Thermo-Mechanical Identification of Orthotropic Engineering Constants of Composites Using an Extended Non-Destructive Impulse Excitation Technique
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
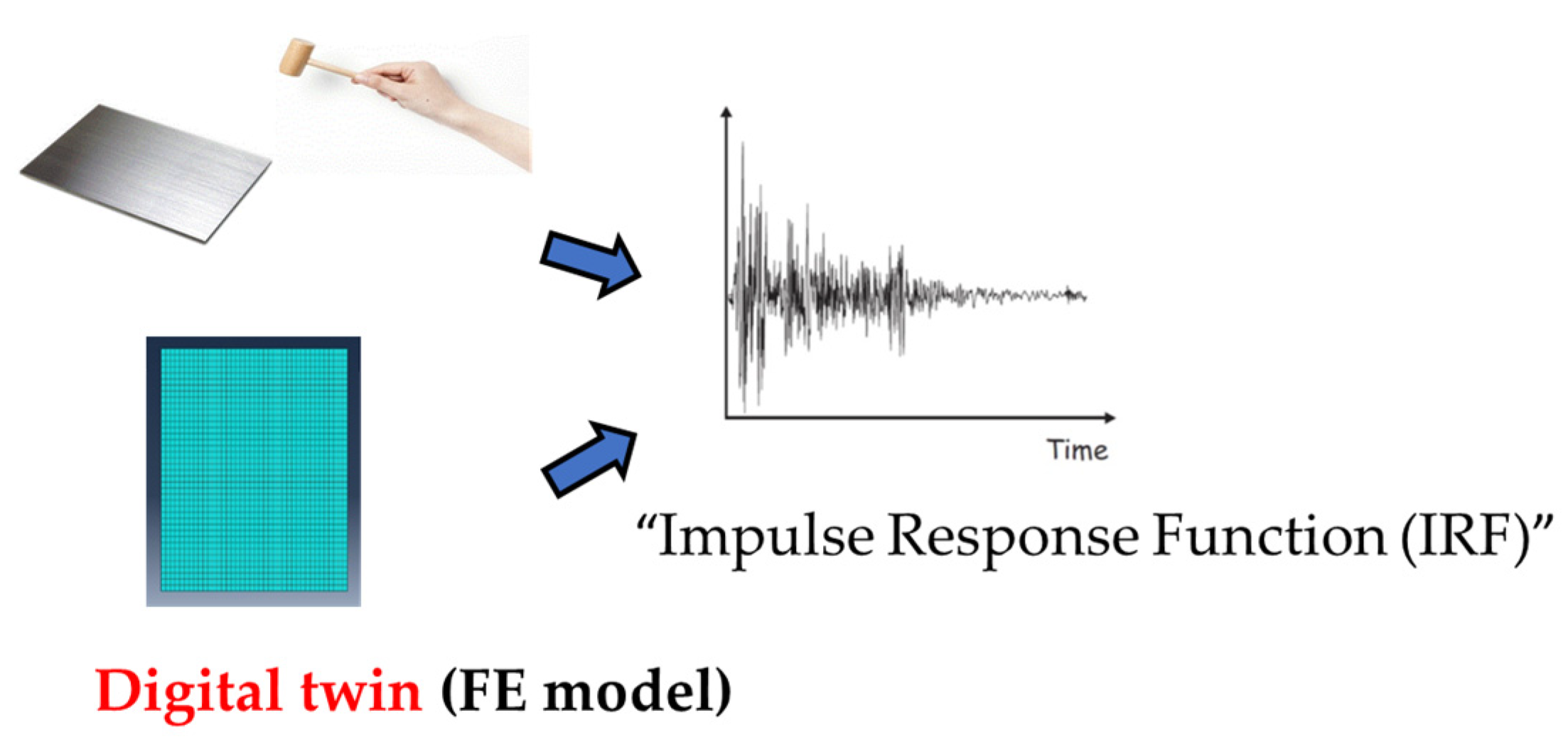
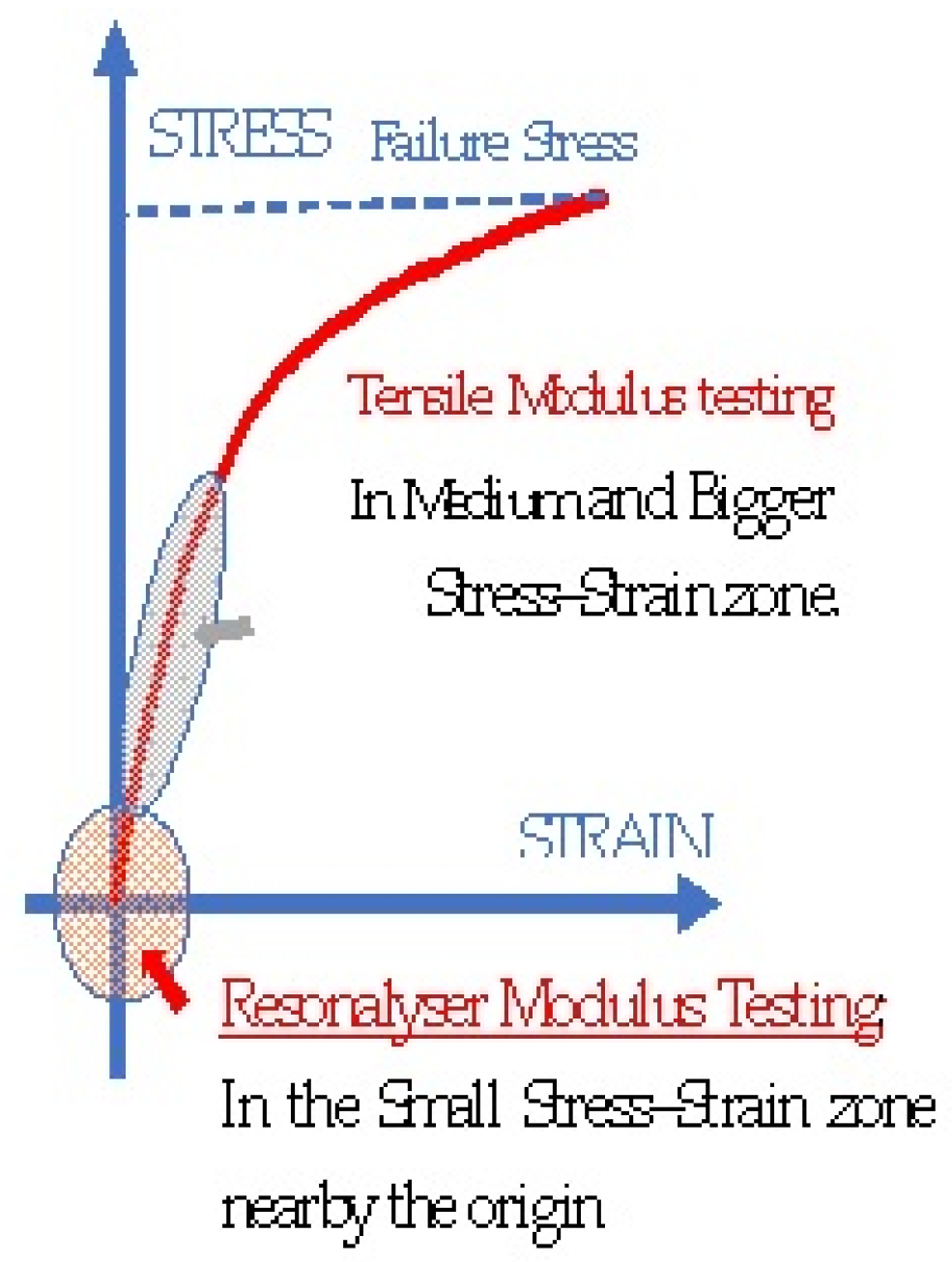
2.1. The Resonalyser Procedure
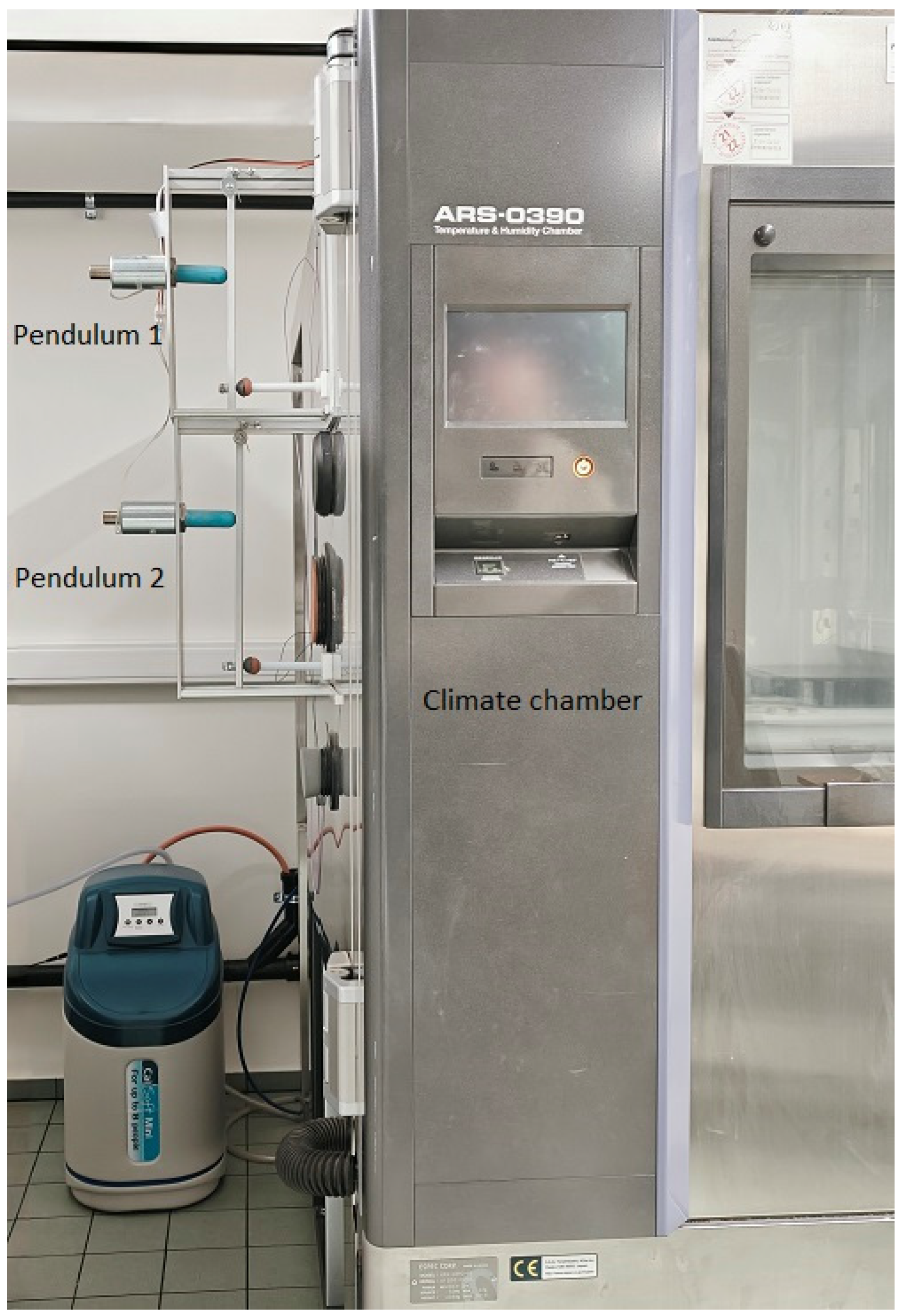
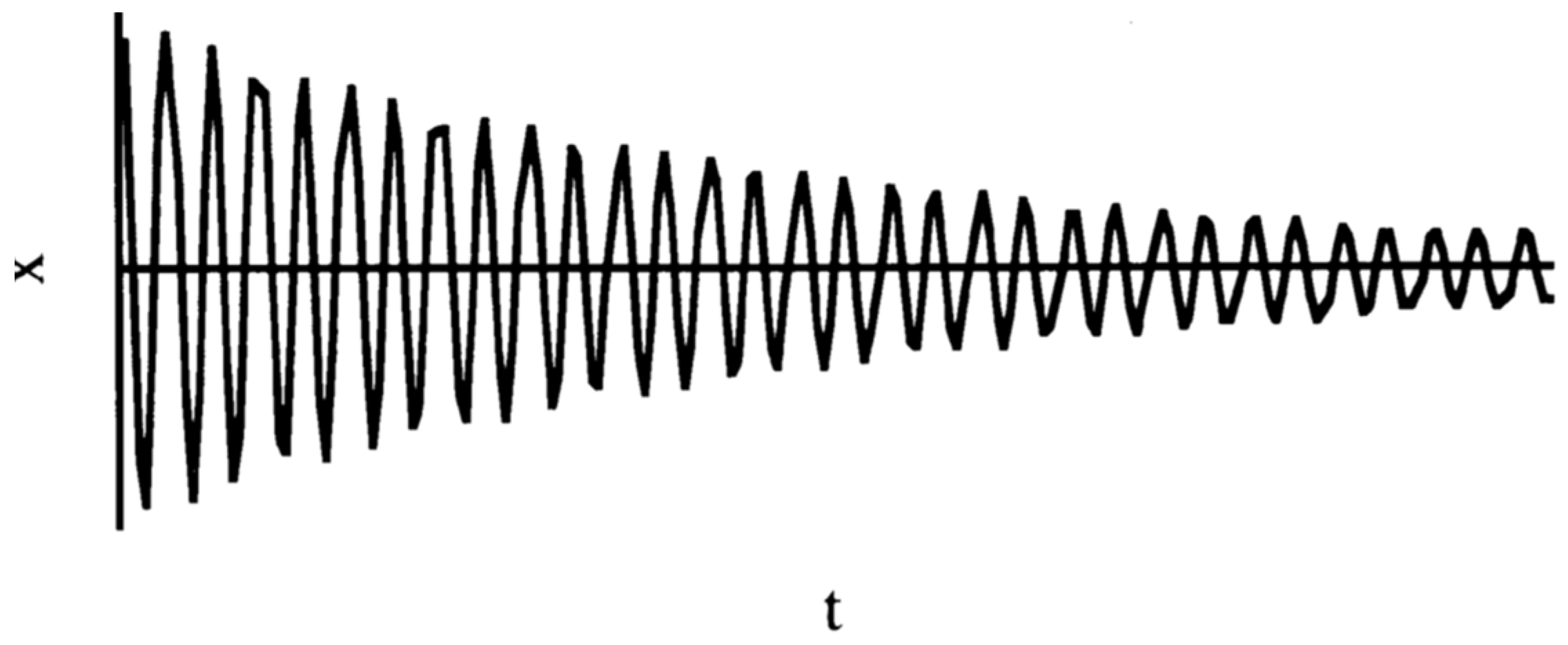
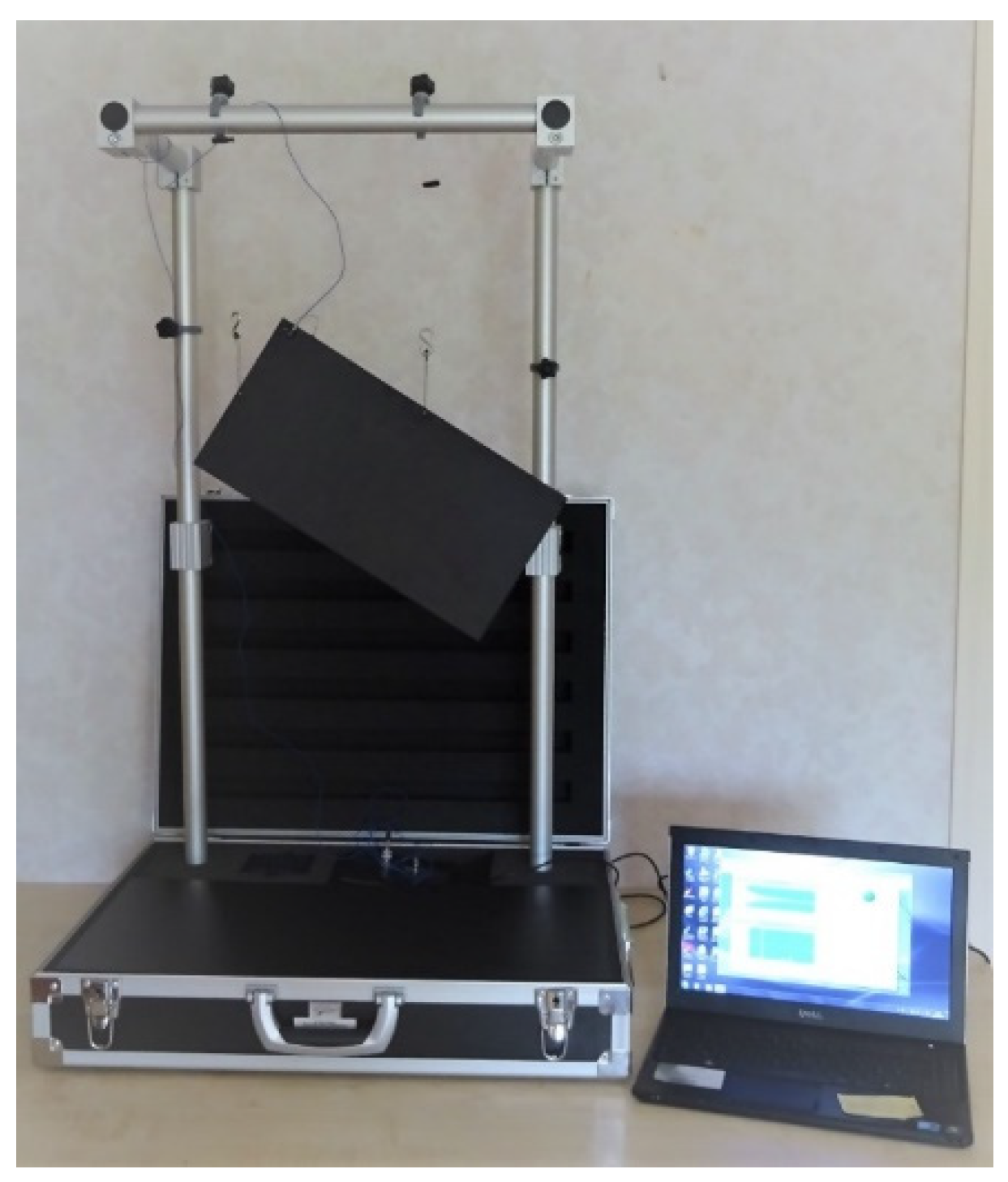
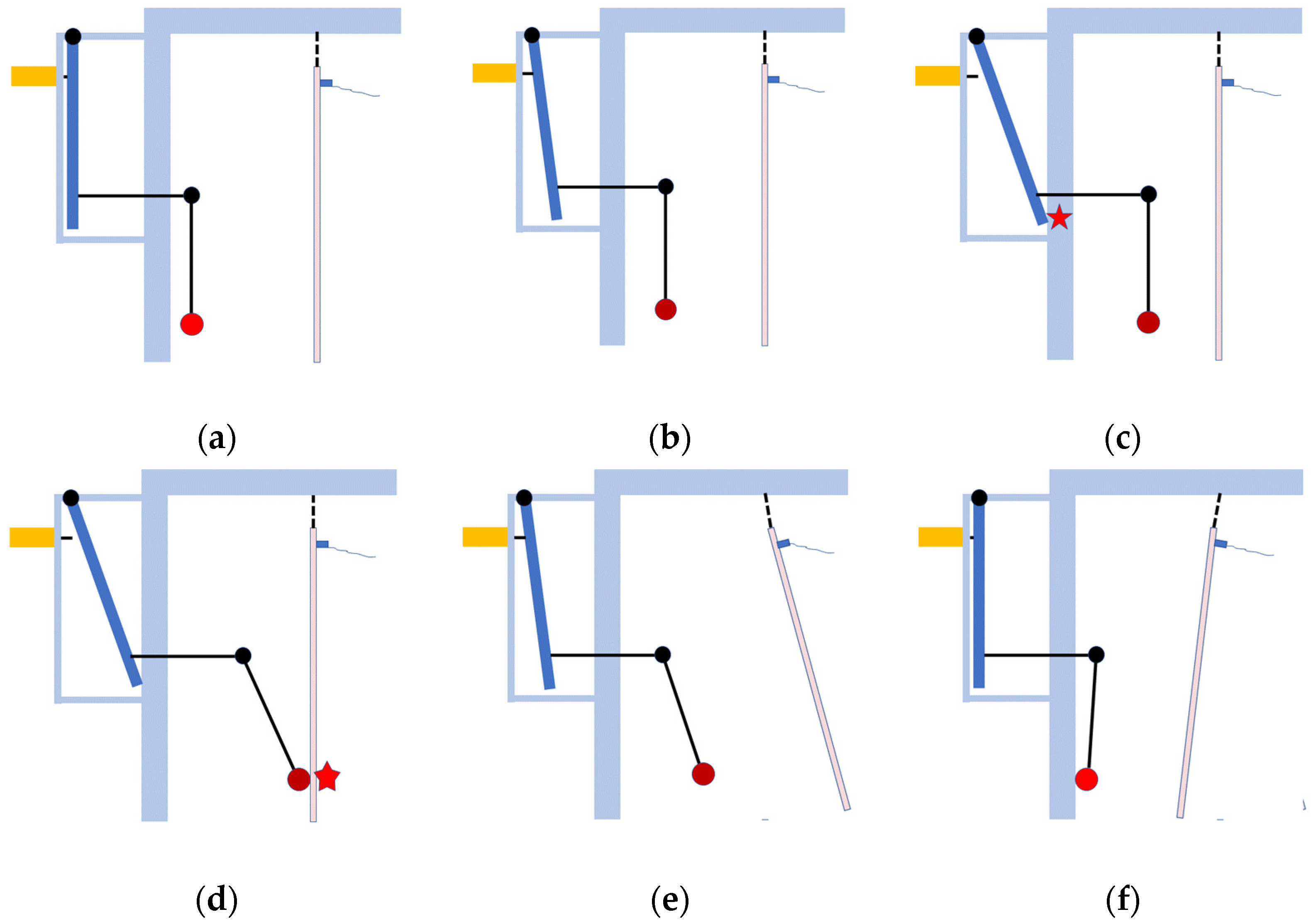
2.2. The Automated Pendulum Excitation
2.3. Temperature Control
2.4. Measurement Procedure
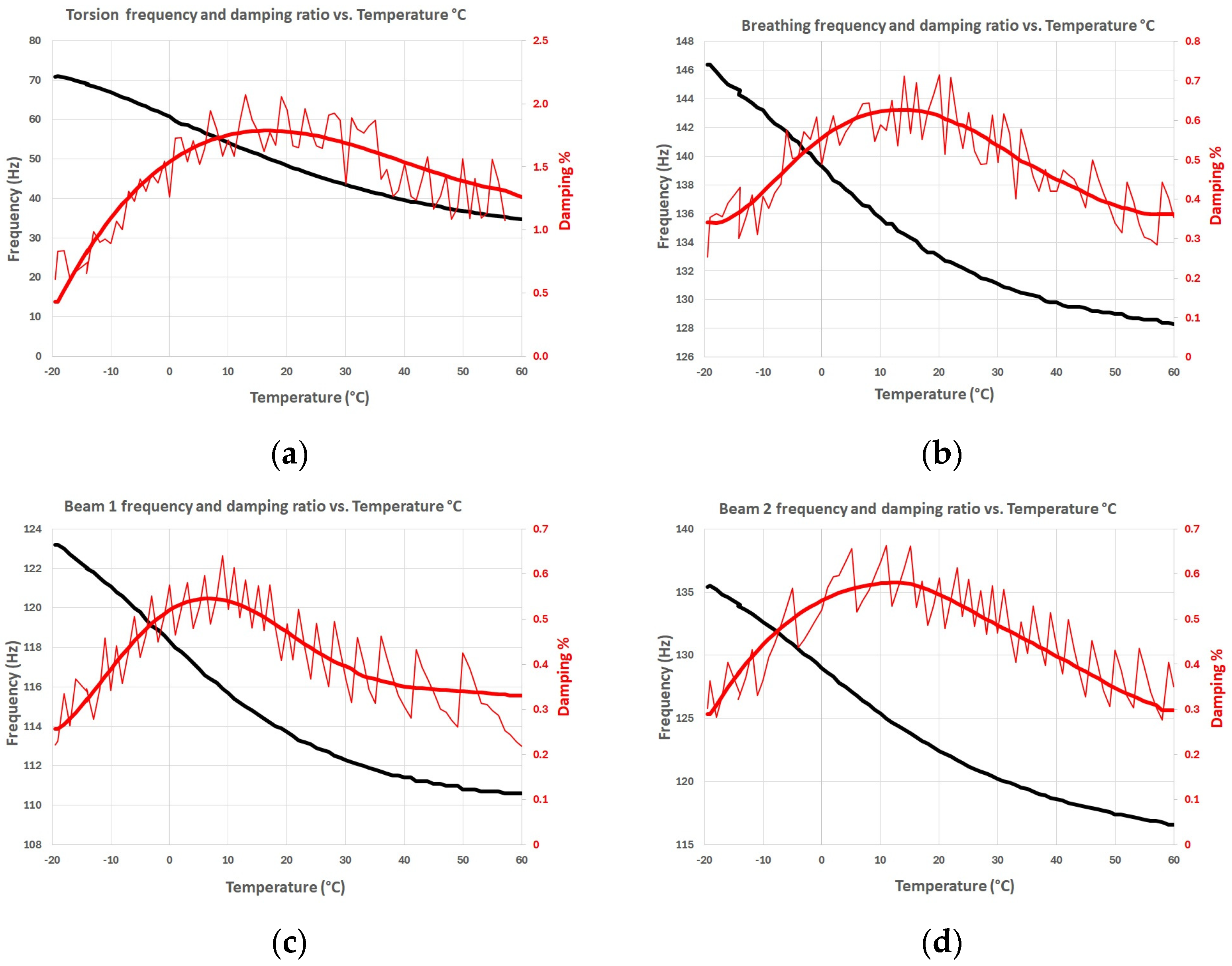
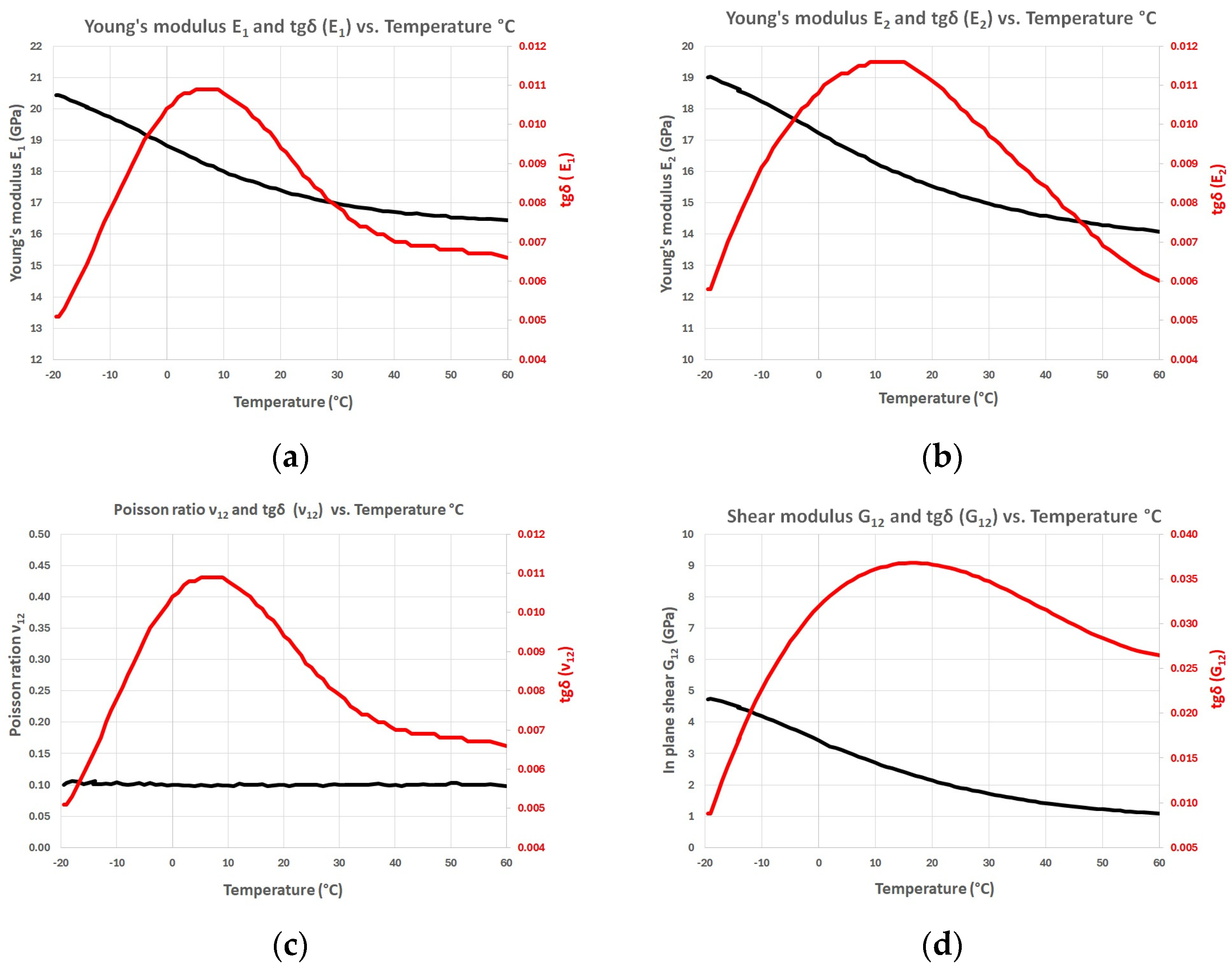
3. Results
- Convection heat transfer coefficient h = 30 W/m2 °C;
- Specific heat Cp = 1800 J/kg°C;
- Thermal conduction coefficient k = 0.29 W/m °C;
- Density rho = 1145 kg/m3.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IET | Impulse excitation technique |
| IRF | Impulse response function |
| DMA | Dynamic mechanical analysis |
| EMA | Experimental modal analysis |
| OMA | Operational modal analysis |
| FE | Finite element |
| ASTM | American Standard Testing Materials |
References
- Jones, R. Mechanics of Composite Materials; McGraw-Hill: New York, NJ, USA, 1975; ISBN 0-07-032790-40. Available online: https://books.google.be/books?hl=nl&lr=&id=oMph2kNG3yAC&oi=fnd&pg=PR13&dq=Mechanics+of+composite+materials&ots=kaM_KLDJZh&sig=GPwF1HyGMQnDCdhyG2IiB_XprXY#v=onepage&q=Mechanics%20of%20composite%20materials&f=false (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Ozturk, F.; Cobanoglu, M.; Ece, R.E. Recent advancements in thermoplastic composite materials in aerospace industry. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2023, 37, 3084–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, B.; Hiremath, S.R.; Mahapatra, D.R. A review of micromechanics-based models for effective elastic properties of reinforced polymer matrix composites. Compos. Struct. 