 | 0.751 | 0.722 | 0.751 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.636 | 0.641 | 0.62 | 0.641 | 0.684 | 0.681 | 0.663 | 0.681 | 0.728 | 0.744 | 0.716 | 0.744 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.626 | 0.639 | 0.612 | 0.639 | 0.686 | 0.683 | 0.665 | 0.683 | 0.738 | 0.755 | 0.726 | 0.755 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.627 | 0.636 | 0.61 | 0.636 | 0.685 | 0.683 | 0.664 | 0.683 | 0.743 | 0.76 | 0.732 | 0.76 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.626 | 0.635 | 0.61 | 0.635 | 0.686 | 0.683 | 0.665 | 0.683 | 0.739 | 0.755 | 0.727 | 0.755 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.586 | 0.581 | 0.569 | 0.581 | 0.684 | 0.678 | 0.661 | 0.678 | 0.673 | 0.685 | 0.663 | 0.685 |
| D-ML-All | 0.608 | 0.604 | 0.586 | 0.604 | 0.69 | 0.686 | 0.669 | 0.686 | 0.667 | 0.681 | 0.659 | 0.681 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.593 | 0.591 | 0.58 | 0.591 | 0.688 | 0.685 | 0.667 | 0.685 | 0.671 | 0.683 | 0.661 | 0.683 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.58 | 0.585 | 0.569 | 0.585 | 0.686 | 0.683 | 0.665 | 0.683 | 0.676 | 0.683 | 0.661 | 0.683 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.609 | 0.605 | 0.588 | 0.605 | 0.686 | 0.683 | 0.665 | 0.683 | 0.67 | 0.683 | 0.66 | 0.683 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.586 | 0.583 | 0.571 | 0.583 | 0.686 | 0.683 | 0.665 | 0.683 | 0.673 | 0.681 | 0.658 | 0.681 |
| Method | Random Forest | Random Subspace | AdaBoost | |||||||||
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.733 | 0.745 | 0.722 | 0.745 | 0.734 | 0.744 | 0.719 | 0.744 | 0.68 | 0.667 | 0.652 | 0.667 |
| ML | 0.74 | 0.751 | 0.724 | 0.751 | 0.764 | 0.775 | 0.751 | 0.775 | 0.676 | 0.642 | 0.636 | 0.642 |
| AL-W | 0.727 | 0.739 | 0.716 | 0.739 | 0.738 | 0.749 | 0.726 | 0.749 | 0.686 | 0.673 | 0.658 | 0.673 |
| ML-W | 0.744 | 0.754 | 0.726 | 0.754 | 0.765 | 0.776 | 0.753 | 0.776 | 0.674 | 0.646 | 0.638 | 0.646 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.732 | 0.743 | 0.72 | 0.743 | 0.735 | 0.744 | 0.719 | 0.744 | 0.68 | 0.668 | 0.655 | 0.668 |
| U-AL-All | 0.732 | 0.744 | 0.721 | 0.744 | 0.748 | 0.754 | 0.733 | 0.754 | 0.677 | 0.672 | 0.656 | 0.672 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.729 | 0.742 | 0.718 | 0.742 | 0.743 | 0.751 | 0.728 | 0.751 | 0.686 | 0.676 | 0.66 | 0.676 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.732 | 0.744 | 0.72 | 0.744 | 0.742 | 0.754 | 0.73 | 0.754 | 0.686 | 0.674 | 0.659 | 0.674 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.729 | 0.741 | 0.717 | 0.741 | 0.744 | 0.75 | 0.728 | 0.75 | 0.683 | 0.672 | 0.657 | 0.672 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.729 | 0.741 | 0.717 | 0.741 | 0.748 | 0.754 | 0.732 | 0.754 | 0.687 | 0.676 | 0.661 | 0.676 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.63 | 0.614 | 0.606 | 0.614 | 0.605 | 0.574 | 0.564 | 0.574 | 0.498 | 0.446 | 0.452 | 0.446 |
| D-AL-All | 0.721 | 0.72 | 0.703 | 0.72 | 0.672 | 0.653 | 0.631 | 0.653 | 0.597 | 0.535 | 0.534 | 0.535 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.639 | 0.627 | 0.614 | 0.627 | 0.59 | 0.565 | 0.553 | 0.565 | 0.478 | 0.428 | 0.434 | 0.428 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.66 | 0.649 | 0.633 | 0.649 | 0.638 | 0.612 | 0.598 | 0.612 | 0.555 | 0.498 | 0.494 | 0.498 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.709 | 0.714 | 0.696 | 0.714 | 0.68 | 0.681 | 0.659 | 0.681 | 0.582 | 0.545 | 0.541 | 0.545 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.669 | 0.658 | 0.642 | 0.658 | 0.632 | 0.613 | 0.599 | 0.613 | 0.539 | 0.488 | 0.487 | 0.488 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.745 | 0.756 | 0.729 | 0.756 | 0.768 | 0.78 | 0.756 | 0.78 | 0.668 | 0.646 | 0.64 | 0.646 |
| U-ML-All | 0.74 | 0.752 | 0.723 | 0.752 | 0.764 | 0.774 | 0.751 | 0.774 | 0.67 | 0.642 | 0.637 | 0.642 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.738 | 0.751 | 0.725 | 0.751 | 0.763 | 0.773 | 0.75 | 0.773 | 0.683 | 0.646 | 0.643 | 0.646 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.745 | 0.756 | 0.729 | 0.756 | 0.772 | 0.782 | 0.757 | 0.782 | 0.669 | 0.649 | 0.641 | 0.649 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.741 | 0.751 | 0.723 | 0.751 | 0.761 | 0.772 | 0.747 | 0.772 | 0.675 | 0.654 | 0.646 | 0.654 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.734 | 0.749 | 0.721 | 0.749 | 0.768 | 0.777 | 0.753 | 0.777 | 0.675 | 0.655 | 0.647 | 0.655 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.741 | 0.749 | 0.727 | 0.749 | 0.732 | 0.741 | 0.719 | 0.741 | 0.604 | 0.57 | 0.569 | 0.57 |
| D-ML-All | 0.739 | 0.749 | 0.725 | 0.749 | 0.737 | 0.748 | 0.726 | 0.748 | 0.603 | 0.557 | 0.557 | 0.557 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.745 | 0.752 | 0.73 | 0.752 | 0.733 | 0.744 | 0.721 | 0.744 | 0.604 | 0.568 | 0.567 | 0.568 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.733 | 0.743 | 0.721 | 0.743 | 0.732 | 0.739 | 0.718 | 0.739 | 0.609 | 0.574 | 0.571 | 0.574 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.738 | 0.749 | 0.724 | 0.749 | 0.739 | 0.75 | 0.727 | 0.75 | 0.599 | 0.582 | 0.581 | 0.582 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.737 | 0.746 | 0.724 | 0.746 | 0.732 | 0.742 | 0.718 | 0.742 | 0.609 | 0.572 | 0.569 | 0.572 |
| Method | K-Nearest Neighbors | Decision Tree | Gradient Boosting | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.574 | 0.58 | 0.564 | 0.58 | 0.697 | 0.707 | 0.684 | 0.707 | 0.712 | 0.722 | 0.698 | 0.722 |
| ML | 0.587 | 0.613 | 0.581 | 0.613 | 0.696 | 0.701 | 0.68 | 0.701 | 0.718 | 0.731 | 0.705 | 0.731 |
| AL-W | 0.567 | 0.579 | 0.56 | 0.579 | 0.695 | 0.706 | 0.682 | 0.706 | 0.719 | 0.728 | 0.704 | 0.728 |
| ML-W | 0.586 | 0.609 | 0.578 | 0.609 | 0.692 | 0.701 | 0.677 | 0.701 | 0.716 | 0.728 | 0.704 | 0.728 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.578 | 0.585 | 0.568 | 0.585 | 0.694 | 0.703 | 0.68 | 0.703 | 0.714 | 0.721 | 0.698 | 0.721 |
| U-AL-All | 0.571 | 0.575 | 0.559 | 0.575 | 0.696 | 0.701 | 0.68 | 0.701 | 0.712 | 0.724 | 0.7 | 0.724 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.574 | 0.585 | 0.566 | 0.585 | 0.694 | 0.704 | 0.68 | 0.704 | 0.704 | 0.715 | 0.691 | 0.715 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.582 | 0.586 | 0.569 | 0.586 | 0.69 | 0.699 | 0.675 | 0.699 | 0.717 | 0.724 | 0.701 | 0.724 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.561 | 0.572 | 0.555 | 0.572 | 0.692 | 0.701 | 0.677 | 0.701 | 0.715 | 0.724 | 0.7 | 0.724 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.574 | 0.584 | 0.566 | 0.584 | 0.69 | 0.699 | 0.675 | 0.699 | 0.707 | 0.716 | 0.692 | 0.716 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.51 | 0.448 | 0.444 | 0.448 | 0.696 | 0.704 | 0.681 | 0.704 | 0.478 | 0.461 | 0.456 | 0.461 |
