The Mechanical Strength of Ecological Cement Mortars Based on Fly Ash from the Combustion of Municipal Waste and Cement Kiln Dust
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Research Methods
3. Results and Discussion
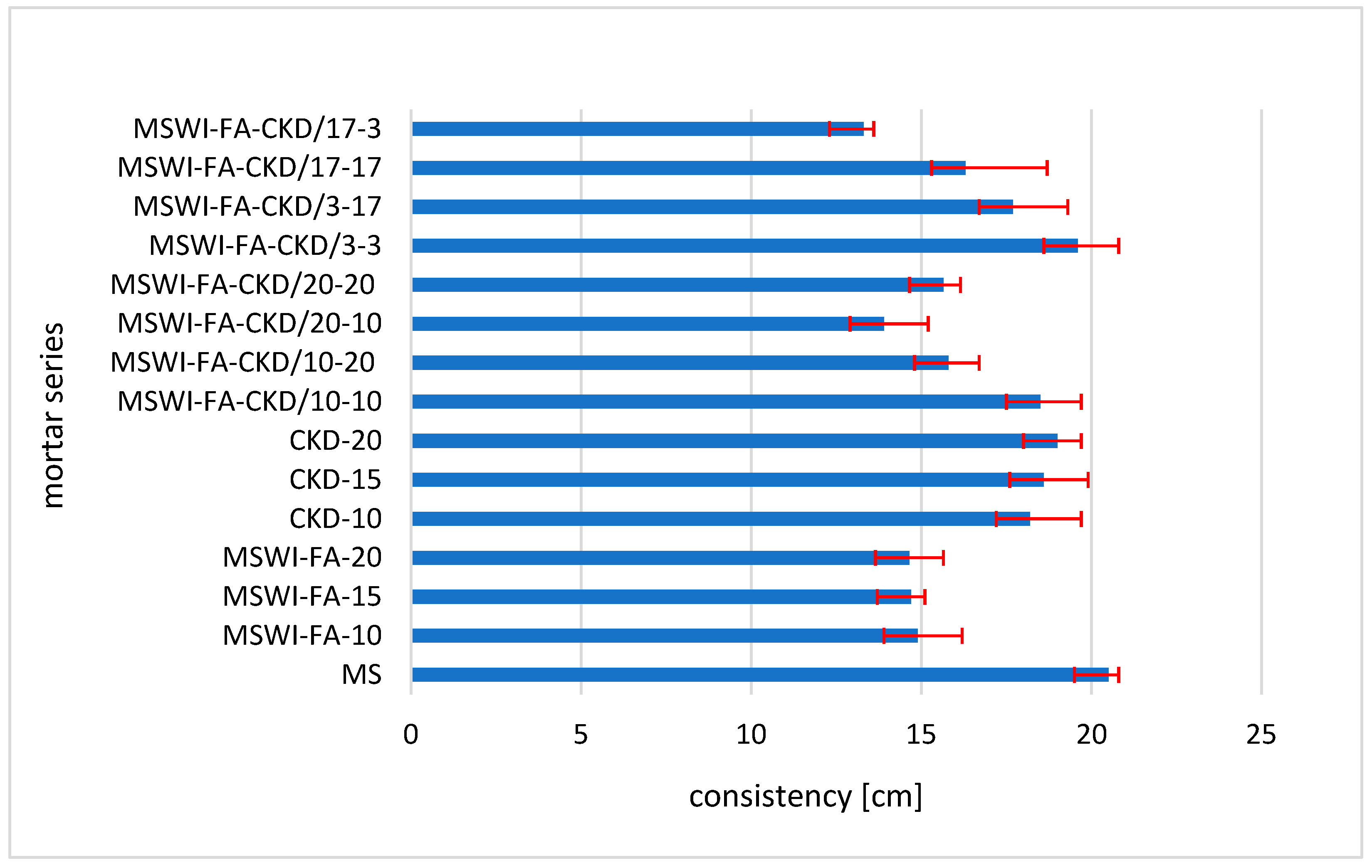
3.1. Consistency
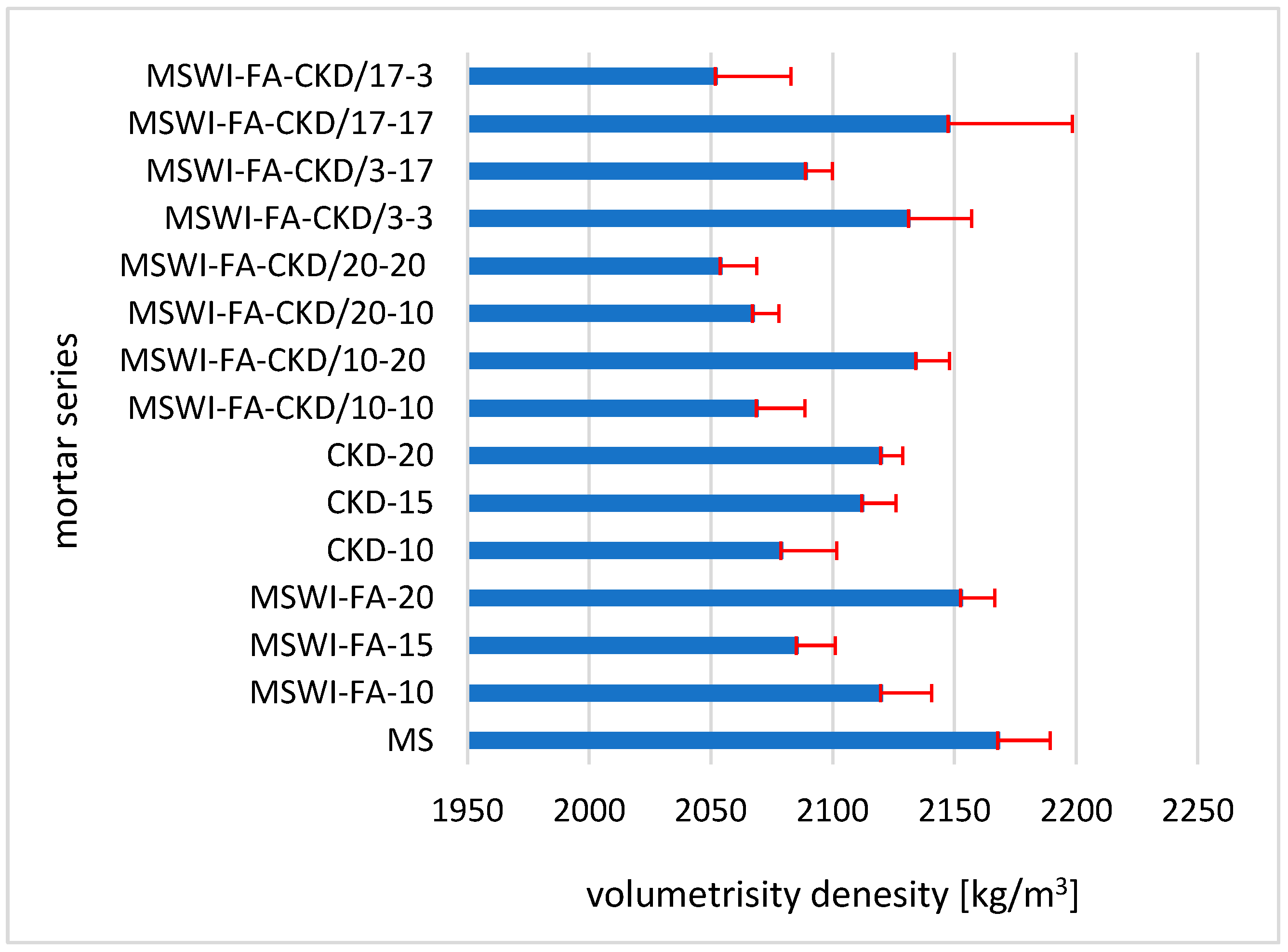
3.2. Volumetrisity Denesity
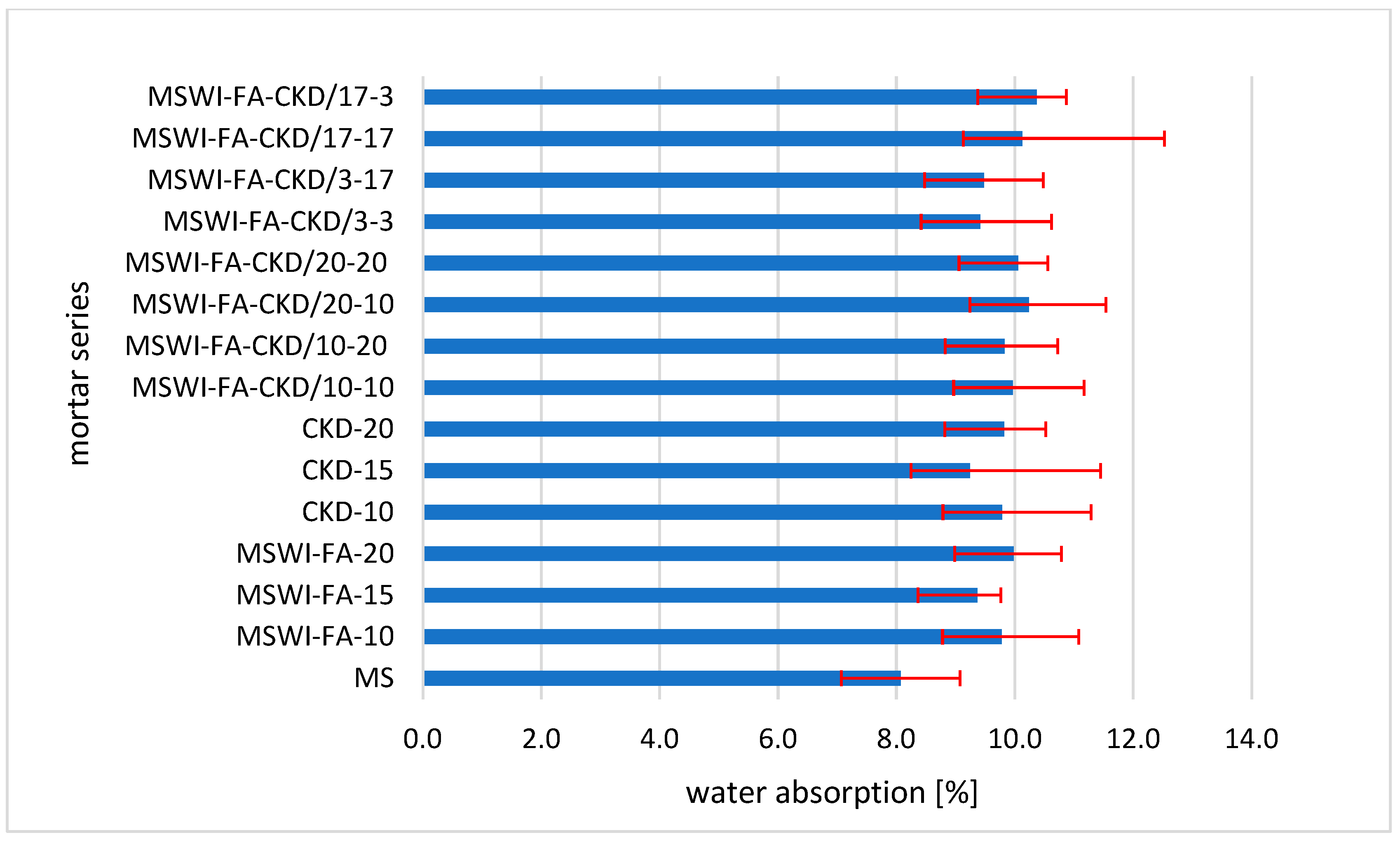
3.3. Water Absorption
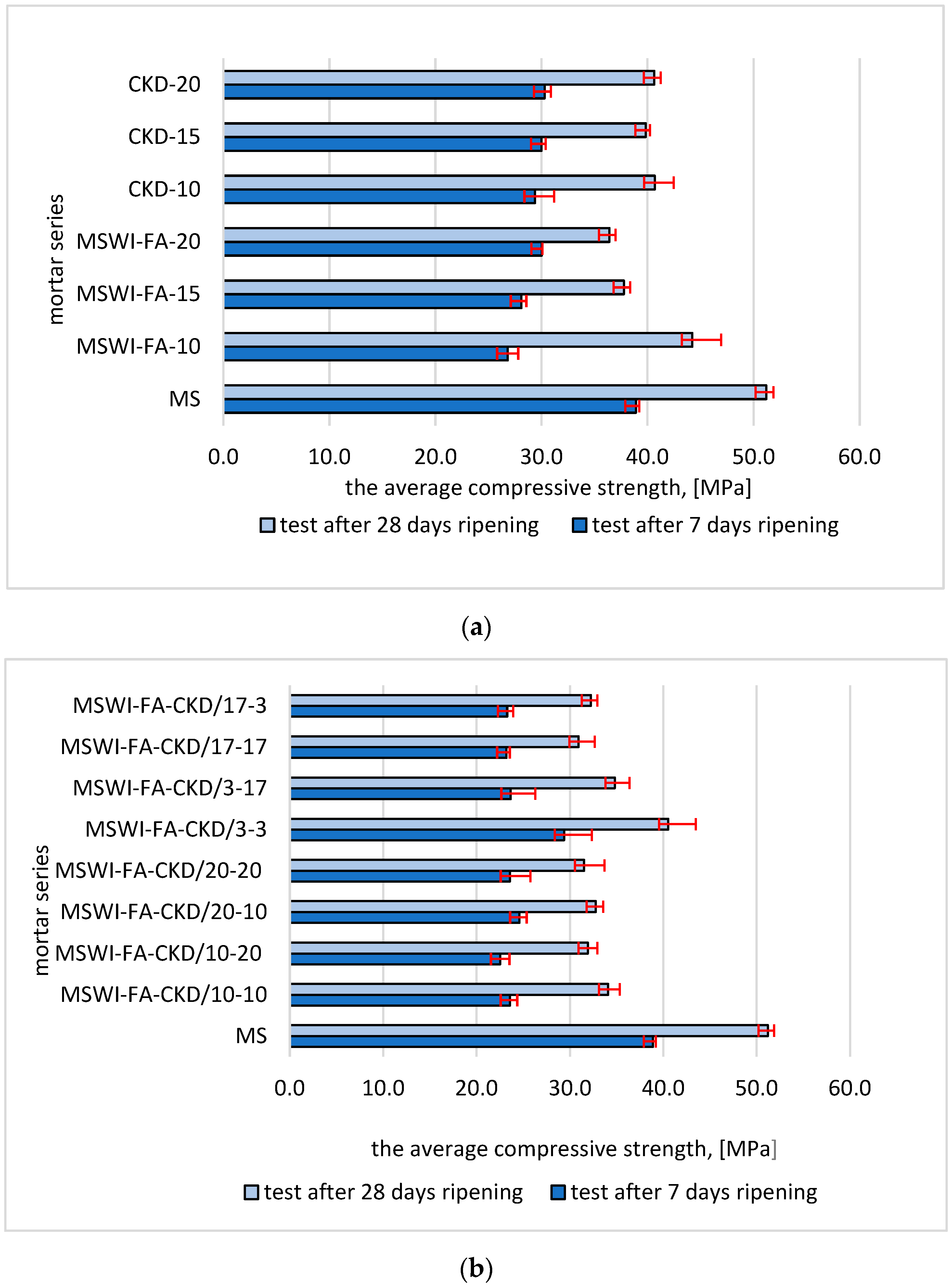
3.4. Compressive Strength
3.5. Flexural Strength
3.6. Frost Resistance
3.7. Evaluation of Results in the Context of Practical Use
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1087115/global-cement-production-Volume/ (accessed on 5 September 2024).
- Cemburean. Activity Report 2023; Cemburean the European Cement Association: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Jabri, K.S.; Taha, R.A.; Al-Hashmi, A.; Al-Harthy, A.S. Effect of copper slag and cement by-pass dust addition on mechanical properties of concreto. Constr. Build. Mater. 2006, 20, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jabri, K.S.; Taha, R.A.; Al-Ghassani, M. Use of copper slag and cement by-pass dust as cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Aggreg. 2002, 24, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Council; European Parliament. Directive (Eu) 2018/851 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 May 2018 Amending Directive 2008/98/EC on Waste; European Union: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, D.H.; Wazne, M.; Yoon, I.H.; Grubb, D.G. Assessment of Cement Kiln Dust (CKD) for Stabilization/Solidification (S/S) of Arsenic Contaminated Soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 159, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Pandey, M.K.; Srivastava, R.K. Evaluation of Cement Kiln Dust Stabilized Heavy Metals Contaminated Expansive Soil-A Laboratory. Study Eur. J. Adv. Eng. Technol. 2015, 2, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, K.; Sariosseiri, F.; Muhunthan, B. Engineering Properties of Cement Kiln Dust-Modified Soils in Western Washington State. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2011, 29, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albusoda, B.S.; Salem, L.A.K. Stabilization of Dune Sand by Using Cement Kiln Dust (CKD). J. Earth Sci. Geotech. Eng. 2012, 2, 131–143. [Google Scholar]