2018, 204, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D3039; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S014294181100078X (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- ASTM D7078; Standard Test Method for Shear Properties of Matrix Composite Materials. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-57729-2_7 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Timoshenko, S. Vibration Problems Is Engineering; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1937; Available online: https://books.google.be/books?hl=nl&lr=&id=YZ7t8LgRqi0C&oi=fnd&pg=PR11&dq=S.+Timoshenko:+Vibration+Problems+is+Engineering&ots=N4lCLnFjxG&sig=WSdLXxC2vTpTOILvlTIyilU-Rfg&redir_esc=y%23v=onepage&q=S.%20Timoshenko%3A%20Vibration%20Problems%20is%20Engineering&f=false (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Kostic, S.; Miljojkovic, J.; Simunovic, G.; Vukelic, D.; Tadic, B. Uncertainty in the determination of elastic modulus by tensile testing. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2022, 25, 100998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, J.D.; Morrell, R.M. Elastic Modulus Measurement; Good Practice Guide No.98; National Physical Laboratory: London, UK, 2006; Available online: https://eprintspublications.npl.co.uk/3782/ (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- ASTM C1259-98; Standard Test Methods for Dynamic Young’s Modulus, Shear Modulus and Poisson’s Ratio for Advanced Ceramics by Impulse Excitation of Vibration. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2001. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/11/22/10802 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- He, J.; Fu, Y. Modal Analysis; Butterworth-Heineman: Oxford, UK, 2001; ISBN 0750650796. Available online: https://books.google.be/books?hl=nl&lr=&id=ElwhqUtJUj8C&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=he+fu+modal+analysis&ots=Vf3DYs53Ey&sig=iLqe957_1xyXInwsGyR2oG0UlsM#v=onepage&q=he%20fu%20modal%20analysis&f=false (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Schalnat, J.; Gómez, D.G.; Daelemans, L.; De