Abstract
This study presents a comprehensive kinetic analysis of sulfamethoxazole (SMX) degradation by the photo-Fenton process, highlighting its potential for removing emerging micropollutants in water treatment. The degradation of SMX followed pseudo-first-order kinetics, with increasing Fe(II) concentrations significantly accelerating the oxidation rate. A kinetic model was developed to describe SMX removal, aromaticity loss, and color changes during treatment. Although SMX was rapidly eliminated, intermediate aromatic and chromophoric compounds persisted, requiring extended reaction times for complete mineralization. The kinetic modeling of aromaticity and color revealed distinct degradation pathways and rate constants, showing a strong dependence on iron dosage. The formation of nitrate and sulfate was used to monitor nitrogen and sulfur mineralization, respectively. Optimal nitrate formation was achieved at 22 mol SMX: 1 mol Fe(II), beyond which excessive iron promoted radical scavenging and the formation of stable Fe–aminophenol complexes, inhibiting complete nitrogen oxidation and aromatic degradation. Moreover, excessive Fe(II) led to increased water coloration due to complexation with partially oxidized aromatic byproducts. These findings emphasize the need for optimized catalyst dosing to balance degradation efficiency and minimize secondary effects. The proposed kinetic models offer a predictive tool for improving photo-Fenton-based treatments and integrating them with biological processes to enhance micropollutant bioremediation.
1. Introduction
The emerging contaminants (ECs) are a wide range of chemical compounds, such as pharmaceuticals, personal care products (PCPs), industrial chemicals, and microplastics, that have been detected in diverse environments, especially in aquatic ecosystems [1]. In recent years, the scientific community has focused on these compounds due to a lack of regulation, a scarcity of data on their environmental presence, fate, and toxicological effects, and potential to cause adverse ecological impacts [2]. These contaminants reach the environment mainly through wastewater treatment plant effluents, agricultural runoff, and industrial discharges, and their removal in conventional treatment systems is often ineffective [3,4], resulting in their persistence and possible bioaccumulation in the food chain. The presence of ECs in aquatic ecosystems can induce adverse effects in aquatic organisms, such as hormonal alterations, reproductive toxicity, and the development of antibiotic resistance, compromising biodiversity and ecological stability [5,6]. In addition, human exposure to these contaminants through the consumption of contaminated drinking water and aquatic products poses potential health risks, including endocrine disruption and other toxic effects [7]. Global antibiotic consumption has experienced a sustained increase in recent decades, mainly due to its intensive use in human medicine, livestock farming, and aquaculture [8]. This consumption pattern has led to an increasingly frequent presence of antibiotics in aquatic environments, since many of them are not completely eliminated during conventional wastewater treatment [9].
Sulfamethoxazole (SMX, C10H11N3O3S), a broad-spectrum sulfonamide antibiotic, is among the most frequently detected pharmaceuticals in surface waters and represents a growing environmental concern. In a study conducted in Spain, SMX was found in 100% of surface water samples, with concentrations ranging from 4.1 to 119.3 ng/L [10], highlighting its widespread presence. This concern stems from the high environmental persistence of SMX, as it is resistant to degradation and can remain in surface water, groundwater, and even treated effluents, limiting the efficacy of conventional wastewater treatment processes. Its extensive application in both human and veterinary medicine, particularly in combination with trimethoprim as co-trimoxazole, further contributes to its continuous release into aquatic ecosystems via excretion and improper disposal. Even at low concentrations, SMX can induce ecotoxicological effects, such as oxidative stress, liver damage, and immune dysfunction in aquatic species like Oreochromis niloticus [11], and it can disrupt microbial communities essential for ecosystem functioning. Moreover, SMX poses a significant risk in promoting the development and spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and resistance genes, with aquatic environments serving as reservoirs for such resistance. Although SMX has a low bioaccumulation potential, its interaction with other pharmaceuticals may amplify its ecological impact. These findings underscore the urgent need to enhance wastewater treatment technologies and implement systematic monitoring of antibiotics in aquatic environments to mitigate their adverse effects on both environmental and human health [12,13,14].
To address the problem of emerging pollutants in aquatic environments, the search for more advanced and specific treatment technologies has been promoted [15,16]. Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) have been proposed as effective solutions due to their ability to generate highly reactive species, mainly hydroxyl radicals (HO•), which can degrade a wide range of complex organic compounds until their complete mineralization [17,18,19]. These processes include diverse techniques such as Fenton oxidation, photocatalysis, ozonation, catalytic wet oxidation, and electrooxidation [20]. The classical Fenton reaction involves the reaction of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) with iron salts (Fe(II)) to produce hydroxyl radicals, while the photo-Fenton variant incorporates ultraviolet radiation (UV) or sunlight to regenerate Fe(II) from Fe(III), thus improving the process efficiency [21,22]. Recent studies have shown that the photo-Fenton process is particularly effective in the degradation of emerging pollutants due to its ability to generate a higher amount of hydroxyl radicals and its applicability in ambient conditions [23,24].
Despite the progress made in the application of the photo-Fenton process for the removal of emerging contaminants, significant gaps in knowledge remain regarding the intermediate transformation of contaminants and their actual degree of mineralization [25,26,27]. Most studies have focused on the degradation of the parent compound [28,29], but have not delved into the persistence of intermediate aromatic structures or the kinetic evolution of indicator properties such as water color or loss of aromaticity, which are directly linked to the degree of oxidation and detoxification of the treated system.
Furthermore, although the catalytic role of ferrous ions in the generation of hydroxyl radicals has been recognized [30,31], the impact of catalyst dosage on side effects such as the formation of iron-reaction intermediate complexes, which can stabilize partially oxidized compounds, impairing iron regeneration and reducing overall process efficiency, has not been comprehensively evaluated. In this context, identifying operating conditions that prevent radical recombination and the formation of colored or poorly biodegradable products is key to treatment optimization.
