An Axial Compression Transformer for Efficient Human Pose Estimation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Text is human-generated, highly condensed information, while images are natural information containing a lot of redundancy and noise. Compression operations can reduce the useless information in images.
- (2)
- For human pose estimation tasks, compression operations do not significantly lose global semantic information. CNNs initially extract the local features from images, while Transformer structures tend to establish global dependencies.
- (3)
- From a biological perspective, human vision can partially fill in missing parts of an image. Similarly, the performance loss caused by missing some visual information in Transformers is relatively low.
- Novel Compress–Merge Strategy: This paper introduces a novel compress–merge strategy, implemented in the proposed axial compression pose Transformer (ACPose) network for efficient human pose estimation. By employing compression operations to reduce the computational cost, while utilizing feature fusion to maintain Transformer’s global receptive field, this strategy mitigates performance degradation caused by irrelevant information in human pose estimation tasks.
- Local Enhancement Method: This work proposes a local enhancement method that leverages the difference between the compressed and original inputs to amplify the lost local details. This technique effectively enhances the extraction of local features, leading to a significant improvement in prediction accuracy.
- Competitive Performance with Reduced Complexity: Extensive experiments conducted on prominent public datasets demonstrate that our approach achieves a substantial 81.2% reduction in computational cost of the Transformer part, while maintaining competitive accuracy. These results highlight the effectiveness of our proposed method in achieving lightweight, yet high-performing human pose estimation.
2. Related Work
2.1. Efficient Vision Transformer
2.2. Transformer-Based Pose Estimation Methods
3. Methods
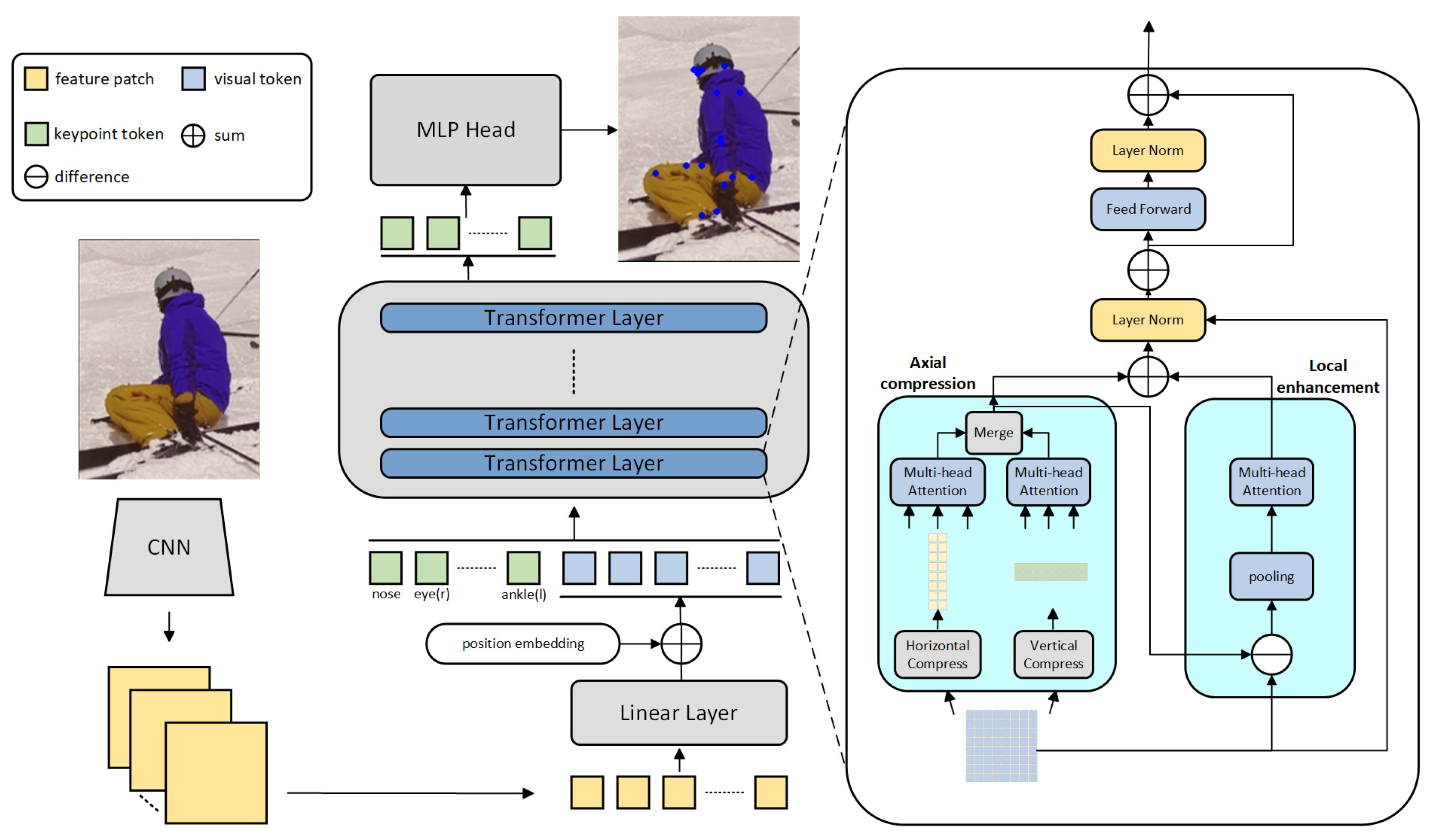
3.1. Tokenization
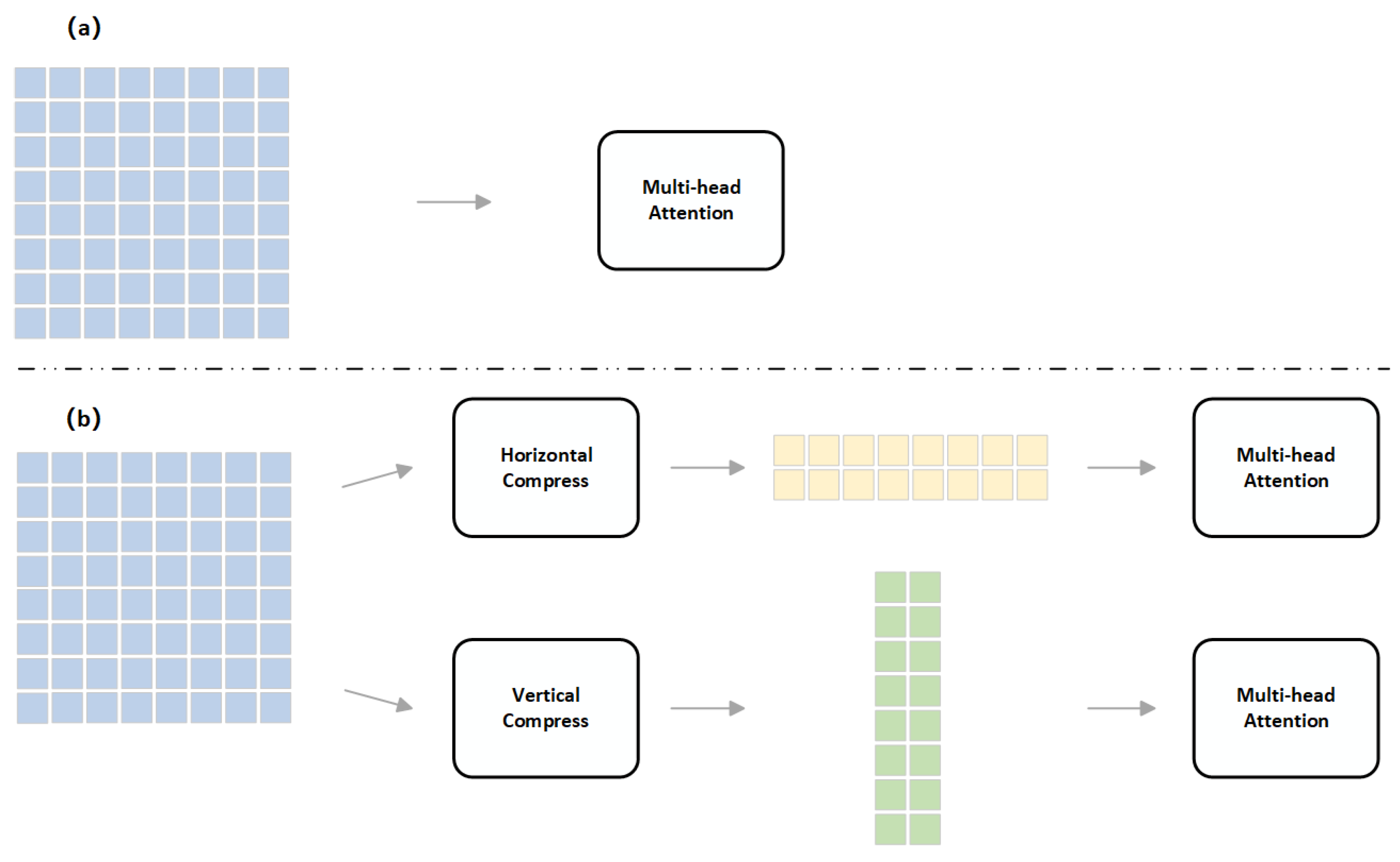
3.2. Axial Compression Module
3.3. Detail Augmentation Module
3.4. Transformer Architecture
3.5. Heatmap
4. Results
4.1. Setup
4.2. Quantitative Results
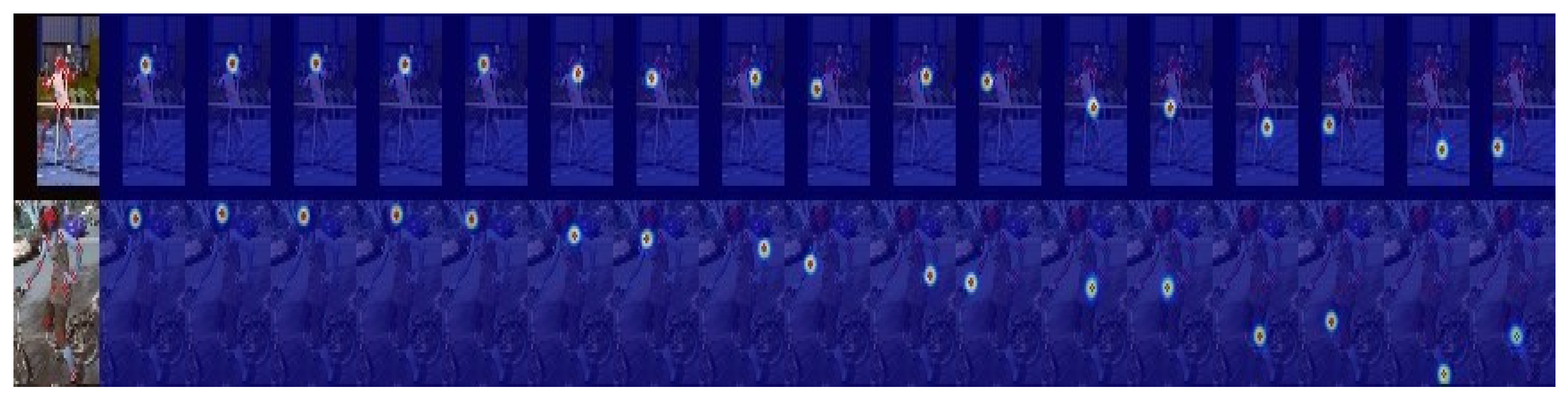
4.3. Qualitative Results
4.4. Ablation Study