Baere, I.; De Clerck, K.; Van Paepegem, W. Influencing parameters on measurement accuracy in dynamic mechanical analysis of thermoplastic polymers and their composites. Polym. Test. 2020, 91, 106799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heritage, K.; Frisby, C.; Wolfenden, A. Impulse excitation technique for dynamic flexural measurements at moderate temperature. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1988, 59, 973–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brebels, A.; Bollen, B. Non-Destructive Evaluation of Material Properties as Function of Temperature by the Impulse Excitation Technique. e-J. Non-Destr. Test. 2015, 20, 6. Available online: https://www.ndt.net/article/nde-india2014/papers/CP0023_full.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Sol, H. Identification of Anisotropic Plate Rigidities Using Free Vibration Data. Ph.D. Thesis, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussels, Belgium, 1986. Available online: https://researchportal.vub.be/en/publications/identification-of-anisotropic-plate-rigidities-by-vibration-analy (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- De Baer, I. Experimental and Numerical Study of Different Setups for Conducting and Monitoring Fatigue Experiments of Fibre-Reinforced Thermoplastics. Ph.D. Thesis, University Ghent, Ghent, Belgium, 2008. Available online: https://biblio.ugent.be/publication/470995 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Lauwagie, T.; Sol, H.; Heylen, W. Handling uncertainties in mixed numerical-experimental techniques for vibration-based material identification. J. Sound Vib. 2006, 291, 723–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauwagie, T.; Sol, H.; Roebben, G.; Heylen, W.; Shi, Y. Validation of the Resonalyser method: An inverse method for material identification. In Proceedings of the ISMA 2002, International Conference on 734 Noise and Vibration Engineering, Leuven, Belgium, 16–18 September 2002; pp. 687–694. Available online: http://resonalyser.com/wp-content/uploads/Validation-of-the-resonalyser-method-ISMA.