On the Use of a Water Potential Probe for Suction and Temperature Measurements in Unsaturated Natural Clayey Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Outcropping Soil on Pilot Case Study: The Pisciolo Hillslope
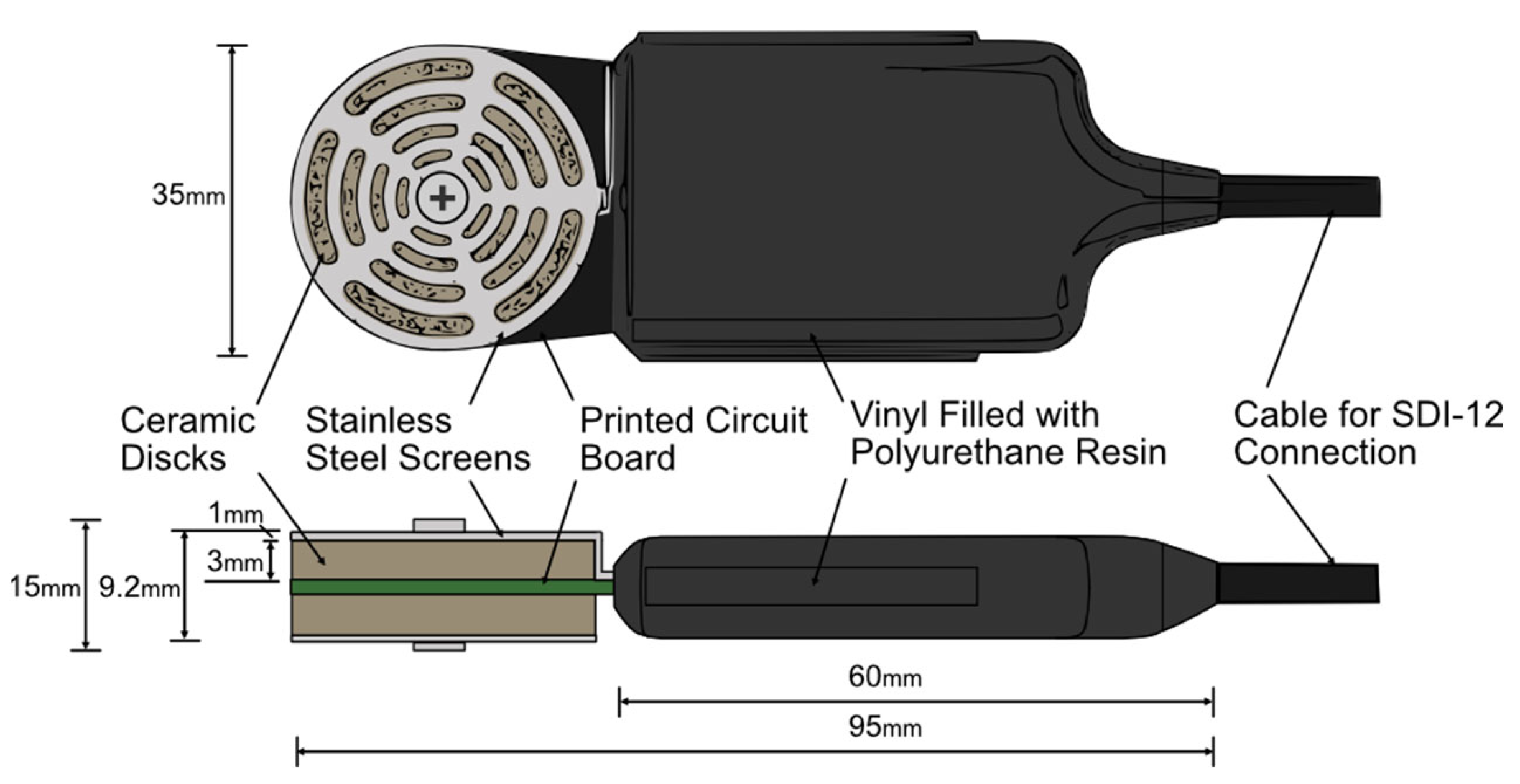
2.2. Methods for Matric Suction Measurements
2.3. Experimental Setup
3. Results
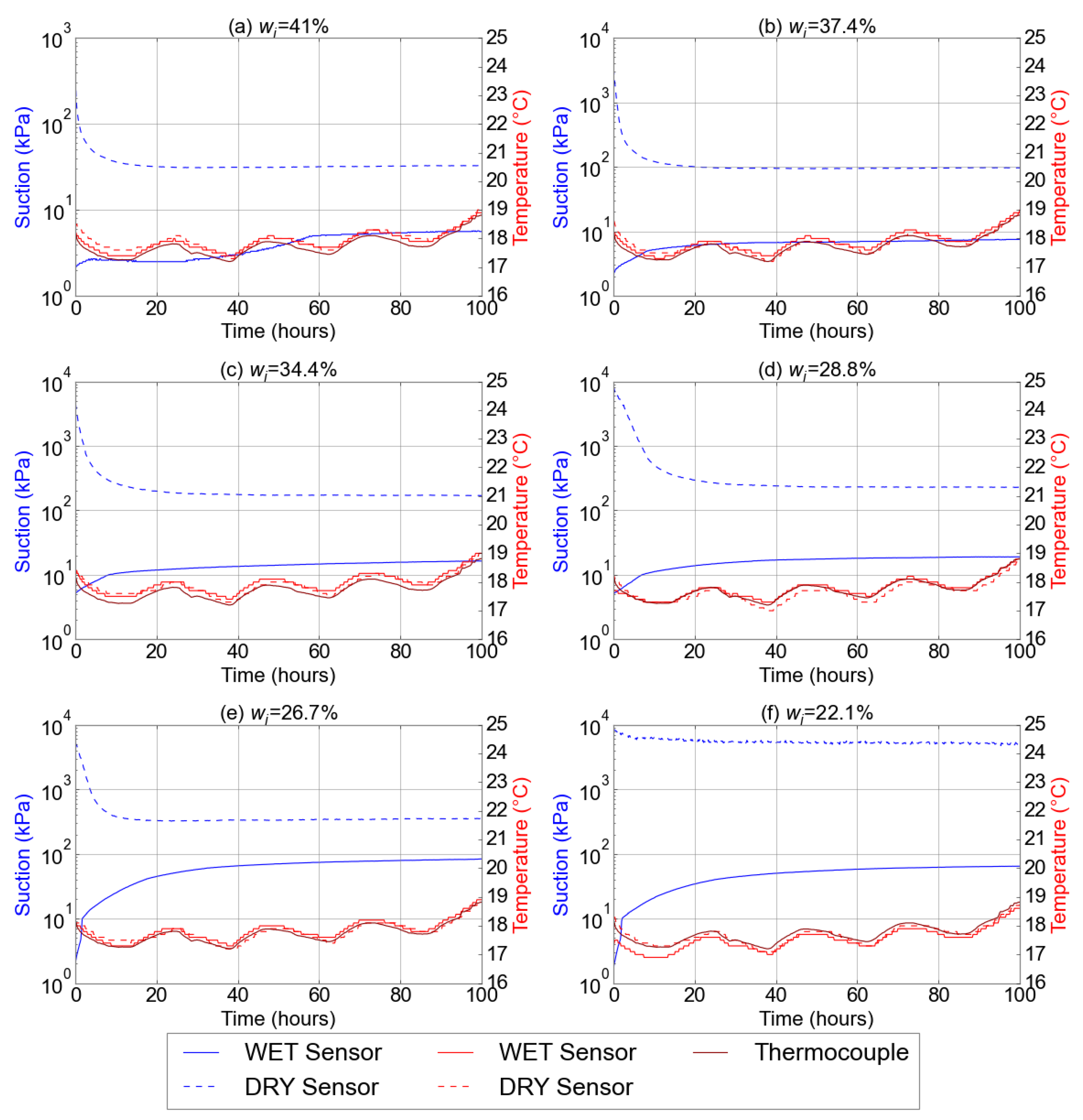
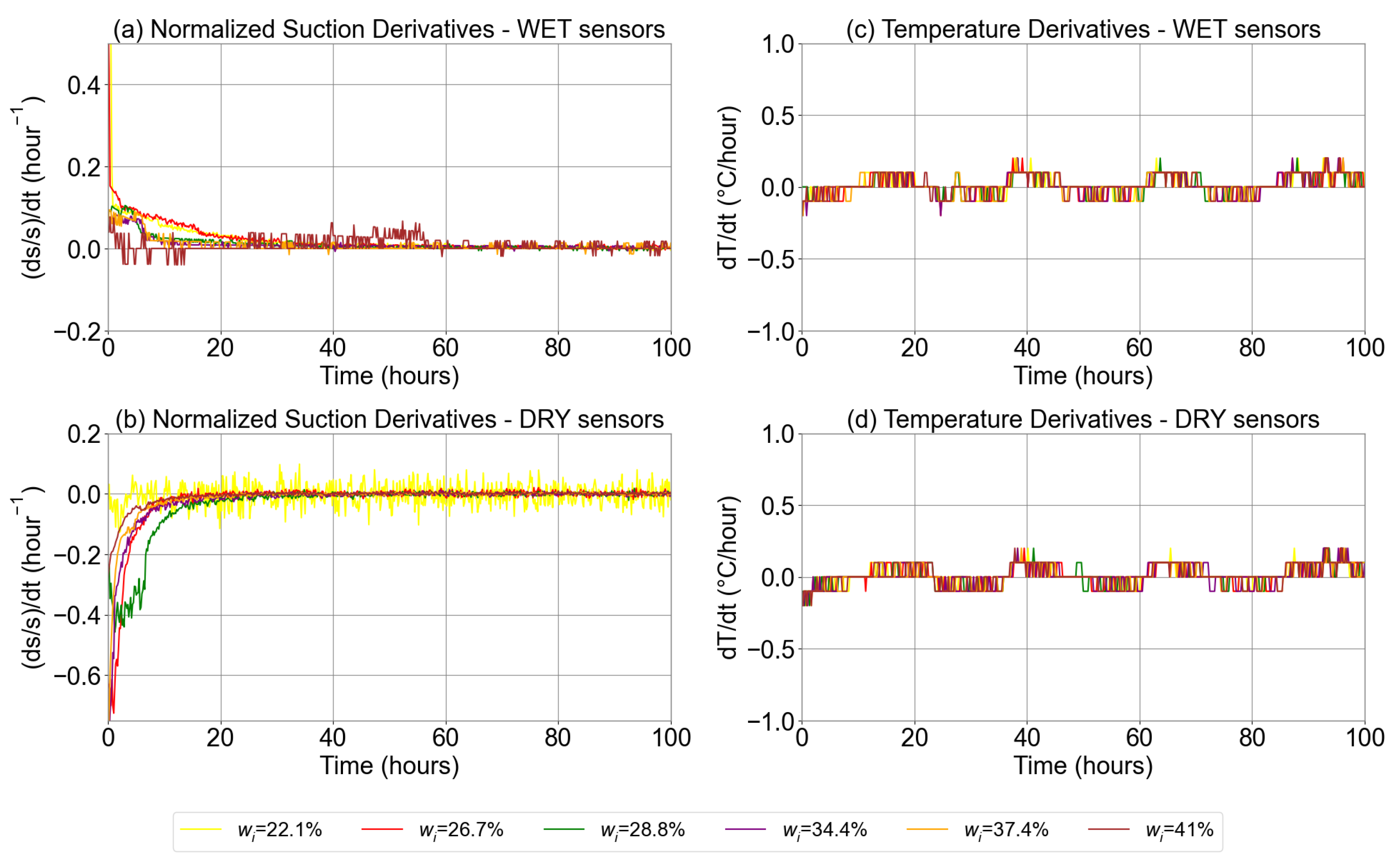
3.1. Test 1: Suction Equilibrium Time
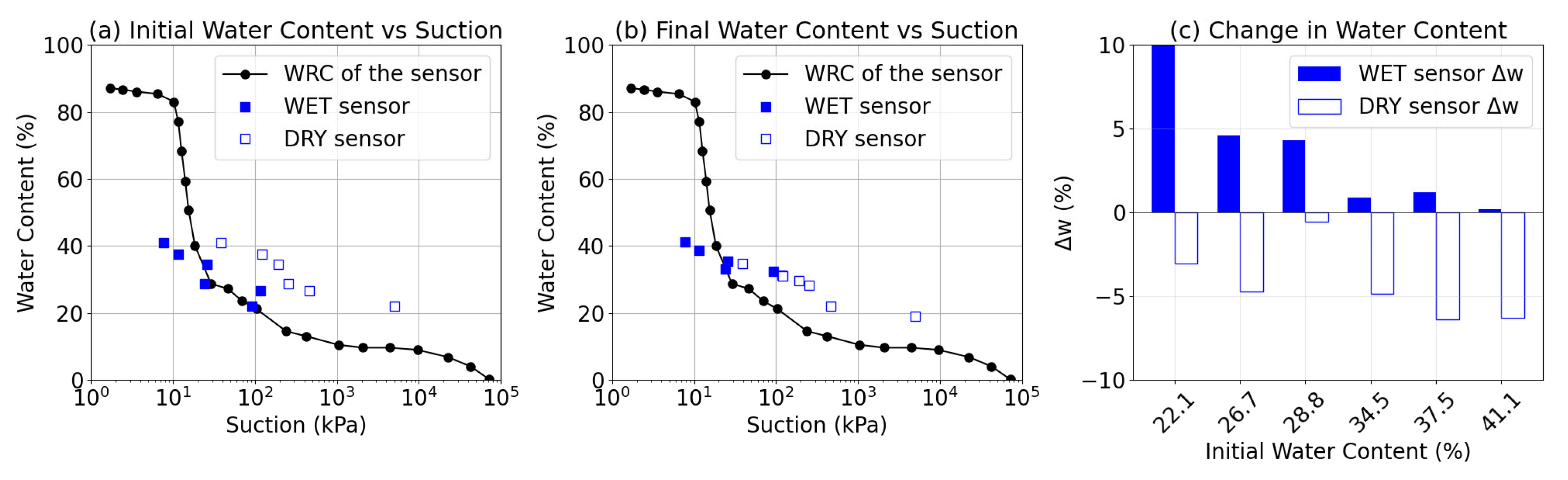
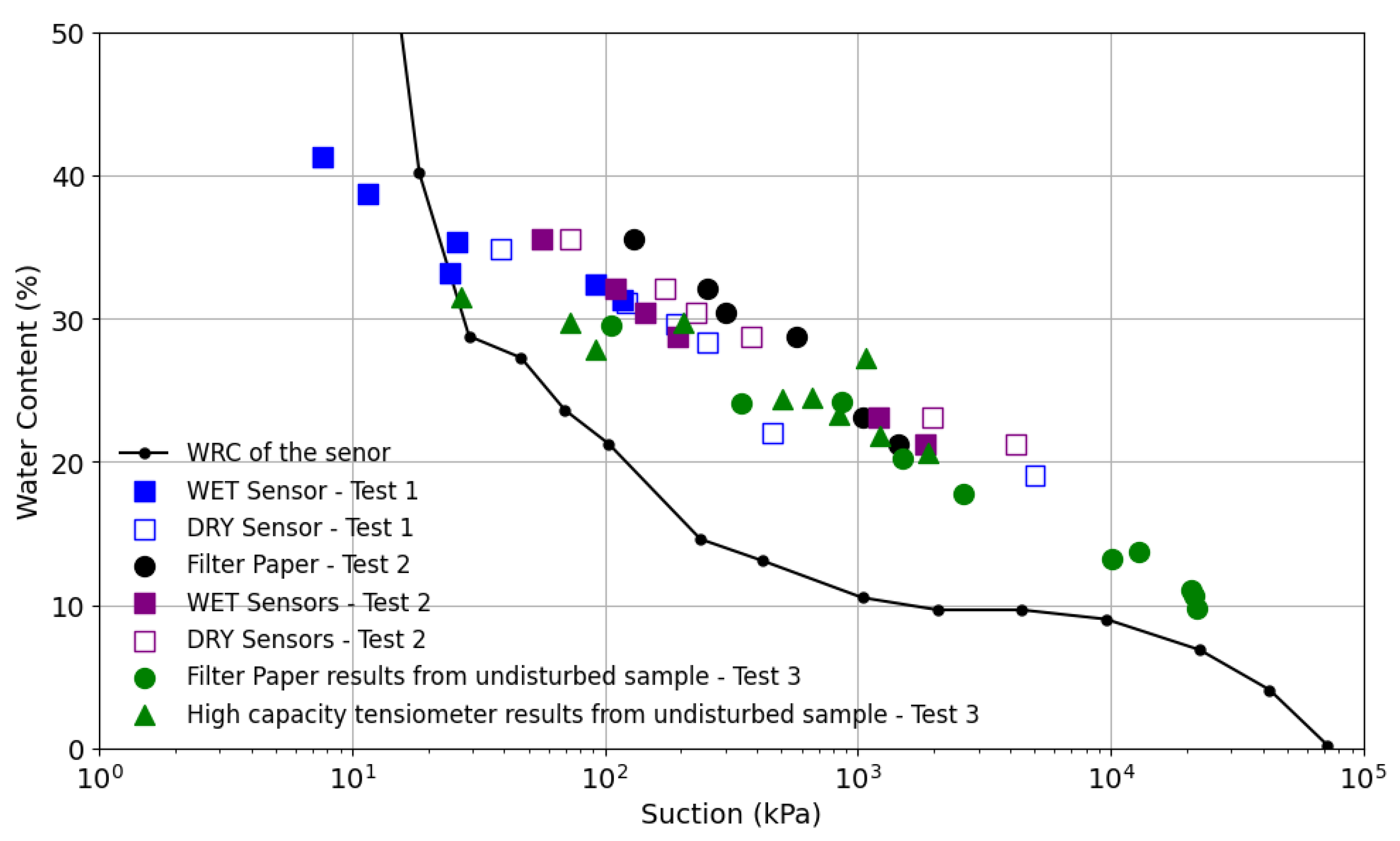
3.2. Impact of Wet and Dry Sensors on the Soil Water Retention
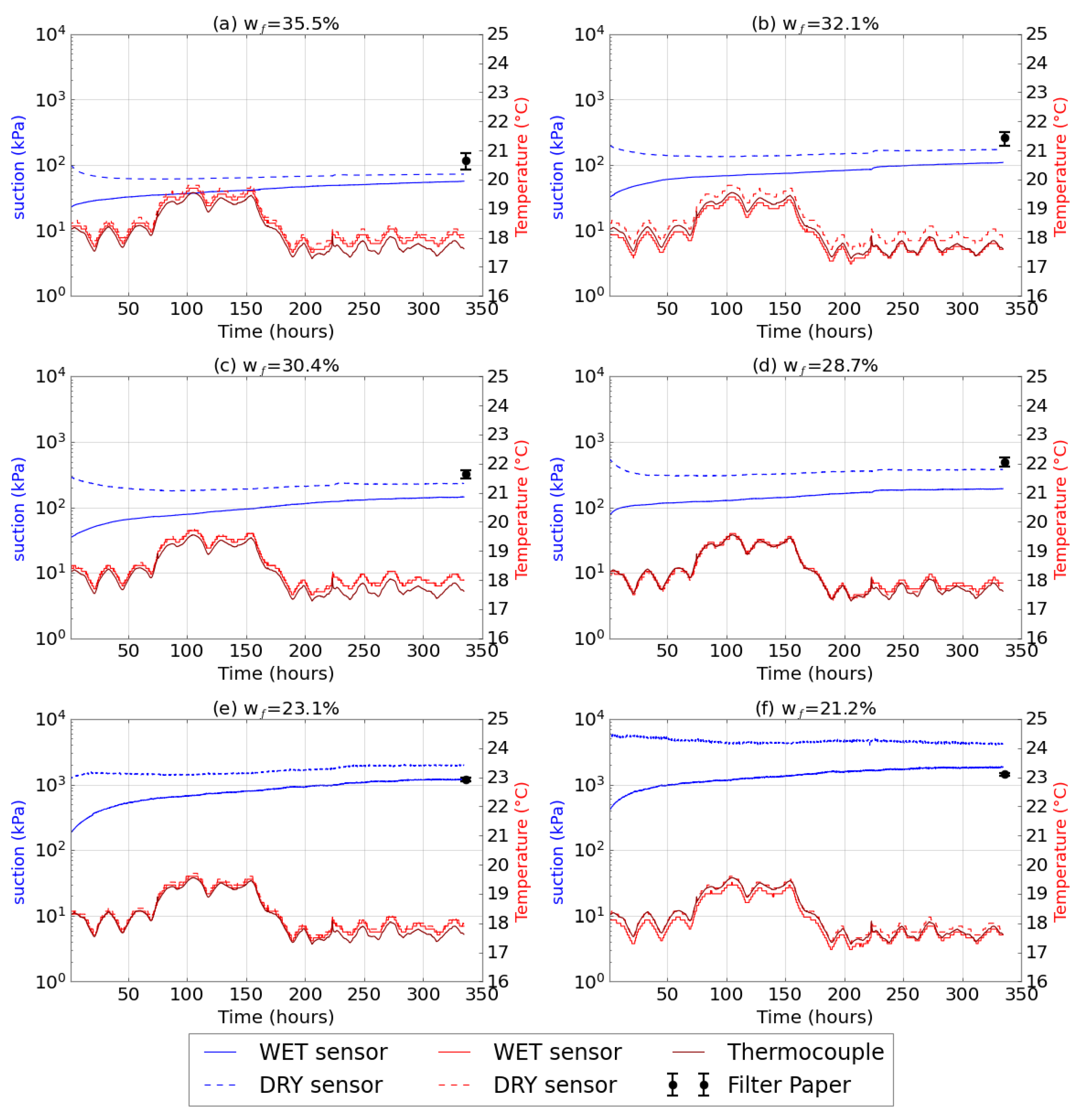
3.3. Test 2: Comparison of Filter Paper and Water Potential Sensor
3.4. Test 3: Comparison of Measurements with Undisturbed Soil Test Result
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cotecchia, F.; Tagarelli, V.; Pedone, G.; Ruggieri, G.; Guglielmi, S.; Santaloia, F. Analysis of climate-driven processes in clayey slopes for the early-warning system design. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Geotech. Eng. 2019, 172, 463–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagarelli, V.; Cotecchia, F. Deep movements in clayey slopes relating to climate: Modeling for early warning system design. In Geotechnical Research for Land Protection and Development: Proceedings of CNRIG 2019 7, Lecco, Italy, 3–5 July 2019; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 205–214. [Google Scholar]
