Analysis of Heavy Metal Sources in Xutuan Mining Area Based on APCS-MLR and PMF Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
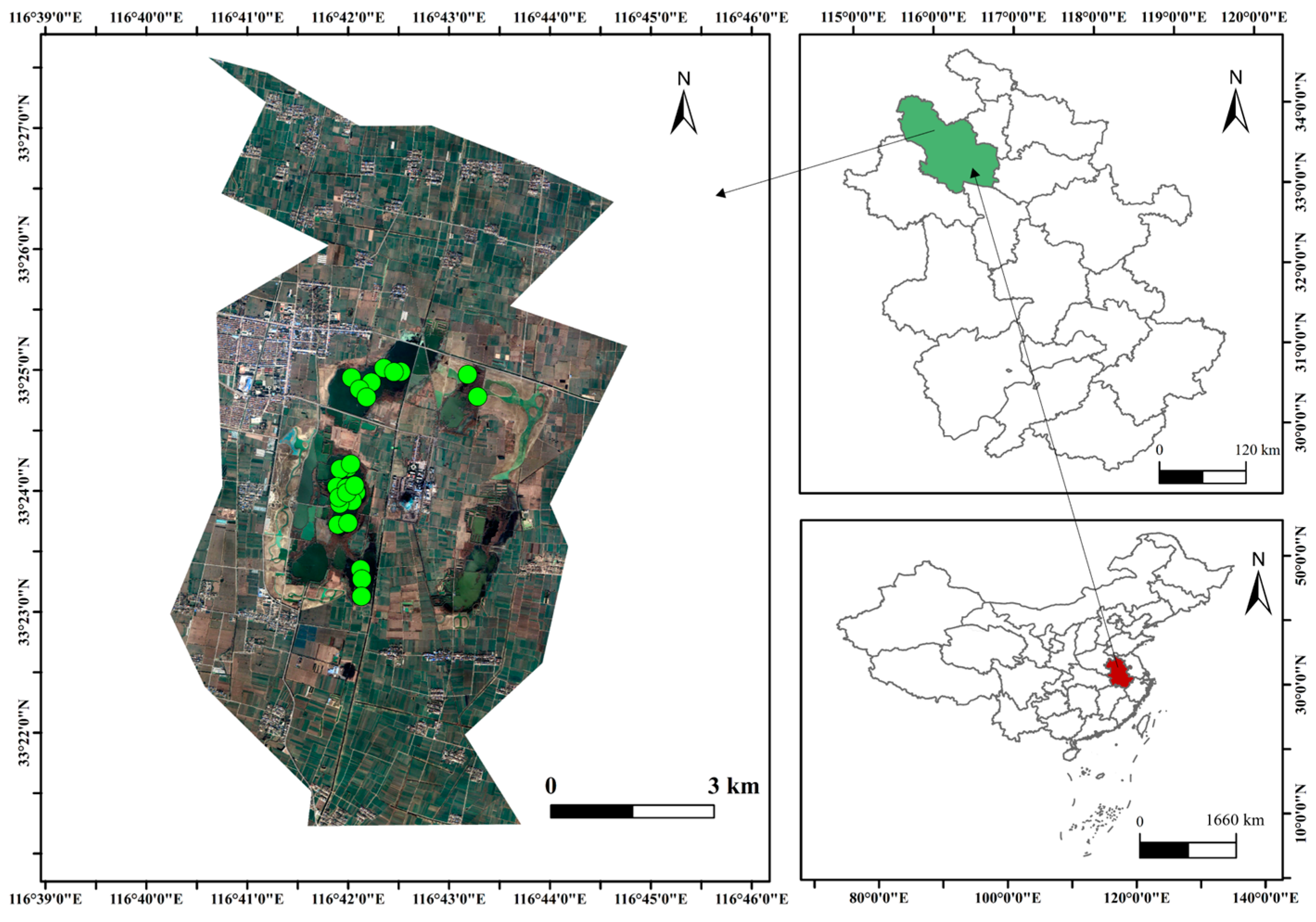
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Analytical Method
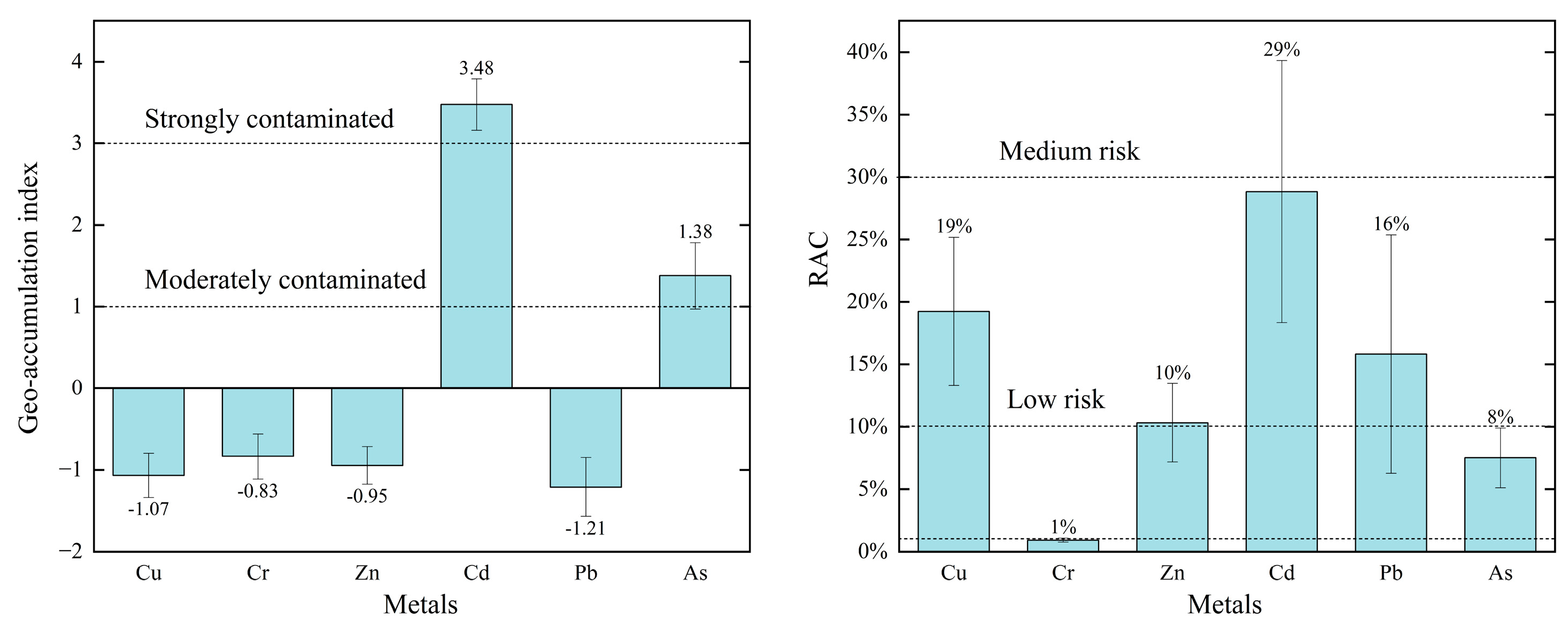
2.3.1. Geological Accumulation Index Method
2.3.2. Ecological Risk Assessment Coding Methods
2.3.3. APCS-MLR Model
2.3.4. PMF Source Analysis Model
2.4. Data Processing Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Distributions of the Water and Sediment Heavy Metal Contents
3.2. Morphological Distribution Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Sediments
3.3. Heavy Metal Risk Assessment
3.4. Analysis of the Potential Sources of the Sediment Heavy Metal Elements
3.4.1. Correlation Analysis
3.4.2. APCS-MLR-Based Source Analysis
3.4.3. PMF-Based Source Analysis
3.4.4. Comparison of APCS-MLR and PMF Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, H.; Deng, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, L.; Huang, Y. The spatial distribution and source of heavy metals in soil-plant-atmosphere system in a large coal mining area. Ore Energy Resour. Geol. 2024, 17, 100059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Bai, Z.K.; Shi, H.D.; Zhou, W.; Liu, X.C. Heavy metal pollution of soils from coal mines in China. Nat. Hazards 2019, 99, 1163–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Song, B.; Zhou, Z.Y. Pollution assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in soil from lead-Zinc mining areas of south China. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.-M.; Liu, S.; Song, L.; Wu, C.-S.; Yang, B.; Lu, H.-Z.; Wang, X.; Zakari, S. Contamination and source-specific risk analysis of soil heavy metals in a typical coal industrial city, central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaman, R.; Peng, C.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Guo, Z.; Xiao, X. Identifying sources and transport routes of heavy metals in soil with different land uses around a smelting site by GIS based PCA and PMF. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Nemr, A.; El-Said, G.F.; Khaled, A.; Ragab, S. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of some heavy metals in coastal surface sediments along the Red Sea, Egypt. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2016, 31, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ye, S.Y.; Laws, E.A.; Yuan, H.M.; Ding, X.G.; Zhao, G.M. Surface sediment properties and heavy metal pollution assessment in the Shallow Sea Wetland of the Liaodong Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 120, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Lei, S.; Bian, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Gan, Y. Geographic distribution of heavy metals and identification of their sources in soils near large, open-pit coal mines using positive matrix factorization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, G.; Sutharsan, P.; Ramasamy, V.; Venkatachalapathy, R. Assessment of spatial distribution and potential ecological risk of the heavy metals in relation to granulometric contents of Veeranam lake sediments, India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 84, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadlillah, L.N.; Utami, S.; Rachmawati, A.A.; Jayanto, G.D.; Widyastuti, M. Ecological risk and source identifications of heavy metals contamination in the water and surface sediments from anthropogenic impacts of urban river, Indonesia. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, N.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, T. Pollution, cumulative ecological risk and source apportionment of heavy metals in water bodies and river sediments near the Luanchuan molybdenum mining area in the Xiaoqinling Mountains, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 205, 116621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Cao, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Ma, T.; Irfan, M.; Zheng, L. Source-specific ecological risk analysis and critical source identification of heavy metal(loid)s in the soil of typical abandoned coal mining area. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Xie, X.; Wang, P.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, H. Heavy metal pollution caused by small-scale metal ore mining activities: A case study from a polymetallic mine in South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradl, H.B. Adsorption of heavy metal ions on soils and soils constituents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 277, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, F.; Song, J.; Tan, M.L.; Kung, H.-T.; Johnson, V.C. Pollutant source, ecological and human health risks assessment of heavy metals in soils from coal mining areas in Xinjiang, China. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejman, A.; Nabi Bidhendi, G.; Ardestani, M.; Saeedi, M.; Baghvand, A. Fractionation of heavy metals in sediments and assessment of their availability risk: A case study in the northwestern of Persian Gulf. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Zhao, W.; Yu, X.; Li, H.; Gao, Z.; Ding, M.; Yue, J. Evaluating heavy metal pollution and potential risk of soil around a coal mining region of Tai’an City, China. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 2156–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Li, T.; Feng, Y.; Su, H.; Yang, Q. Source apportionment and risk assessment for available occurrence forms of heavy metals in Dongdahe Wetland sediments, southwest of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, H.; Meng, W.; Liu, N.; Wu, P. Accumulation and source apportionment of heavy metal(loid)s in agricultural soils based on GIS, SOM and PMF: A case study in superposition areas of geochemical anomalies and zinc smelting, Southwest China. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 159, 964–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, L.Z.; Wu, Q.H.; Luo, D.G.; Xiao, T.F.; Wu, Q.H.; Huang, X.X.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, P. Impact of acid mine drainage on groundwater hydrogeochemistry at a pyrite mine (South China): A study using stable isotopes and multivariate statistical analyses. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, Y.-H.; Li, G.-L.; Wang, X.-M.; Peng, P. Combination of Unmix and PMF receptor model to apportion the potential sources and contributions of PAHs in wetland soils from Jiaozhou Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 90, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, E.J.; Liu, H.Y.; Dinis, F.