Abstract
Skeleton-based human activity recognition is a key research topic in the fields of deep learning and computer vision. However, existing approaches are less effective at capturing short-term sub-action information at different granularity levels and long-term motion correlations, which affect recognition accuracy. To overcome these challenges, an innovative multi-grained temporal clip transformer (MTC-Former) is proposed. Firstly, based on the transformer backbone, a multi-grained temporal clip attention (MTCA) module with multi-branch architecture is proposed to capture the characteristics of short-term sub-action features. Secondly, an innovative multi-scale spatial–temporal feature interaction module is proposed to jointly learn sub-action dependencies and facilitate skeletal motion interactions, where long-range motion patterns are embedded to enhance correlation modeling. Experiments were conducted on three datasets, including NTU RGB+D, NTU RGB+D 120, and InHARD, and achieved state-of-the-art Top-1 recognition accuracy, demonstrating the superiority of the proposed MTC-Former.
1. Introduction
Human activity recognition (HAR) and behavior analysis play key roles in empowering embodied intelligent systems with the capability to comprehend and adapt to human living and working environments. They therefore have wide applications, such as video surveillance [1], human–computer interaction [2,3], and medical healthcare [4]. Human activity can be represented through various data modalities [5], such as RGB videos, Depth maps, skeleton joints, infrared images, etc. RGB videos [6] provide rich appearance information such as color and texture, while Depth maps offer geometric cues like distance and shape. Most modern frameworks jointly utilize RGB and Depth maps to improve recognition performance through the early or late fusion of the complementary strengths of RGB and Depth modalities, depending on the application. Different from RGB and Depth modalities, 3D skeletons offer precise positional and dynamic details about human skeleton joints, without being influenced by changes in background, lighting, or viewing angle. Additionally, skeleton data are easily obtained via pose estimation algorithms [7] or Microsoft Kinect [8,9]. Thus, skeleton-based HAR has gradually garnered widespread interest from researchers.
Driven by the rapid advancements in deep learning for skeleton-based activity recognition, contemporary techniques are predominantly categorized into Graph Convolutional Network (GCN)-based [10,11,12,13,14,15] and transformer-based approaches [16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. GCN-based models demonstrate strong capabilities in processing skeleton data and capturing spatiotemporal correlations within skeleton sequences. Liu et al. [11] introduced a multi-scale aggregation strategy to broaden the receptive field and addressed the biased weight issue. They found that when handling rapidly changing sub-actions, the short-term features may lack sufficient granularity. Wu et al. [14] proposed a local–global GCN combined with a dynamic frame weighting module for joint global temporal modeling, relying on a fixed skeleton topology and predefined adjacency relationships, which limited its ability to model long-range periodic actions (e.g., dance sequences). Liu et al. [19] introduced hierarchical temporal partitioning and aggregation to capture long-term dependencies, whereas global temporal relationships were constrained by the fixed-window mechanism of transformers. Despite the remarkable advancements made by the aforementioned methods, these methods solely focus on spatial dependencies among joints within individual frames, while neglecting the complex spatiotemporal correlations across consecutive frames, thereby failing to handle both short-term sub-action features and long-term motion correlations.
To address these problems, Qiu et al. [18] proposed a segment partitioning approach and employed self-attention mechanisms to model short-term sub-action information within the intra-clip. Cui et al. [20] introduced a temporal–local spatial–temporal attention mechanism (TL-STA) designed to model inter-joint correlations across sequential frames. Liu et al. [22] utilized physical topology constraints of the human skeleton to fully explore dependency between joints within a tuple to capture local and global temporal motion information. However, most aforementioned approaches failed to account for the inherent variations in temporal dynamics across different actions, thereby lacking in human motion domain knowledge-embedded feature extraction and interpretability.
In actuality, the domain knowledge of human motion plays a critical role in skeleton-based activity recognition, including the dynamics of human motion, behavioral habit patterns, and spatial–temporal contextual information. As shown in Figure 1, the activities of “clapping” and “long jumping” differ in terms of motion phases, motion patterns, and motion speeds. Consequently, selecting an appropriate clip partition strategy is crucial for extracting short-term sub-action information. To address this, an innovative multi-grained temporal clip transformer (MTC-Former) employing self-attention mechanisms is proposed to model correlations among joints, thereby improving activity recognition accuracy by integrating both fine-grained details and contextual information. Our contributions can be summarized from three perspectives, as follows:
- A multi-grained temporal clip attention (MTCA) module is proposed to capture multi-granularity short-term action clip features. This module consists of several intra-clip self-attention (ICSA) modules and a multi-grained feature fusion (MGFF) module for multi-granularity feature extraction and fusion, respectively.
- Additionally, a multi-scale spatial–temporal feature interaction (MSTI) module is proposed to effectively capture long-term correlations between short action clips and enhance spatial information interaction between human skeleton joints.
- Extensive experiments were conducted on two large-scale datasets and an industrial scenario dataset, demonstrating the effectiveness and strong generalization of our method.
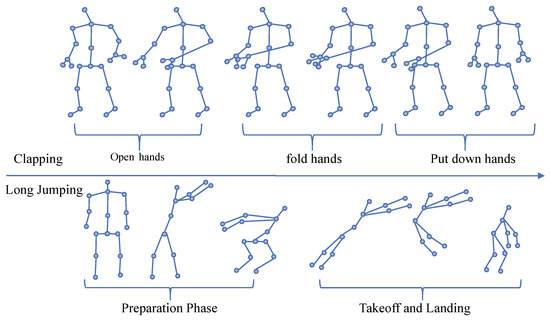
Figure 1.