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- De Visscher, J. Identification of the Complex Stiffness Matrix of Orthotropic Materials by a Mixed Numerical Experimental Method. Ph.D. Thesis, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussel, Belgium, 1995. Available online: https://researchportal.vub.be/en/publications/identification-of-the-complex-stiffness-matrix-of-orthotropic-mat (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Deobald, L.R.; Gibson, R.F. Determination of elastic constants of orthotropic plates by a modal analysis/Rayleigh-Ritz technique. J. Sound Vib. 1988, 124, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pederson, P.; Frederiksen, P.S. Identification of orthotropic material moduli by a combined experimental/numerical approach. Measurement 1992, 10, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayorinde, E.O.; Gibson, R.F. Elastic constants of orthotropic composite materials using plate resonance frequencies, classical lamination theory and an optimized three mode Rayleigh formulation. Compos. Eng. 1993, 3, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussu, F.; Nivoit, M. Determination of the elastic constants of orthotropic plates by a modal analysis method of superposition. J. Sound Vib. 1993, 165, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederiksen, P.S. Estimation of elastic moduli in thick composite plates by inversion of vibrational data. In Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on Inverse Problems, Paris, France, 2–4 November 1994; pp. 111–118. Available online: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/002199839703100403 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Ayorinde, E.O. Elastic constants of thick orthotropic composite plates. J. Compos. Mater. 1995, 29, 1025–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, J. Application des Techniques de Recalage en Dynamique a L’identification des Constantes Elastiques des Materiaux Composites. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Franche-Comté, Besançon, France, 1997. Available online: https://theses.fr/1997BESA2007 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Qian, G.-L.; Hoa, S.V.; Xiao, X. A vibration method for measuring mechanical properties of composite, theory and experiment. Compos. Struct. 1997, 39, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkanov, E.; Akishin, P.; Lvov, G.; Chate, A. An influence of hypotheses used for a material description on identified mechanical properties of laminated composites. Mech. Compos. Mater. 2025, 61, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Narita, Y. Analysis and optimal design for the damping property of laminated viscoelastic plates under general edge conditions. Compos. Part B 2013, 45, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.-F.; Chang, C.-S. Determination of elastic constants of materials by vibration testing. Compos. Struct. 2000, 49, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.R.; Lam, K.Y.; Han, X. Determination of elastic constants of anisotropic laminated plates using elastic waves and a progressive neural network. J. Sound Vib. 2002, 52, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthurajan, K.G.; Sanakaranarayanasamy, K.; Rao, B.N. Evaluation of elastic constants of specially orthotropic plates through vibration testing. J. Sound Vib. 2004, 272, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayorinde, E.O.; Yu, L. On the elastic characterization of composite plates with vibration data. J. Sound Vib. 2005, 283, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfano, M.; Pagnotta, L. Determining the elastic constants of isotropic materials by modal vibration testing of rectangular thin plates. J. Sound Vib. 2006, 293, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillet, J.; Carmona, J.C.; Mazzoni, D. Estimation of plate elastic moduli through vibration testing. Appl. Acoust. 