Likewise, there is little research evaluating the mineralization of heteroatomic elements contained in pharmaceuticals, such as nitrogen and sulfur, by monitoring inorganic species like nitrates and sulfates. These species can be used as mineralization markers, allowing stoichiometric balances to be established and complete oxidation pathways to be analyzed.
This study proposes a detailed kinetic approach that considers not only the disappearance of the parent contaminant, but also the loss of aromaticity, water color change, and the evolution of inorganic species ( and ) as indicators of the degree of mineralization. Furthermore, the influence of ferric catalyst concentration on the formation of complexes with aromatic intermediates and its impact on treatment efficiency is analyzed. This comprehensive analysis allows for the identification of optimal conditions to maximize the generation of oxidative radicals, avoid inhibitory effects, and facilitate future integration with biological processes to achieve the complete and sustainable removal of emerging contaminants.
2. Materials and Methods
The experiments were conducted using a photocatalytic reactor equipped with a 150 W medium-pressure mercury lamp (Heraeus, 85.8 V, 148.8 W, 1.79 A, 95% transmittance within the 300–570 nm wavelength range) and a magnetic stirrer (Figure 1). The reactor temperature was maintained at a constant 30 °C using a recirculating cooling bath (Frigiterm-P, Selecta, Barcelona, Spain). Photocatalytic oxidation experiments were performed by introducing 1.0 L of an aqueous sulfamethoxazole solution (50.0 mg/L; SMX, Fragon, Rotterdam, The Netherlands; C10H11N3O3S) into the reactor. Subsequently, varying initial concentrations of ferrous ion [Fe(II)]0 = 0–5.0 mg/L (Panreac, FeSO4·7H2O, 99%) were added to investigate their catalytic effect. The pH of the solution was adjusted to 3.0 by adding a few drops of 0.1 M hydrochloric acid (Panreac, Castellar del Vallès, Spain; HCl, 37% v/v), and monitored using a pH meter (Kent EIL9142, Cambridge, UK). At this stage, baseline measurements were recorded for SMX concentration, color, turbidity, and aromaticity. The UV lamp was then switched on, initiating the reaction, followed by the addition of hydrogen peroxide at an initial concentration of [H2O2]0 = 2.0 mM (Panreac, Castellar del Vallès, Spain; H2O2, 30% w/v). The photocatalytic process was carried out for 120 min, during which time sequential measurements of water quality parameters were taken to monitor the progression of the reaction.
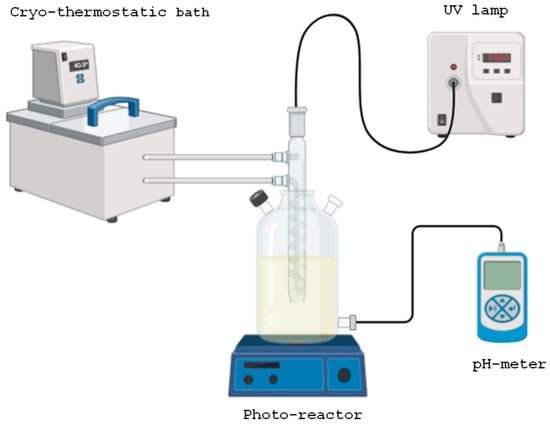
Figure 1.
Scheme of the photocatalytic reactor for water oxidation.
Maintaining the reaction medium at pH 3.0 is essential to ensure high oxidation efficiency in the Fenton-based degradation of SMX. Operating within this acidic range maximizes the generation of hydroxyl radicals due to the favorable redox cycling of Fe(II) to Fe(III), which is critical for initiating the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide [32]. Deviations from this optimal pH can significantly impact the degradation efficiency of SMX. At pH values above 4, iron solubility decreases, leading to the precipitation of ferric hydroxide, which reduces the availability of catalytic Fe(II) in solution. Additionally, hydrogen peroxide tends to decompose non-productively, generating oxygen and water rather than reactive oxygen species. Conversely, at pH levels below 2.5, the stability of hydrogen peroxide may be compromised, and competitive side reactions can occur, both of which hinder the formation of hydroxyl radicals.
Using a UV–Vis spectrophotometer (model V-630, Jasco, Madrid, Spain), aromaticity ([Aromaticity], AU) was measured at a wavelength of 254 nm and color ([Color], AU) at a wavelength of 455 nm. A multiparameter photometer with COD (HI83399 model, Hanna Instruments S.L., Eibar, Spain) was used for the measurement of sulfates, with a sulfate reagent (HI93751-01, Hanna Instruments S.L., Eibar, Spain), and nitrates, with a nitrate reagent (HI93728-0, Hanna Instruments S.L., Eibar, Spain). SMX degradation was measured using a High-Performance Liquid Chromatograph (HPLC, Model 2695, Waters Cromatografía S.A., Cerdanyola del Valles, Spain) coupled to a dual wavelength absorbance detector (Model 2487, Waters Cromatografía S.A., Cerdanyola del Valles, Spain). The determination was carried out with the use of a Zorbax Eclipse PAH column (150 mm, 4.6 mm, particle size 5 μm) and a guard column Zorbax Eclipse PAH (4.6 mm, 12.5 mm), both supplied by Agilent (Santa Clara, CA, USA). The chromatographic separation was carried out at room temperature, with an injection volume of 50 μL and under gradient mode with a mobile phase composed of water and acetonitrile (ACN) at 0.8 mL/min. Initial gradient conditions were set at 20% ACN and increased from 45% ACN for 3 min, then held for 6 min, and finally decreased to 20% ACN at 1 min. Total run time was 10 min. Detection was carried out at 275 nm, and for the identification of the SMX, a standard was used.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Kinetic Model for Sulfamethoxazole Oxidation
Figure 2 shows the SMX degradation by photo-Fenton, varying the iron catalyst dosage. It is observed that the SMX concentration decreases rapidly in the first minutes of the reaction, suggesting first-order kinetics in the degradation. As the initial Fe(II) concentration increases, the degradation rate increases, achieving a faster elimination of SMX. For higher Fe(II) concentrations (4.0 and 5.0 mg/L), the decrease in SMX is very rapid in the first minutes, reaching concentrations close to zero in approximately 5 min. Although it is necessary to consider that the presence of Fe(II) at higher concentrations accelerates the elimination of SMX, in excess it can generate unwanted effects such as radical recombination. After 10 min, the SMX concentration is practically zero under all experimental conditions, indicating that the process is efficient in degrading this contaminant.
