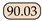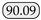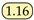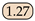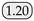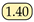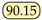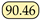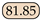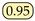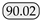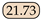Abstract
Intelligent jet systems are widely used in various fields, including firefighting, marine operations, and underwater exploration. Accurate extraction and prediction of jet trajectories are essential for optimizing their performance, but challenges arise due to environmental factors such as climate, wind direction, and suction efficiency. To address these issues, we introduce two novel jet segmentation datasets, Libary and SegQinhu, which cover both indoor and outdoor environments under varying weather conditions and temporal intervals. These datasets present significant challenges, including occlusions and strong light reflections, making them ideal for evaluating jet trajectory segmentation methods. Through empirical evaluation of several state-of-the-art (SOTA) techniques on these datasets, we observe that general methods struggle with highly imbalanced pixel distributions in jet trajectory images. To overcome this, we propose a data-driven pipeline for jet trajectory extraction and segmentation. At its core is MobileHDC, a new baseline model that leverages the MobileNetV2 architecture and integrates dilated convolutions to enhance the receptive field without increasing computational cost. Additionally, we introduce a parallel convolutional block and a decoder to fuse multi-level features, enabling a better capture of contextual information and improving the continuity and accuracy of jet segmentation. The experimental results show that our method outperforms existing SOTA techniques on both jet-specific datasets, highlighting the effectiveness of our approach.
1. Introduction
Intelligent jet systems play a crucial role in various industries and applications, from firefighting to marine and underwater operations. These systems are employed in environments ranging from land to sea, with usage in engines, sprayers, water cannons, and underwater vehicles. As technology continues to advance, intelligent suction and jet equipment has undergone significant technical evolution. In recent years, the development of various suction and jet devices has been predominantly driven by trends toward intelligent systems and automation. In firefighting, for instance, traditional fire extinguishing systems primarily operating through high-pressure pumps to generate powerful water jets are used for firefighting and emergency response. However, these systems often fall short of achieving optimal efficiency, ease of use, and reliability, and even pose inherent risks in some cases [1]. Consequently, enhancing the precision of intelligent jet system targeting and the automation of jet control has become a focal point of research. In practical applications, the rapid identification and localization of targets, as well as the precise trajectory extraction of the water jet, are critical to ensuring the effectiveness of intelligent jet systems. In this paper, we take a step toward computer-aided jet system strikes and present two jet segmentation datasets, Libary and SegQinhu, with a view to advancing the study of water jet trajectory extraction in complex scenarios, as well as its application in jet-based operations.
At the current stage of intelligent jet systems, jet extraction segmentation is one of the key technologies for achieving precise control and targeting. The primary objective of jet segmentation is to ensure that the water jet, whether in firefighting, marine operations, or underwater vehicles, accurately reaches its target—be it a fire source, a designated area, or a moving object. Accurate jet extraction and prediction can significantly improve the precision of jet-based operations, allowing the water jet to reliably reach the target area along a predetermined path, thus increasing operational efficiency and minimizing the impact on the surrounding environment. However, existing general segmentation methods often perform poorly in jet segmentation tasks. Traditional segmentation algorithms typically rely on the overall structure of the image and large-area target features, but these approaches face several challenges when dealing with jets. First, the proportion of the jet relative to the entire image is small, making it difficult for general algorithms to accurately extract subtle jet features from complex backgrounds. Second, the dynamic changes and irregular shapes of jets present additional challenges to traditional segmentation algorithms, resulting in segmentation outcomes that struggle to maintain continuity and stability.
To address these issues, we propose benchmark datasets specifically for jet trajectory extraction and an improved MobileNetV2 method. Through extensive experimentation, we validated that depthwise separable convolutions in the MobileNetV2 network effectively reduce parameters and accelerate inference time compared to standard convolutions. Moreover, combining depthwise separable convolutions with residual networks significantly enhances network efficiency, making it more suitable for our proposed jet datasets. Hence, we selected the lightweight MobileNetV2 network as the baseline and improved it, achieving significant segmentation accuracy gains with minimal additional parameters. We envision that our open-access datasets will enable researchers to develop more robust and data-efficient algorithms for jet trajectory extraction and other related problems.
The main contributions of this paper are as follows:
- We introduce a benchmark for water jet trajectory extraction accompanied by two publicly available datasets, Libary and SegQinhu, providing a challenging set of real-world data to facilitate the development of intelligent jet systems;
- In light of the extreme pixel imbalance characteristic of the jet datasets, we propose a new evaluation protocol that comprehensively assesses the model’s segmentation results from the aspects of accuracy, continuity, and efficiency;
- We propose a pipeline solution with a novel backbone named MobileHDC, and extensive comparative experiments demonstrate that our method achieves optimal performance on the proposed benchmark.