- Dippenaar, M.A.; van Rooy, J.L.; Diamond, R.E. Engineering, hydrogeological, and vadose zone hydrological aspects of Proterozoic dolomites (South Africa). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 147, 24–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, G.; Cotecchia, F.; Pedone, G.; Vaunat, J.; Vardon, P.J.; Pereira, C.; Springman, S.M.; Rouainia, M.; Van Esch, J.; Koda, E.; et al. Numerical modelling of slope–vegetation–atmosphere interaction: An overview. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 2017, 50, 249–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredlund, D.G.; Rahardjo, H.; Fredlund, M.D. Unsaturated Soil Mechanics in Engineering Practice; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, N.; Godt, J.W. Hillslope Hydrology and Stability; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathy, S.; Al-Khyat, S.; Cleall, P.J.; Baille, W.; Schanz, T. Soil suction measurement of unsaturated soils with a sensor using fixed-matrix porous ceramic discs. Indian Geotech. J. 2016, 46, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.; Tadza, M.Y.M.; Thomas, H.R. Soil-water characteristic curves of clays. Can. Geotech. J. 2014, 51, 869–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Liao, K.; Xu, Y.; Yang, G.; Wu, S.; Zhou, S. Monitoring and prediction of soil moisture spatial–temporal variations from a hydropedological perspective: A review. Soil Res. 2012, 50, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Godt, J.W. Infinite slope stability under steady unsaturated seepage conditions. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W114049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, R.H. Soil Slips, Debris Flows, and Rainstorms in the Santa Monica Mountains and Vicinity, Southern California; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1975; Volume 851. [Google Scholar]
