Effect of Zn2+ Ion Concentration on the Light-Induced Scattering and Holographic Storage Properties of Zn:Cu:Fe:LiNbO3 Crystals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Preparation
2.2. Characterization of Infrared Absorption Spectrum
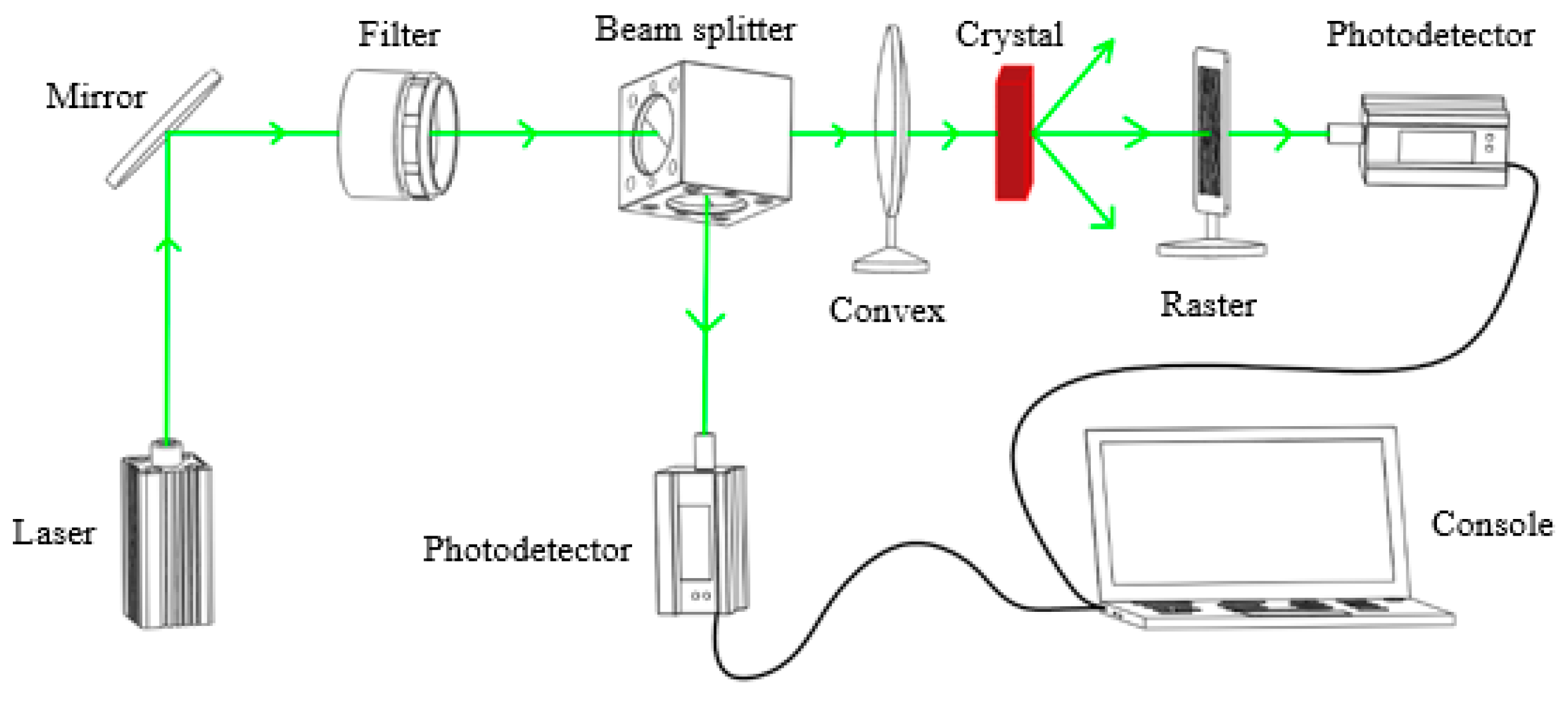
2.3. Characterization of Light-Induced Scattering
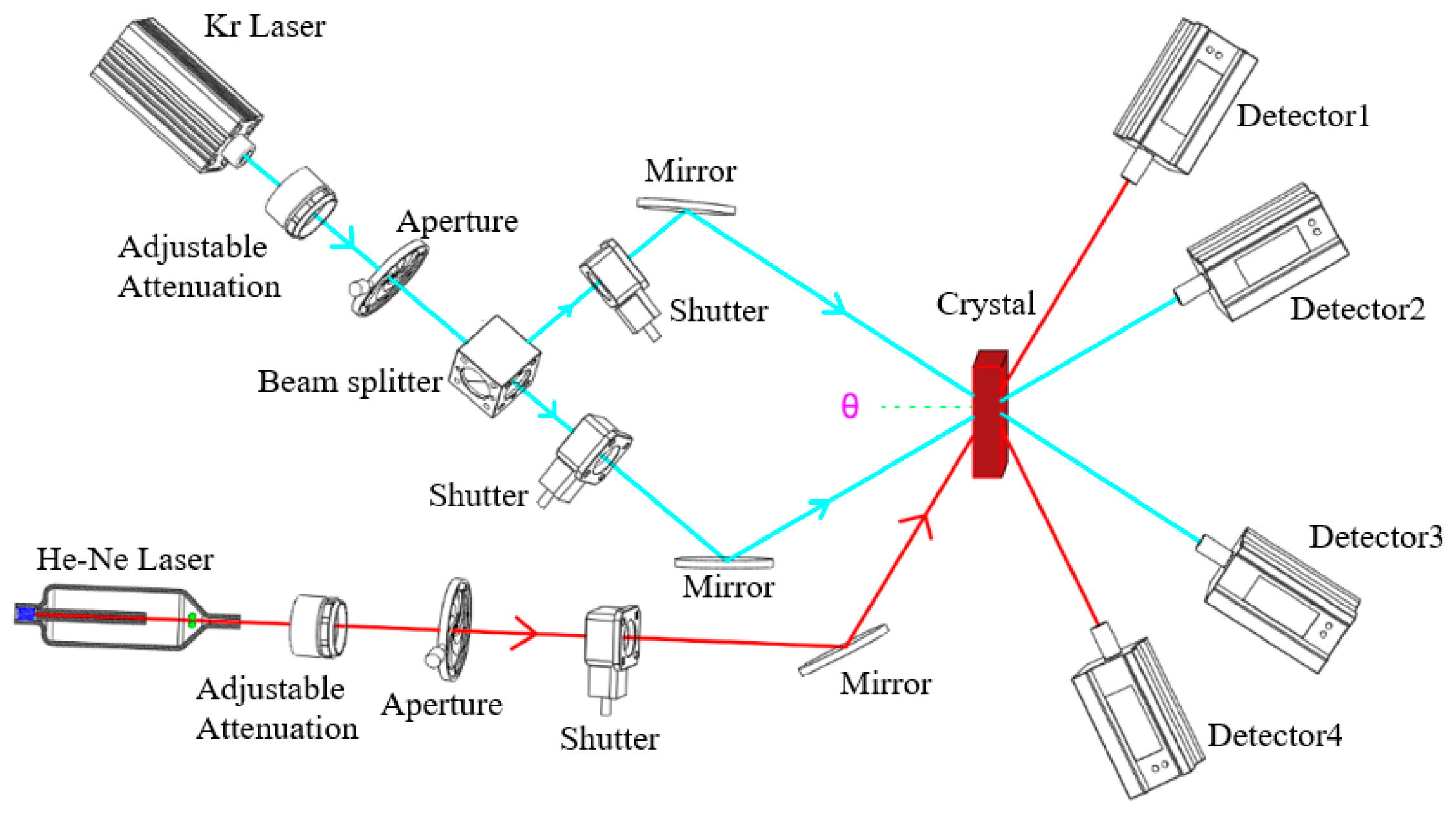
2.4. Characterization of Two-Wavelength Coupling Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
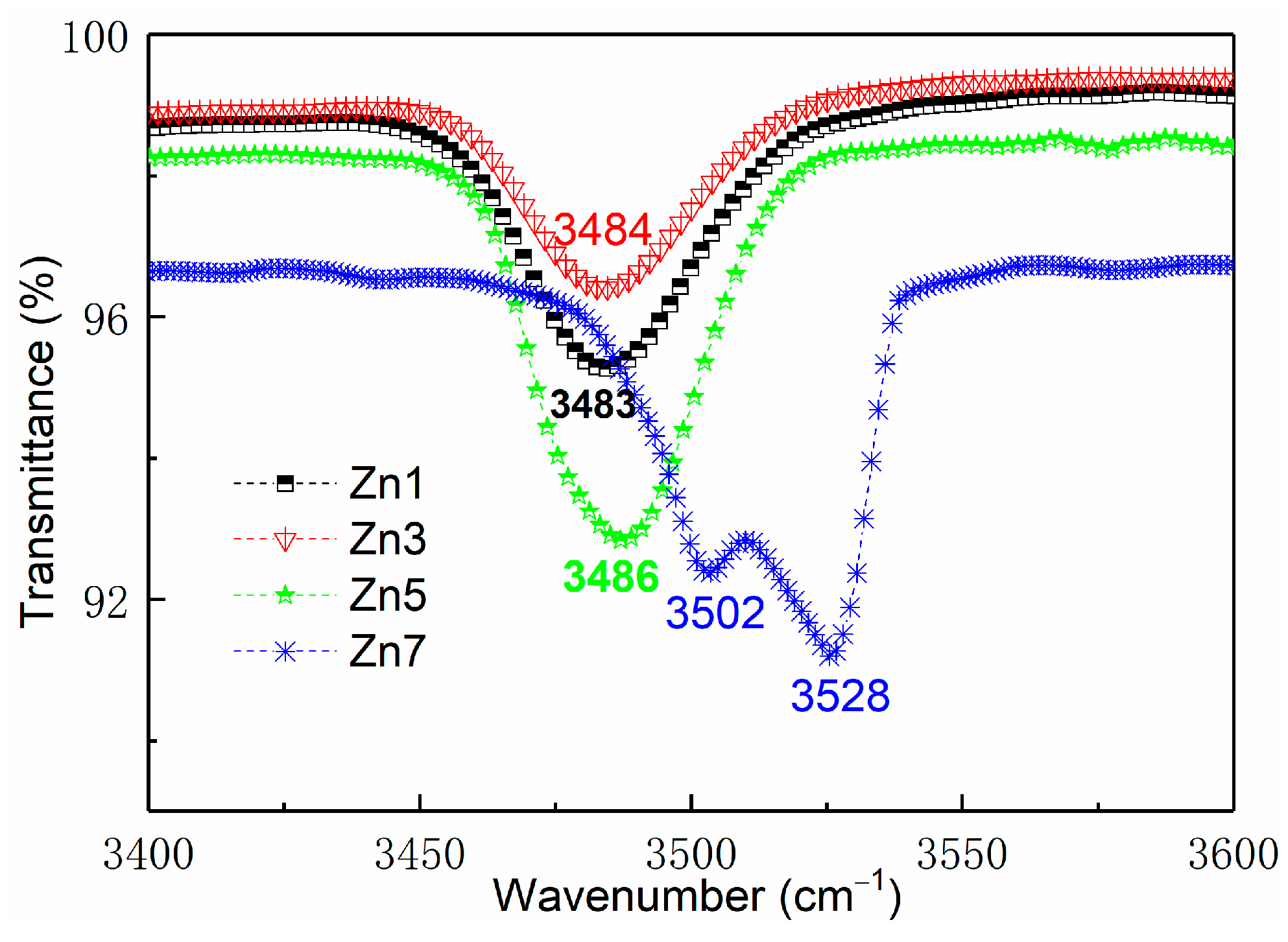
3.1. Infrared Absorption Spectrum
3.2. Light-Induced Scattering
3.3. Two-Wavelength Coupling Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, L.; Chen, G. Optimization of blue photorefractive properties and exponential gain of photorefraction in Sc-doped Ru:Fe:LiNbO3 crystals. Crystals 2022, 12, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heanue, J.F.; Bashaw, M.C.; Hesselink, L. Volume holographic storage and retrieval of digital data. Science 1994, 265, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adibi, A.; Buse, K.; Psaltis, D. Theoretical analysis of two-step holographic recording with high-intensity pulses. Phys. Rev. A 2001, 63, 023813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillen, D.K.; Hudson, T.D.; Wagner, J.; Singleton, J. Holographic recording in specially doped lithium niobate crystals. Opt. Express 1998, 2, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, K.; Jermann, F.; Krätzig, E. Infrared holographic recording in LiNbO3:Fe and LiNbO3:Cu. In European Materials Research Society Symposia Proceedings; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 48, pp. 237–240. