A Novel Method for Analyzing the Kinetics of Convective/IR Bread Drying (CIRD) with Sensor Technology
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
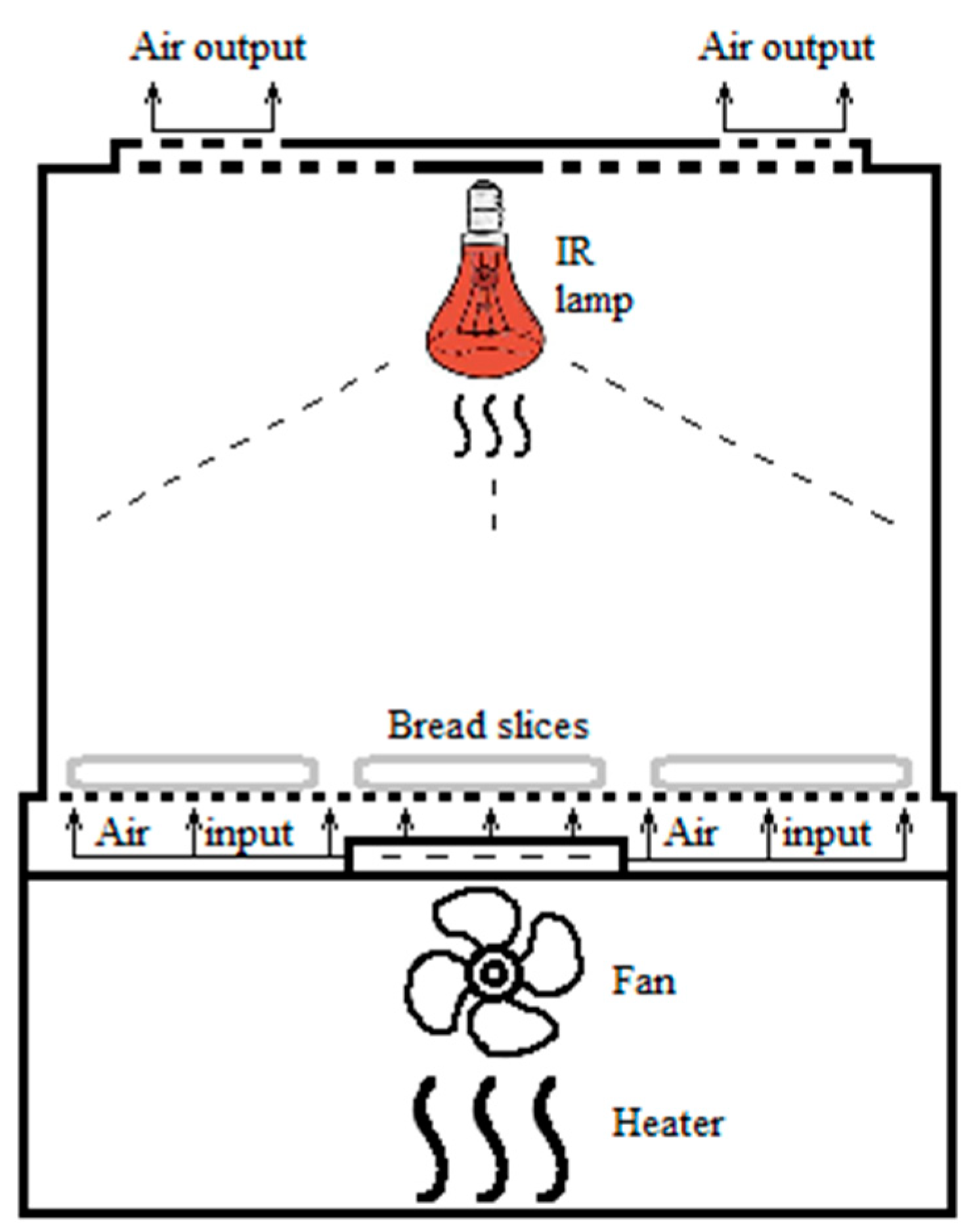
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
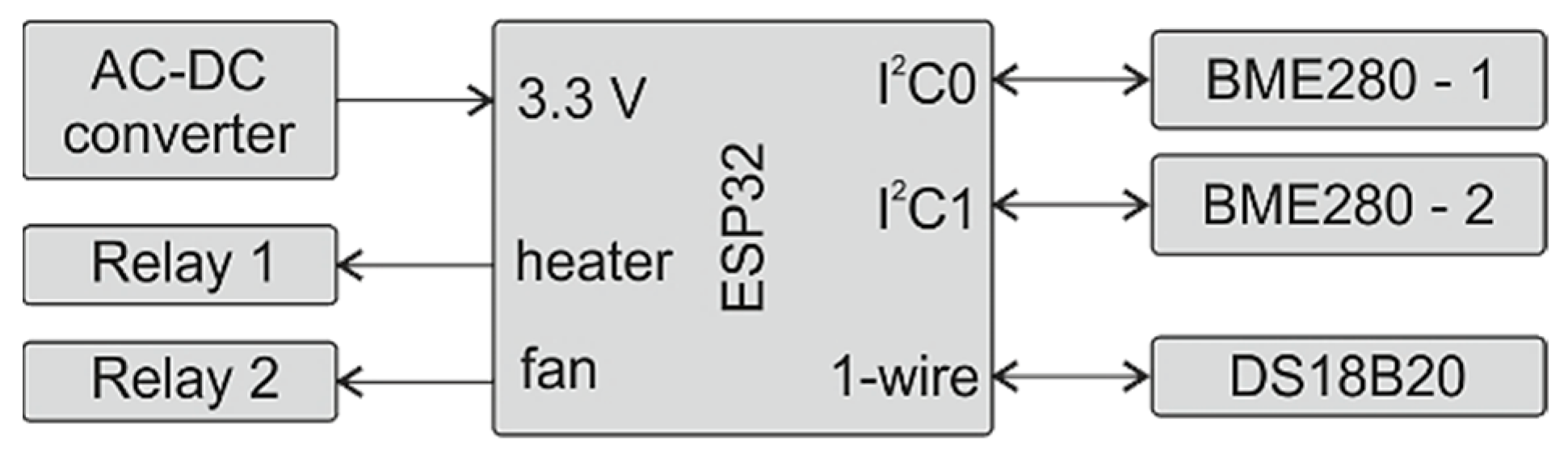
3.1. Sensor Systems and Data Collection
3.2. The Telegram Bot and Kinetics Calculation
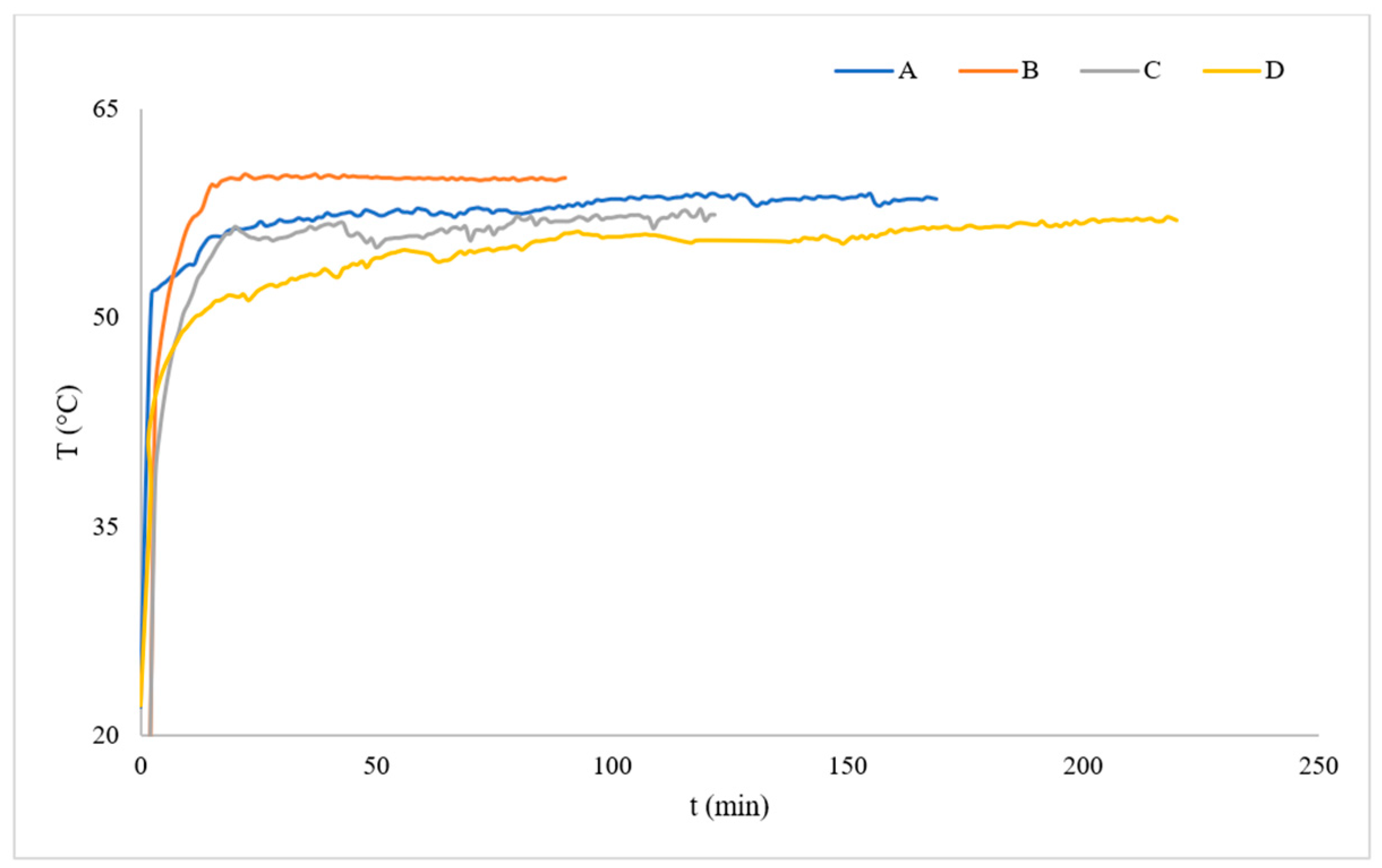
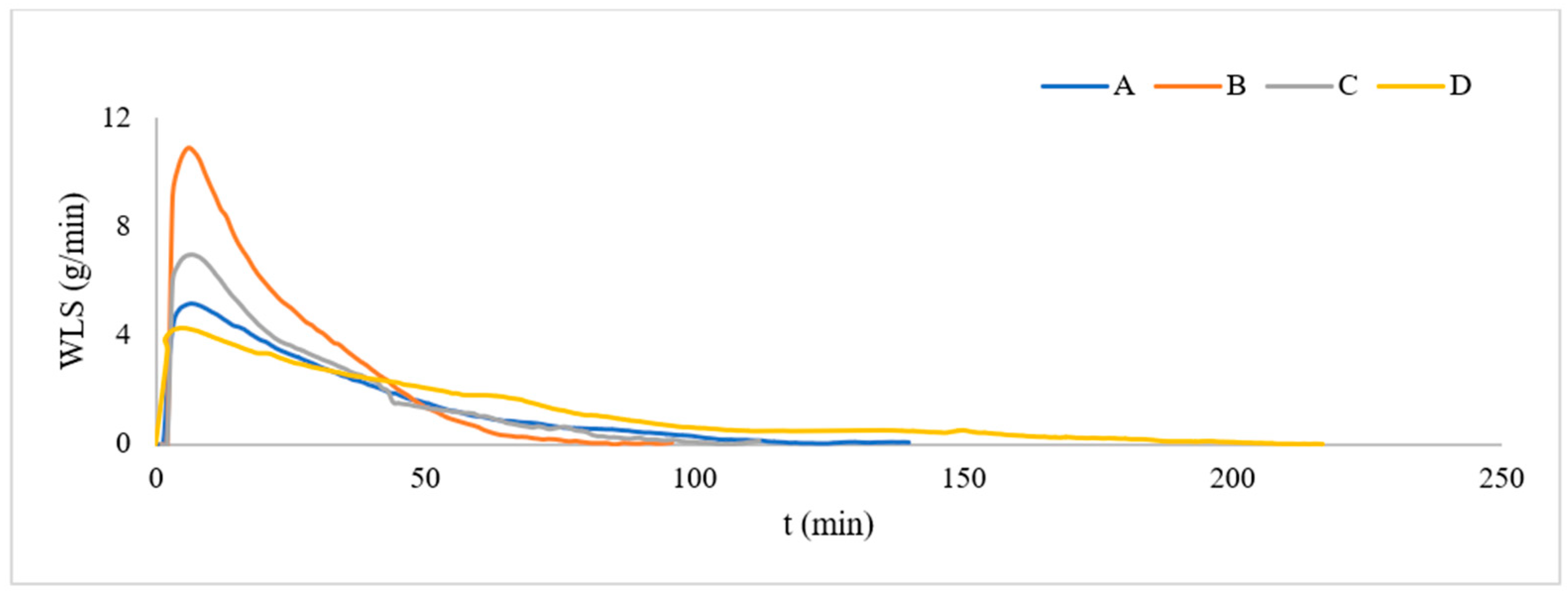
3.3. Statistical Parameters for Evaluating the Kinetics of CIRD Using Sensor Technology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CIRD | Convective and infra-red drying |
| IR | Infra-red drying |
| WL | Weight loss, (g) |
| WLm | Weight loss (measured), (g) |
| WLi | Weight loss (integrated), (g) |
| WLS | Water Loss Speed, (g/min) |
| t | Dehydration time, (min) |
| m | Weight of fresh bread slices, (g) |
| md | Content of dry matter in fresh bread slices, (g) |
| mH2O | Moisture content in fresh bread slices, (g) |
| E (IR) | Energy consumption of Infra-Red lamp, (kWh) |
| Eh, f, a | Energy consumption of heater, fan and arduino, (kWh) |
| EE | Energy efficiency, (kWh/kg removed water) |
References
- Li, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, N.; Raghavan, G.S.V.; Pei, Y.; Song, C.; Zhu, G. Novel Sensing Technologies During the Food Drying Pro-cess. Food Eng. Rev. 2020, 12, 121–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radojčin, M.; Pavkov, I.; Bursać Kovačević, D.; Putnik, P.; Wiktor, A.; Stamenković, Z.; Kešelj, K.; Gere, A. Effect of Selected Drying Methods and Emerging Drying Intensification Technologies on the Quality of Dried Fruit: A Review. Processes 2021, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakare, P.; Prasad, N.; Thombare, N.; Singh, R.; Sharma, S.C. Infrared Drying of Food Materials: Recent Advances. Food Eng. Rev. 2020, 12, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obajemihi, O.I.; Cheng, J.H.; Sun, D.W. Novel sequential and simultaneous infrared-accelerated drying technologies for the food industry: Principles, applications and challenges. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 1465–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adonis, M.; Khan, M.T.E. Combined convective and infrared drying model for food applications. IEEE Africon 2004, 2, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Guiné, R. The drying of foods and its effect on the physical-chemical, sensorial and nutritional properties. Int. J. Food Eng. 2018, 2, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobachevsky, Y.P.; Pavlov, S.A. Infrared Drying of Seeds in a Fluidized Bed. Dir. Open Access J. 2018, 12, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, X.; Xiao, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, T. Effect of Combined Infrared Hot Air Drying on Yam Slices: Drying Kinetics, Energy Consumption, Microstructure, and Nutrient Composition. Foods 2023, 12, 3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heirani, S.; Movagharnejad, K.; Nanvakenari, S. Optimization and modeling of stale bread drying using three different dryers. Innov. Food Technol. 2024, 12, 17–33. [Google Scholar]
- Turgut, S.S.; Karacabey, E.; Küçüköner, E. A Novel System—The Simultaneous Use of Ohmic Heating with Convective Drying: Sensitivity Analysis of Product Quality Against Process Variables. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2022, 15, 440–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panirani, P.N.; Darvishi, H.; Hosainpour, A.; Behroozi-Khazaei, N. Comparative study of different bread baking methods: Combined ohmic–infrared, ohmic–conventional, infrared–conventional, infrared, and conventional heating. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2023, 86, 103349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hii, C.L.; Ong, S.P.; Yap, J.Y.; Putranto, A.; Mangindaan, D. Hybrid drying of food and bioproducts: A review. Dry. Technol. 2021, 39, 1554–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, N.; Ma, H.; Liu, D.; Guo, L.