- Montrasio, L.; Valentino, R. A model for triggering mechanisms of shallow landslides. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 8, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuomo, S.; Della Sala, M. Rainfall-induced infiltration, runoff, and failure in steep unsaturated shallow soil deposits. Eng. Geol. 2013, 162, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredlund, D.G.; Sheng, D.; Zhao, J. Estimation of soil suction from the soil-water characteristic curve. Can. Geotech. J. 2011, 48, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likos, W.J.; Jaafar, R. Pore-scale model for water retention and fluid partitioning of partially saturated granular soil. J. Geotech. Geoenvironmental Eng. 2013, 139, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredlund, D.G. Unsaturated soil mechanics in engineering practice. J. Geotech. Geoenvironmental Eng. 2006, 132, 286–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, S.J.; Sharma, R.S.; Buisson, M.S.R. Coupling of hydraulic hysteresis and stress–strain behaviour in unsaturated soils. Géotechnique 2003, 53, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfried, M.S.; Grant, L.E. Temperature effects on soil dielectric properties measured at 50 MHz. Vadose Zone J. 2007, 6, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwank, M.; Green, T.R.; Mätzler, C.; Benedickter, H.; Fluhler, H. Laboratory characterization of a commercial capacitance sensor for estimating permittivity and inferring soil water content. Vadose Zone J. 2006, 5, 1048–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottiglieri, O.; Cafaro, F.; Cotecchia, F. Two-Scale Investigation of the Retention