Prediction of Total Organic Carbon Content in Shale Based on PCA-PSO-XGBoost
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Correlation Analysis
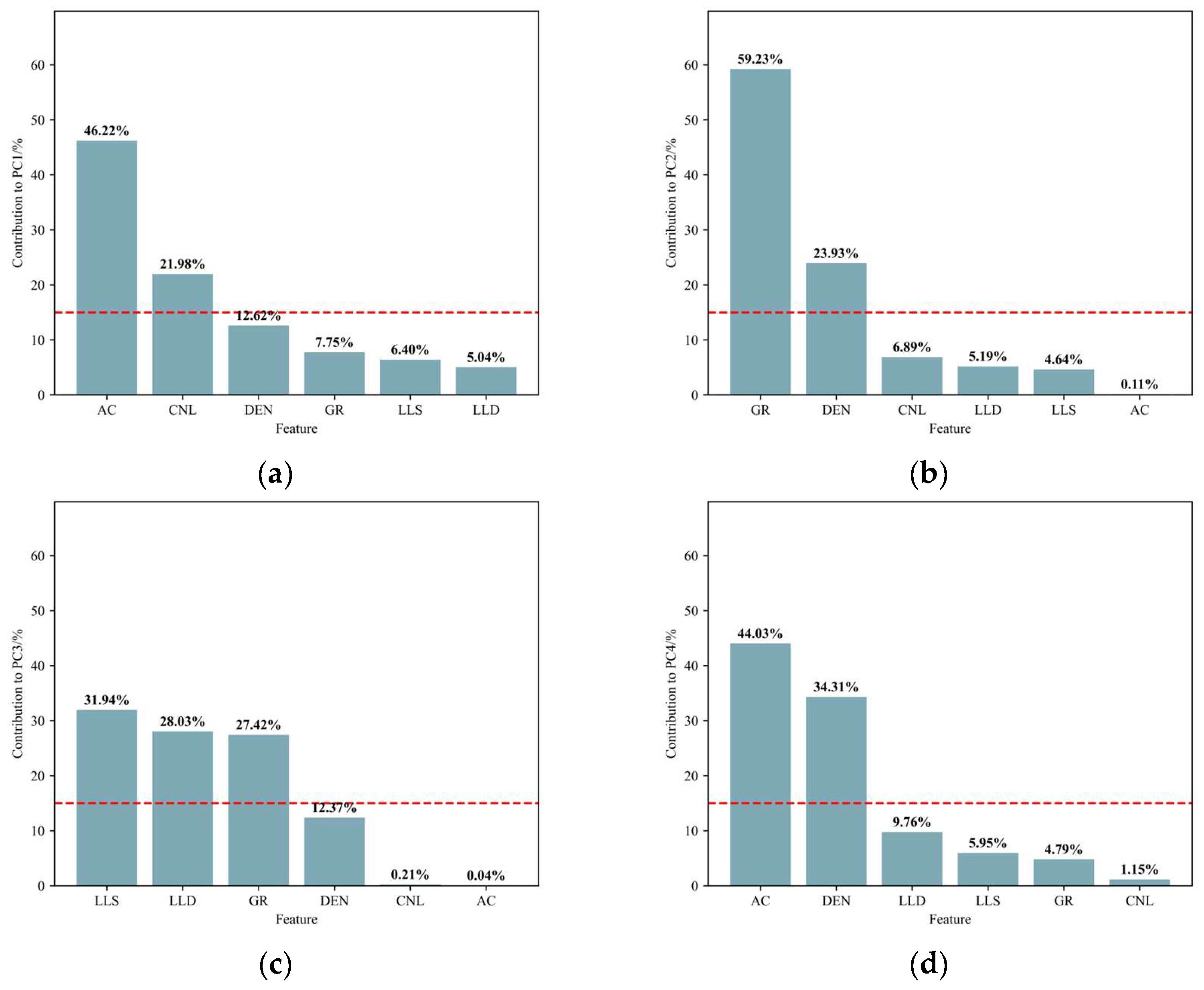
2.3. Principal Component Analysis
2.4. Particle Swarm Optimization
2.5. Machine Learning
2.5.1. BPNN
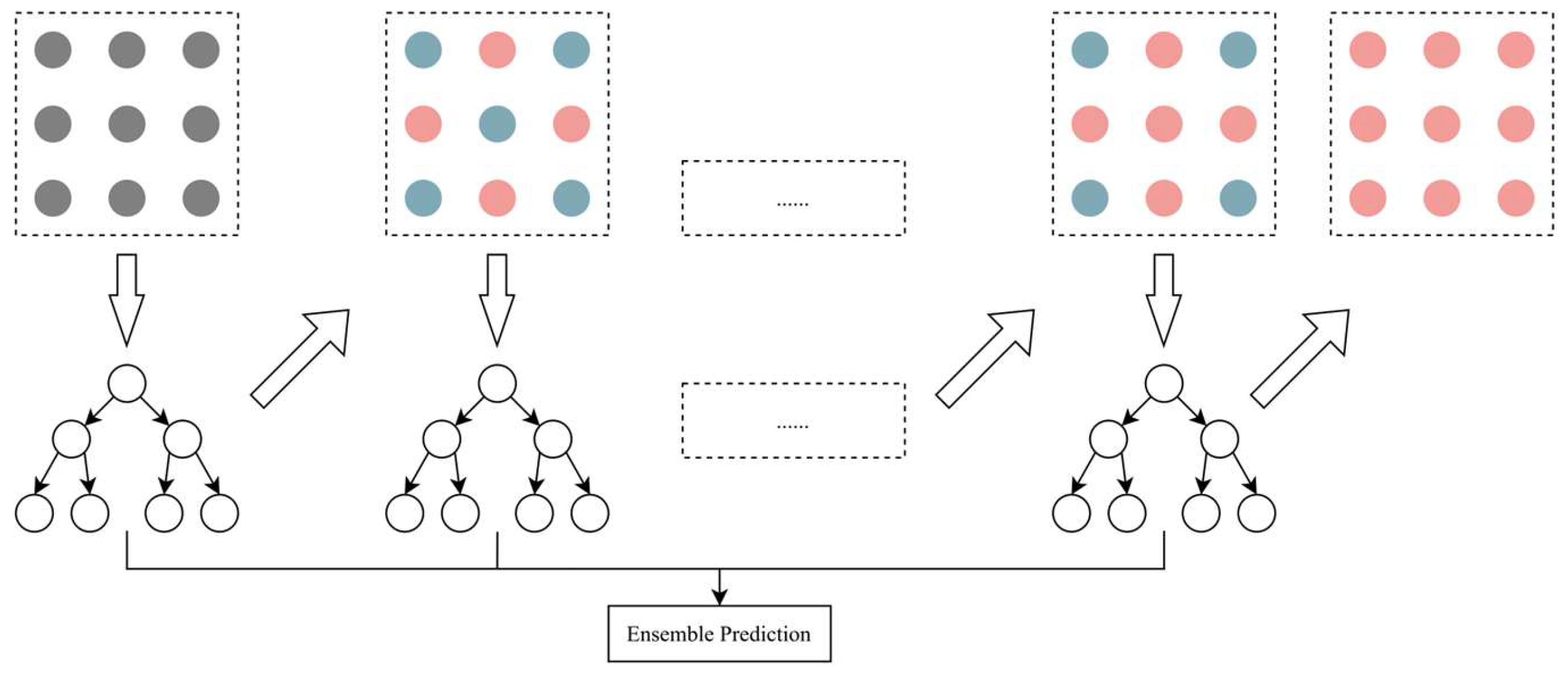
2.5.2. GBDT
2.5.3. XGBoost
2.6. Evaluation Metrics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Logging Parameter Analysis
3.2. Logging Response Characterization
3.3. Build Prediction Model
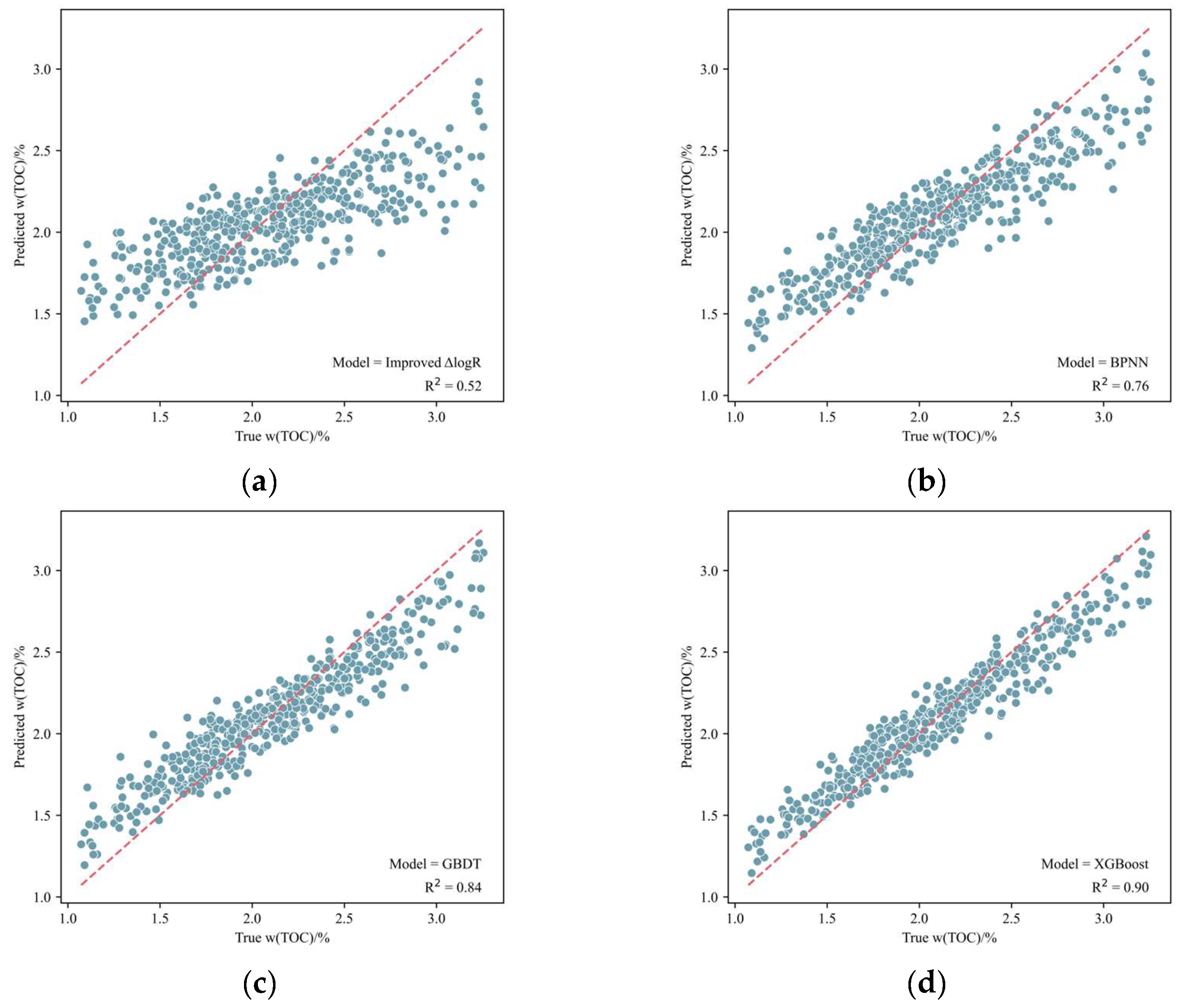
3.4. Comparative Analysis of Different Models
3.5. Comparative Analysis of Model Application
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, G. Challenges and Countermeasures of Log Evaluation in Unconventional Petroleum Exploration and Development. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 1033–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Feng, Z.; Luo, J.; Shao, H.; Bai, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yan, M. Geochemical Characteristics of Mature to High-Maturity Shale Resources, Occurrence State of Shale Oil, and Sweet Spot Evaluation in the Qingshankou Formation, Gulong Sag, Songliao Basin. Energies 2024, 17, 2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Xiao, Y.; Lei, Z.; Wang, R.; Hu, S.; Hou, X. Controlling Factors for Oil Production in Continental Shales: A Case Study of Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation in Songliao Basin. Pet. Res. 2023, 8, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Sun, N.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, J.; Gao, J.; Sheng, P. Genetic Mechanism and Petroleum Geological Significance of Calcite Veins in Organic-Rich Shales of Lacustrine Basin: A Case Study of Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation in Songliao Basin, China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2024, 51, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Feng, Z.; He, K.; Wang, H.; Fu, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C. Gulong