2. Related Work
2.1. Segmentation Datasets
In recent years, numerous datasets have been introduced for image segmentation, with a primary focus on densely recognizing general objects and “stuff” in various image scenes, such as street views [2,3], natural environments [4,5], and indoor spaces [6]. These datasets have greatly contributed to advancing the field of image segmentation by providing diverse scenarios and challenges. However, there is a notable scarcity in the literature when it comes to datasets specifically designed for the more complex and specialized task of automated jet segmentation. Despite the increasing interest in this area, publicly available datasets tailored to the unique challenges of jet segmentation seem to be limited, and we have found only a few studies that begin to address this issue. Therefore, we present two novel datasets specifically for jet segmentation, addressing the lack of resources and references in this specialized domain. These datasets are intended to provide a foundation for future research in jet segmentation and to supplement the existing literature.
2.2. Jet Trajectory Extraction Methods
According to the different extraction methods, jet extraction can be divided into jet localization based on physical calculation and jet segmentation based on image processing.
Jet positioning based on physical calculation is based on physical theory and combines the angle and parameters of the jet vice itself to predict the jet trajectory using a formula. Xin [7] et al. established a jet trajectory model based on the angle of the jet and the velocity of the water flow. While this method reduces the error caused by the change in water pressure, it requires the initial striking position and direction of the jet to remain constant, making it unsuitable for complex scenarios when the target is in motion.
Image-processing-based jet segmentation is achieved by analyzing the shape, color, gray scale, and other features of the jet trajectory, using image detection and segmentation techniques to process the video and images captured by the camera, enabling the extraction of jet trajectories through continuous frame image processing. Zhu [8,9] et al. segmented the jet trajectory by collaborative enhancement of the image and then selecting the threshold value. This method can effectively extract the jet curve with high recognition accuracy, but it requires the position of the camera and the jet apparatus to remain fixed, limiting its flexibility in application.
To efficiently and accurately extract jet trajectories, image segmentation techniques clearly outperform physical computations. The essence of jet segmentation lies in performing semantic segmentation on jet images. Currently, mainstream efficient semantic segmentation methods are predominantly based on lightweight CNNs. The MobileNet series [10,11] decomposes standard convolution operations into depthwise separable convolutions and pointwise convolutions, allowing for a significant reduction in parameters while maintaining segmentation accuracy. DFANet [12] introduces a lightweight backbone by modifying the architecture of Xception [13], which is based on depthwise separable convolutions, reducing the input size for faster inference speed. ShuffleSeg [14] utilizes ShuffleNet [15] as its backbone, combining channel shuffling and group convolutions to lower computational costs. BiSeNet [16,17] proposes a dual-branch architecture to fuse low-level details with high-level contextual information. The Deeplab series [18,19,20] employs atrous convolutions with varying dilation rates, expanding the receptive field without compromising spatial resolution. DSNet [21] revisits the application of dilated convolutions, demonstrating that the use of large kernels in dilated convolutions may represent a more powerful paradigm. TopFormer [22] introduces a novel architecture combining CNNs and ViTs, achieving high semantic segmentation accuracy while conserving computational resources. RTFormer [23] effectively leverages global context, improving semantic segmentation through deep attention mechanisms without sacrificing efficiency. SeaFormer [24] introduces an attention mechanism that simultaneously leverages compression-enhanced axial and detail-enhanced features, tailored for semantic segmentation in the mobile computing domain.
3. Benchmark Description
In this section, we present our datasets and benchmark together with the evaluation metrics.
3.1. Motivation
As shown in Table 1, public datasets such as COCO, Pascal VOC, and Cityscapes have achieved significant success in object detection, semantic segmentation, and instance segmentation tasks within the computer vision domain. However, these datasets typically focus on fixed entities, such as vehicles, pedestrians, and static objects, and are less comprehensive in covering dynamic or non-fixed phenomena. Moreover, datasets related to water bodies are relatively scarce in the public domain, particularly those that address complex water dynamics and visual characteristics such as ripples, reflections, and variations in visibility. Although datasets like USVInland and WaterScenes involve large-scale water body monitoring, their primary application is in water surface driving scenarios, such as detecting and segmenting obstacles on the water surface; few datasets focus on specialized phenomena such as jet flows. Unlike these datasets, our datasets are characterized by significantly smaller object pixel ratios, accounting for only 1.4% and 2.8% in the Libary and SegQinhu datasets, respectively, which greatly increases the difficulty of segmentation.

Table 1.
A brief overview of popular public segmentation datasets, including natural scenes, driving environments, and water surfaces. The pixel ratio represents the proportion of average object size in the dataset, with background and void classes excluded.
In the absence of a publicly accessible jet segmentation dataset, we have constructed a bespoke one. The aim of our benchmark is, on the one hand, providing high-quality and consistently labeled diverse datasets to facilitate the progress of research in the field of jet segmentation. On the other hand, by focusing on the water scenarios, the benchmark should accurately and efficiently extract the trajectories of the jets, accelerating the development of the field of intelligent jet systems.