The action of clapping can be regarded as consisting of three sub-actions, “Open hands”, “fold hands”, and “Put down hands”. The action of jumping can be regarded as consisting of two sub-actions, “Preparation Phase”, “Take off”, and “Landing”.
Section 2 first presents the related works of skeleton-based HAR and its theoretical foundations. Subsequently, Section 3 introduces the proposed MTC-Former, including the research motivations and technical details of the proposed ICSA, MTCA, and MSTI modules. Finally, the experiments, comprehensive ablation, and comparative studies conducted on three standard large-scale datasets and one industrial scenario dataset are presented in Section 4. Conclusion and future works are presented in Section 5.
2. Related Works
2.1. Skeleton-Based Activity Recognition
Pioneering studies utilized curved manifold Lie groups to represent skeleton structures, modeling 3D human joint points through geometric algebra in three-dimensional space [23]. Skeleton optical spectra [24] were introduced to map skeleton joints onto color images, enabling convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to capture discriminative information of action. Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) models [25,26,27] were utilized to capture both local and global temporal dynamics. Concurrently, CNN-based approaches [28,29,30] transformed skeleton data into pseudo-data through specific methodologies. However, both CNN-based and RNN-based methods demonstrate limitations in effectively capturing the correlations among joints.
In contrast, GCN-based methods [10,12,31,32] demonstrate superior performance in capturing spatial–temporal dependencies due to their ability to handle irregular graph structures. Yan et al. [10] first applied graph convolution to skeleton data. Shi et al. [32] introduced a dual-stream framework with an adaptive method for dynamic learning, significantly improving the accuracy of human activity classification. Despite these advancements, GCN-based methods struggle to model long-term motion correlations in skeleton sequences. To address this limitation, Chen et al. [12] expanded the spatial–temporal receptive field by stacking the MT-GC module to capture long-term correlations. Similarly, Duan et al. [31] employed a multi-branch architecture to model both long- and short-range correlations. While GCN-based models demonstrate superior capability in capturing spatial–temporal dynamics compared to RNN and CNN methods, they remain limited in modeling short-term sub-actions.
2.2. Transformer for Skeleton-Based Activity Recognition
Transformer [33] and its variants [18,19,34,35,36,37,38] have demonstrated strong effectiveness in the field of activity recognition. Plizzari et al. [36] integrated self-attention and graph convolution to model spatial–temporal dependencies among joints. Shi et al. [37] utilized attention blocks specifically designed to address the unique characteristics of skeleton data, enabling the modeling of spatial–temporal correlations among joints. Gao et al. [38] explored the dependencies between joints and parts using cross self-attention mechanism within the intra-frame. Lin et al. [35] applied self-attention to model multi-scale spatial–temporal features, and leveraged cross-attention to combine cross-features. However, these methods only focus on modeling dependencies between joints or body parts within a single frame, neglecting the correlations between joints in consecutive frames and failing to model the characteristics of sub-actions.
3. Method
As illustrated in Figure 2, the architecture of the proposed multi-grained temporal clip transformer (MTC-Former) is provided. First, a position embedding layer was adopted to encode the skeleton sequences. Then, the MTCA module was designed to capture short-term sub-action information at various granularities. In addition, the MSTI module was designed, aimed at capturing long-term correlations among action clips and facilitating interactions between joints.
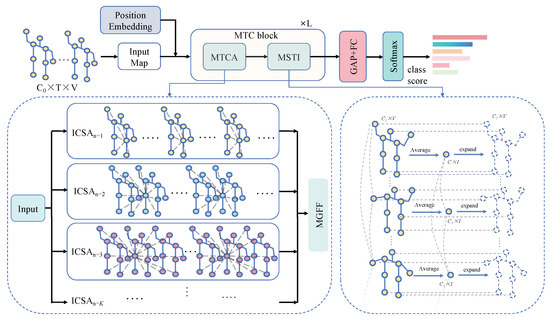
Figure 2.
The architecture of the proposed multi-grained temporal clip transformer (MTC-Former), which mainly consists of L MTC-Block, each consisting of the multi-grained temporal clip attention module (MTCA) and multi-scale spatial–temporal feature interaction (MSTI) module.
3.1. Position Embedding
Compared with traditional RGB data, skeleton data contain the positional information of human skeleton joints, unaffected by background and lighting conditions. The spatial–temporal position information of joints plays a crucial role in activity recognition [39]. Therefore, we encode the skeleton sequence to incorporate spatial–temporal position information. Specifically, the initial skeleton sequence , which contains channels, T frames, and V joints, is transformed into a -dimensional feature tensor through a linear mapping layer implemented by a 2D convolution, as follows:
However, the feature tensor obtained through linear mapping fails to distinguish joint identities due to the absence of positional information, leading to a performance decline. To this, a position encoding module is introduced to encode the spatial location of each joint. We encode the relative positional information of joints, as follows:
where denotes the location of a joint and i corresponds to the index of the encoded feature tensor. Subsequently, the feature vector sequence and the position encoding tensor are combined through element-wise addition, as follows:
3.2. Intra-Clip Self-Attention
By kinematic analysis of human action categories, it is observed that inter-joint correlations across consecutive frames is important for the HAR. For instance, in “long jump” action, arm movements in frame t exhibit strong dynamical coupling with leg motions of frame at various temporal resolutions, demonstrating the necessity of cross-frame joint feature extraction. Therefore, it is very useful to extract the related features of different joints between adjacent frames and the sub-action clip information of short time intervals at various temporal resolutions.