Behavior of a Well-Graded Mixed Soil. Geosciences 2021, 11, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oorthuis, R.; Hürlimann, M.; Fraccica, A.; Lloret, A.; Moya, J.; Puig-Polo, C.; Vaunat, J. Monitoring of a full-scale embankment experiment regarding soil–vegetation–atmosphere interactions. Water 2018, 10, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najdi, A.; Encalada, D.; Mendes, J.; Prat, P.C.; Ledesma, A. Evaluating innovative direct and indirect soil suction and volumetric measurement techniques for the determination of soil water retention curves following drying and wetting paths. Eng. Geol. 2023, 322, 107179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Tang, C.S.; Cui, Y.J.; Najdi, A. Compressive stress induced by desiccation shrinkage in clayey soils. Appl. Clay Sci. 2025, 267, 107729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toll, D.G.; Lourenço, S.D.N.; Mendes, J. Advances in suction measurements using high suction tensiometers. Eng. Geol. 2013, 165, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridley, A.M.; Burland, J.B. A new instrument for the measurement of soil moisture suction. Géotechnique 1993, 43, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagarelli, V.; Stasi, N.; Cotecchia, F.; Cafaro, F. Root-induced changes in the hydraulic properties of a fine slope cover. In E3S Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Ulys, France, 2024; Volume 544, p. 16002. [Google Scholar]