In order to achieve these goals, our benchmark addresses the general problem of jet semantic segmentation, with the objective of identifying the image regions of small target objects during the training process. In particular, the jet dataset possesses the following characteristics: (i) the morphology of the jet varies depending on the angle and strength of the jet vice strikes, with the jets appearing in the images with non-fixed positions and sizes. Additionally, there is a significant imbalance in the distributions of the pixel classes, which negatively impacts the segmentation accuracy; (ii) the jets are similar in appearance to the background elements, such as water and sky, resulting in blurred edges and susceptibility to noise and background interference. This makes it challenging to accurately distinguish the boundaries of the target from the background; (iii) due to complex lighting conditions, the jet may exhibit strong reflections and highlight regions in certain cases, leading to overexposure in the images. Additionally, reflections on the lake surface and the divergent, mist-like shape of the water column reduce the visibility of the jet target, further complicating the segmentation task.
In our segmentation of the jet dataset, we first experimented with the popular large model SAM, anticipating that this pre-trained general model would perform well in the specific context of our dataset. We employed three approaches: automatic segmentation, point prompts, and box prompts. However, the experimental results did not meet expectations, as illustrated in Figure 1. Specifically, the issues are as follows: (i) although the SAM model performs well in common scenarios, it demonstrates limitations in generalization when applied to specific contexts such as the jet dataset. Even with prompts (point prompts and box prompts), the segmentation results did not achieve the desired accuracy; (ii) the coarse-grained nature of the large model results in suboptimal performance for fine-grained segmentation, leading to blurred edges or mis-segmentation, often confusing the jet with the sky or other similar backgrounds, as shown in Figure 1b; (iii) the high computational resource requirements of the large model pose challenges for rapid iteration and deployment in specific tasks.
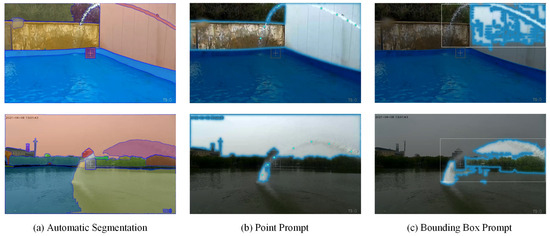
Figure 1.
Segmentation performance of the SAM model on the Libary and SegQinhu datasets, revealing issues in segmentation where the model tends to misclassify background as jet flow.
Given these challenges, we recognized that existing large models struggle to achieve the desired performance in such specific scenarios. Therefore, we propose a specialized small model tailored to the characteristics of the jet dataset, as detailed in Section 4.
3.2. Benchmark and Datasets
We now present a proposed benchmark and two datasets built for jet image segmentation in detail. Generally speaking, there are three main ways to collect jet image datasets in practical applications: electro-optical acquisition, camera acquisition, and mobile phone acquisition. The datasets presented in this paper were all collected using an electro-optical gimbal. The primary advantage of using electro-optical gimbals is their ability to capture high-quality, stable images even in dynamic environments. Table 2 below provides a detailed breakdown of the number of images collected under various challenging conditions.

Table 2.
The number of images in challenging scenarios from the Libary and SegQinhu datasets. The minimal pixel coverage specifically refers to images containing only the impact points or partial water columns.
Libary. The images in the Libary dataset were acquired in a relatively closed-pool environment: a small, manually constructed test cell for jet experiments. It contains 1300 pixel-level annotated image data. Due to the limitation of the site size, the camera has a restricted viewing angle when acquiring the images, and the jet vice has a limited range when performing target strikes, resulting in the jet dataset exhibiting a significant pixel class imbalance. The distribution of the jet sizes is shown in Figure 2a. The background pixels make up the vast majority of the image, whereas the coverage of the pixels of true jet trajectory is just less than 5% of the entire image, with most of them concentrating in the range of 0.5% to 2%. Figure 3 illustrates the typical characteristics of the dataset, including images captured from various viewpoints and the appearance of the jet under conditions of strong lighting or minimal pixel coverage. When exposed to strong lighting, the jet stream appears brighter and lighter, reducing contrast with the background. This issue is particularly pronounced against visually similar backgrounds, such as white walls, as shown in Figure 3b, where the distinction between the jet and the background is significantly diminished, greatly increasing the difficulty of jet trajectory extraction.

Figure 2.
Relative frequency of annotated jet pixels within an image over the 1300 images in the Libary dataset (a) and the 823 images in the SegQinhu dataset (b), respectively. Here, the fraction of jet pixels serves as proxy for the size of the objects of interest within an image. (a) Libary, (b) SegQinhu.