Based on the above analysis, we propose the intra-clip self-attention (ICSA) module to effectively capture short-term motion information, as shown in Figure 3. Specifically, the encoded skeleton feature is first partitioned into clips. Each clip is then flattened by reshaping the tensor, as follows:
where , , and n indicates the total frames within a clip.
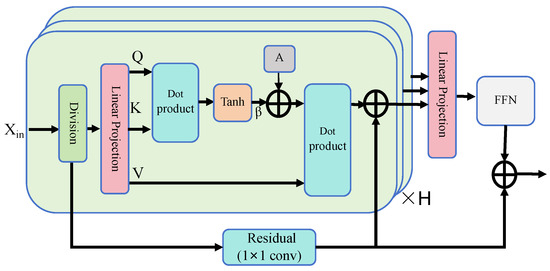
Figure 3.
The structure of the intra-clip self-attention (ICSA) module.
Subsequently, the flattened tensor is projected into through a 2D convolution layer. Then, the query (), key (), and value () are obtained by splitting along the channel dimension using the Split operation, as follows:
To model the intrinsic correlations between joints, we introduce a learnable parameter matrix to encode the topology information of the human body. Additionally, a learnable parameter is employed to dynamically reweigh the correlation matrix. The output is then computed by multiplying the correlation matrix with the corresponding value , as follows:
Finally, we employ H multi-head self-attention mechanisms to capture richer and more complex dependencies among joints.
In the following, a feed-forward network (FFN) and two residual connections are utilized to improve the model’s representation capacity and training stability.
3.3. Multi-Grained Temporal Clip Attention Module
The researchers of [40] revealed that in the visual cortex, the local receptive field (RF) sizes of neurons in the same area are different, which enables the neurons to collect multi-scale spatial information in the same processing stage. Furthermore, the RF sizes of neurons in the visual cortex are not fixed, but modulated by the stimulus. We employed an adaptive approach to generate attention weights for temporal motion features at different granularities, assigning varying importance weights to short-term motion features across scales before ultimately fusing them.
Based on the above analysis, we propose the multi-grained temporal clip attention (MTCA) module, as shown in Figure 4. Specifically, the input feature is segmented into K clips along the channel. These K features are then processed by ICSA modules with varying granularity to capture short-term motion information at different granularities. Finally, the outputs from the ICSA modules are reshaped for further processing, as follows:
where is obtained by splitting along the channel dimension, with , and indicates the output features from the i-th ICSA module.
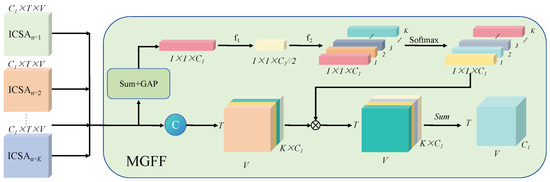
Figure 4.
The architecture of the multi-grained temporal clip attention (MTCA) module, where MTCA consists of K ICSA modules and a multi-grained feature fusion (MGFF) module. MGFF module is designed to dynamically fuse short-term motion features with various granularities from K ICSA modules.
Next, as shown in Figure 4 for MGFF, we aggregate the output features from the ICSA modules with K different granularities through summation, followed by an average pooling operation to generate a global representation .
Subsequently, is applied on for channel reduction, and the result is sequentially passed through and a softmax function to adjust the weights of features at different granularities, obtaining weight vector . Finally, is divided along the channel dimension using a Split operation to obtain weight vectors with different granularities.
where represents the weight vector corresponding to the i-th granularity, and denote 2D convolutional operations. Then, a dot-product operation is applied between and to reweight the output features from different ICSA modules. Finally, to strengthen the training stability, a residual connection is incorporated to obtain the output :
3.4. Multi-Scale Spatial–Temporal Feature Interaction (MSTI)
From a human action kinematic perspective, human motion exhibits multi-scale temporal characteristics, encompassing both rapidly changing local details (e.g., finger movements) and slower-evolving global patterns (e.g., trunk motion). Consequently, multi-scale temporal convolution is designed to extract these hierarchical motion features. Furthermore, human movement requires coordinated interactions among multiple joints. For instance, a throwing motion demands precisely timed coordination of the shoulder, elbow, and wrist joints [41]. Thus, modeling individual joints solely through temporal convolution is insufficient; it is essential to simultaneously account for kinematic interactions across different joints.
To this, we introduce a multi-scale spatial–temporal feature interaction (MSTI) module to capture the correlations between sub-actions at different granularity levels and enhance the skeleton motion information interactions among joints, as illustrated in Figure 5. Specifically, the feature first undergoes an average pooling operation along the joint dimension, producing a global representation . Then, both and are processed by multi-scale temporal convolution (MSTC) to capture multi-scale temporal information. The MSTC consists of six branches, each of which applies a 2D convolution for channel reduction. The first four branches employ temporal convolutions with different dilation rates of 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively. The fifth branch incorporates a 3 × 1 max-pooling layer, while the sixth branch retains the original input. Finally, all the outputs from the six branches are concatenated along the channel dimension.