| D-AL-All | 0.578 | 0.528 | 0.525 | 0.528 | 0.696 | 0.701 | 0.68 | 0.701 | 0.537 | 0.507 | 0.488 | 0.507 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.513 | 0.451 | 0.447 | 0.451 | 0.689 | 0.695 | 0.673 | 0.695 | 0.472 | 0.457 | 0.452 | 0.457 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.521 | 0.467 | 0.463 | 0.467 | 0.691 | 0.699 | 0.675 | 0.699 | 0.469 | 0.453 | 0.447 | 0.453 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.576 | 0.524 | 0.52 | 0.524 | 0.691 | 0.699 | 0.675 | 0.699 | 0.494 | 0.493 | 0.482 | 0.493 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.533 | 0.474 | 0.471 | 0.474 | 0.691 | 0.699 | 0.675 | 0.699 | 0.48 | 0.466 | 0.46 | 0.466 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.598 | 0.62 | 0.587 | 0.62 | 0.696 | 0.706 | 0.682 | 0.706 | 0.724 | 0.736 | 0.711 | 0.736 |
| U-ML-All | 0.585 | 0.609 | 0.577 | 0.609 | 0.696 | 0.706 | 0.682 | 0.706 | 0.72 | 0.731 | 0.706 | 0.731 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.58 | 0.605 | 0.573 | 0.605 | 0.696 | 0.706 | 0.682 | 0.706 | 0.717 | 0.73 | 0.704 | 0.73 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.603 | 0.62 | 0.589 | 0.62 | 0.69 | 0.699 | 0.675 | 0.699 | 0.722 | 0.734 | 0.71 | 0.734 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.592 | 0.606 | 0.578 | 0.606 | 0.692 | 0.701 | 0.677 | 0.701 | 0.72 | 0.731 | 0.706 | 0.731 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.582 | 0.606 | 0.574 | 0.606 | 0.69 | 0.699 | 0.675 | 0.699 | 0.716 | 0.728 | 0.703 | 0.728 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.557 | 0.536 | 0.528 | 0.536 | 0.689 | 0.7 | 0.676 | 0.7 | 0.527 | 0.534 | 0.519 | 0.534 |
| D-ML-All | 0.565 | 0.555 | 0.547 | 0.555 | 0.696 | 0.704 | 0.681 | 0.704 | 0.539 | 0.554 | 0.535 | 0.554 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.558 | 0.541 | 0.534 | 0.541 | 0.689 | 0.7 | 0.676 | 0.7 | 0.532 | 0.539 | 0.524 | 0.539 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.561 | 0.543 | 0.537 | 0.543 | 0.691 | 0.699 | 0.675 | 0.699 | 0.548 | 0.554 | 0.54 | 0.554 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.568 | 0.56 | 0.553 | 0.56 | 0.691 | 0.699 | 0.675 | 0.699 | 0.565 | 0.579 | 0.559 | 0.579 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.561 | 0.543 | 0.538 | 0.543 | 0.691 | 0.699 | 0.675 | 0.699 | 0.556 | 0.562 | 0.547 | 0.562 |
| Method | Random Forest | Random Subspace | AdaBoost | |||||||||
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.73 | 0.742 | 0.713 | 0.742 | 0.72 | 0.742 | 0.712 | 0.742 | 0.625 | 0.629 | 0.609 | 0.629 |
| ML | 0.733 | 0.746 | 0.717 | 0.746 | 0.727 | 0.747 | 0.716 | 0.747 | 0.599 | 0.59 | 0.574 | 0.59 |
| AL-W | 0.727 | 0.738 | 0.709 | 0.738 | 0.716 | 0.739 | 0.707 | 0.739 | 0.628 | 0.642 | 0.616 | 0.642 |
| ML-W | 0.731 | 0.744 | 0.715 | 0.744 | 0.724 | 0.745 | 0.715 | 0.745 | 0.595 | 0.588 | 0.571 | 0.588 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.728 | 0.743 | 0.714 | 0.743 | 0.725 | 0.745 | 0.716 | 0.745 | 0.621 | 0.621 | 0.604 | 0.621 |
| U-AL-All | 0.731 | 0.743 | 0.714 | 0.743 | 0.725 | 0.739 | 0.715 | 0.739 | 0.618 | 0.636 | 0.609 | 0.636 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.728 | 0.74 | 0.711 | 0.74 | 0.718 | 0.74 | 0.711 | 0.74 | 0.623 | 0.626 | 0.607 | 0.626 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.726 | 0.74 | 0.711 | 0.74 | 0.719 | 0.736 | 0.71 | 0.736 | 0.617 | 0.62 | 0.599 | 0.62 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.725 | 0.739 | 0.709 | 0.739 | 0.716 | 0.733 | 0.707 | 0.733 | 0.613 | 0.627 | 0.601 | 0.627 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.725 | 0.739 | 0.709 | 0.739 | 0.717 | 0.739 | 0.709 | 0.739 | 0.616 | 0.628 | 0.603 | 0.628 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.582 | 0.572 | 0.562 | 0.572 | 0.543 | 0.515 | 0.502 | 0.515 | 0.441 | 0.421 | 0.423 | 0.421 |
| D-AL-All | 0.653 | 0.647 | 0.632 | 0.647 | 0.675 | 0.634 | 0.623 | 0.634 | 0.423 | 0.425 | 0.414 | 0.425 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.588 | 0.579 | 0.565 | 0.579 | 0.554 | 0.527 | 0.514 | 0.527 | 0.421 | 0.407 | 0.403 | 0.407 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.6 | 0.58 | 0.564 | 0.58 | 0.573 | 0.542 | 0.527 | 0.542 | 0.495 | 0.437 | 0.429 | 0.437 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.667 | 0.671 | 0.65 | 0.671 | 0.658 | 0.654 | 0.635 | 0.654 | 0.512 | 0.455 | 0.445 | 0.455 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.605 | 0.587 | 0.57 | 0.587 | 0.583 | 0.554 | 0.539 | 0.554 | 0.516 | 0.454 | 0.445 | 0.454 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.732 | 0.745 | 0.716 | 0.745 | 0.736 | 0.753 | 0.726 | 0.753 | 0.606 | 0.606 | 0.587 | 0.606 |
| U-ML-All | 0.738 | 0.749 | 0.72 | 0.749 | 0.733 | 0.752 | 0.722 | 0.752 | 0.609 | 0.615 | 0.597 | 0.615 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.739 | 0.75 | 0.721 | 0.75 | 0.736 | 0.754 | 0.724 | 0.754 | 0.609 | 0.602 | 0.587 | 0.602 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.732 | 0.747 | 0.718 | 0.747 | 0.732 | 0.752 | 0.723 | 0.752 | 0.602 | 0.607 | 0.587 | 0.607 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.739 | 0.75 | 0.721 | 0.75 | 0.73 | 0.75 | 0.721 | 0.75 | 0.61 | 0.617 | 0.598 | 0.617 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.737 | 0.75 | 0.72 | 0.75 | 0.733 | 0.752 | 0.722 | 0.752 | 0.602 | 0.609 | 0.589 | 0.609 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.703 | 0.704 | 0.688 | 0.704 | 0.691 | 0.701 | 0.678 | 0.701 | 0.588 | 0.539 | 0.536 | 0.539 |
| D-ML-All | 0.707 | 0.709 | 0.693 | 0.709 | 0.705 | 0.712 | 0.689 | 0.712 | 0.605 | 0.554 | 0.551 | 0.554 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.702 | 0.703 | 0.688 | 0.703 | 0.694 | 0.704 | 0.682 | 0.704 | 0.588 | 0.537 | 0.533 | 0.537 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.705 | 0.706 | 0.689 | 0.706 | 0.7 | 0.709 | 0.686 | 0.709 | 0.599 | 0.555 | 0.553 | 0.555 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.713 | 0.713 | 0.697 | 0.713 | 0.709 | 0.718 | 0.696 | 0.718 | 0.6 | 0.545 | 0.542 | 0.545 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.707 | 0.708 | 0.691 | 0.708 | 0.704 | 0.713 | 0.689 | 0.713 | 0.599 | 0.553 | 0.55 | 0.553 |
| Method | K-Nearest Neighbors | Decision Tree | Gradient Boosting | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.538 | 0.398 | 0.287 | 0.398 | 0.638 | 0.43 | 0.625 | 0.43 |