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y. Improvement and Development of Physical Field Drying Technology: Principles, Models, Optimizations and Hybrids. Food Eng. Rev. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyeye, S.A.O.; Ashaolu, T.J.; Babu, A.S. Food drying: A review. Agric. Rev. 2002, 46, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pateiro, M.; Vargas-Ramella, M.; Franco, D.; da Cruz, A.G.; Zengin, G.; Kumar, M.; Dhama, K.; Lorenzo, J.M. The role of emerging technologies in the dehydration of berries: Quality, bioactive compounds, and shelf life. Food Chem. 2022, 16, 100465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingeaua, M.; Prisecaru, T.; Pirna, I.; Sorică, C. Analysis of a convective drying process of plums. INMATEH Agric. Eng. 2015, 46, 2068–2239. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva Ferreira, M.V.; Ahmed, M.W.; Oliveira, M.; Sarang, S.; Ramsay, S.; Liu, X.; Malvandi, A.; Lee, Y.; Kamruzzaman, M. AI-Enabled Optical Sensing for Smart and Precision Food Drying: Techniques, Applications and Future Directions. Food Eng. Rev. 2024, 17, 75–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Huertas, A.; Rebeiro-Hargrave, A.; Fung, P.L.; Varjonen, S.; Hieta, T. Low-Cost Formaldehyde Sensor Evaluation and Calibration in a Controlled Environment. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 11791–11802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, M. Characteristics evaluation of MEMS atmospheric pressure sensors. Meas. Sens. 2024, 101679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolanakis, D.E. MEMS barometers in a wireless sensor network for position location applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Virtual Conference on Applications of Commercial Sensors (VCACS), Piscataway, NJ, USA, 15 June 2016–15 January 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bolanakis, D.E. Evaluating performance of MEMS barometric sensors in differential altimetry systems. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2017, 32, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcesilas, R.; Bastien, J.C.; Sansa, M.; Jouvaud, C.; Rey, P.; Delaveaud, C. Co-Design and Characterization of a Differential Wireless Passive Micro-Electromechanical System Pressure Sensor. Proceedings 2024, 97, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emperhoff, S.; Eberl, M.; Dwertmann, T.; Wöllenstein, J. Humidity Impact on Thermal Conductivity Sensors. Proceedings 2024, 97, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukyanov, A.D.; Studennikova, S.G.; Alekseenko, L.A.; Bidenko, D.E.; Mladenović, V.; Petković, M.; Mardasova, E.A. Microcontroller control system for a convective dehydrator. SymBioTech 2023, 32, 365–374. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/2030agenda#:~:text=We%20are%20committed%20to%20ending,including%20through%20social%20protection%20systems (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Bosch Sensortec. BME280 Datasheet Rev. 1.23; Bosch Sensortec: Reutlingen, Germany, 2022; p. 60. [Google Scholar]
- FastBot. Available online: https://www.arduinolibraries.info/libraries/fast-bot (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- FastBot. Available online: https://github.com/GyverLibs/FastBot/blob/main/library.properties (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Kowalska, M.; Janas, S.; Woźniak, M. Innovative application of the moisture analyzer for determination of dry mass content of processed cheese. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 54, 3071–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, A.L. New equations for computing vapor pressure enhancement factor. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1981, 20, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplya, V.I.; Kaplya, E.V.; Silaev, A.A. Identification of the Transient Response of a Capacitive Relative Humidity Sensor. Meas. Tech. 2020, 62, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamee, P.K.; Mishra, G.C.; Chahar, B.R. Design of minimum water-loss canal sections. J. Hydraul. Res. 2002, 40, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mesery, H.S.; Abomohra, A.E.F.; Kang, C.U.; Cheon, J.K.; Basak, B.; Jeon, B.H. Evaluation of infrared radiation combined with hot air convection for energy-efficient drying of biomass. Energies 2019, 12, 2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfiya, D.S.A.; Prashob, K.; Murali, S.; Alfiya, P.V.; Samuel, M.P.; Pandiselvam, R. Drying kinetics of food materials in infrared radiation drying: A review. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 45, e13810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mesery, H.S.; Mwithiga, G. Performance of a convective, infrared and combined infrared- convective heated conveyor-belt dryer. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 2721–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghinezhad, E.; Szumny, A.; Kaveh, M.; Rasooli Sharabiani, V.; Kumar, A.; Shimizu, N. Parboiled Paddy Drying with Different Dryers: Thermodynamic and Quality Properties, Mathematical Modeling Using ANNs Assessment. Foods 2020, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calín-Sánchez, Á.; Lipan, L.; Cano-Lamadrid, M.; Kharaghani, A.; Masztalerz, K.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A.; Figiel, A. Comparison of Traditional and Novel Drying Techniques and Its Effect on Quality of Fruits, Vegetables and Aromatic Herbs. Foods 2020, 9, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbaspour-Gilandeh, Y.; Kaveh, M.; Fatemi, H.; Khalife, E.; Witrowa-Rajchert, D.; Nowacka, M. Effect of Pretreatments on Convective and Infrared Drying Kinetics, Energy Consumption and Quality of Terebinth. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhanwal, N.; Ezhilarasi, P.N.; Indrani, D.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Influence of electrical and hybrid heating on bread quality during baking. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 4467–4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherono, K.; Mwithiga, G.; Schmidt, S. Infrared drying as a potential alternative to convective drying for biltong production. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2016, 5, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeevarathinam, G.; Pandiselvam, R.; Pandiarajan, T.; Preetha, P.; Krishnakumar, T.; Balakrishnan, M.; Thirupathi, V.; Ganapathy, S.; Amirtham, D. Design, development, and drying kinetics of infrared-assisted hot air dryer for turmeric slices. J. Food Process Eng. 2022, 45, e13876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaboos, S.H.H.; Ardabili, S.M.S.; Kashaninejad, M.; Asadi, G.; Aalami, M. Combined infrared-vacuum drying of pumpkin slices. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktaş, M.; Şevik, S.; Aktekeli, B. Development of heat pump and infrared-convective dryer and performance analysis for stale bread drying. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 113, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Jiménez, A.; García-Villanova, B.; Guerra-Hernández, E. Effect of toasting time on the browning of sliced bread. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2001, 81, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani Pour-Damanab, A.; Jafary, A.; Rafiee, S. Kinetics of the crust thickness development of bread during baking. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 51, 3439–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purlis, E.; Salvadori, V.O. Modelling the browning of bread during baking. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanelli, G.; Cappa, C. 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Formation in Bread as a Function of Heat Treatment Intensity: Correlations with Browning Indices. Foods 2021, 10, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranwal, A.; Verma, P.; Agrawal, K. 9 Statistical Strategies for Analyzing the Production of Polyphenol Oxidase. In Polyphenol Oxidases: Function, Wastewater Remediation, and Biosensors; Pradeep, V., Komal, A., Maulin, P.S., Eds.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 223–256. [Google Scholar]
