Sedimentary Characteristics of the Sandstone Intervals in the Fourth Member of Triassic Akekule Formation, Tarim Basin: Implications for Petroleum Exploration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
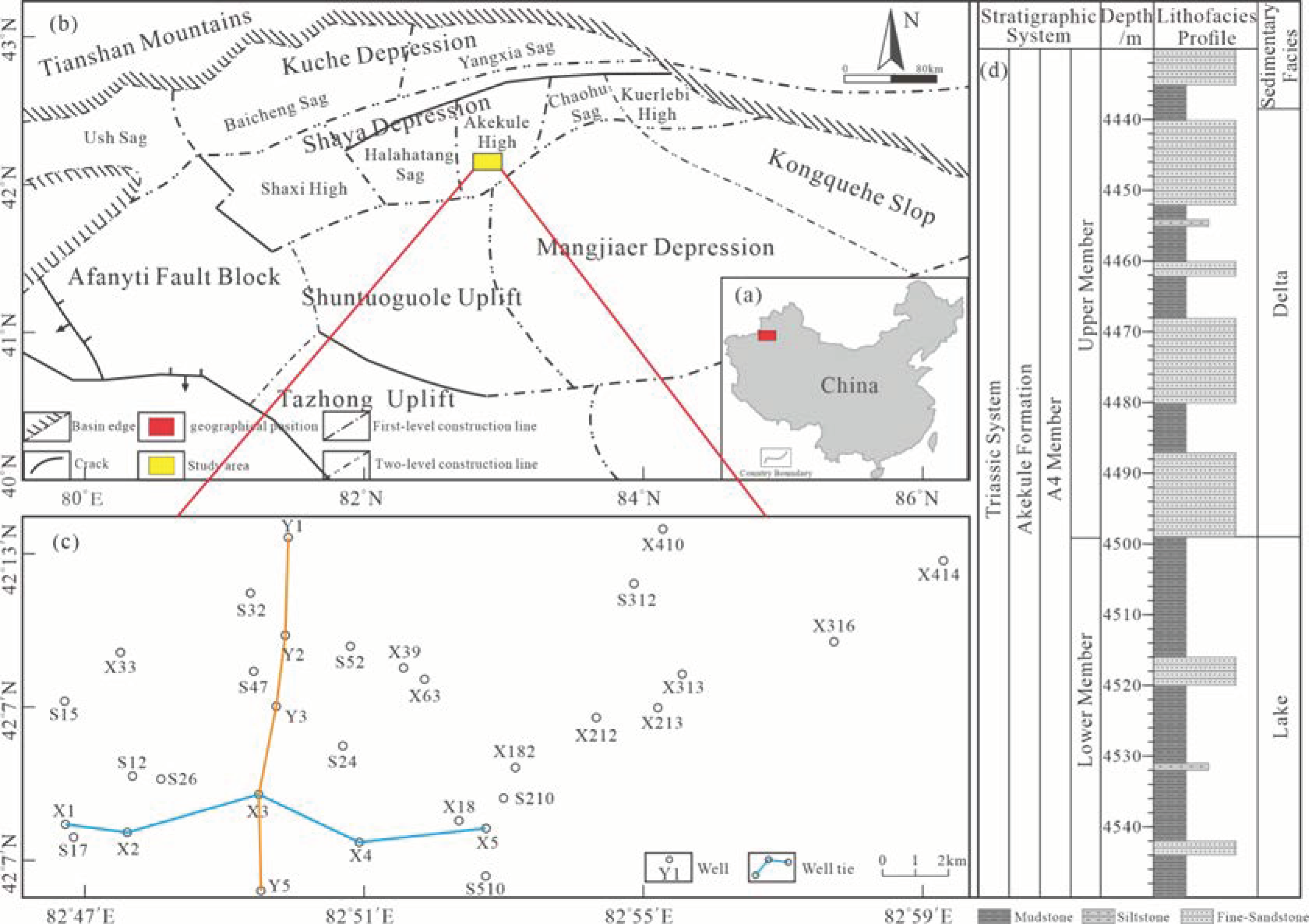
2. Geological Setting
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
4.1. Sedimentary Facies Indicators