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Adibi, A.; Berben, D.; Buse, K.; Psaltis, D. The role of Mn in photorefractive LiNbO3. In Photorefractive Effects, Materials and Devices, Proceedings; Optica Publishing Group: Delavan, WI, USA, 2001; Volume 62, pp. 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Hatano, H.H.; Yamaji, T.Y.; Tanaka, S.T.; Furukawa, Y.F.; Kitamura, K.K. Investigation of the oxidation state of Fe in stoichiometric Fe:LiNbO3 for digital holographic recording. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 38, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Tao, S.; Wang, D.; Yuan, W.; Liu, G.; Ding, X.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, C. Holographic disk data storage at a high areal density of 33.7 bits/µm2. Proc. SPIE—Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2003, 5069, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Cao, L.; Ma, X.; He, Q.; Jin, G. Experiment on parallel correlated recognition of 2030 human faces based on speckle modulation. Opt. Express 2004, 12, 4047–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebasti&án-Vicente, C.; Zamboni, R.; Garc&ía-Cabañes, A.; Carrascosa, M. Photovoltaic Charge Lithography on Passive Dielectric Substrates Using Fe:LiNbO3 Stamps. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2025, 11, 2400327. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Qu, D.; Wang, W.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Meng, X. Improved nonvolatile holographic storage sensitivity of near-stoichiometric LiNbO3:Fe:Mn crystals. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2012, 10, 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y. Research on Optical Holographic Storage Properties in In:Fe:Cu:LiNbO3 Crystals. Semicond. Optoelectron. 2012, 33, 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, G.Q.; Yu, W.B.; Guo, Z.Z.; Zhao, Y.Q. Theoretical Studies On Nonvolatile Holographic Recording for LiNbO3:Cu:Ce Crystal. Opt. Laser Eng. 2014, 54, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Dai, L.; Xu, C.; Qian, Z.; Li, D.; Lin, J.; Wang, R.; Xu, Y. Enhancement of nonvolatile holographic storage properties in In:Ce:Mn:LiNbO3 Crystal by [Li]/[Nb] Ratios. J. Mol. Struct. 2013, 1053, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badalyan, A.; Hovsepyan, R.; Mantashyan, P.; Mekhitaryan, V.; Drampyan, R. Nondestructive Readout of Holograms Recorded by Bessel Beam Technique in LiNbO3:Fe and LiNbO3:Fe:Cu Crystals. Eur. Phys. J. D 2014, 68, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, D.; Geng, A.; Chen, X.; Li, B.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, S. Oscillation of nonvolatile holographic recording in LiNbO3:Fe:Cu crystals. Optik 2013, 124, 4397–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankratov, V.; Millers, D.; Grigorjeva, L.; Matkovskii, A.O.; Potera, P.; Pracka, I.; Łukasiewicz, T. The role of Fe and Cu dopants in electron–hole trapping and relaxation process in congruent LiNbO3. Opt. Mater. 