| ML | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.437 | 0.384 | 0.279 | 0.384 | 0.463 | 0.42 | 0.625 | 0.42 |
| AL-W | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.491 | 0.461 | 0.332 | 0.461 | 0.672 | 0.575 | 0.72 | 0.575 |
| ML-W | 0.634 | 0.473 | 0.345 | 0.473 | 0.467 | 0.445 | 0.323 | 0.445 | 0.765 | 0.568 | 0.724 | 0.568 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.52 | 0.398 | 0.287 | 0.398 | 0.649 | 0.443 | 0.634 | 0.443 |
| U-AL-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.45 | 0.336 | 0.245 | 0.336 | 0.474 | 0.332 | 0.56 | 0.332 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.52 | 0.398 | 0.287 | 0.398 | 0.688 | 0.457 | 0.644 | 0.457 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.474 | 0.45 | 0.325 | 0.45 | 0.663 | 0.575 | 0.72 | 0.575 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.474 | 0.45 | 0.325 | 0.45 | 0.664 | 0.575 | 0.72 | 0.575 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.474 | 0.45 | 0.325 | 0.45 | 0.667 | 0.575 | 0.72 | 0.575 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.62 | 0.518 | 0.371 | 0.518 | 0.495 | 0.355 | 0.38 | 0.355 | 0.572 | 0.232 | 0.357 | 0.232 |
| D-AL-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.465 | 0.393 | 0.284 | 0.393 | 0.246 | 0.102 | 0.389 | 0.102 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.578 | 0.498 | 0.358 | 0.498 | 0.491 | 0.425 | 0.305 | 0.425 | 0.573 | 0.255 | 0.374 | 0.255 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.668 | 0.591 | 0.415 | 0.591 | 0.472 | 0.448 | 0.321 | 0.448 | 0.658 | 0.557 | 0.453 | 0.557 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.668 | 0.591 | 0.415 | 0.591 | 0.472 | 0.448 | 0.321 | 0.448 | 0.658 | 0.557 | 0.453 | 0.557 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.668 | 0.591 | 0.415 | 0.591 | 0.472 | 0.448 | 0.321 | 0.448 | 0.658 | 0.557 | 0.453 | 0.557 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.532 | 0.411 | 0.298 | 0.411 | 0.463 | 0.42 | 0.625 | 0.42 |
| U-ML-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.532 | 0.411 | 0.298 | 0.411 | 0.463 | 0.42 | 0.625 | 0.42 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.532 | 0.411 | 0.298 | 0.411 | 0.463 | 0.42 | 0.625 | 0.42 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.634 | 0.473 | 0.345 | 0.473 | 0.461 | 0.443 | 0.32 | 0.443 | 0.758 | 0.568 | 0.724 | 0.568 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.634 | 0.473 | 0.345 | 0.473 | 0.461 | 0.443 | 0.32 | 0.443 | 0.759 | 0.568 | 0.724 | 0.568 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.634 | 0.473 | 0.345 | 0.473 | 0.461 | 0.443 | 0.32 | 0.443 | 0.761 | 0.568 | 0.724 | 0.568 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.769 | 0.55 | 0.394 | 0.55 | 0.485 | 0.289 | 0.458 | 0.289 | 0.657 | 0.234 | 0.199 | 0.234 |
| D-ML-All | 0.769 | 0.55 | 0.394 | 0.55 | 0.467 | 0.4 | 0.287 | 0.4 | 0.658 | 0.257 | 0.216 | 0.257 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.769 | 0.55 | 0.394 | 0.55 | 0.467 | 0.4 | 0.287 | 0.4 | 0.65 | 0.261 | 0.219 | 0.261 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.769 | 0.55 | 0.394 | 0.55 | 0.465 | 0.436 | 0.313 | 0.436 | 0.753 | 0.539 | 0.449 | 0.539 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.769 | 0.55 | 0.394 | 0.55 | 0.465 | 0.436 | 0.313 | 0.436 | 0.753 | 0.539 | 0.449 | 0.539 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.769 | 0.55 | 0.394 | 0.55 | 0.465 | 0.436 | 0.313 | 0.436 | 0.753 | 0.539 | 0.449 | 0.539 |
| Method | Random Forest | Random Subspace | AdaBoost | |||||||||
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.487 | 0.461 | 0.338 | 0.461 | 0.487 | 0.457 | 0.335 | 0.457 | 0.458 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| ML | 0.491 | 0.466 | 0.341 | 0.466 | 0.457 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.481 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| AL-W | 0.481 | 0.47 | 0.343 | 0.47 | 0.539 | 0.48 | 0.348 | 0.48 | 0.461 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| ML-W | 0.649 | 0.507 | 0.367 | 0.507 | 0.457 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.697 | 0.493 | 0.358 | 0.493 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.486 | 0.457 | 0.334 | 0.457 | 0.547 | 0.468 | 0.374 | 0.468 | 0.451 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-All | 0.459 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.465 | 0.452 | 0.363 | 0.452 | 0.447 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.486 | 0.457 | 0.334 | 0.457 | 0.519 | 0.464 | 0.371 | 0.464 | 0.458 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.48 | 0.47 | 0.343 | 0.47 | 0.534 | 0.48 | 0.381 | 0.48 | 0.452 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.48 | 0.47 | 0.343 | 0.47 | 0.534 | 0.48 | 0.381 | 0.48 | 0.452 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.48 | 0.47 | 0.343 | 0.47 | 0.534 | 0.48 | 0.381 | 0.48 | 0.461 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.647 | 0.511 | 0.398 | 0.511 | 0.684 | 0.443 | 0.382 | 0.443 | 0.214 | 0.189 | 0.455 | 0.189 |
| D-AL-All | 0.484 | 0.457 | 0.335 | 0.457 | 0.527 | 0.473 | 0.376 | 0.473 | 0.465 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.652 | 0.516 | 0.37 | 0.516 | 0.676 | 0.498 | 0.392 | 0.498 | 0.214 | 0.189 | 0.455 | 0.189 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.652 | 0.561 | 0.396 | 0.561 | 0.729 | 0.525 | 0.409 | 0.525 | 0.472 | 0.443 | 0.322 | 0.443 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.658 | 0.555 | 0.393 | 0.555 | 0.665 | 0.509 | 0.399 | 0.509 | 0.472 | 0.443 | 0.322 | 0.443 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.658 | 0.555 | 0.393 | 0.555 | 0.665 | 0.509 | 0.399 | 0.509 | 0.472 | 0.443 | 0.322 | 0.443 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.521 | 0.468 | 0.342 | 0.468 | 0.458 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.481 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| U-ML-All | 0.52 | 0.464 | 0.339 | 0.464 | 0.458 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.481 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.521 | 0.468 | 0.342 | 0.468 | 0.458 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.481 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.649 | 0.507 | 0.367 | 0.507 | 0.458 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.517 | 0.47 | 0.343 | 0.47 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.649 | 0.507 | 0.367 | 0.507 | 0.458 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.517 | 0.47 | 0.343 | 0.47 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.649 | 0.507 | 0.367 | 0.507 | 0.458 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.697 | 0.493 | 0.358 | 0.493 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.762 | 0.552 | 0.395 | 0.552 | 0.551 | 0.482 | 0.351 | 0.482 | 0.709 | 0.5 | 0.681 | 0.5 |
