Computational Model and Constructal Design Applied to Thin Stiffened Plates Subjected to Elastoplastic Buckling Due to Combined Loading Conditions
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Computational Modeling of Buckling
2.1.1. Computational Modeling of Elastic Buckling
2.1.2. Computational Modeling of Elastoplastic Buckling
2.1.3. Computational Model Discretization
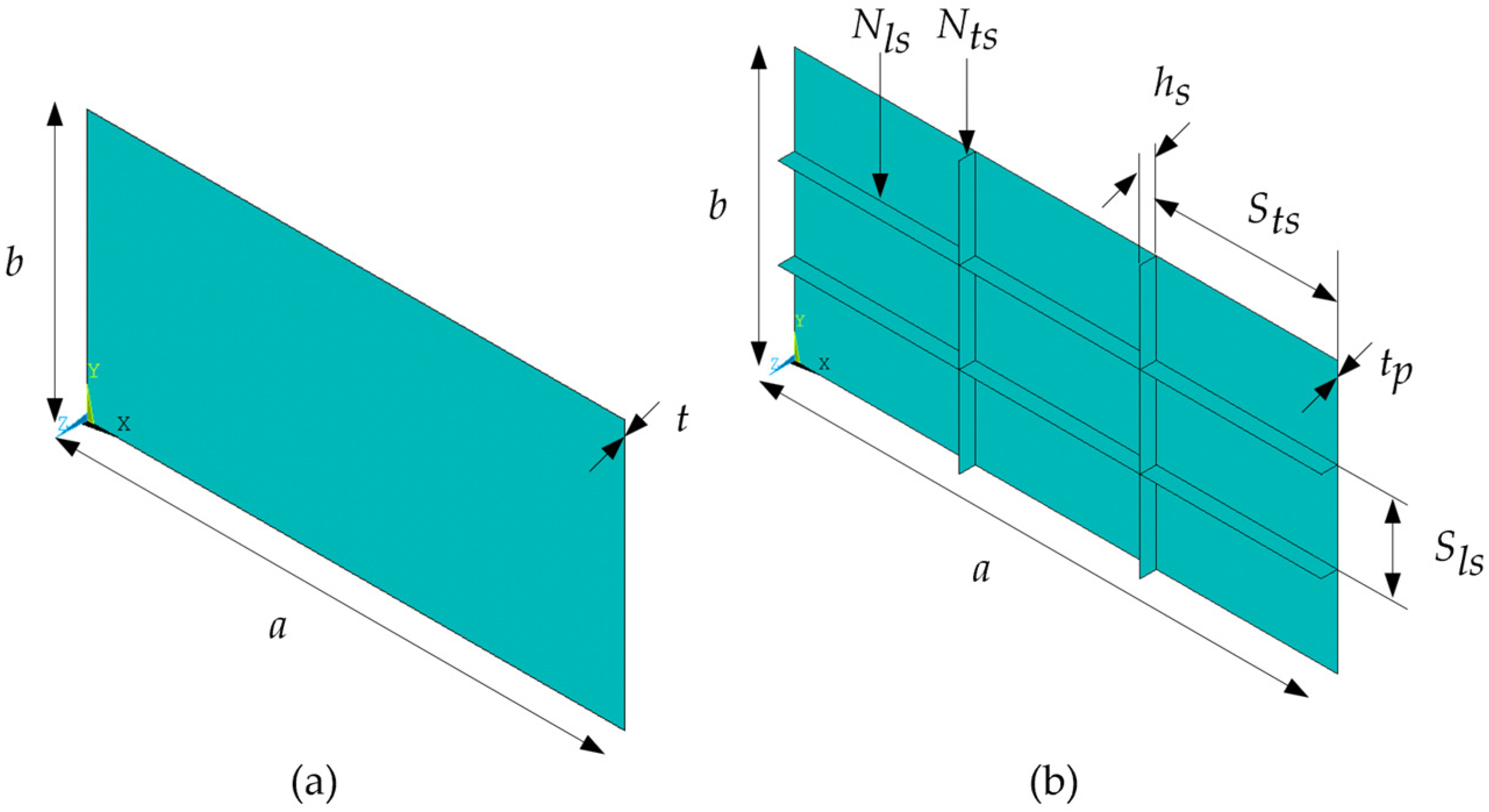
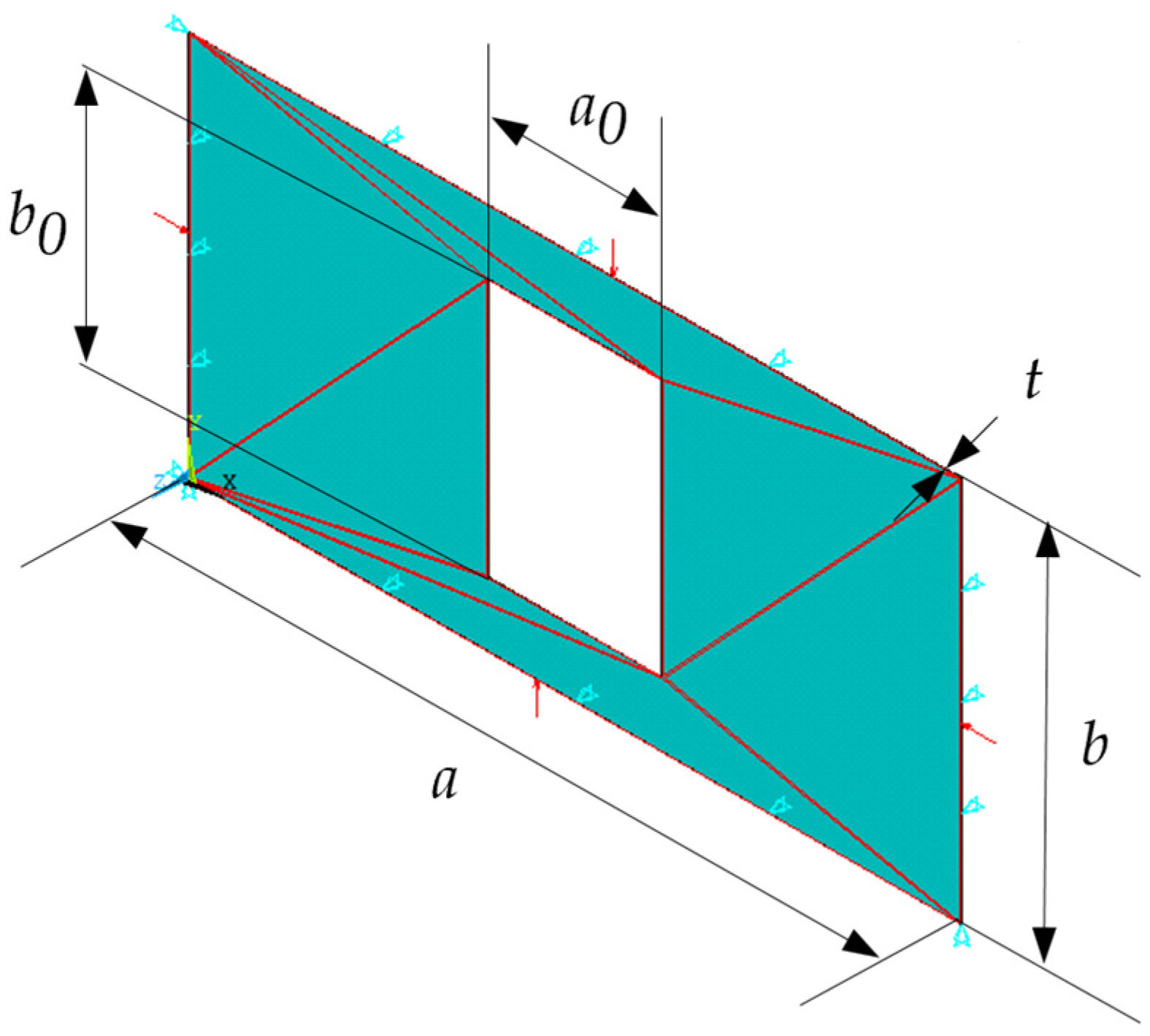
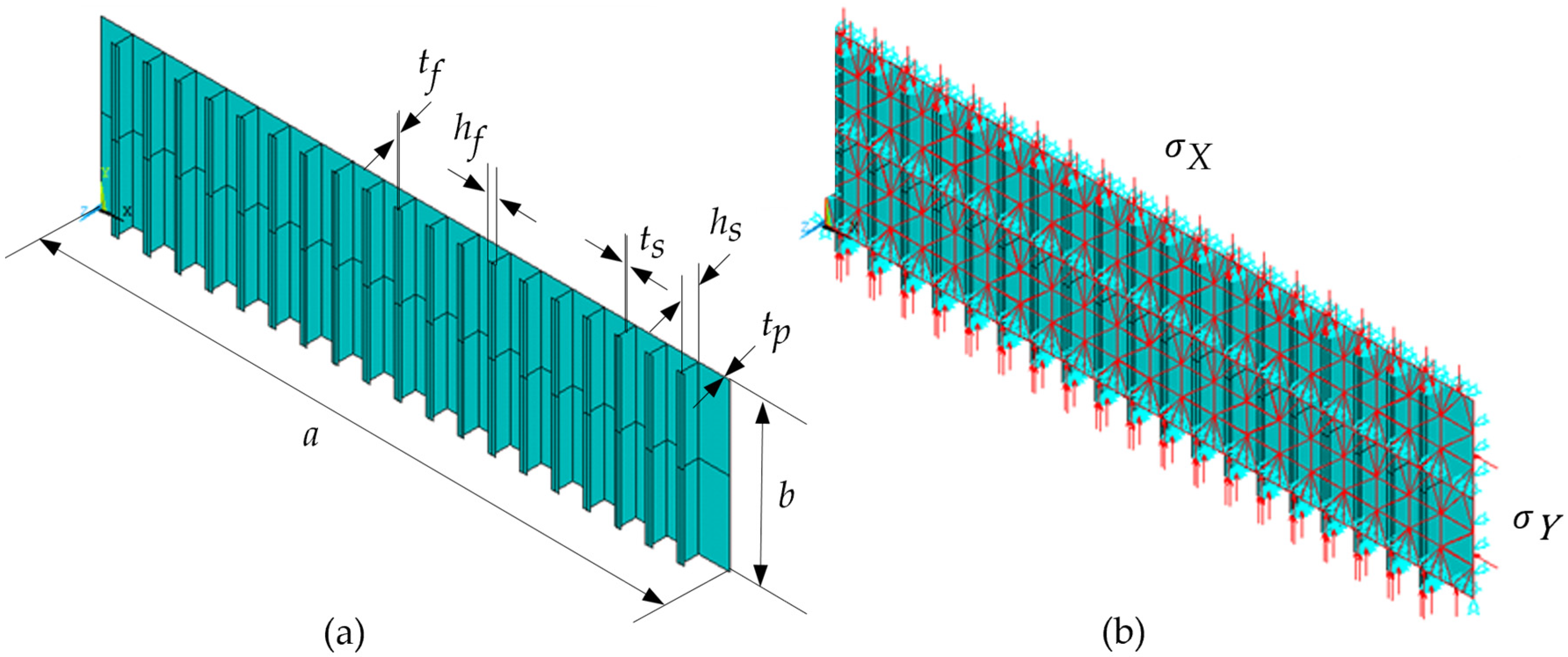
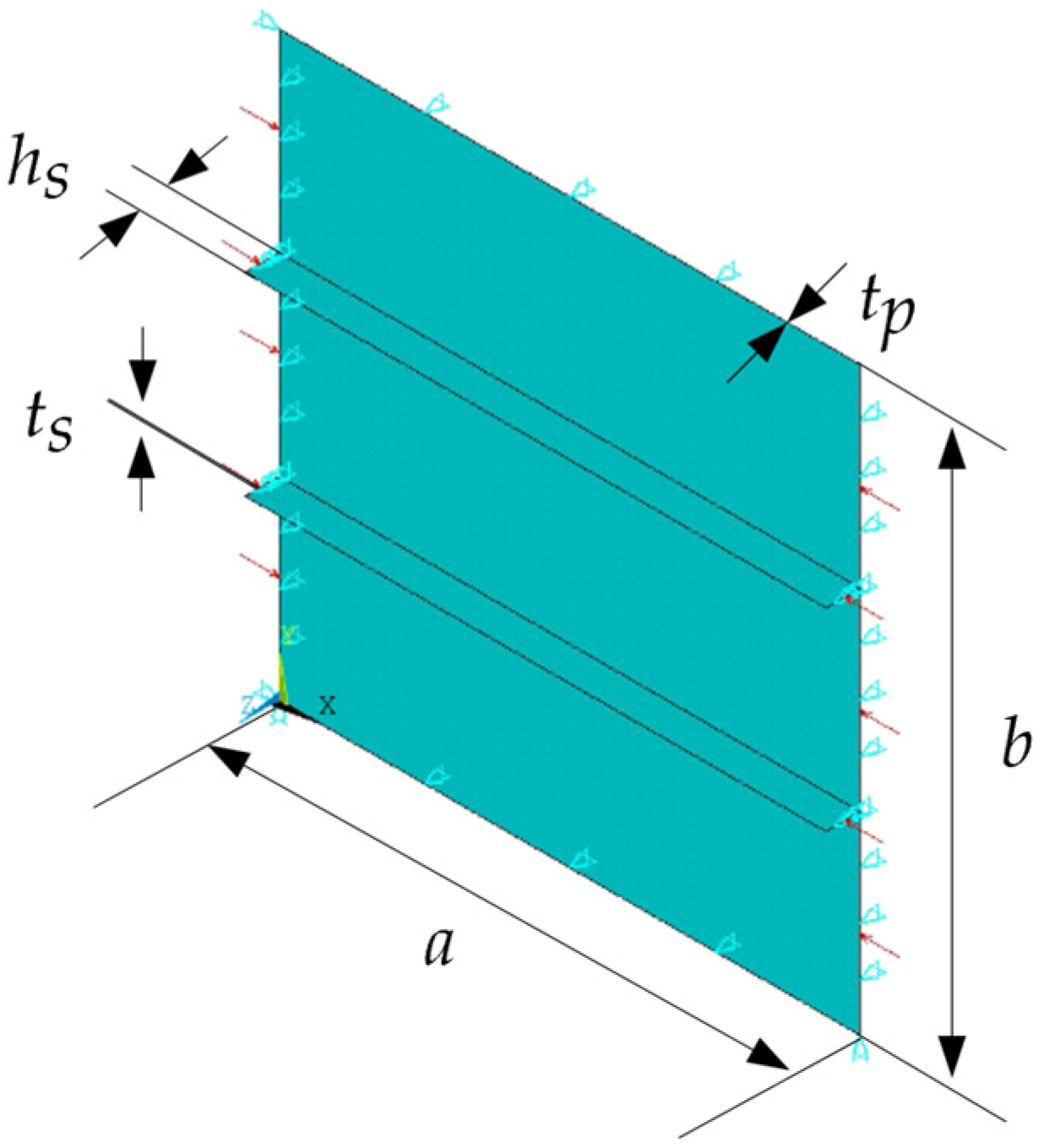
2.2. Computational Modeling of Plates
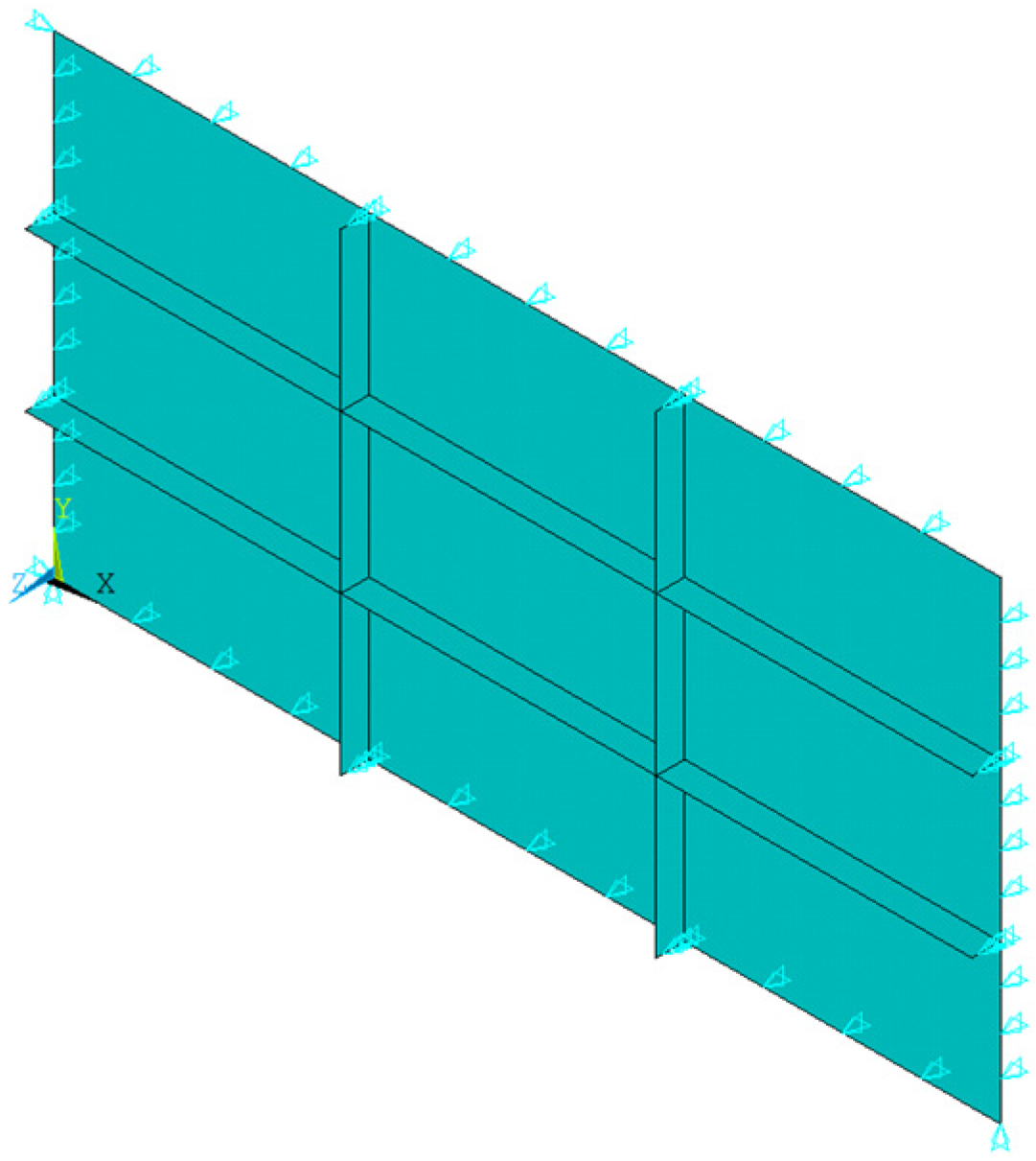
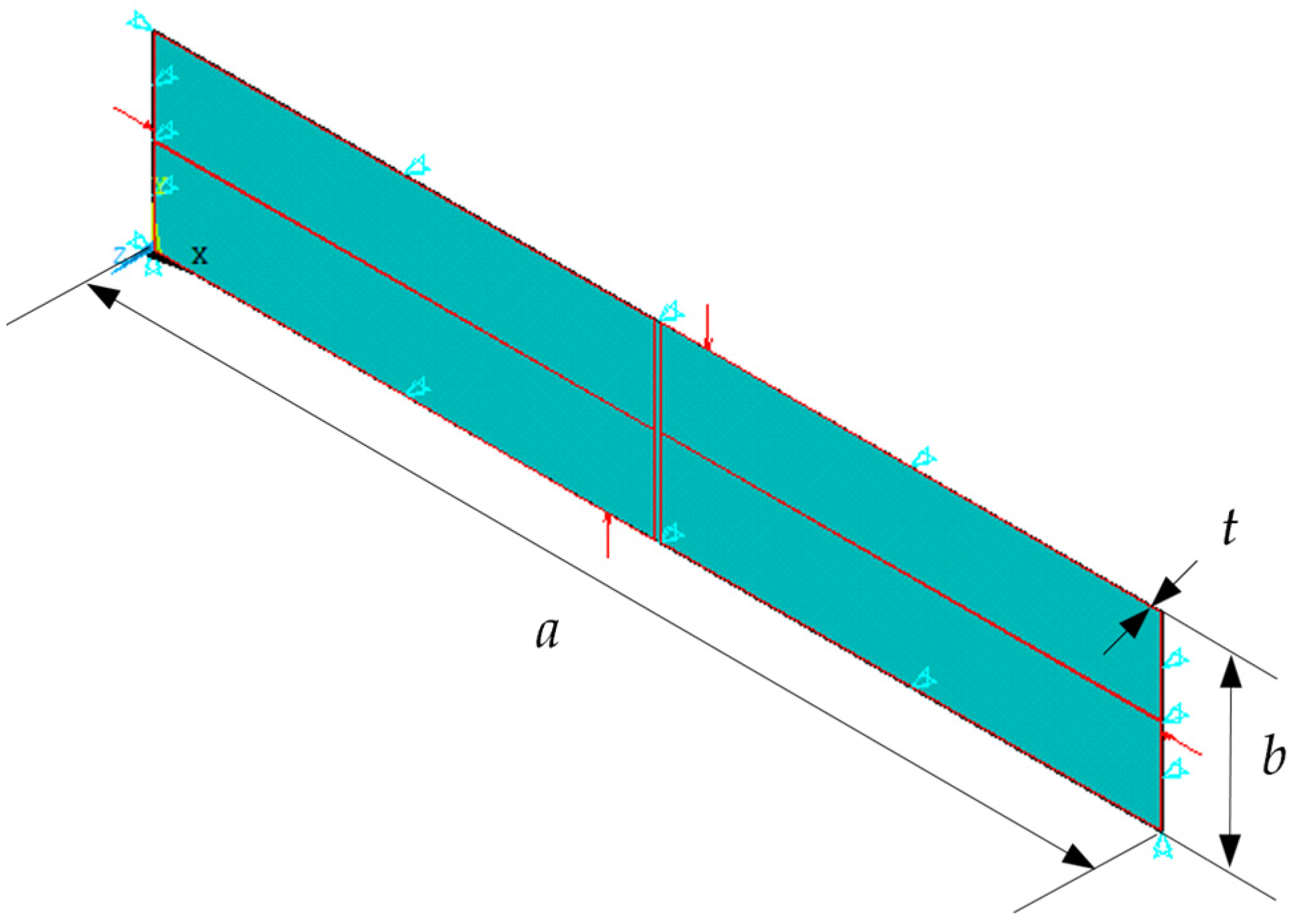
2.2.1. Boundary Conditions
2.2.2. Loading Application
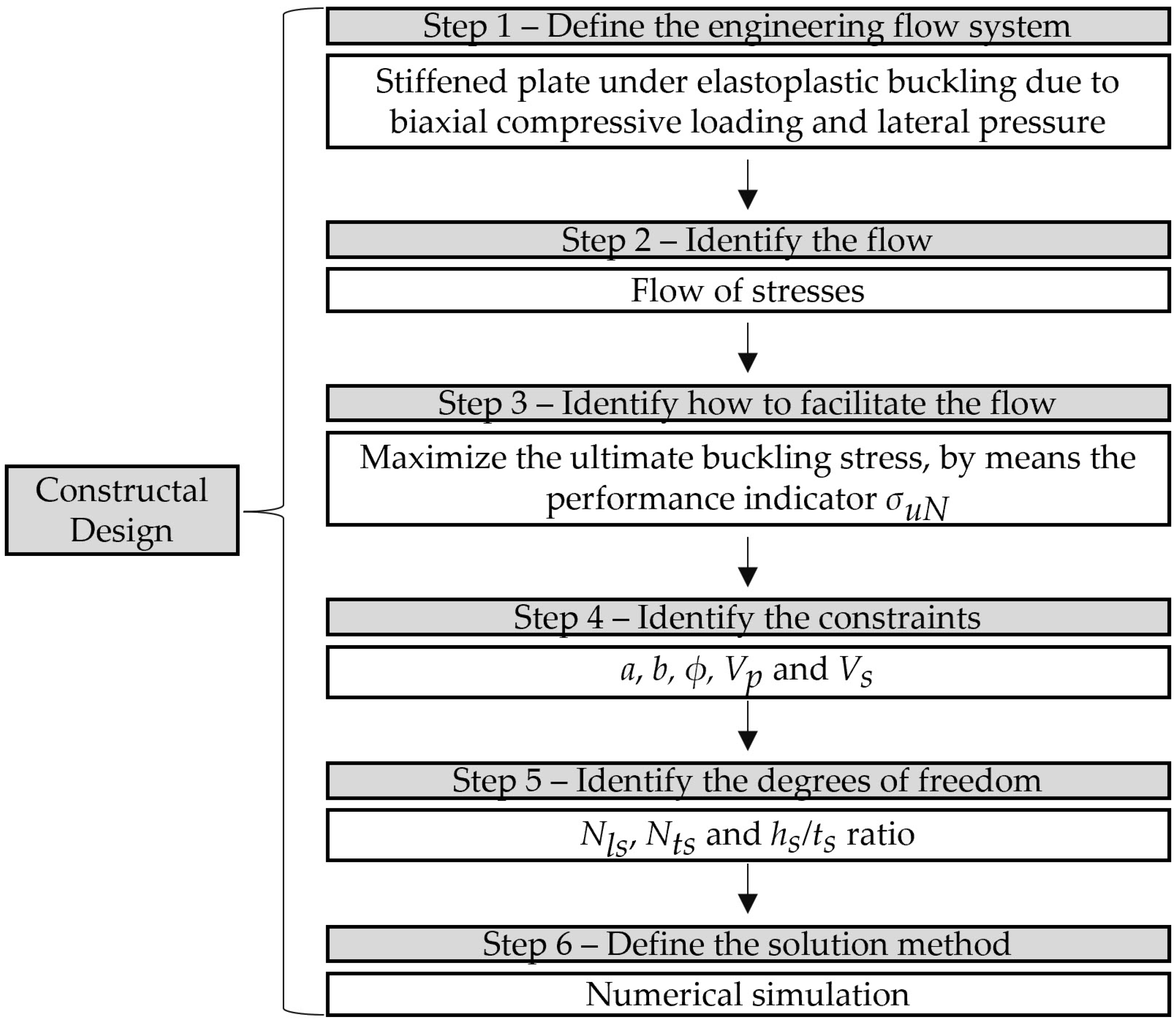
2.3. Constructal Design Method and Exhaustive Search Technique
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Verification and Validation of Computational Modeling of Buckling
3.1.1. Verification of Elastoplastic Buckling Model Under Combined Loading on Unstiffened Plates
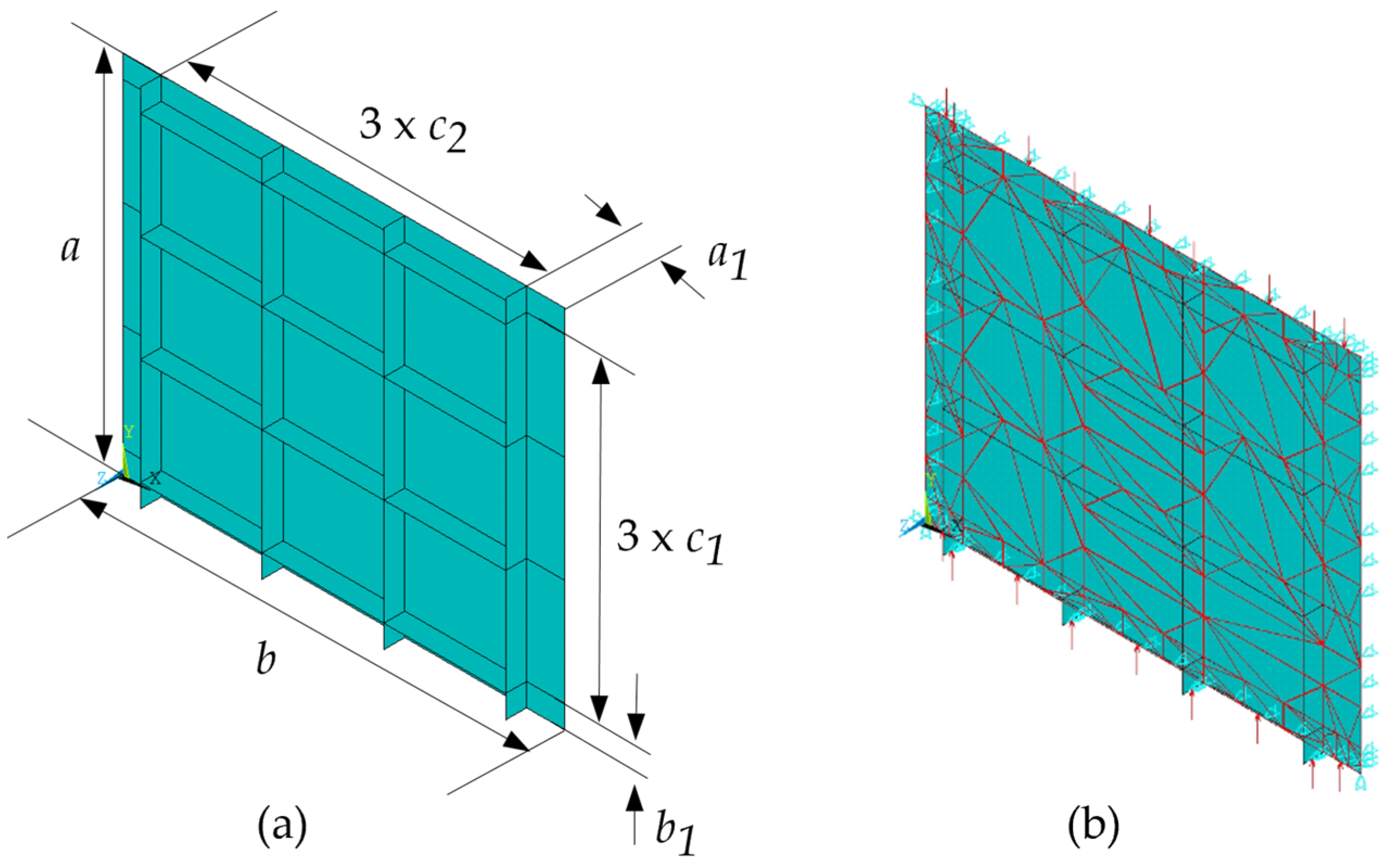
3.1.2. Verification of Elastoplastic Buckling Model Under Combined Loading on Stiffened Plates
3.1.3. Validation of Elastoplastic Buckling Model Under Combined Loading on Stiffened Plate
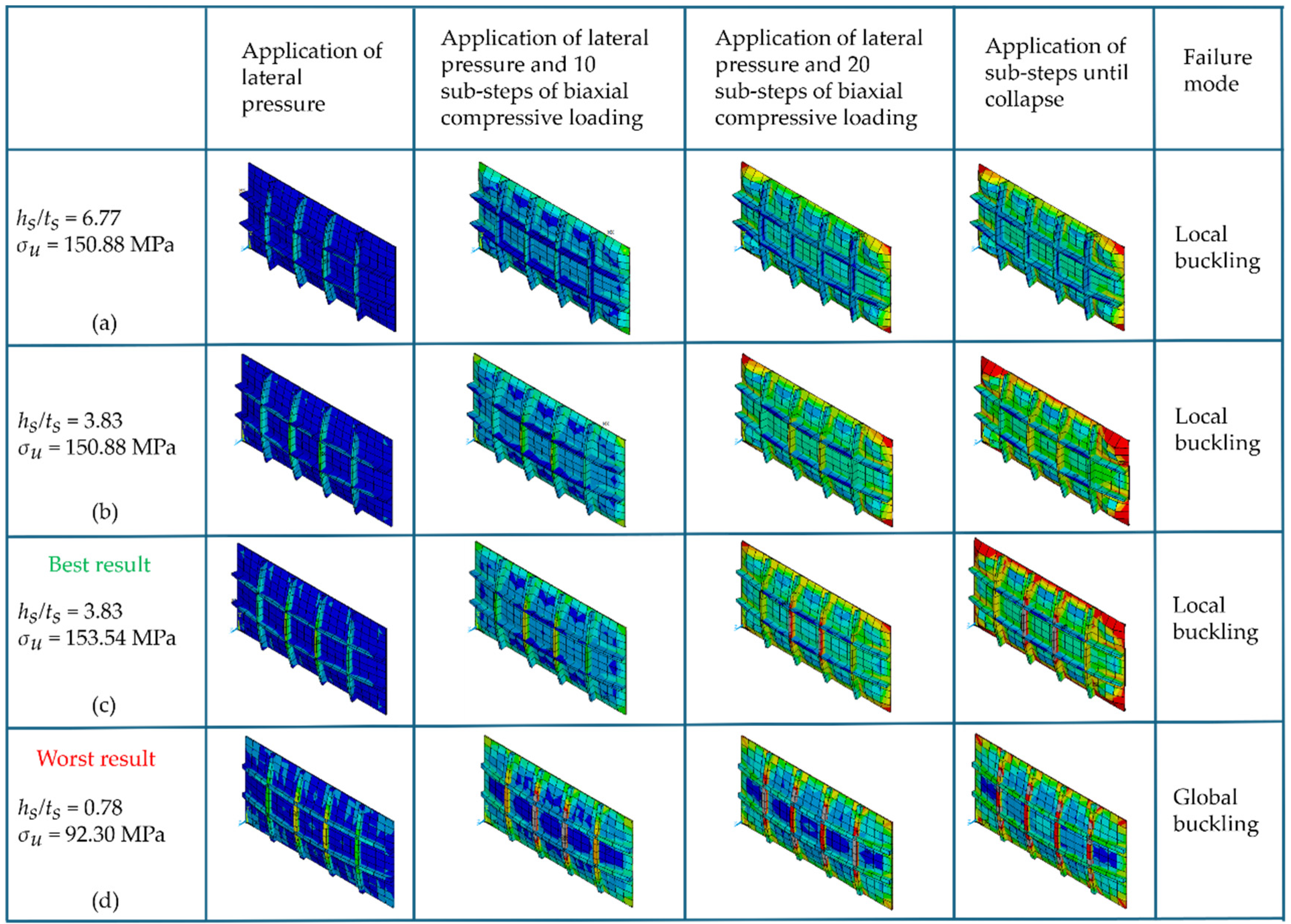
3.2. Case Study
3.2.1. Mesh Convergence Test
3.2.2. Sub-Steps Convergence Test
3.3. Geometric Evaluation
3.3.1. Reference Plate
3.3.2. Influence of and / over
3.3.3. Highest Values of /, , and over
3.3.4. Influence of and over Once Optimized and Once Maximized