- Tagarelli, V.; Stasi, N.; Cotecchia, F. Numerical back-analysis of in-situ constant head tests in partially saturated soil cover to determine the permeability function. In Proceedings of the National Conference of the Researchers of Geotechnical Engineering, Palermo, Italy, 5–7 July 2023; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Pedone, G.; Cotecchia, F.; Tagarelli, V.; Bottiglieri, O.; Murthy, M.B. An investigation into the water retention behaviour of an unsaturated natural fissured clay. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esu, F. Behaviour of slopes in structurally complex formations. In Proceedings of the Symposium on the Geotechnics of Structurally Complex Formations, Capri, Italy, 19–21 September 1977; pp. 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Cafaro, F.; Cotecchia, F.; Cherubini, C. Influence of structure and stress history on the drying behaviour of clays. In Unsaturated Soils for Asia: Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Unsaturated Soils UNSAT-ASIA 2000, Singapore, 18–19 May 2000; Rahardjo, H., Toll, D.G., Leong, E.C., Eds.; A.A. Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 633–638. [Google Scholar]
- Jackisch, C.; Germer, K.; Graeff, T.; Andrä, I.; Schulz, K.; Schiedung, M.; Haller-Jans, J.; Schneider, J.; Jaquemotte, J.; Helmer, P.; et al. Soil moisture and matric potential–An open field comparison of sensor systems. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Ahmed, M.A.; Abdalla, M.; Carminati, A. Root hydraulic phenotypes impacting water uptake in drying soils. Plant Cell Environ. 2022, 45, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagarelli, V.; Cotecchia, F. Preliminary field data of selected deep-rooted vegetation effects on the slope-vegetation-atmosphere interaction: Results from an in-situ test. Riv. Ital. Geotec. 2022, 56, 62–83. [Google Scholar]