- Arulrajah, A.; Mohammadinia, A.; D’Amico, A.; Horpibulsuk, S. Cement Kiln Dust and Fly Ash Blends as an Alternative Binder for the Stabilization of Demolition Aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 145, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekpo, D.U.; Fajobi, A.B.; Ayodele, A.L.; Etim, R.K. Potentials of Cement Kiln Dust-Periwinkle Shell Ash Blends on Plasticity Properties of Two Selected Tropical Soils for Use as Sustainable Construction Materials. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Ota, Nigeria, 27–28 July 2020; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 1036, p. 012033. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, A.M.O.; El Gamal, M.M. Solidification of Cement Kiln Dust Using Sulfur Binder. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadinia, A.; Arulrajah, A.; D’Amico, A.; Horpibulsuk, S. Alkali-Activation of Fly Ash and Cement Kiln Dust Mixtures for Stabilization of Demolition Aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 186, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okafor, F.O.; Egbe, E.A. Potentials of Cement Kiln Dust in Sub-Grade Improvement. Niger. J. Technol. 2013, 32, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Edil, T.B.; Son, Y.-H. Effectiveness of Cement Kiln Dust in Stabilizing Recycled Base Materials. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2012, 24, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekrishnavilasam, A.; Rahardja, S.; Kmetz, R.; Santagata, M. Soil Treatment Using Fresh and Landfilled Cement Kiln Dust. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mohsen, M.A.; Anwar, A.M.; Adam, I.A. Mechanical Properties of Self-Consolidating Concrete Incorporating Cement Kiln Dust. HBRC J. 2015, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, D.M.; El-Attar, M.M.; Ali, A.M. Physico-Mechanical and Durability Characteristics of Concrete Paving Blocks Incorporating Cement Kiln Dust. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 157, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, H.M.; Salman, A.A.; Faheim, A.A.; El-Sayed, A.M. Sustainable Composite of Improved Lightweight Concrete from Cement Kiln Dust with Grated Poly (Styrene). J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harthy, A.S.; Taha, R.; Al-Maamary, F. Effect of Cement Kiln Dust (CKD) on Mortar and Concrete Mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2003, 17, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marku, J.; Dumi, I.; Lico, E.; Dilo, T.; Çakaj, O. Ckd in Mortar & Conc Prodctn. Mater. Prot. 2012, 53, 334–345. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, A.M.; Hilal, N. Re-Using The By-Product of Cement Industry (Cement Kiln Dust) To Produce The Concrete. Anbar J. Eng. Sci. 2010, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, S.M.; Koushkbaghi, M.; Mohseni, E.; Koushkbaghi, S.; Tahmouresi, B. Evaluation of Environment and Economy Viable Recycling Cement Kiln Dust for Use in Green Concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 32, 101809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, G.S.; Rao, R. Experimental Studies on Concrete Containing Cement Kiln Dust and Fly Ash. Singaporean J. Sci. Res. 2014, 6, 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Ewais, E.M.M.; Ahmed, Y.M.Z.; El-Amir, A.A.M.; El-Didamony, H. Cement Kiln Dust-Quartz Derived Wollastonite Ceramics. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 123, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogila, W.A. Recycling of Cement Kiln Dust in Red Clay Bricks and Its Impact on Their Physico-Mechanical Behaviors. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2014, 5, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar]
- El-Attar, M.M.; Sadek, D.M.; Salah, A.M. Recycling of High Volumes of Cement Kiln Dust in Bricks Industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkareem, A.H.; Eyada, S.O. Production of Building Bricks Using Cement Kiln Dust CKD Waste. In Proceedings of the Sustainable Civil Infrastructures, Cairo, Egypt, 24–28 November 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 102–113. [Google Scholar]
- Depczyński, R. Assessing raw material efficiency and waste management for Sustainable Development: A VIKOR and TOPSIS Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis. In Production Engineering Archives; Sciendo: Warsaw, Poland, 2024; Volume 30, pp. 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulewicz, M.; Jura, J.; Gnatowski, A. Cement Mortars Based on Polyamide Waste Modified with Fly Ash from Biomass Combustion—A New Material for Sustainable Construction. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jura, J. Influence of type of biomass burned on the properties of cement mortar containing fly ash. CoOEP 2020, 9, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jura, J.; Ulewicz, M. Assessment of the possibility of using fly ash from biomass combustion for concrete. Materials 2021, 14, 6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalak, T.; Szypura, P.; Cierpiszewski, R.; Ulewicz, M. Modification of Concrete Composition Doped by Sewage Sludge Fly Ash and Its Effect on Compressive Strength. Materials 2023, 16, 4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popławski, J.; Lelusz, M. Assessment of Sieving as a Mean to Increase Utilization Rate of Biomass Fly Ash in Cement-Based Composites. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popławski, J. Influence of biomass fly-ash blended with bituminous coal fly-ash on properties of concrete. CoOEP 2020, 9, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pribulov, A.; Futas, A.; Baricova, P.D. Processing and utilization of metallurgical slags. In Production Engineering Archives; Sciendo: Warsaw, Poland, 2016; Volume 11, pp. 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lis, T.; Nowacki, K. Pro-ecological possibilities of using metallurgical waste in the production of aggregates. In Production Engineering Archives; Sciendo: Warsaw, Poland, 2022; Volume 28, pp. 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, D.; Hashempour, M.; Heidari, A. Use of Waste Materials in Concrete: A review. Pertani. J. Sci. Technol. 2018, 26, 499–522. [Google Scholar]
- Saikia, N.; de Brito, J. Use of plastic waste as aggregate in cement mortar and concrete preparation: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 34, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassam, I.A.; Tayeh, A.; Alyousef, R.; Alabduljabbar, H.; Mohamed, A.M.; Alaskar, A. Use of recycled plastic as fine aggregate in cementitious composites: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 253, 19146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzak, A.; Ulewicz, M. Influence of post-consumer waste thermoplastic elastomers obtained from used car floor mats on concrete properties. Materials 2023, 16, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulewicz, M.; Pietrzak, A. Properties and structure of concretes doped with production waste of thermoplastic elastomers from the production of car floor mats. Materials 2021, 14, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzak, A. The effect of ashes generated from the combustion of sewage sludge on the basic mechanical properties of concrete’. CoOEP 2019, 8, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helbrych, P. Recycling of sulfur polymers derived from the purification process of copper and other non-ferrous metals in concrete composites. CoOEP 2019, 8, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Xie, G.; Li, Z.; Fan, X.; Zhang, W.; Xing, F.; Tang, L.; Ren, J. Resource utilization of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash—cement and alkali-activated cementitious materials: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulewicz, M.; Jura, J.; Zieliński, A.; Pietraszek, J. The Application of Converter Sludge and Slag to Produce Ecological Cement Mortars. Materials 2024, 17, 4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Nie, Q.; Yang, Z.; Sheng, W.; Qian, G. Municipal solid waste incineration residues recycled for typical construction materials—A review. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 6279–6291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, P.; Nazarko, M.; Włosińska, E.; Kanciruk, A.; Zarębska, K. Synthesis of geopolymers derived from fly ash with an addition, of perlite. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 293, 126112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarębska, K.; Zabierowski, P.; Gazda-Grzywacz, M.; Czuma, N.; Baran, P. Fly ash-based geopolymers with refractoriness properties. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2022, 24, 2161–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulewicz, M.; Jura, J. Influence of mix fly and bottom ashes from biomass on selected properties of cement mortars. Key Eng. Mater. 2020, 828, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristelo, N.; Segadães, L.; Coelho, J.; Chaves, B.; Sousa, N.R.; de Lurdes Lopes, M. Recycling municipal solid waste incineration slag and fly ash as precursors in low-range alkaline cements. Waste Manag. 2020, 104, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrzak, A.; Ulewicz, M.; Kozień, E.; Pietraszek, J. Application of a Mixture of Fly Ash and Solid Waste from Gas Treatment from Municipal Solid Waste Incineration in Cement Mortar. Materials 2025, 18, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Gao, X.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, S. Utilization of MSWI fly ash as partial cement or sand substitute with focus on cementing efficiency and health risk assessment. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2020, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, R. Utilization of MSWI ash in cement and mortar. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2010, 54, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jin, Y.; Nie, Y.; Li, R. Recycling of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash for ordinary Portland cement production: A real-scale test. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 1428–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.C.; Wanga, W.J.; Shih, P.Y.; Lin, K.L. Enhancement in early strengths of slag-cement mortars by adjusting basicity of the slag prepared from fly-ash of MSWI. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Ash-Incorporated Concrete: One Step towards Environmental Justice. Buildings 2021, 11, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, L.; Carsana, M.; Cassago, D.; Curzio, A.Q.; Collepardi, M. MSWI ashes as mineral additions in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 1899–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, J.E.; Husson, B.; Sarramone, N. Utilization of municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash in blended cement Part 2. Mechanical strength of mortars and environmental impact. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poranek, N.; Pizoń, J.; Łaźniewska-Piekarczyk, B.; Czajkowski, A.; Lagashkin, R. Recycle Option for Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash (MSWIFA) as a Partial Replacement for Cement in Mortars Containing Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cement (CSA) and Portland Cement to Save the Environment and Natural Resources. Materials 2024, 17, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.; Ślosarczyk, A. Effect of Municipal Solid Waste Slag on the Durability of Cementitious Composites in Terms of Resistance to Freeze–Thaw Cycling. Materials 2023, 16, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.L.; Wang, K.S.; Tzeng, B.Y.; Lin, C.Y. The reuse of municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash slag as a cement substitute. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2003, 39, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rémond, S.; Pimient, P.; Bentz, D.P. Effects of the incorporation of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration fly ash in cement pastes and mortars: I. Experimental study. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, E.; Asadollahfardi, G.; Salehi, A.; Akbardoost, J.; Esmaeili, N.; Panahandeh, A. Using Municipal Solid-Waste Incinerator Fly Ash, Wash Water, and Propylene Fibers in Self-Compacting Repair Mortar, Greenhouse Gas Emissions Potential. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2024, 18, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoldo, N.; Qureshi, T.; Simpkins, D.; Arrigoni, A.; Dotelli, G. Concrete with Organic Waste Materials as Aggregate Replacement. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PN-EN 197-1:2012; Cement—Cement—Part 1. Composition, Requirements and Compliance Criteria for Common-Use Cements. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2012.
- PN-EN 196-1:2016; Cement Test Methods—Part 1: Determination of Strength. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2016.