Shale Oil Enrichment Mechanism and Orderly Distribution of Conventional– Unconventional Oils in the Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation, Songliao Basin, NE China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2023, 50, 1045–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; He, K.; Guan, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, B.; Wang, H. Petroleum Retention, Intraformational Migration and Segmented Accumulation within the Organic-Rich Shale in the Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation of the Gulong Sag, Songliao Basin, Northeast China. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. Ed. 2023, 97, 1568–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, L.; Fu, X.; Huo, Q.; Bai, L.; Lyu, J.; Wang, B. Identification, Evolution and Geological Indications of Solid Bitumen in Shales: A Case Study of the First Member of Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation in Songliao Basin, NE China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2023, 50, 1345–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Sui, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Li, Y.; Dai, C. Geophysical Prediction Technology for Sweet Spots of Continental Shale Oil: A Case Study of the Lianggaoshan Formation, Sichuan Basin, China. Fuel 2024, 365, 131146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W. Artificial Intelligence Research Status and Applications in Well Logging. Well Logging Technol. 2020, 44, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, B.; Dutta, S.; Kumar, S. TOC Calculation of Organic Matter Rich Sediments Using Rock-Eval Pyrolysis: Critical Consideration and Insights. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2017, 169, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Sun, P.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, P.; Tang, B. Prediction of Organic Carbon Content in Oil Shale Based on Logging: A Case Study in the Songliao Basin, Northeast China. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resour. 2022, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Bai, T.; Su, Y.; Zhao, F.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, G.; Xiao, C. Researches progress in well log recognition and evaluation of source rocks. Geol. Rev. 2024, 70, 721–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Zhou, J.; Duan, Y. Prediction Model of Total Organic Carbon Content in Shale Gas. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2023, 23, 12917–12925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Yang, B.; Jin, J.; Liu, H.; Dai, X.; Pu, J. Comparative Study on Total Organic Carbon Content Logging Prediction Method Based on Machine Learning. Well Logging Technol. 2024, 48, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, J.; Li, K.; Cheng, Z. Total Organic Carbon Content Estimation for Mixed Shale Using Xgboost Method and Implication for Shale Oil Exploration. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Xu, T.; Luo, S.; Chen, T.; Li, Y.; Tang, J. Method and Practice of Deep Favorable Shale Reservoirs Prediction Based on Machine Learning. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2022, 49, 1056–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, X.; Fan, H.; Shen, B.; Sun, K. TOC Estimation from Logging Data Using Principal Component Analysis. Energy Geosci. 2023, 4, 100197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Huang, C.; Wei, M. Shale Gas Production Prediction Based on PCA-PSO-LSTM Combination Model. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 2024, 33, 2450176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahangari, D.; Daneshfar, R.; Zakeri, M.; Ashoori, S.; Soulgani, B.S. On the Prediction of Geochemical Parameters (TOC, S1 and S2) by Considering Well Log Parameters Using ANFIS and LSSVM Strategies. Petroleum 2022, 8, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Jiang, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Li, J. Shale Oil Production Prediction and Fracturing Optimization Based on Machine Learning. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 217, 110900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D. Prediction Method of TOC Content in Mudstone Based on Artificial Neural Network. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 781, 022087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Dong, Z.; Shi, Q.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Wu, L.; Zhang, T.; Li, W. Optimization of Shale Gas Fracturing Parameters Based on Artificial Intelligence Algorithm. Artif. Intell. Geosci. 2023, 4, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Xiao, Y.; Lei, Z.; Yang, Z.; Lou, Y.; Liu, Y. Machine Learning Algorithms for Lithofacies Classification of the Gulong Shale from the Songliao Basin, China. Energies 2023, 16, 2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Dang, W.; Wang, F.; Nie, H.; Wei, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, S.; Feng, Y.; Li, F. Prediction of TOC Content in Organic-Rich Shale Using Machine Learning Algorithms: Comparative Study of Random Forest, Support Vector Machine, and XGBoost. Energies 2023, 16, 4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, W.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, J. An Improved ΔlogR Model for Evaluating Organic Matter Abundance. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 206, 109016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| GR/API | SP/mV | LLS/(Ω·m) | LLD/(Ω·m) | MSFL/(Ω·m) | AC/(μs/m) | CNL/% | DEN/(g·cm−3) | w(TOC)/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| count | 461 | 461 | 461 | 461 | 461 | 461 | 461 | 461 | 461 |
| mean | 121.59 | −118.21 | 6.26 | 5.88 | 7.54 | 102.32 | 24.42 | 2.52 | 2.10 |
| 25% | 116.51 | −121.66 | 5.25 | 4.98 | 5.78 | 97.28 | 22.79 | 2.48 | 1.75 |
| 50% | 121.63 | −116.33 | 5.98 | 5.66 | 7.23 | 101.79 | 24.17 | 2.51 | 2.11 |
| 75% | 127.13 | −119.97 | 6.76 | 6.41 | 8.97 | 107.07 | 26.21 | 2.56 | 2.44 |