| D-ML-All | 0.754 | 0.552 | 0.395 | 0.552 | 0.521 | 0.477 | 0.348 | 0.477 | 0.709 | 0.5 | 0.681 | 0.5 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.754 | 0.552 | 0.395 | 0.552 | 0.521 | 0.477 | 0.348 | 0.477 | 0.709 | 0.5 | 0.681 | 0.5 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.68 | 0.543 | 0.387 | 0.543 | 0.583 | 0.493 | 0.358 | 0.493 | 0.638 | 0.534 | 0.38 | 0.534 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.714 | 0.545 | 0.389 | 0.545 | 0.581 | 0.489 | 0.355 | 0.489 | 0.638 | 0.534 | 0.38 | 0.534 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.692 | 0.534 | 0.381 | 0.534 | 0.551 | 0.484 | 0.352 | 0.484 | 0.638 | 0.534 | 0.38 | 0.534 |
| Method | K-Nearest Neighbors | Decision Tree | Gradient Boosting | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.525 | 0.418 | 0.623 | 0.418 |
| ML | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.449 | 0.439 | 0.638 | 0.439 |
| AL-W | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| ML-W | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.525 | 0.418 | 0.623 | 0.418 |
| U-AL-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.673 | 0.386 | 0.6 | 0.386 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.529 | 0.434 | 0.635 | 0.434 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.604 | 0.493 | 0.356 | 0.493 | 0.663 | 0.473 | 0.52 | 0.473 | 0.625 | 0.186 | 0.358 | 0.186 |
| D-AL-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.333 | 0.023 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.613 | 0.493 | 0.356 | 0.493 | 0.641 | 0.484 | 0.497 | 0.484 | 0.669 | 0.195 | 0.302 | 0.195 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.603 | 0.516 | 0.367 | 0.516 | 0.743 | 0.732 | 0.501 | 0.732 | 0.746 | 0.693 | 0.473 | 0.693 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.577 | 0.48 | 0.349 | 0.48 | 0.743 | 0.732 | 0.501 | 0.732 | 0.746 | 0.693 | 0.473 | 0.693 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.603 | 0.516 | 0.367 | 0.516 | 0.743 | 0.732 | 0.501 | 0.732 | 0.746 | 0.693 | 0.473 | 0.693 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.449 | 0.439 | 0.638 | 0.439 |
| U-ML-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.496 | 0.464 | 0.334 | 0.464 | 0.266 | 0.182 | 0.45 | 0.182 | 0.006 | 0.023 | 0.333 | 0.023 |
| D-ML-All | 0.496 | 0.464 | 0.334 | 0.464 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.006 | 0.023 | 0.333 | 0.023 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.496 | 0.464 | 0.334 | 0.464 | 0.386 | 0.3 | 0.537 | 0.3 | 0.006 | 0.023 | 0.333 | 0.023 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.571 | 0.502 | 0.358 | 0.502 | 0.453 | 0.455 | 0.394 | 0.455 | 0.458 | 0.418 | 0.334 | 0.418 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.496 | 0.464 | 0.334 | 0.464 | 0.449 | 0.45 | 0.327 | 0.45 | 0.458 | 0.418 | 0.334 | 0.418 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.571 | 0.502 | 0.358 | 0.502 | 0.453 | 0.455 | 0.394 | 0.455 | 0.458 | 0.418 | 0.334 | 0.418 |
| Method | Random Forest | Random Subspace | AdaBoost | |||||||||
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| ML | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| AL-W | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| ML-W | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.483 | 0.473 | 0.6 | 0.473 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.637 | 0.464 | 0.482 | 0.464 | 0.679 | 0.566 | 0.624 | 0.566 | 0.514 | 0.466 | 0.478 | 0.466 |
| D-AL-All | 0.507 | 0.47 | 0.63 | 0.47 | 0.487 | 0.475 | 0.633 | 0.475 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.64 | 0.466 | 0.483 | 0.466 | 0.669 | 0.573 | 0.566 | 0.573 | 0.461 | 0.393 | 0.462 | 0.393 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.757 | 0.711 | 0.676 | 0.711 | 0.767 | 0.673 | 0.786 | 0.673 | 0.667 | 0.634 | 0.713 | 0.634 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.754 | 0.709 | 0.643 | 0.709 | 0.766 | 0.67 | 0.753 | 0.67 | 0.667 | 0.634 | 0.713 | 0.634 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.73 | 0.684 | 0.66 | 0.684 | 0.766 | 0.67 | 0.753 | 0.67 | 0.667 | 0.634 | 0.713 | 0.634 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.483 | 0.473 | 0.6 | 0.473 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.483 | 0.473 | 0.6 | 0.473 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.483 | 0.473 | 0.6 | 0.473 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.476 | 0.439 | 0.385 | 0.439 | 0.517 | 0.468 | 0.374 | 0.468 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| D-ML-All | 0.458 | 0.443 | 0.388 | 0.443 | 0.517 | 0.468 | 0.374 | 0.468 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.477 | 0.439 | 0.385 | 0.439 | 0.517 | 0.468 | 0.374 | 0.468 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.546 | 0.464 | 0.396 | 0.464 | 0.607 | 0.509 | 0.463 | 0.509 | 0.659 | 0.657 | 0.761 | 0.657 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.491 | 0.441 | 0.382 | 0.441 | 0.607 | 0.509 | 0.463 | 0.509 | 0.659 | 0.657 | 0.761 | 0.657 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.525 | 0.466 | 0.398 | 0.466 | 0.607 | 0.509 | 0.463 | 0.509 | 0.659 | 0.657 | 0.761 | 0.657 |
| Method | K-Nearest Neighbors | Decision Tree | Gradient Boosting | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| ML | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| AL-W | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| ML-W | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.639 | 0.5 | 0.361 | 0.5 | 0.706 | 0.618 | 0.626 | 0.618 | 0.531 | 0.373 | 0.425 | 0.373 |
| D-AL-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.573 | 0.405 | 0.297 | 0.405 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.593 | 0.489 | 0.352 | 0.489 | 0.692 | 0.609 | 0.619 | 0.609 | 0.527 | 0.366 | 0.39 | 0.366 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.603 | 0.516 | 0.367 | 0.516 | 0.763 | 0.755 | 0.835 | 0.755 | 0.585 | 0.541 | 0.7 | 0.541 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.484 | 0.457 | 0.335 | 0.457 | 0.751 | 0.741 | 0.635 | 0.741 | 0.476 | 0.436 | 0.605 | 0.436 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.603 | 0.516 | 0.367 | 0.516 | 0.763 | 0.755 | 0.835 | 0.755 | 0.551 | 0.507 | 0.679 | 0.507 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.496 | 0.464 | 0.334 | 0.464 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 | 0.48 | 0.455 | 0.65 | 0.455 |