- PN-EN 1008:2004; Mixing Water for Concrete—Specification for Sampling, Testing and Assessment of Suitability of Mixing Water for Concrete, Including Water Recovered from Concrete Production Processes. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2004.
- PN-EN 196-6:2019-01; Cement Testing Methods—Part 6: Determination of Fineness of Grinding. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2019.
- PN-EN 1015-3:2000; Test Methods for Mortars for Walls—Determination of the Consistency of Fresh Mortar (Using A Flow Table). Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2000.
- PN-B-04500:1985; Building Mortars—Testing of Physical and Strength Properties. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 1985.
- PN-EN 1015-6:2000; Testing the Bulk Density of Cement Mortar in A Dry State in Accordance with the Standard. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2000.

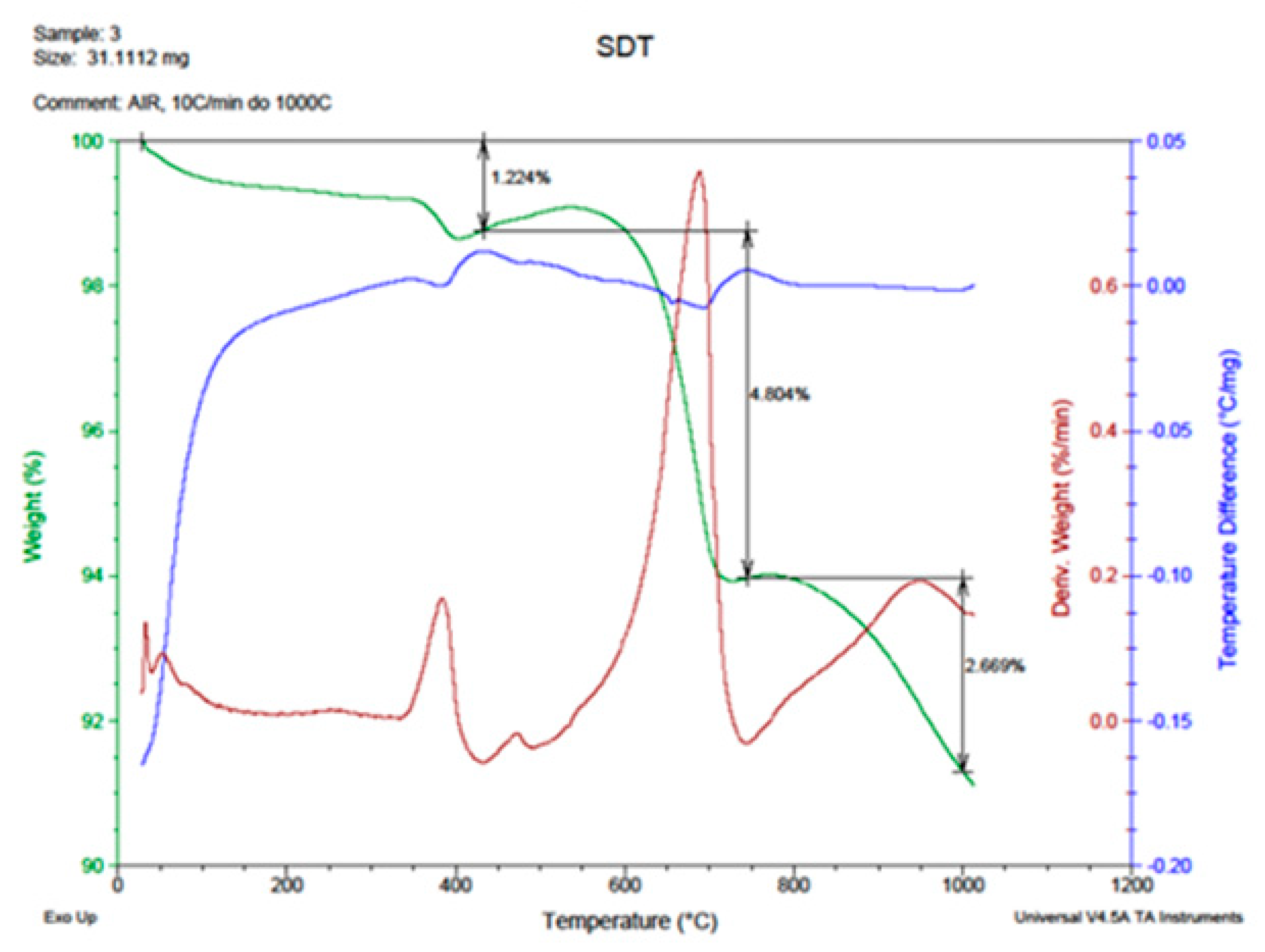


| Waste | SiO2 | CaO | MgO | Al2O3 | F2O3 | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | S | Cl |
| MSWI-FA * | 17.22 | 37.22 | 4.31 | 9.62 | 2.91 | 9.02 | 1.45 | 1.13 | 3.14 | 4.51 |
| CKD ** | 8.87 | 62.15 | 1.51 | 5.45 | 1.05 | 6.7 | 0.87 | - | - | 0.29 |
| Waste | Mn | Zn | Ti | Pb | Sn | Cu | Cr | Ba | Sr | Br |
| MSWI-FA | 0.09 | 0.83 | 1.31 | 0.93 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.05 | 0.02 |
| CKD | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.01 | - | - | - | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.02 |
| Mortar Series | Ingredients | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | Sand | Water | MSWI-FA | CKD | |
| [g] | [g] | [cm3] | [g] | [g] | |
| MS | 450 | 1350.0 | 225 | - | - |
| MSWI-FA-10 | 450 | 1294.2 | 225 | 45.0 | - |
| MSWI-FA-15 | 450 | 1266.3 | 225 | 67.5 | - |
| MSWI-FA-20 | 450 | 1238.39 | 225 | 90.0 | - |
| CKD-10 | 405 | 1350.0 | 225 | - | 45.0 |
| CKD-15 | 382.5 | 1350.0 | 225 | - | 67.5 |
| CKD-20 | 360 | 1350.0 | 225 | - | 90.0 |
| MSWI-FA-CKD/10-10 | 405 | 1299.78 | 225 | 40.5 | 45.0 |
| MSWI-FA-CKD/10-20 | 360 | 1305.36 | 225 | 36.0 | 90.0 |
| MSWI-FA-CKD/20-10 | 405 | 1299.78 | 225 | 81.0 | 45.0 |
| MSWI-FA-CKD/20-20 | 360 | 1327.68 | 225 | 72.0 | 90.0 |
