Abstract
Chimonanthus nitens Oliv. leaves (COL), a commonly used traditional Chinese medicine, are rich in a variety of bioactive components, with flavonoids being one of the most abundant. In the current study, RAW264.7 macrophages were induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and treated with COL flavonoids (COLFs). The results demonstrated that COLFs could inhibit the release of nitric oxide (NO) and related inflammatory factors in macrophages. RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis revealed 627 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the COLF group, which were further analyzed using Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analyses. We found that genes involved in biological processes in the LPS and COLF groups were significantly regulated, as indicated by the GO enrichment analysis. The NF-κB signaling pathway was identified through KEGG enrichment analysis for further exploration of the mechanism by which COLFs affect macrophages. Additionally, Western blotting analysis indicated that COLFs could influence the activity of the NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway via the TLR4 receptor, thereby modulating its anti-inflammatory function. Overall, our results reveal a novel role for COLFs as natural inflammation regulators and provide a theoretical and molecular basis for their development and utilization.
1. Introduction
As a vital defense mechanism, inflammation is a complex and comprehensive immune response to tissue or cell damage caused by infection, immune reactions, or microbial stimulation [1]. It primarily manifests as swelling, redness, pain, and fever, serving as an external indicator of significant changes in local metabolism [2]. Depending on its duration, inflammation is typically classified as acute or chronic. Acute inflammation usually lasts no longer than three weeks, while persistent acute inflammation can progress to chronic inflammation [3]. Recent research has indicated a strong association between the inflammatory response and the emergence of various diseases, including autoimmune disorders, allergies, cancer, diabetes, and rheumatoid arthritis [4]. Therefore, reducing excessive inflammatory responses is the primary therapeutic approach for disorders linked to inflammation.
The mechanism of cell signaling is intricate. When information molecules are stimulated, certain cells emit a range of signaling molecules, and target cells control intracellular biochemical events and interactions to control their own metabolism and the metabolism of other cells [5]. During an inflammatory process, related signaling pathways are activated, and then inflammatory factors and adhesion factors are released; ultimately, the inflammatory response is aggravated [6]. Macrophages are essential to the innate immune response, significantly contributing to immune defense and the inflammatory response. They are also pivotal in the pathogenesis of various chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases [7]. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) activates macrophages via toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 on the cell membrane, stimulating the production of inflammatory mediators such as iNOS, TNF-α, and interleukin (IL), thus initiating an inflammatory response [8]. TNF-α, as a crucial inflammatory mediator, exerts its regulatory function by modulating the metabolic activities of various tissues. By activating neutrophils and lymphocytes, it fosters the synthesis and secretion of other cytokines, thereby playing a pivotal role in the inflammatory process [9]. NO, a mediator of inflammation, is mainly regulated by iNOS. High levels of NO reacting with O2– lead to damages to DNA, lipids, and healthy cells [10]. Numerous natural compounds demonstrate significant anti-inflammatory action, exerting their effects by modulating cytokine production and activating signaling pathways. Xian et al. reported that patchouli alcohol isolated from Pogostemonis herba exhibited anti-inflammatory effects by downregulating the secretion of inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and NO, and their corresponding gene expression levels [11]. Polyphenols from Cinnamomum camphora seed kernel have been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the expression of related signaling molecules and downregulating the activity of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway [12].
Chimonanthus nitens Oliv. is a semi-evergreen shrub belonging to the genus Chimonanthus Lindley. Its leaves, commonly referred to as golden tea or Shi-Liang tea, are recognized as a functional green tea with medicinal properties [13]. The leaves of Chimonanthus nitens Oliv. leaves (COL) contain flavonoids, polysaccharides, volatile oil alkaloids, and a variety of trace elements [14,15]. Pharmacological studies have demonstrated that these leaves possess antioxidant, antibacterial, hypoglycemic, and lipid-lowering activities [16,17]. Furthermore, the application of COL in inhibiting inflammatory responses has garnered significant attention. Ethanol extracts of COL were reported to exhibit anti-inflammatory activity by reducing the expression levels of TNF-α and IL-6 genes in an LPS-induced zebrafish model [18]. Additionally, essential oil derived from COL has been shown to alleviate DSS-induced colonic inflammation and injury in mice [19]. However, the anti-inflammatory properties of COL flavonoids remain underexplored, and the precise molecular mechanisms underlying their anti-inflammatory actions have yet to be fully elucidated. Despite the limited research in this area, there is an urgent need to investigate the anti-inflammatory effects of COL flavonoids and their associated molecular mechanisms, as this could provide valuable insights for future therapeutic applications.
LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells serve as a classic model for studying cellular inflammation and are extensively used to investigate the anti-inflammatory properties of dietary constituents. Consequently, this study focused on the fundamental mechanisms of COL flavonoids (COLFs) in the LPS-induced inflammatory response within RAW264.7 cells. Our results reveal a novel function of COLFs and expand the repertoire of plant extracts with anti-inflammatory activities.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
COL was purchased from Lishui, Zhejiang Province, China. RAW 264.7 macrophage-specific culture medium was procured from Procell Life Science &Technology Co., Ltd. (Wuhan, China). LPS was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). A CCK-8 assay kit was obtained from Dalian Bogeling Biotechnology Co. LTD (Dalian, China). The assay kit for NO was purchased from Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute (Nanjing, China). ELISA kits were obtained from Boster Biological Engineering Co., LTD. (Wuhan, China). All the primary antibodies used in the Western blot analysis, as well as the secondary antibodies and chemiluminescence (ECL) detection kits, were sourced from Proteintech Group, Inc. (Wuhan, China).
2.2. Preparation of COLFs
The preparation of COLFs was slightly modified from the previously established method [20]. Dried COL powder was sieved and extracted twice with 40% ethanol aqueous solution (v/v). The extract was concentrated and adsorbed onto an HPD500 macroporous resin column. Gradient elution was performed using different concentrations of ethanol aqueous solution as the mobile phase. The substance obtained by freeze-drying the 70% elution component was defined as COLF and used for subsequent tests. The total flavonoid content was determined using the aluminum nitrate colorimetric method, yielding a value of 76.11%. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) quantified quercetin and kaempferol at 99.27 ± 0.08 μg/mg and 28.80 ± 0.07 μg/mg, respectively [21].
2.3. Cell Culture
RAW264.7 cells were purchased from Dalian Bogeling Biotechnology Co. Ltd. (Dalian, China). The cells were cultured in DMEM medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) supplemented with 10% FBS and 1% penicillin–streptomycin and incubated at 37 °C with 5% CO2.
2.4. Cell Viability
The cytotoxicity of COLFs toward RAW264.7 cells was assessed using a CCK-8 assay kit. In brief, the cells were incubated in medium with various concentrations of COLFs (12.5, 25, 50, 100, 200, 400 μg/mL) for 24 h, after which the supernatant was removed prior to analysis. Subsequently, a medium containing 10% CCK-8 was added in liquid form and incubated at 37 °C for 1 h. Finally, the OD values at 450 nm were determined. The medium containing 10% CCK-8 served as the blank control. The vitality of cells was determined using the following formula:
Cell survival rate (%) = [(A COLF − A Blank)/(A Control − A Blank)] × 100
2.5. Inflammation Stimulation
The method for inducing LPS-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells was adapted from previous reports with slight modifications [22]. Briefly, the cells were seeded into 6-well cell culture plates at a density of 2 × 105 cells per well and incubated overnight to allow for adherence. The cells were pretreated with varying concentrations of COLF (25, 50, 100 μg/mL) for 2 h, followed by stimulation with LPS at a final concentration of 1 μg/mL for 24 h. The supernatant and cell pellet were collected for further experimental analysis.
2.6. Determination of NO and Inflammatory Factors
The collected supernatant was centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C. The concentrations of NO, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-18 in the supernatant were quantified using commercial kits or ELISA kits (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.7. RNA-Seq Analysis
Total RNA was extracted from samples using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) following the manufacturer’s protocol. RNA libraries were constructed and sequenced on the Illumina NovaseqTM 6000 platform (OE Biotech Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). Differential gene expression analysis was conducted using DESeq2 5, with significance thresholds set at a false discovery rate (Q value) of <0.05 and an absolute fold change of >2. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were further analyzed for enrichment, which included principal component analysis (PCA) for dimensionality reduction, Gene Ontology (GO) functional annotation, and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway mapping. The statistical significance of enriched terms was assessed using R software (v3.2.0).
2.8. RT-qPCR Analysis
RNA extraction from macrophages was performed according to the protocol provided by the TransZol Up Plus RNA kit (TransGen Biotech Co., Ltd. Beijing, China). The concentration and purity of the extracted mRNA were assessed using the A260/A280 ratio, followed by reverse transcription to obtain cDNA [23]. The RT-PCR reaction was conducted using perfectstartTM Green qPCR superMix (TransGen Biotech Co., Ltd. Beijing, China). The mRNA expression levels of the pro-inflammatory signaling molecules (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-18) in the cells were determined based on previously reported methods [23]. We used β-actin as the reference mRNA and measured relative gene expression with 2−ΔΔCt. The sequences of the primers used in the study are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Primer sequences of RT-qPCR.