3.3.5. Influence of , , and over
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tatsumi, A.; Htoo Ko, H.H.; Fujikubo, M. Ultimate strength of container ships subjected to combined hogging moment and bottom local loads, Part 2: An extension of Smith’s method. Mar. Struct. 2020, 69, 102683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Kee Paik, J. Ultimate strength characteristics of as-built ultra-large containership hull structures under combined vertical bending and torsion. Ships Offshore Struct. 2021, 15 (Suppl. S1), S143–S160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, M.; Ergin, A.; Yanagihara, D.; Tanaka, S.; Yao, T. A new method to estimate ultimate strength of stiffened panels under longitudinal thrust based on analytical formulas. Mar. Struct. 2018, 59, 510–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X. Numerical investigation on the ultimate strength behavior and assessment of continuous hull plate under combined biaxial cyclic loads and lateral pressure. Mar. Struct. 2023, 89, 103408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemian, R. Guide to Stability Design for Metal Structures, 6th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Xu, Z.; Okada, T.; Kawamura, Y.; Hayakawa, G.; Ishibashi, K.; Koyama, H. A study on the scantling formulae of a stiffener against lateral pressure under the simultaneous action of axial load. Mar. Struct. 2024, 95, 103595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, A.H. Constructal theory: From engineering to physics, and how flow systems develop shape and structure. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2006, 59, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejan, A. Constructal-theory network of conducting paths for cooling a heat generating volume. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1997, 40, 799–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silveira, T.; Pinto, V.T.; Lima, J.P.S.; Pavlovic, A.; Rocha, L.A.O.; Dos Santos, E.D.; Isoldi, L.A. Applicability Evidence of Constructal Design in Structural Engineering: Case Study of Biaxial Elasto-Plastic Buckling of Square Steel Plates with Elliptical Cutout. J. Appl. Comput. Mech. 2021, 7, 922–934. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Kong, X.; Wu, W.; Kim, D.K. An advanced design diagram of stiffened plate subjected to combined in-plane and lateral loads considering initial deflection effects. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 203, 112144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgardt, G.R.; Fragassa, C.; Rocha, L.A.O.; Dos Santos, E.D.; Da Silveira, T.; Isoldi, L.A. Computational Model Verification and Validation of Elastoplastic Buckling Due to Combined Loads of Thin Plates. Metals 2023, 13, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Xiong, Q.; Wang, D. Experimental and numerical study on the ultimate strength of stiffened plates subjected to combined biaxial compression and lateral loads. Ocean Eng. 2021, 228, 108928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, J.P.S.; Cunha, M.L.; dos Santos, E.D.; Rocha, L.A.O.; Real, M.V.; Isoldi, L.A. Constructal Design for the ultimate buckling stress improvement of stiffened plates submitted to uniaxial compressive load. Eng. Struct. 