Medical Image Segmentation Network Based on Dual-Encoder Interactive Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
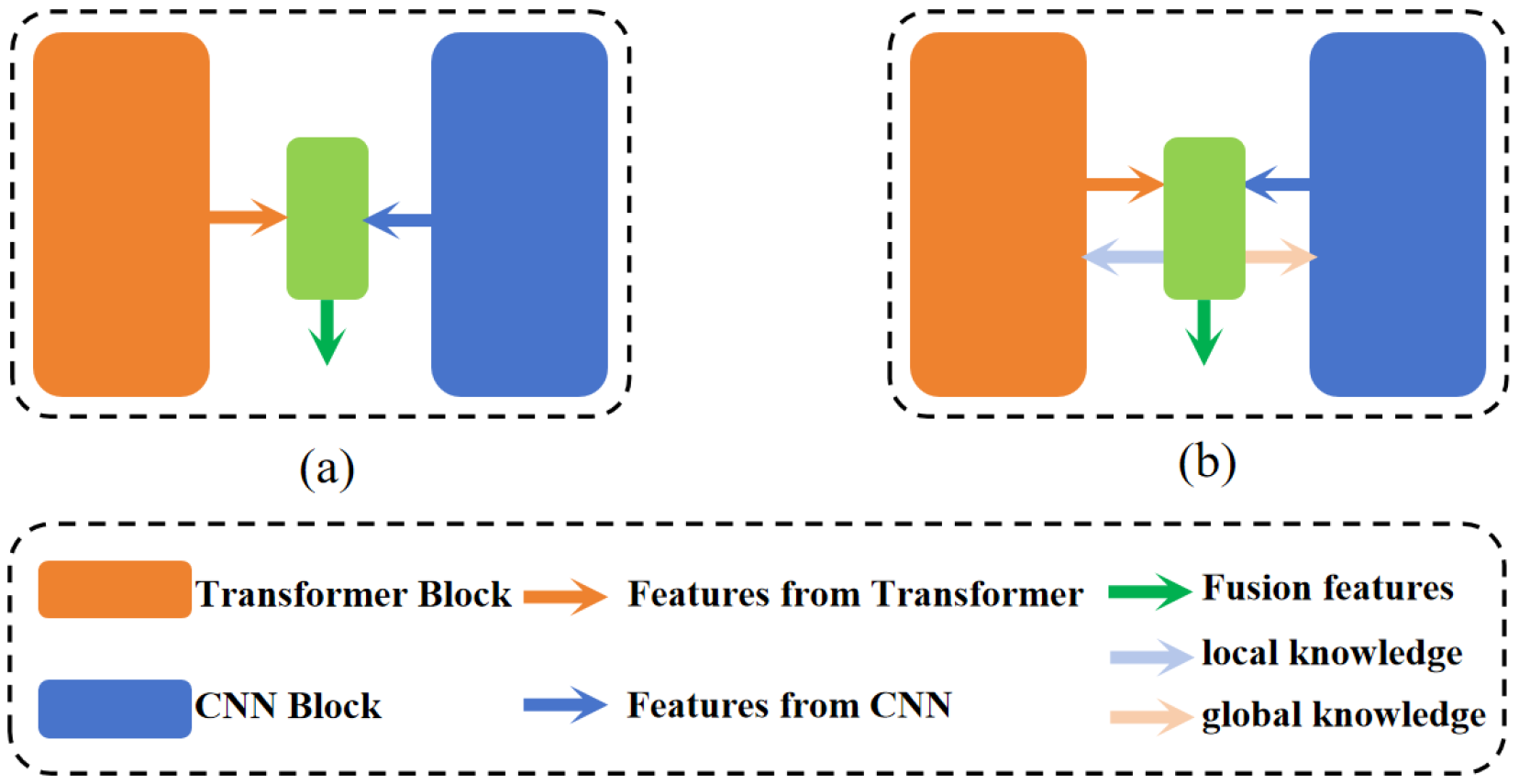
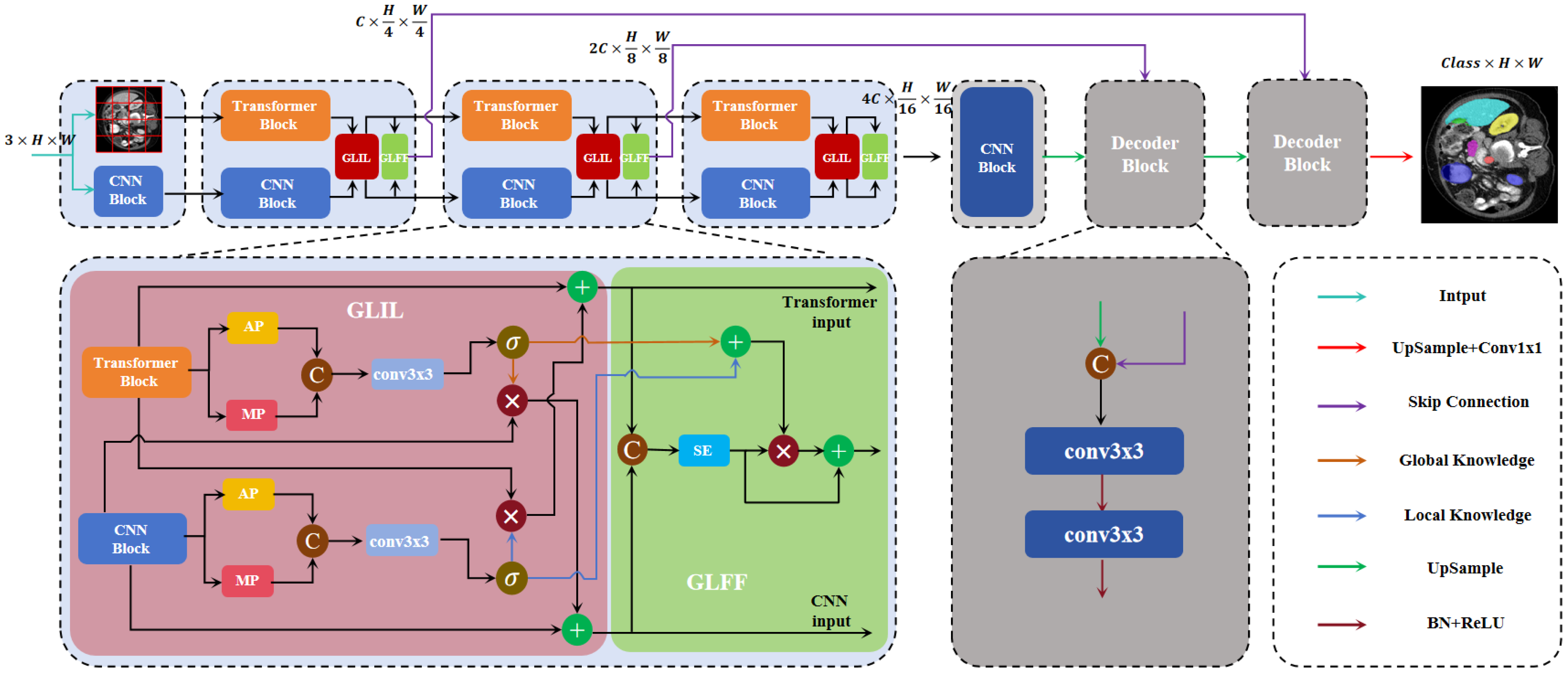
- The introduction of a novel network, DEFI-Net, notably enhancing the MIS performance through Transformer–CNN interactive learning. This interaction is facilitated by the GLIL module. The GLIL module consists of two parallel spatial attention modules: one module extracts global semantic information from the features of the Transformer encoder while the other captures local detail information from the features of the CNN encoder. Effective interaction between the two encoders is achieved by using the global semantic information to weight the features from the CNN encoder and refining the features from the Transformer encoder with local detail information.
- The development of a GLFF module that utilizes the global semantic information and local detail information produced by the GLIL module to integrate features from both the Transformer and CNN encoders. The GLFF module concatenates the features from the two encoders and employs a channel attention mechanism to enhance relevant channel features while suppressing less significant ones. The global semantic and local detail information from the GLIL module is then used to weight the concatenated features, resulting in a more precise feature representation.