2.9. Western Blotting
Western blotting was conducted as outlined in our prior research [20]. The cells underwent a washing process three times using pre-chilled PBS and were lysed on ice utilizing the RIPA lysis buffer (Beijing Tianenze Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). Protein concentrations were homogenized using the BCA quantification kit (Nanjing Vazyme Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China) and denatured with boiling water. Following quantification, protein samples were resolved by 10% SDS-PAGE and electrophoretically transferred to PVDF membranes. The membranes were blocked for 1.5 h in TBST containing 5% skim milk, followed by four washes with TBST. The membranes were incubated overnight at 4 °C with primary antibodies (1:1000 dilution), the primary antibodies used in the study included anti-β-Actin, anti-TLR4, anti-P65, anti-P-P65, anti-IκBα, anti-JNK, anti-P-JNK, anti-P38, anti-P-P38, anti-ERK, and anti-P-ERK. After four additional washes with TBST, the membranes were incubated for 1 h with horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibody (1:2000 dilution). Protein bands were visualized using enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) reagent, and band intensities were quantified using ImageJ software (Versoin 1.8.0). The relative protein expression levels were calculated by normalizing the intensity of the target protein band to that of the internal β-Actin band, and the control group was normalized.
2.10. Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed using SPSS 21 software, employing one-way ANOVA and the Duncan test to compare differences between groups. All data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD), with statistical significance defined as p < 0.05. All figures were made using Origin8.5.
3. Results
3.1. Cell Cytotoxicity of COLFs
The impact of COLFs on the viability of RAW264.7 cells is illustrated in Figure 1A. COLFs did not significantly affect the viability of RAW264.7 cells at concentrations ranging from 0 to 100 μg/mL. This indicates that COLFs have no significant cytotoxic effect within this concentration range. Consequently, concentrations of 25, 50, and 100 μg/mL were selected for follow-up experiments in this study.
3.2. COLFs Inhibited the Secretion of NO and Inflammatory Factors
LPS treatment notably increased the secretion of NO, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-18 in RAW264.7 cells by 371.43%, 680.73%, 111.74%, and 117.15%, respectively (p < 0.01) (Figure 1B–E). COLF pretreatment significantly inhibited the LPS-mediated secretion of NO, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-18 in RAW264.7 cells in a dose-dependent manner (p < 0.01). Compared to the LPS group, the levels of NO, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-18 decreased by 77.27%, 40.46%, 51.98%, and 68.11%, respectively, when COLFs were administered at the highest dose. These results indicate that COLFs exhibit anti-inflammatory properties by regulating NO secretion and inflammatory factors in RAW264.7 cells.
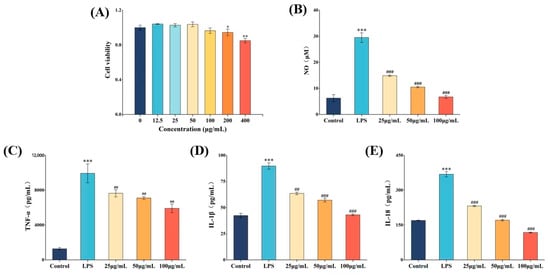

Figure 1.
Effect of COLFs on the viability of RAW264.7 cells (A) and effects of COLFs on the release of NO (B), TNF-α (C), IL-1β (D), and IL-18 (E) in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3). Different symbols correspond to statistically significant differences between groups. * p < 0.05, ** p <0.01, *** p < 0.001, compared with control; ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001, compared with LPS.
3.3. Differentially Expressed Genes
Transcriptomic analysis was conducted to elucidate the anti-inflammatory mechanism of COLFs in macrophages. The results of the principal component analysis (PCA) revealed that the samples from the three groups did not cluster together and exhibited significant differences (Figure 2A). A Venn diagram was created to display the number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) (p < 0.05, 1.5-fold difference) between the LPS group and the control group, as well as between the COLF group and the LPS group. The volcano plots illustrate the upregulated and downregulated genes between the groups. The results indicated that 2974 DEGs were identified in the comparison between the LPS group and the control group, with 1631 genes upregulated and 1343 genes downregulated (Figure 2B,C). In contrast, the COLF treatment resulted in 627 DEGs, with 286 genes upregulated and 341 genes downregulated (Figure 2B,D).
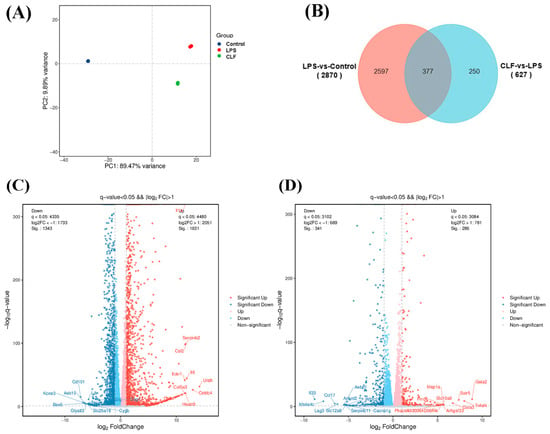
Figure 2.
RNA-seq analysis of RAW264.7 cells. (A) PCA analysis of the whole transcriptome of RAW264.7 cells. Different colors in the graph represent different groups. (B) Venn diagram displays the number of DEGs (p < 0.05, 1.5-fold difference) between LPS and control groups, and COLF and LPS groups. Volcano plot of DEGs between (C) LPS group and control group, and (D) COLF group and LPS group. Upregulated genes are shown in red and downregulated genes are shown in blue. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3).