| D-ML-All | 0.496 | 0.464 | 0.334 | 0.464 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.472 | 0.441 | 0.545 | 0.441 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.496 | 0.464 | 0.334 | 0.464 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 | 0.48 | 0.455 | 0.65 | 0.455 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.496 | 0.464 | 0.334 | 0.464 | 0.538 | 0.45 | 0.646 | 0.45 | 0.538 | 0.45 | 0.646 | 0.45 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.496 | 0.464 | 0.334 | 0.464 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 | 0.48 | 0.439 | 0.638 | 0.439 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.496 | 0.464 | 0.334 | 0.464 | 0.538 | 0.45 | 0.646 | 0.45 | 0.538 | 0.45 | 0.646 | 0.45 |
| Method | Random Forest | Random Subspace | AdaBoost | |||||||||
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| ML | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| AL-W | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| ML-W | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.718 | 0.6 | 0.612 | 0.6 | 0.614 | 0.493 | 0.571 | 0.493 | 0.355 | 0.28 | 0.363 | 0.28 |
| D-AL-All | 0.487 | 0.475 | 0.633 | 0.475 | 0.511 | 0.473 | 0.658 | 0.473 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.653 | 0.566 | 0.59 | 0.566 | 0.62 | 0.52 | 0.558 | 0.52 | 0.356 | 0.28 | 0.332 | 0.28 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.767 | 0.716 | 0.806 | 0.716 | 0.763 | 0.755 | 0.835 | 0.755 | 0.772 | 0.734 | 0.82 | 0.734 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.747 | 0.691 | 0.759 | 0.691 | 0.763 | 0.755 | 0.835 | 0.755 | 0.772 | 0.734 | 0.82 | 0.734 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.767 | 0.716 | 0.806 | 0.716 | 0.763 | 0.755 | 0.835 | 0.755 | 0.772 | 0.734 | 0.82 | 0.734 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.453 | 0.45 | 0.33 | 0.45 | 0.485 | 0.459 | 0.368 | 0.459 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| D-ML-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.458 | 0.457 | 0.367 | 0.457 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.453 | 0.45 | 0.33 | 0.45 | 0.485 | 0.459 | 0.368 | 0.459 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.702 | 0.48 | 0.505 | 0.48 | 0.517 | 0.468 | 0.406 | 0.468 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.521 | 0.443 | 0.482 | 0.443 | 0.517 | 0.468 | 0.406 | 0.468 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.702 | 0.48 | 0.505 | 0.48 | 0.517 | 0.468 | 0.406 | 0.468 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| Method | K-Nearest Neighbors | Decision Tree | Gradient Boosting | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| ML | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| AL-W | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| ML-W | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.591 | 0.577 | 0.398 | 0.577 | 0.66 | 0.366 | 0.414 | 0.366 | 0.577 | 0.323 | 0.417 | 0.323 |
| D-AL-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.333 | 0.023 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.598 | 0.58 | 0.4 | 0.58 | 0.357 | 0.286 | 0.463 | 0.286 | 0.605 | 0.341 | 0.398 | 0.341 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.716 | 0.636 | 0.419 | 0.636 | 0.763 | 0.755 | 0.835 | 0.755 | 0.763 | 0.755 | 0.835 | 0.755 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.699 | 0.627 | 0.413 | 0.627 | 0.501 | 0.498 | 0.454 | 0.498 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.716 | 0.636 | 0.419 | 0.636 | 0.507 | 0.493 | 0.676 | 0.493 | 0.763 | 0.755 | 0.835 | 0.755 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.496 | 0.464 | 0.334 | 0.464 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.333 | 0.023 | 0.113 | 0.057 | 0.358 | 0.057 |
| D-ML-All | 0.496 | 0.464 | 0.334 | 0.464 | 0.353 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.333 | 0.023 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.496 | 0.464 | 0.334 | 0.464 | 0.189 | 0.114 | 0.4 | 0.114 | 0.113 | 0.057 | 0.358 | 0.057 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.496 | 0.464 | 0.334 | 0.464 | 0.702 | 0.525 | 0.695 | 0.525 | 0.77 | 0.534 | 0.703 | 0.534 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.496 | 0.464 | 0.334 | 0.464 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.496 | 0.464 | 0.334 | 0.464 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 | 0.77 | 0.534 | 0.703 | 0.534 |
| Method | Random Forest | Random Subspace | AdaBoost | |||||||||
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| ML | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| AL-W | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| ML-W | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.649 | 0.459 | 0.545 | 0.459 | 0.614 | 0.323 | 0.418 | 0.323 | 0.648 | 0.357 | 0.442 | 0.357 |
| D-AL-All | 0.487 | 0.475 | 0.633 | 0.475 | 0.374 | 0.264 | 0.478 | 0.264 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.649 | 0.459 | 0.545 | 0.459 | 0.683 | 0.348 | 0.465 | 0.348 | 0.364 | 0.307 | 0.478 | 0.307 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.763 | 0.755 | 0.835 | 0.755 | 0.763 | 0.755 | 0.835 | 0.755 | 0.763 | 0.755 | 0.835 | 0.755 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.614 | 0.602 | 0.742 | 0.602 | 0.763 | 0.755 | 0.835 | 0.755 | 0.541 | 0.511 | 0.678 | 0.511 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.743 | 0.732 | 0.821 | 0.732 | 0.763 | 0.755 | 0.835 | 0.755 | 0.763 | 0.755 | 0.835 | 0.755 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.514 | 0.461 | 0.338 | 0.461 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| D-ML-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.706 | 0.509 | 0.559 | 0.509 | 0.563 | 0.511 | 0.463 | 0.511 | 0.458 | 0.457 | 0.367 | 0.457 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.504 | 0.475 | 0.538 | 0.475 | 0.553 | 0.5 | 0.456 | 0.5 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.676 | 0.502 | 0.555 | 0.502 | 0.553 | 0.5 | 0.456 | 0.5 | 0.458 | 0.457 | 0.367 | 0.457 |