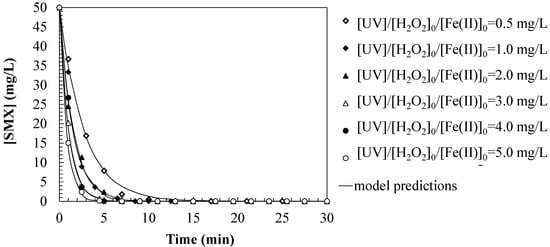
Figure 2.
Predictions of the first-order kinetic model for SMX oxidation by photo-Fenton. Experimental conditions: [SMX]0 = 50.0 mg/L; [H2O2]0 = 2.0 mM; [UV] = 150 W; [pH]0 = 3.0; [T] = 25 °C.
The photo-Fenton process is based on the combination of hydrogen peroxide and ferrous iron in the presence of UV radiation to generate hydroxyl radicals (Equation (1)), which are highly reactive species responsible for the degradation of SMX (Equation (2)). The main chemical reactions involved are outlined below [33]:
Fenton Reaction: In this reaction, ferrous ion acts as a catalyst and reacts with hydrogen peroxide to generate hydroxyl radicals.
Hydroxyl radical attack on SMX: Hydroxyl radicals oxidize SMX, breaking its chemical structure and generating degradation by-products. The combination of ferrous ion, hydrogen peroxide and UV radiation maximizes the production of radicals, promoting oxidation of the contaminant.
Regeneration of ferrous ion by UV radiation: UV radiation promotes the regeneration of ferrous ion from ferric ion, allowing the cycle to continue and enhancing the production of hydroxyl radicals.
Compared to the classical Fenton process, the photo-Fenton process significantly enhances the generation of hydroxyl radicals by continuously regenerating Fe(II) through the photo-reduction of Fe(III) under UV light. This not only sustains the catalytic cycle but also prevents the accumulation of Fe(III), which can otherwise inhibit radical formation. Moreover, UV radiation can also directly photolyze hydrogen peroxide (Equation (4)), adding an additional pathway for radical generation. The synergistic effect of UV light and iron catalysis thus leads to a more efficient and sustained production of hydroxyl radicals, resulting in faster and more complete degradation of persistent pollutants like SMX.
The results indicate that SMX degrades following first-order kinetics to degradation intermediates (Equation (2)) with a first-order kinetic constant kSMX (1/min). By establishing the material balance for SMX degradation (Equation (5)) and integrating the rate equation, the first-order kinetic equation for SMX degradation is obtained (Equation (6)), whose predictions based on experimental results are shown in Figure 2.
Mass balance for the degradation of SMX:
being,
- [SMX]0: initial concentration of SMX contained in the water (=50.0 mg/L)
- [SMX]: concentration of SMX contained in the water (mg/L)
- kSMX: first-order kinetic constant for the degradation of SMX (1/min)
- t: time (min)
First-order kinetic equation for degradation of SMX:
From the adjustments of the proposed kinetic model to the experimental results obtained, the value of the first-order kinetic constant for the oxidation of SMX has been estimated as a function of the concentration of ferrous ion added in the tests, obtaining the relationship shown in Equation (7). The values of the estimated kinetic parameters are shown in Table 1. The results, shown in Table 1, show a progressive increase in the SMX degradation rate, reaching a maximum value of 1.3079 min−1 at 5.0 mg/L Fe(II). This constant greatly exceeds that observed in other advanced systems [15], demonstrating the high reactivity of the photo-Fenton system under acidic conditions (pH 3.0) and UV light. However, the use of Fe(II) requires controlling possible side effects such as the accumulation of residual iron or the stabilization of partially oxidized aromatic intermediates.

Table 1.
Kinetic parameters obtained in the proposed kinetic models. Experimental conditions: [SMX]0 = 50.0 mg/L; [H2O2]0 = 2.0 mM; [UV] = 150 W; [pH]0 = 3.0; [T] = 25 °C.
3.2. Kinetic Model for Water Aromaticity Loss
Figure 3 shows the evolution of water aromaticity expressed in normalized values, which represents the loss of aromaticity during SMX degradation by the photo-Fenton process and allows for the evaluation of the degradation of the aromatic rings contained in the SMX molecular structure. Although SMX disappears rapidly, the loss of aromaticity is more gradual, suggesting that the intermediate by-products still contain aromatic structures before their complete mineralization (carbon dioxide and water) takes place [34]. The aromaticity of water decreases over time, but more slowly than the SMX concentration, suggesting that the aromatic rings persist in the by-products before being completely destroyed. At higher Fe(II) concentrations, the degradation of aromaticity is faster, similar to the behavior observed in Figure 2. Higher Fe(II) concentrations accelerate the loss of aromaticity, favoring the conversion of intermediates into final products consisting of CO2 and water.
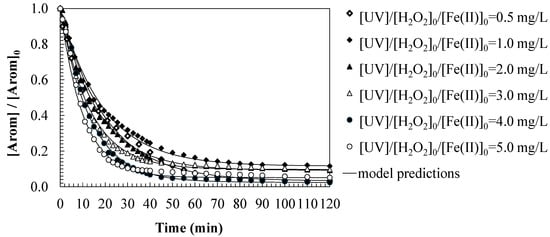
Figure 3.