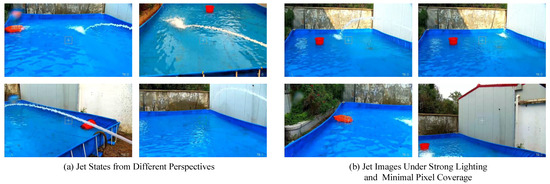
Figure 3.
Sample images of jet states from the Libary dataset under various conditions, including strong lighting and minimal pixel coverage.
SegQinhu. The dataset was taken in an open natural lake scene. It consists of 823 images with pixel-level annotations, where the proportion of jet pixels in all images does not exceed 10%, with the majority concentrated in the 1% to 4% range. The distribution of the jet sizes is shown in Figure 2b. Considering the complexity of real-life scenarios and to ensure the diversity of the data, we collected the images at different times under different weather conditions, such as sunny, overcast, and cloudy, and at 10:00, 13:00, 15:00, and 17:00 on the same day. Compared with the Libary dataset, the SegQinhu dataset contains different light conditions and weather conditions that cover a wider range of scenarios. This makes it more representative of the actual operating conditions of intelligent jet systems in complex scenarios, and thus facilitates the training of more robust models. Figure 4 presents various forms of jets captured in the dataset, including cases where the jet is occluded or only partially visible. In open natural environments, the extended distance of the jet and the dispersed impact points lead to the jet’s edge contours being susceptible to noise interference, resulting in blurred boundaries. Moreover, under strong lighting conditions, the lake surface often exhibits intense glare. This effect is particularly problematic when the jet trajectory overlaps or is in close proximity to the glare region, causing the segmentation algorithm to mistakenly classify the glare as part of the jet or misidentify portions of the jet as background. These factors collectively increase the complexity of the segmentation task.

Figure 4.
Sample images of jet morphologies from the SegQinhu dataset under various conditions, including occlusion, partial coverage, and reflective scenarios.
3.3. Metrics
3.3.1. Accuracy Evaluation Metrics
The objective of a jet segmentation model is to separate the jet regions and the background, i.e., pixel-wise image classification. Herein, five common evaluation metrics, including precision, recall, F1 score, mean intersection over union (mIoU), and the Hausdorff distance, are used to comprehensively assess the performance of the different models.
Precision is the proportion of pixels that are correctly predicted as a jet, defined as follows:
Recall is the proportion of pixels predicted to be correct, which is the predicted proportion of pixels with a jet. It is defined as follows:
F1 score is the harmonic mean of precision and recall, providing a balance between the two. It is defined as follows:
Intersection over union (IoU) is the ratio of the intersection area of two rectangular boxes to their union area. In a segmentation network, it is the ratio of the intersection area of the predicted result and the ground truth label to their union area. Mean intersection over union (mIoU) is the average value of the IoU of all images. It is defined as follows:
wherein true positive (TP) means that the true class of the pixel is a jet and that it is correctly predicted as a jet. False positive (FP) means that the true class of the pixel is the background and it is incorrectly predicted as a jet. True negative (TN) means that the true class of the pixel is the background and it is correctly predicted as the background. False negative (FN) means that the true class of the pixel is a jet and it is incorrectly predicted as the background.
Hausdorff distance is a metric used to quantify the similarity between two sets of points, which primarily focuses on the boundary accuracy in segmentation tasks. It is a specific definition of the distance between two point sets: given two sets and , the Hausdorff distance between these two point sets is defined as follows:
where represents the distance between points a and b (typically the Euclidean distance). In this case, the 95% Hausdorff distance is used to exclude unreasonable distances caused by outliers, thereby maintaining the overall stability of the measure.
3.3.2. Continuity Evaluation Metrics
Furthermore, we introduce two new metrics, the number of connected components and the connected component pixel ratio, to evaluate the continuity of jet segmentation.
Prior to computing these continuity metrics, we first apply a uniform 3 × 3 morphological closing operation to all segmentation results. This step is intended to eliminate small noise and fill internal gaps within the targets, thereby making the connected components more compact and continuous. The closing operation is composed of dilation followed by erosion:
where I represents the binary segmentation image, and B is the structuring element, typically a square kernel. Dilation expands the target regions while erosion reduces the regions. The closing operation, achieved by performing dilation followed by erosion, smooths the boundaries of the targets and suppresses noise.
A connected component is defined as a group of pixels that are connected through adjacency relations (e.g., 4-connectivity or 8-connectivity), with 8-connectivity being used in this study. The number of connected components measures the count of independent target regions (connected components) within the image. By calculating the number of connected components, we can assess whether the targets appear as multiple dispersed regions, which is particularly useful for revealing the sparsity and fragmentation of targets in images where the jet occupies a small proportion. For a binary segmentation image, , where 0 represents the background and 1 represents the jet region. The number of connected components is defined as the total count of all connected components in the image:
where denotes the set of all connected components and represents the cardinality of this set (the number of connected components). A higher value indicates a stronger discontinuity and fragmentation in the segmented jet whereas a lower value suggests a more continuous segmentation with less noise interference.