2007, 68, 334–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledzki, K.; Kessler, A.; Rikards, R.; Chate, A. Determination of elastic constants of glass/epoxy unidirectional laminates by the vibration testing of plates. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1999, 59, 2015–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauwagie, T.; Sol, H.; Heylen, W.; Roebben, G. Determination of the in-plane elastic properties of the different layers of laminated plates by means of vibration testing and model updating. J. Sound Vib. 2004, 274, 529–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottiglieri, M.; Sol, H. Identification of the elastic properties on composite materials as a function of temperature. In Proceedings of the PACAM XI 11th Pan-American Congress of Applied Mechanics, Foz do Iguaçu, PR, Brazil, 4–8 January 2010; Available online: https://researchportal.vub.be/en/publications/identification-of-the-elastic-properties-on-composite-materials-a (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Chandra, S.; Maeder, M.; Bienert, J.; Beinersdorf, H.; Jiang, W.; Matsagar, V.A.; Marburg, S. Identification of temperature-dependent elastic and damping parameters of carbon-epoxy composite plates based on experimental modal data. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 187, 109945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauwagie, T.; Lambrinou, K.; Sol, H.; Heylen, W. Resonant-Based Identification of the Poisson’s Ratioof Orthotropic Materials. Exp. Mech. 2010, 50, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierron, F.; Grediac, M. The Virtual Fields Method; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; ISBN 9781761418258. Available online: https://books.google.be/books?hl=nl&lr=&id=GGGQ6OVLSc8C&oi=fnd&pg=PR3&dq=the+virtual+fields+method+&ots=9cQLIzcR26&sig=IDIMfwpNIF9KN8OHtY_hSiK9PTc#v=onepage&q=the%20virtual%20fields%20method&f=false (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Sol, H.; Rahier, H.; Gu, J. Prediction and Measurement of the Damping Ratios of Laminated