Predictions of the first-order kinetic model for aromaticity loss during the SMX oxidation by photo-Fenton. Experimental conditions: [SMX]0 = 50.0 mg/L; [H2O2]0 = 2.0 mM; [UV] = 150 W; [pH]0 = 3.0; [T] = 25 °C.
The photo-Fenton process not only oxidizes SMX but also attacks aromatic structures through hydroxyl radicals. SMX undergoes hydroxylation, bond cleavage, and partial opening of the aromatic rings. The aromatic rings gradually open, forming compounds such as dicarboxylic acids. The final products of the process are carbon dioxide and water, indicating the complete degradation of the pollutant. Based on this approach, a first-order kinetic model for the loss of aromaticity in water is proposed (Equation (8)), where the aromatic rings would open according to a kinetic constant kArom (1/min). A rate equation (Equation (9)) has been proposed, including the parameter [Arom]final (AU), because the reagents (hydrogen peroxide) are consumed without degrading all the aromatic load contained in the water, and therefore, an aromatic residue remains in the treated water.
Mass balance for the degradation of aromatic intermediates:
being,
- [Arom]0: aromaticity of initial aqueous solution of SMX (AU).
- [Arom]: aromaticity of water (AU).
- [Arom]final: aromaticity of treated water (AU).
- kArom: first-order kinetic constant for the degradation of aromatic load contained in water solutions (1/min).
Integrating Equation (9), the kinetic equation is obtained for the loss of aromaticity of the aqueous SMX solutions oxidized by treatment (Equation (10)).
From the fits, the value of the first kinetic constant for the loss of aromaticity was estimated as a function of ferrous ion concentration (Equation (11)). Table 1 shows the estimated kinetic parameters.
3.3. Kinetic Model for Water Color Changes
Figure 4 presents the evolution of the color parameter (in absorbance units, AU) as a function of time during the degradation of SMX by the photo-Fenton process. Together with Figure 2 and Figure 3, it provides a comprehensive view of the contaminant removal and the transformation of its intermediate products, since it evaluates the evolution of water color, which is related to the presence of organic intermediates and conjugated structures. Although SMX disappears quickly, the color persists for longer, indicating the formation of colored by-products. At the beginning of the process (0–10 min), a rapid initial color formation is observed in the water, until reaching a maximum value, suggesting the formation of colored intermediates derived from the degradation of SMX, of highly conjugated nature (quinones, oxidized aromatic compounds, etc.) [35,36]. Subsequently (10–40 min), the color gradually decreases over time, indicating the degradation and transformation of these intermediates as the radicals fragment the colored intermediates. Finally (>40 min), almost complete elimination of the color occurs, indicating advanced mineralization of the organic compounds to carboxylic acids, CO2, and H2O.
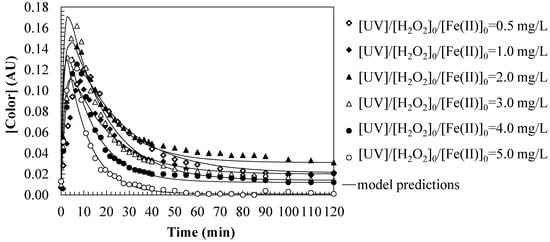
Figure 4.
Predictions of first-order series kinetic model for water color changes during the SMX oxidation by photo-Fenton. Experimental conditions: [SMX]0 = 50.0 mg/L; [H2O2]0 = 2.0 mM; [UV] = 150 W; [pH]0 = 3.0; [T] = 25 °C.
Analyzing the effect of iron catalyst dosage, it is observed that operating with lower Fe(II) concentrations (0.5–2.0 mg/L), color removal is slower, since the generation of hydroxyl radicals is limited. Operating at higher Fe(II) concentrations (4.0–5.0 mg/L), color degradation occurs more rapidly, indicating a greater availability of oxidizing species to attack the organic intermediates.
SMX disappears within a few minutes, but the intermediates still contain aromatic and chromophore structures. The color reduction follows kinetics similar to the loss of aromaticity, suggesting that the compounds responsible for the color are aromatic intermediates. As hydroxyl radicals attack the aromatic rings, they open and lose their ability to absorb visible light. The complete elimination of color indicates that the system not only transforms SMX into intermediates (carboxylic acids) but eventually converts them to CO2 and water. Combining photo-Fenton treatment with biological bioremediation techniques can offer a more comprehensive solution for the removal of emerging contaminants. Initially, chemical processes can degrade contaminants into simpler compounds, which are then fully mineralized by microorganisms in subsequent biological processes.
The kinetics follow first-order behavior, as the color reduction occurs exponentially. Based on this approach, a series reaction model (Equation (12)) has been proposed, in which SMX degrades to colored reaction intermediates according to a first-order kinetic constant kf,color (1/min). Then, once the maximum concentration of colored intermediates has been formed, the color of the water begins to fade according to a first-order kinetic constant kd,color (1/min).
The mass balance proposed for the water color changes is shown in Equation (13). It is worth noting that a parameter α has been incorporated, which is the conversion factor between concentration and absorbance units (AU L/mg).
being,
[Color]0: initial color of aqueous solution of SMX (AU).
[Color]: color of water (AU).
[Color]final: color in the water at the end of the treatment (AU).
kf,color: first-order kinetic constant for the color formation in water (1/min).
kd,color: first-order kinetic constant for the color degradation in water (1/min).
Integrating Equation (13), the kinetic equation for the water color changes of the aqueous SMX solutions oxidized by photo-Fenton treatment is shown in Equation (14).
From the experimental results obtained, the kinetic parameters of the proposed equation have been adjusted, obtaining the values shown in Table 2. The estimates made allow us to verify that as the Fe(II) concentration increases, the rate of color formation and removal also increases, suggesting a greater generation of hydroxyl radicals that attack the compounds responsible for the coloration (Equations (15) and (16)). The dependence of the α parameter (Equation (17)) and the initial and final color of the treated water (Equation (18)) on the catalyst concentration used has also been estimated.

