Evaluation of the Acoustic Noise Inside the Main Steam Line of a BWR/5 Nuclear Reactor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory
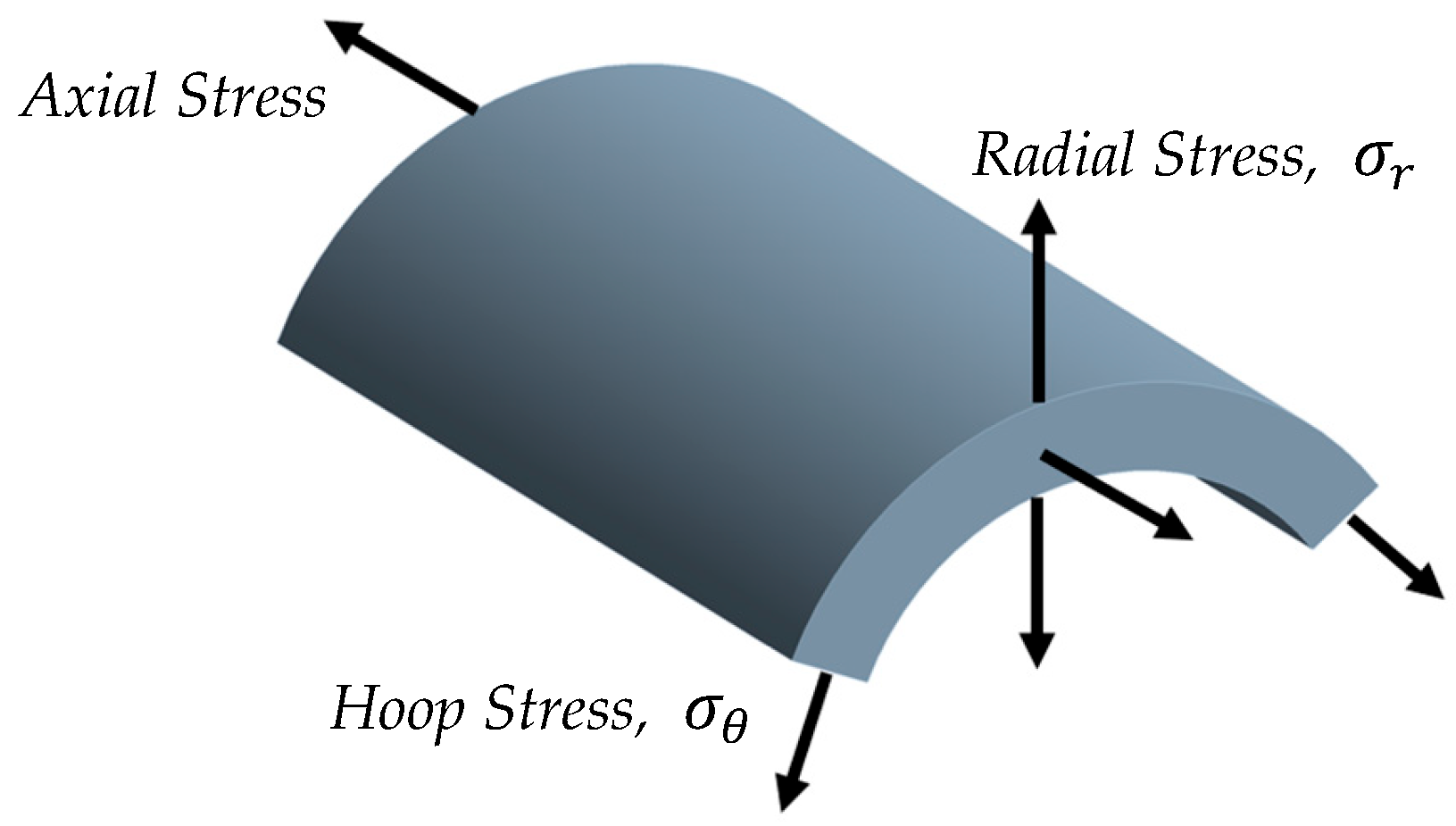
2.1. Thick-Walled Cylinder
2.2. Model (k-(e))
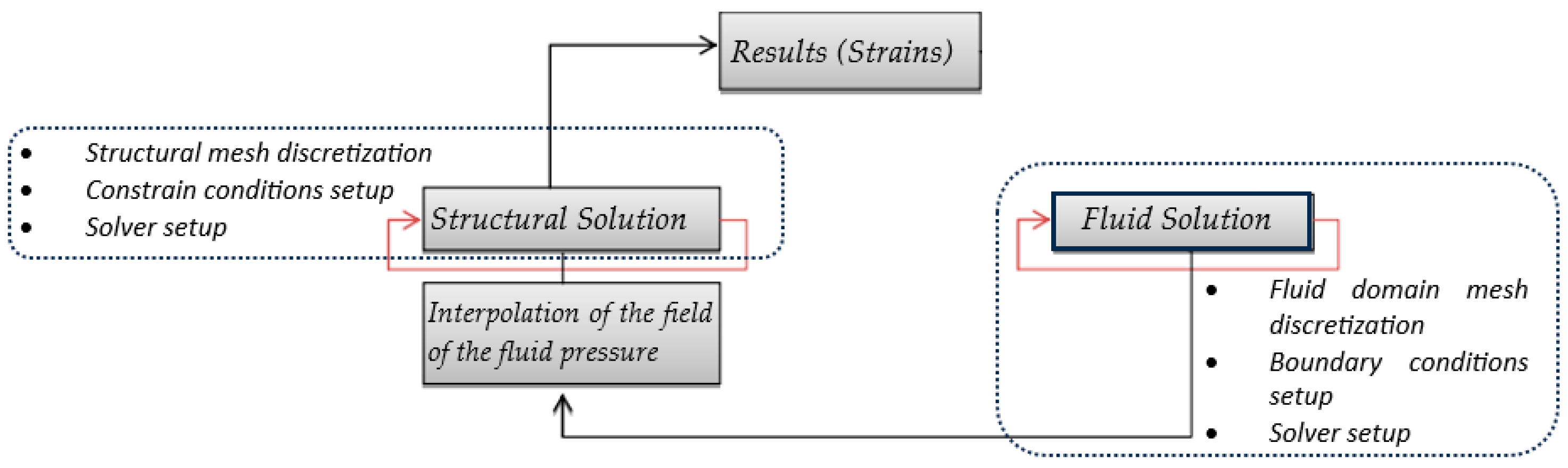
2.3. Model FSI (One-Way)
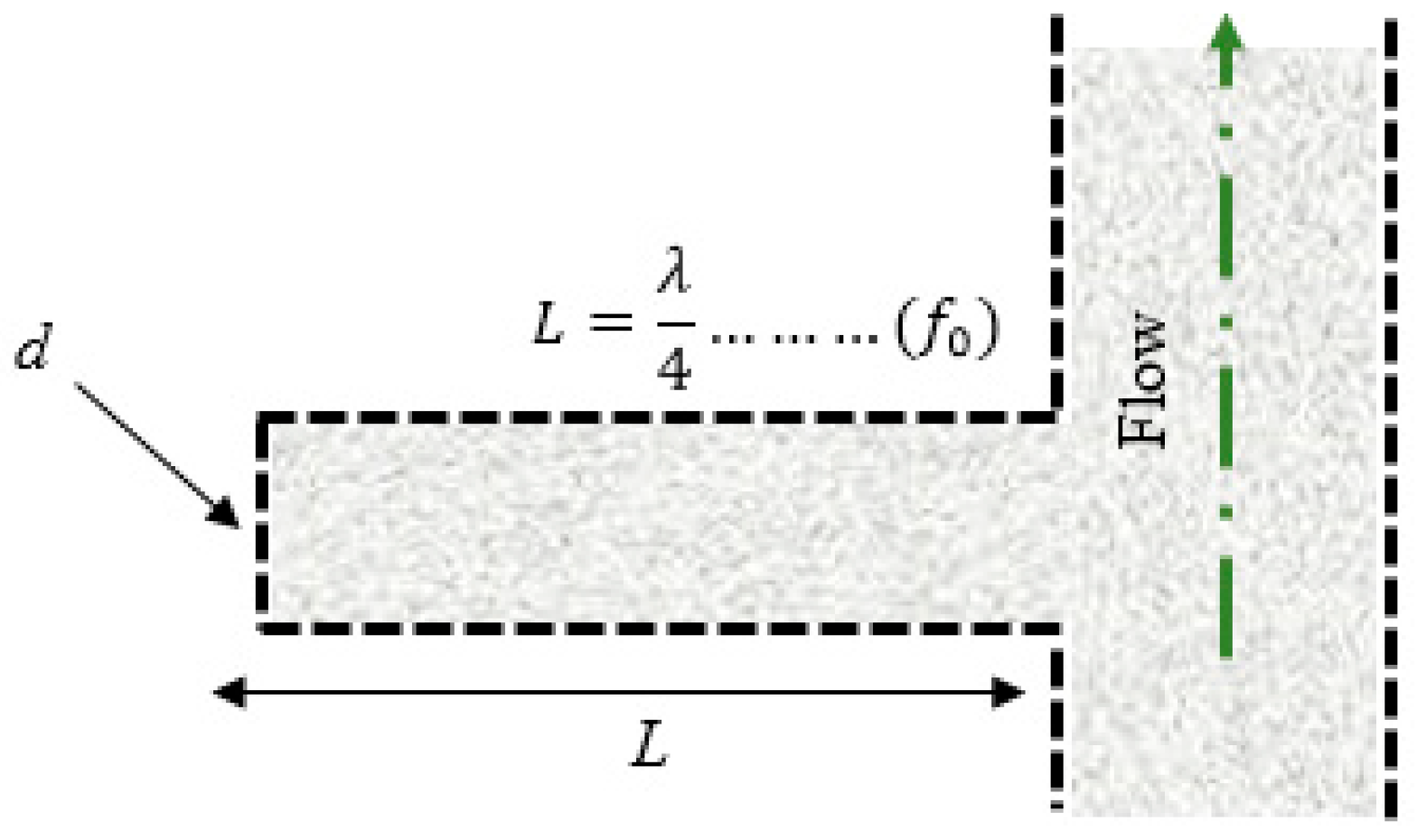
2.4. Quarter Wave Resonator
3. Materials and Methods
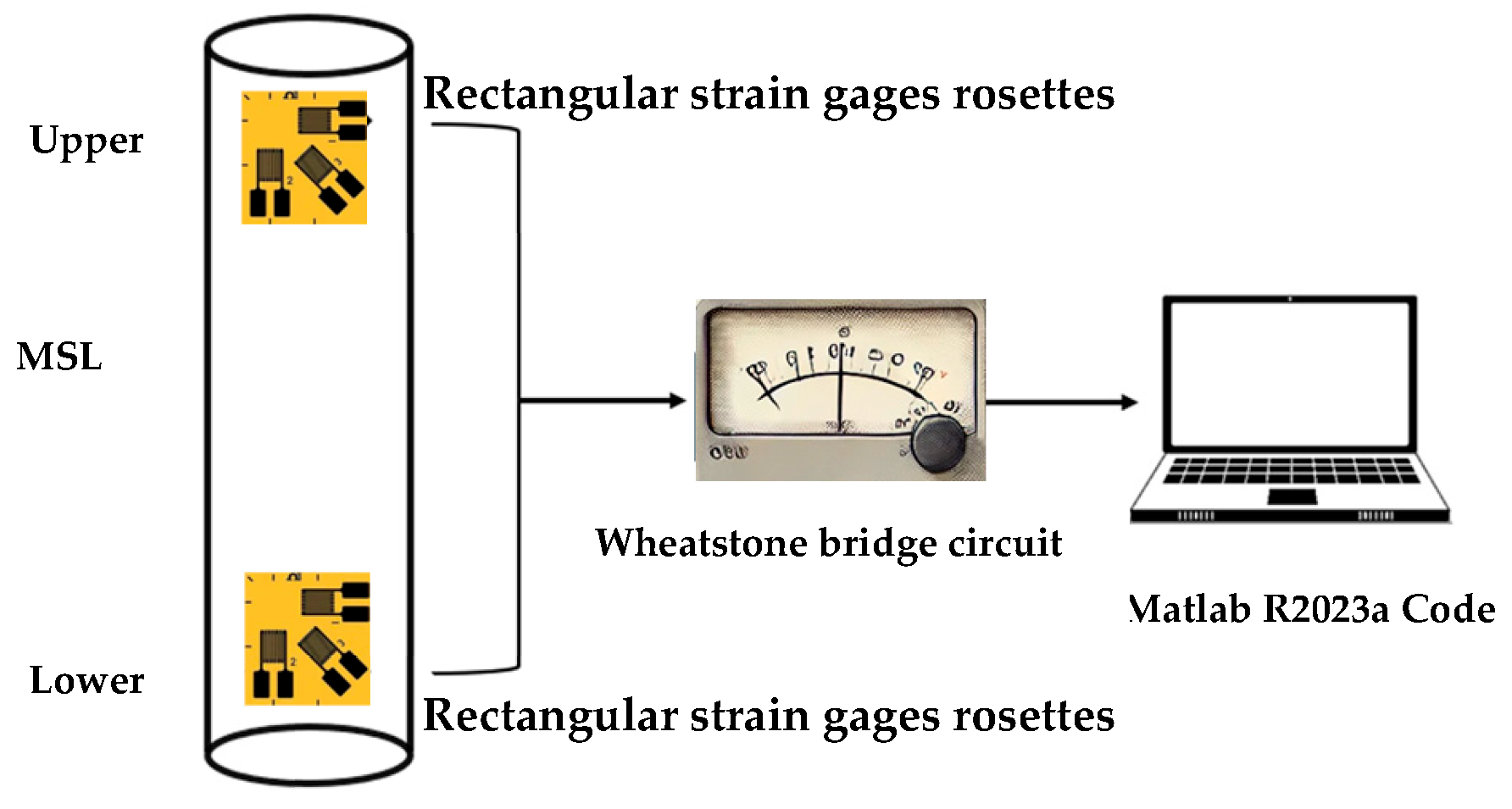
3.1. Experimental Method
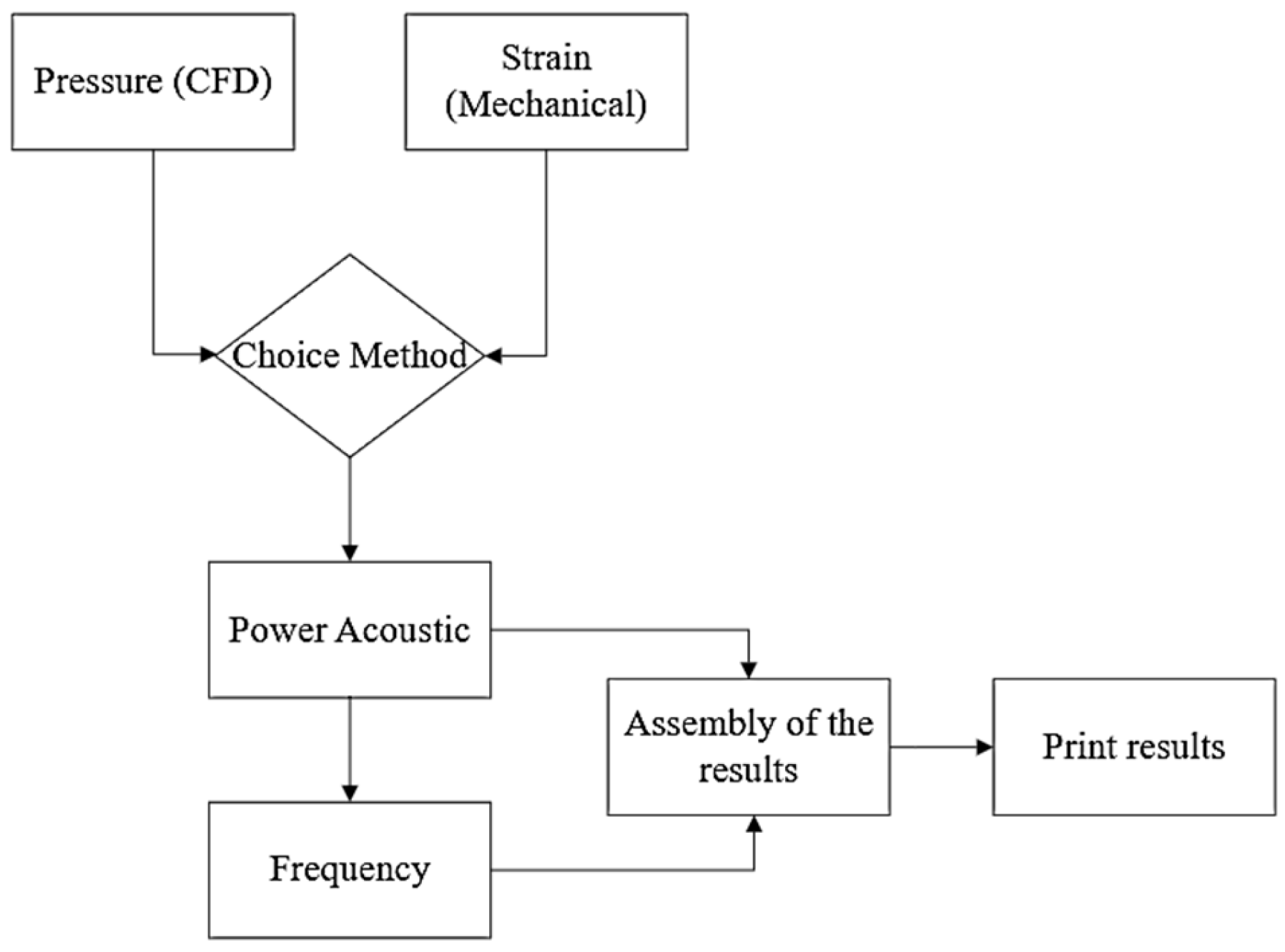
3.2. Computational Method
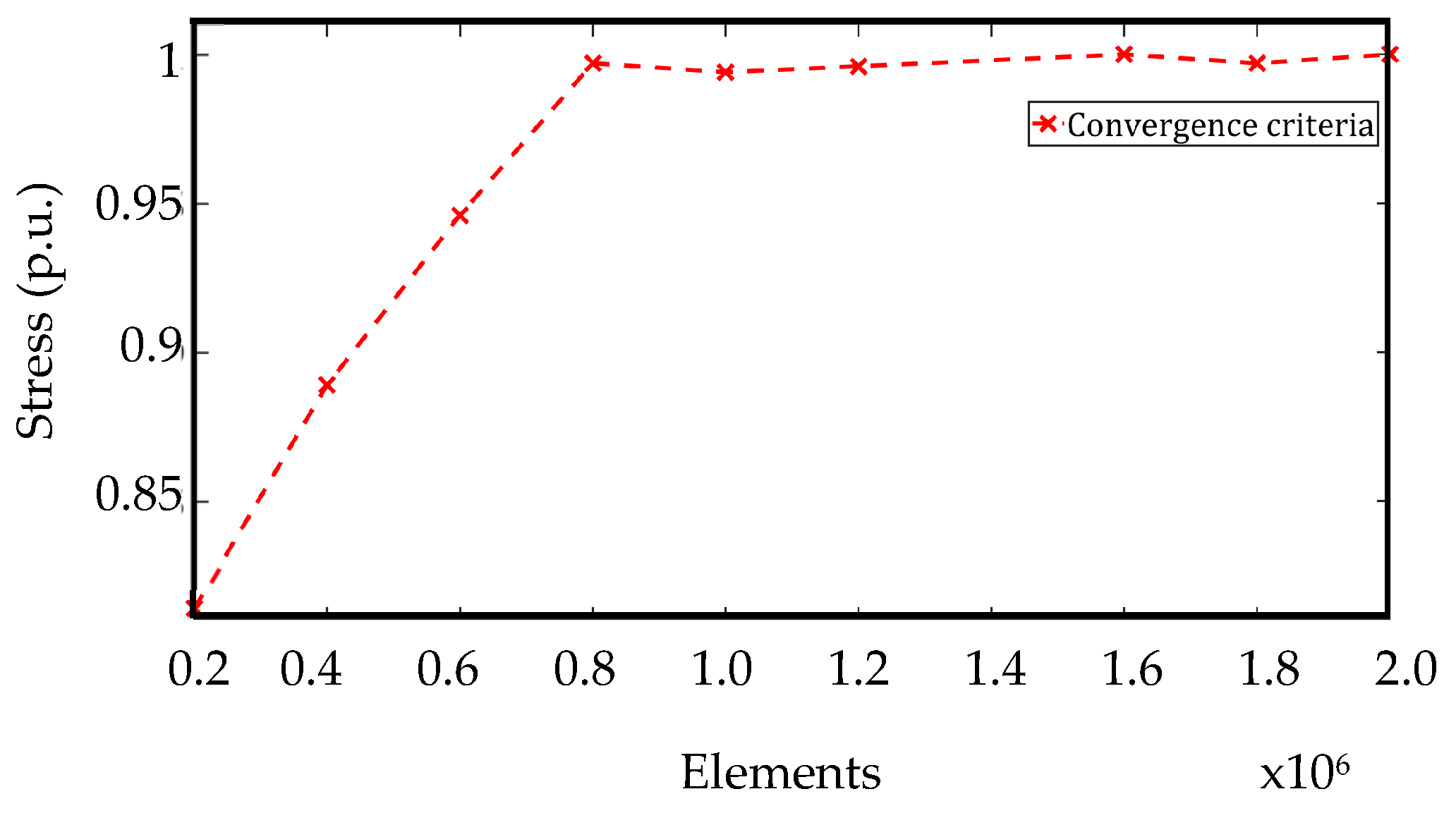
3.3. Convergence Criteria
4. Results
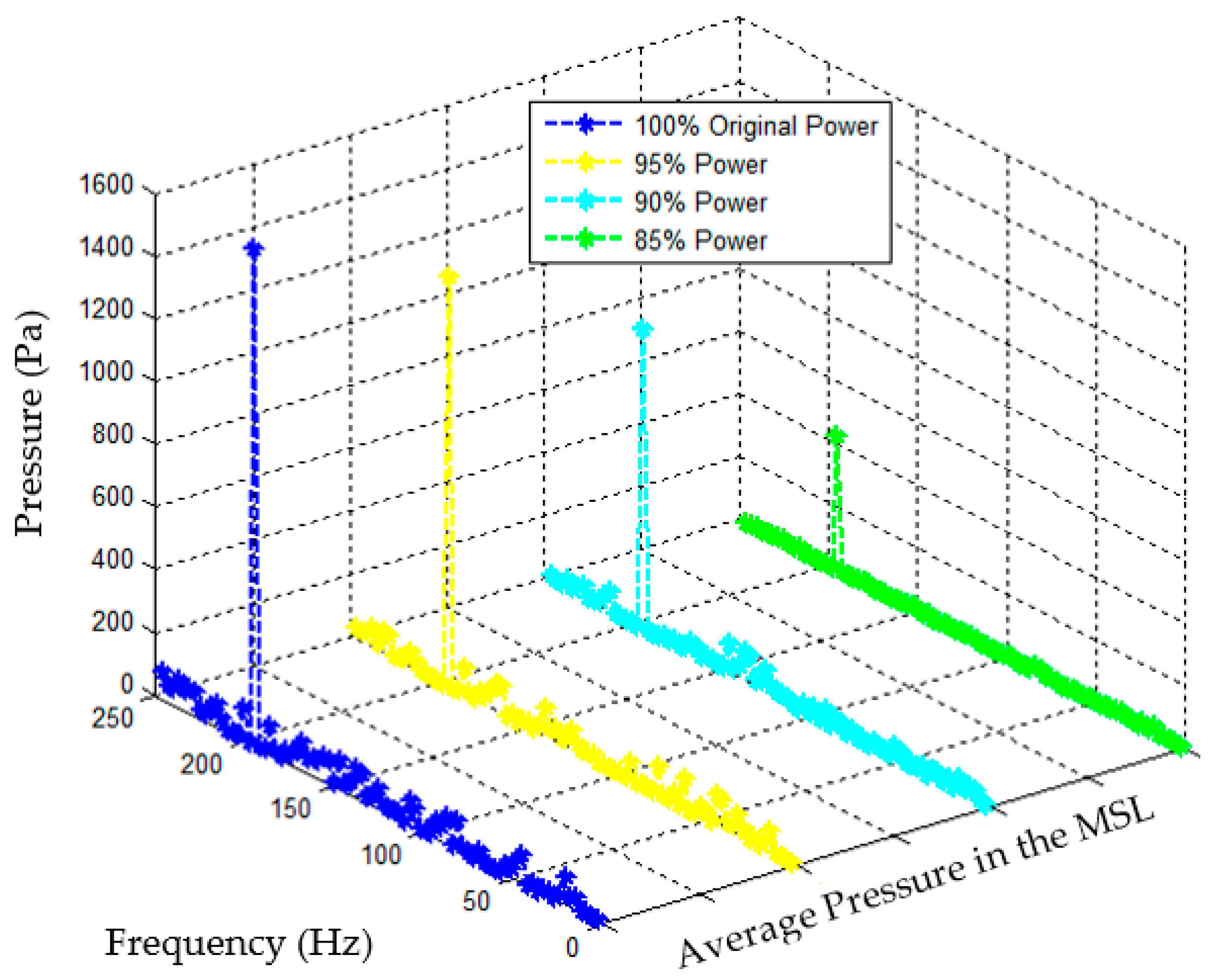
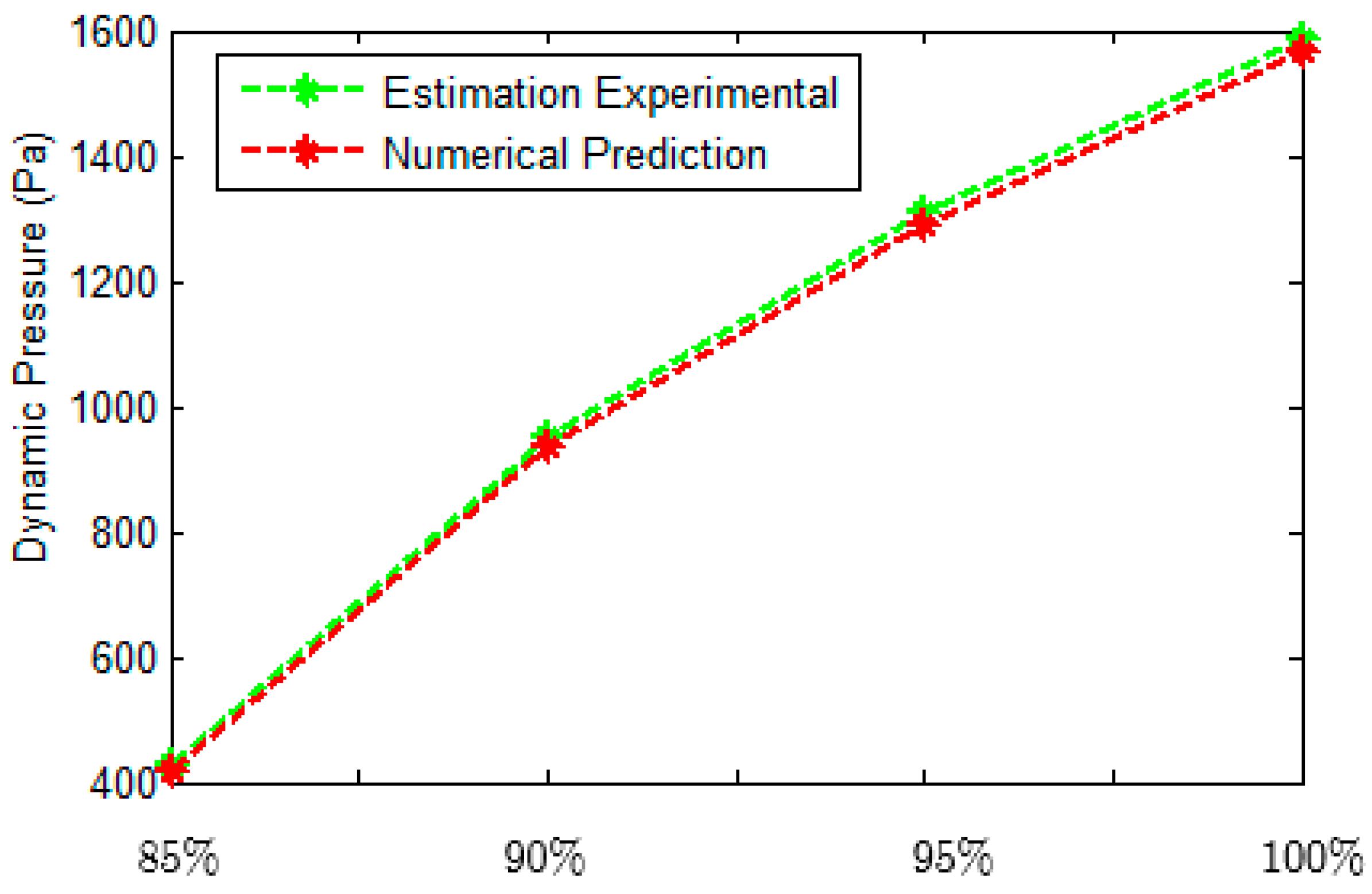
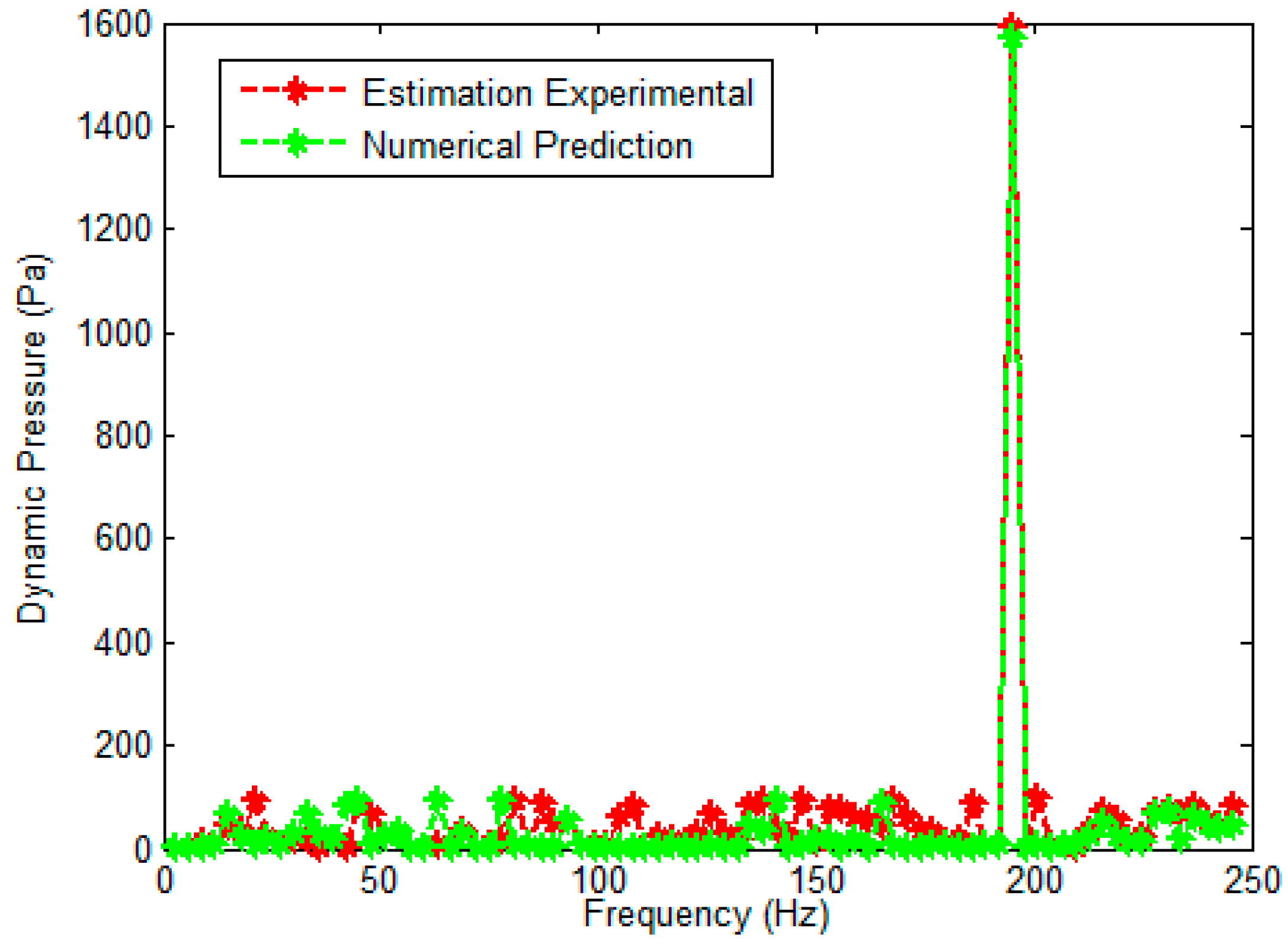
4.1. Estimation Experimental (Scale 1:1)
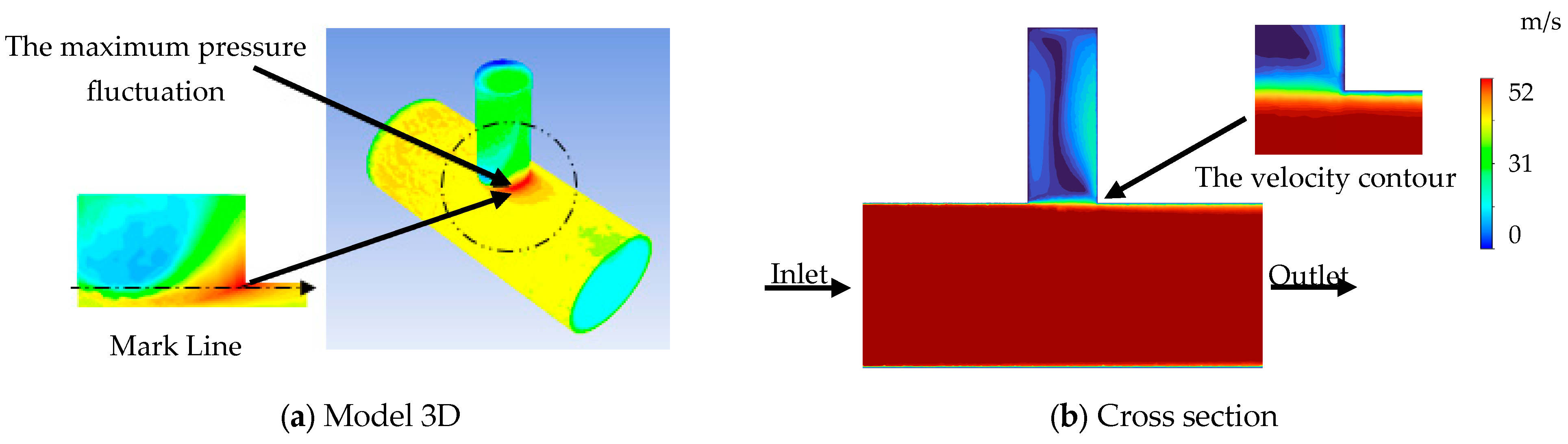
4.2. Numerical Results (Scale 1:8)
4.3. Comparison of the Results (Scale 1:1)
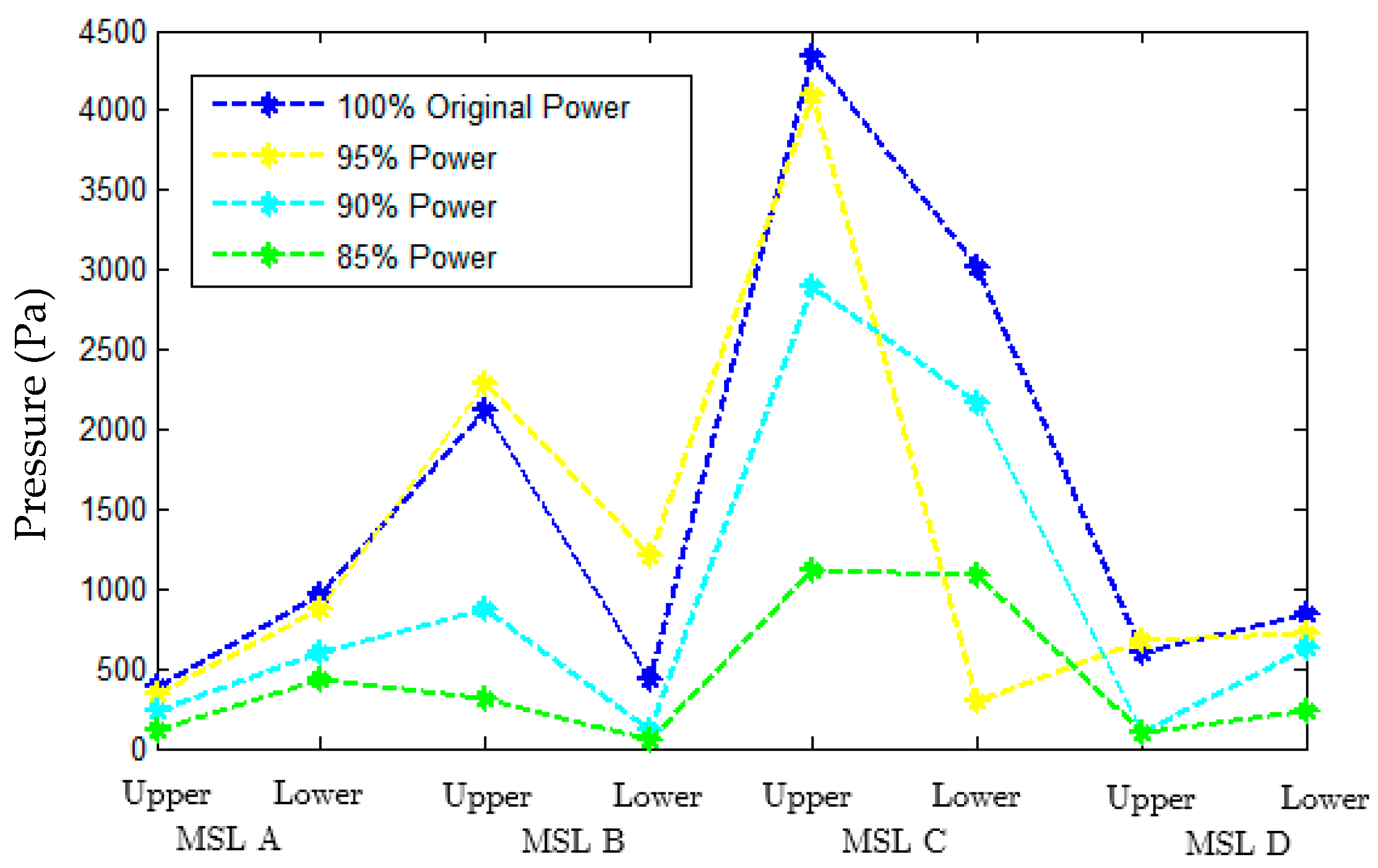
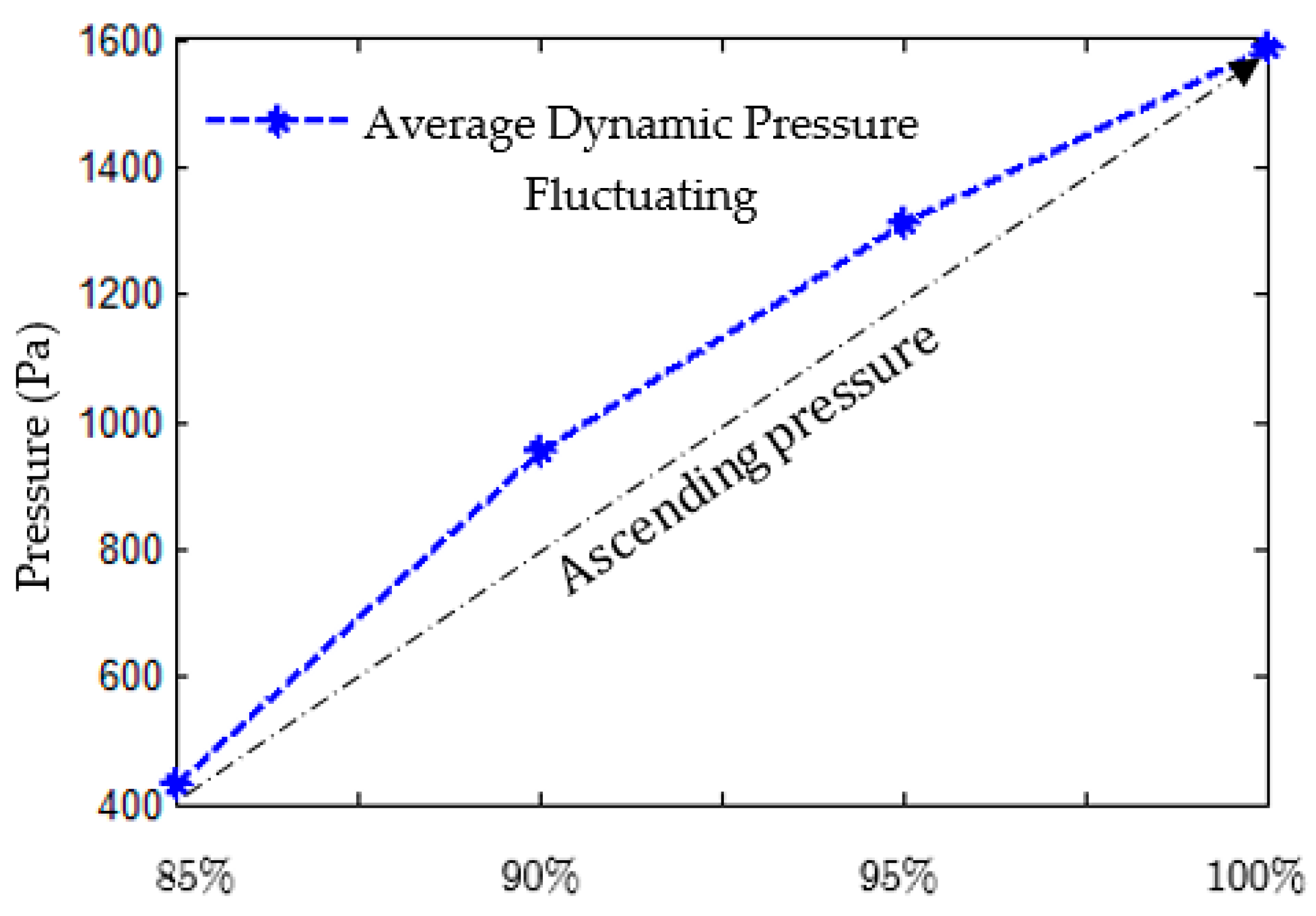
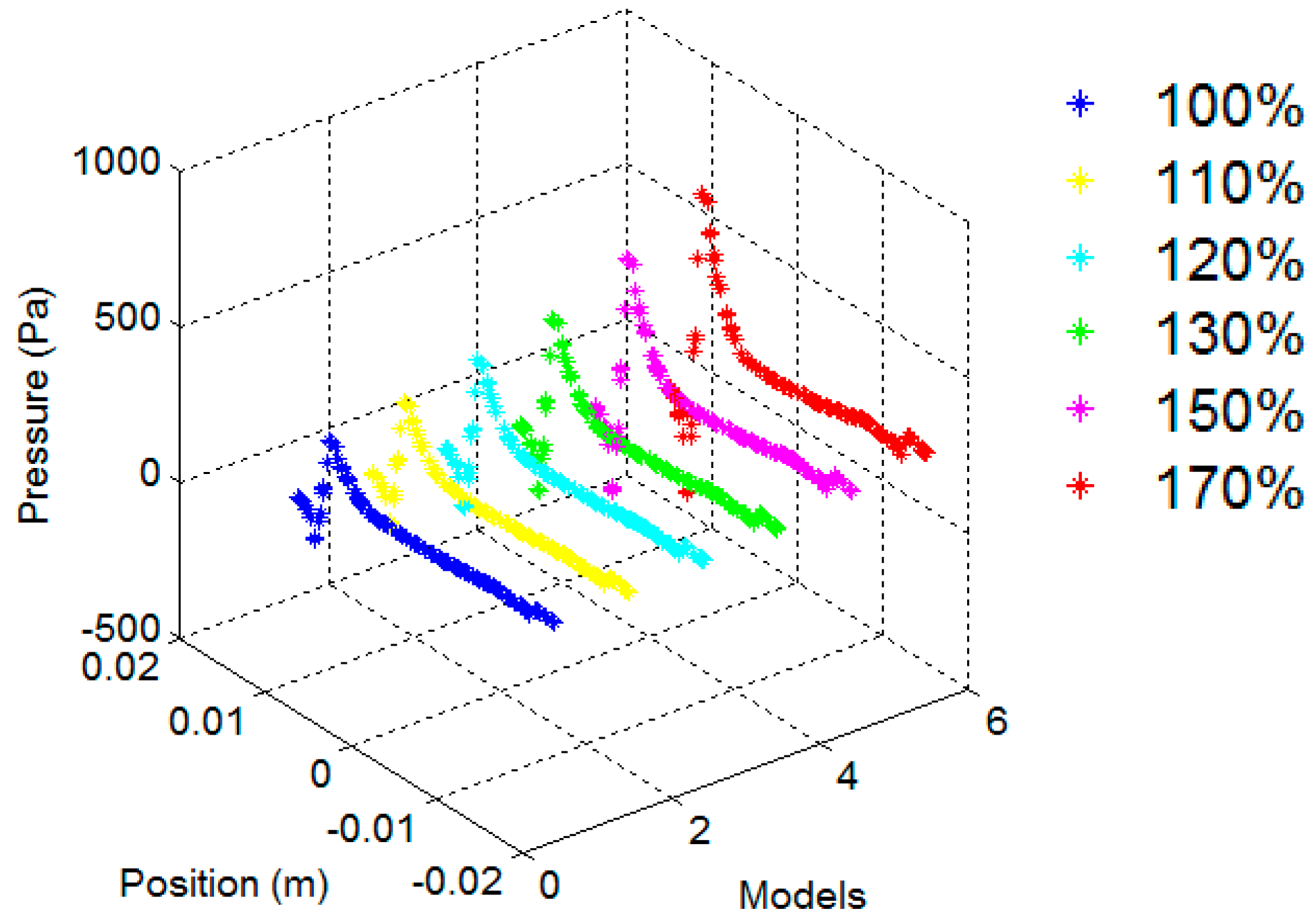
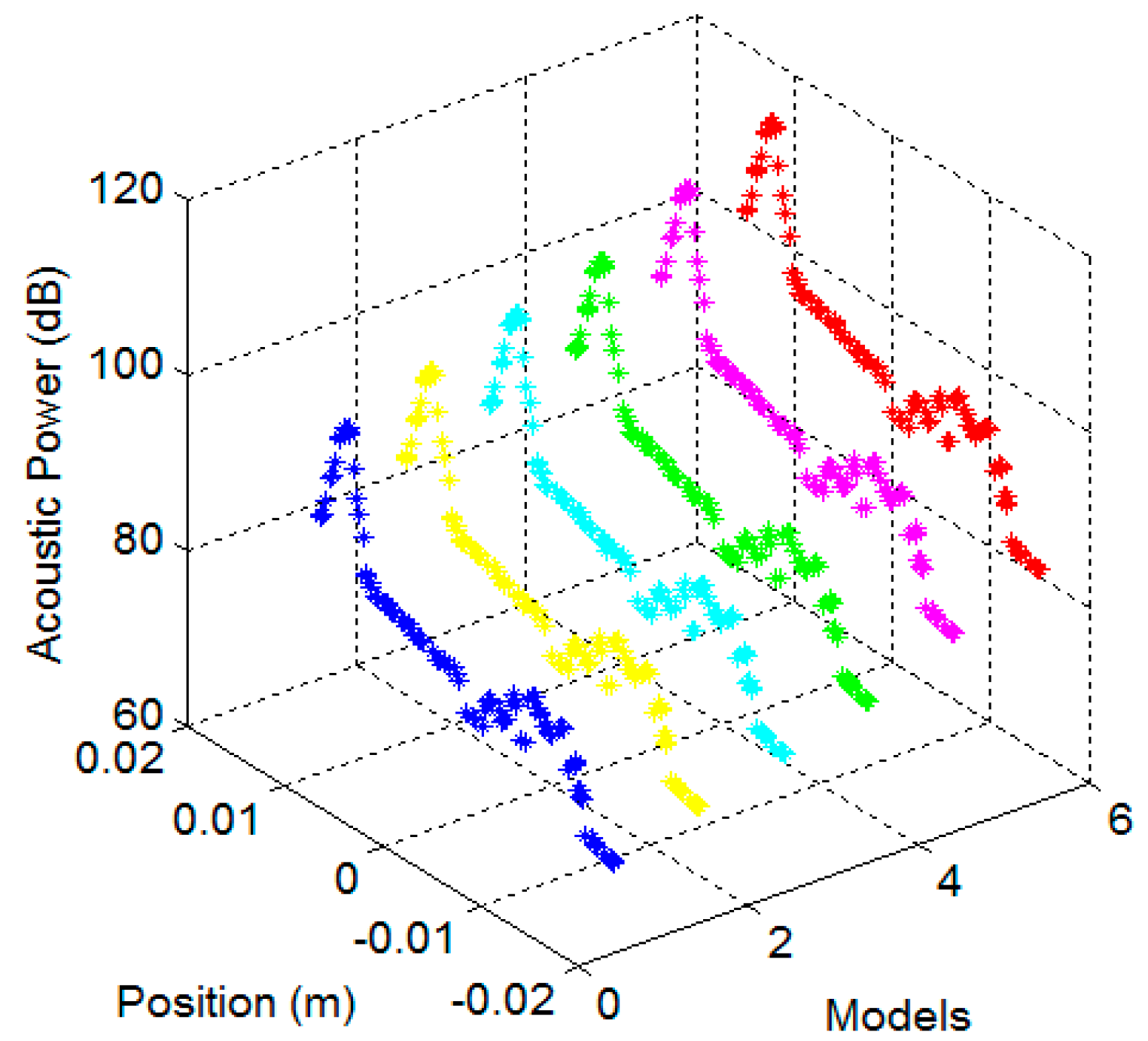
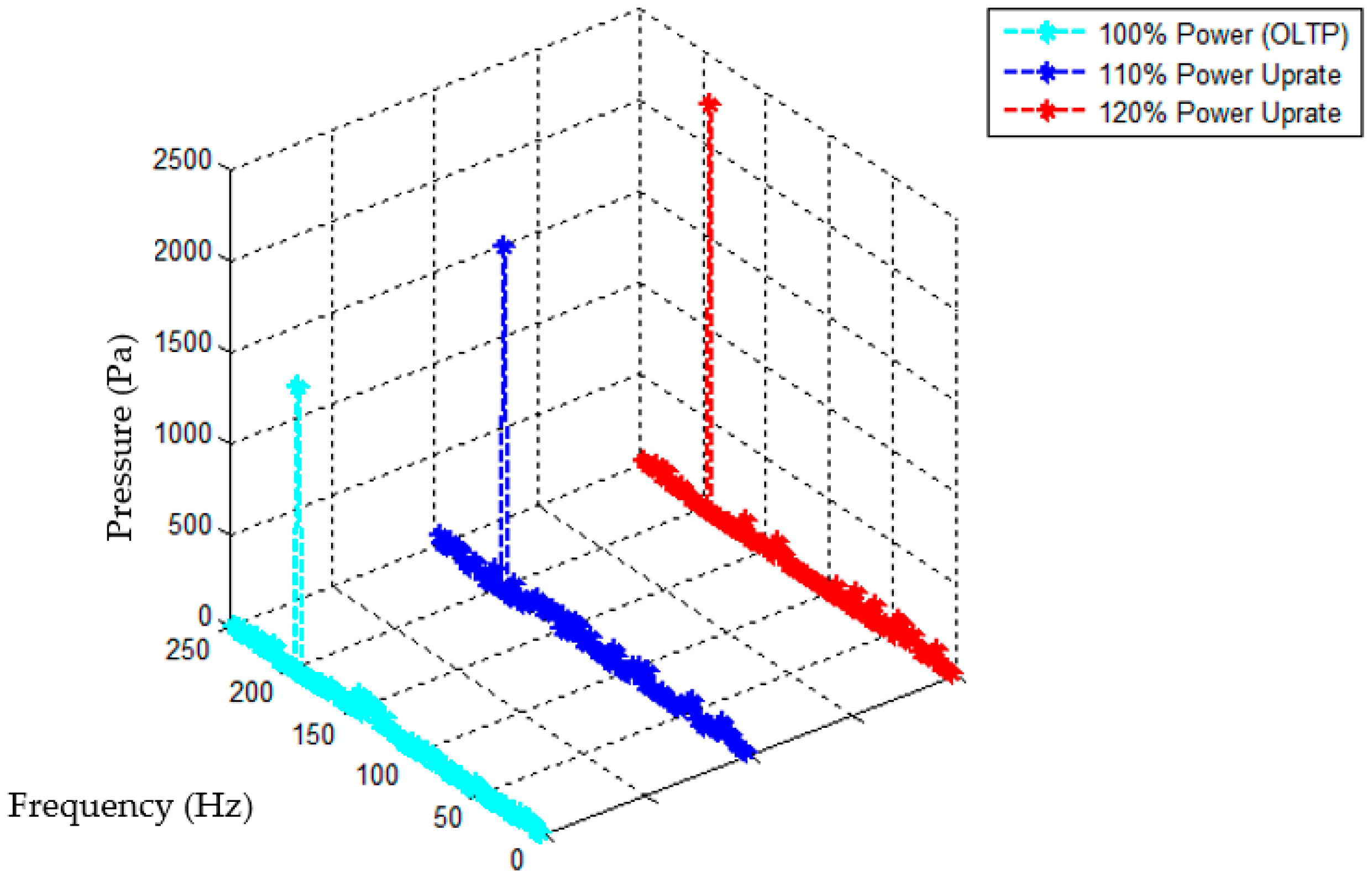
4.4. Prediction of the Power Uprate Condition (Scale 1:1)
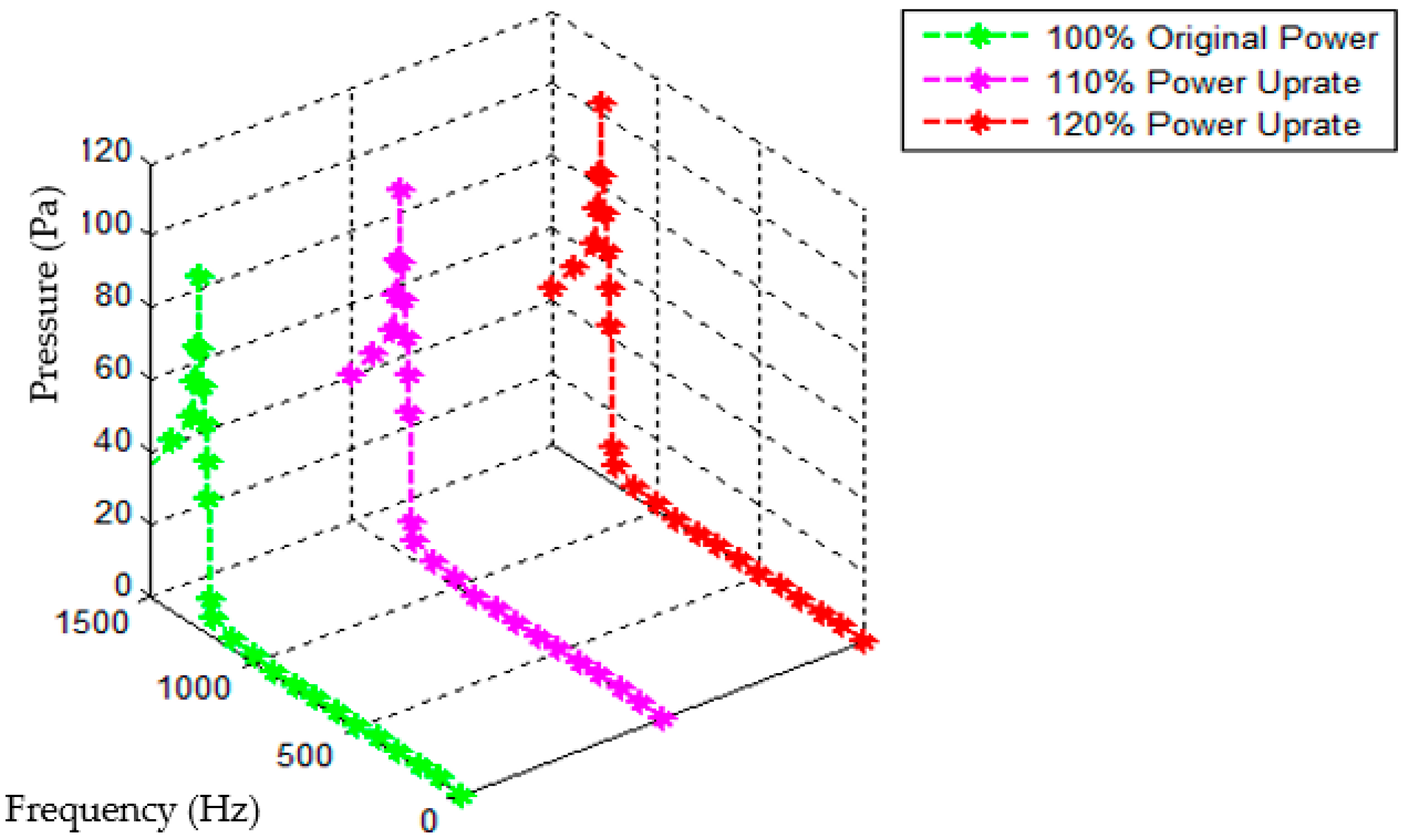
4.5. Prediction of the Power Uprate Condition (Scale 1:8)