| MSWI-FA-CKD/3-3 | 436.5 | 1322.94 | 225 | 13.1 | 13.5 |
| MSWI-FA-CKD/3-17 | 373.5 | 1326.84 | 225 | 11.21 | 76.5 |
| MSWI-FA-CKD/17-17 | 373.5 | 1303.68 | 225 | 63.5 | 76.5 |
| MSWI-FA-CKD/17-3 | 436.5 | 1250.33 | 225 | 74.21 | 13.5 |
| Mortar Series | Average Reduction in Compressive Strength (%) | Average Reduction in Flexural Strength (%) | Average Mass Loss (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MS | −32.66 | −47.7 | 0.82 |
| MSWI-FA-10 | −27.10 | −15.1 | 0.15 |
| MSWI-FA-15 | −13.70 | −7.4 | 0.18 |
| MSWI-FA-20 | −6.10 | −0.7 | 0.28 |
| CKD-10 | −35.21 | −77.9 | 0.15 |
| CKD-15 | −21.56 | −73.7 | 0.21 |
| CKD-20 | −19.52 | −77.3 | 0.15 |
| MSWI-FA-CKD/10-10 | −11.38 | −76.6 | 0.05 |
| MSWI-A-CKD/10-20 | −8.63 | −25.6 | 0.36 |
| MSWI-FA-CKD/20-10 | −15.67 | −48.5 | 0.19 |
| MSWI-FA-CKD/20-20 | −1.72 | −9.9 | 0.24 |
| MSWI-FA-CKD/3-3 | −5.95 | −8.2 | 0.28 |
| MSWI-FA-CKD/3-17 | −13.22 | −44.0 | 0.34 |
| MSWI-FA-CKD/17-17 | −19.95 | −56.6 | 0.17 |
| MSWI-FA-CKD/17-3 | −3.66 | −20.2 | 0.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pietrzak, A.; Ulewicz, M. The Mechanical Strength of Ecological Cement Mortars Based on Fly Ash from the Combustion of Municipal Waste and Cement Kiln Dust. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3215. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063215
Pietrzak A, Ulewicz M. The Mechanical Strength of Ecological Cement Mortars Based on Fly Ash from the Combustion of Municipal Waste and Cement Kiln Dust. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(6):3215. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063215
Chicago/Turabian StylePietrzak, Alina, and Malgorzata Ulewicz. 2025. "The Mechanical Strength of Ecological Cement Mortars Based on Fly Ash from the Combustion of Municipal Waste and Cement Kiln Dust" Applied Sciences 15, no. 6: 3215. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063215
APA StylePietrzak, A., & Ulewicz, M. (2025). The Mechanical Strength of Ecological Cement Mortars Based on Fly Ash from the Combustion of Municipal Waste and Cement Kiln Dust. Applied Sciences, 15(6), 3215. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063215