| Method | K-Nearest Neighbors | Decision Tree | Gradient Boosting | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.652 | 0.611 | 0.426 | 0.611 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| ML | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| AL-W | 0.737 | 0.732 | 0.501 | 0.732 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| ML-W | 0.496 | 0.464 | 0.334 | 0.464 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.652 | 0.611 | 0.426 | 0.611 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-All | 0.594 | 0.52 | 0.37 | 0.52 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.652 | 0.611 | 0.426 | 0.611 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.737 | 0.732 | 0.501 | 0.732 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.737 | 0.732 | 0.501 | 0.732 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.737 | 0.732 | 0.501 | 0.732 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.503 | 0.359 | 0.403 | 0.359 | 0.707 | 0.23 | 0.485 | 0.23 | 0.697 | 0.218 | 0.477 | 0.218 |
| D-AL-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.673 | 0.386 | 0.6 | 0.386 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.333 | 0.023 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.518 | 0.368 | 0.411 | 0.368 | 0.702 | 0.227 | 0.483 | 0.227 | 0.662 | 0.22 | 0.478 | 0.22 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.431 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.333 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.333 | 0.023 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.333 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.333 | 0.023 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.431 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.333 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.333 | 0.023 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.496 | 0.464 | 0.334 | 0.464 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.496 | 0.464 | 0.334 | 0.464 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.496 | 0.464 | 0.334 | 0.464 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.496 | 0.464 | 0.334 | 0.464 | 0.179 | 0.091 | 0.067 | 0.091 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.333 | 0.023 |
| D-ML-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.179 | 0.091 | 0.067 | 0.091 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.333 | 0.023 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.496 | 0.464 | 0.334 | 0.464 | 0.179 | 0.091 | 0.067 | 0.091 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.333 | 0.023 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.484 | 0.457 | 0.335 | 0.457 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.333 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.333 | 0.023 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.577 | 0.48 | 0.349 | 0.48 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.333 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.333 | 0.023 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.484 | 0.457 | 0.335 | 0.457 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.333 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.333 | 0.023 |
| Method | Random Forest | Random Subspace | AdaBoost | |||||||||
| Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | Prec. | Recall | BAcc | Acc | |
| AL | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| ML | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| AL-W | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| ML-W | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-AL-W-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| D-AL-1 | 0.654 | 0.364 | 0.412 | 0.364 | 0.682 | 0.398 | 0.501 | 0.398 | 0.362 | 0.284 | 0.525 | 0.284 |
| D-AL-All | 0.437 | 0.427 | 0.567 | 0.427 | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.63 | 0.43 | 0.491 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.477 |
| D-AL-2 | 0.69 | 0.377 | 0.422 | 0.377 | 0.569 | 0.355 | 0.406 | 0.355 | 0.366 | 0.289 | 0.528 | 0.289 |
| D-AL-W-1 | 0.622 | 0.432 | 0.607 | 0.432 | 0.717 | 0.582 | 0.715 | 0.582 | 0.749 | 0.739 | 0.601 | 0.739 |
| D-AL-W-All | 0.392 | 0.377 | 0.589 | 0.377 | 0.779 | 0.616 | 0.734 | 0.616 | 0.702 | 0.548 | 0.703 | 0.548 |
| D-AL-W-2 | 0.423 | 0.339 | 0.55 | 0.339 | 0.772 | 0.605 | 0.726 | 0.605 | 0.749 | 0.739 | 0.601 | 0.739 |
| U-ML-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-W-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-W-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| U-ML-W-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| D-ML-1 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.216 | 0.198 | 0.145 | 0.198 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| D-ML-All | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| D-ML-2 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 0.375 | 0.352 | 0.258 | 0.352 | 0.455 | 0.455 | 0.333 | 0.455 |
| D-ML-W-1 | 0.57 | 0.477 | 0.475 | 0.477 | 0.375 | 0.35 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.458 | 0.457 | 0.367 | 0.457 |
| D-ML-W-All | 0.469 | 0.464 | 0.467 | 0.464 | 0.422 | 0.468 | 0.438 | 0.468 | 0.458 | 0.457 | 0.367 | 0.457 |
| D-ML-W-2 | 0.55 | 0.47 | 0.471 | 0.47 | 0.347 | 0.37 | 0.334 | 0.37 | 0.458 | 0.457 | 0.367 | 0.457 |
References
- Trajdos, P.; Burduk, R. Ensemble of classifiers based on score function defined by clusters and decision boundary of linear base learners. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2024, 303, 112411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepka, I.; Lango, M.; Stefanowski, J. A Multi–Criteria Approach for Selecting an Explanation from the Set of Counterfactuals Produced by an Ensemble of Explainers. Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci. 2024, 34, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Głowania, S.; Kozak, J.; Juszczuk, P. New voting schemas for heterogeneous ensemble of classifiers in the problem of football results prediction. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 207, 3393–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayeelyan, J.; Utomo, S.; Rouniyar, A.; Hsu, H.C.; Hsiung, P.A. Federated learning design and functional models: Survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2025, 58, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekala, B.; Szkoła, J.; Grochowalski, P.; Gil, D.; Kosior, D.; Dyczkowski, K. A Novel Method for Human Fall Detection Using Federated Learning and Interval-Valued Fuzzy Inference Systems. J. Artif. Intell. Soft Comput. Res. 2025, 15, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, A.; Amira, A.; Nouali, O. Securing decentralized federated learning: Cryptographic mechanisms for privacy and trust. Clust. Comput. 2025, 28, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, H.; Chikontwe, P.; Kang, M.; Jin, K.H.; Adeli, E.; Pohl, K.M.; Park, S.H. Communication Efficient Federated Learning for Multi-Organ Segmentation via Knowledge Distillation with Image Synthesis. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2025, 44, 2079–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, W.; Yu, B.; Zhang, C.; Qin, A.K.; Xie, Y. FedKT: Federated learning with knowledge transfer for non-IID data. Pattern Recognit. 2025, 159, 111143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Lei, H.; Chen, G.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Gao, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Ma, G.; et al. Multi-center sparse learning and decision fusion for automatic COVID-19 diagnosis. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 115, 108088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Nguyen, D.L.; Nguyen, T.B.; Nguyen, T.H.; Pham, H.H.; Nguyen, T.T.; Le Nguyen, P. Cadis: Handling cluster-skewed non-iid data in federated learning with clustered aggregation and knowledge distilled regularization. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/ACM 23rd International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Internet Computing (CCGrid), Bangalore, India, 1–4 May 2023; pp. 249–261. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Tarkoma, S. FedGK: Communication-Efficient Federated Learning through Group-Guided Knowledge Distillation. ACM Trans. Internet Technol. 2024, 24, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado, F.E.; Lema, D.; Iglesias, R.; Regueiro, C.V.; Barro, S. Ensemble and continual federated learning for classification tasks. Mach. Learn. 2023, 112, 3413–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Yu, F.; Huang, P.; Liu, G.; Zhang, M.; Sun, R. Game-theoretic evolution in renewable energy systems: Advancing sustainable energy management and decision optimization in decentralized power markets. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 217, 115776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, Z. Some remarks on conflict analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2005, 166, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, Z. Conflict analysis. In Proceedings of the Fifth European Congress on Intelligent Techniques and Soft Computing (EUFIT’97), Aachen, Germany, 8–12 September 1997; pp. 1589–1591. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlak, Z. Rough sets. Int. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. 1982, 11, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybyła-Kasperek, M.; Wakulicz-Deja, A. A dispersed decision-making system–The use of negotiations during the dynamic generation of a system’s structure. Inf. Sci. 2014, 288, 194–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillani, Z.; Bashir, Z.; Aquil, S. A game theoretic conflict analysis model with linguistic assessments and two levels of game play. Inf. Sci. 2024, 677, 120840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y. Three-way decisions with probabilistic rough sets. Inf. Sci. 2010, 180, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.; Li, S.; Li, J. Three-way conflict analysis model under agent-agent mutual selection environment. Inf. Sci. 2024, 673, 120718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yan, Y. A dynamic three-way conflict analysis model with adaptive thresholds. Inf. Sci. 2024, 657, 119999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepaniuk, J.; Skowron, A. Three-way approximation of decision granules based on the rough set approach. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2023, 155, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinelli, M.; Kadziński, M.; Gonzalez, M.; Słowiński, R. How to support the application of multiple criteria decision analysis? Let us start with a comprehensive taxonomy. Omega 2020, 96, 102261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrente, S.; Figueira, J.R.; Greco, S.; Słowiński, R. Multiple criteria decision support. In Handbook of Group Decision and Negotiation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 893–920. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Dleu, T.; Nguyen, L.; Xu, H. Conflict analysis based on rough set in e-commerce. Int. J. Adv. Manag. Sci. 2013, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Skowron, A.; Ramanna, S.; Peters, J.F. Conflict analysis and information systems: A rough set approach. In Rough Sets and Knowledge Technology, First International Conference, RSKT 2006; Chongquing, China, 24–26 July 2006, Proceedings 1; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Przybyła-Kasperek, M.; Sacewicz, J. Ensembles of random trees with coalitions-a classification model for dispersed data. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2024, 246, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybyła-Kasperek, M.; Kusztal, K.; Addo, B.A. Dispersed Data Classification Model with Conflict Analysis and Parameterized Allied Relations. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2024, 246, 2215–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybyła-Kasperek, M.; Kusztal, K. Rules’ quality generated by the classification method for independent data sources using pawlak conflict analysis model. In International Conference on Computational Science; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 390–405. [Google Scholar]
- Bohanec, M. Car Evaluation. UCI Machine Learning Repository. 1997. Available online: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/dataset/19/car+evaluation (accessed on 5 December 2025).
- Michalski, R.S.; Chilausky, R.L. Knowledge acquisition by encoding expert rules versus computer induction from examples: A case study involving soybean pathology. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Stud. 1999, 51, 239–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowforth, P.; Shepherd, B. Statlog (Vehicle Silhouettes) [Dataset]. UCI Machine Learning Repository. Available online: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/dataset/149/statlog+vehicle+silhouettes (accessed on 5 December 2025).
- Zwitter, M.; Soklic, M. Lymphography Domain; University Medical Center, Institute of Oncology: Ljubljana, Yugoslavia, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Fiebig, L.; Soyka, J.; Buda, S.; Buchholz, U.; Dehnert, M.; Haas, W. Avian Influenza A(H5N1) in Humans—Line List. 2011. Available online: https://edoc.rki.de/handle/176904/7480 (accessed on 15 February 2024).
- Marfo, K.F.; Przybyła-Kasperek, M. Objects Diversity and its Impact on Classification Quality in Dispersed Data Environments. Vietnam J. Comput. Sci. 2024, 12, 253–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
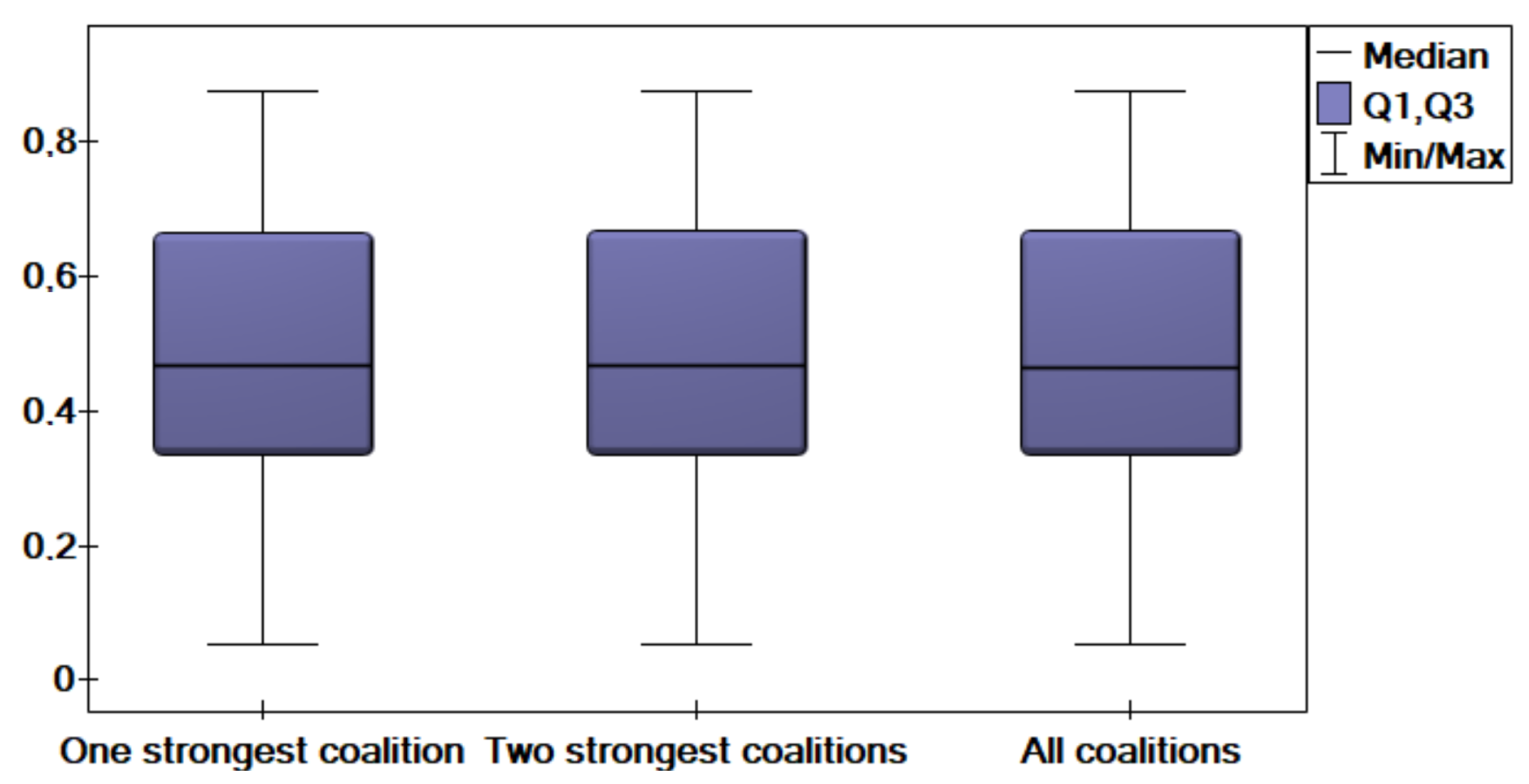

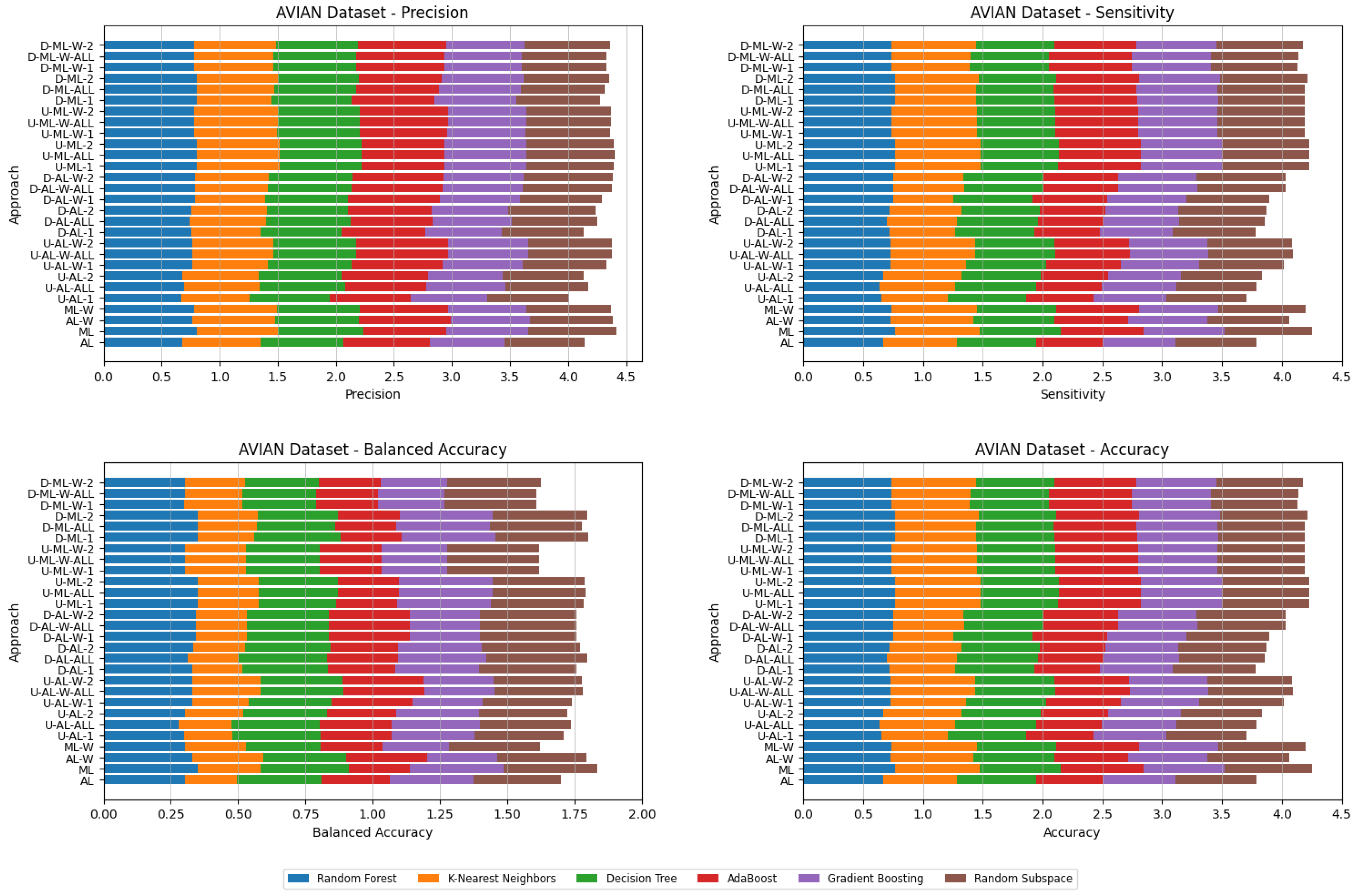