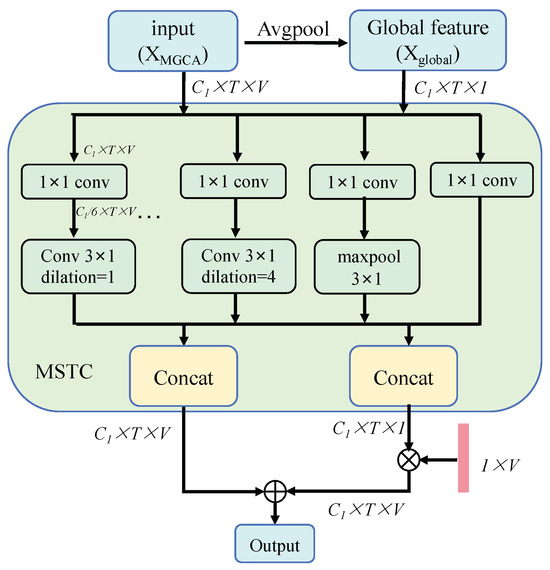
Figure 5.
The architecture of the multi-scale spatial–temporal feature interaction (MSTI) module.
Then, a learnable vector is introduced to facilitate spatial information interaction among joints. These features are then combined to fuse spatial–temporal information among joints, obtaining , as formulated below:
4. Experiments
We begin with a brief introduction of the two large public human action recognition datasets, one industrial human action recognition dataset, and the experimental settings. Subsequently, ablation studies and visualizations that were carried out to examine each component’s functionality are presented. Finally, performance comparisons with mainstream methods and analysis are given.
4.1. Datasets
NTU RGB + D [8] is a standard activity recognition dataset, which is widely adopted for HAR. In this dataset, 56,000 samples were gathered and classified into 60 categories. Each sample comprises four data modalities: RGB video, Depth maps, 3D skeleton data, and infrared video. This study specifically utilized 3D skeleton data for experimentation. Following [8], training and testing sets were selected from the dataset using two distinct strategies, where Cross-View (X-View) was determined by camera IDs and Cross-Subject (X-Sub) separated the dataset based on subject IDs.
By introducing 60 action categories with 57,600 new samples, NTU RGB+D 120 [9] has 114,489 samples and 120 activity classes. Consistent with NTU RGB+D, each sample contains all four data modalities, with skeleton data being selected for experimental purposes. Following the same setup of [9], we employed two distinct evaluation protocols. One is the Cross-Subject (X-Sub), where 50% of subjects are used for training. Alternatively, the Cross-Setup (X-Set) protocol divides the setup IDs into two groups: even-numbered IDs are assigned to the training set, while odd-numbered IDs are allocated to the testing set. These partitioning strategies facilitate the evaluation of activity recognition models across the dataset. Some samples are shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6.
Sample examples of RGB modality and skeleton modality from the NTU RGB+D 120 dataset.
InHARD [42] is an industrial human action recognition dataset designed for production environments, primarily targeting human behavior recognition and analysis tasks in human–robot collaborative settings. The dataset comprises 14 industrial action categories with 5303 action samples. Each sample includes RGB video and skeleton modalities captured from three distinct viewpoints. InHARD partitions the samples into training and test sets based on both performers and viewing angles. Some samples are shown in Figure 7.

Figure 7.
The samples from the industrial InHARD datasets. From left to right are samples of the top view, left-side view, right-side view, and skeleton diagram of the “Cutting” action.
4.2. Experimental Setting
The proposed MTC-Former (MATTOLI SRL, Jesi, Italy) was trained utilizing four RTX 3090 GPUs, with each skeleton sequence uniformly extended to 60 frames via activity replay to ensure consistency. The model was optimized using SGD and trained for 120 epochs with a batch size of 32. The architecture comprises seven multi-grained temporal clip (MTC) blocks, with the output channels sequentially set to 72, 72, 144, 144, 288, 288, and 288.
The Impact of Hyperparameters
As shown in Figure 8, graphical illustrations are incorporated to demonstrate how variations in key hyperparameters affect experimental performance, the ratio of dilation in MSTI, and the number of heads in the multi-head attention mechanism (MHSA).
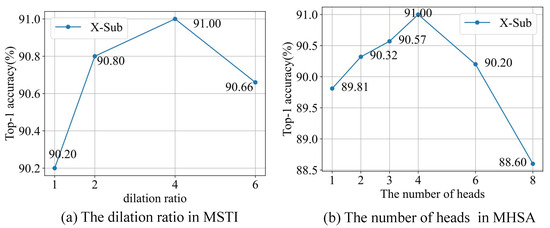
Figure 8.
Top-1 recognition curves with hyperparameters on the X-Sub setting of NTU RGB+D skeleton dataset, including (a) the dilation ratio in MSTI and (b) the number of heads in MHSA.
As shown in Figure 8a, the model achieves 91.0% accuracy (X-Sub) with a dilation rate of 4, effectively capturing both short-term sub-action features and long-term motion relationships. A smaller rate limits modeling to local dynamics, while a larger rate (e.g., 6) reduces accuracy (90.66%) due to diminished per-branch feature capacity from fixed total channels. Figure 8b shows that the model achieves 89.81% accuracy with one attention head, peaking at 91.0% (1.19% improvement) with 4 heads before declining to 88.60% at 8 heads. Fewer heads (e.g., 0–2) limit dependency learning, while more heads (e.g., 6–8) reduce per-head channel dimensions, degrading attention patterns due to constrained total capacity.
4.3. Ablation Studies
On the NTU RGB+D skeleton dataset, our experiments aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of each component in MTC-Former, including the ICSA module with different granularities, the MGFF fusion strategy, and the MSTI module with different numbers of branches.
4.3.1. Ablation Study of ICSA
The intra-clip self-attention (ICSA) module is designed to capture short-term motion features, where n denotes clip length. When n takes different values, the ICSA module can capture short-term motion information at varying granularities. As shown in Figure 9, denotes the number of successive frames within a clip. When , the ICSA module models joint correlations within a single frame, whereas enables the capture of inter-joint dependencies across three consecutive frames.