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Jing, P.; Liu, F.; Ju, X.H. Contamination Evaluation and Source Analysis of Heavy Metals in Karst Soil Using UNMIX Model and Pb-Cd Isotopes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurston, G.D.; Spengler, J.D. A quantitative assessment of source contributions to inhalable particulate matter pollution in metropolitan Boston. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 1985, 19, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Teng, Y.G.; Chen, R.H.; Li, J.; Wang, J.S. Contamination characteristics and source apportionment of trace metals in soils around Miyun Reservoir. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 15331–15342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.X.; Chao, S.H.; Liu, J.W.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Zhang, A.C.; Cao, H.B. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil for a township in Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1658–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; An, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, L.; Lv, S. Geochemical characteristics and health risks of heavy metals in agricultural soils and crops from a coal mining area in Anhui province, China. Environ. Res. 2024, 241, 117670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shi, H.; Bai, Z.; Zhou, W.; Liu, K.; Wang, M.; He, Y. Heavy metal concentrations of soils near the large opencast coal mine pits in China. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G. Index of Geoaccumulation in Sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 1969, 2, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Pardo, R.; Barrado, E.; Lourdes, P.; Vega, M. Determination and speciation of heavy metals in sediments of the Pisuerga river. Water Res. 1990, 24, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Xu, X.; A., Y.; Ren, S. Heavy metals in the continuous river−estuary−sea system of the Yellow River Delta, China: Spatial patterns, potential sources, and influencing factors. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 209, 117247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 14848-2017; Standard for Groundwater Quality. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2017. Available online: https://www.chinesestandard.net/PDF.aspx/GBT14848-2017?English_GB/T%2014848-2017 (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Shahmoradi, B.; Hajimirzaei, S.; Amanollahi, J.; Wantalla, K.; Maleki, A.; Lee, S.M.; Shim, M.J. Influence of iron mining activity on heavy metal contamination in the sediments of the Aqyazi River, Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.L.; Liu, G.N.; Chen, D.L.; Xing, Z.S.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.Y. Heavy Metal Pollution in Sediments of the Yu River in a Polymetallic Ore Concentration Area: Temporal-Spatial Variation, Risk Assessment, and Sources Apportionment. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, F.; Bian, P.; Liu, Y. Spatial distribution and human health risk assessment of soil heavy metals based on sequential Gaussian simulation and positive matrix factorization model: A case study in irrigation area of the Yellow River. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 225, 112752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.-P.; Song, J.-M.; Zhang, N.-X.; Xu, Y.-Y.; Zheng, G.-X.; Zhang, P. Variation characteristics and controlling factors of heavy metals in the South Yellow Sea surface seawaters. Huan Jing Ke Xue = Huanjing Kexue 2008, 29, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar]