- Oorthuis, R.; Vaunat, J.; Hürlimann, M.; Lloret, A.; Moya, J.; Puig-Polo, C.; Fraccica, A. Effect of vegetation and slope orientation on water infiltration in a monitored embankment. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, Online, 19–30 April 2021; p. EGU21-7599. [Google Scholar]
- Menne, D.; Hübner, C.; Trebbels, D.; Willenbacher, N. Robust soil water potential sensor to optimize irrigation in agriculture. Sensors 2022, 22, 4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, R.J.; Gutierrez, C.I. The filter paper method of suction measurements. Géotechnique 1986, 36, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, M.G.; Vilar, O.M. Study of the water retention properties of a tropical soil. Can. Geotech. J. 2009, 46, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, F.A.M.; da Silva Gomes, J.E. The effect of contact on the filter paper method for measuring soil suction. Geotech. Test. J. 2011, 35, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasi, N.; Tagarelli, V.; Cafaro, F.; Cotecchia, F. On the Wildfire-Induced changes in the properties of a vegetated clayey slope cover. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Geotechnical and Geophysical Site Characterization (ISC ‘24), Barcelona, Spain, 18–21 June 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Associazione Geotecnica Italiana (AGI). Raccomandazioni Sulle Prove Geotecniche di Laboratorio; Associazione Geotecnica Italiana: Roma, Italy, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- METER Group AG. TEROS 21 Soil Water Potential Sensor. 