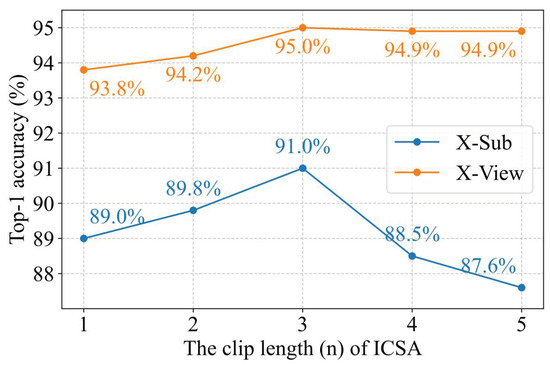
Figure 9.
Top-1 recognition accuracy curves with varying clip lengths (n).
As shown in Figure 9, on the NTU RGB+D dataset, when , the recognition performance of the proposed MTC-Former achieves 89.0% (X-Sub) and 93.8% (X-View). As n increases, the model’s recognition performance reaches its optimal level at , with accuracy rates of 90.3% (X-Sub) and 95.0% (X-View), achieving improvements of 1.3% (90.3% vs. 89.0%) and 1.2% (95.0% vs. 93.8%), respectively, compared to . However, when , the recognition performance of the model gradually declines.
When n = 3, the model achieved the best performance because it captures a sufficient range of temporal dynamics without incorporating irrelevant information. Too small n (e.g., 1 or 2) fails to reflect temporal variations, leading to underutilized motion cues. Too large n (e.g., 4 or more) includes redundant or noisy temporal data, which may distract the attention mechanism.
4.3.2. Ablation Study of MSTI Module
The multi-scale spatial–temporal feature interaction (MSTI) module employs multiple convolutional layers with different receptive fields to capture long-term motion correlations. Additionally, it incorporates a learnable vector to improve spatial information interaction among joints. As shown in Table 1, the ablation study was employed by varying the number of branches and exploring different weight fusion strategies. On the NTU RGB+D dataset, the MSTC-4, i.e., the multi-scale temporal convolution with 4 branches, achieves 90.2% (X-Sub) and 94.2% (X-View). Compared to MSTC-4, MSTC-6, the multi-scale temporal convolution with 6 branches further improves accuracy by 0.3% (X-Sub) and 0.7% (X-View).

Table 1.
Ablation study of MSTI module on the NTU RGB+D 60 dataset.
In addition, compared to MSTC, the MSTI module incorporates a learnable weight vector to enhance spatial information interaction among joints. As shown in Table 1, with fixed weights, MSTI-4 outperforms MSTC-4 by 0.5% (90.7% vs. 90.2%) and 1.2% (95.4% vs. 94.2%). Dynamic weighting further widens the gap to 0.6% (90.8% vs. 90.2%) while retaining the 1.2% advantage (95.4% vs. 94.2%). The MSTI module enhances joint-level interaction within frames. When expanded to six branches with dynamic weight, it achieves optimal performance (91.0% X-Sub, 95.8% X-View), surpassing MSTI-4 with dynamic weight by 0.2% and 0.4%, respectively. This highlights the significance of long-term motion modeling, as MSTI effectively captures long-term motion dependencies and facilitates joint motion information interaction.
4.3.3. Ablation Study of Fusion Strategy
The MGFF module integrates output features from ICSA of varying granularities through three fusion approaches, average fusion, linear fusion, and dynamic fusion. Specifically, denotes the fusion of three ICSA modules, with granularities of 1, 2, and 3, respectively. Average fusion refers to summing the output features of the three ICSA modules and then taking their mean. Linear fusion involves passing the output features of the three ICSA modules through a linear layer for integration. Dynamic fusion, on the other hand, processes the output features of the three ICSA modules through the MGFF module.
As shown in Table 2, MGFF’s dynamic fusion achieves optimal performance (91.0% X-Sub, 95.8% X-View), surpassing linear fusion by 0.4–0.5% and average fusion by 0.2%. This is because linear fusion and average fusion merely perform simple combinations of the output features from different ICSA modules, failing to fully utilize their potential. In contrast, the MGFF module adopts a data-driven approach to generate weight vectors, which effectively leverages the output features of each ICSA module to adaptively produce weight vectors with different granularities. This demonstrates that the proposed MGFF module can effectively fuse output features at different granularity levels.

Table 2.
Ablation study of fusion strategy on NTU RGB+D 60 skeleton dataset with the joint modality.
4.3.4. Ablation Study of Multimodal Data
Due to the inherent characteristics and complementary nature of different modal data, the integration of multiple modalities has been demonstrated to substantially enhance the model’s overall performance and robustness in various applications. Our proposed framework strategically incorporates four distinct yet interrelated data types: joint positions, bone vectors, joint motion trajectories, and bone motion patterns. This multimodal strategy allows the model to extract both static structural information and dynamic temporal evolution from different perspectives. The joint data provide fundamental spatial information, while the bone data convey relative orientation and distance between connected joints. Furthermore, the motion modalities (both joint and bone) effectively model the temporal dynamics and movement patterns, which are crucial for understanding complex activities and gestures.
As shown in Table 3, using only the most common joint modality data, MTC-Former achieves a performance of 91.0% (X-Sub) and 95.8% (X-View) accuracy. However, by integrating data from four modalities, it achieves a performance improvement of 2.2% (93.2% vs. 91.0%) and 1.3% (97.1% vs. 95.8%), respectively. This demonstrates the effectiveness of multimodal fusion.