2003, 22, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Luo, S.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, H. Improvement of blue photorefractive properties in In-doped LiNbO3:Fe:Cu crystals. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 115413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liang, G.; Xu, Z. Defect structure and holographic storage properties of LiNbO3:Zr:Fe:Cu crystals with various Li/Nb ratios. Opt. Mater. 2019, 96, 109318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Wang, H.; Lai, N.; Zhang, L. Effect of [Li]/[Nb] ratios on doping concentration and defect structure of Mg:Fe:Cu:LiNbO3 crystals. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2023, 37, 2350164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Han, X.; Shao, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, L. Hf4+ Ion Concentration Dependence of Holographic Storage Properties in Hf:Fe:Cu:LiNbO3 Crystals. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2019, 54, 1800193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Han, X.; Shao, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Xu, Y. Spectra (UV-Visible, IR transmission) of Sc3+, Fe3+ and Cu2+ tri-doped LiNbO3 crystals with various [Li]/[Nb] ratios. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 32, 1850328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Wang, R.; Xing, L.; Xu, Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, X. Influence of Zn2+ ions concentration on the optical properties of Zn/Er:LiNbO3 crystals. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2011, 46, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, L.; Xu, Y. Growth and photorefractive properties of near-stoichiometric Zn:Fe:LiNbO3 crystal. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2004, 84, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidorov, N.V.; Teplyakova, N.A.; Bobreva, L.A.; Palatnikov, M.N. Optical properties and defects of double doped crystals LiNbO3:Mg (5.05):Fe (0.009) and LiNbO3:Zn (4.34):Fe (0.02)(mol%). J. Struct. Chem. 2019, 60, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herreros, B.; Lifante, G. LiNbO3 optical waveguides by Zn diffusion from vapor phase. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1995, 66, 1449–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Dai, L.; Yang, S.; Ji, Z. Influence of the Zn2+ concentration on the defect structure and optical properties in Zn:Fe:Cu:LiNbO3 crystals. AIP Adv. 2025, 15, 015121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Yin, J.Y.; Nie, S.P.; Xie, M.Y. Applications of infrared spectroscopy in polysaccharide structural analysis: Progress, challenge and perspective. Food Chem. X 2021, 12, 100168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.G.; Fraser, D.B.; Denton, R.T.; Rich, T.C. Correlation of Reduction in Optically Induced Refractive-Index Inhomogeneity with OH Content in LiTaO3 and LiNbO3. J. Appl. Phys. 1968, 39, 4600–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yang, C.; Dai, L.; Sun, L.; Xu, Y.; Cao, L. Influence of Li and Nb ratios on the defect structure and exposure energy in LiNbO3:Fe:Mn:Zr