2025. Available online: https://metergroup.com/products/teros-21/ (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Karagoly, Y.; Tripathy, S.; Cleall, P.J.; Mahdi, T. Suction measurements by a fixed-matrix porous ceramic disc sensor. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Unsaturated Soils, Hong Kong, China, 3–5 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Decagon Devices. Operator’s Manual for MPS-2 & MPS-6 Dielectric Water Potential Sensor; Decagon Devices: Pullman, WA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D2216-19; Standard Test Methods for Laboratory Determination of Water (Moisture) Content of Soil and Rock by Mass. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019.
- Leong, E.C.; He, L.; Rahardjo, H. Factors affecting the filter paper method for total and matric suction measurements. Geotech. Test. J. 2002, 25, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walthert, L.; Schleppi, P. Equations to compensate for the temperature effect on readings from dielectric Decagon MPS-2 and MPS-6 water potential sensors in soils. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2018, 181, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaili, D.; Hatami, K. Comparative study of measured suction in fine-grained soil using different in-situ and laboratory techniques. Int. J. Geosynth. Ground Eng. 2017, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitone, C.; Guglielmi, S.; Pedone, G.; Cotecchia, F. Effects of micro-to meso-features on the permeability of fissured clays. Géotech. Lett. 2019, 9, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badakhshan, E.; Vaunat, J.; Veylon, G. Meteorological and vegetation effects on the thermal analysis of slopes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 