Table 3.
Ablation study of multimodal data on the NTU RGB+D 60 skeleton dataset.
4.3.5. Per Class Accuracy
As illustrated in Figure 10, on the NTU RGB+D dataset, we compared the per category performance between the proposed MTC-Former and that of the baseline ST-GCN, across 60 activity categories. The horizontal axis indicates the 60 distinct activity categories. Compared to ST-GCN, the majority of activity classes, particularly “clapping ”(10), “carrying” (29), “watching TV ” (31), and “eating while standing” (33) show notably substantial performance gains in our model.
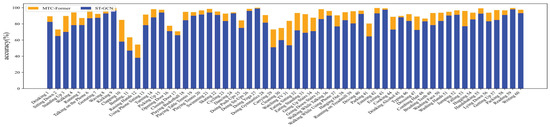
Figure 10.
The comparison of per category performance between MTC-Former and the baseline ST-GCN on the NTU RGB+D dataset. The blue bars represent the recognition performance of ST-GCN, and the orange bars indicate the improvements achieved by MTC-Former.
4.3.6. Visualizations
To evaluate the effectiveness of MTC-Former, we visualize and analyze the ICSA outputs at different granularity levels. Figure 11 presents two representative activities (“put on glasses” and “reading”) for comparative analysis. The horizontal and vertical axes indicate the joint and frame indices, respectively. In the activation map, the darker the color, the more critical the frame is to the short-term motion.
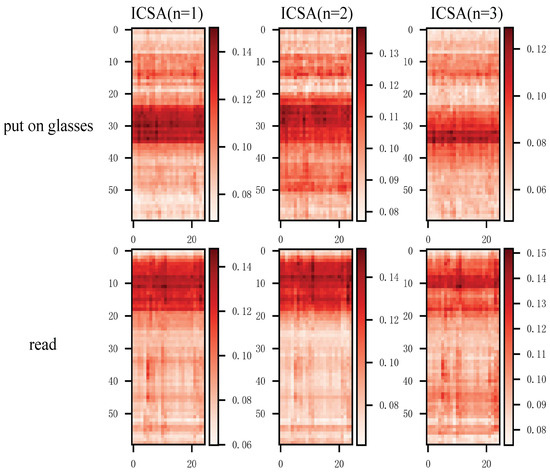
Figure 11.
The attention maps of the output features of ICSA module.
An analysis of the two distinct behaviors reveals that the feature activation for “put on glasses” is primarily concentrated in the mid-temporal region, while for the activity “reading”, the activation is predominantly localized in the early-temporal region. This pattern aligns with the temporal dynamics of the respective actions, indicating that the proposed method effectively focuses on skeleton frames highly relevant to action-specific categorization, while filtering irrelevant information, consequently enhancing human activity recognition (HAR) performance.
Our analysis reveals that different ICSA modules focus on distinct temporal regions, capturing short-term motion features at varying granularity levels. For “put on glasses”, the output feature activations of ICSA (n = 1) and ICSA (n = 2) are mainly concentrated between frames 25 and 35, corresponding to the middle motion phase. In contrast, ICSA (n = 3) focuses on the range of 31 to 35 frames, capturing the motion’s critical phase. This observation demonstrates that the proposed ICSA modules effectively capture short-term motion information at different granularities.
We employed the confusion matrix to evaluate the confusion levels among different categories of human activities. As illustrated in Figure 12a, most activity categories achieve high classification accuracy. Notably, as shown in Figure 12b, action categories 95–100, which require long-term temporal modeling, exhibit high classification accuracy. This indicates that our model can effectively capture long-term motion features. However, as depicted in Figure 12c, the accuracy is relatively lower for certain behaviors within categories 71 to 76. In activity categories involving significant limb movements, such as arm swings and kicks, our method achieves excellent recognition accuracy. However, activities involving subtle movements, such as “making an OK sign” or “make a victory sign”, exhibit lower recognition accuracy. Additionally, activities involving interaction with small tools, such as “cutting nails or paper”, also exhibit lower recognition rates. Specifically, the 73rd activity, “staple book”, exhibits the lowest recognition accuracy and is frequently misclassified as the 76th activity, “cutting paper”, as skeleton data lack object interaction details. Similarly, the 71st activity, “making an OK sign”, and the 72nd activity, “making a victory gesture”, show lower accuracy and are often misclassified as each other. The critical distinction resides in subtle finger posture variations, which are challenging to capture owing to the constrained number of hand joints.
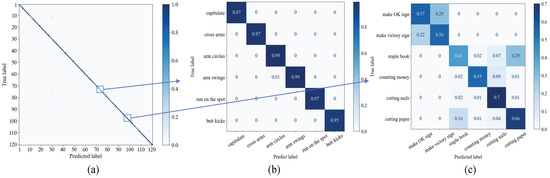
Figure 12.
Confusion matrix of activities on the NTU RGB+D 120 dataset: (a) denotes the confusion matrix across 120 classes; (b) represents the six action categories with higher classification accuracy, corresponding to action categories 95 to 100, which involve body movements; (c) represents the six action categories with lower classification accuracy, corresponding to categories 71 to 76, which involve detailed object-interacted movements.