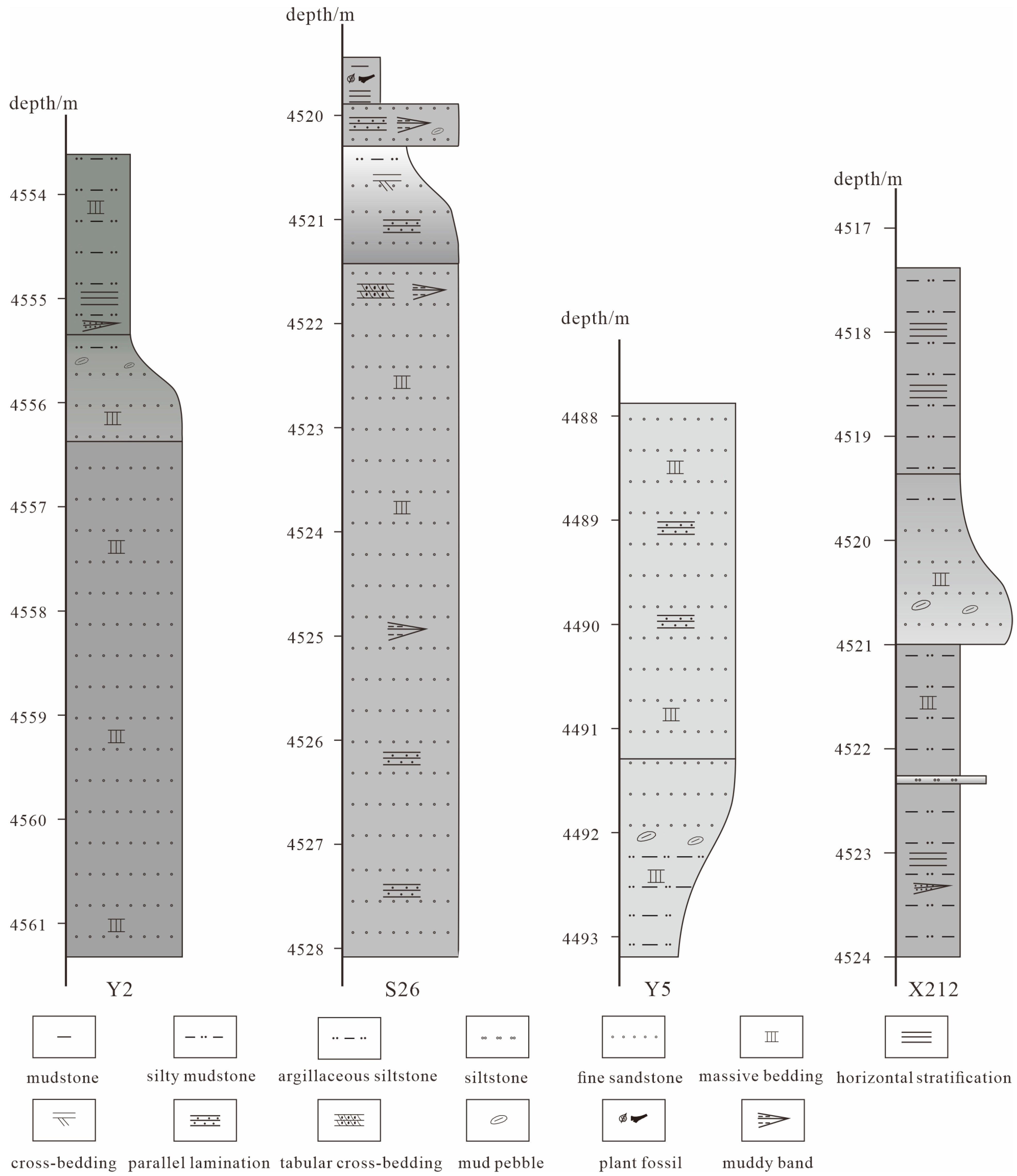
4.1.1. Lithological Characteristics
4.1.2. Sedimentary Structural Characteristics
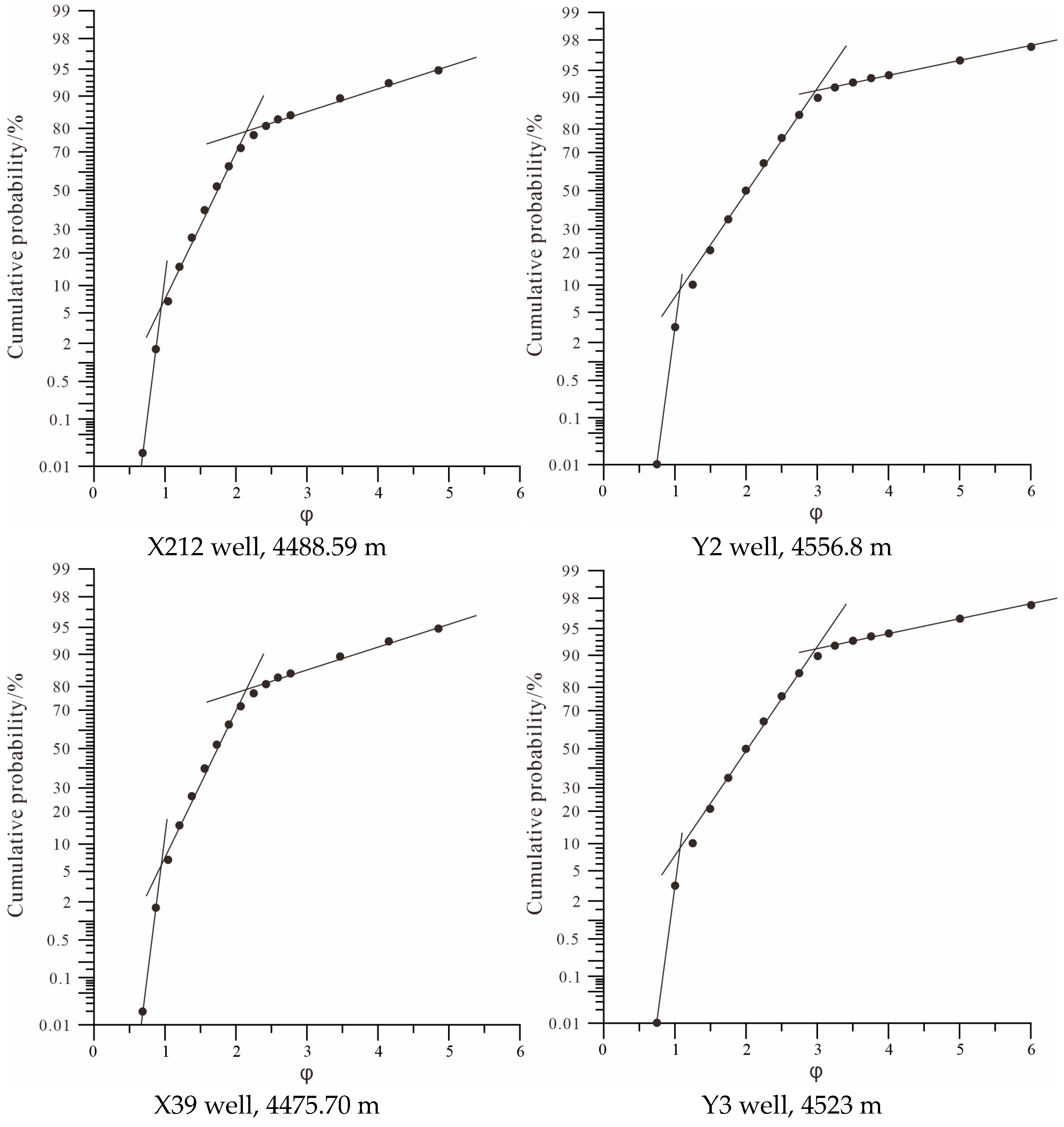
4.1.3. Particle Size Distribution
4.1.4. Characteristics of Phase Sequence Combination
4.2. Sand Body Distribution
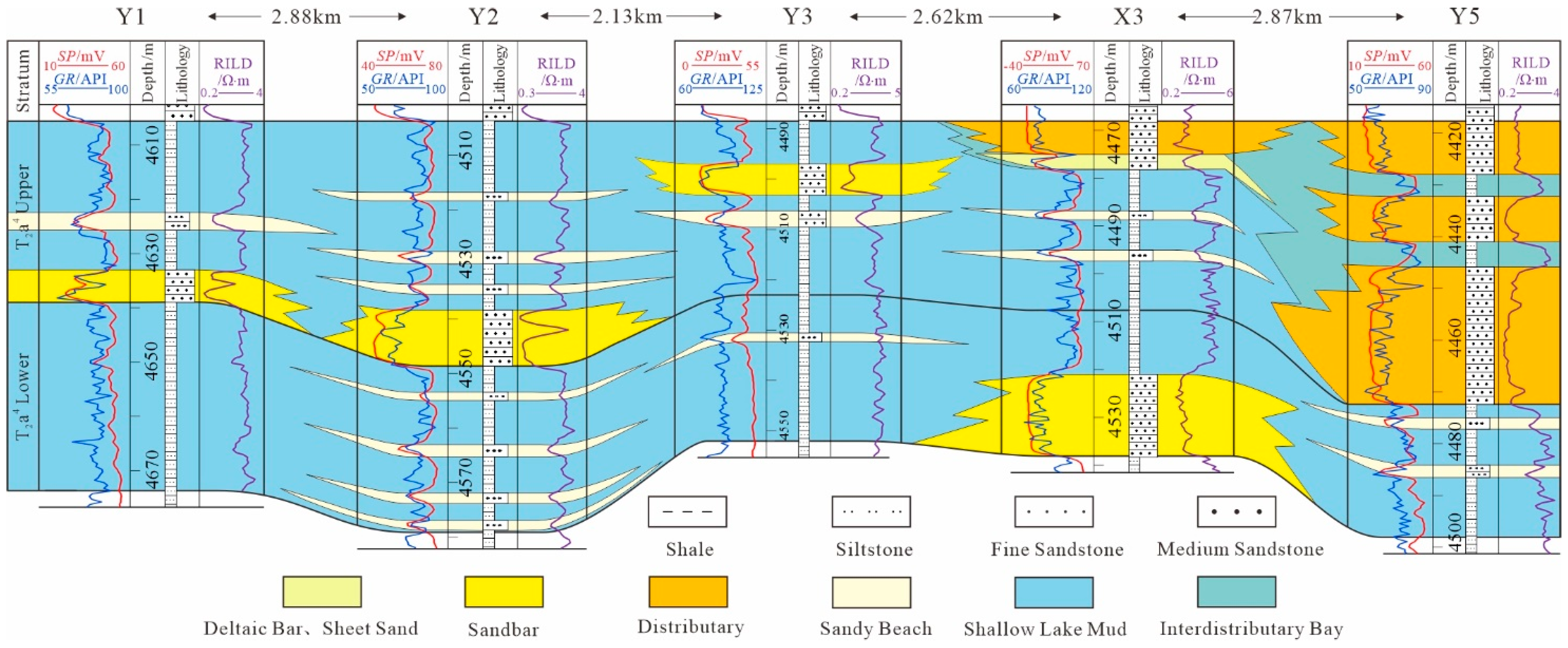
4.2.1. Characteristics of Sedimentary Facies in Profile