crystals. J. Alloys Comp. 2011, 509, 4167–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yang, C.; Zhu, C.; Sun, T.; Wang, R.; Xu, Y. Improved nonvolatile holographic storage properties in Zr:Ru:Fe:LiNbO3 crystal by blue light recording. Mater. Lett. 2012, 67, 320–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.R.; Riscob, B.; Bhatt, R.; Bhaumik, I.; Ganesamoorthy, S.; Vijayan, N.; Bhagavannarayana, G.; Karnal, A.K.; Nair, L. Investigations on crystalline perfection, Raman spectra and optical characteristics of transition metal (Ru) co-doped Mg:LiNbO3 single crystals. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 10807–10815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B. Measurement of space-charge field in doped LiNbO3 single crystals. J. Electroceram. 2013, 30, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienvenu, M.P.; Woodbury, D.; Rabson, T.A. Hologram decay in LiNbO3:Fe with a time varying conductivity. J. Appl. Phys. 1980, 51, 4245–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Kong, Y.; Ge, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Chen, S.; Xu, J. Improved sensitivity of nonvolatile holographic storage in triply doped LiNbO3:Zr,Cu,Ce. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 6333–6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, B.; Lin, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, K. Defect structure and nonvolatile hologram storage properties in Hf:Fe:Mn:LiNbO3 crystals. Optik 2011, 122, 1179–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokko, O.V.; Kadetova, A.V.; Prusskii, A.I.; Smirnov, M.V.; Palatnikov, M.N.; Sidorov, N.V. Structure