- An evaluation of the robustness and generalizability of the proposed network through extensive experiments on three distinct medical image datasets: the Synapse multi-organ dataset, the ACDC cardiac dataset, and the Kvasir-SEG dataset. The experimental results demonstrate significant improvements over several existing MIS methods, thus further validating the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
2. Related Work
2.1. CNN for MIS
2.2. Vision Transformer for MIS
2.3. Combining CNN and Transformer for MIS
2.4. Channels and Spatial Attention Mechanisms
3. Methodology
3.1. Transformer–CNN Dual-Encoder
3.2. Global–Local Interaction Learning Module
3.3. Global–Local Feature Fusion Module
3.4. Loss Function
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Implementation Details
4.2. Datasets
4.2.1. Synapse Multi-Organ Segmentation
4.2.2. Automated Cardiac Diagnosis Challenge (ACDC) Segmentation
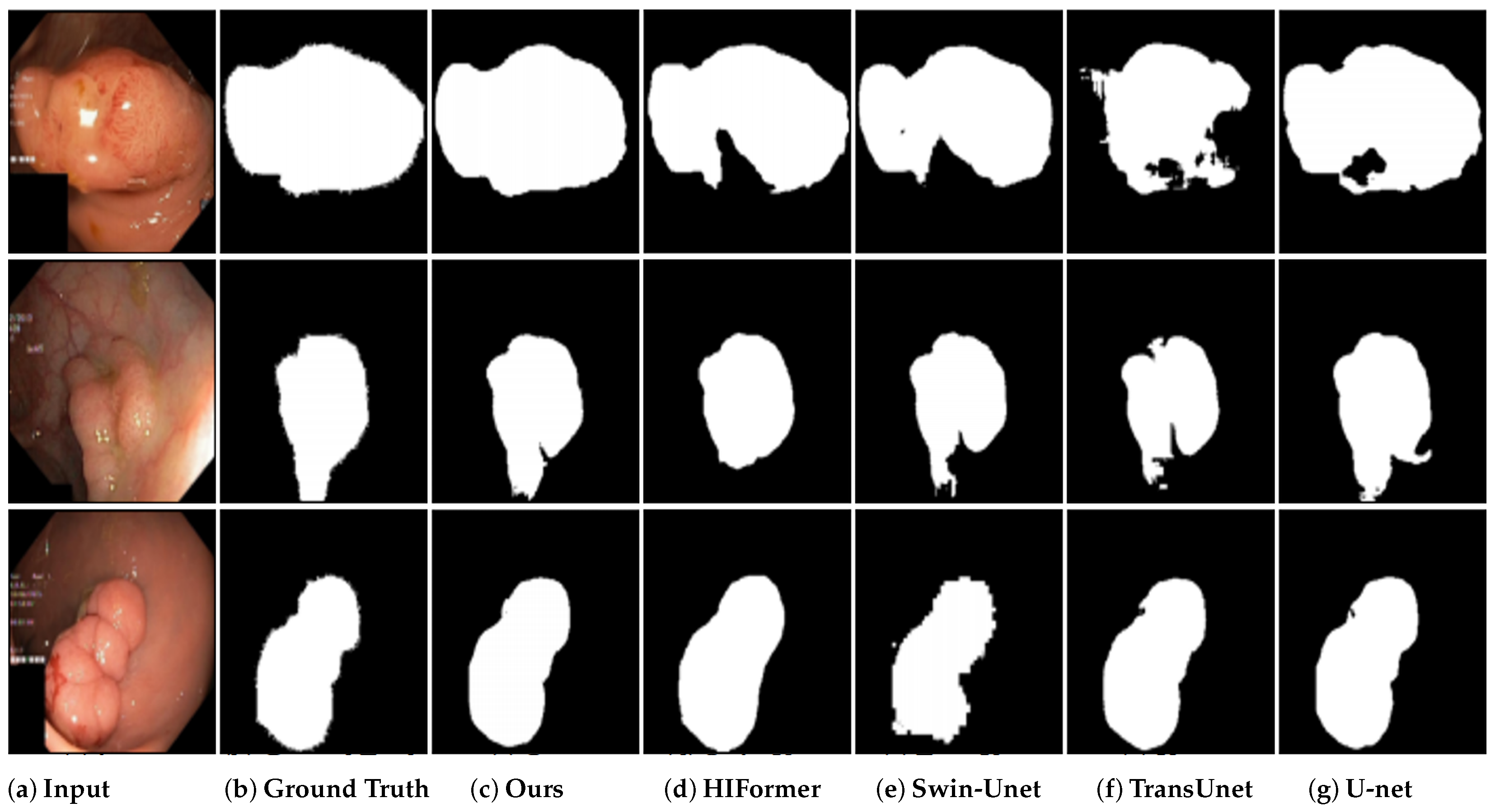
4.2.3. Kvasir-SEG Dataset
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
4.3.1. Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) and Intersection over Union (IoU)
4.3.2. Hausdorff Distance at the 95th Percentile (HD95)
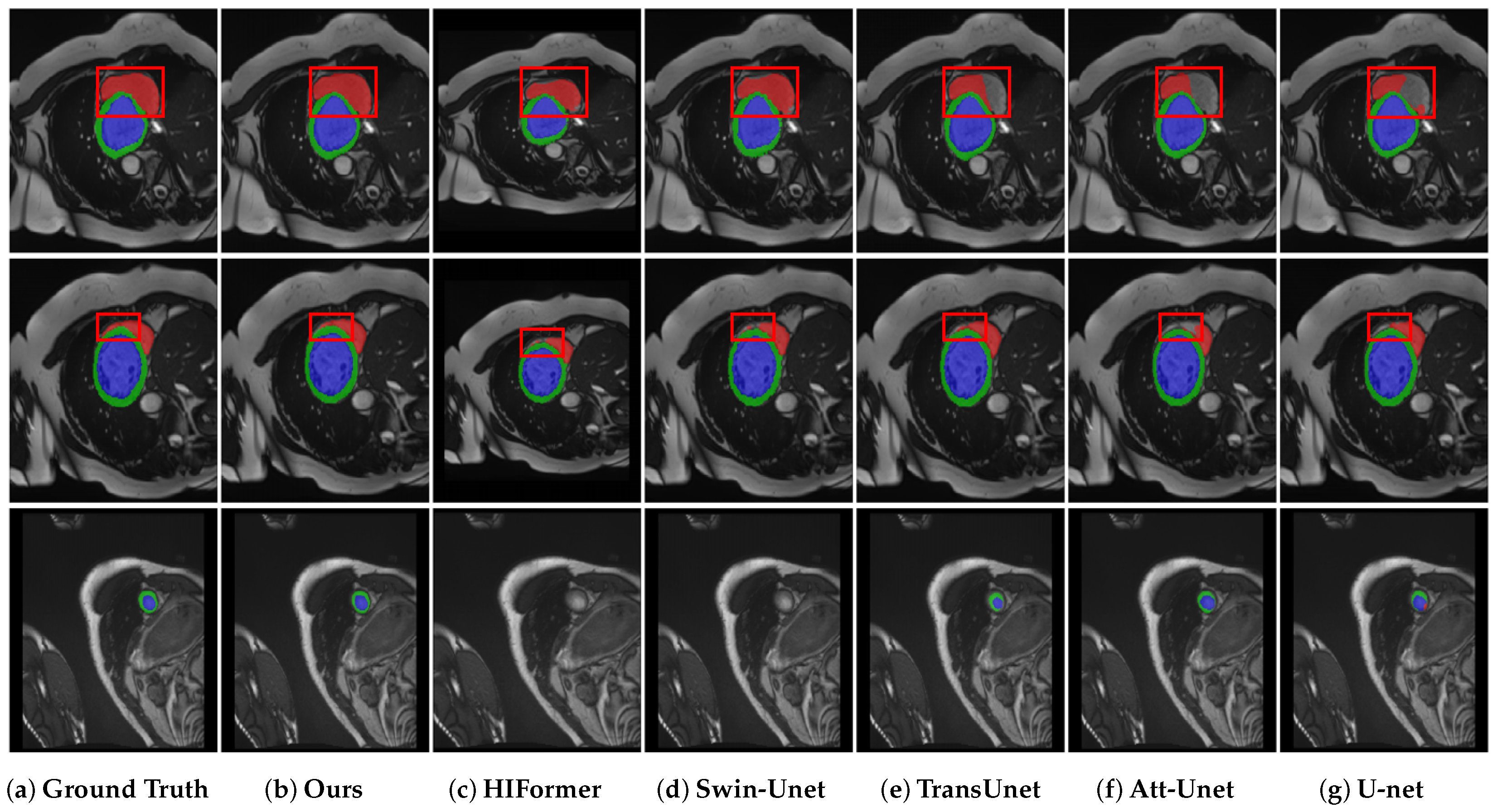
4.4. Results on Synapse Multi-Organ Segmentation
4.5. Results on ACDC Segmentation
4.6. Results on Kvasir-SEG Segmentation
4.7. Ablation Experiments
4.8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; proceedings, part III 18; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Milletari, F.; Navab, N.; Ahmadi, S.A. V-net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D vision (3DV), Stanford, CA, USA, 25–28 October 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 565–571. [Google Scholar]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Folgoc, L.L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B.; et al. Attention u-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Ma, Z.; Na, H.; Duan, W. DCSAU-Net: A deeper and more compact split-attention U-Net for medical image segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 154, 106626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, D.; Dong, C.; Yan, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Xu, S. I2U-Net: A dual-path U-Net with rich information interaction for medical image segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2024, 97, 103241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shamshad, F.; Khan, S.; Zamir, S.W.; Khan, M.H.; Hayat, M.; Khan, F.S.; Fu, H. Transformers in medical imaging: A survey. Med. Image Anal. 2023, 88, 102802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, Q.; Xi, Z.; Yin, S.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, L. Advantages of transformer and its application for medical image segmentation: A survey. Biomed. Eng. Online 2024, 23, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirunavukarasu, R.; Kotei, E. A comprehensive review on transformer network for natural and medical image analysis. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2024, 53, 100648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Gan, C.; Li, Z.; Rekik, I.; Yin, Z.; Ji, W.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Shen, D. Transformers in medical image analysis. Intell. Med. 2023, 3, 59–78. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, D.; Vasylechko, S.D.; Gholipour, A. Convolution-free medical image segmentation using transformers. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2021: 24th International Conference, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021; proceedings, part I 24; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 78–88. [Google Scholar]
- Alexey, D. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Naseer, M.; Hayat, M.; Zamir, S.W.; Khan, F.S.; Shah, M. Transformers in vision: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2022, 54, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvaiz, A.; Khalid, M.A.; Zafar, R.; Ameer, H.; Ali, M.; Fraz, M.M. Vision Transformers in medical computer vision—A contemplative retrospection. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 122, 106126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touvron, H.; Cord, M.; Douze, M.; Massa, F.; Sablayrolles, A.; Jégou, H. Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; PMLR: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 10347–10357. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Xie, E.; Li, X.; Fan, D.P.; Song, K.; Liang, D.; Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Shao, L. Pyramid vision transformer: A versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 568–578. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Q.; Wang, M. Swin-unet: Unet-like pure transformer for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 205–218. [Google Scholar]
- Azad, R.; Heidari, M.; Shariatnia, M.; Aghdam, E.K.; Karimijafarbigloo, S.; Adeli, E.; Merhof, D. Transdeeplab: Convolution-free transformer-based deeplab v3+ for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the InternationalWorkshop on PRedictive Intelligence in MEdicine, Singapore, 22 September 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 91–102. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Deng, Z.; Li, D.; Yuan, X.; Fu, Y. Missformer: An effective transformer for 2d medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2022, 42, 1484–1494. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Adeli, E.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuille, A.L.; Zhou, Y. Transunet: Transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.04306. [Google Scholar]
- Azad, R.; Jia, Y.; Aghdam, E.K.; Cohen-Adad, J.; Merhof, D. Enhancing medical image segmentation with TransCeption: A multi-scale feature fusion approach. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.10847. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Hu, Q. Transfuse: Fusing transformers and cnns for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2021: 24th International Conference, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021; proceedings, Part I 24; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, F.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, Z. An effective CNN and Transformer complementary network for medical image segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 136, 109228. [Google Scholar]