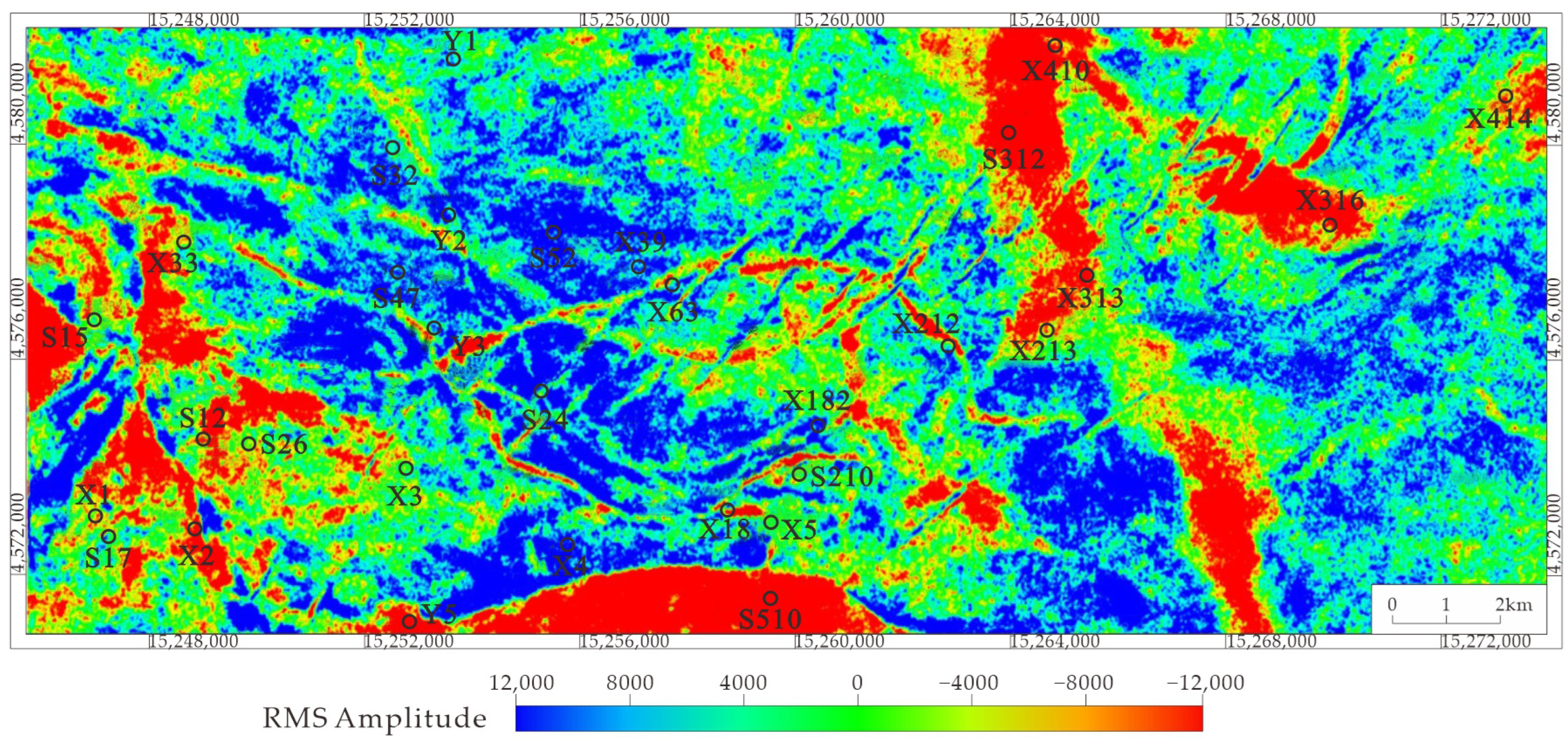
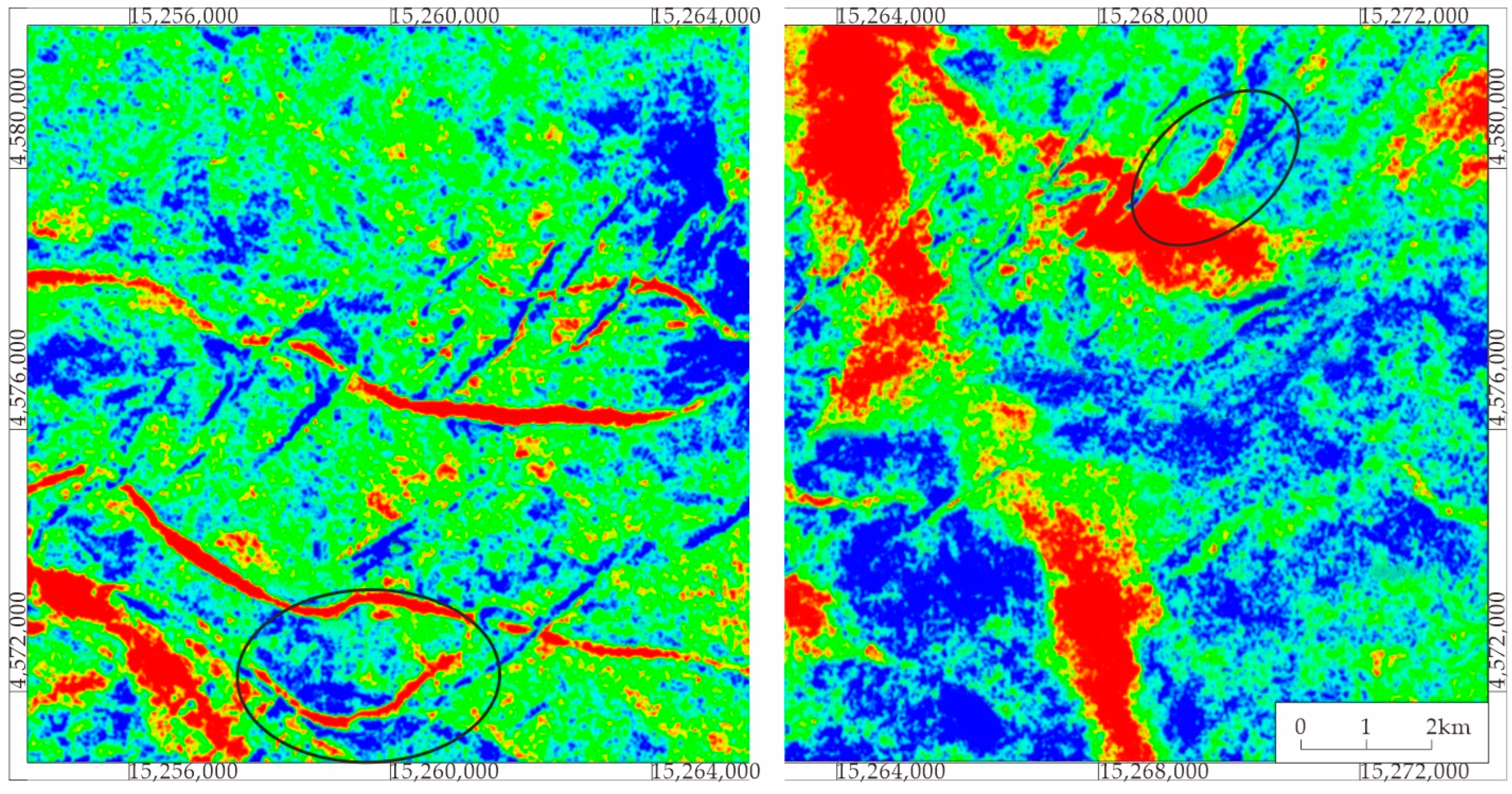
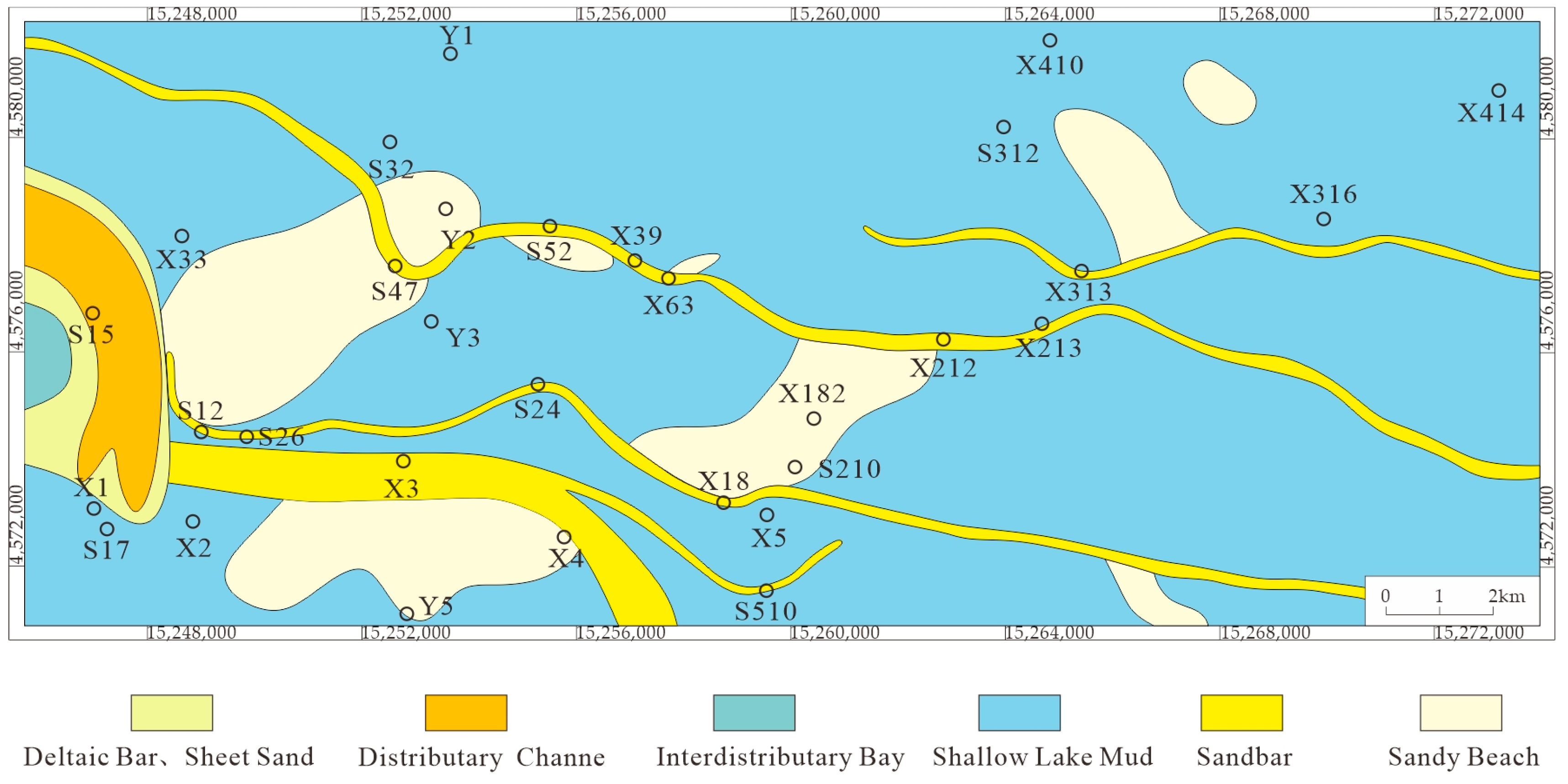
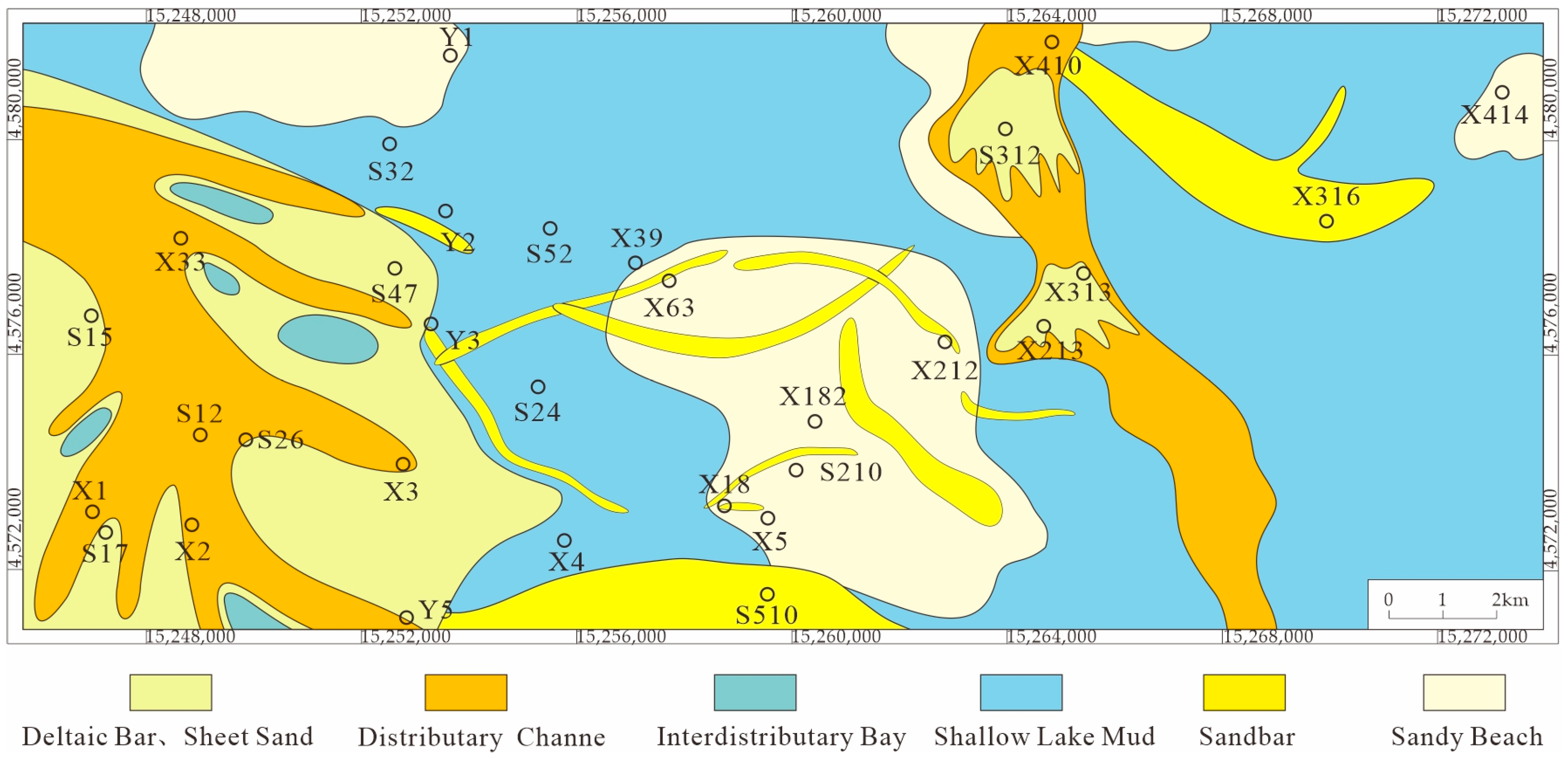
4.2.2. Plane Characteristics of Sand Body
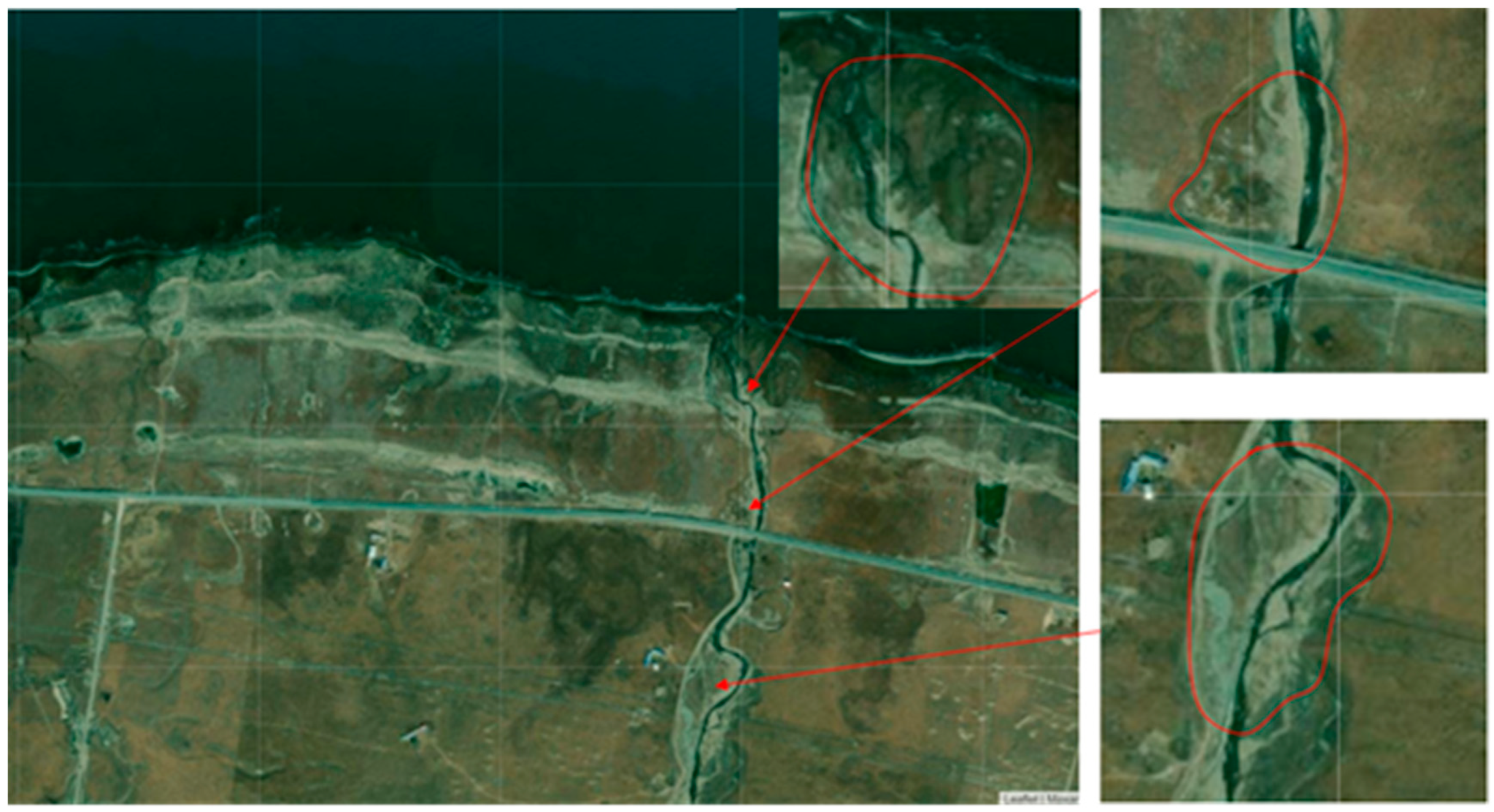
4.3. Modern Sedimentary Characteristics of Qinghai Lake
5. Discussion
5.1. Sedimentary Environment Analysis