and Luminescent Properties of Double-Doped LiNbO3:Zn:Mg Crystals. Phys. Status Solidi A 2024, 221, 2300796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G. Defect chemistry analysis of the defect structure in Mg-doped LiNbO3 crystals. Phys. Stat. Sol. A 1996, 156, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Chen, H.L.; Chen, G.J.; Kuo, C.L.; Hsieh, P.H.; Hwang, W.S. Investigation of the defect structure of congruent and Fe-doped LiNbO3 powders synthesized by the combustion method. Materials 2017, 10, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xu, Y.; Chen, G. Defect structure and upconversion luminescence properties of LiNbO3 highly doped congruent In:Yb:Ho:LiNbO3 crystals. Crystals 2022, 12, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valley, G.C.; Klein, M.B. Optimal properties of photorefractive materials for optical data processing. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Optic. Eng. 1983, 22, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
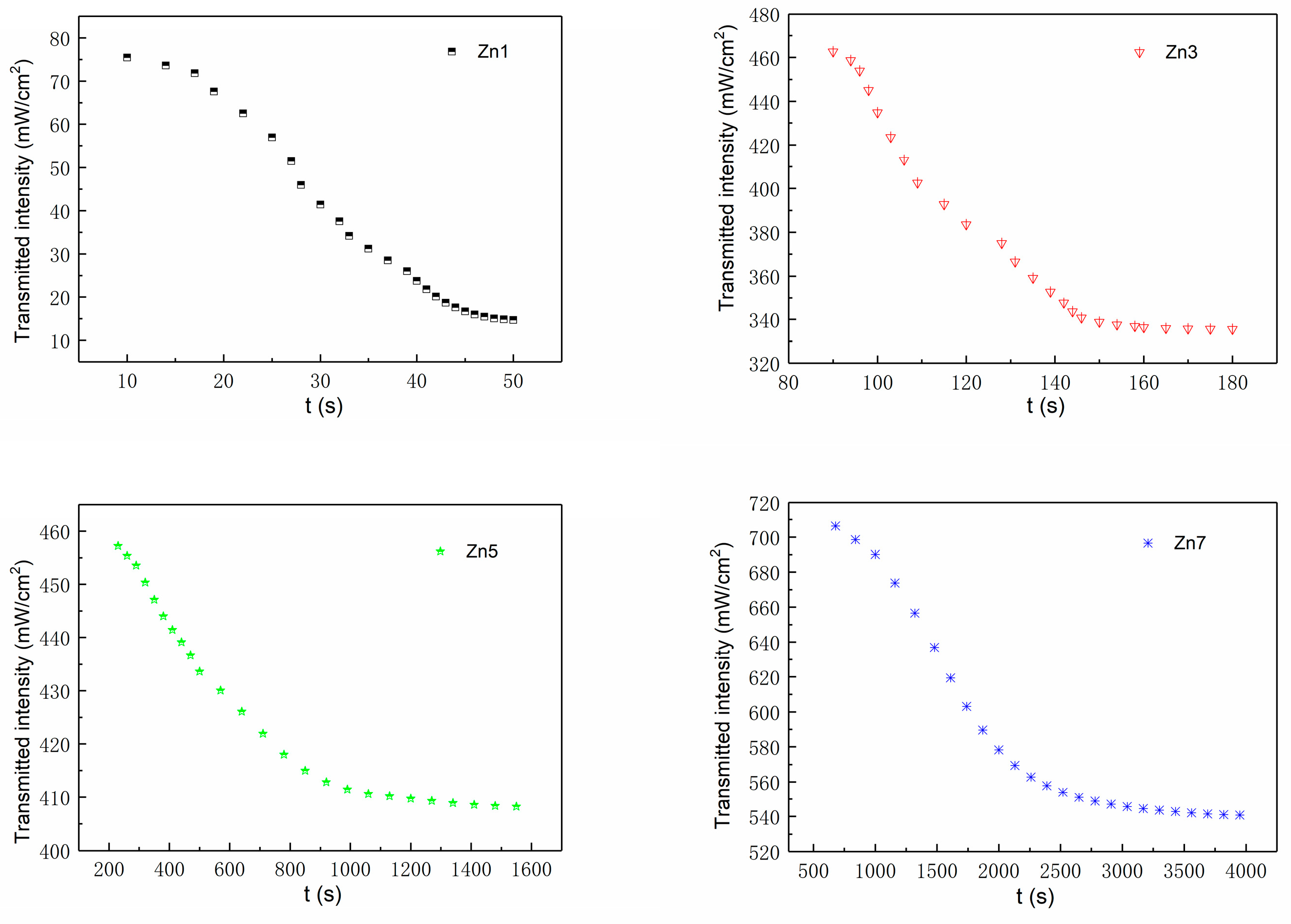
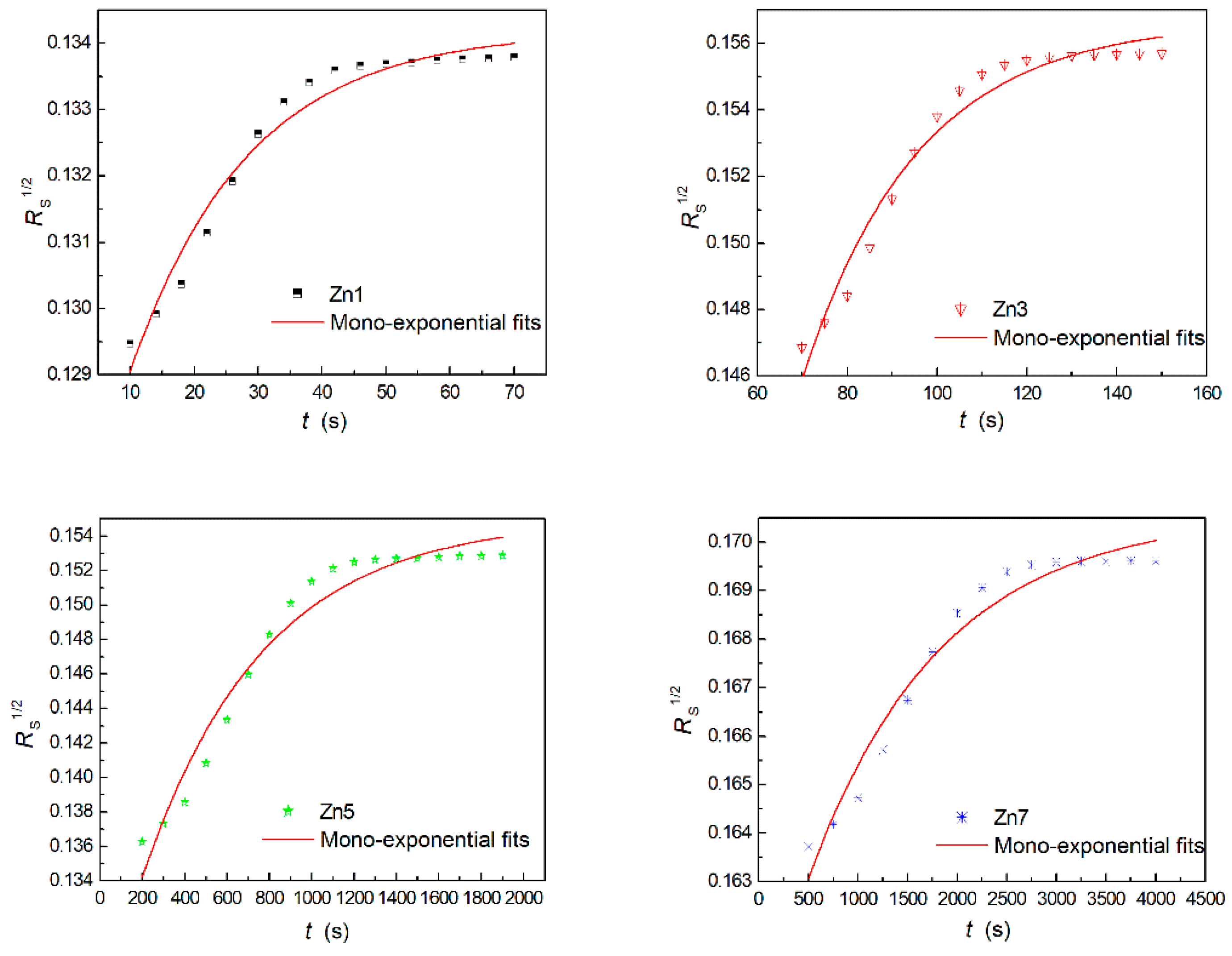
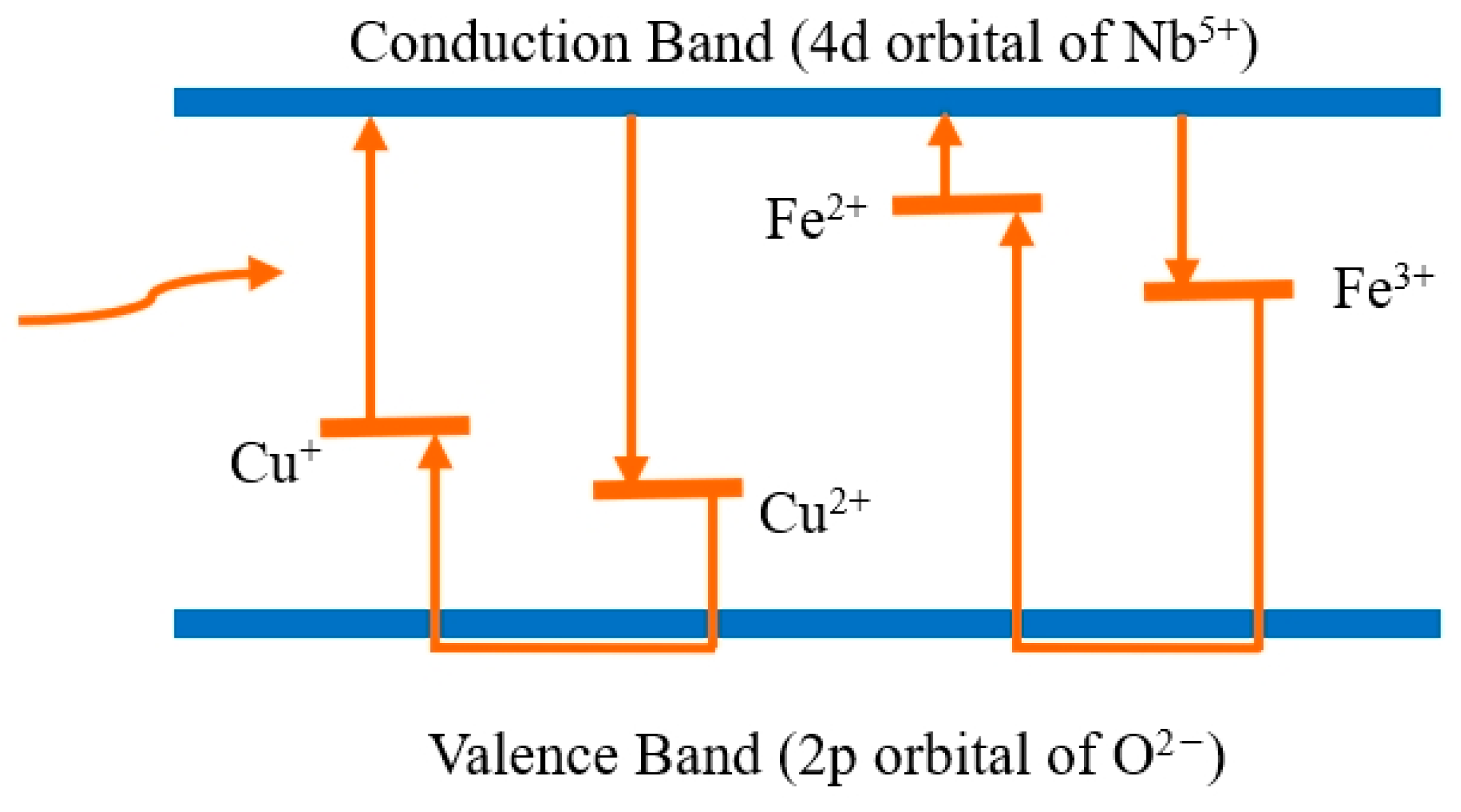
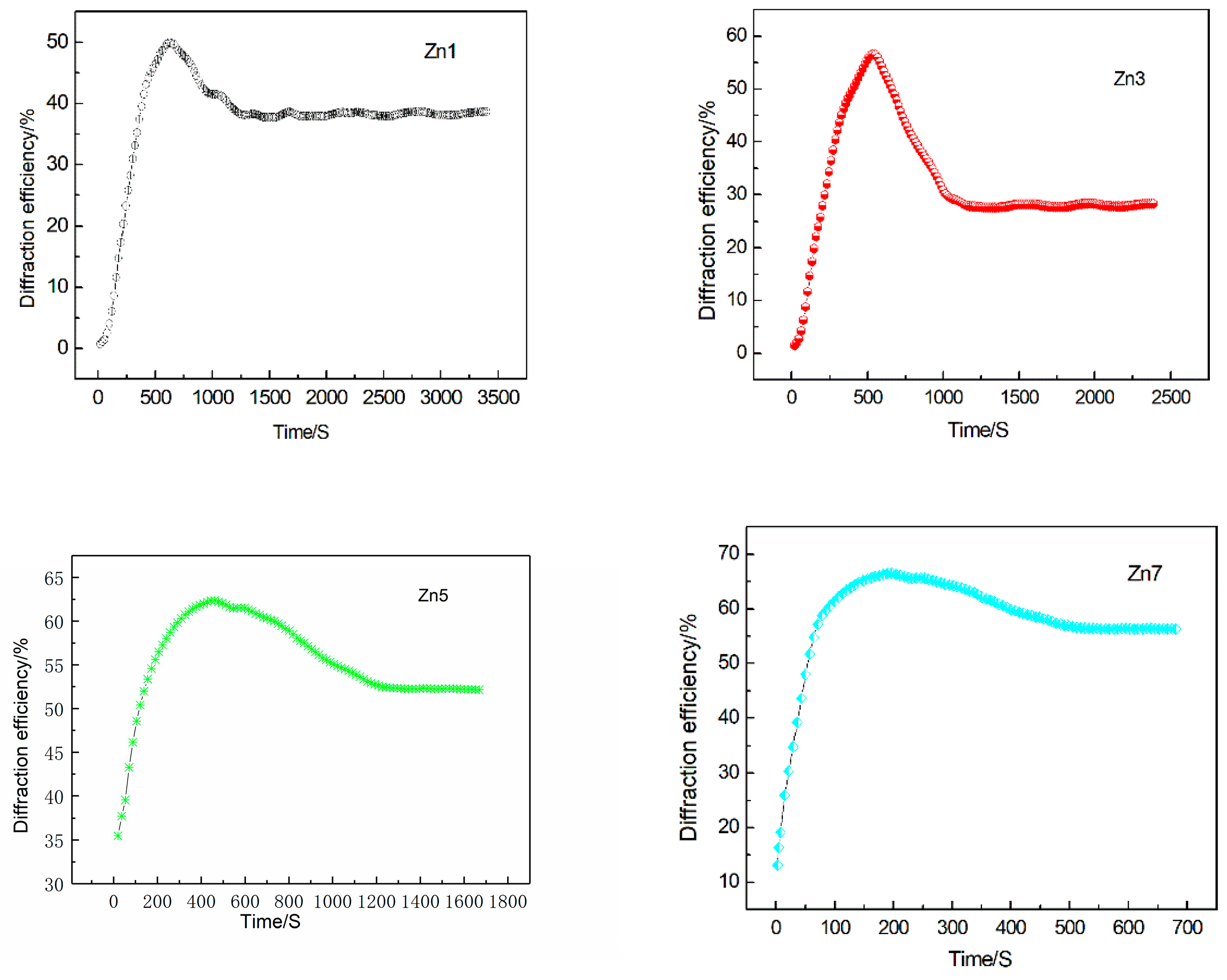
| Crystals | t (s) | I (mW/cm2) | Ieff (mW/cm2) | Er (J/cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn1 | 22.84 | 96.76 | 82.7 | 1.89 |
| Zn3 | 498.06 | 670.41 | 573 | 285.37 |
| Zn5 | 785.37 | 699.78 | 598.1 | 469.71 |
| Zn7 | 931.69 | 987.71 | 844.2 | 786.55 |