- Jamanca-Gonzales, N.C.; Ocrospoma-Dueñas, R.W.; Eguilas-Caushi, Y.M.; Padilla-Fabian, R.A.; Silva-Paz, R.J. Food grain quality: Analysis of physical, biometric, and colorimetric properties to promote consumption. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musielak, G.; Mierzwa, D.; Pawłowski, A.; Rajewska, K.; Szadzińska, J. Hybrid and Non-stationary Drying—Process Effectiveness and Products Quality. In Practical Aspects of Chemical Engineering; Lecture Notes on Multidisciplinary Industrial Engineering; Ochowiak, M., Woziwodzki, S., Doligalski, M., Mitkowski, P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 319–337. [Google Scholar]
- Abbaspour-Gilandeh, Y.; Zadhossein, S.; Kaveh, M.; Szymanek, M.; Hassannejad, S.; Wojciechowska, K. Drying Time, Energy and Exergy Efficiency Prediction of Corn (Zea mays L.) at a Convective-Infrared-Rotary Dryer: Approach by an Artificial Neural Network. Energies 2025, 18, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, K.J. Applications of Several Hybrid Drying Methods for a Bioproduct: Effects on Drying Kinetics Product Colour. Int. J. Food Eng. 2007, 2, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Süfer, Ö.; Çalışkan, K.O.Ç.G.; Öztekin, S.; Özkan Karabacak, A.; Su, D.; Wang, D.; Eroğlu, S.; Durgut Malçok, S.; Hilal Uslu, Ü.; Ada, S.; et al. Evaluation of the Effect of Sustainable Drying Techniques and Intensification Technologies on Color Profile of Dehydrated Fruits and Vegetables. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2024, 18, 3148–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Linter, B.R.; Linforth, R.; Foster, T.J. A comprehensive investigation of gluten free bread dough rheology, proving and baking performance and bread qualities by response surface design and principal component analysis. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 5333–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


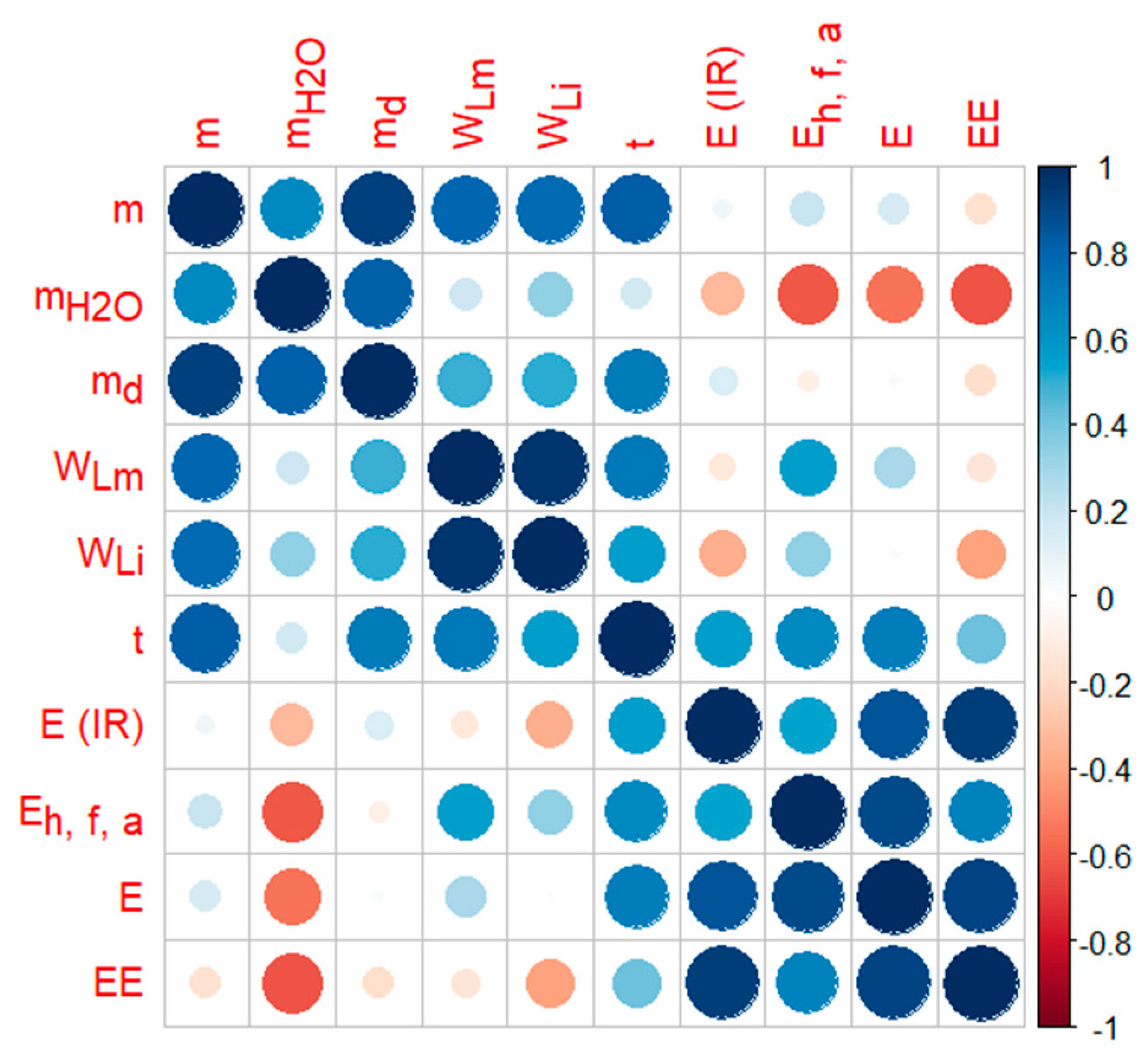
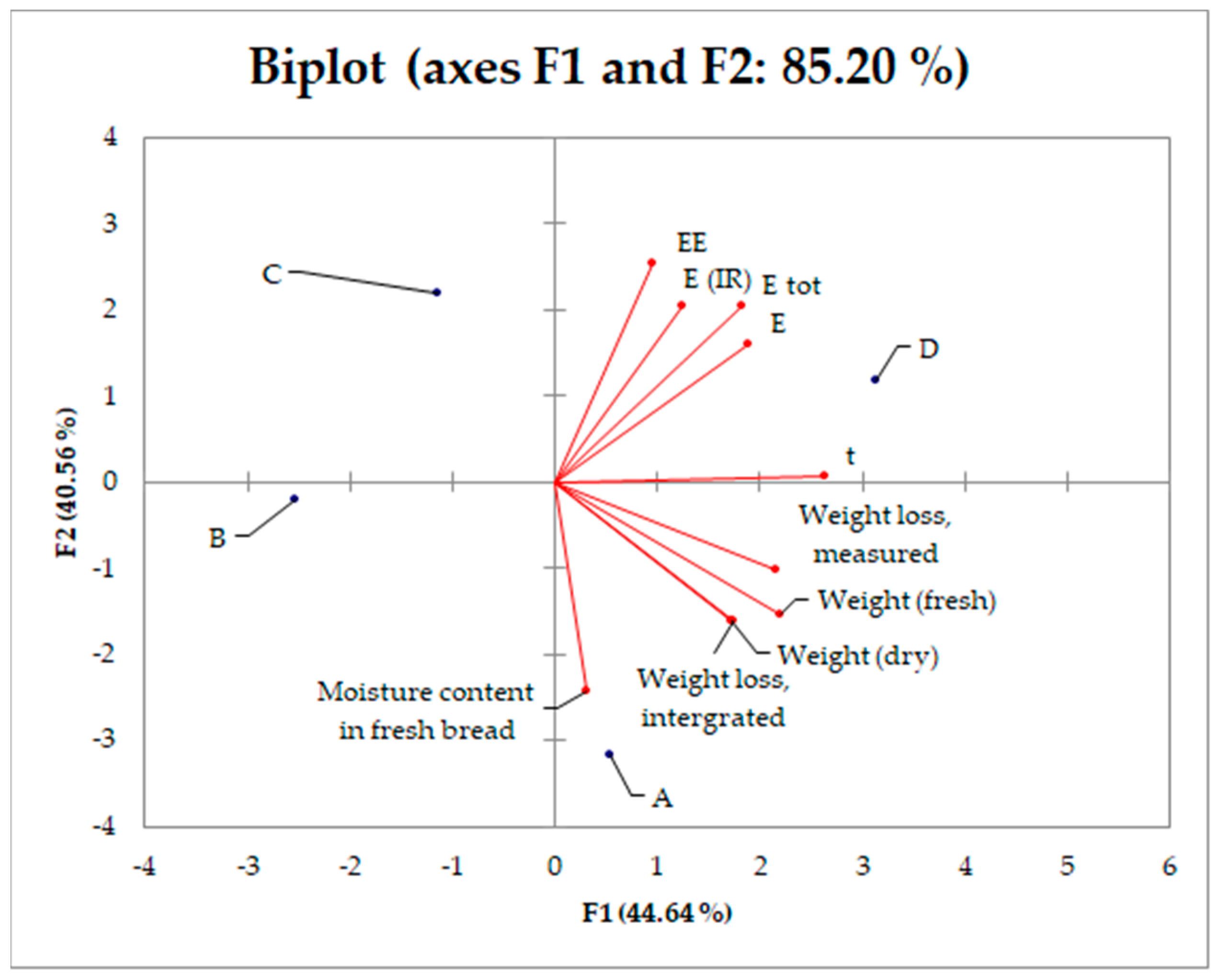