The connected component pixel ratio measures the proportion of pixels belonging to all connected components relative to the total number of pixels in the image. It is used to evaluate the coverage of connected components within the image. This metric reflects the overall integrity and concentration of the connected components, thereby quantifying whether the jet target appears as a large, continuous region in the image, and provides an effective basis for assessing the structural coherence and regional concentration of the jet. For a segmented image , let denote the sum of pixels within all connected components and represent the total number of pixels in the image. The connected component pixel ratio is defined as follows:
where is the number of pixels belonging to the connected components, and is the total number of pixels in the image I. A lower value indicates a smaller actual coverage of the target while a higher value suggests a denser and more coherent segmentation result.
3.3.3. Efficiency Evaluation Metrics
T (ms) represents the average processing time per image, used to evaluate the inference speed of the model. The calculation formula is as follows:
where N denotes the number of images and represents the time required for the segmentation of the i-th image.
4. Method
In this section, we first introduce the overall architecture of the proposed network, as shown in Figure 5. Furthermore, we provide a detailed explanation of our newly proposed backbone, named MobileHDC, which incorporates the design of hybrid dilated convolution layers and convolutional block layers. Finally, we describe how the decoder module effectively merges multi-level feature representations, enabling more efficient semantic information integration and improved segmentation accuracy.
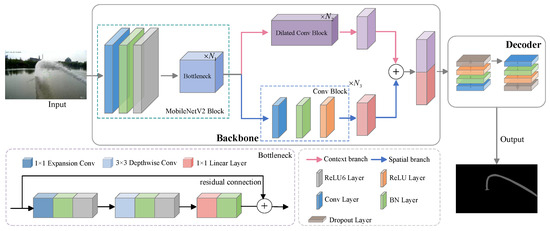
Figure 5.
An overview of the basic architecture of our proposed model. Here, we set the parameters N1, N2, N3 for the repeated times as N1 = 6, N2 = 4 and N3 = 2. The operation ⊕ represents the concatenation operation.
4.1. Overall Architecture
The overall architecture of our proposed network is detailed below. Table 3 shows the parameter configurations for each layer of the network in this paper. Since the number of channels in the MobileNetV2 network increases significantly starting from the eighth layer, to reduce inference time and achieve more efficient segmentation, we only selected the first seven layers of MobileNetV2 as the baseline for our model. The fundamental building block of this baseline is a bottleneck depthwise separable convolution with residual connections, which enhances the model’s representational capacity while maintaining low computational cost and latency, as depicted in Figure 5.

Table 3.
Specification for our proposed model. Each line describes a sequence of 1 or more identical (modulo stride) layers, repeated n times. Here, t, c, and s denote expansion factor, output channels, and stride, respectively.
To further enhance the network’s ability to capture both global and local information, we introduce the MobileHDC (MobileNetV2 Hybrid Dilated Convolutions) backbone, which incorporates hybrid dilated convolution layers and standard convolution blocks. By concatenating these two types of convolutional layers, we can obtain global information while preserving the precise capture of detailed features. Specifically, the hybrid dilated convolution extends the receptive field of the convolutional kernel, capturing broader contextual information without increasing the computational burden. In contrast, the standard convolutional block excels in processing local features, effectively extracting edges, textures, and other detailed information from the image. This ensures that the model can effectively tackle the challenges posed by the jet segmentation task, particularly demonstrating strong performance when dealing with small and dispersed target regions. Additionally, a decoder is included to fuse the extracted global and local features, enhancing overall segmentation performance.
4.2. MobileHDC: A Novel Hybrid MobileNetV2 Backbone
Hybrid Dilated Convolution Layers. Jets typically exhibit dynamic variations and irregular shapes, manifesting at different scales in images—sometimes fine and compact, and at other times wide and diffuse. A larger receptive field enables the model to better capture and maintain the continuity of the jet across different regions, thereby reducing the occurrence of segmentation discontinuities or incompleteness caused by insufficient local information. Dilated convolution is a distinctive convolutional technique that expands the receptive field by introducing “dilations” into the convolutional kernel. The dilation rate of this operation is controlled by the parameter a. As shown in Figure 6, when a = 1, dilated convolution behaves identically to standard convolution. However, when a exceeds 1, certain intermediate pixels are skipped, which may adversely affect network performance. Some previous works, such as Auto-DeepLab [32], were hesitant to use dilated convolutions in the shallow layers of the encoder. On the one hand, this may cause “The Gridding Effect” [33]. On the other hand, just like a large kernel [34], dilated convolution struggles to maintain a balance between contextual and detailed information, which can affect the model’s performance. Therefore, to mitigate the gridding effect, the design of the hybrid dilated convolution layers in this work follows an odd–even mixing strategy, ensuring that the dilation rates do not share a common divisor. Additionally, to prevent the loss of fine details due to overly large dilation rates during the first dilated convolution, the dilation rates must satisfy the condition described in Equation (10).
wherein denotes the dilation rate of the i-th layer and represents the maximum dilation rate in that layer. Assuming that there are n dilated convolution layers in total, it is set by default that , and it is required that , where k represents the kernel size.