- Nemati, K.; Abu Bakar, N.K.; Sobhanzadeh, E.; Abas, M.R. A modification of the BCR sequential extraction procedure to investigate the potential mobility of copper and zinc in shrimp aquaculture sludge. Microchem. J. 2009, 92, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Liu, E.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, E.; Yang, F.; Wei, C.; Shen, J. Comprehensive assessment of heavy metal pollution and ecological risk in lake sediment by combining total concentration and chemical partitioning. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.G.; Yang, L.S. A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchem. J. 2010, 94, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setu, S.; Strezov, V. Impacts of non-ferrous metal mining on soil heavy metal pollution and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 969, 178962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.Q.; Cui, R.Y.; Li, J.; Wei, H.L.; Zhao, J.T.; Bai, F.L.; Song, W.Y.; Ding, X. Occurrence and distribution of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Changhua River Estuary and adjacent shelf (Hainan Island). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 76, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, S.L.; Zhao, Q.H.; Deng, L.; Dong, S.K. Spatial variation and contamination assessment of heavy metals in sediments in the Manwan Reservoir, Lancang River. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 82, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Oyola, S.; Valverde-Armas, P.E.; Romero-Crespo, P.; Capa, D.; Valdivieso, A.; Coronel-León, J.; Guzmán-Martínez, F.; Chavez, E. Heavy metal(loid)s contamination in water and sediments in a mining area in Ecuador: A comprehensive assessment for drinking water quality and human health risk. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 4929–4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, L.Y.; Lei, K.; Huang, L.; Kang, D. Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals in street dust of Baoji, NW China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Huang, D.; Yang, J.; Song, Y.; Zeng, G. Heavy metals in road dust from Xiandao District, Changsha City, China: Characteristics, health risk assessment, and integrated source identification. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 13100–13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Gao, Q.; Cheng, H.; Wang, J. Heavy metals distribution and their ecological risk in the surface sediments of Haizhou Bay, China. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2024, 78, 103772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.R.M.T.; Rabbi, A.H.M.F.; Anik, A.H.; Khan, R.; Masud, M.A.A.; Nedjoud, G.; Idris, A.M.; Rahman, M.N.; Senapathi, V. Source distribution, ecological risks, and controlling factors of heavy metals in river sediments: Receptor model-based study in a transboundary river basin. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2025, 40, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.T.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.Z.; Yang, M.J.; Wang, J.F.; Du, P.J.; Li, Z.C. Pollution Assessment and Source Apportionment of Heavy Metals in Sediments of Subsidence Section of Luling Mine in the Tuohe River, China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2025, 34, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; van der Kuijp, T.J.; Yuan, Z.; Huang, L. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wang, Q.; Guan, Q.; Ma, Y.; Ni, F.; Yang, E.; Zhang, J. Heavy metal pollution levels, source apportionment and risk assessment in dust storms in key cities in Northwest China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.H.; Mustafa, A.-R.A.; El-Sheikh, A.A. Geochemistry and spatial distribution of selected heavy metals in surface soil of Sohag, Egypt: A multivariate statistical and GIS approach. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, B.; Ao, L.; Tang, Y. Study on environmental characteristics of sustainable biomimetic soil preparation and its application in gangue reclamation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 435, 136874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, B.U.; Malang, A.; Webster, R.; Mohapatra, K.P.; Verma, B.C.; Kumar, M.; Das, A.; Islam, M.; Hazarika, S. Acid drainage from coal mining: Effect on paddy soil and productivity of rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 583, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Lou, Z.; Xiao, R.; Ren, Z.; Lv, X. Contamination assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil through the synthesis of PMF and GeogDetector models. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhao, M.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Cai, B.; Han, Z.; Huang, H.; Fan, Z. Determination of priority control factors for the management of soil trace metal(loid)s based on source-oriented health risk assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, K.; Li, M.; Liu, L.; Yang, J.-L.; Zhao, H.-J. Evaluation and Source Analysis of Heavy Metal Pollution in Sediments of the Yellow River Basin Based on Monte Carlo Simulation and PMF Model. Huanjing Kexue/Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 4008–4017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Du, Q.; Guan, Q.; Luo, H.; Shan, Y.; Shao, W. A Monte Carlo simulation-based health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils of an oasis agricultural region in northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, C.; Liu, R.; Xu, L.; Wang, Q.; Guo, L.; Miao, Y.; Shen, Z. Source-specific ecological risk analysis and critical source identification of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.-H. Source Analysis of Heavy Metals in Typical Farmland Soils Based on PCA-APCS-MLR and Geostatistics. Huan Jing Ke Xue = Huanjing Kexue 2023, 44, 3509–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J. Multivariate receptor models and robust geostatistics to estimate source apportionment of heavy metals in soils. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Igeo [28] | RAC [29] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Igeo | Pollution level | RAC | Pollution level |