2020, 203, 109883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, R.R.; Troina, G.S.; Fragassa, C.; Pavlovic, A.; Cunha, M.L.; Rocha, L.A.O.; dos Santos, E.D.; Isoldi, L.A. Constructal design method dealing with stiffened plates and symmetry boundaries. Theor. Appl. Mech. Lett. 2020, 10, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ong, Y.S.; Cai, J. A survey of adaptive sampling for global metamodeling in support of simulation-based complex engineering design. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2018, 57, 393–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amouzgar, K.; Strömberg, N. Radial basis functions as surrogate models with a priori bias in comparison with a posteriori bias. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2017, 55, 1453–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.M.; Wang, C.Y.; Reddy, J.N. Exact Solutions for Buckling of Structural Members. In CRC Series in Computational Mechanics and Applied Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przemieniecki. Theory of Matrix Structural Analysis; Dover Publications: Mineola, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sawy, K.M.; Nazmy, A.S.; Martini, M.I. Elasto-plastic buckling of perforated plates under uniaxial compression. Thin-Walled Struct. 2004, 42, 1083–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, E.M.M. Steel Columns under Compression with Different Sizes of Square Hollow Cross-Sections, Lengths, and End Constraints. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSYS Inc. Element reference. In Ansys Mechanical APDL Manual; ANSYS Inc.: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Jeon, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Seo, H.D.; Ahn, H.J.; Lee, J.M. Effect of reinforcement on buckling and ultimate strength of perforated plates. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2015, 92, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, J.K.; Kim, B.J.; Seo, J.K. Methods for ultimate limit state assessment of ships and ship-shaped offshore structures: Part I-Unstiffened plates. Ocean Eng. 2008, 35, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, J.K.; Kim, B.J.; Seo, J.K. Methods for ultimate limit state assessment of ships and ship-shaped offshore structures: Part II-Stiffened plates. Ocean Eng. 2008, 35, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, D.; Kuhlmann, U.; Davaine, L.; Braun, B. Design of plated structures: Eurocode 3: Design of steel structures. Part 1–5, design of plated structures. In ECCS—European Convention for Constructional Steelwork; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Suneel Kumar, M.; Lavana Kumar, C.; Alagusundaramoorthy, P.; Sundaravadivelu, R. Ultimate strength of orthogonal stiffened plates subjected to axial and lateral loads. J. Civ. Eng. 2010, 14, 197–206. [Google Scholar]




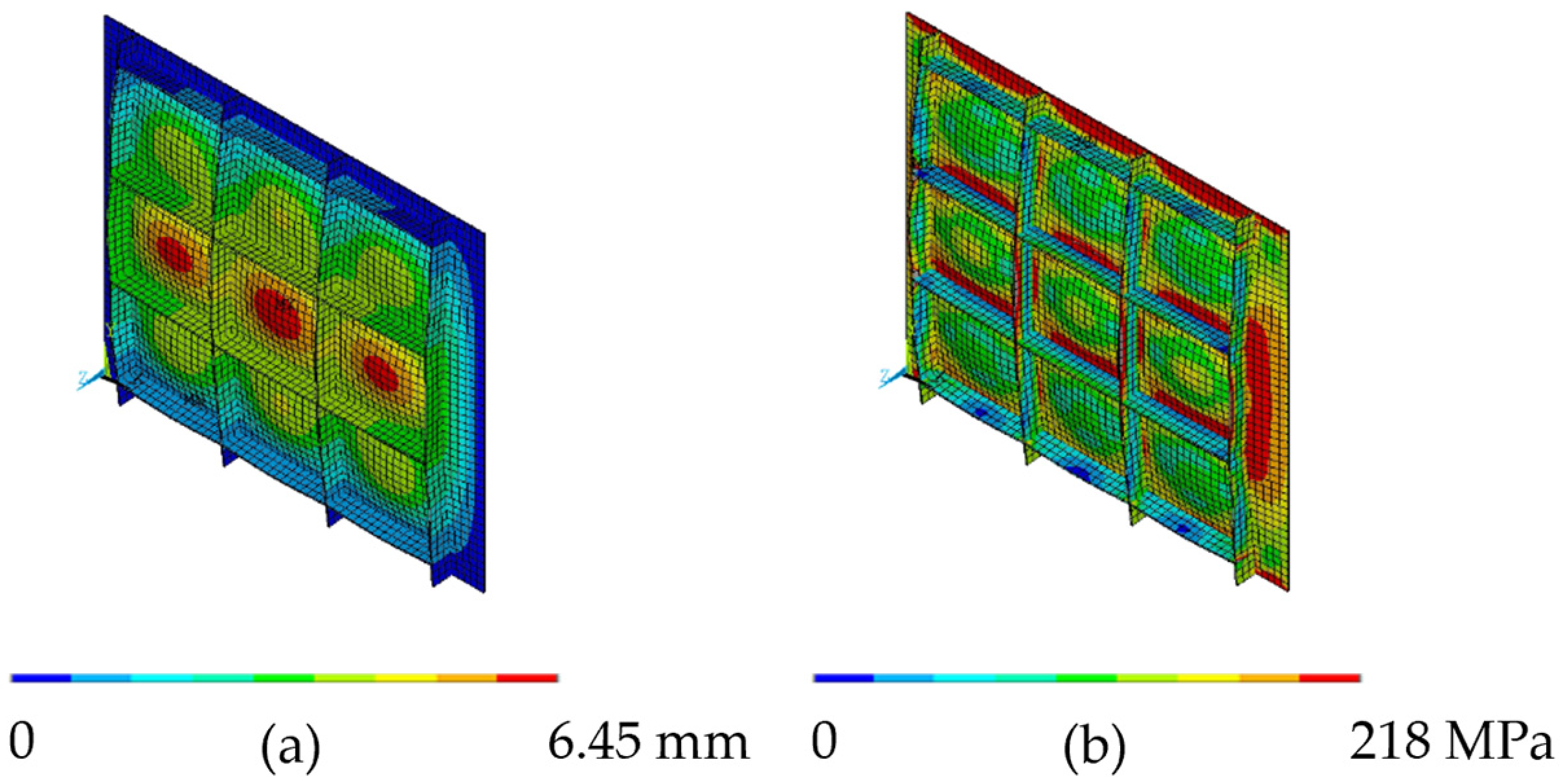
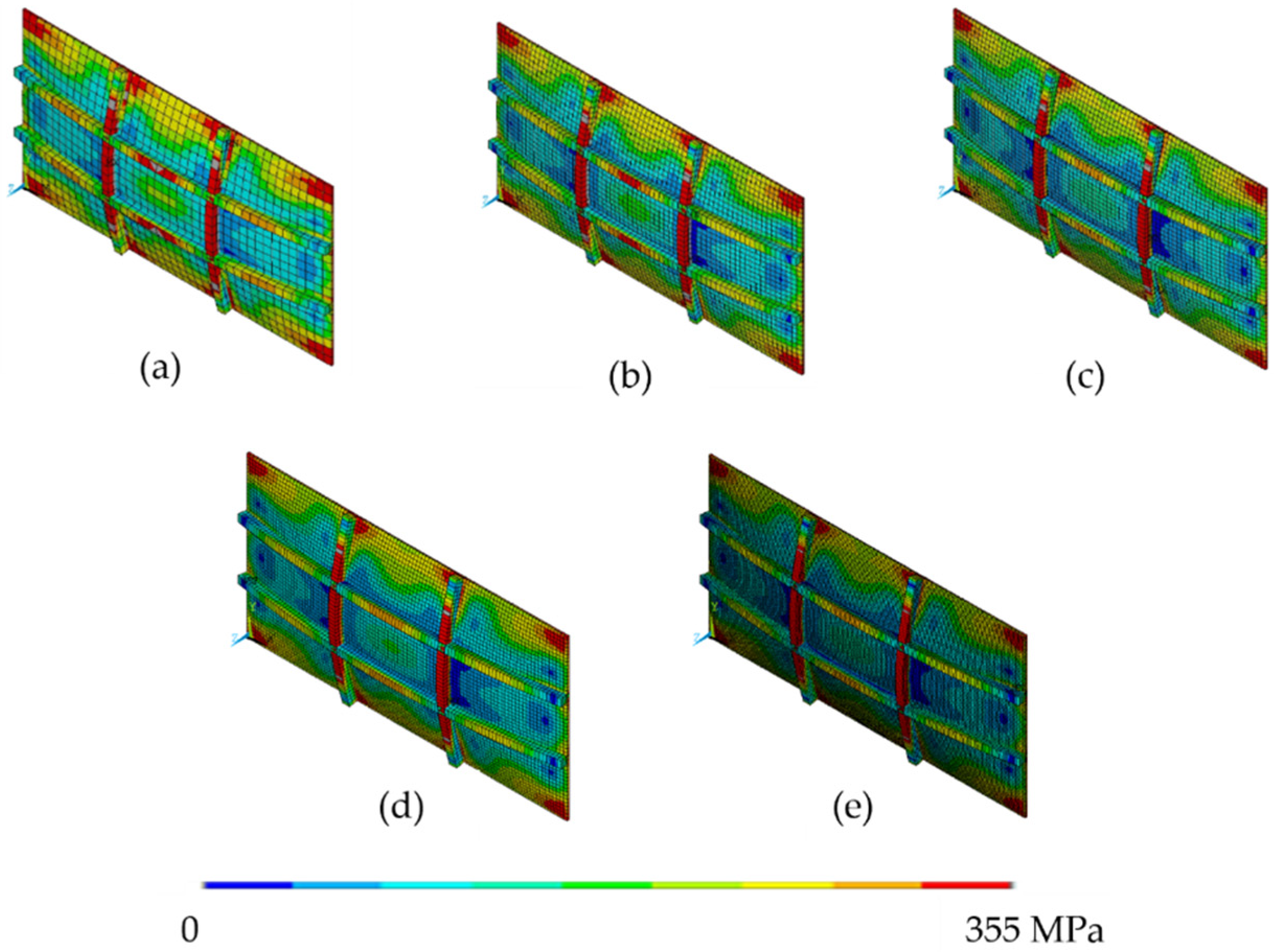


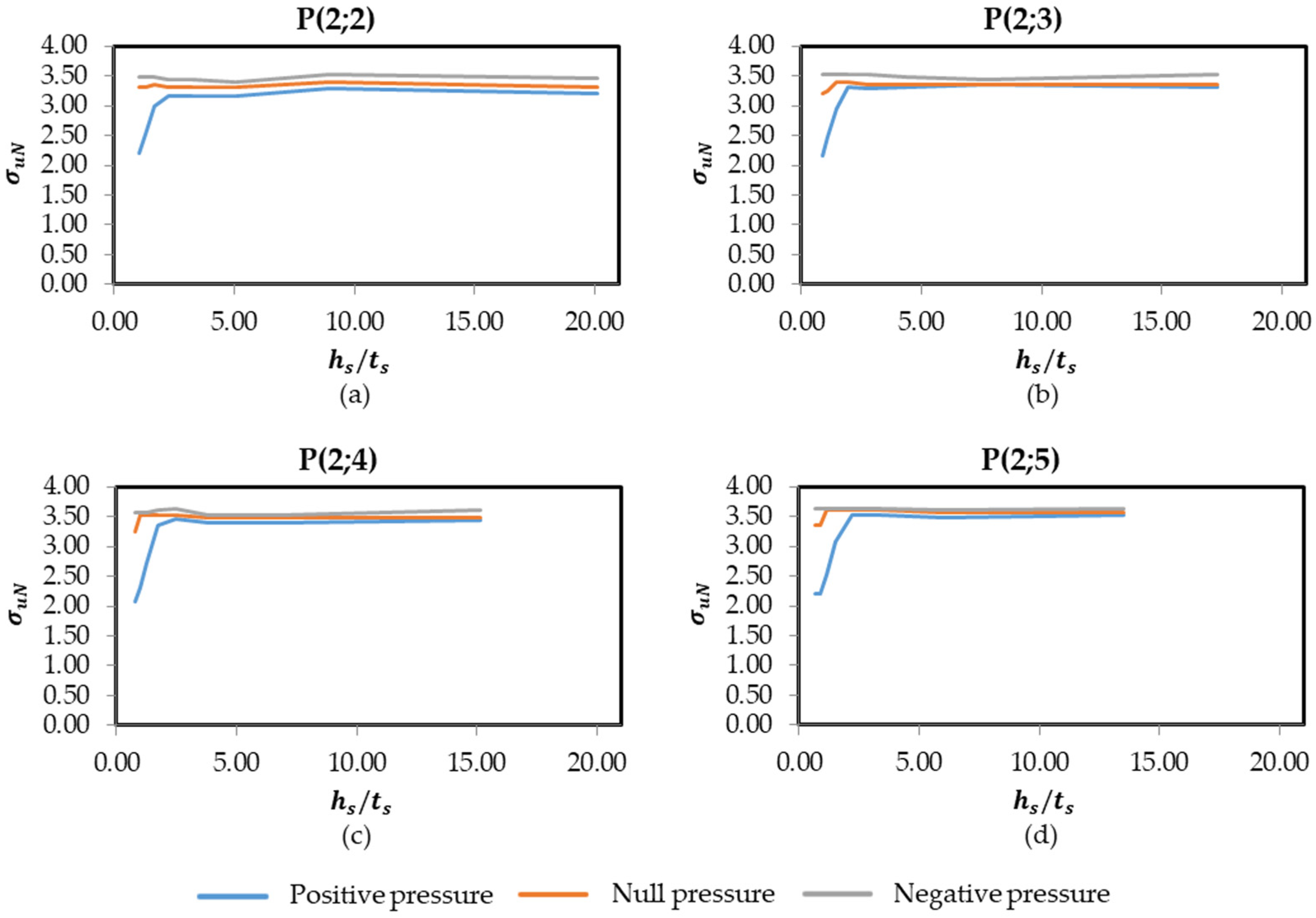
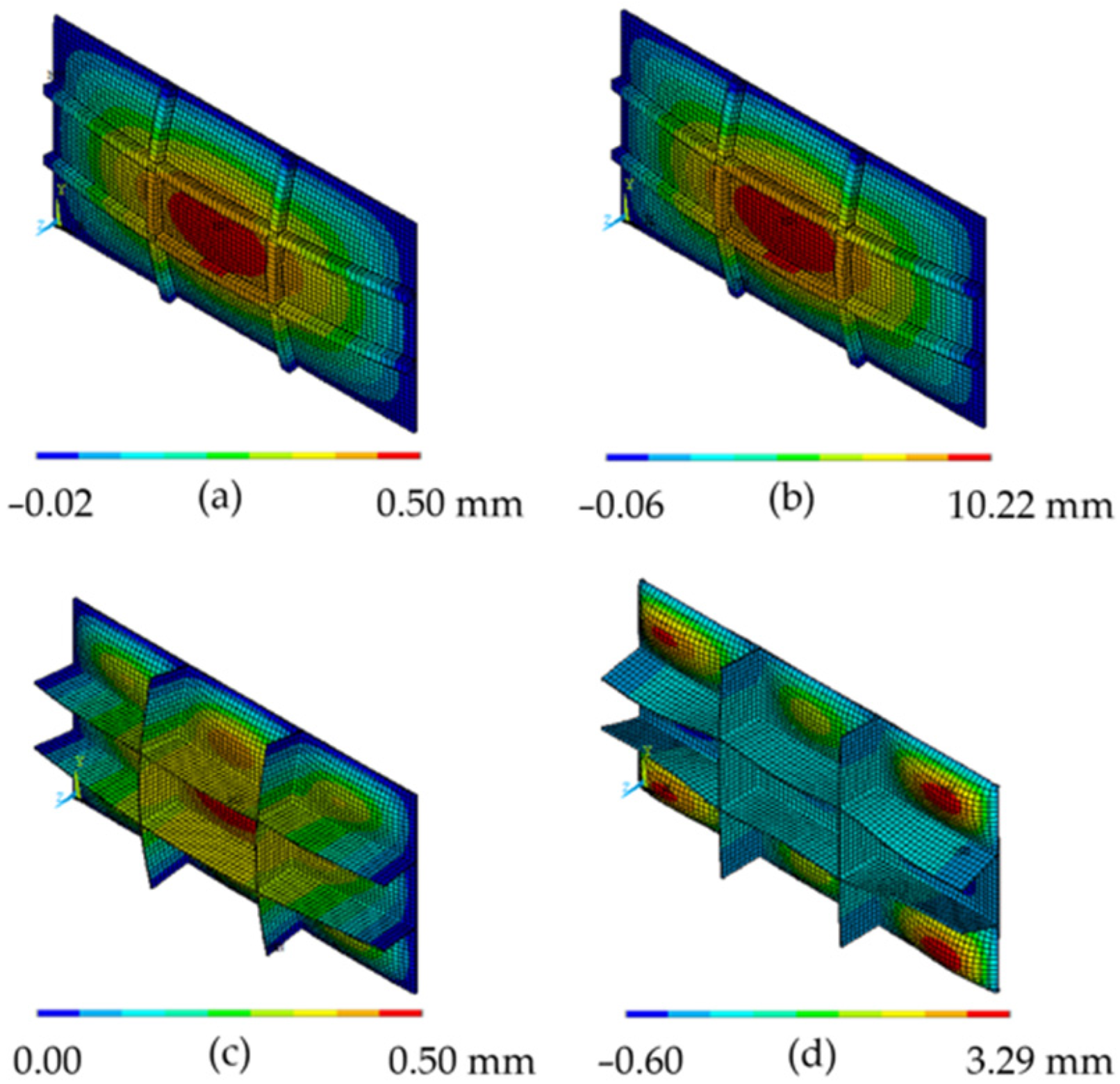