3.4. Mechanistic Exploration of LPS-Induced Macrophages
After identifying the differentially expressed genes, we described their biological functions based on Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis. The top 30 items with the most significant enrichment across the three categories—biological process (BP), cellular component (CC), and molecular function (MF)—are presented in Figure 3A,B. Compared to lipopolysaccharide (LPS), COLF pretreatment significantly altered the expression of genes associated with the cellular response to LPS, innate immune response, inflammatory response, immune system processes, and immune responses within the BP category. These results suggest that COLFs influence these genes to exhibit anti-inflammatory activity.
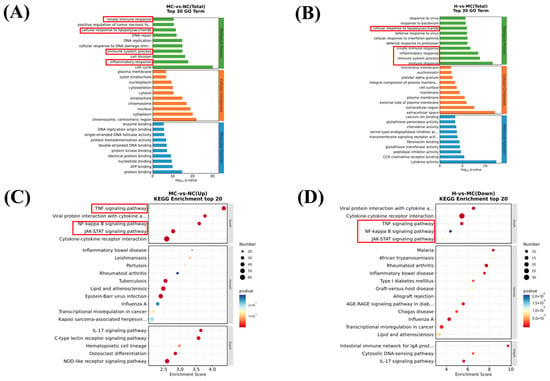
Figure 3.
The GO enrichment analysis and KEGG pathway analysis of the DEGs. GO enrichment analysis of DEGs between (A) LPS and control groups and between (B) COLF and LPS groups. KEGG pathway analysis of upregulated DEGs between (C) LPS and control groups and between (D) COLF and LPS groups.
KEGG enrichment analysis showed that among the 20 pathways with a high enrichment of DEGs, five inflammatory pathways exhibited particularly significant enrichment. Notably, the NF-κB signaling pathway, cytokine–cytokine receptor interactions, and other inflammatory signaling pathways were significantly upregulated (Figure 3C). Conversely, in the comparison between the COLF group and the LPS group, the NF-κB signaling pathway, cytokine–cytokine receptor interactions, and other inflammatory signaling pathways were significantly downregulated (Figure 3D). Therefore, COLFs may influence anti-inflammatory responses by modulating the interaction between cytokines and their receptors, thereby activating the NF-κB signaling pathway.
3.5. COLFs Regulated Gene Expression of Cytokines
To validate the RNA-seq findings, RT-qPCR analysis was conducted to assess the mRNA levels of the key pro-inflammatory cytokines associated with the TLR4/NF-κB/MAPK pathway (Figure 4). COLF treatment significantly suppressed the transcription of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-18, and IL-6 compared to the LPS-stimulated group. These results indicate that COLFs mitigate inflammatory responses by inhibiting the transcriptional activation of pro-inflammatory mediators, which is consistent with their anti-inflammatory activity.
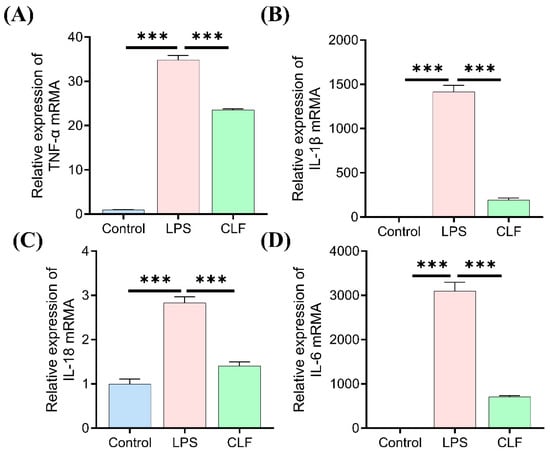
Figure 4.
Verification of differentially expressed genes in RNA-seq. (A) TNF-α, (B) IL-1β, (C) IL-18, and (D) IL-6. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3). *** p < 0.001.
3.6. COLFs Exerted Anti-Inflammatory Activities via NF-κB and MAPK Pathway
We utilized a Western blotting assay to analyze the effect of COLFs on the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. LPS treatment significantly elevated the level of phosphorylated p65, TLR4, and IκBα in the NF-κB pathway (p < 0.05) (Figure 5). In contrast, after pretreatment with 100 μg/mL of COLFs, the expression levels of p-p65/p65, TLR4, and IκBα decreased. Administering the appropriate amount of COLFs may activate the NF-κB signaling pathway by modulating the levels of specific proteins such as p-p65/p65, TLR4, and IκBα, indicating their potential to help reduce inflammation.