- Heidari, M.; Kazerouni, A.; Soltany, M.; Azad, R.; Aghdam, E.K.; Cohen-Adad, J.; Merhof, D. Hiformer: Hierarchical multi-scale representations using transformers for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 2–7 January 2023; pp. 6202–6212. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, D.; Smedsrud, P.; Riegler, M.; Halvorsen, P.; De Lange, T.; Johansen, D.; Johansen, H. Kvasir-SEG: A Segmented Polyp Dataset. In MultiMedia Modeling; MMM 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; p. 11962. [Google Scholar]
- Bernard, O.; Lalande, A.; Zotti, C.; Cervenansky, F.; Yang, X.; Heng, P.A.; Cetin, I.; Lekadir, K.; Camara, O.; Ballester, M.A.G.; et al. Deep learning techniques for automatic MRI cardiac multi-structures segmentation and diagnosis: Is the problem solved? IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 2514–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landman, B.; Xu, Z.; Igelsias, J.; Styner, M.; Langerak, T.; Klein, A. Miccai multi-atlas labeling beyond the cranial vault–workshop and challenge. In Proceedings of the MICCAI Multi-Atlas Labeling Beyond Cranial Vault—Workshop Challenge, Munich, Germany, 9 October 2015; Volume 5, p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Rahman Siddiquee, M.M.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: A nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support: 4th International Workshop, DLMIA 2018, and 8th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2018, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2018, Granada, Spain, 20 September 2018; Proceedings 4; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Lin, L.; Tong, R.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Iwamoto, Y.; Han, X.; Chen, Y.W.; Wu, J. Unet 3+: A full-scale connected unet for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1055–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, A.; Dolz, J. Multi-scale self-guided attention for medical image segmentation. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 25, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.; Lian, S.; Luo, Z.; Li, S. Weighted res-unet for high-quality retina vessel segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 9th International Conference on Information Technology in Medicine and Education (ITME), Hangzhou, China, 19–21 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 327–331. [Google Scholar]