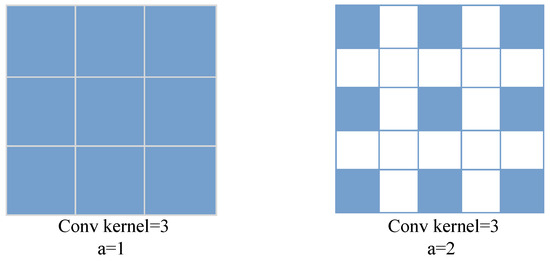
Figure 6.
Diagram of dilated convolution. When the dilation rate is 1, it behaves identically to a standard convolution.
To achieve better perceptual capability across different scales and enhance the model’s ability to capture global information, inspired by STDC [35], we designed four hybrid dilated convolution layers in the backbone network based on the first seven feature maps of MobileNetV2. As illustrated in Figure 7, each dilated convolution layer employs different dilation rates to expand the receptive field. After each convolution operation, the feature map can be expressed as follows:
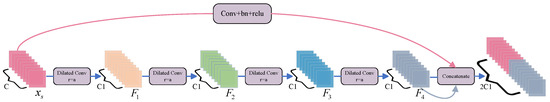
Figure 7.
Diagram of hybrid dilated convolution layers, where C and C1 represent the number of channels, with C = 160 and C1 = 256, and r = a indicates the dilation rate = a. Additionally, represents the feature maps from the 7th layer of the MobileNetV2 network.
Here, denotes the feature map of the i-th layer, represents the dilated convolution operation, is the feature map from the previous layer, and denotes the corresponding dilation rate.
After performing four convolution operations, the feature map is concatenated with the feature map processed by the convolutional block. This process enables the model to effectively learn semantic information at multiple scales, enhancing the synergy between global and local features.
Convolutional Block. In parallel to the hybrid dilated convolution layers, the convolutional block is designed to preserve the spatial dimensions of the original input image while encoding rich spatial information. It is important to note that although the hybrid dilated convolution layers effectively capture global information and perform well in semantic understanding, they often lose substantial spatial and geometric details when processing boundary regions and small objects, especially in our proposed jet segmentation dataset. To address this limitation, the convolutional block reuses feature maps in a manner similar to the hybrid dilated convolution layers. This block consists of a convolution with a stride of 1 to maintain spatial dimensions, followed by batch normalization [36] and ReLU activation. This structure is applied twice to enhance the network’s learning capacity and the nonlinearity of feature representations. This design effectively preserves critical spatial details from the input image, particularly in small objects and boundary regions, significantly improving the network’s accuracy and robustness.
4.3. Decoder Module
The hybrid dilated convolution layers are used to capture contextual information but lack rich detail, while the two consecutive convolutional block layers capture spatial information but lack high-level semantic information. Although the contextual and spatial feature representations extracted from these layers are complementary, they remain mutually unaware. Therefore, a decoder module is designed to fuse these two types of feature representations, integrating high-level semantic information into low-level spatial information. Given the different feature levels, we first concatenate the output features of the hybrid dilated convolution layers and the convolutional block layers. Then, a 3 × 3 convolution is applied to the aggregated features, followed by batch normalization and ReLU activation to enhance feature representation. A dropout layer is also employed to randomly deactivate certain parameters, reducing overfitting. After repeating the operation on the output feature maps, the final result is produced. This decoder effectively integrates both types of features, significantly improving segmentation accuracy, as detailed in Figure 5.
5. Experiments
5.1. Datasets
We perform semantic segmentation experiments over our proposed Libary dataset and SegQinhu dataset. The Libary dataset covers 2 categories and contains 1300 images, which are split into 1100 for training, 100 for validation, and 100 for testing. During training and testing, all images are resized to 512 × 512. The SegQinhu dataset is also a dataset that we publicly provide for jet semantic segmentation tasks. It encompasses a training set of 823 finely annotated images, a validation set of 23 images, and a testing set of 100 images. The original image resolution is 1920 × 1080, and each image is resized to 512 × 512 pixels.