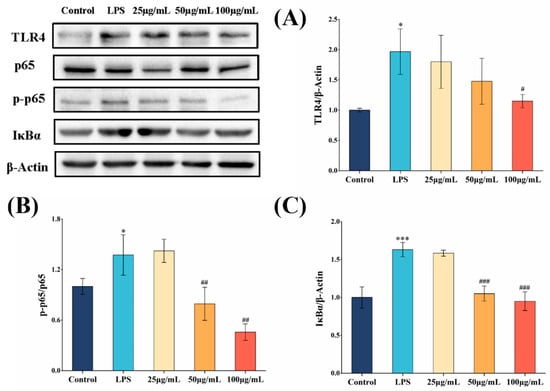
Figure 5.
The protein expression of NF-κB in RAW264.7 macrophages was detected by Western blotting. (A) TLR4/β-Actin, (B) p-p65/p65, and (C) IκBα/β-Actin. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3). Different letters correspond to statistically significant differences between groups. * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001, compared with control; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001, compared with LPS.
Finally, we assessed the effect of COLFs on the MAPK pathway. As shown in Figure 6A–C, the phosphorylation of JNK, ERK, and p38 in the MAPK signaling pathway was activated in RAW264.7 cells following LPS treatment. However, pretreatment with 100 μg/mL of COLFs significantly inhibited the phosphorylation of JNK, ERK, and p38 in LPS-induced macrophages (p < 0.05).
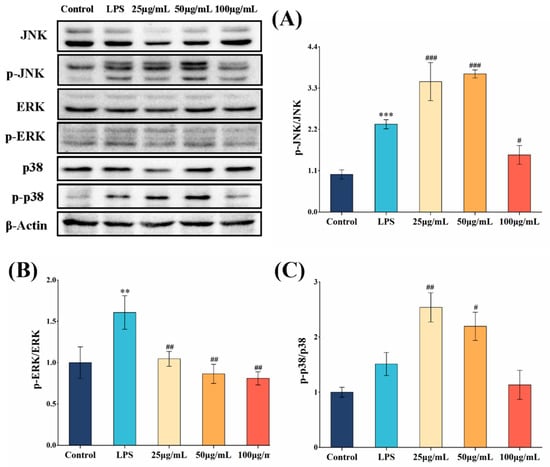
Figure 6.
The expression of MAPK proteins in RAW264.7 macrophages was detected by Western blotting. (A) p-JNK/JNK, (B) p-ERK/ERK, and (C) p-p38/p38. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3). Different letters correspond to statistically significant differences between groups. ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, compared with control; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001, compared with LPS.
4. Discussion
Previous studies have demonstrated that macrophages secrete a significant number of inflammatory mediators and cytokines during inflammation, which further contribute to the progression of the inflammatory response [24]. Therefore, inhibiting the production of these inflammatory mediators and cytokines may represent an effective anti-inflammatory strategy [25]. Fan et al. reported that polyphenols isolated from selenium-enriched green tea exert therapeutic effects on inflammation by inhibiting the production of NO, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 [26]. These findings align with the current study, which demonstrates that COLFs possess strong anti-inflammatory effects, potentially by reducing the production of various inflammatory markers.
There are numerous methods to analyze cell phenotype and function, with RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) being a prominent technique for examining gene expression and regulatory mechanisms at the RNA level. RNA-seq is an effective approach for identifying differentially expressed genes and measuring mRNA expression levels within the transcriptome [27]. Reports indicate that RNA-seq technology has been utilized to identify therapeutic targets and molecular markers in various inflammatory diseases [28,29]. One study revealed the interaction between mung bean polysaccharide (MBP) and macrophages, highlighting the alterations in the entire signaling pathway following MBP treatment. RNA-seq, along with GO analysis and KEGG analysis, suggested significant enrichment of the TLR4 and NF-κB signaling pathways [30]. Hence, RNA-seq technology was used to detect changes in the transcriptome spectrum of each group, and bioinformatics analysis was used to compare the DEGs between groups. In our study, we found that a large number of gene expressions were changed in macrophages after LPS stimulation and similar results were found for previous studies [31]. However, a total of 627 DEGs were produced between the COLF group and LPS group after COLF intervention, including 286 upregulated genes and 341 downregulated genes. GO and KEGG enrichment analyses were performed on the screened DEGs to comprehensively integrate the genomic, chemical, and systemic function information, and to explore the anti-inflammatory mechanism of COLFs on RAW264.7 cells. The results of the GO enrichment analysis indicated that genes involved in biological processes in the LPS and COLF groups were significantly regulated, among which the functional sets of innate immune response, inflammatory response, immune system process, and immune response were significantly enriched. To further investigate the impact of COLFs on signaling pathways, KEGG enrichment analysis was employed. The findings demonstrated that both the LPS and COLF groups exhibited significant enrichment in the regulation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. COLFs play a major inhibitory function in genes associated with the LPS-NF-κB signaling pathway, resulting in the reduction in the expression of downstream pro-inflammatory mediators, thereby inhibiting LPS-induced inflammation.