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luvizon, D.C.; Picard, D.; Tabia, H. 2D/3D Pose Estimation and Action Recognition Using Multitask Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 5137–5146. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Z.; Wang, C.; Wei, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Hu, H. Human Pose as Compositional Tokens. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 660–671. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Liu, S. BCCLR: A Skeleton-Based Action Recognition with Graph Convolutional Network Combining Behavior Dependence and Context Clues. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2024, 78, 4489–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, Y. High-resolution multi-scale feature fusion network for running posture estimation. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.H.; Xia, N. PCNet: A Human Pose Compensation Network Based on Incremental Learning for Sports Actions Estimation. Complex Intell. Syst. 2025, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luvizon, D.C.; Picard, D.; Tabia, H. Multi-task deep learning for real-time 3D human pose estimation and action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 43, 2752–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, P.; Yadav, G.P.K.; Bandhu, D.; Hemalatha, N.; Mandava, R.K.; Adin, M.Ş.; Saxena, K.K.; Patel, M. Human–machine interaction and implementation on the upper extremities of a humanoid robot. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2024, 6, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, M.H.; Jalal, A. Human-Human Interaction Recognition Using Mask R-CNN and Multi-Class SVM. In Proceedings of the 2024 3rd International Conference on Emerging Trends in Electrical, Control, and Telecommunication Engineering (ETECTE), Lahore, Pakistan, 26–27 November 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández, Ó.G.; Morell, V.; Ramon, J.L.; Jara, C.A. Human pose detection for robotic-assisted and rehabilitation environments. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Song, C.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; Yang, H.; Wang, L. A deep learning-enabled visual-inertial fusion method for human pose estimation in occluded human-robot collaborative assembly scenarios. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2025, 93, 102906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atari, R.; Bamani, E.; Sintov, A. Human Arm Pose Estimation with a Shoulder-worn Force-Myography Device for Human-Robot Interaction. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2025, 10, 2974–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16×16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations ICLR 2021, Vienna, Austria, 4 May 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Du, G. An enhanced real-time human pose estimation method based on modified YOLOv8 framework. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Zhang, T. Self-attention network for human pose estimation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.S.; Xie, S.; Tai, Y.W.; Lu, C. RMPE: Regional Multi-Person Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2334–2343. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, B.; Wu, H.; Wei, Y. Simple Baselines for Human Pose Estimation and Tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 466–481. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, W.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, J. A Robustly Optimized BERT Pre-Training Approach with Post-Training. In Proceedings of the China National Conference on Chinese Computational Linguistics (CNCL), Hohhot, China, 13–15 August 2021; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 471–484. [Google Scholar]
- Raffel, C.; Shazeer, N.; Roberts, A.; Lee, K.; Narang, S.; Matena, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, P.J. Exploring the limits of transfer learning with a unified text-to-text transformer. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 21, 5485–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Dai, M.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, X. HRPVT: High-Resolution Pyramid Vision Transformer for Medium and Small-Scale Human Pose Estimation. Neurocomputing 2025, 619, 129154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, A.; Fan, H.; Xue, X. Vision-Based Body Pose Estimation of Excavator Using a Transformer-Based Deep-Learning Model. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2025, 39, 04024064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Fu, W.; Woźniak, M.; Liu, S. PCDPose: Enhancing the lightweight 2D human pose estimation model with pose-enhancing attention and context broadcasting. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2025, 28, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Quan, Z.; Nie, M.; Yang, W. Transpose: Keypoint Localization via Transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 11802–11812. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Yang, W.; Xia, S.T.; Zhou, E. TokenPose: Learning Keypoint Tokens for Human Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 11313–11322. [Google Scholar]
- An, X.; Zhao, L.; Gong, C.; Wang, N.; Wang, D.; Yang, J. SharpPose: Sparse High-Resolution Representation for Human Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), Palo Alto, CA, USA, 25–27 March 2024; AAAI Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2024; Volume 38, pp. 691–699. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, H.; Qiu, Z.; Yang, K.; Tan, X.; Zheng, X. HP-YOLO: A Lightweight Real-Time Human Pose Estimation Method. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Jeon, W.S.; Rhee, S.Y. LW-FastPose: A Lightweight Network for Human Pose Estimation Based on Improvements to FastPose. In Proceedings of the 2025 International Conference on Electronics, Information, and Communication (ICEIC), Rome, Italy, 16–17 January 2025; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2025; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Noh, W.J.; Moon, K.R.; Lee, B.D. SMS-Net: Bridging the Gap Between High Accuracy and Low Computational Cost in Pose Estimation. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Dong, L.; Piao, S.; Wei, F. Beit: Bert pre-training of image transformers. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.08254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Huang, Z.; Lu, J.; Yu, G.; Zhang, L. SeaFormer: Squeeze-Enhanced Axial Transformer for Mobile Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Kigali, Rwanda, 1–5 February 2023; ICLR: New Orleans, LA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, J.; Tang, Y.M.; Lin, K.Y.; Gao, Y.; Ma, A.J.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, W.S. Dilateformer: Multi-scale dilated transformer for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 25, 8906–8919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Ge, Y.; Shen, C.; Tian, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z. Tfpose: Direct human pose estimation with transformers. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.15320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Tao, D. Vitpose: Simple vision transformer baselines for human pose estimation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 38571–38584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Fu, R.; Huang, L.; Lin, W.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, J. Hrformer: High-resolution vision transformer for dense predict. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 7281–7293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Xiao, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Deep High-Resolution Representation Learning for Human Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5693–5703. [Google Scholar]


| Model | #Params | CNN Backbone | Heads | Layers | GFLOPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACPose-Base | 13.9M | HRNetW32-stage3 | 8 | 12 | 5.1 |
| ACPose-Large/D6 | 20.8M | HRNetW48-stage3 | 8 | 6 | 9.1 |
| ACPose-Large/D24 | 27.5M | HRNetW48-stage3 | 12 | 24 | 9.8 |
| Method | #Params | GFLOPs | AP | AR | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TransPose-R-A4 | 6.0M | 8.9 | 3.38 | 72.6 | 89.1 | 79.9 | 68.8 | 79.8 | 78.0 |
| TransPose-H-S | 8.0M | 10.2 | 4.88 | 74.2 | 89.6 | 80.8 | 70.6 | 81.0 | 79.5 |
| TransPose-H-A6 | 17.5M | 21.8 | 11.4 | 75.8 | 90.1 | 82.1 | 71.9 | 82.8 | 80.8 |
| TokenPose-B * | 13.5M | 5.7 | 1.29 | 75.6 | 89.8 | 81.4 | 71.3 | 81.4 | 80.0 |
| TokenPose-L/D6 * | 20.8M | 10.3 | 1.97 | 77.7 | 90.0 | 81.8 | 71.8 | 82.4 | 80.4 |