5.2. Implementation Details
Training. We use the RMSprop optimizer with a momentum of 0.9. As a common practice, the “poly” learning rate policy is adopted to decay the initial learning rate with factor 0.9 by default. Data augmentation contains random horizontal flip, contrast enhancement, etc. For our model, the number of iterations, initial learning rate, weight decay, cropped size, and batch size are all set as the same for both the Library and SegQinhu dataset, which could be summarized as [500, 0.0001, 0.0005, 512 × 512, 8]. For simplicity, we do not adopt widely used tricks, such as OHEM, auxiliary losses, or class balance loss.
Inference. Before testing, our models are trained by both the train and val set for Libary and SegQinhu. We measure the metrics on the platform, which consists of single TITAN XP, PyTorch 1.11, CUDA 11.3, cuDNN 8.2, and an Ubuntu environment, with the batch size set to 1 for the test set.
5.3. Ablation Study
Efficiency of Hybrid Dilated Convolution Layers. To demonstrate the effectiveness of hybrid dilated convolution layers, we conducted a simple comparative experiment. We removed the hybrid dilated convolution layers while keeping the rest of the network unchanged and compared the network performance with the results presented in this paper. Assuming that the dilation rates of the four dilated convolution layers are , we conducted network training with different dilation rates to find the optimal dilation rates for the hybrid dilated convolution layers. As shown in Table 4, we can observe that the network achieves the best performance when the four dilated convolutions are concatenated with a dilation rate of in terms of recall and mIoU. However, due to the extremely low average pixel proportion of jets in the Libary dataset, which is only 1.4%, the use of dilated convolutions may lead to excessive loss of detailed information, thereby impacting accuracy.

Table 4.
Ablation study on the design of hybrid dilated convolution layers with different atrous rates.
Efficiency of Decoder. The decoder plays an important role in integrating global context from multi-scale features for segmentation models. Here, we analyze the impact of the decoder module on network performance. As shown in Table 5, although the U-shape structure of the encoder–decoder network introduces additional parameters, which increases the time complexity to some extent, it obviously enhances the network’s feature representation capability and achieves a substantial performance improvement by integrating deep and shallow features within the network.

Table 5.
Ablation study on the design of decoder module.
5.4. Comparison
In this subsection, we conduct extensive comparative experiments between our method and state-of-the-art CNN-based approaches, such as PIDNet and DSNet, as well as transformer-based methods, like SETR. The benchmark results on the Libary and SegQinhu datasets include accuracy metrics: accuracy, recall, F1 score, and mean intersection over union (mIoU); continuity metrics: the number of connected components and the proportion of pixels in connected components; and the efficiency evaluation metric: inference time.
Accuracy. Overall, we observed that several mainstream semantic segmentation methods do not generalize well to jet segmentation, indicating that our two datasets pose new challenges for this task. For instance, models with purely transformer-based architectures, such as SETR, emphasize long-range dependencies and focus more on global information, often neglecting local details when segmenting jet trajectories, which leads to suboptimal performance. Conversely, CNN-based networks are more adept at capturing local features, but they exhibit certain limitations in acquiring global context. Although the UNet [37] model achieved a reasonable performance, its relatively complex architecture and high computational complexity may impact efficiency in practical applications. Consequently, we enhanced our model by introducing dilated convolutions into a lightweight MobileNetV2 backbone to expand the receptive field and improve the model’s ability to learn global features, while also incorporating a decoder to fuse multi-scale features. Specifically, compared to the baseline, our model achieves improvements of 9.78% and 6.86% on the Libary and SegQinhu datasets, respectively, and outperforms current state-of-the-art methods DSNet and PIDNet in terms of mean intersection over union (mIoU), with gains of 1.28% and 0.67% on the Libary dataset and 2.93% and 5.01% on the SegQinhu dataset.
Continuity. Table 6 and Table 7 present comparative results of different models regarding the number of connected components and the proportion of pixels in connected components. Our model exhibits fewer connected components and a higher proportion of pixels in connected components compared to most models, indicating a more continuous and complete segmentation result. Comprehensive consideration of these two metrics reveals that, on the Libary dataset, the SeaFormer and DSNet models exhibit strong competitiveness, with the number of connected components being slightly lower than our model. On the SegQinhu dataset, while our model does not achieve the lowest number of connected components, its higher proportion of pixels in connected components indicates its capability to generate larger contiguous regions, resulting in more complete and concentrated segmentation outcomes.

Table 6.
Comparisons with other state-of-the-art semantic segmentation methods on Libary test set. Gold, silver, and bronze indicate the top three scores in each metric.

Table 7.
Comparisons with other state-of-the-art semantic segmentation methods on SegQinhu test set. Gold, silver, and bronze indicate the top three scores in each metric.
Inference time. Under the same testing conditions, including input image resolution, batch size, and hardware environment, we conducted a fair comparison of the inference times across different models. As shown in Table 8, our model demonstrates a significant advantage in inference speed over other models, reflecting its high computational efficiency. Although slightly slower than the baseline in terms of inference time, our model exhibits notable improvements in other evaluation metrics, indicating a well-balanced trade-off between accuracy and speed.