4.6. Discussion of the Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morita, R.; Takahashi, S.; Okuyama, K.; Inada, F.; Ogawa, Y.; Yoshikawa, K. Evaluation of acoustic and flow induced vibration of the BWR main steam lines and dryer. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2012, 48, 759–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBoo, G.; Ramsden, K.; Gesior, R.; Strub, B. Identification of Quad Cities main steam line acoustic source and vibration reduction. In Proceedings of the Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference, San Antonio, TX, USA, 22–26 July 2007; Volume 4, pp. 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, A.; Prieto, A.; Espinosa, G. Current status of steam dryer performance under power uprate in Boiling Water Reactors. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2014, 72, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavaraju, C.; Manoly, K.A.; Murphy, M.C.; Jessup, W.T. BWR Steam Dryer Issues and Lessons Learned Related to Flow-Induced Vibration. In Proceedings of the ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference, Paris, France, 14–18 July 2013; Volume 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Moigne, Y.; Andren, A.; Greis, I.; Kornfeldt, H.; Sundlof, P.; Sjunnesson, J.; Karlsson, A.K. BWR Steam Dryer for Extended Power Uprate. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2008, 238, 2106–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo, A.; Hernández, L.H.; Ruiz, P.; Moreno, N.; Urriolagoitia, G.M.; Beltrán, J.A.; Urriolagoitia, G.; Fernández, D. Simulation of the Acoustic Loads Generated in the Intersection of a Main Steam Line and its Safety Relief Valve Branch of a BWR Plant under Extended Power Uprate Conditions. Defect Diffus. Forum 2015, 362, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambric, S.A.; Ziada, S.; Morante, R.J. Overview of Boiling Water Reactor Steam Dryer Alternating Stress Assessment Procedures. ASME J. Nucl. Rad. Sci. 2018, 4, 021002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, A.; Okuyama, K.; Takahashi, S.; Ohtsuka, M. Development of numerical analysis method of flow-acoustic resonance in stub pipes of safety relief valves. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au-Yang, M.K. Flow-Induced Vibration: Guidelines for Design, Diagnosis and Troubleshooting of Common Power Plant Components. ASME J. Press. Vessel. Technol. 1985, 107, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambric, S.A.; Mulcahy, T.M.; Shah, V.N.; Scarbrough, T.; Wu, C. Flow Induced Vibration Effects on Nuclear Power Plant Components Due to Main Steam Line Valve Singing. In Proceedings of the Ninth NRC/ASME Symposium on Valves, Pumps and Inservice Testing, NRC NUREG CP-0152, Washington, DC, USA, 17–19 July 2006; Volume 6. Available online: https://www.nrc.gov/docs/ml0727/ml072700042.