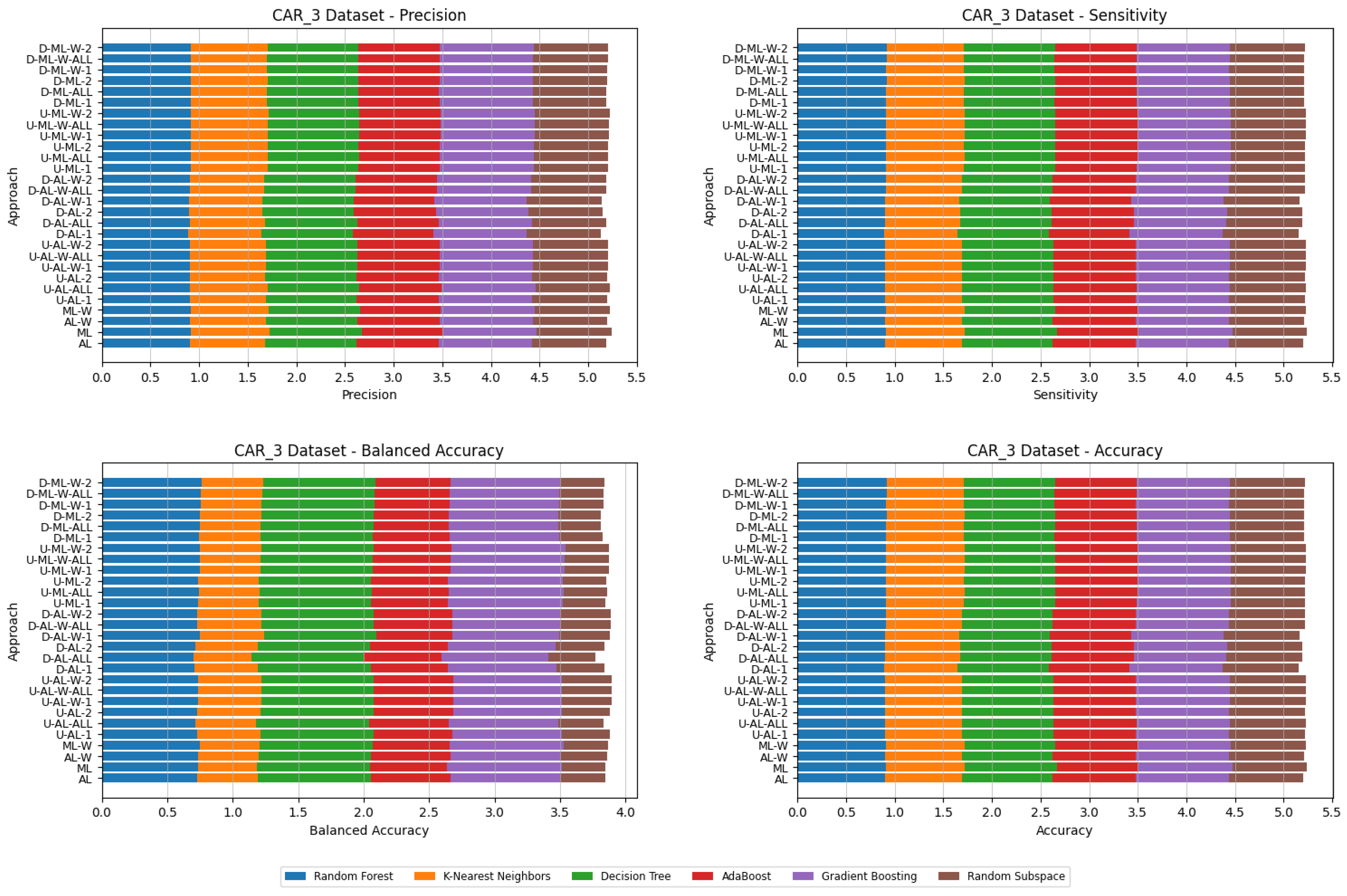
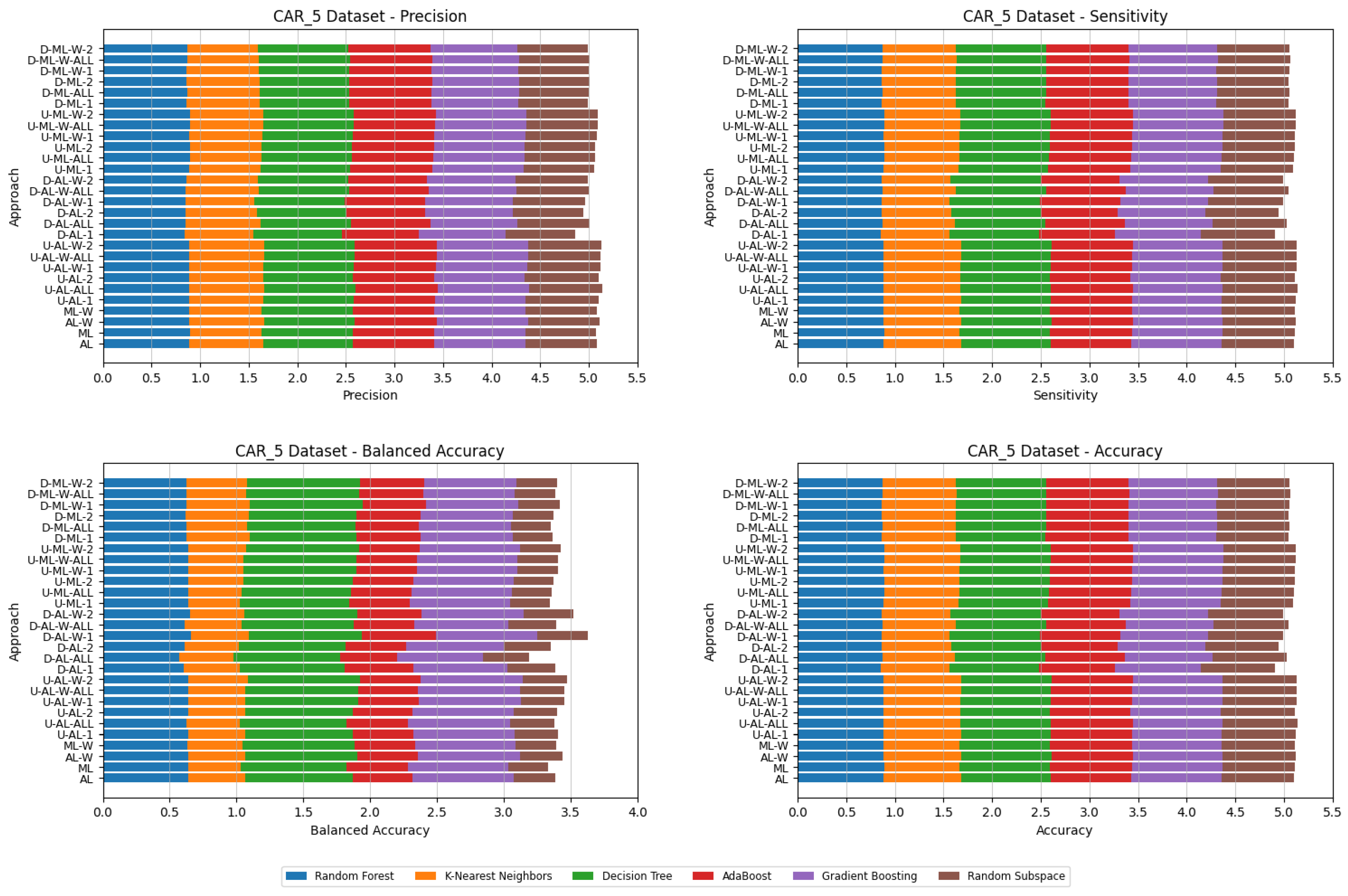
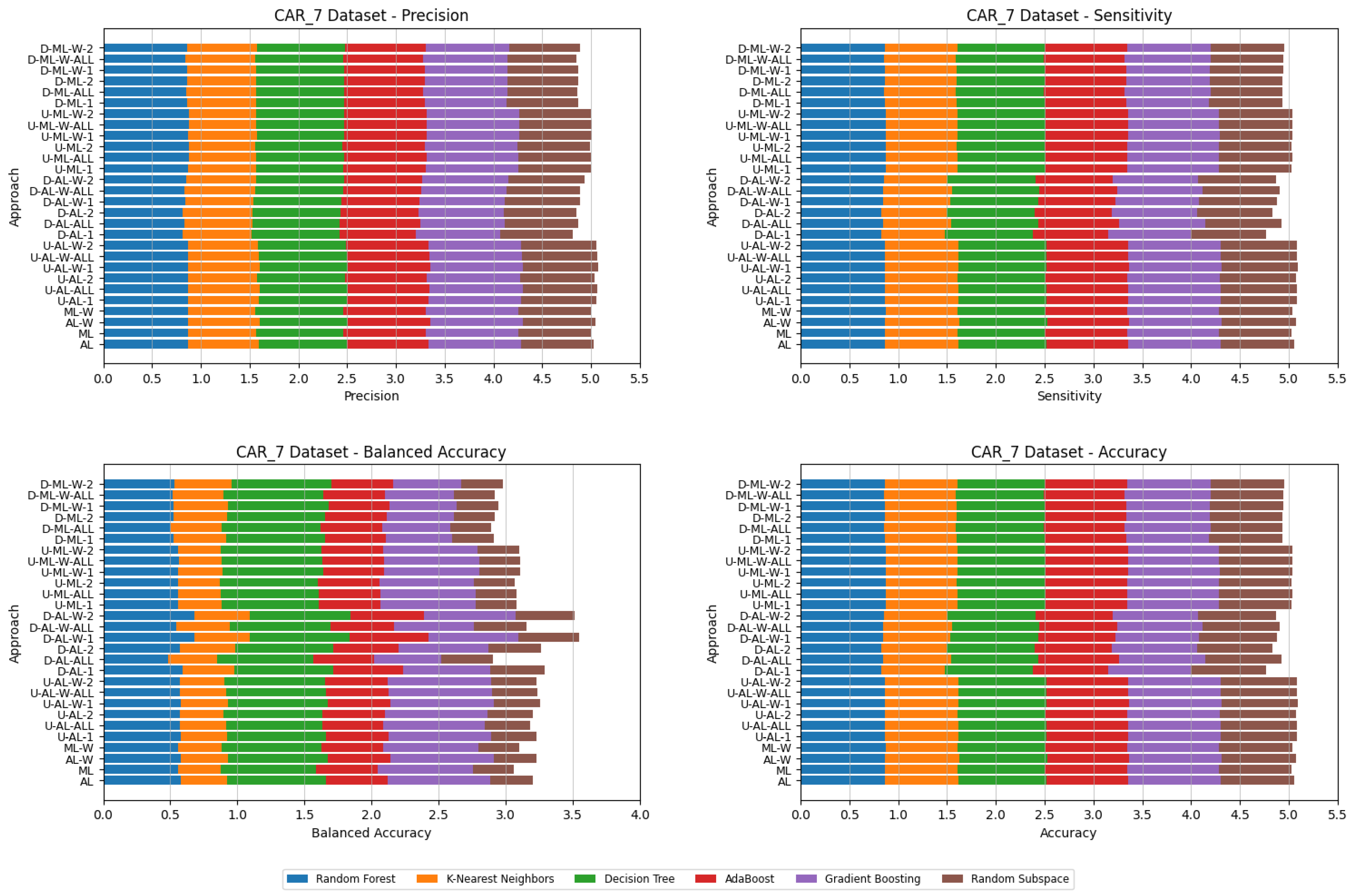
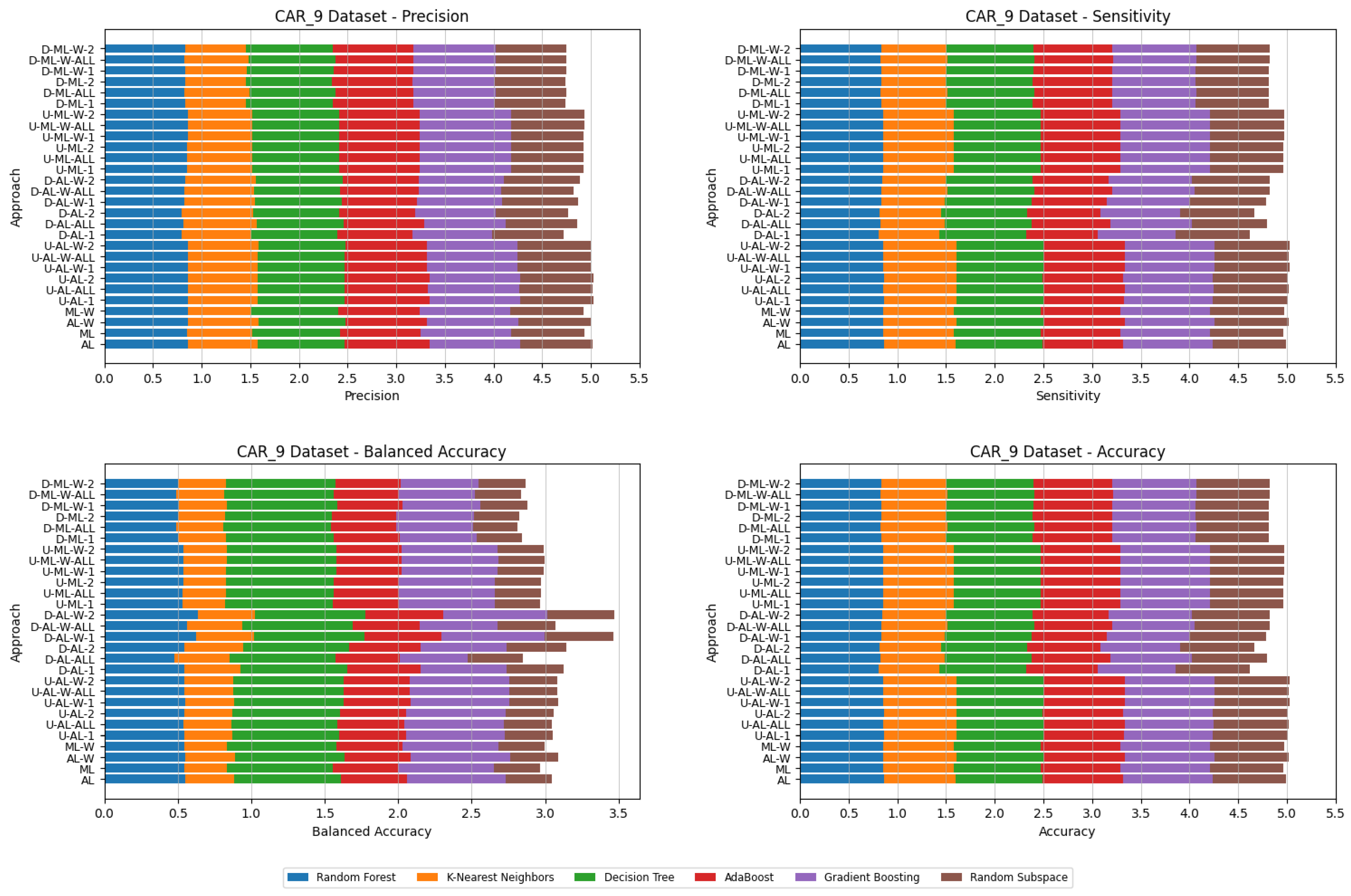
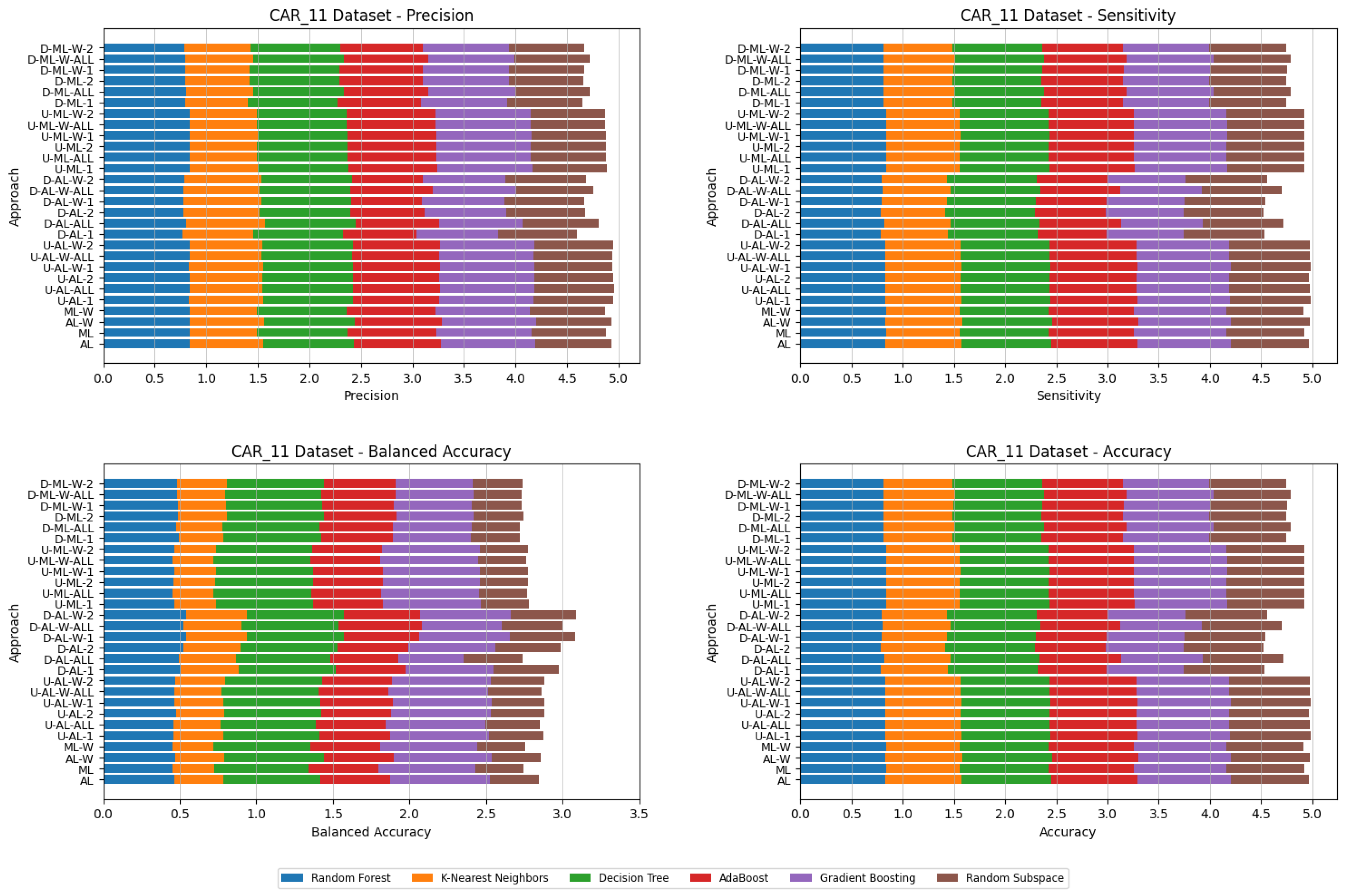
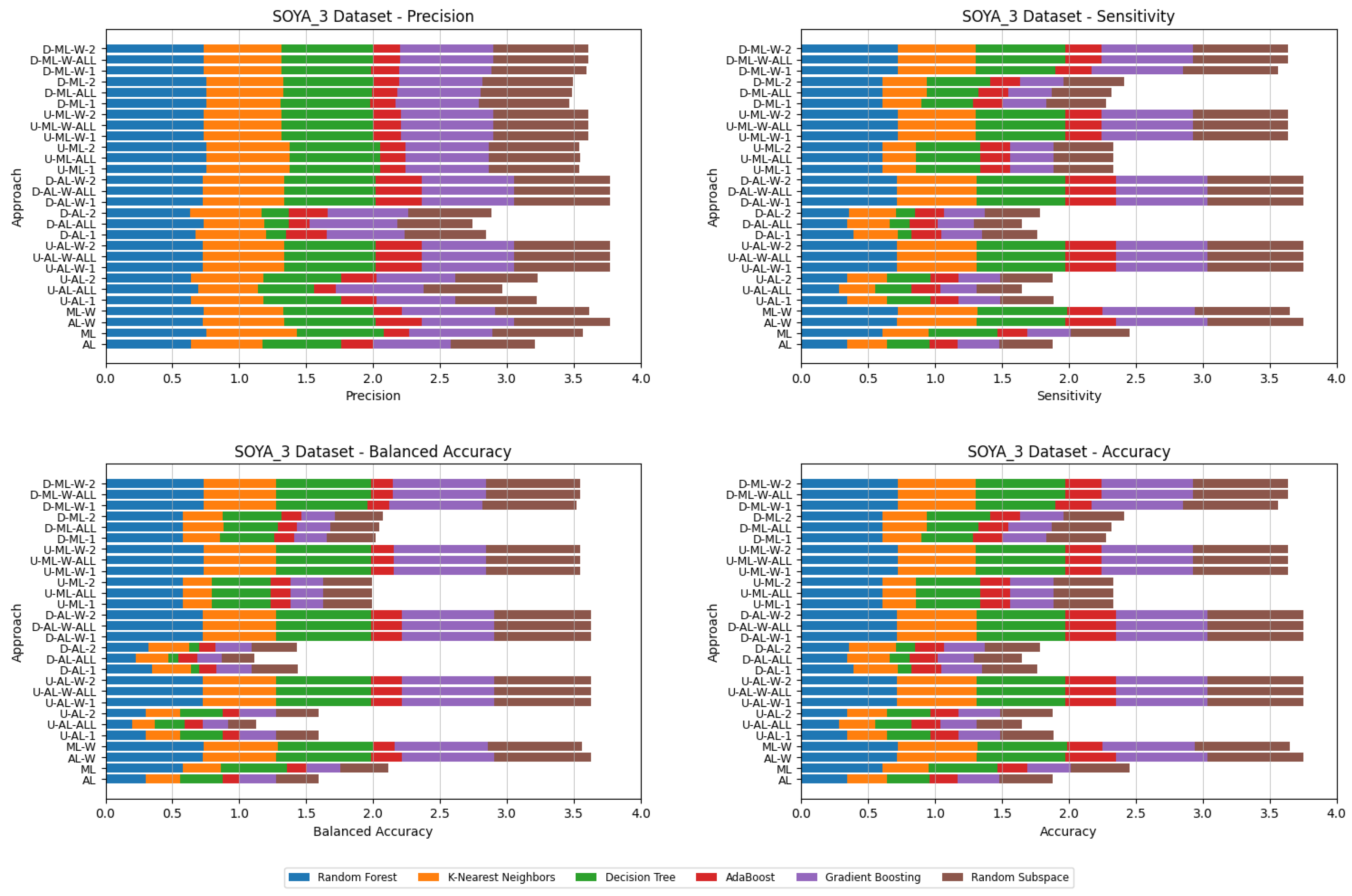
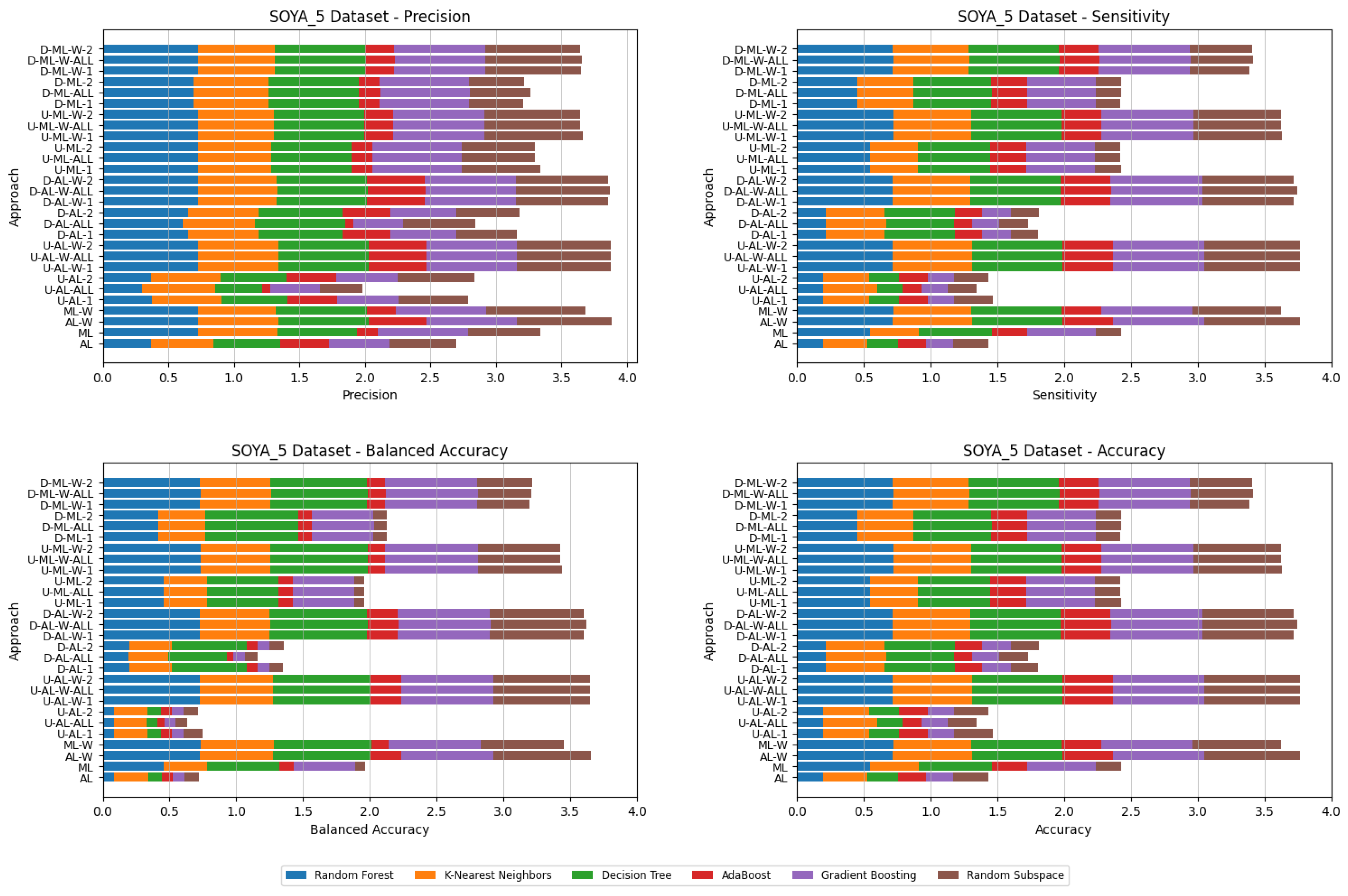
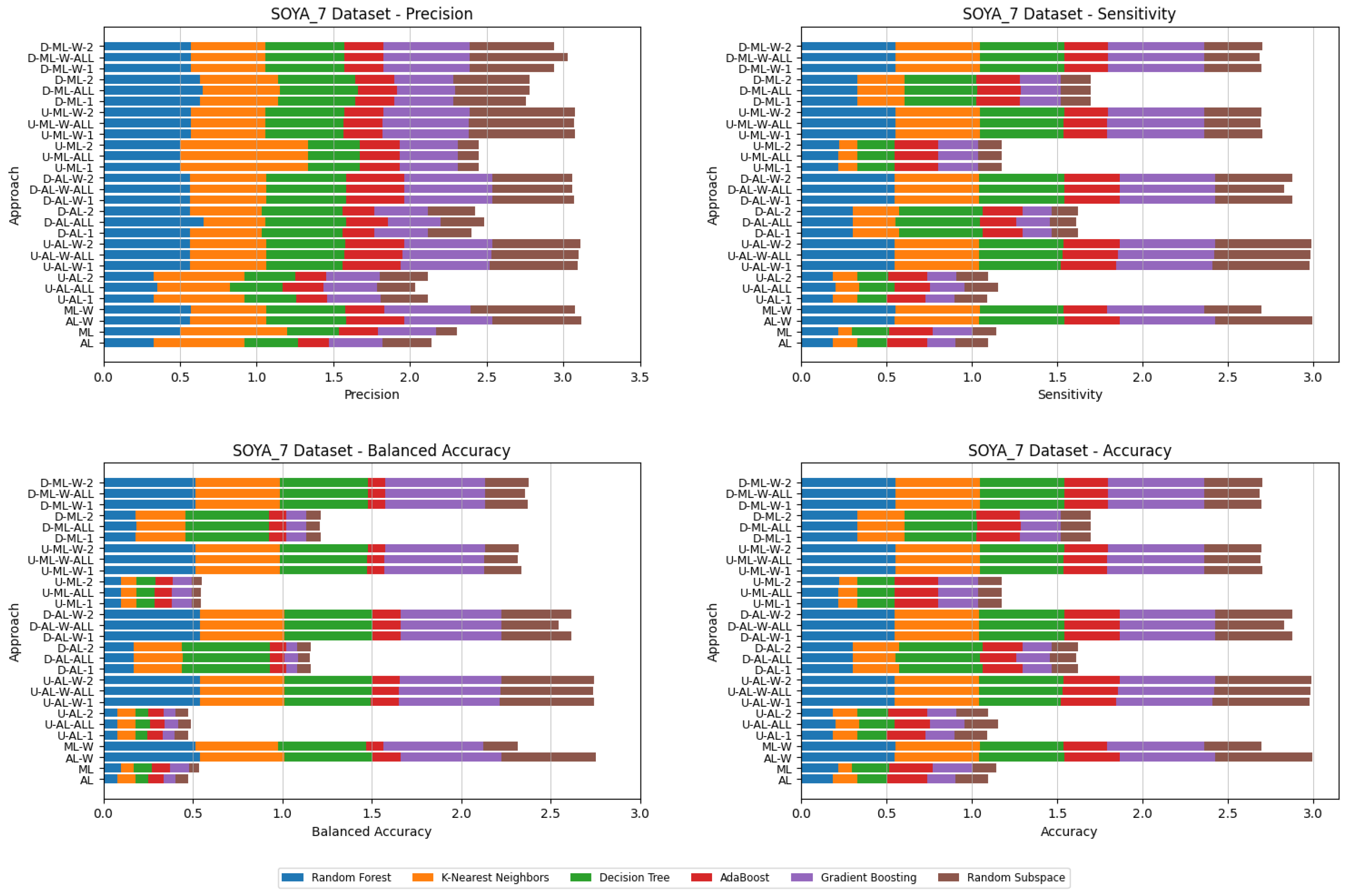

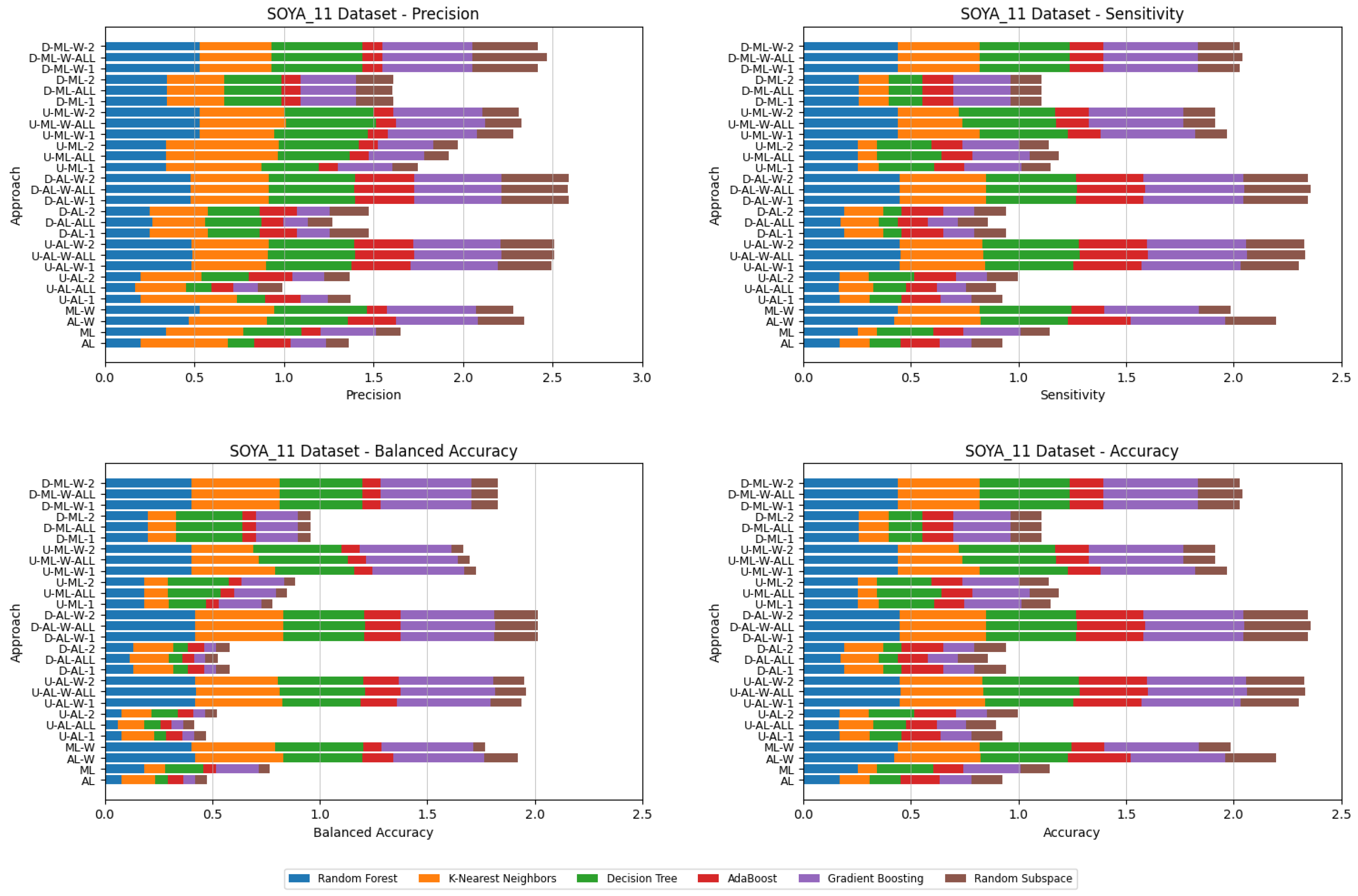

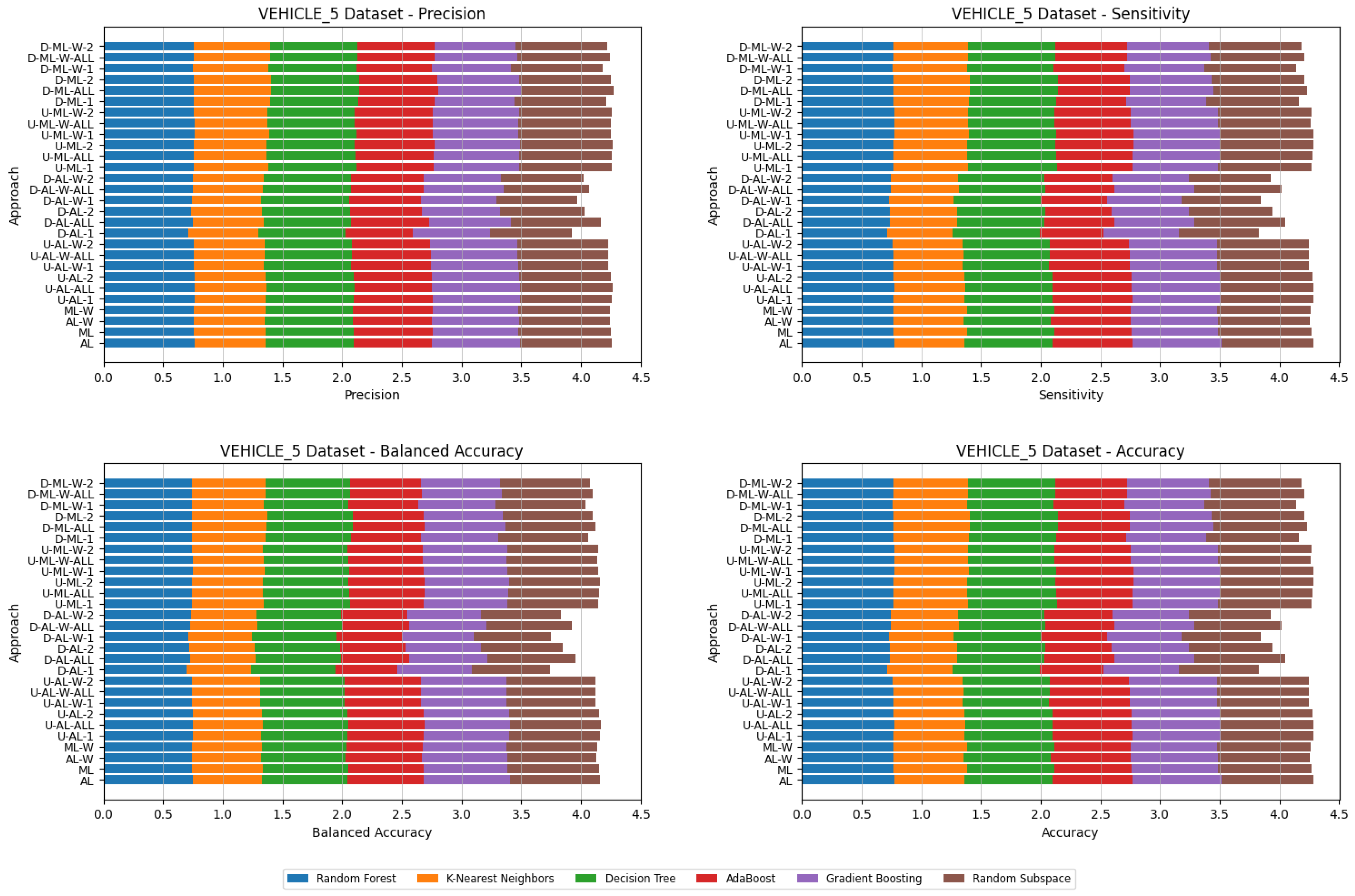
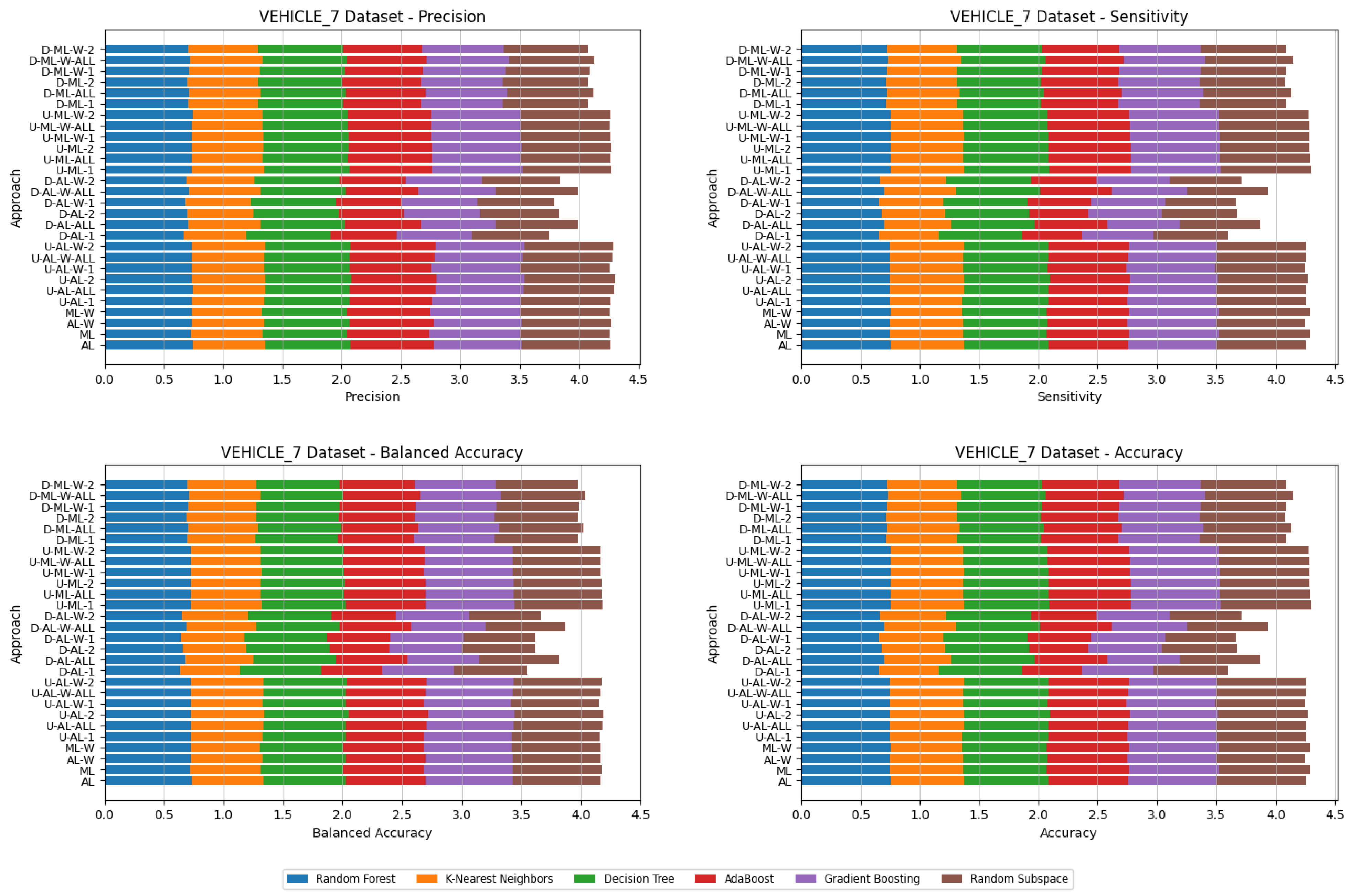
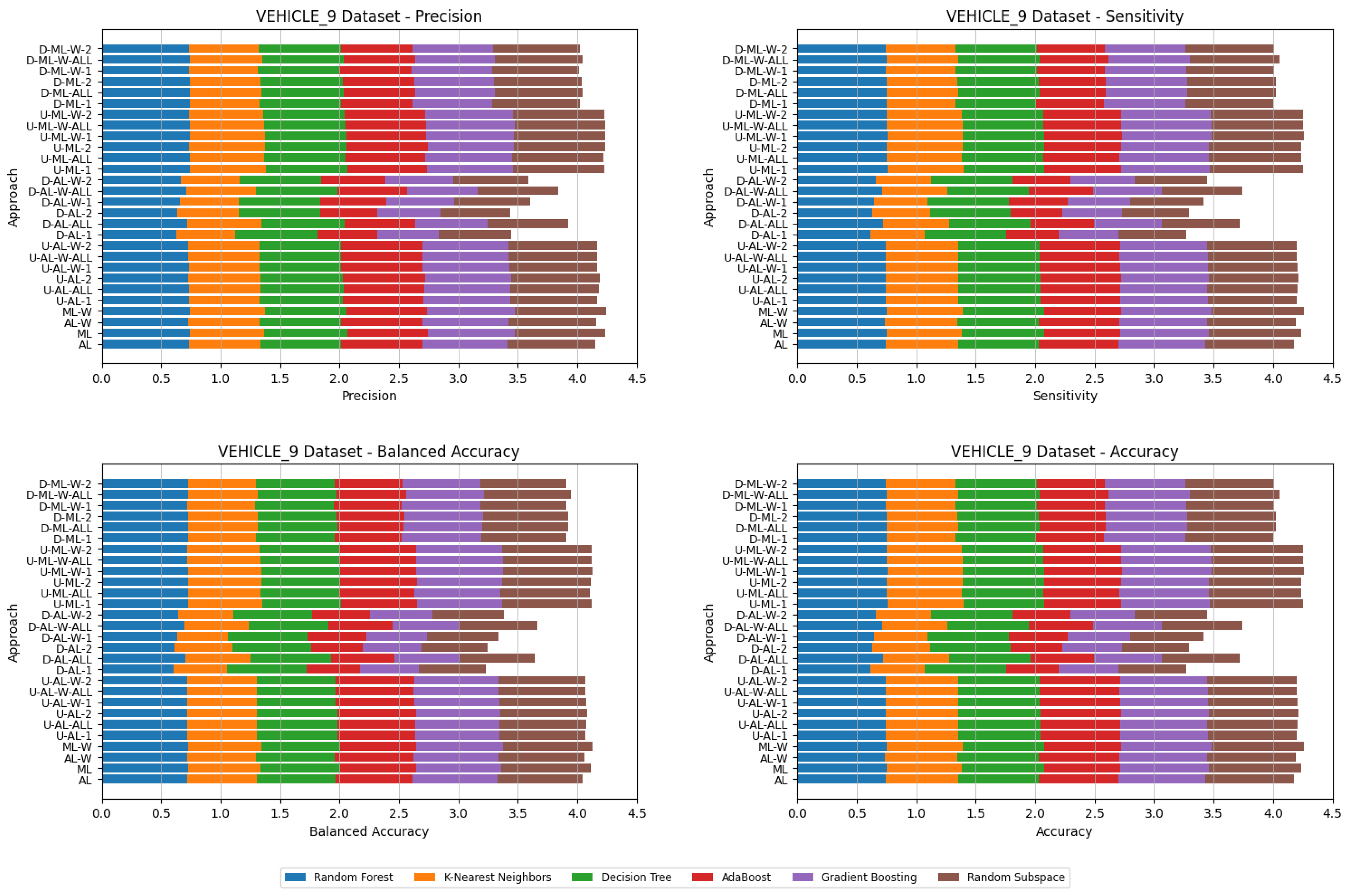

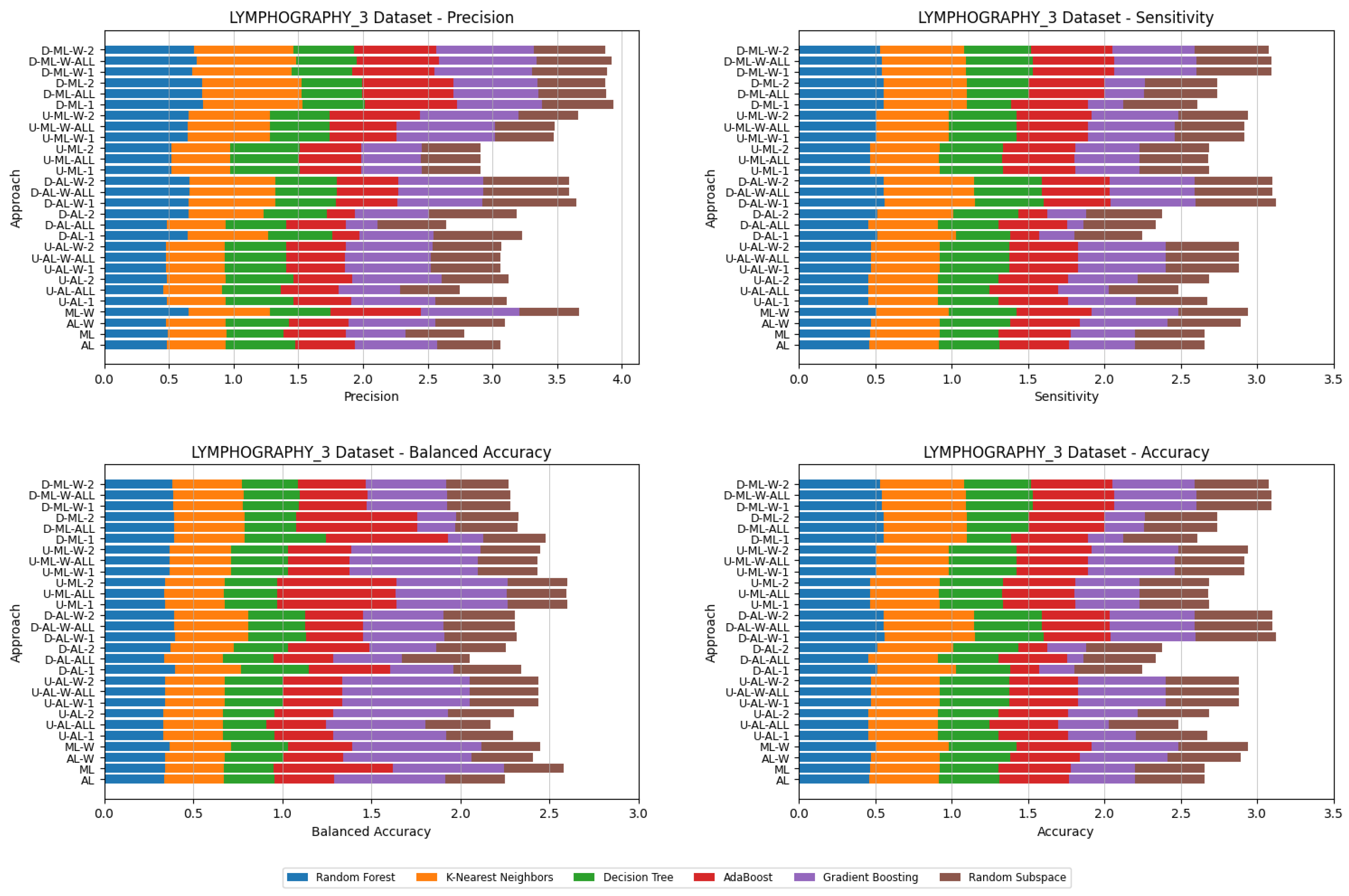
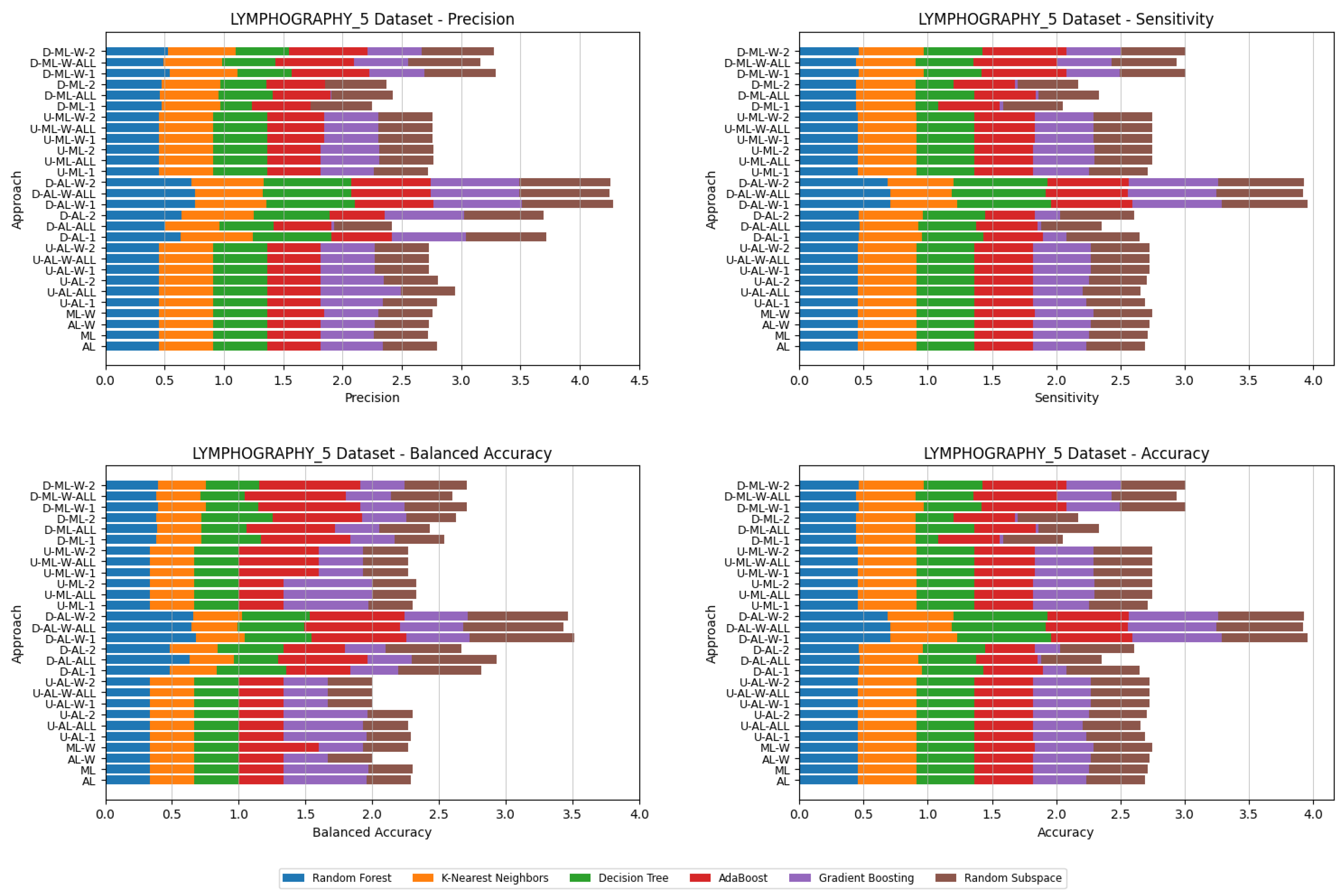

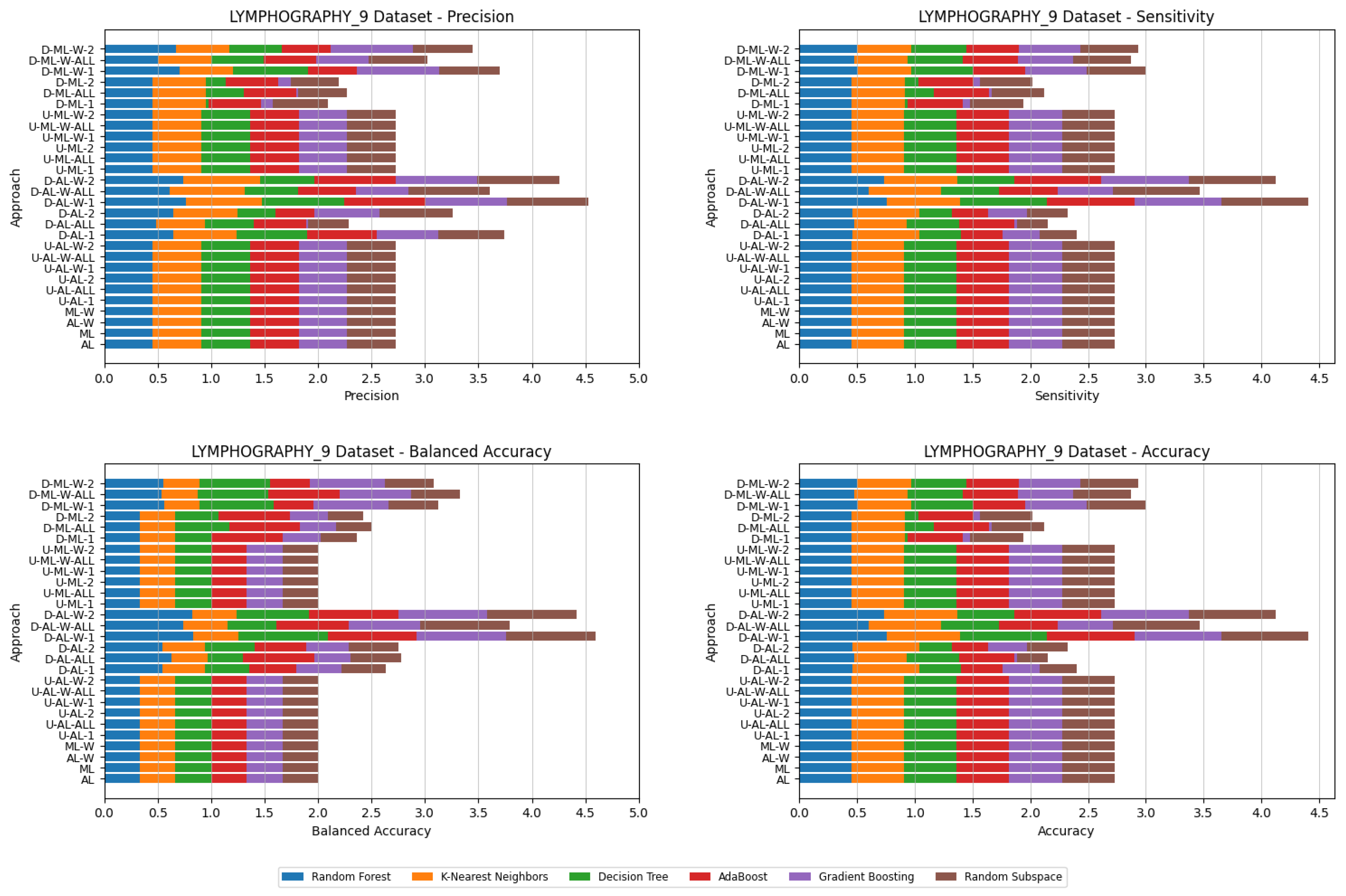
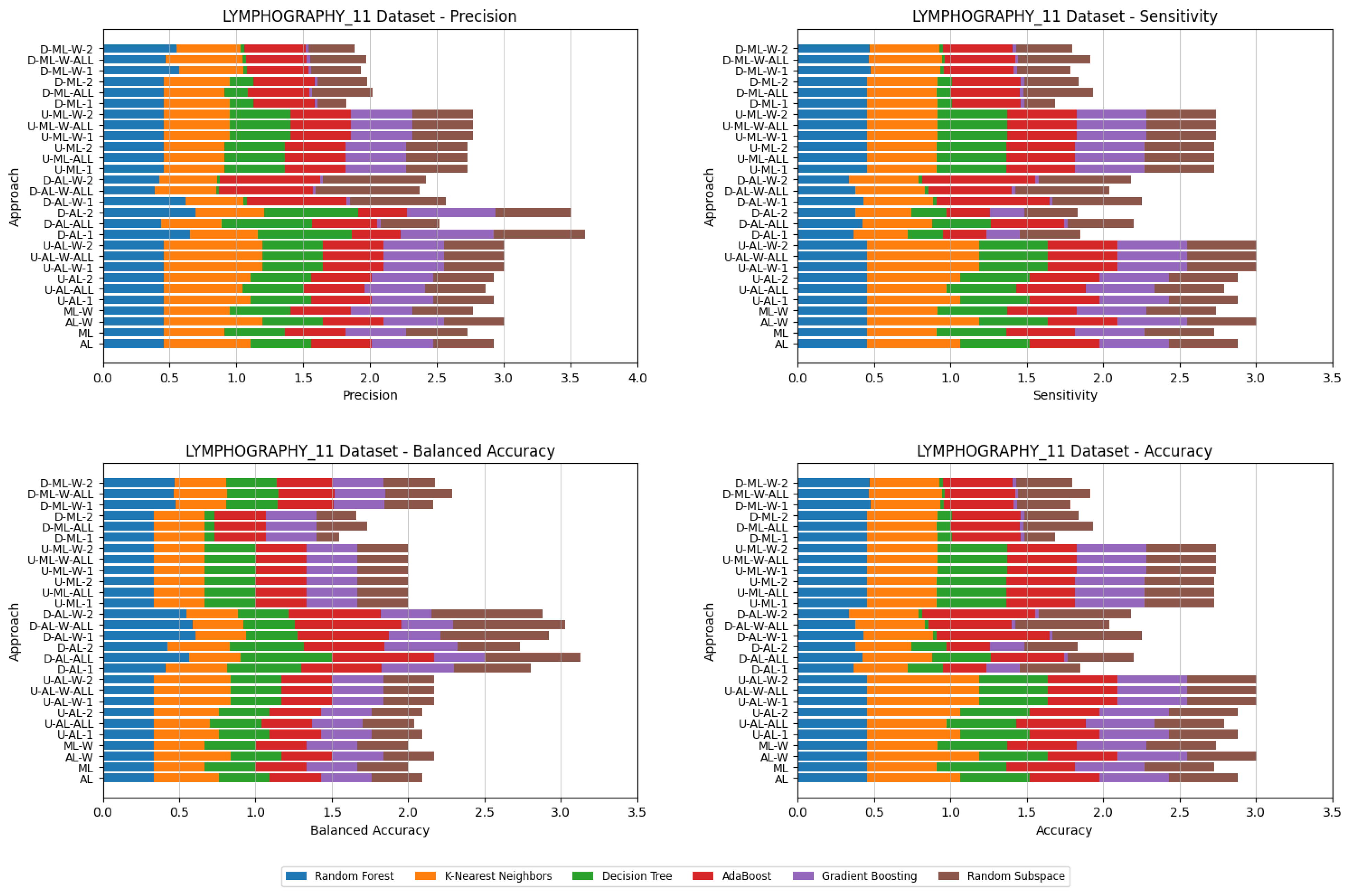

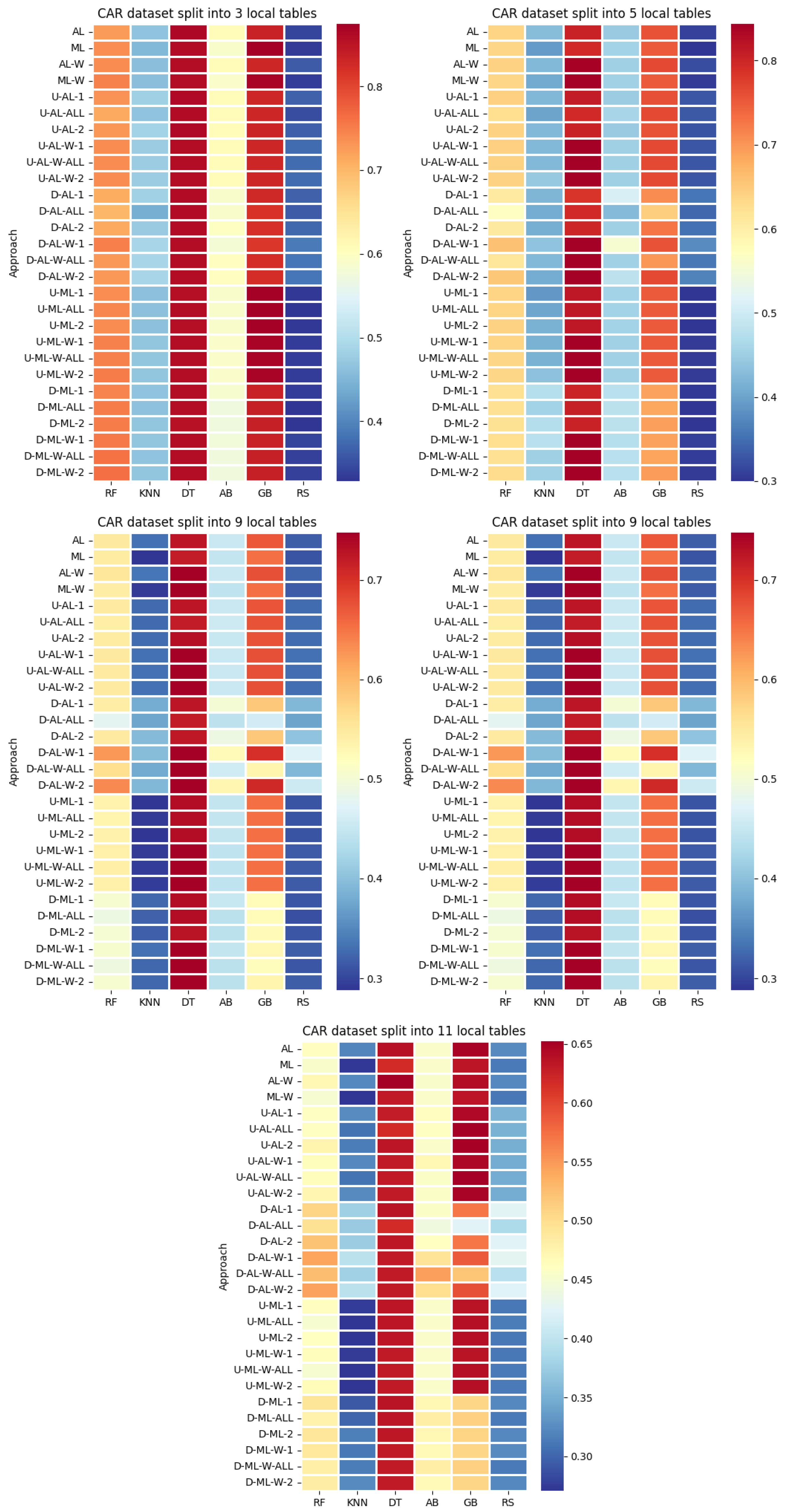
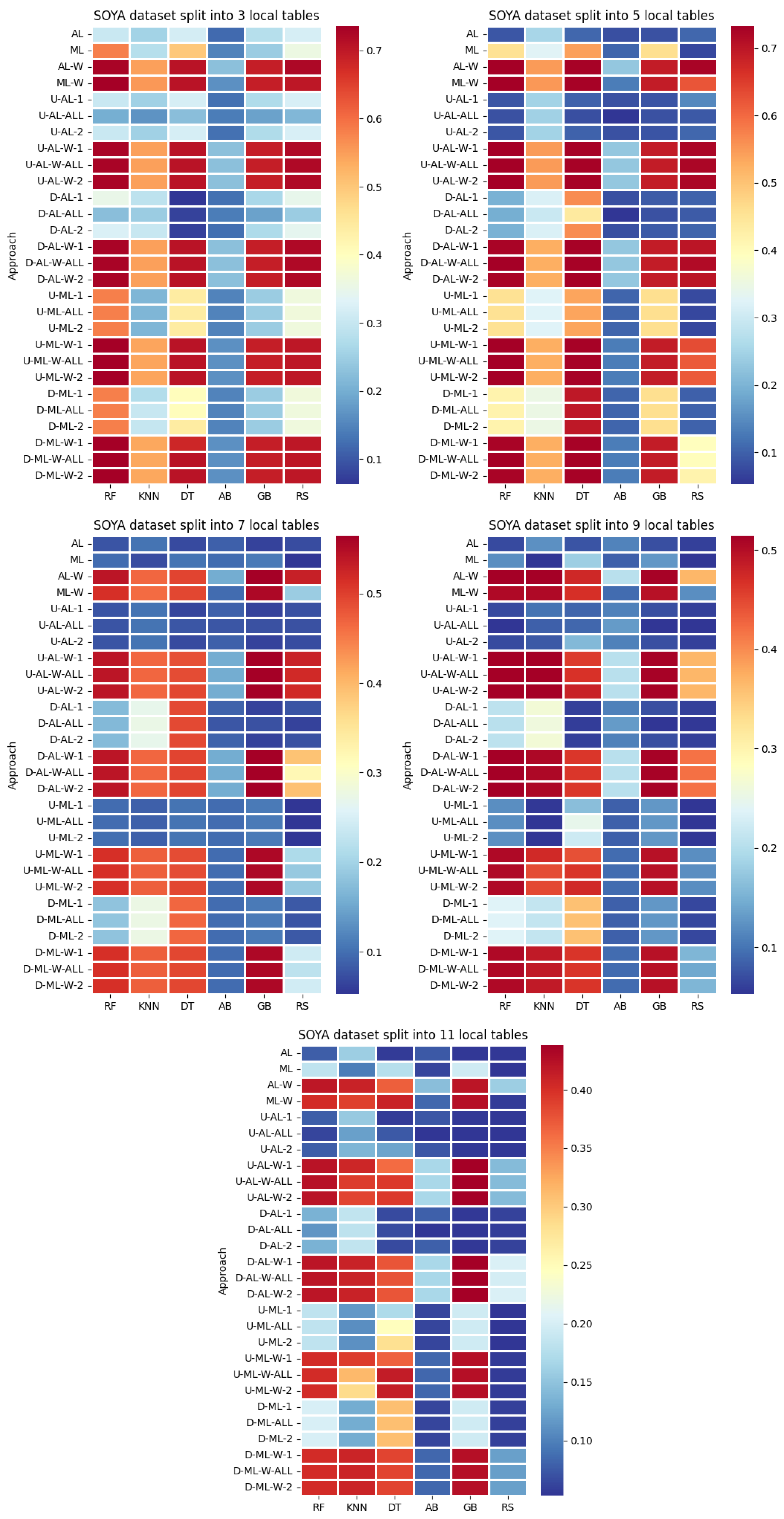
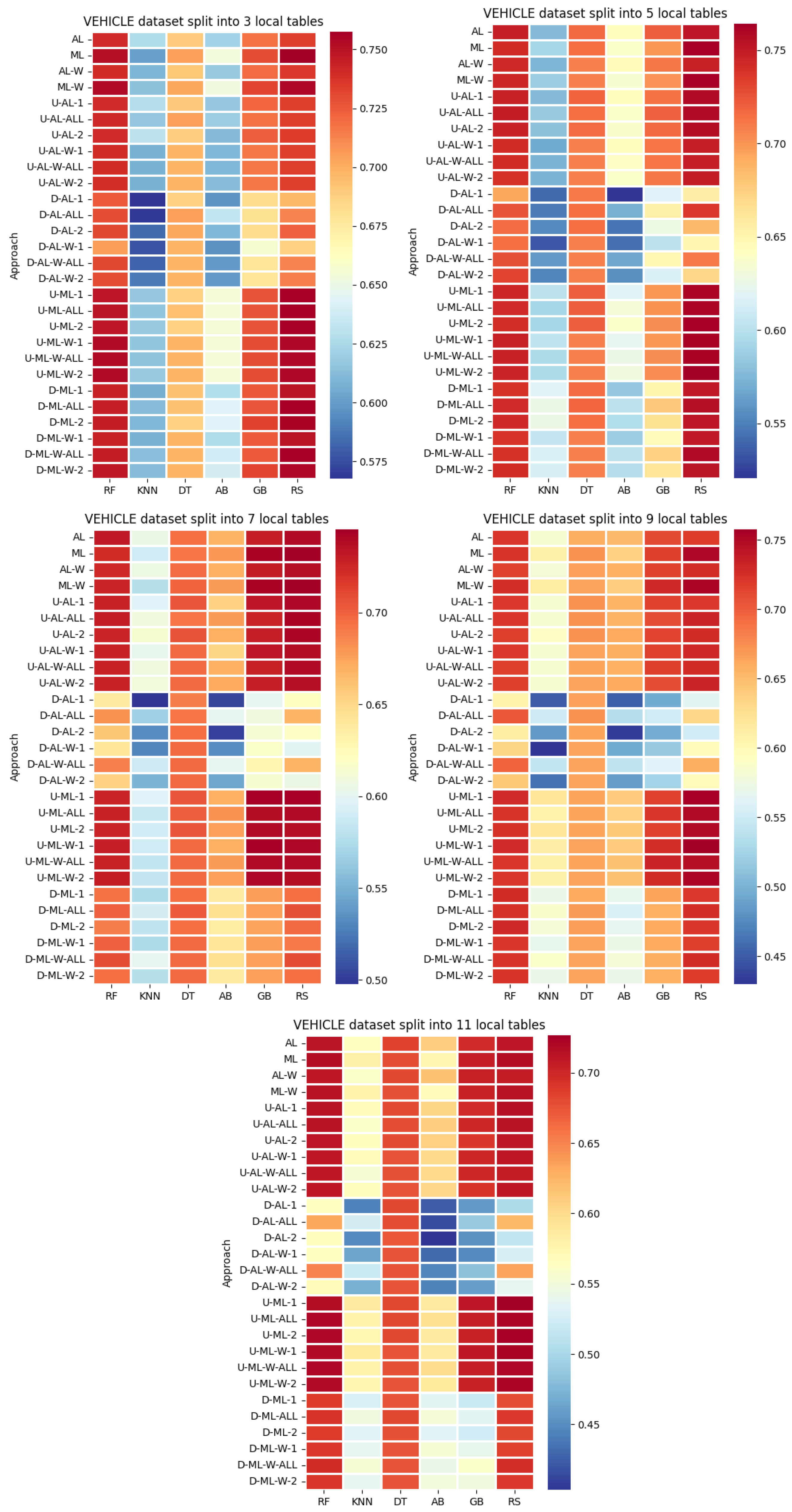
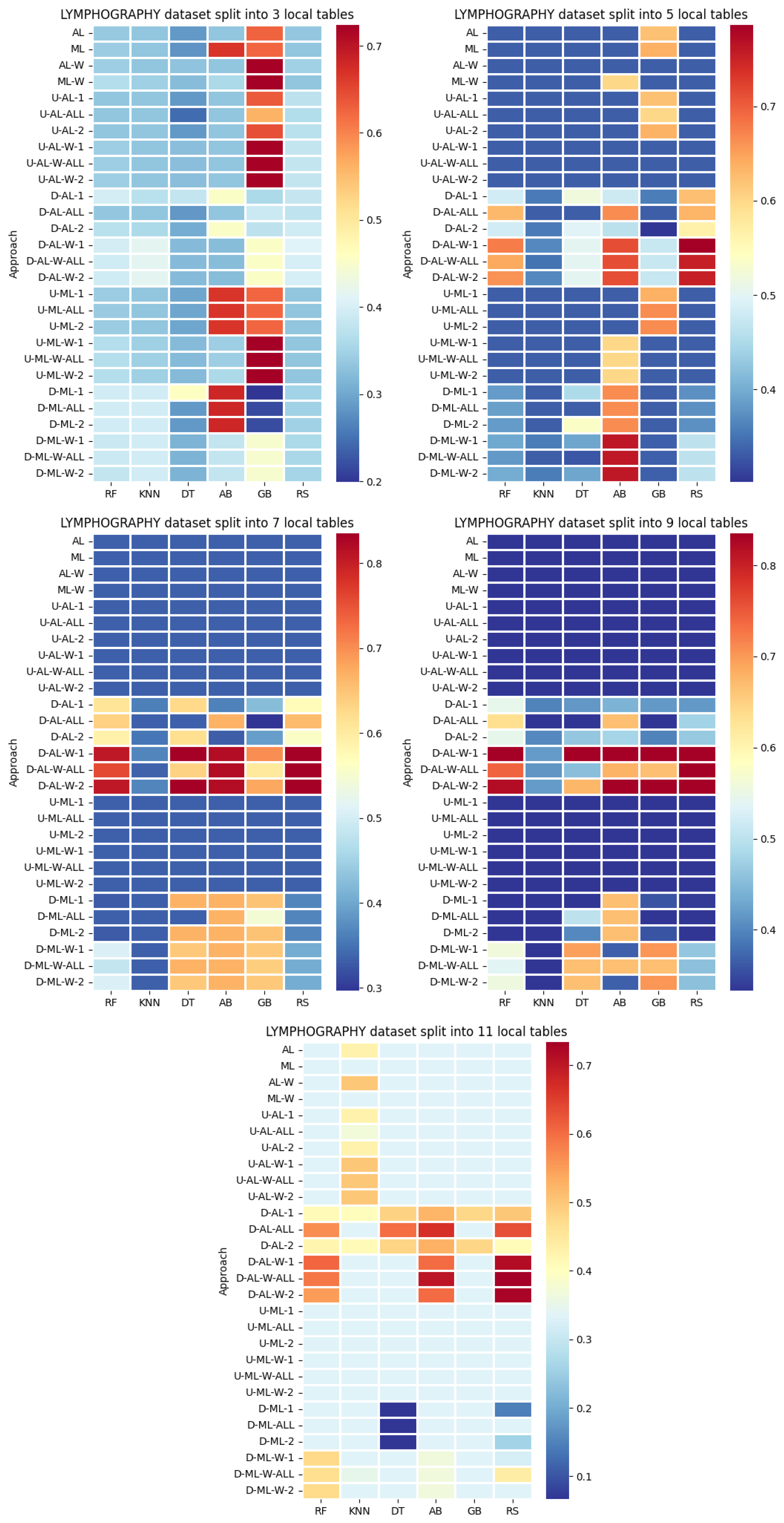
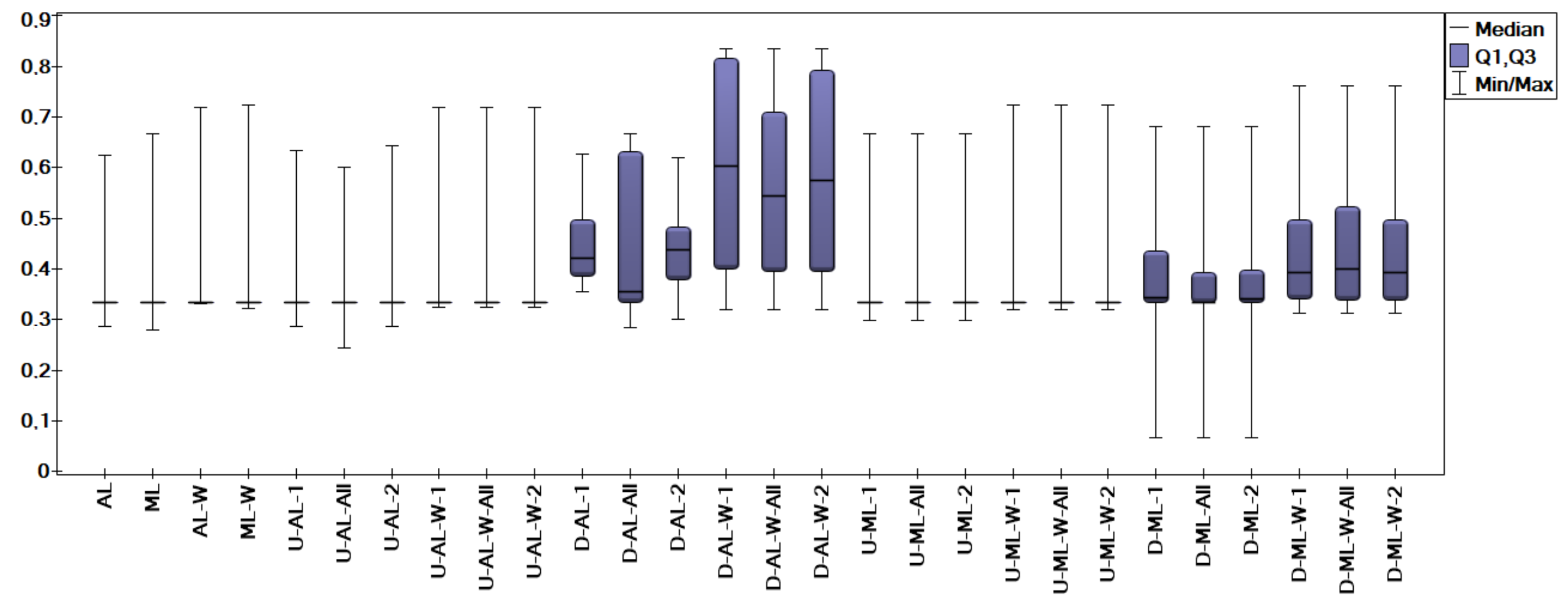
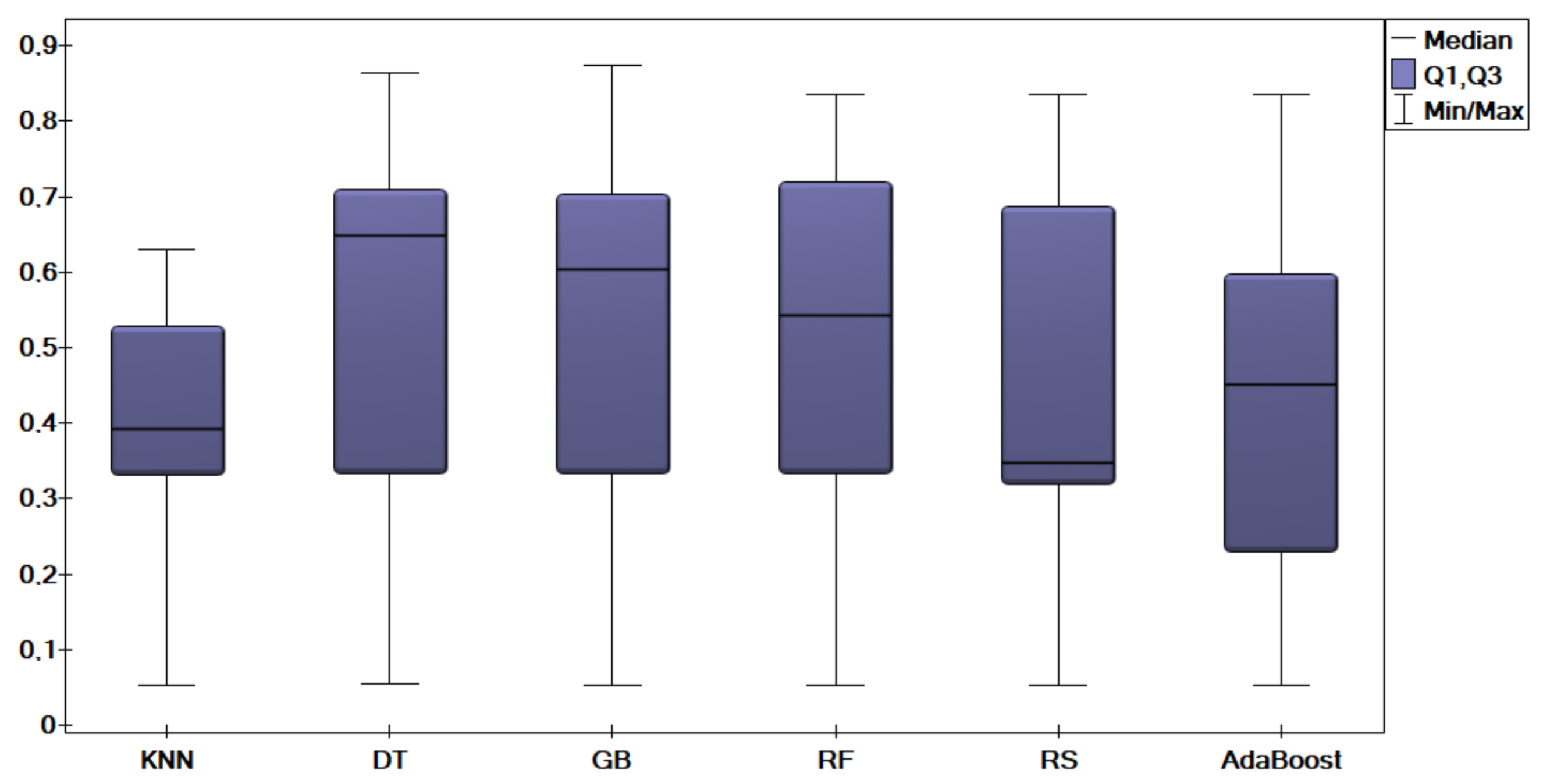

| LM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| 2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| 3 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| 4 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| 5 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.1 |
| LM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | −1 | 0 | −1 |
| 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 0 |
| 4 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 1 |
| 5 | −1 | 0 | 1 | −1 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.75 |
| 2 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.75 |
| 3 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0 | 0.75 | 1 |
| 4 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0 | 0.5 |
| 5 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 1 | 0.5 | 0 |
| Dataset | # The Training Set | # The Test Set | # Conditional Attributes | Attributes Type | # Decision Classes | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avian Influenza | 205 | 89 | 5 | Categorical and Integer | 4 | [34] |
| Car Evaluation | 1210 | 518 | 6 | Categorical | 4 | [30] |
| Soybean | 307 | 376 | 35 | Categorical | 19 | [31] |
| Vehicle Silhouettes | 592 | 254 | 18 | Integer | 4 | [32] |
| Lymphography | 104 | 44 | 18 | Categorical | 4 | [33] |
| Dataset | Decision Classes |
|---|---|
| Avian Influenza | probable, confirmed fatal, probable fatal, suspected under treatment |
| Car Evaluation | Unacceptable, Acceptable, Good, Very good |
| Soybean | diaporthe-stem-canker, charcoal-rot, rhizoctonia-root-rot, phytophthora-rot, brown-stem-rot, powdery-mildew, downy-mildew, brown-spot, bacterial-blight, bacterial-pustule, purple-seed-stain, anthracnose, phyllosticta-leaf-spot, alternarialeaf-spot, frog-eye-leaf-spot, diaporthe-pod-&-stem-blight, cyst-nematode, 2-4-d-injury, herbicide-injury |
| Vehicle Silhouettes | Bus, Opel, Saab, Van |
| Lymphography | normal find, metastases, malign lymph, fibrosis |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.01 | |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.03 | |
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | |
| 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.02 | |
| 9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.02 | |
| 10 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.02 | |
| 11 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.33 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 12 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.62 | 0.10 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 13 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 14 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.04 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 15 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.62 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.15 | 0.98 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 16 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.10 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.40 | 0.02 | 0.17 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 17 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | |
| 18 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | |
| 19 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | |
| 20 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.02 | |
| 21 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.02 | |
| 22 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.02 | |
| 23 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.18 | 1 | 0.40 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 24 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.33 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 25 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.07 | 0.98 | 0.17 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 26 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 27 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 28 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| p-Value | KNN | DT | GB | RF | RS | AdaBoost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KNN | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.06 | |
| DT | 0.01 | 1 | 0.50 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| GB | 0.01 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| RF | 0.01 | 0.50 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| RS | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| AdaBoost | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| p-Value | One Strongest | Two Strongest | All Coalitions |
|---|---|---|---|
| One strongest | 0.67 | 0.89 | |
| Two strongest | 0.67 | 0.07 | |
| All coalitions | 0.89 | 0.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Przybyła-Kasperek, M.; Sacewicz, J. Weighted Decision Aggregation for Dispersed Data in Unified and Diverse Coalitions. Appl. Sci. 2026, 16, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010103
Przybyła-Kasperek M, Sacewicz J. Weighted Decision Aggregation for Dispersed Data in Unified and Diverse Coalitions. Applied Sciences. 2026; 16(1):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010103
Chicago/Turabian StylePrzybyła-Kasperek, Małgorzata, and Jakub Sacewicz. 2026. "Weighted Decision Aggregation for Dispersed Data in Unified and Diverse Coalitions" Applied Sciences 16, no. 1: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010103
APA StylePrzybyła-Kasperek, M., & Sacewicz, J. (2026). Weighted Decision Aggregation for Dispersed Data in Unified and Diverse Coalitions. Applied Sciences, 16(1), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010103