- Ibtehaz, N.; Rahman, M.S. MultiResUNet: Rethinking the U-Net architecture for multimodal biomedical image segmentation. Neural Netw. 2020, 121, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, A.; Chen, B.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, G.; Zhang, D. Ds-transunet: Dual swin transformer u-net for medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Hatamizadeh, A.; Tang, Y.; Nath, V.; Yang, D.; Myronenko, A.; Landman, B.; Roth, H.R.; Xu, D. Unetr: Transformers for 3d medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Virtual, 3–8 January 2022; pp. 574–584. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Zhou, M.; Metaxas, D.N. UTNet: A hybrid transformer architecture for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2021: 24th International Conference, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021; Proceedings, Part III 24; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- Manzari, O.N.; Kaleybar, J.M.; Saadat, H.; Maleki, S. BEFUnet: A Hybrid CNN-Transformer Architecture for Precise Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.08793. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar]
- Jaderberg, M.; Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Spatial transformer networks. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2015, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Azad, R.; Al-Antary, M.T.; Heidari, M.; Merhof, D. Transnorm: Transformer provides a strong spatial normalization mechanism for a deep segmentation model. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 108205–108215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, R.; Arimond, R.; Aghdam, E.K.; Kazerouni, A.; Merhof, D. Dae-former: Dual attention-guided efficient transformer for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the InternationalWorkshop on PRedictive Intelligence in MEdicine, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8 October 2023; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 83–95. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Kaul, C.; Wang, J.; Anagnostopoulos, C.; Murray-Smith, R.; Deligianni, F. Optimizing vision transformers for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023-2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]


| Methods | DSC (%) ↑ | HD (mm) ↓ | Aorta | Gallbladder | Kidney (L) | Kidney (R) | Liver | Pancreas | Spleen | Stomach |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V-Net [2] | 68.81 | - | 75.34 | 51.87 | 77.10 | 80.75 | 87.84 | 40.05 | 80.56 | 56.98 |
| U-net [1] | 76.85 | 39.70 | 89.07 | 69.72 | 77.77 | 68.60 | 93.43 | 53.98 | 86.67 | 75.58 |
| Att-Unet [3] | 77.77 | 36.02 | 89.55 | 68.88 | 77.98 | 71.11 | 93.57 | 58.04 | 87.30 | 75.75 |
| Res-Unet [32] | 78.56 | 22.51 | 87.95 | 53.44 | 84.89 | 87.38 | 93.74 | 52.56 | 90.65 | 78.21 |
| TransUnet [20] | 77.48 | 31.69 | 87.23 | 63.13 | 81.87 | 77.02 | 94.08 | 55.86 | 85.08 | 75.62 |
| TransNorm [42] | 78.40 | 30.25 | 86.23 | 65.10 | 82.18 | 78.63 | 94.22 | 55.34 | 89.50 | 76.01 |
| CTC–Net [23] | 78.41 | - | 86.46 | 63.53 | 83.71 | 80.79 | 93.78 | 59.73 | 86.87 | 72.39 |
| Swin U-Net [17] | 79.13 | 21.55 | 85.47 | 66.53 | 83.28 | 79.61 | 94.29 | 56.58 | 90.66 | 76.60 |