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Espinosa-Paredes, G.; Prieto-Guerrero, A.; Núñez-Carrera, A.; Vázquez-Rodríguez, A.; Centeno-Pérez, J.; Espinosa-Martínez, E.-G.; Quezada-García, S.; Cázares-Ramírez, R. Signal analysis of acoustic and flow-induced vibrations of BWR main steam line. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2016, 301, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission. Comprehensive Vibration Assessment Program for Reactor Internals during Preoperational and Initial Startup Testing 3, Regulatory Guide 1.20, Rev.4. 2017. Available online: https://www.nrc.gov/docs/ML1605/ML16056A338.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- NRC. 2002. Failure of Steam Dryer Cover Plate After a Recent Power Uprate. U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission. Washington, DC, NRC Information Notice 2002-26. Available online: https://www.nrc.gov/docs/ML0225/ML022530291.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- NRC. 2013. Programs for Monitoring Boiling-Water Reactor Steam Dryer Integrity. U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission, Washington, DC, NRC Information Notice 2013-10, ADAMS Accession No. ML13003A049. Available online: https://www.nrc.gov/docs/ML1300/ML13003A049.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Brazhenko, V.; Cai, J.-C.; Fang, Y. Utilizing a Transparent Model of a Semi-Direct Acting Water Solenoid Valve to Visualize Diaphragm Displacement and Apply Resulting Data for CFD Analysis. Water 2024, 16, 3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, W.P.; Launder, B.E. The Prediction of Laminarization with a Two-Equation Model of Turbulence. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1972, 15, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazek, J. Turbulence Modelling. In Computational Fluid Dynamics: Principles and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 7, pp. 227–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSYS Fluent User’s Guide, Chapter 15. 2024. Modelling Turbulence, R2, 2061-2161. Available online: https://ansyshelp.ansys.com (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Benra, F.K.; Dohmen, H.J.; Pei, J.; Schuster, S.; Wan, B. A comparison of one-way and two-way coupling methods for numerical analysis of fluid structure interactions. J. Appl. Math. 2011, 2011, 853560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.S. Guidelines for the Instability Flow Velocity of Tube Arrays in Cross-flow. J. Press. Sound Vib. 1984, 93, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziada, S.; Shine, S. Strouhal Numbers of Flow-Excited Acoustic Resonance of Closed Side Branches. J. Fluids Struct. 