| Element Length (mm) | Number of Elements | (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 387 | 225.22 |
| 75 | 638 | 225.22 |
| 50 | 1462 | 225.22 |
| 25 | 5676 | 225.22 |
| Element Length (mm) | Number of Elements | (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 174 | 28.75 |
| 75 | 345 | 28.40 |
| 50 | 704 | 28.40 |
| 30 | 1974 | 28.40 |
| 25 | 2747 | 28.40 |
| Element Length (mm) | Number of Elements | (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| 600 | 776 | 236.25 |
| 500 | 970 | 236.25 |
| 250 | 4290 | 236.25 |
Ratio | Present Study | Paik and Seo [24] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANSYS | ALPS/ULSAP | DNV PULS | ||||||
| 0.79:0.21 | 236.25 | 62.80 | 223.65 | 59.85 | 199.33 | 53.55 | 245.70 | 66.15 |
| 0.40:0.60 | 76.65 | 114.97 | 66.78 | 100.17 | 62.02 | 93.02 | 73.05 | 109.56 |
| Element Length (mm) | Number of Elements | (MPa) | (kN) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 396 | 277.73 | 4524.12 |
| 75 | 672 | 277.76 | 4524.12 |
| 50 | 1512 | 277.79 | 4566.01 |
| 25 | 5904 | 277.79 | 4566.01 |
| Methodology | (MPa) | Difference (%) | Pu (kN) | Difference (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present study | 277.76 | - | 4566.01 | - |
| EBPlate (a) | 276.00 | 0.64 | - | - |
| EBPlate (b) | 289.00 | −3.89 | - | - |
| ABAQUS | 268.00 | 3.64 | 4424.00 | 3.21 |
| EN1993-1-5 A.2 [26] | 290.00 | −4.22 | - | - |
| Element Length (mm) | Number of Elements | (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| 75 | 382 | 140.32 |
| 50 | 894 | 123.55 |