| ViTPose-Base | 86.0M | 18.6 | - | 75.8 | 90.7 | 83.2 | 78.4 | 68.7 | 81.1 |
| SHaRPose-Base | 93.9M | 17.1 | - | 75.5 | 90.6 | 82.3 | 82.2 | 72.2 | 80.8 |
| ACPose-B * | 13.9M | 5.1 (−11%) | 0.68 (−47.3%) | 75.7 (+0.1%) | 92.5 | 82.7 | 72.8 | 80.0 | 78.2 |
| ACPose-L/D6 * | 21.0M | 8.8 (−15%) | 0.37 (−81.2%) | 77.4 (−0.4%) | 93.6 | 84.8 | 74.3 | 81.8 | 79.9 |
| ACPose-L/D24 * | 27.5M | 9.9 | 1.52 | 77.4 | 93.6 | 83.8 | 74.4 | 81.9 | 79.9 |
| Method | #Params | Hea | Sho | Elb | Wri | Hip | Kne | Ank | Mean | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SimpleBaseline-R50 | 34.0M | - | 96.4 | 95.3 | 89.0 | 83.2 | 88.4 | 84.0 | 79.6 | 88.5 |
| SimpleBaseline-R101 | 53.0M | - | 96.9 | 95.9 | 95.9 | 84.4 | 88.4 | 84.5 | 80.7 | 89.1 |
| SimpleBaseline-R152 | 53.0M | - | 97.0 | 95.9 | 90.0 | 85.0 | 89.2 | 85.3 | 81.3 | 89.6 |
| HRNetW32 | 28.5M | - | 96.9 | 96.0 | 90.6 | 85.8 | 88.7 | 86.6 | 82.6 | 90.1 |
| TokenPose-L/D6 | 21.4M | 0.64 | 97.1 | 95.9 | 91.0 | 85.8 | 89.5 | 86.1 | 82.7 | 90.2 |
| ACPose-L/D6 (Ours) | 21.66M | 0.39 (−39.0%) | 97.1 | 96.1 | 90.9 | 86.1 | 88.9 | 86.1 | 81.6 | 90.0 (−0.2%) |
| Model | k | #Params | GFLOPs | Mean | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TokenPose-L/D6 | - | 21.49 M | 11.85 | 0.64 | 90.2 |
| ACPose-L/D6 | 4 | 21.49 M | 11.56 | 0.35 (−45.3%) | 89.4 (−0.9%) |
| ACPose-L/D6 | 3 | 21.53 M | 11.57 | 0.36 (−43.8%) | 89.8 (−0.4%) |
| ACPose-L/D6 | 2 | 21.66 M | 11.60 | 0.39 (−39.0%) | 90.0 (−0.2%) |
| Model | h | #Params | GFLOPs | Mean | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TokenPose-L/D6 | - | 21.49 M | 11.85 | 0.64 | 90.2 |
| ACPose-L/D6 | 36 | 21.96 M | 11.78 | 0.57 (−10.9%) | 90.1 (−0.1%) |
| ACPose-L/D6 | 24 | 21.73 M | 11.66 | 0.45 (−29.7%) | 90.0 (−0.2%) |
| ACPose-L/D6 | 12 | 21.66 M | 11.60 | 0.39 (−39.0%) | 90.0 (−0.2%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, W.; Zhang, H.; Song, X. An Axial Compression Transformer for Efficient Human Pose Estimation. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4746. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094746
Tan W, Zhang H, Song X. An Axial Compression Transformer for Efficient Human Pose Estimation. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(9):4746. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094746
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Wen, Haixiang Zhang, and Xinyi Song. 2025. "An Axial Compression Transformer for Efficient Human Pose Estimation" Applied Sciences 15, no. 9: 4746. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094746
APA StyleTan, W., Zhang, H., & Song, X. (2025). An Axial Compression Transformer for Efficient Human Pose Estimation. Applied Sciences, 15(9), 4746. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094746