1999, 13, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziada, S.; Lafon, P. Flow-Excited Acoustic Resonance Excitation Mechanism, Design Guidelines, and Counter Measures. Appl. Mech. 2014, 66, 010802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szasz, G.; Fujikawa, K.K.; Ananth, R. Dynamic Pressure Data Acquisition Via Strain Gage Measurements. In Proceedings of the ASME International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Long Beach, CA, USA, 24–28 September 2005; Volume 1, pp. 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szasz, G.; Fujikawa, K.K.; DeBoo, G. Assessment of Steam Line Dynamic Pressures Using External Strain Gage Measurement. In Proceedings of the ASME 2006 Pressure Vessels and Piping/ICPVT-11, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 23–27 July 2006; Volume 3, pp. 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coloniusa, T.; Lele, S.K. Computational aeroacoustics: Progress on nonlinear problems of sound generation. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2004, 40, 345–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSYS Fluent User’s Guide, Chapter 23.2024. Predicting Aerodynamically Generated Noise, R2, 2659–2701. Available online: https://ansyshelp.ansys.com (accessed on 1 March 2024).



| Pipe length (Lt) | 88.90 mm. | Diameter branch (db) | 12.10 mm. |
| Branch length (Lb) | 138.12 mm. | Pipe thickness (et) | 6.54 mm. |
| Diameter main pipe (dt) | 28.47 mm. | Branch thickness (eb) | 3.17 mm. |
| Velocity (100%) | 47 m/s | Velocity (130%) | 61.1 m/s |
| Velocity (110%) | 51.7 m/s | Velocity (150%) | 70.5 m/s |
| Velocity (120%) | 56.4 m/s | Velocity (170%) | 79.9 m/s |
| Features and Limitations of Numerical Models | CAA Computational Aeroacoustics | Acoustic Analogy (LES and FWH) | Harmonic and Modal Analysis | Broadband Noise Modeling | FSI Coupling [This Work] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Computation cost | Too high | High | Moderate | Low | Low |
| Solution | Transient | Transient | Steady state | Steady state | Steady state |
| Accuracy | Excellent | Best | Good | Limited | Good |
| Fn1:1 (Hz) | Fn1:8 (Hz) | U (m/s) | d1:1 (m) | d1:8 (m) | St |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 195 | 1560 | 47.0 | 0.0968 | 0.0121 | 0.40 |
| 51.7 | 0.36 | ||||
| 56.4 | 0.33 | ||||
| 61.1 | 0.30 | ||||
| 70.5 | 0.26 | ||||