| 35 | 1472 | 123.25 |
| 20 | 3936 | 122.90 |
| Element Length (mm) | Number of Elements | Processing Time (s) | (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 1134 | 82 | 101.17 |
| 30 | 3114 | 112 | 99.40 |
| 25 | 4140 | 158 | 97.62 |
| 20 | 6426 | 216 | 97.62 |
| 10 | 24,744 | 975 | 97.62 |
| Number of Sub-Steps | Maximum Number of Sub-Steps | Minimum Number of Sub-Steps | Processing Time (s) | (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 200 | 50 | 168 | 97.62 |
| 200 | 400 | 100 | 212 | 98.51 |
| 300 | 600 | 150 | 385 | 98.51 |
| 400 | 800 | 200 | 440 | 98.51 |
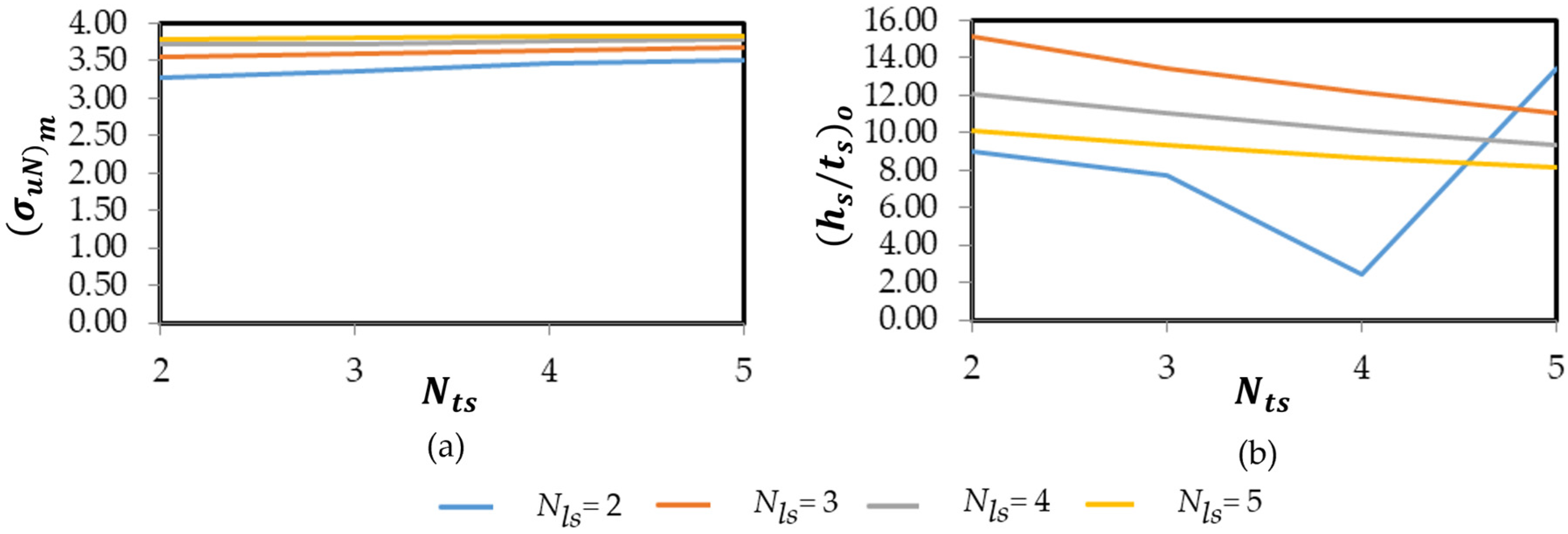
| Plate Configuration | Nls | Nts | (hs/ts)o | (σuN)m |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P(2;2) | 2 | 2 | 8.98 | 3.28 |
| P(2;3) | 2 | 3 | 7.72 | 3.36 |
| P(2;4) | 2 | 4 | 2.46 | 3.46 |
| P(2;5) | 2 | 5 | 13.48 | 3.52 |
| P(3;2) | 3 | 2 | 15.11 | 3.56 |
| P(3;3) | 3 | 3 | 13.47 | 3.60 |
| P(3;4) | 3 | 4 | 12.15 | 3.64 |
| P(3;5) | 3 | 5 | 11.06 | 3.68 |
| P(4;2) | 4 | 2 | 12.10 | 3.72 |
| P(4;3) | 4 | 3 | 11.03 | 3.72 |
| P(4;4) | 4 | 4 | 10.14 | 3.76 |
| P(4;5) | 4 | 5 | 9.38 | 3.78 |
| P(5;2) | 5 | 2 | 10.08 | 3.78 |
| P(5;3) | 5 | 3 | 9.34 | 3.80 |
| P(5;4) | 5 | 4 | 8.70 | 3.84 |
| P(5;5) | 5 | 5 | 8.14 | 3.84 |
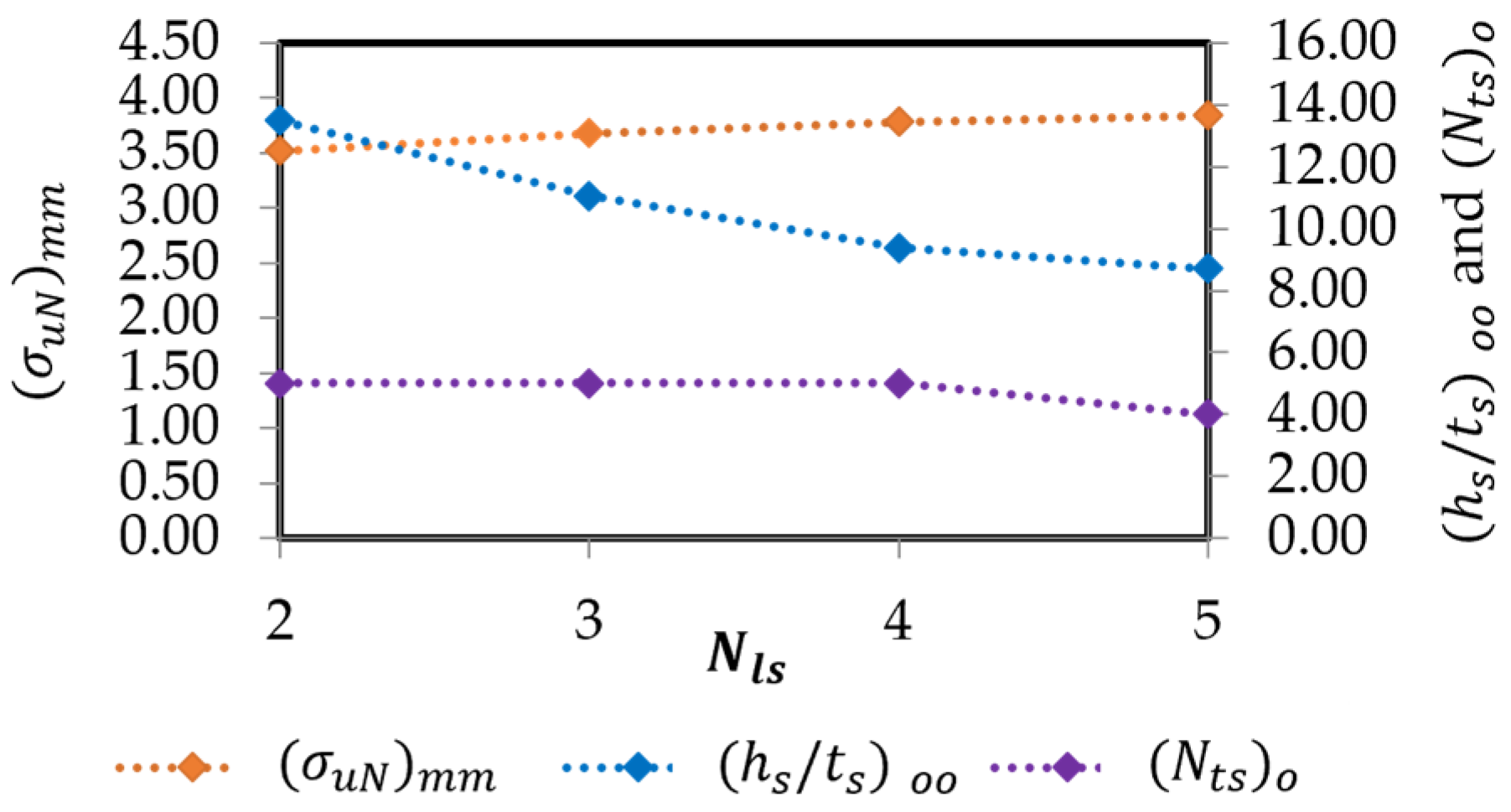
| Plate Configuration | Nls | (Nts)o | (hs/ts)oo | (σuN)mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P(2;5) | 2 | 5 | 13.48 | 3.52 |
| P(3;5) | 3 | 5 | 11.06 | 3.68 |
| P(4;5) | 4 | 5 | 9.38 | 3.78 |