| Sample | m (g) | mH2O (g) | md (g) | WLm (g) | WLi (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 94.0 ± 0.2 d | 33.4± 0.1 d | 64.5 ± 0.2 d | 29.9 ± 0.1 c | 29.4 ± 0.1 c |
| B | 82.0 ± 0.2 a | 29.1± 0.1 a | 54.0 ± 0.2 a | 28.0 ± 0.1 b | 27.8 ± 0.1 b |
| C | 83.4 ± 0.2 b | 29.6 ± 0.1 b | 57.8 ± 0.2 b | 25.6 ± 0.1 a | 25.0 ± 0.1 a |
| D | 92.0 ± 0.2 c | 32.7± 0.1 c | 60.2 ± 0.2 c | 31.8 ± 0.1 d | 29.8 ± 0.1 d |
| Sample | t (min) | E (IR) (kWh) | Eh,f,a (kWh) | E (kWh) | EE (kWh/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 170 ± 6 c | 0.425 ± 0.015 c | 0.220 ± 0.008 a | 0.645 ± 0.023 a | 21.572 ± 0.930 a |
| B | 90 ± 3 a | 0.375 ± 0.013 b | 0.268 ± 0.033 a, b | 0.655 ± 0.026 a | 23.393 ± 0.171 a |
| C | 140 ± 5 b | 0.583 ± 0.021 a | 0.276 ± 0.024 b | 0.838 ± 0.027 b | 32.734 ± 1.627 b |
| D | 220 ± 7 d | 0.550 ± 0.018 a | 0.426 ± 0.001 c | 0.976 ± 0.018 c | 30.692 ± 3.770 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petković, M.; Lukyanov, A.; Đurović, I.; Miletić, N. A Novel Method for Analyzing the Kinetics of Convective/IR Bread Drying (CIRD) with Sensor Technology. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4964. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094964
Petković M, Lukyanov A, Đurović I, Miletić N. A Novel Method for Analyzing the Kinetics of Convective/IR Bread Drying (CIRD) with Sensor Technology. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(9):4964. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094964
Chicago/Turabian StylePetković, Marko, Alexander Lukyanov, Igor Đurović, and Nemanja Miletić. 2025. "A Novel Method for Analyzing the Kinetics of Convective/IR Bread Drying (CIRD) with Sensor Technology" Applied Sciences 15, no. 9: 4964. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094964
APA StylePetković, M., Lukyanov, A., Đurović, I., & Miletić, N. (2025). A Novel Method for Analyzing the Kinetics of Convective/IR Bread Drying (CIRD) with Sensor Technology. Applied Sciences, 15(9), 4964. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094964