NF-κB serves as a crucial transcription factor that regulates various genes involved in immune and inflammatory responses, modulating both innate and adaptive immune responses [32,33]. NF-κB is composed of two proteins, p50 and p65 [34]. In resting cells, NF-κB typically remains inactive in the cytoplasm by binding to IκB. Once activated by extracellular signals, IκB is dissociated from NF-κB through ubiquitination and phosphorylation [8]. The released NF-κB translocates to the nucleus, where it is activated by phosphorylation, binds to target DNA, and induces the transcription of inflammatory marker genes [35]. Many studies show that different natural products can affect biological processes by blocking the NF-κB signaling pathway, which helps lower the release of pro-inflammatory molecules. The ethanol extract of Cinnamomum camphora leaves showed anti-inflammatory properties through the suppression of NF-κB pathway expression [36]. Isoflavones daidzin and daidzein can inhibit the secretion of inflammatory factors and inhibit LPS-induced inflammation by regulating the NF-κB/MAPK pathway in RAW264.7 cells [37]. In our study, the activation of key proteins in LPS-induced macrophage-related signaling pathways by COLFs was examined. Protein expression analysis showed that COLFs could significantly decrease the ratio of p-p65/p65 and IκBα, indicating that COLFs inhibited the degradation of IκBα through the NF-κB pathway, thereby promoting the binding of NF-κB and P65 in the cytoplasm, reducing the translocation of NF-κB, and finally inhibiting the production of cytokines.
The MAPK pathway, which includes regulatory proteins such as JNK, ERK, and p38, is a classical inflammation-related signaling pathway that plays a crucial role in regulating the NF-κB pathway [38,39]. It primarily functions by phosphorylating various molecular signals, thereby amplifying and integrating signals from diverse stimuli and regulating gene expression [40]. Consequently, inhibiting the expression or phosphorylation levels of molecules involved in the MAPK pathway may serve as a target for the development of anti-inflammatory drugs. Hostaflavone A, derived from Hosta plantaginea, exhibits anti-inflammatory effects in macrophages by suppressing the activation of multiple signaling pathways, including the MAPK pathway [41]. Studies have demonstrated that COLFs significantly inhibit the phosphorylation of key proteins such as JNK, ERK, and p38 within the MAPK signaling pathway, indicating that COLFs exert anti-inflammatory effects by regulating the MAPK pathway.
The presence of quercetin and kaempferol in COLFs may contribute to their potent anti-inflammatory activity. Previous research has shown that quercetin and kaempferol inhibit NF-κB activation by preventing the nuclear translocation of the p50 and p65 subunits of NF-κB, as well as suppressing the phosphorylation of IκBα protein, which in turn reduces the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines [42]. Additionally, quercetin and kaempferol mitigate inflammatory responses by exerting distinct regulatory effects on the MAPK pathway. Huang et al. demonstrated that quercetin inhibits ERK, JNK, and their phosphorylated forms, thereby regulating the MAPK pathway and ultimately producing anti-inflammatory effects [43]. Kaempferol, on the other hand, impedes the activation of the MAPK signaling pathway by modulating the phosphorylation of P38 and JNK [44]. Therefore, quercetin and kaempferol may function by downregulating the NF-κB/MAPK pathway in COLFs.
TLRs are a family of cell surface receptors that play a critical role in signal transduction from the cell surface to the interior of the cell [45]. Increasing evidence suggests that TLR4 is a key receptor for lipopolysaccharide (LPS) recognition and mediates inflammatory responses via the NF-κB/MAPK pathway [46]. Protein expression analysis demonstrated that COLFs significantly inhibited the expression of the TLR4 receptor protein. These findings indicate that COLFs influence the activity of the NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway through the TLR4 receptor, thereby modulating its anti-inflammatory function.
Despite the progress made in this study, there are certain limitations. The research was conducted using a single mouse macrophage cell line (RAW264.7) for in vitro experiments. Although RAW264.7 is a widely used model for studying inflammatory responses, it may not fully capture the biological complexity of human macrophages. Therefore, our findings will be further validated using other cell lines, particularly human cell lines, in future studies. Additionally, in vivo experiments will be conducted to assess the anti-inflammatory effects of COLFs in animal models, with results to be published at a later date.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, COLFs demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory activity and effectively alleviated the inflammatory response in macrophages. COLFs were found to reduce the expression of TLR4 and intervene in key components of the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. They downregulated the gene expression of inflammatory cytokines, thereby inhibiting the production of inflammatory markers and ultimately achieving the effect of suppressing the inflammatory response. Our data suggest that COLFs may serve as natural anti-inflammatory agents, with potential applications in the treatment or prevention of inflammation.
Author Contributions
L.S. carried out the experiments, analyzed the results, and wrote the manuscript. W.M. carried out experiments and analyzed the experimental results. W.W. guided the experiments and revised the manuscript. H.C., L.C., S.L. and K.O. provided help during the experiment and during the article writing process. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31560459), Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. 20224ACB205014), and the Earmarked Fund for Jiangxi Agriculture Research System (No. JXARS-13).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest related to this work.