| Sample | τw (s) | τe (s) | ηs (%) | S (cm/J) | M/# | Δns (×10−5) | σph (×10−12 cm/ΩW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn1 | 603.9 | 782.4 | 50.2 | 0.29 | 0.92 | 4.60 | 0.41 |
| Zn3 | 528.1 | 1108.6 | 57.3 | 0.36 | 1.59 | 4.92 | 0.47 |
| Zn5 | 483.5 | 1390.9 | 62.8 | 0.41 | 2.28 | 5.15 | 0.51 |
| Zn7 | 196.4 | 2358.2 | 66.7 | 1.04 | 9.81 | 5.30 | 1.26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Z.; Dai, L.; Yang, S.; Ji, Z.; Wang, L. Effect of Zn2+ Ion Concentration on the Light-Induced Scattering and Holographic Storage Properties of Zn:Cu:Fe:LiNbO3 Crystals. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4129. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084129
Yan Z, Dai L, Yang S, Ji Z, Wang L. Effect of Zn2+ Ion Concentration on the Light-Induced Scattering and Holographic Storage Properties of Zn:Cu:Fe:LiNbO3 Crystals. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(8):4129. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084129
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Zhehua, Li Dai, Shunxiang Yang, Zesheng Ji, and Luping Wang. 2025. "Effect of Zn2+ Ion Concentration on the Light-Induced Scattering and Holographic Storage Properties of Zn:Cu:Fe:LiNbO3 Crystals" Applied Sciences 15, no. 8: 4129. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084129
APA StyleYan, Z., Dai, L., Yang, S., Ji, Z., & Wang, L. (2025). Effect of Zn2+ Ion Concentration on the Light-Induced Scattering and Holographic Storage Properties of Zn:Cu:Fe:LiNbO3 Crystals. Applied Sciences, 15(8), 4129. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084129