Polymer Composite Plates. Materials 2020, 13, 3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bytec, B.V. Theoretical Background and Examples of the Resonalyser Procedure. Available online: https://resonalyser.com/ (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Sol, H.J.B.; Gu, J. Combined tensile and dynamic testing for the accurate measurement of mechanical properties of composite materials. In Proceedings of the SAMPE Europe Conference 2022, Hamburg, Germany, 15–17 November 2022; Available online: https://www.nasampe.org/store/viewproduct.aspx?id=23970522 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- ASTM D790; Standard Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017. Available online: https://store.astm.org/standards/d790 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Delouei, A.A.; Emamian, A.; Sajjadi, H.; Atashafrooz, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.-P.; Jing, D. A Comprehensive Review on Multi-Dimensional Heat Conduction of Multi-Layer and Composite Structures: Analytical Solutions. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 30, 1875–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengel, Y. Heat Transfer, a Practical Approach; McGraw-Hill: New York, NJ, USA, 1998; ISBN 0-07-011505-2. Available online: https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1130573936331734035 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Treviso, A.; Van Genechten, B.; Mundo, D.; Tournour, M. Damping in composite materials: Properties and models. Compos. Part B 2015, 78, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
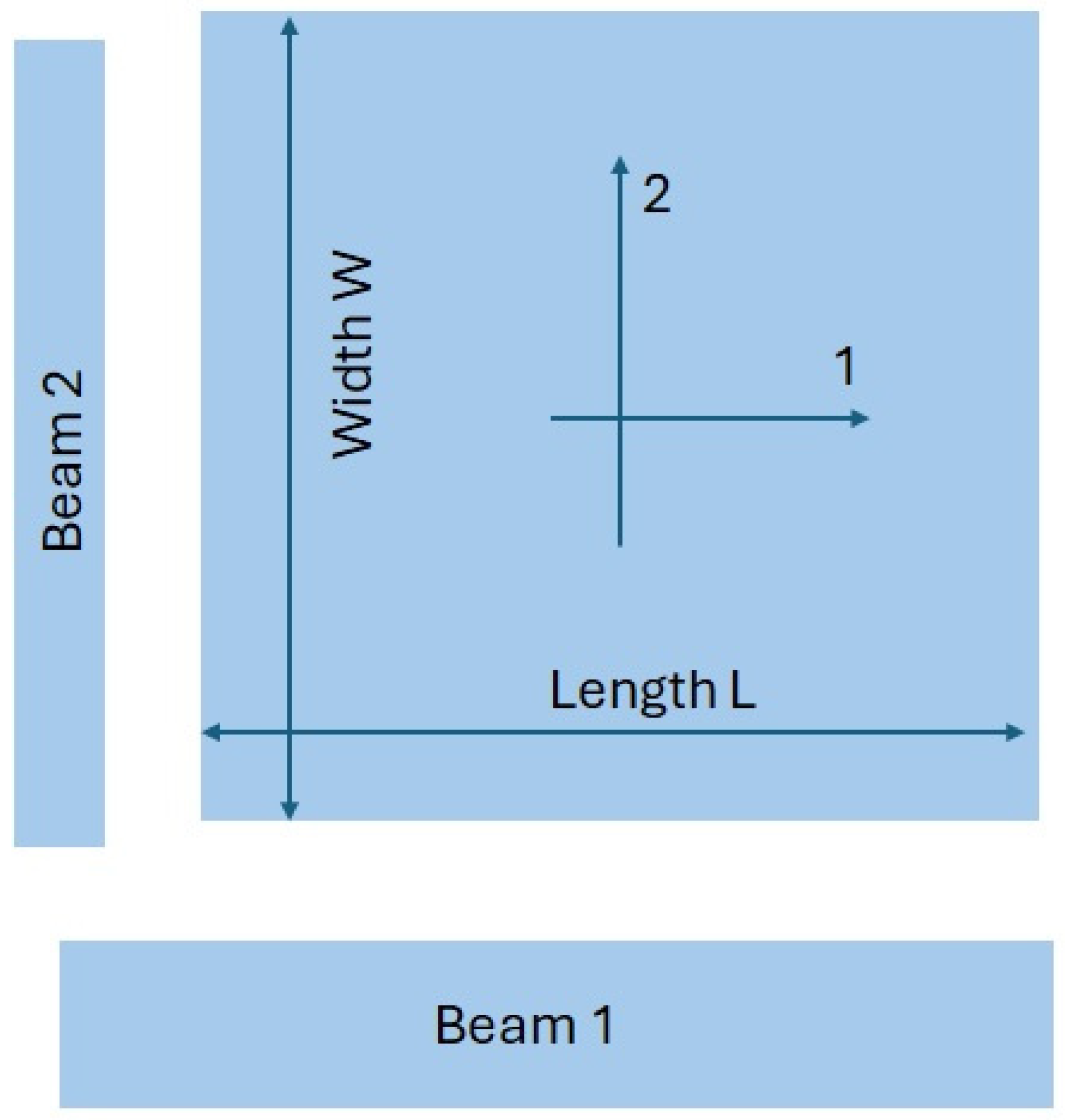

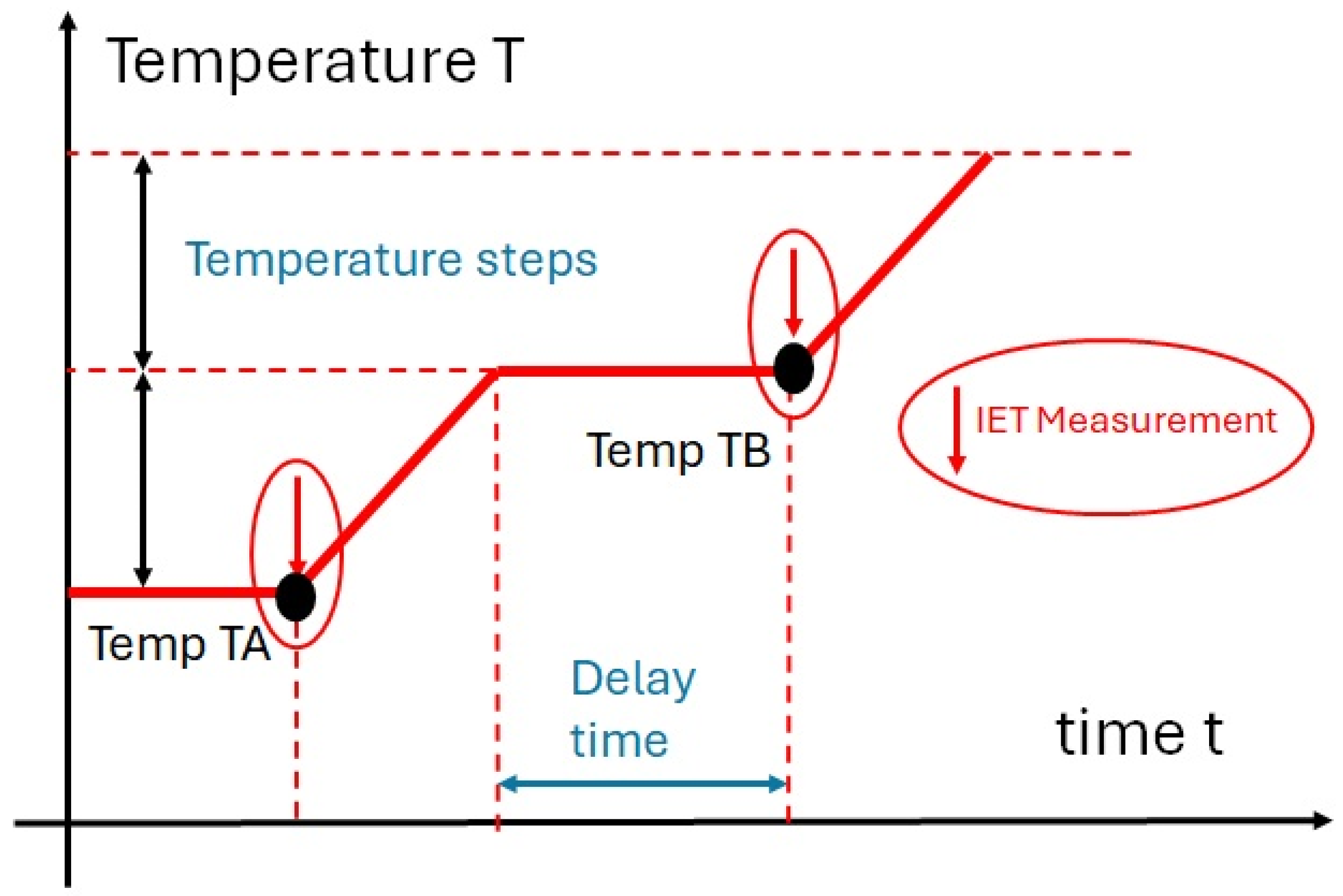
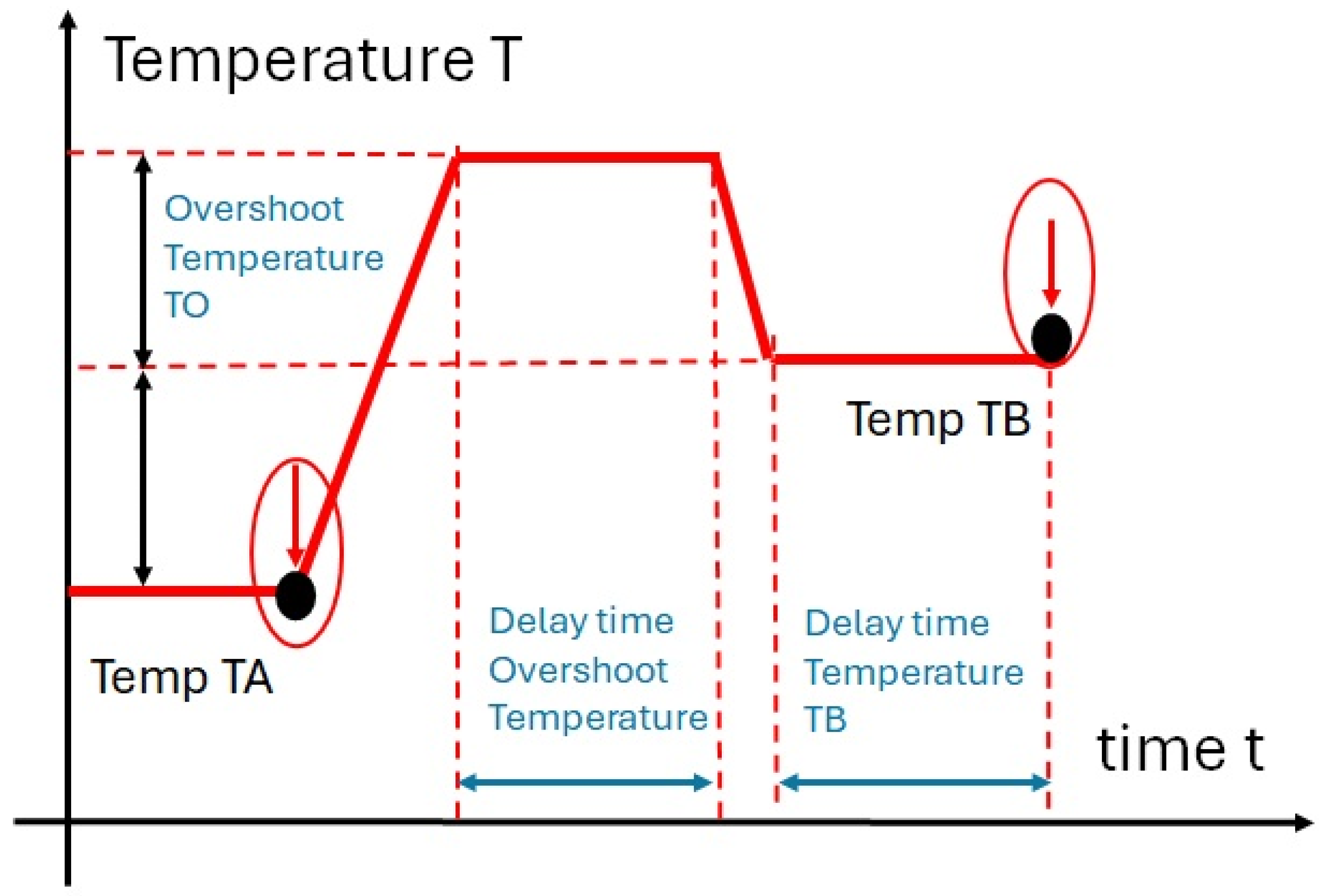

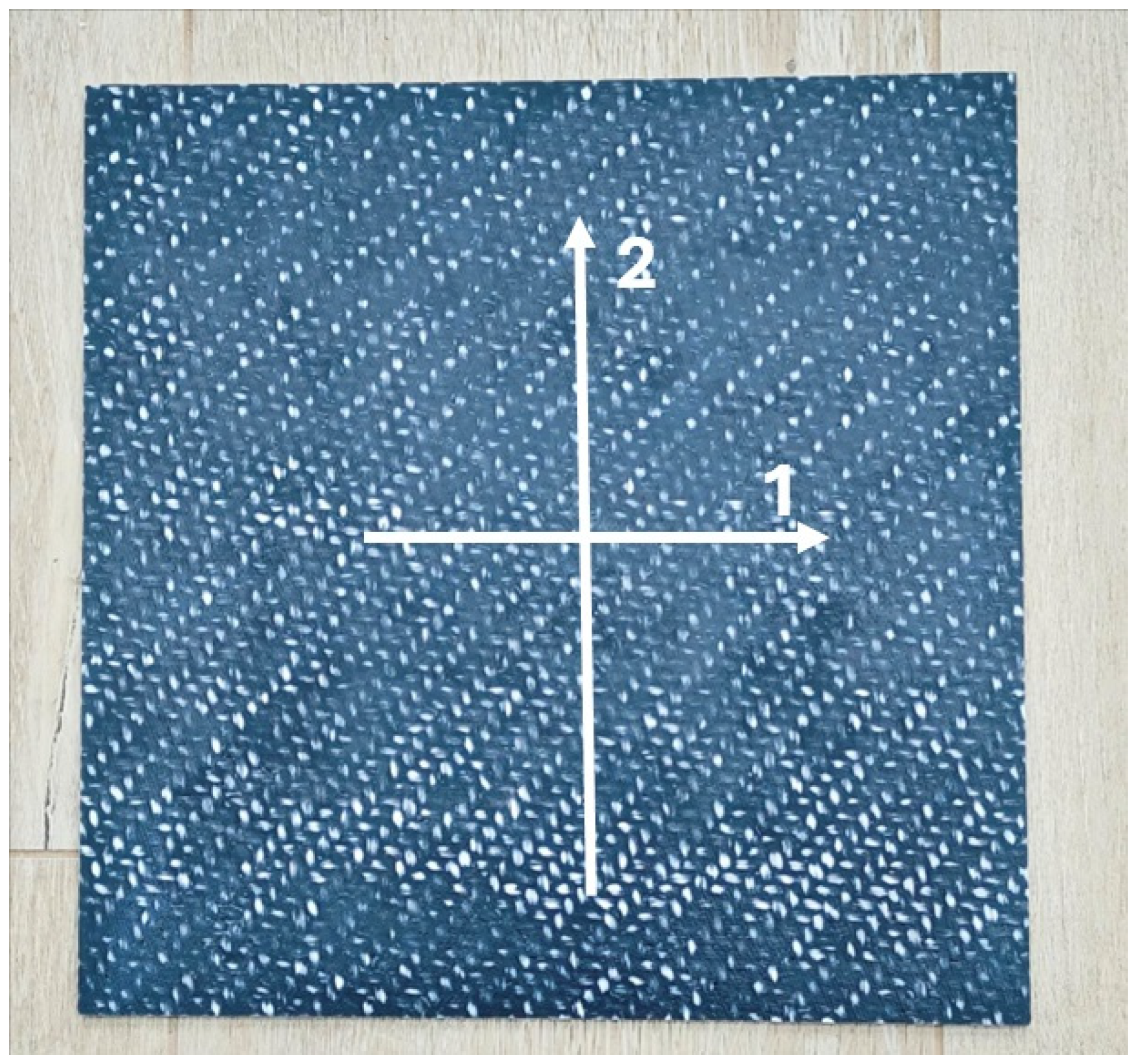
| Span Length Support L [m] | Width b [m] | Thickness t [m] | Slope m = F/d [N/m] | Young’s Modulus E [N/m2] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beam 1 | 0.250 | 0.0193 | 0.00315 | 0.0213 | 17.0 GPa |
| Beam 2 | 0.250 | 0.0206 | 0.00315 | 0.0313 | 14.9 GPa |