References
- Ahmed, A.U. An overview of inflammation: Mechanism and consequences. Front. Biol. 2011, 6, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnayake, W.M.K.M.; Suresh, T.S.; Abeysekera, A.M.; Salim, N.; Chandrika, U.G. Acute anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive activities of crude extracts, alkaloid fraction and evolitrine from Acronychia pedunculata leaves. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 238, 111827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N.; Savill, J. Resolution of inflammation: The beginning programs the end. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Tsao, R.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, L.; Sun, Y.; Xiong, H. Polyphenol content of green pea (Pisum sativum L.) Hull under in vitro digestion and effects of digestive products on anti-inflammatory activity and intestinal barrier in the Caco-2/Raw264.7 cculture model. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 3477–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiel, C.; Yus, E.; Serrano, L. Engineering Signal Transduction Pathways. Cell 2010, 140, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Yao, Y.; Wu, N.; Du, H.; Xu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Tu, Y. VF-4 and DR-8 derived from salted egg white inhibit inflammatory activity via NF-κB/PI3K-Akt/MAPK signal transduction pathways in HT-29 cells induced by TNF-α. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 66, e2100682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissmann, F.; Manz, M.G.; Jung, S.; Sieweke, M.H.; Merad, M.; Ley, K. Development of monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Science 2010, 327, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Li, X.; Zhu, J.; Wu, J.; Geng, S.; Zhong, C. Magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate suppresses LPS-induced inflammation and oxidative stress through inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK pathways in RAW264.7 cells. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Zysman, M.; Elgrabli, D.; Murayama, T.; Haruta, M.; Lanone, S.; Ishida, T.; Boczkowski, J. Anti-inflammatory effect of gold nanoparticles supported on metal oxides. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loscalzo, J. The identification of nitric oxide as endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Circ. Res. 2013, 113, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Y.-F.; Li, Y.-C.; Ip, S.-P.; Lin, Z.-X.; Lai, X.-P.; Su, Z.-R. Anti-inflammatory effect of patchouli alcohol isolated from Pogostemonis Herba in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. Exp. Ther. Med. 2011, 2, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Yan, X.; Xia, J.; Zhao, J.; Ma, M.; Yu, P.; Gong, D.; Zeng, Z. Assessment of the effect of ethanol extracts from Cinnamomum camphora seed kernel on intestinal inflammation using simulated gastrointestinal digestion and a Caco-2/RAW264.7 co-culture system. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 9197–9210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; An, Q.; Ye, X.; Zhao, Z.; Cai, L.; Han, Y.; et al. Antibacterial mechanism of the synergistic combination between streptomycin and alcohol extracts from the Chimonanthus salicifolius S. Y. Hu. leaves. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 250, 112467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.-X.; Cao, L.; Xiong, J.; Xia, G.; Hu, J.-F. Constituents from Chimonanthus praecox (wintersweet). Phytochem. Lett. 2011, 4, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xi, J.; Schröder, S.; Wang, W.; Xie, T.; Wang, Z.; Bao, S.; Fei, J. Chimonanthus nitens var. salicifolius aqueous extract protects against 5-fluorouracil induced gastrointestinal mucositis in a mouse model. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 789263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ouyang, K.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Hu, W.; Xiong, L.; Wang, N.; Liu, X.; Wang, W. Constituent analysis of the ethanol extracts of Chimonanthus nitens Oliv. leaves and their inhibitory effect on α-glucosidase activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Chen, H.; Xiong, L.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; An, Q.; Ye, X.; Wang, W. Phytochemical profile of ethanolic extracts of Chimonanthus salicifolius S. Y. Hu. leaves and its antimicrobial and antibiotic-mediating activity. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 125, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, H.; Sun, Q.; Zhu, J.; Cao, F.; Chen, F. Anti-inflammatory properties of extracts from Chimonanthus nitens Oliv. leaf. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181094. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ouyang, K.; Chen, L.; Meng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W. Extraction, chemical composition, and protective effect of essential oil from Chimonanthus nitens Oliv. leaves on dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 9701938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, L.; Lin, S.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Ouyang, K.; Wang, W. Total flavonoids from Chimonanthus nitens Oliv. leaves ameliorate HFD-induced NAFLD by regulating the gut–liver axis in mice. Foods 2022, 11, 2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Lin, S.; Ouyang, K.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W. Screening and inhibition mechanism of xanthine oxidase inhibitors in ethanolic extracts of Chimonanthus salicifolius Hu leaves. Chem. Biodivers. 2023, 20, e202200480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Lu, Q.; Cui, L.; Zong, M.; Guo, Y.; Liu, L.; Pan, D.; Wu, Z. The fatty acid profiles of mixed fermented milk and its anti-inflammation properties in an LPS-induced RAW264.7 cell model. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 2465–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Lin, L.; Zheng, G. A flavonoid-rich Smilax china L. extract prevents obesity by upregulating the adiponectin-receptor/AMPK signalling pathway and modulating the gut microbiota in mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 5862–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Samarakoon, K.W.; Lee, W.W.; Kim, H.