| Igeo < 0 | Pollution-free | RAC < 1% | Risk-free |
| 0 ≤ Igeo < 1 | No pollution to moderate pollution | RAC < 10% | Low risk |
| 1 ≤ Igeo < 2 | Moderate pollution | 10% ≤ RAC < 30% | Moderate risk |
| 2 ≤ Igeo < 3 | Moderate pollution to strong pollution | 30% ≤ RAC < 50% | High risk |
| 3 ≤ Igeo < 4 | Strong pollution | RAC ≥ 50% | Extremely high risk |
| 4 ≤ Igeo < 5 | Strong pollution to extremely intense pollution | ||
| 5 ≤ Igeo | Extreme pollution | ||
| Mean | SD | CV. | Minimum | Maximum | Chinese National Standards * | % of SER | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | 6.28 | 1.77 | 0.28 | 3.26 | 11.05 | 1000 | 0.00 |
| Cr | 37.26 | 8.91 | 0.24 | 24.15 | 65.79 | 50 | 10.00 |
| Cd | 0.41 | 0.33 | 0.81 | BDL | 1.68 | 5 | 0.00 |
| Zn | 26.15 | 15.19 | 0.58 | 9.79 | 89.92 | 1000 | 0.00 |
| Pb | 2.29 | 1.03 | 0.45 | 0.89 | 4.96 | 50 | 0.00 |
| As | 32.86 | 23.25 | 0.71 | BDL | 104.25 | 50 | 20.00 |
| pH | 7.19 | 0.73 | 0.10 | 5.96 | 8.35 |
| Maximum | Minimum | Mean | SD | CV | Background Values | Level II Standards | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | 23.12 | 10.79 | 16.44 | 3.02 | 0.18 | 22.6 | 100 |
| Cr | 73.56 | 34.92 | 51.89 | 9.94 | 0.19 | 60.6 | 250 |
| Cd | 2.80 | 1.28 | 1.98 | 0.43 | 0.22 | 0.1162 | 0.6 |
| Zn | 50.74 | 28.15 | 37.29 | 6.07 | 0.16 | 47.3 | 300 |
| Pb | 25.58 | 10.77 | 16.42 | 4.20 | 0.26 | 24.6 | 350 |
| As | 46.25 | 15.89 | 31.49 | 8.11 | 0.26 | 7.8 | 25 |
| pH | 7.65 | 6.10 | 7.09 | 0.39 | 0.05 | ||
| OM | 10.05 | 5.14 | 7.24 | 1.32 | 0.18 |
| Sediment | Cu | Cr | Cd | Zn | Pb | As |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | 1 | |||||
| Cr | 0.761 ** | 1 | ||||
| Cd | −0.430 | −0.179 | 1 | |||
| Zn | 0.540 * | 0.484 * | −0.327 | 1 | ||
| Pb | 0.247 | 0.017 | −0.014 | 0.181 | 1 | |
| As | 0.646 ** | 0.610 ** | −0.170 | 0.413 | −0.073 | 1 |
| Components | Cu | Cr | Zn | As | Pb | Cd | Contributing Percentage % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.942 | 0.926 | 0.909 | 0.855 | 0.728 | 0.617 | 70.247% |
| 2 | −0.217 | −0.184 | −0.066 | −0.315 | 0.405 | 0.663 | 83.376% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, J.; Gao, L.; Yang, J. Analysis of Heavy Metal Sources in Xutuan Mining Area Based on APCS-MLR and PMF Model. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4249. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084249
Xia J, Gao L, Yang J. Analysis of Heavy Metal Sources in Xutuan Mining Area Based on APCS-MLR and PMF Model. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(8):4249. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084249
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Jieyu, Liangmin Gao, and Jinxiang Yang. 2025. "Analysis of Heavy Metal Sources in Xutuan Mining Area Based on APCS-MLR and PMF Model" Applied Sciences 15, no. 8: 4249. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084249
APA StyleXia, J., Gao, L., & Yang, J. (2025). Analysis of Heavy Metal Sources in Xutuan Mining Area Based on APCS-MLR and PMF Model. Applied Sciences, 15(8), 4249. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084249