Table 2.
Kinetic parameters obtained in the proposed kinetic model for water color changes. Experimental conditions: [SMX]0 = 50.0 mg/L; [H2O2]0 = 2.0 mM; [UV] = 150 W; [pH]0 = 3.0; [T] = 25 °C.
3.4. Analysis of the Mineralization System by Sulfate and Nitrate Markers
The molecular structure of SMX contains a benzene ring, a sulfonamide group (–SO2NH2), and an isoxazole ring (heterocyclic with oxygen and nitrogen). In the photo-Fenton process, highly oxidizing hydroxyl radicals are generated that non-selectively attack SMX, breaking bonds and decomposing the SMX molecule. The general reaction that represents this process is shown in Equation (19) [26]. Based on this global reaction, the sulfate and nitrate species have been analyzed because they have been considered markers for monitoring the degradation of sulfur and nitrogen atoms, thus allowing the degree of mineralization achieved with the treatment to be established.
The process of sulfate formation during SMX oxidation involves several chemical reactions, mainly related to the degradation of the SMX heterocyclic ring and the oxidation of the sulfonamide group, which releases sulfate ions as the final product upon complete oxidation. Hydroxyl radicals attack the SMX molecule at different positions, including the sulfonamide group, and oxidized intermediate species such as sulfinic and sulfonic acids, and finally, sulfate ions, are produced.
Figure 5a shows the sulfate concentration analyzed in the treated water samples once a steady state was reached (see Table 3). It is worth noting that the stoichiometric concentration of sulfate generated in the water from 50.0 mg/L of SMX corresponds to 19.0 mg/L. This measurement is the one obtained by performing the oxidation without using an iron catalyst (UV/H2O2). However, by enhancing the treatment by adding the catalyst in the form of ferrous sulfate, sulfate measurements higher than the stoichiometric value are obtained. This is because it is necessary to subtract the sulfate concentration added in the form of a catalyst ([]total, mg/L) from the sulfate concentration measured in the water ([]catalyst, mg/L) (Equation (20)). The results obtained confirm that in all the tests performed, SMX is oxidized to the stoichiometric concentration of sulfate. Analyzing the general oxidation mechanism of SMX shown in Figure 6 [37,38], this result confirms that under the tested operating conditions, SMX degrades to aniline and sulfate.
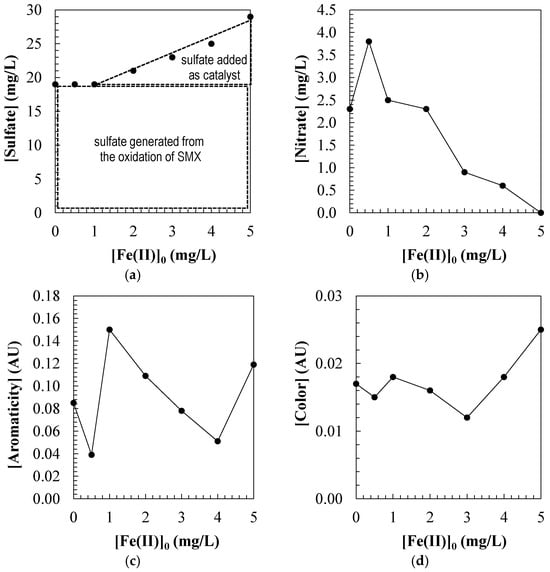
Figure 5.
(a) Sulfate; (b) nitrate; (c) aromaticity; (d) color measured in the SMX aqueous solutions treated by photo-Fenton. Experimental conditions: [SMX]0 = 50.0 mg/L; [H2O2]0 = 2.0 mM; [UV] = 150 W; [pH]0 = 3.0; [T] = 25 °C.

Table 3.
Sulfate and nitrate concentrations measured in the treated water. Experimental conditions: [SMX]0 = 50.0 mg/L; [H2O2]0 = 2.0 mM; [UV] = 150 W; [pH]0 = 3.0; [T] = 25 °C.
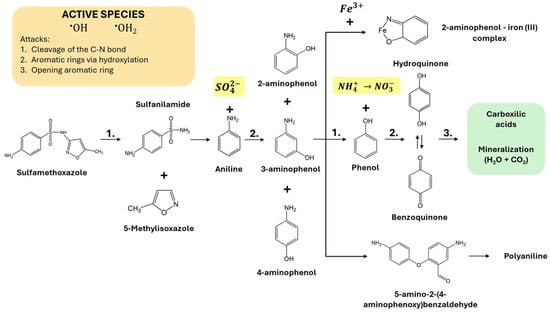
Figure 6.
Proposed pathway for SMX degradation by photo-Fenton.
Figure 5b shows the nitrate concentration analyzed in the treated water samples. During the oxidation of SMX by the photo-Fenton process, a non-linear measurement between the ferrous ion concentration and the formation of nitrate as an oxidation product of the nitrogen present in the contaminant molecule will be observed. The results show that the nitrate concentration in the aqueous samples increases with increasing catalyst concentration until reaching a maximum value at a concentration of [Fe(II)]0 = 0.5 mg/L. From this point, a further increase in the iron concentration resulted in a progressive decrease in the amount of nitrate generated.
This behavior can be attributed to the kinetics of the photo-Fenton process, where, operating at low catalyst concentrations, the generation of hydroxyl radicals is efficient, favoring the oxidation of the organic nitrogen contained in the SMX to its most oxidized form, which is the nitrate ion. However, when the concentration of [Fe(II)]0 > 0.5 mg/L increases, a self-competition phenomenon occurs, in which the excess ferrous ion acts as a hydroxyl radical scavenger, according to the following reaction (Equation (21)). This consumption of radicals reduces their availability to attack the pollutant, limiting the complete conversion of nitrogen to . Additionally, at higher iron concentrations, partial oxidation pathways may prevail, leading to the formation of less oxidized nitrogen products, such as ammonium ion, to the detriment of nitrate.