4.4. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
Our MTC-Former is evaluated against state-of-the-art methods on the NTU RGB+D, NTU RGB+D 120, and InHARD datasets The symbol “-” denotes cases where results were not reported in the original papers. As shown in Table 4, on the NTU RGB+D dataset, our MTC-Former with four-stream fusion achieves 93.1% (X-Sub) and 97.1% (X-View) accuracies, achieving the best performance. On the NTU RGB+D 120 dataset, compared to GCN-based methods [14], our MTC-Former achieves competitive results. Moreover, our MTC-Former outperforms transformer-based methods [19,22], CNN-based methods [43,44], and SIT-MLP [45]. Compared with the lightweight model [14,18,19,44,45,46], our model demonstrates significant performance advantages. In summary, our method achieves high performance while maintaining a low model parameter count.

Table 4.
Comparison results of experiment on the NTU RGB+D and NTU RGB+D 120 datasets.
To further evaluate the performance and generalization ability of the proposed method in different scenarios, we conducted comparisons with other state-of-the-art methods on the industrial human action recognition dataset InHARD. As shown in Table 5, the proposed method achieves a Top-1 recognition accuracy of 88.3% on the InHARD datasets, outperforming transformer-based methods TSM and VideoSwin. Furthermore, our approach utilizes skeleton-based modality for human action recognition, which not only delivers superior recognition performance but also maintains lower parameter count. These results demonstrate that our method exhibits excellent generalization capability in industrial production scenarios.

Table 5.
Comparison results on the InHARD datasets.
5. Conclusions
To model inter-sub-action relationships and enable skeleton joint-level motion interaction, we proposed a multi-grained temporal clip transformer (MTC-Former) for skeleton-based activity recognition. The proposed MTCA can effectively learn multi-grained short-term sub-action motion information, where domain-specific priors on short-range motion patterns are embedded to enhance correlation modeling. The MSTI module can model long-term motion dependencies, correlations of short action clips, and skeletal motion interactions between human skeleton joints. Experimental results on NTU RGB+D, NTU RGB+D 120, and InHARD datasets demonstrate that the MTC-Former achieves state-of-the-art performance, achieving improved recognition performance compared to fixed transformer-based methods. Future work involves exploring the fusion of integrating RGB modality to compensate for the lack of fine-grained color and texture information for multimodal HAR in complex scene-understanding tasks.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.L. and P.Z.; Data curation, P.Z. and S.J.; Formal analysis, P.Z.; Funding acquisition, C.L.; Investigation, P.Z., S.J. and Y.L.; Methodology, P.Z. and C.L.; Project administration, C.L.; Resources, C.L.; Software, P.Z. and Y.L.; Supervision, C.L.; Validation, C.L. and P.Z.; Visualization, P.Z., S.J. and Y.L.; Writing—original draft preparation, P.Z.; Writing—review and editing, C.L., S.J. and Y.L.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was founded in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62176086, in part by the Science and Technology Development of Henan Province under Grants 242102211055 and 242102210032, and by the Soft Science Research Program of Henan Province under Grant 252400410618.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. The NTU RGB+D dataset and NTURGB+D 120 dataset can be downloaded at https://rose1.ntu.edu.sg/dataset/actionRecognition (accessed on 1 January 2020).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sharma, R.; Sungheetha, A. An efficient dimension reduction based fusion of CNN and SVM model for detection of abnormal incident in video surveillance. J. Soft Comput. Paradig. (JSCP) 2021, 3, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zheng, P.; Fan, J.; Wang, L. Toward proactive human—Robot collaborative assembly: A multimodal transfer-learning-enabled action prediction approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 8579–8588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumi, M. Simulation of artificial intelligence robots in dance action recognition and interaction process based on machine vision. Entertain. Comput. 2025, 52, 100773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazhooman, H.; Alamri, M.S.; Pomeroy, R.L.; Cobb, S.C. Foot kinematics in runners with plantar heel pain during running gait. Gait Posture 2023, 104, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Ke, Q.; Rahmani, H.; Bennamoun, M.; Wang, G.; Liu, J. Human action recognition from various data modalities: A review. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 3200–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Ogunbona, P.O.; Wang, P.; Tang, C. RGB-D-based action recognition datasets: A survey. Pattern Recognit. 2016, 60, 86–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.; Sheikh, Y. Realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7291–7299. [Google Scholar]
- Shahroudy, A.; Liu, J.; Ng, T.T.; Wang, G. Ntu rgb+ d: A large scale dataset for 3d human activity analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1010–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Shahroudy, A.; Perez, M.; Wang, G.; Duan, L.Y.; Kot, A.C. Ntu rgb+ d 120: A large-scale benchmark for 3d human activity understanding. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 42, 2684–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Xiong, Y.; Lin, D. Spatial temporal graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ouyang, W. Disentangling and unifying graph convolutions for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, C.; Li, B.; Deng, Y.; Hu, W. Channel-wise topology refinement graph convolution for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 13359–13368. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, S.; Lee, H.; Kim, W.J.; Lee, J.; Woo, S.; Lee, S. Multi-scale Structural Graph Convolutional Network for Skeleton-based Action Recognition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 7244–7258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Ding, Y.; Wan, L.; Li, T.; Nian, F. Local and global self-attention enhanced graph convolutional network for skeleton-based action recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2025, 159, 111106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, M.; Lee, D.; Lee, S. Hierarchically decomposed graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 10444–10453. [Google Scholar]