5.2. Distribution of Sedimentary Facies Plane
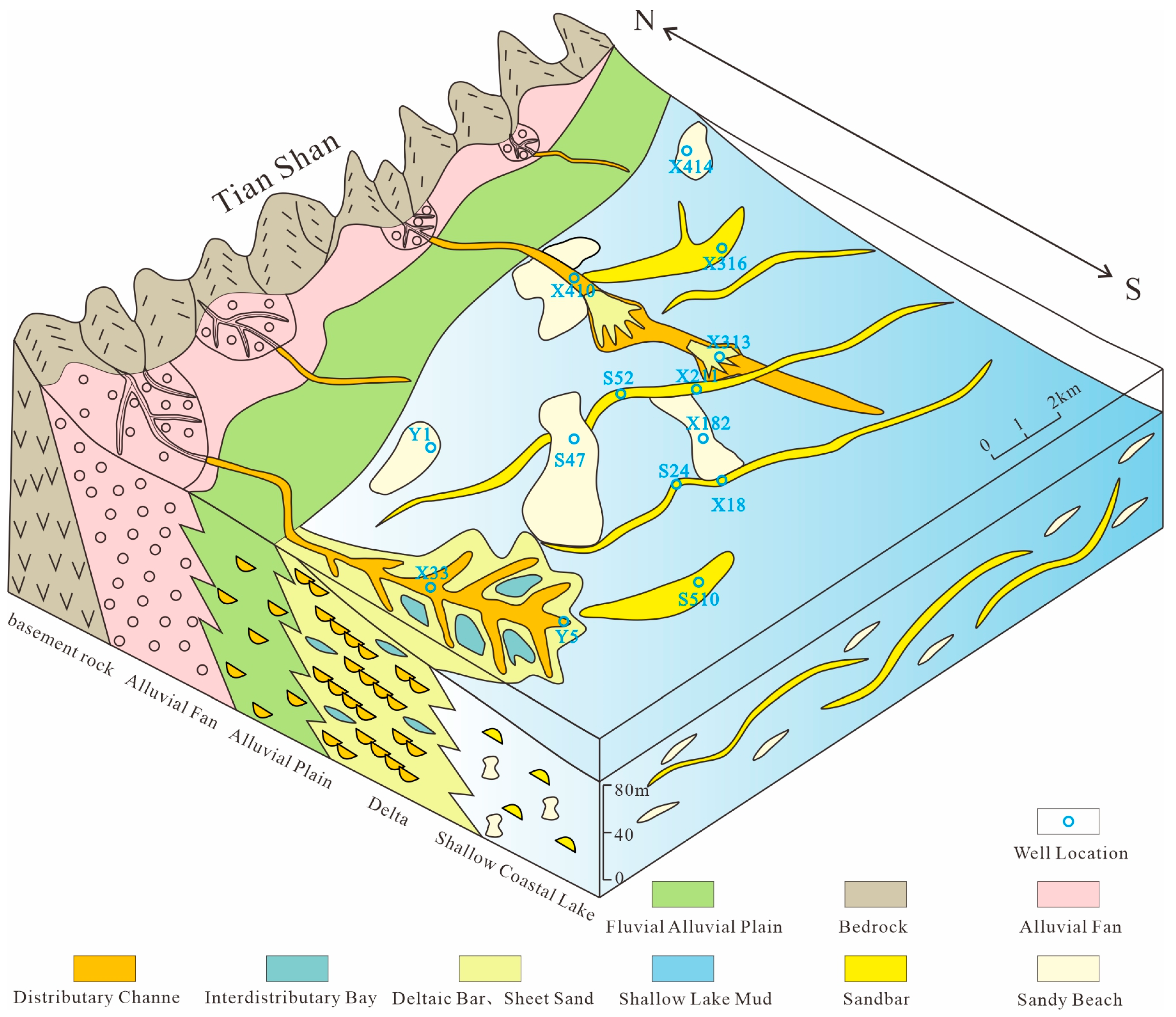
5.3. Sedimentary Model of the Fourth Member of the Triassic Akekule Formation
5.4. Significance of Oil and Gas Exploration
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The fourth member is dominated by shore–shallow lake subfacies deposits, with locally developed delta-front subfacies. In the early stage, under the control of the northwestern provenance, small-scale delta depositional systems developed, characterized by subaqueous distributary channel sands. Frequent lake-level fluctuations facilitated the reworking of sands by lake waves, forming stable sand bars nearly parallel to the lake shoreline. The planar distribution of these sand bars was jointly controlled by paleotectonic patterns and lake-level fluctuations, exhibiting strip-shaped or lenticular geometries. In the late stage, as lake levels declined, the delta deposition expanded, with subaqueous distributary channels extending southward and southeastward. Concurrently, new delta deposits emerged in the central–eastern part of the study area.