Therefore, these results show that there is an optimal concentration of ferrous catalyst [Fe(II)]0 = 0.5 mg/L corresponding to 22 mol SMX: 1 mol Fe(II) that maximizes the efficiency of the photo-Fenton process in terms of conversion of SMX nitrogen to oxidized species such as nitrate.
Another relevant factor that may contribute to the decrease in nitrate formation at high catalyst concentrations is the interaction of iron with the phenolic by-products [39] generated during SMX oxidation. Specifically, the cleavage of the isoxazole ring and the oxidation of the sulfonamide group can lead to the formation of aminophenol-like structures, which have an affinity for forming stable complexes with Fe(III) [40]. This complexation limits the availability of iron to participate in the catalytic cycle of the photo-Fenton process, decreasing the generation of hydroxyl radicals and, consequently, inhibiting the complete oxidation of organic nitrogen to nitrate. Furthermore, Fe–aminophenol complexes can stabilize amino groups, preventing their transformation into oxidized species such as . This phenomenon reinforces the need to optimize iron concentration to avoid catalytic deactivation effects associated with the formation of complexes with oxidation intermediates. When there is a higher concentration of Fe(II) in the medium, part of this iron is oxidized to Fe(III), which can form stable complexes with the phenolic by-products (Equation (22)) [41]:
These complexes have two relevant effects on the process:
Iron sequestration: Iron is trapped in stable complexes that do not participate in the photo-Fenton cycle (they are not regenerated to Fe(II)). This reduces the availability of Fe(III) for the further generation of hydroxyl radicals.
Inhibition of the oxidation of nitrogenous intermediates: Fe–aminophenol complexes can mask nitrogenous functional groups (such as amino), which protects nitrogen from being completely oxidized to . This favors the accumulation of partially oxidized products, such as NH4⁺.
The decrease in nitrate concentration observed when using [Fe(II)]0 > 0.5 mg/L can be explained, in part, by the increased formation of Fe–aminophenol complexes, which reduce the fraction of active iron in the photo-Fenton cycle, interfere with the mineralization of organic nitrogen to nitrate, and increase the stability of intermediate byproducts, reducing their reactivity toward hydroxyl radicals.
On the other hand, the formation of complexes between Fe(III) and aromatic byproducts, such as aminophenols generated during SMX oxidation, can influence the persistence of aromaticity in treated water samples (Figure 5c). If a significant proportion of these Fe–aromatic complexes are formed, a greater persistence of residual aromaticity in the treated water and a decrease in the mineralizing efficiency of the process can be observed. This can be explained by the fact that the ferric ion is sequestered outside the catalytic cycle. Aromatic compounds are not easily cleaved if they are protected by the metal complex, and the opening of the aromatic ring is hindered. These complexes exhibit high stability and can inhibit the cleavage of aromatic rings by protecting them from hydroxyl radical attack. As a result, a greater retention of aromatic structures in the aqueous matrix is observed, evidenced by a smaller decrease in UV absorbance at 254 nm. This phenomenon, in addition to compromising the complete mineralization of the contaminant, could contribute to the formation of less biodegradable and potentially ecotoxic byproducts. Therefore, controlling iron concentration and suppressing pathways that favor the formation of stable complexes is crucial to maximizing the efficiency of the photo-Fenton process.
Finally, Figure 5d shows the color of the treated water samples once a steady state was reached. In the present study, a direct relationship was observed between ferrous ion concentration and the color of the treated water after SMX oxidation by the photo-Fenton process. Color in wastewater, especially after oxidative treatments such as photo-Fenton, may be due to the formation of partially oxidized aromatic intermediates (quinones, anilines, aminophenols, catechols, etc.) and the formation of colored complexes between Fe3⁺ and these compounds.
Operating at concentrations of [Fe(II)]0 = 0–3.0 mg/L, the water color progressively decreased, reaching a minimum value at 3.0 mg/L, suggesting a high efficiency in the degradation of aromatic intermediates and a low formation of colored species. Iron does not accumulate in the form of colored complexes, and colorless or minimally colored waters are obtained. However, by increasing the concentration of [Fe(II)]0 = 3.0–5.0 mg/L, a linear increase in the color of the treated waters was evident. Excess iron favors the formation of Fe(III)–aromatic intermediate complexes, such as those with aminophenols and quinones, which are highly colored (brown–yellowish). These complexes have conjugated structures and strongly absorb in the visible, linearly increasing the water color. The accumulation of these complexes, in addition to altering the color, can compromise the quality of the treated water, especially in reuse applications or discharge into receiving bodies.
4. Conclusions
This study presents a comprehensive kinetic analysis of the photo-Fenton degradation of SMX, a representative emerging micropollutant, under varying ferrous ion concentrations. The results confirm the high efficiency of the photo-Fenton process for the rapid elimination of SMX from aqueous systems, following first-order kinetics with respect to the pollutant concentration. The process also induces significant transformations in water quality indicators, including aromaticity and color, which were successfully modeled using first-order and series reaction kinetics.
The degradation of SMX proceeds rapidly, yet the persistence of aromaticity and color in the water indicates the formation of stable intermediate products. These intermediates gradually degrade, with their transformation rates closely linked to the availability of hydroxyl radicals generated in situ. Increasing the concentration of Fe(II) accelerates all degradation pathways, although excessive dosages can promote radical scavenging and the formation of stable iron–organic complexes, which hinder complete mineralization and lead to residual color and aromaticity in the treated water.