| Model | Hyperparameters | The Concept of Hyperparameters | Settings |
|---|---|---|---|
| BPNN | hidden_layer_sizes | The ith element represents the number of neurons in the ith hidden layer | (64, 64, 32) |
| activation_function | Activation function for the hidden layer | ||
| GBDT | learning_rate | Weight reduction factor for weak learners | 0.07 |
| n_estimators | The number of iterations for weak learners | 190 | |
| min_samples_split | The minimum number of samples required to split internal nodes | 2 | |
| min_samples_leaf | The minimum number of samples on leaf nodes | 1 | |
| max_depth | The maximum depth of tree | 4 | |
| XGBoost | learning_rate | Weight reduction factor for weak learners | 0.08 |
| n_estimators | The number of iterations for weak learners | 180 | |
| subsample | Ratio of subsampling | 0.7 | |
| colsample_bytree | Controls the sampling scale of the number of columns in the tree | 0.6 | |
| max_depth | The maximum depth of tree | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, Y.; Xu, C.; Li, T.; Liu, T.; Tang, L.; Zhang, J. Prediction of Total Organic Carbon Content in Shale Based on PCA-PSO-XGBoost. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3447. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073447
Meng Y, Xu C, Li T, Liu T, Tang L, Zhang J. Prediction of Total Organic Carbon Content in Shale Based on PCA-PSO-XGBoost. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(7):3447. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073447
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Yingjie, Chengwu Xu, Tingting Li, Tianyong Liu, Lu Tang, and Jinyou Zhang. 2025. "Prediction of Total Organic Carbon Content in Shale Based on PCA-PSO-XGBoost" Applied Sciences 15, no. 7: 3447. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073447
APA StyleMeng, Y., Xu, C., Li, T., Liu, T., Tang, L., & Zhang, J. (2025). Prediction of Total Organic Carbon Content in Shale Based on PCA-PSO-XGBoost. Applied Sciences, 15(7), 3447. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073447