- (2)
- The formation of sand bodies in shore–shallow lake–delta facies is closely related to hydrodynamic conditions at the lake basin margin. Deltaic sand bodies are prone to reworking by lake waves and littoral currents, forming strip-shaped sand bar deposits distributed along the lake shoreline. This depositional model not only reveals the influence mechanisms of physical processes on sediment distribution in shore–shallow lake environments but also provides crucial reference cases for understanding sand body formation and distribution in analogous delta–lacustrine systems along foreland basin margins worldwide, particularly in environmental settings subjected to multiple lake transgression and regression cycles.
- (3)
- Early-stage sand bars along the shoreline were formed through reworking and redistribution by lake waves, exhibiting well-sorted grains and high porosity and permeability. Late-stage subaqueous distributary channel sands in the delta front experienced stacked development, resulting in greater thickness. Sand bodies pinch out into mudstones, forming lithologic traps that provide favorable conditions for hydrocarbon accumulation.
- (4)
- The NE-SW-trending major faults in the study area connect with Paleozoic hydrocarbon source rocks, forming efficient migration pathways. Combined with lithologic traps formed by sand pinch-outs, these features establish a “fault-controlled lithologic composite” hydrocarbon accumulation model, demonstrating significant exploration potential. However, the pervasive NE-SW-oriented secondary short-offset faults within the study area compartmentalize sand bodies, leading to complex internal reservoir architecture. Future research should prioritize unraveling the internal structure and heterogeneity of the fourth-member reservoirs, as these factors are critical for optimizing hydrocarbon exploration strategies.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C. The Development Trend of Domestic Oil and Gas External Dependence. China Pet. Chem. Stand. Qual. 2023, 43, 124–126, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.C. The resource potential and exploration for oil and gas in the Tarim Basin. Pet. Sci. Bull. 2018, 3, 369–375, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Huang, J.W. Exploration actuality and countermeasure of the triassic oil reservoirs in tahe oilfield of the tarimbasisn. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2008, 30, 552–556, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gu, W.L.; Li, W.; Geng, D.; Ma, D. Identification and prediction of thin oil layers (sand bodies): Aking the A 4 Member of the Triassic in the second area of Tahe Oilfield as an example. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2017, 17, 203–212, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Nuo, Q.; Huang, H.D. Thought and model of deep low amplitude structure interpretation: Taking Triassic in the ninth area of Tahe oilfield in Tarim Basin as an example. Oil Gas Technol. 2013, 35, 58–62+174, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jing, D. Research on the sedimentary system and main controlling factors of T2a4 the Triassic in Tahe Oilfield. China Pet. Chem. Stand. Qual. 2017, 37, 176+178, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Song, B.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.Z.; Liu, S.Z.; Chen, X.G.; Lu, W.Z. Fenetic types and distribution rules of thin sand layers in the fourth member of Shaejie Formation in Shubei Area of the western sag, Liaohe Depression. Geol. Resour. 2021, 30, 698–706, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.P.; Yao, G.Q.; Mao, W.J. Genetic Types and Superimposition Patterns of Subaqueous DistributaryChannel Thin Sandbodies in Delta Front: A case study from the IV-VI reservoir groups of H3 in Biqian 10 area of Gucheng oilfield. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2016, 34, 582–593, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jamil, M.; Siddiqui, N.A.; Rahman, A.H.B.A.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Ismail, M.S.B.; Ahmed, N.; Usman, M.; Gul, Z.; Imran, Q.S. Facies Heterogeneity and Lobe Facies Multiscale Analysis of Deep-Marine Sand-Shale Complexity in the West Crocker Formation of Sabah Basin, NW Borneo. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, A.; Umar, M.; Jamil, M.; Qasim, M. Facies analysis and depositional framework of Late Permian-Jurassic sedimentary successions, Western Salt Range, Pakistan: Implications for sequence stratigraphic trends and paleogeography of the Neo-Tethys Sea. Kuwait J. Sci. 2023, 50, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Guo, R.; Ma, H.T.; Xia, B.Y.; Xian, W.; Jiang, A.M.; Ge, Z.J. A new understanding of the causes of the banded sand body in the fourth member of Akekule Formation, eastern Tahe Oilfield, Tarim Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2019, 30, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Liu, J.H.; Xian, W.; Guo, R.; Xia, B.Y. Description of the Boundary of Banded Sand Body in the Fourth Member of Akekule Formation in Eastern Tahe Oilfield, Tarim Basin. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 2019, 40, 430–436, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Pszonka, J.; Sala, D. Application of the mineral liberation analysis (MLA) for extraction of grain size and shape measurements in siliciclastic sedimentary rocks. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 66, 02002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pszonka, J.; Godlewski, P.; Fheed, A.; Dwornik, M.; Schulz, B.; Wendorff, M. Identification and quantification of intergranular volume using SEM automated mineralogy. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 162, 106708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, N. Research on High Resolution Sequence Stratigraphy and Reservoir Prediction—A Case Study from the 4th Member of Triassic Akekule Formation in Tahe oil Field. Master’s Thesis, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.H.; Guo, J.H.; Yong, T.W.; Wang, M.Y. Sequence stratigraphy of the Triassic in Akekule area, Tarim Basin and its control effect on the reservoir sandbody. J. Xi′Shiyou Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2007, 22, 1–5+124. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, C.S.; Zhu, R. Triassic sequence stratigraphy and genesis types of reservoir sand bodies in Akekule area. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2007, 25, 169–176, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, C.M.; Wang, L.; Li, S.H.; Hursthouse, A.; Huang, Y.R.; Cao, T.T. Sedimentary characteristics and genetic mechanism of a deep-water channel system in the Zhujiang Formation of Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin. Deep-Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2021, 168, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, C.M.; Wang, L.; Hursthouse, A.; Li, S.H.; Huang, Y.R.; Cao, T.T. Sedimentary facies characterization of forced regression in the Pearl River Mouth basin. Open Geosci. 