Moreover, the mineralization analysis through sulfur and nitrogen markers revealed distinct trends. Sulfate formation aligned well with stoichiometric predictions, confirming the oxidative cleavage of sulfonamide groups. Nitrate formation, however, displayed a non-linear dependence on Fe(II) concentration, with an optimal catalyst dosage of 0.5 mg/L maximizing nitrogen oxidation (22 mol SMX:1 mol Fe(II)). Higher Fe(II) concentrations diminished nitrate production, likely due to radical consumption by excess iron and the formation of stable Fe–aminophenol complexes that prevent full oxidation.
These findings underscore the critical role of iron dosage in balancing the generation of reactive species and minimizing secondary effects such as complex formation, residual color, and incomplete mineralization. The proposed kinetic models provide a valuable framework for predicting treatment performance and optimizing operational conditions. Importantly, integrating photo-Fenton oxidation with subsequent biological treatments could enhance the overall bioremediation efficiency, enabling the complete removal of emerging contaminants and their transformation products.
This work contributes to advancing bioremediation technologies by offering mechanistic insights and kinetic modeling tools that facilitate the design of effective treatment strategies for the abatement of pharmaceutical micropollutants in water. Although a biological treatment phase was not included in this study, the results provide a solid foundation to propose the use of photo-Fenton processes as a pre-treatment in bioremediation systems. The reduction of the initial pollutant load, the fragmentation of recalcitrant structures, and the decrease in toxic compounds are key factors that could enhance the efficiency of conventional biological processes. Consequently, future studies should focus on the experimental validation of this integrated approach through biodegradability tests, toxicity bioassays, and assessments of microbial activity on partially oxidized effluents. This integrated strategy would not only enable higher removal rates of emerging contaminants but also contribute to the development of more sustainable and effective water treatment technologies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.V.; methodology, U.D. and E.B.-G.; software, U.D., E.B.-G. and N.V.; validation, N.V., U.D. and E.B.-G.; formal analysis, U.D., E.B.-G. and N.V.; investigation, E.B.-G., N.V. and U.D.; resources, U.D., N.V. and E.B.-G.; data curation, U.D., E.B.-G. and N.V.; writing—original draft preparation, N.V. and U.D.; writing—review and editing, N.V.; visualization, N.V. and U.D.; supervision, N.V.; project administration, N.V.; funding acquisition, N.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by PIBA_2023_01_0032—Basic and/or Applied Research Project. Financing entity: Basque Government 2023.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the findings of this study can be found within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Department of Chemical and Environmental Engineering and the Department of Chemical Engineering of the University of the Basque Country UPV/EHU for their support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Li, X.; Shen, X.; Jiang, W.; Xi, Y.; Li, S. Comprehensive review of emerging contaminants: Detection technologies, environmental impact, and management strategies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 278, 116420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofijur, M.; Hasan, M.M.; Ahmed, S.F.; Djavanroodi, F.; Fattah, I.M.R.; Silitonga, A.S.; Kalam, M.A.; Zhou, J.L.; Khan, T.M.Y. Advances in identifying and managing emerging contaminants in aquatic ecosystems: Analytical approaches, toxicity assessment, transformation pathways, environmental fate, and remediation strategies. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 341, 122889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picinini-Zambelli, J.; Garcia, A.L.H.; Da Silva, J. Emerging pollutants in the aquatic environments: A review of genotoxic impacts. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2025, 795, 108519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osuoha, J.O.; Anyanwu, B.O.; Ejileugha, C. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products as emerging contaminants: Need for combined treatment strategy. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 9, 100206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shen, N.; Li, Y.; Hu, C.; Yuan, P. Source, transport, and toxicity of emerging contaminants in aquatic environments: A review on recent studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 121420–121437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yao, B.; Zhou, Y. Occurrence, bioaccumulation, fate, and risk assessment of emerging pollutants in aquatic environments: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 923, 171388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Bourguignon, J.P.; Giudice, L.C.; Hauser, R.; Prins, G.S.; Soto, A.M.; Zoeller, R.T.; Gore, A.C. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: An Endocrine Society scientific statement. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 293–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, E.Y.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Martinez, E.M.; Pant, S.; Gandra, S.; Levin, S.A.; Goossens, H.; Laxminarayan, R. Global increase and geographic convergence in antibiotic consumption between 2000 and 2015. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3463–E3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulkowska, A.; Leung, H.W.; So, M.K.; Taniyasu, S.; Yamashita, N.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Richardson, B.J.; Lei, A.P.; Giesy, J.P.; Lam, P.K.S. Removal of antibiotics from wastewater by sewage treatment facilities in Hong Kong and Shenzhen, China. Water Res. 2008, 42, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Roldán, R.; de Alda, M.L.; Gros, M.; Petrovic, M.; Martín-Alonso, J.; Barceló, D. Advanced monitoring of pharmaceuticals and estrogens in the Llobregat River basin (Spain) by liquid chromatography–triple quadrupole-tandem mass spectrometry in combination with ultra performance liquid chromatography–time of flight-mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Dong, F.; Yin, L.; Wang, H.; Zheng, M.; Fu, S.; Zhang, W. Effects of sulfamethoxazole on the growth, oxidative stress and inflammatory response in the liver of juvenile Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2021, 543, 736935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Sánchez-Polo, M.; Ferro-García, M.Á.; Prados-Joya, G.; Ocampo-Pérez, R. Pharmaceuticals as emerging contaminants and their removal from water. A review. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1268–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Vaz-Moreira, I.; Varela Della Giustina, S.; Llorca, M.; Barceló, D.; Schubert, S.; Berendonk, T.U.; Michael-Kordatou, I.; Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Martinez, J.L.; et al. Antibiotic residues in final effluents of European wastewater treatment plants and their impact on the aquatic environment. Environ. Int. 2020, 140, 105733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, L.; Manaia, C.; Merlin, C.; Schwartz, T.; Dagot, C.; Ploy, M.C.; Michael, I.