-S.; Kang, N.; Ranasinghe, P.; Lee, H.-S.; Jeon, Y.-J. A fucoidan fraction purified from Chnoospora minima; a potential inhibitor of LPS-induced inflammatory responses. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dia, V.P.; Bringe, N.A.; de Mejia, E.G. Peptides in pepsin–pancreatin hydrolysates from commercially available soy products that inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in macrophages. Food Chem. 2014, 152, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Jia, W.; Du, A.; Shi, L. Pseudo-targeted metabolomics analysis of the therapeutic effect of phenolics-rich extract from Se-enriched green tea (Camellia sinensis) on LPS-stimulated murine macrophage (RAW264.7). Food Res. Int. 2022, 159, 111666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagalakshmi, U.; Waern, K.; Snyder, M. RNA-seq: A method for comprehensive transcriptome analysis. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2010, 89, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, S. The natural compound puerarin alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in experimental cell and rat preeclampsia models. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 99, 108001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, M. Hesperetin, a dietary flavonoid, inhibits AGEs-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in RAW264.7 cells. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 81, 104480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Chen, S.; Xie, L.; Yu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Shen, M.; Xie, J. Mechanisms of RAW264.7 macrophages immunomodulation mediated by polysaccharide from mung bean skin based on RNA-seq analysis. Food Res. Int. 2022, 154, 111017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xiao, K.; Wang, S.; Ansari, A.R.; Niu, X.; Yang, W.; Lu, M.; Yang, Z.; ur Rehman, Z.; Zou, W.; et al. Visfatin is a multifaceted molecule that exerts regulation effects on inflammation and apoptosis in RAW264.7 cells and mice immune organs. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1018973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.H.; Jin, G.Y.; Li, G.Z.; Yan, G.H. Cornuside suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory mediators by inhibiting nuclear factor-Kappa B activation in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinz, M.; Scheidereit, C. The IκB kinase complex in NF-κB regulation and beyond. EMBO Rep. 2013, 15, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Signaling to NF-κB. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 2195–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.M.; Lee, E.K.; Gong, S.Y.; Sohng, J.K.; Kang, Y.J.; Jung, H.J. Sparassis crispa exerts anti-inflammatory activity via suppression of TLR-mediated NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophage cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 231, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-R.; Fu, C.-S.; Yang, W.-J.; Wang, X.-L.; Feng, D.; Wang, X.-N.; Ren, D.-M.; Lou, H.-X.; Shen, T. Investigation of constituents from Cinnamomum camphora (L.) J. Presl and evaluation of their anti-inflammatory properties in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 221, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cheang, W.S. Isoflavones daidzin and daidzein inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 macrophages. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Meng, T.; Hao, N.; Tao, H.; Zou, S.; Li, M.; Ming, P.; Ding, H.; Dong, J.; Feng, S.; et al. Immune regulation mechanism of Astragaloside IV on RAW264.7 cells through activating the NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 49, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xiao, X.-H.; Hu, L.-B.; Jie, H.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Ye, W.-C.; Li, M.-M.; Liu, Z. Anhuienoside C ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis through inhibition of MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.-T.; Hu, T.; Jiang, J.-G.; Zhao, J.-W.; Zhu, W. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of polyphenols extracted fromIlex latifoliaThunb. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7134–7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Cao, L.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; He, J. Hostaflavone A from Hosta plantaginea (Lam.) Asch. blocked NF-κB/iNOS/COX-2/MAPKs/Akt signaling pathways in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 282, 114605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santangelo, C.; Varì, R.; Scazzocchio, B.; Benedetto, R.D.; Masella, R. Polyphenols, intracellular signalling and inflammation. Ann. Dell’istituto Super. Sanita 2007, 43, 394–405. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.M.; Wu, C.H.; Yen, G.C. Effects of flavonoids on the expression of the pro-inflammatory response in human monocytes induced by ligation of the receptor for AGEs. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 50, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Chen, J.; Zheng, X.; Song, J.; Yin, L.; Guo, H.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, H.; et al. Kaempferol attenuates doxorubicin-induced renal tubular injury by inhibiting ROS/ASK1-mediated activation of the MAPK signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 157, 114087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, H.; Takeuchi, S.; Kubota, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Kozakai, S.; Ukai, I.; Shichiku, A.; Okubo, M.; Numasaki, M.; Kanemitsu, Y.; et al. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein stimulates CD14-dependent Toll-like receptor 4 internalization and LPS-induced TBK1–IKKϵ–IRF3 axis activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 10186–10201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-D.; Pan, W.-J.; Mehmood, S.; Cheng, X.-D.; Chen, Y. Polysaccharide isolated from Sarcodon aspratus induces RAW264.7 activity via TLR4-mediated NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).