| 79.9 | 0.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ocampo Ramirez, A.; Hernández Gómez, L.H.; Núñez Carrera, A.; Armenta Molina, A.; Fernández Valdés, D.; Escalona Cambray, F.; Guzmán Escalona, M.A. Evaluation of the Acoustic Noise Inside the Main Steam Line of a BWR/5 Nuclear Reactor. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3974. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073974
Ocampo Ramirez A, Hernández Gómez LH, Núñez Carrera A, Armenta Molina A, Fernández Valdés D, Escalona Cambray F, Guzmán Escalona MA. Evaluation of the Acoustic Noise Inside the Main Steam Line of a BWR/5 Nuclear Reactor. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(7):3974. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073974
Chicago/Turabian StyleOcampo Ramirez, Arturo, Luis Héctor Hernández Gómez, Alejandro Núñez Carrera, Alejandra Armenta Molina, Dayvis Fernández Valdés, Felipe Escalona Cambray, and Marcos Adrián Guzmán Escalona. 2025. "Evaluation of the Acoustic Noise Inside the Main Steam Line of a BWR/5 Nuclear Reactor" Applied Sciences 15, no. 7: 3974. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073974
APA StyleOcampo Ramirez, A., Hernández Gómez, L. H., Núñez Carrera, A., Armenta Molina, A., Fernández Valdés, D., Escalona Cambray, F., & Guzmán Escalona, M. A. (2025). Evaluation of the Acoustic Noise Inside the Main Steam Line of a BWR/5 Nuclear Reactor. Applied Sciences, 15(7), 3974. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073974