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes spread into the environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Luo, Y.; Yu, Q.; Cheng, J.; Qin, Q.; Zhu, X.; Feng, W. Enhanced Charge Transfer and Photocatalytic Activity of BiOBr/Bi₂WO₆ p–n Heterojunctions. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1304, 137719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenická, B.; Weidlich, T. A Comparison of Different Reagents Applicable for Destroying Halogenated Anionic Textile Dye Mordant Blue 9 in Polluted Aqueous Streams. Catalysts 2023, 13, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalska-Tuomi, K.; Kaijanen, L.; Monteagudo, J.M.; Mänttäri, M. Efficient removal of pharmaceuticals from wastewater: Comparative study of three advanced oxidation processes. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 375, 124276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Jiang, R.; Zhao, Y. Self-Powered advanced oxidation processes for removing contaminants from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 510, 161443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, S.; Yang, R.; Fang, M.; Xu, Z. Advanced oxidation processes for the removal of artificial sweeteners from aqueous environments: A comprehensive review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 197, 107049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübner, U.; Spahr, S.; Lutze, H.; Wieland, A.; Rüting, S.; Gernjak, W.; Wenk, J. Advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment—Guidance for systematic future research. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oller, I.; Malato, S. Photo-Fenton applied to the removal of pharmaceutical and other pollutants of emerging concern. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 29, 100458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado-Piña, D.; Romero, R.; Salazar Carmona, E.; Ramírez-Serrano, A.; Gómez-Oliván, L.M.; Elizalde-Velázquez, G.; Natividad, R. Photo-Fenton Treatment under UV and Vis Light Reduces Pollution and Toxicity in Water from Madín Dam, Mexico. Catalysts 2024, 14, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Całus-Makowska, K.; Dziubińska, J.; Grosser, A.; Grobelak, A. Application of the Fenton and photo-Fenton processes in pharmaceutical removal: New perspectives in environmental protection. Desalin. Water Treat. 2025, 321, 100949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dowd, K.; Pillai, S.C. Photo-Fenton disinfection at near neutral pH: Process, parameter optimization and recent advances. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Fan, Y.; Liu, K.; Kong, D.; Lu, J. Thermo activated persulfate oxidation of antibiotic sulfamethoxazole and structurally related compounds. Water Res. 2015, 87, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, M.; Moussavi, G. Investigation of chemical-less UVC/VUV process for advanced oxidation of sulfamethoxazole in aqueous solutions: Evaluation of operational variables and degradation mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 190, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovó, A.G.; Nogueira, R.F.P.; Agüera, A.; Fernandez-Alba, A.R.; Sirtori, C.; Malato, S. Degradation of sulfamethoxazole in water by solar photo-Fenton. Chemical and toxicological evaluation. Water Res. 2009, 43, 3922–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, F.; Ramavandi, B.; Arfaeinia, H.; Nasrzadeh, F.; Hashemi, S. Sulfamethoxazole antibiotic removal from aqueous solution and hospital wastewater using photo-Fenton process. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 184, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Vinent, N.; Cruz-Alcalde, A.; Santacruz, A.P.; Sans, C. Green approach for micropollutants removal: Study of constructed wetlands as pretreatment of solar photo-Fenton catalyzed by organic fertilizers. Catal. Today 2024, 430, 114540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, V.; Palanivelu, K. The role of ferrous ion in Fenton and photo-Fenton processes for the degradation of phenol. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.R.; Araujo, T.J.R.; da Fonseca, M.T.S.; Santos, N.C.; Gomes, G.E.; Gomes, J.P.; de Araujo, G.T.; Rocha, A.P.T. Application of Photo-Fenton oxidative process followed by adsorption in dairy effluents treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 68, 106365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duesterberg, C.K.; Mylon, S.E.; Waite, T.D. pH Effects on Iron-Catalyzed Oxidation Using Fenton’s Reagent. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8522–8527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pignatello, J.J.; Oliveros, E.; MacKay, A. Advanced oxidation processes for organic contaminant destruction based on the Fenton reaction and related chemistry. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 36, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Dong, C.D.; Chen, C.W.; Lin, Y.L. Mineralization of sulfamethoxazole by ozone-based and Fenton/Fenton-like-based processes. Reac. Kinet. Mech. Cat. 2024, 135, 441–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villota, N.; Duoandicoechea, U.; Lombraña, J.I.; De Luis, A.M. Kinetic modelling of aromaticity and colour changes during the degradation of sulfamethoxazole using photo-Fenton technology. Catalysts 2024, 14, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villota, N.; Jankelevitch, S.; Lomas, J.M. Kinetic modelling of colour and turbidity formation in aqueous solutions of sulphamethoxazole degraded by UV/H2O2. Environ. Technol. 2024, 45, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Hao, G.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, D.; Li, X.; Yang, Z.; Xu, J.; Ruan, Z.; Mu, Y. Biodegradation and metabolic pathway of sulfamethoxazole by Sphingobacterium mizutaii. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, A.; Penadés, A.; Lliberia, J.L.; Gonzalez-Olmos, R. Degradation pathways of aniline in aqueous solutions during electro-oxidation with BDD electrodes and UV/H₂O₂ treatment. Chemosphere 2017, 166, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijangos, F.; Varona, F.; Villota, N. Changes in Solution Color during Phenol Oxidation by Fenton Reagent. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 5538–5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massacesi, M.; Ponticelli, G.; Maxia, V.; Serci, S. 2,5-Diphenyloxazole, 3,5-diphenylisoxazole and 3-amino, 5-methylisoxazole complexes with iron(III) salts. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Spectrosc. 1981, 37, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcellos, L.C.G.; Oliveira, C.P.; Castellano, E.E.; Ellena, J.; Moreira, Í.S. Structure and Properties of Iron–Cyclam Complex of 2-Aminophenol. Polyhedron 2001, 20, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).