| TransDeepLab [18] | 80.16 | 21.25 | 86.04 | 69.16 | 84.08 | 79.88 | 93.53 | 61.19 | 89.00 | 78.40 |
| TransFuse [22] | 80.31 | 30.76 | 87.99 | 69.12 | 83.19 | 80.06 | 93.80 | 62.83 | 88.69 | 76.82 |
| HiFormer [24] | 80.39 | 14.70 | 86.21 | 65.69 | 85.23 | 79.77 | 94.61 | 59.52 | 90.99 | 81.08 |
| MISSFormer [19] | 81.96 | 18.20 | 86.99 | 68.65 | 85.21 | 82.00 | 94.41 | 65.67 | 91.92 | 80.81 |
| TransCeption [21] | 82.24 | 20.89 | 87.60 | 71.82 | 86.23 | 80.29 | 95.01 | 65.27 | 91.68 | 80.02 |
| DEFI-Net (ours) | 83.29 | 18.15 | 88.38 | 71.36 | 86.05 | 81.51 | 95.05 | 68.69 | 92.45 | 82.81 |
| Methods | DSC (%) ↑ | HD (mm) ↓ | RV | Myo | LV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net [1] | 89.36 | 1.81 | 90.25 | 83.28 | 94.57 |
| Att-UNet [3] | 90.28 | 1.56 | 90.38 | 84.89 | 95.58 |
| TransUNet [20] | 89.71 | 1.16 | 88.86 | 84.53 | 95.73 |
| CTC–Net [23] | 90.77 | - | 90.09 | 85.52 | 96.72 |
| Swin U-Net [17] | 90.00 | 1.32 | 88.55 | 85.62 | 95.83 |
| HiFormer [24] | 90.43 | 1.14 | 88.75 | 87.35 | 95.20 |
| MISSFormer [19] | 87.90 | 2.25 | 86.34 | 82.75 | 94.62 |
| DAE-Former [43] | 90.24 | 1.68 | 89.32 | 86.38 | 95.04 |
| TransCeption [21] | 88.73 | 1.72 | 87.68 | 83.87 | 94.66 |
| CS-Unet [44] | 91.37 | - | 89.20 | 89.47 | 95.42 |
| DEIF-Net (ours) | 92.02 | 1.08 | 90.75 | 89.27 | 96.04 |
| Methods | DSC (%) ↑ | IoU (%) ↑ |
|---|---|---|
| V-Net [2] | 80.79 | 68.07 |
| U-Net [1] | 82.99 | 71.01 |
| Att-UNet [3] | 82.85 | 70.45 |
| MultiResUnet [33] | 81.34 | 68.66 |
| TransUnet [20] | 85.61 | 78.15 |
| SwinU-Net [17] | 85.44 | 78.21 |
| MISSFormer [19] | 75.35 | 62.64 |
| TransCeption [21] | 77.32 | 65.21 |
| HiFormer [24] | 85.96 | 78.26 |
| DEIF-Net | 87.45 | 80.51 |
| Model | Synapse | ACDC | Kvasir SEG | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSC ↑ | HD95 ↓ | DSC ↑ | HD95 ↓ | DSC ↑ | IoU ↑ | |
| Concat | 80.98 | 24.17 | 88.72 | 1.44 | 85.54 | 78.23 |
| +GLIL | 82.64 | 18.45 | 91.83 | 1.11 | 86.50 | 79.16 |
| +GLFF | 81.65 | 19.21 | 91.62 | 1.18 | 86.14 | 78.64 |
| DEIF-Net | 83.29 | 18.15 | 92.02 | 1.08 | 87.45 | 80.51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Fan, Y.; Yang, P. Medical Image Segmentation Network Based on Dual-Encoder Interactive Fusion. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3785. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073785
Yang H, Fan Y, Yang P. Medical Image Segmentation Network Based on Dual-Encoder Interactive Fusion. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(7):3785. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073785
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Hong, Yong Fan, and Ping Yang. 2025. "Medical Image Segmentation Network Based on Dual-Encoder Interactive Fusion" Applied Sciences 15, no. 7: 3785. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073785
APA StyleYang, H., Fan, Y., & Yang, P. (2025). Medical Image Segmentation Network Based on Dual-Encoder Interactive Fusion. Applied Sciences, 15(7), 3785. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073785