2022, 14, 208–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Liang, H.Y.; Tan, M.Y.; Cheng, X.J.; Dong, D.T.; Sun, M.J.; Gao, N.H. Sedimentary characteristics and forming conditions of beach-bar sandbodies in theupper fourth member of the Shahejie Formation in the south slope of the Huimin Sag. Oil Gas Geol. 2014, 35, 410–416, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.G.; Xian, W.; Li, W.P. Identification and Description Technique for Ultra-Deep, Thin Reservoir, Narrow Channel Sand, Tahe Oilfied. Geol. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2015, 34, 180–183, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xian, W.; Jing, S.Z.; Jian, D. Characteristics Analysis of the Triassic A-section Reservoir in TK7226 Well Area of Tahe Oilfield. China Pet. Chem. Stand. Qual. 2017, 37, 89–90+93, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, H.L.; Zhao, X.Z.; Zhu, X.M.; Jin, F.M.; Dong, Y.L.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhu, M.; Zheng, R.H. Seismic sedimentology of sub-clinoformal shallow-water meandering river delta: A case from the Suning area of Raoyang sag in Jizhong depression, Bohai Bay Basin, NE China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2015, 42, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Zhu, H.T.; Zeng, Z.W.; Zhou, X.H. Sedimentary facies analysis using sequence stratigraphy and seismic sedimentology in the Paleogene Pinghu Formation, Xihu Depression, East China Sea Shelf Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 93, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, W.Y.; Bai, Y.C.; Xu, H.J. Experimental study on evolution of lacustrine shallow-water delta. Catena 2019, 182, 104125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.L.; Zhang, M.Y.; Zhu, X.M.; Jiang, Q.; Guo, L.; Wei, M.P. Seismic geomorphology and depositional system of delta and terminal fan: A case study of the Neogene Shawan Formation in the Chepaizi Uplift, Junggar Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 83, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Xie, L.H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.P. T-R Sequence of sangonghe formation and deposition mode of depression lake basin in the hinterland of the junggar basin. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2021, 30, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.T.; Luo, S.; Lu, X.L.; Wang, H.T.; Li, Z.; Cao, H.; Wang, G.J.; Li, Y. Discrimination of sedimentary system characteristics of the fourth member of shahejie formation in dongying sag, China. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2020, 29, 481–489. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Qiu, L.W.; Fu, J.; Dong, D.T.; Yang, Y.Q.; Khan, D.; Wu, Z.J.; Song, F.; Wen, X.; Liu, X.B. Architectural characteristics, evolutionary stages, and sedimentary models of clastic beach bars. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2022, 146, 105976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.B.; Xi, A.H.; Li, Z.Y.; Yang, J.; Di, J.; Long, L.W.; Zheng, X.M.; Yu, P.H. Identification, formation conditions and distribution regularity of beach bar sand bodies in major depression lake basins: A case study of the chang8 member in the ordos basin, China. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2020, 29, 566–575. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.N.; Zhou, D.J. Scale characteristics and growth process of shallow water delta under different lake levels- based on Delft3D numerical simulation research. Front. Earth Sci. 2024, 12, 1489238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olariu, C.; Zhou, C.M.; Steel, R.; Zhang, Z.J.; Yuan, X.J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Chen, S.; Cheng, D.W.; Kim, W. Controls on the stratal architecture of lacustrine delta successions in low-accommodation conditions. Sedimentology 2021, 68, 1941–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Cai, L.H.; Zhang, C.M.; Wang, L.; Zhu, R.; Huang, Y.R.; Cao, T.T. Sedimentary Sequence, Evolution Model and Pe-troleum Geological Significance of Forced Regression: A Case Study of the Miocene Zhujiang Formation of the Pearl River Mouth Basin in the Northern South China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.L.; Liu, Y.; Jing, S.D.; Zhou, Y. Sedimentary features of gentle-slope tide-influenced braided delta: A case study of Carboniferous Kalashayi Formation in Tahe Oilfield. Sediment. Geol. Tethyan Geol. 2024, 44, 295–310. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.L.; Hu, X.F.; Wang, D.X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wen, L. Characteristics of Triassic lithofacies palaeogeography in Tarim Basin. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field 2012, 19, 696–700, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tong, Q.; Jiao, T.; Qi, Z.; Wang, H.H.; Liu, Y.C.; Zhu, Y.S.; Liu, H.L. Spatiotemporal evolution of single sandbodies controlled by allocyclicity and autocyclicity in the shallow-water braided river delta front of an open lacustrine basin. Open Geosci. 2021, 13, 98–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wei, G.Q.; Li, D.J.; Liu, M.C.; Xie, W.R.; Jin, H.; Shen, J.H.; Hao, C.G.; Wang, X.D. Geological characteristics and exploration prospect of oil and gas from the sandstone of the Silurian Xiaoheba Formation in the Sichuan Basin, China. J. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2020, 5, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.P. The Characteristics of Intelayers Distribution of Channel Sand Reservoir and Application of Horizontal Well in Tahe Oil Field. Geophys. Prospect. Pet. 2010, 49, 275–279+6, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Deng, H.N.; Xian, W.; Deng, F. Triassic Channel Sand Body Identification and Efficient Well Placement in Tahe Oilfield. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 2018, 39, 224–229, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wu, H.; Lin, Q. Sedimentary Characteristics of the Sandstone Intervals in the Fourth Member of Triassic Akekule Formation, Tarim Basin: Implications for Petroleum Exploration. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063297
Liu Z, Yu Y, Wang L, Wu H, Lin Q. Sedimentary Characteristics of the Sandstone Intervals in the Fourth Member of Triassic Akekule Formation, Tarim Basin: Implications for Petroleum Exploration. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(6):3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063297
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zehua, Ye Yu, Li Wang, Haidong Wu, and Qi Lin. 2025. "Sedimentary Characteristics of the Sandstone Intervals in the Fourth Member of Triassic Akekule Formation, Tarim Basin: Implications for Petroleum Exploration" Applied Sciences 15, no. 6: 3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063297
APA StyleLiu, Z., Yu, Y., Wang, L., Wu, H., & Lin, Q. (2025). Sedimentary Characteristics of the Sandstone Intervals in the Fourth Member of Triassic Akekule Formation, Tarim Basin: Implications for Petroleum Exploration. Applied Sciences, 15(6), 3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063297