| P(5;4) | 5 | 4 | 8.70 | 3.84 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vieira, R.L.; Baumgardt, G.R.; dos Santos, E.D.; Rocha, L.A.O.; da Silveira, T.; Lima, J.P.S.; Isoldi, L.A. Computational Model and Constructal Design Applied to Thin Stiffened Plates Subjected to Elastoplastic Buckling Due to Combined Loading Conditions. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3354. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063354
Vieira RL, Baumgardt GR, dos Santos ED, Rocha LAO, da Silveira T, Lima JPS, Isoldi LA. Computational Model and Constructal Design Applied to Thin Stiffened Plates Subjected to Elastoplastic Buckling Due to Combined Loading Conditions. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(6):3354. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063354
Chicago/Turabian StyleVieira, Raí Lima, Guilherme Ribeiro Baumgardt, Elizaldo Domingues dos Santos, Luiz Alberto Oliveira Rocha, Thiago da Silveira, João Paulo Silva Lima, and Liércio André Isoldi. 2025. "Computational Model and Constructal Design Applied to Thin Stiffened Plates Subjected to Elastoplastic Buckling Due to Combined Loading Conditions" Applied Sciences 15, no. 6: 3354. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063354
APA StyleVieira, R. L., Baumgardt, G. R., dos Santos, E. D., Rocha, L. A. O., da Silveira, T., Lima, J. P. S., & Isoldi, L. A. (2025). Computational Model and Constructal Design Applied to Thin Stiffened Plates Subjected to Elastoplastic Buckling Due to Combined Loading Conditions. Applied Sciences, 15(6), 3354. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063354