- Plizzari, C.; Cannici, M.; Matteucci, M. Skeleton-based action recognition via spatial and temporal transformer networks. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2021, 208, 103219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shi, S.; He, J.; Peng, J.; Liu, T.; Weng, R. Iip-transformer: Intra-inter-part transformer for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (BigData), Sorrento, Italy, 15–18 December 2023; pp. 936–945. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, H.; Hou, B.; Ren, B.; Zhang, X. Spatio-temporal segments attention for skeleton-based action recognition. Neurocomputing 2023, 518, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, C.; Li, B.; Hu, W. TranSkeleton: Hierarchical spatial-temporal transformer for skeleton-based action recognition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 4137–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Hayama, T. STSD: Spatial–temporal semantic decomposition transformer for skeleton-based action recognition. Multimed. Syst. 2024, 30, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Xie, X.; Chen, K.; Wang, X.; Shi, G. STDM-transformer: Space-time dual multi-scale transformer network for skeleton-based action recognition. Neurocomputing 2024, 563, 126903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Chen, Y.; Gai, F.; Liu, Y.; Miao, Q.; Wu, S. Local and Global Spatial-Temporal Transformer for skeleton-based action recognition. Neurocomputing 2025, 634, 129820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemulapalli, R.; Arrate, F.; Chellappa, R. Human action recognition by representing 3d skeletons as points in a lie group. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 588–595. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, W. Skeleton optical spectra-based action recognition using convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2016, 28, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Lan, C.; Xing, J.; Zeng, W.; Xue, J.; Zheng, N. View adaptive recurrent neural networks for high performance human action recognition from skeleton data. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2117–2126. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Lan, C.; Xing, J.; Zeng, W.; Li, Y.; Shen, L.; Xie, X. Co-occurrence feature learning for skeleton based action recognition using regularized deep LSTM networks. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 12–17 February 2016; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Xue, J.; Lan, C.; Zeng, W.; Gao, Z.; Zheng, N. Adding attentiveness to the neurons in recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 135–151. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, D.; Kang, Y.; Yao, A.; Chen, Y. Ske2Grid: Skeleton-to-grid representation learning for action recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; pp. 3431–3441. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.; Yang, J.; Du, R.; Hu, W.; Hou, N. Temporal-channel attention and convolution fusion for skeleton-based human action recognition. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 64937–64948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dai, Y.; Cheng, X.; Chen, H.; Lin, Y.; He, M. Skeleton based action recognition using translation-scale invariant image mapping and multi-scale deep CNN. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), Hong Kong, China, 10–14 July 2017; pp. 601–604. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, K.; Lin, D. Dg-stgcn: Dynamic spatial-temporal modeling for skeleton-based action recognition. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.05895. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lu, H. Two-stream adaptive graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 12026–12035. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, H.; Hou, B. Multi-grained clip focus for skeleton-based action recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 148, 110188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Gao, Y.; Li, D. Cross-Attention Multi-Scale Spatial Temporal Transformer for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Plizzari, C.; Cannici, M.; Matteucci, M. Spatial temporal transformer network for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the Pattern Recognition. ICPR International Workshops and Challenges, Virtual Event, 10–15 January 2021; pp. 694–701. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lu, H. Decoupled spatial-temporal attention network for skeleton-based action-gesture recognition. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 30 November–4 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Wang, P.; Lv, P.; Jiang, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, P.; Xu, M.; Li, W. Focal and global spatial-temporal transformer for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Macau, China, 4–8 December 2022; pp. 382–398. [Google Scholar]
- Irani, H.; Metsis, V. Positional Encoding in Transformer-Based Time Series Models: A Survey. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.12370. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, W.; Hu, X.; Yang, J. Selective Kernel Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 510–519. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, B. A review of “The Co-ordination and Regulation of Movements” By N. Bernstein. (Pergamon Press, 1967.) [Pp. xii+ 196.] 505. Ergonomics 1968, 11, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallel, M.; Havard, V.; Baudry, D.; Savatier, X. InHARD—Industrial Human Action Recognition Dataset in the Context of Industrial Collaborative Robotics. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Human-Machine Systems (ICHMS), Rome, Italy, 7–9 September 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, Q.; Bennamoun, M.; An, S.; Sohel, F.; Boussaid, F. Learning clip representations for skeleton-based 3D action recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 2842–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Ye, F.; Zhong, Q.; Xie, D. Topology-aware convolutional neural network for efficient skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual Event, 22 February–1 March 2022; Volume 36, pp. 2866–2874. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Yin, J.; Dang, Y.; Fu, J. SiT-MLP: A simple MLP with point-wise topology feature learning for skeleton-based action recognition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 8122–8134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y. Learning discriminative representations for skeleton based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 10608–10617. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Chen, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q. Actional-structural graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 3595–3603. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Chen, W.; Cheng, J.; Lu, H. Skeleton-based action recognition with shift graph convolutional network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Zhong, J.; Lian, D.; Cao, W. Spatiotemporal progressive inward-outward aggregation network for skeleton-based action recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 150, 110262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Lin, D.; Tang, X.; Van Gool, L. Temporal segment networks: Towards good practices for deep action recognition. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; pp. 20–36. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Gan, C.; Han, S. Tsm: Temporal shift module for efficient video understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November; 2019; pp. 7083–7093. [Google Scholar]
- Carreira, J.; Zisserman, A. Quo vadis, action recognition? a new model and the kinetics dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6299–6308. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Girshick, R.; Gupta, A.; He, K. Non-local neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7794–7803. [Google Scholar]
- Bertasius, G.; Wang, H.; Torresani, L. Is space-time attention all you need for video understanding? In Proceedings of the ICML, Vienna, Austria, 18–24 July 2021; Volume 2, p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Ning, J.; Cao, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Hu, H. Video swin transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 3202–3211. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).