| Length [m] | Width [m] | Thickness [m] | Mass [kg] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plate | 0.282 | 0.2760 | 0.00315 | 0.4198 |
| Beam 1 | 0.300 | 0.0193 | 0.00315 | 0.0213 |
| Beam 2 | 0.281 | 0.0206 | 0.00315 | 0.0313 |
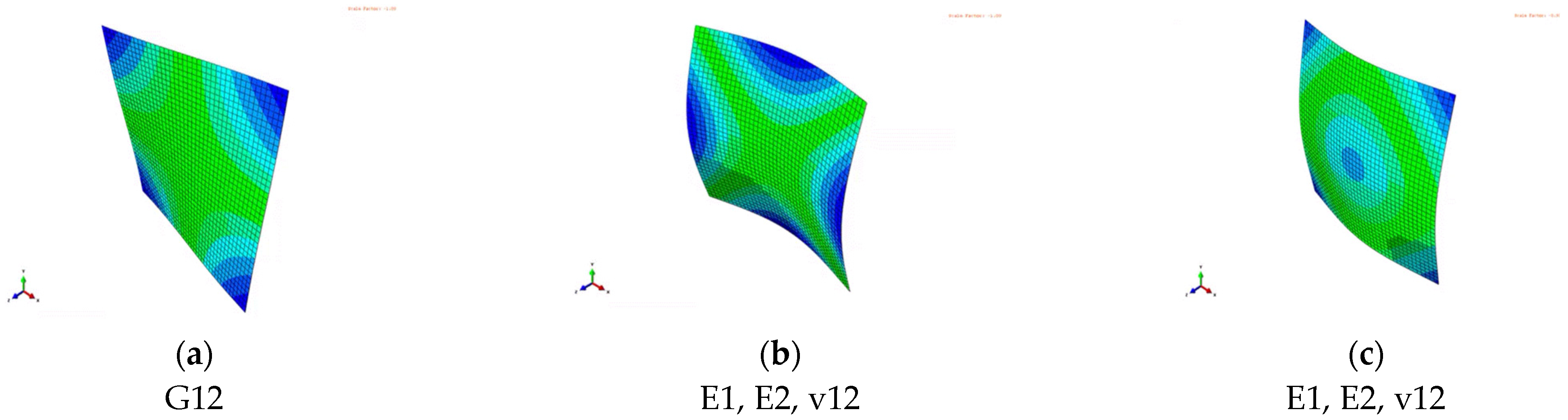
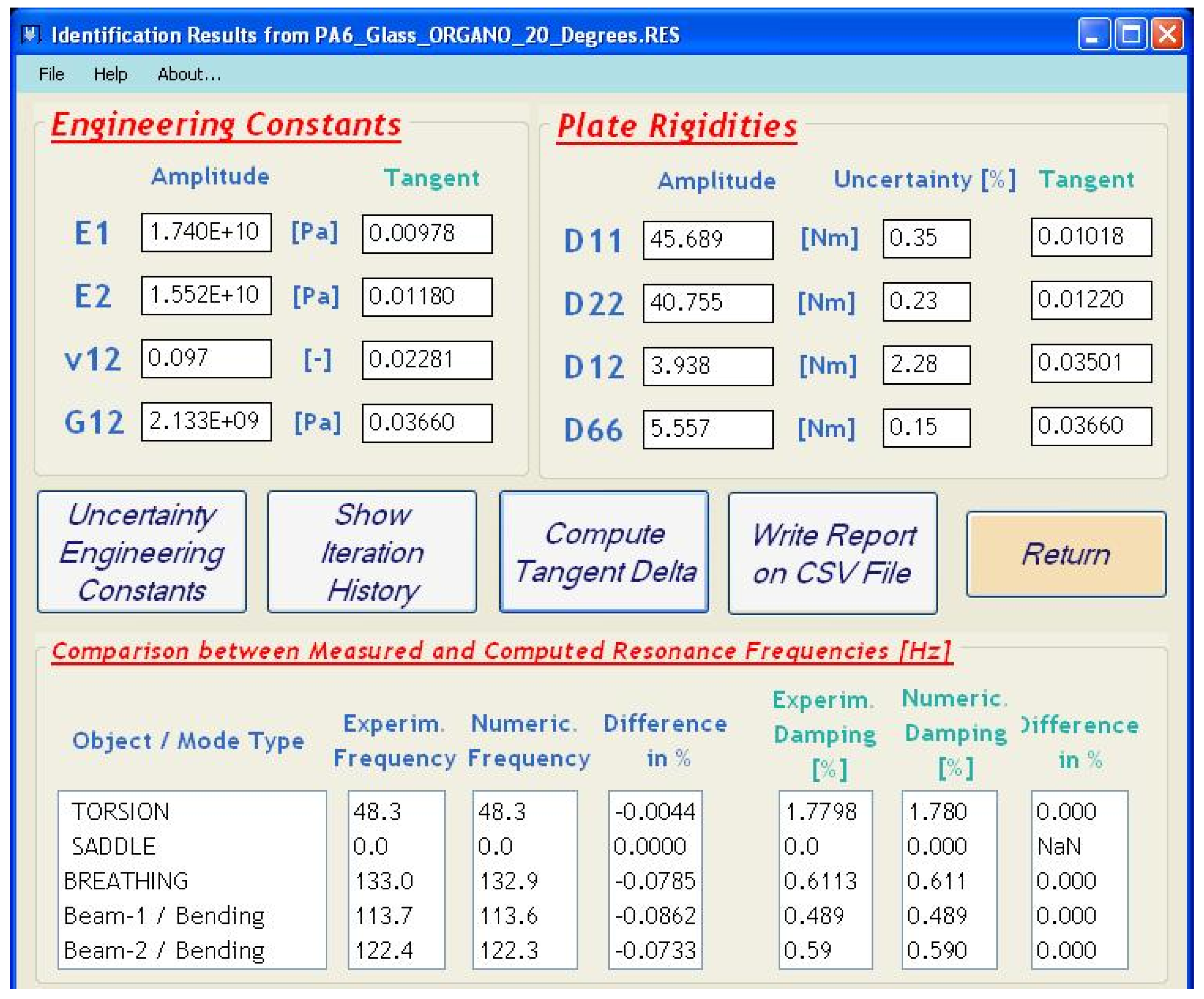
| Resonalyser Results at 20 °C (see Figure 7) | Results of Automated Measurement at 20 °C | |
|---|---|---|
| Young’s modulus E1 | 17.4 GPa | 17.4 GPa |
| Young’s modulus E2 | 15.5 GPa | 15.5 GPa |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.097 | 0.10 |
| Shear modulus G12 | 2.13 GPa | 2.10 GPa |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sol, H.; Gu, J.; Hernandez, G.M.; Nazerian, G.; Rahier, H. Thermo-Mechanical Identification of Orthotropic Engineering Constants of Composites Using an Extended Non-Destructive Impulse Excitation Technique. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3621. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073621
Sol H, Gu J, Hernandez GM, Nazerian G, Rahier H. Thermo-Mechanical Identification of Orthotropic Engineering Constants of Composites Using an Extended Non-Destructive Impulse Excitation Technique. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(7):3621. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073621
Chicago/Turabian StyleSol, Hugo, Jun Gu, Guillermo Meza Hernandez, Gulsen Nazerian, and Hubert Rahier. 2025. "Thermo-Mechanical Identification of Orthotropic Engineering Constants of Composites Using an Extended Non-Destructive Impulse Excitation Technique" Applied Sciences 15, no. 7: 3621. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073621
APA StyleSol, H., Gu, J., Hernandez, G. M., Nazerian, G., & Rahier, H. (2025). Thermo-Mechanical Identification of Orthotropic Engineering Constants of Composites Using an Extended Non-Destructive Impulse Excitation Technique. Applied Sciences, 15(7), 3621. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073621