196, 114352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotecchia, F.; Lollino, P.; Petti, R. Efficacy of drainage trenches to stabilise deep slow landslides in clay slopes. Géotech. Lett. 2016, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoni, M.; Bittelli, M.; Valentino, R.; Chersich, S.; Meisina, C. Improving the estimation of complete field soil water characteristic curves through field monitoring data. J. Hydrol. 2017, 552, 283–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stasi, N.; Tagarelli, V.; Bottiglieri, O.; Cafaro, F. On the Use of a Water Potential Probe for Suction and Temperature Measurements in Unsaturated Natural Clayey Soil. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3021. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063021
Stasi N, Tagarelli V, Bottiglieri O, Cafaro F. On the Use of a Water Potential Probe for Suction and Temperature Measurements in Unsaturated Natural Clayey Soil. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(6):3021. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063021
Chicago/Turabian StyleStasi, Nico, Vito Tagarelli, Osvaldo Bottiglieri, and Francesco Cafaro. 2025. "On the Use of a Water Potential Probe for Suction and Temperature Measurements in Unsaturated Natural Clayey Soil" Applied Sciences 15, no. 6: 3021. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063021
APA StyleStasi, N., Tagarelli, V., Bottiglieri, O., & Cafaro, F. (2025). On the Use of a Water Potential Probe for Suction and Temperature Measurements in Unsaturated Natural Clayey Soil. Applied Sciences, 15(6), 3021. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063021