Table 8.
Comparison of MobileHDC with other models on Libary and SegQinhu dataset. The inference time is measured at resolution 512 × 512.
Visualization. To further demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, we present a series of visualization examples from the Libary and SegQinhu datasets, as shown in Figure 8 and Figure 9. These visualizations provide compelling insights into the segmentation performance of various models. From these visualizations, we observe that models with poorer segmentation performance, such as SETR and MobileNetV3, exhibit a significant number of missed detections and fail to accurately segment jet pixels, resulting in noticeable discontinuities in the segmented jet. On the other hand, models with better segmentation performance, such as SegFormer and PIDNet, although being able to accurately segment the jet regions, tend to introduce some noise during segmentation. This noise can obscure the fine details of the jet flow and may complicate further processing tasks. In contrast, our method produces segmentation results that are not only smoother and more continuous but also contain fewer noise pixels. This highlights the robustness and superior performance of our approach in accurately segmenting jet trajectories.
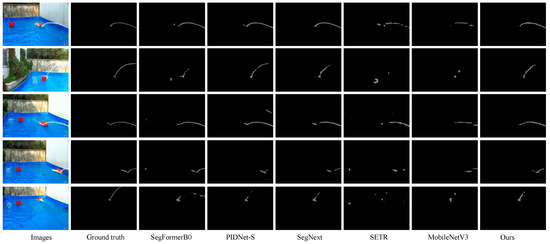
Figure 8.
Visualization of the jet segmentation results of the different methods on the Libary testing dataset.
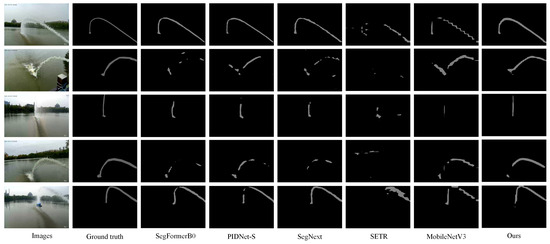
Figure 9.
Visualization of the jet segmentation results of the different methods on the SegQinhu testing dataset.
6. Conclusions
In this work, we introduce two publicly available jet segmentation datasets, Libary and SegQinhu, designed as benchmarks for training and evaluating fully supervised semantic segmentation methods. Additionally, we propose a novel approach that comprises a backbone network named MobileHDC and a decoder. It avoids common complex designs in previous methods, leading to both high efficiency and high performance. Compared to the original MobileNetV2, the improved model achieved 9.78% and 6.86% accuracy gains while also achieving better performance on the proposed continuity metric, with a slight increase in inference time of 3ms and 3.6ms on the Libary and SegQinhu datasets, respectively. The experimental results demonstrate that both of our datasets show a distinct separation in terms of performance between the methods that are specifically designed for jet segmentation and those that are not. Current mainstream semantic segmentation methods are not entirely effective for handling these specific jet scenarios and extensive comparative experiments have shown that our proposed method achieves superior performance on jet datasets, highlighting the necessity for further research in this domain. However, improving computational efficiency without sacrificing segmentation accuracy remains a challenge, especially when dealing with large-scale datasets or high-resolution images. In the future, we plan to explore more lightweight structures and optimize the model further for intelligent jet system applications, such as real-time control systems and embedded devices. We hope that our datasets will serve as a solid foundation for the semantic segmentation of jets, encouraging the computer vision community to develop more data-efficient methods applicable to a wider range of real-world computer vision problems.
Author Contributions
Investigation, Y.C. and Y.L.; methodology, W.W. and Q.Q.; resources, Y.C.; software, Q.Q.; supervision, Y.C. and W.W.; validation, Y.C., W.W. and Y.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.Q.; writing—review and editing, W.W.; visualization, Q.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation under Grant 62202347, Central Science and Technology Development Project led by Hubei Province (2023EGA001).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Pérez-Guerrero, C.; Palacios, A.; Ochoa-Ruiz, G.; Mata, C.; Gonzalez-Mendoza, M.; Falcón-Morales, L.E. Comparing machine learning based segmentation models on jet fire radiation zones. In Proceedings of the Advances in Computational Intelligence: 20th Mexican International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, MICAI 2021, Mexico City, Mexico, 25–30 October 2021; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 161–172. [Google Scholar]
- Cordts, M.; Omran, M.; Ramos, S.; Rehfeld, T.; Enzweiler, M.; Benenson, R.; Franke, U.; Roth, S.; Schiele, B. The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3213–3223. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Xian, W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, F.; Madhavan, V.; Darrell, T. Bdd100k: A diverse driving dataset for heterogeneous multitask learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 2636–2645. [Google Scholar]
- Caesar, H.; Uijlings, J.; Ferrari, V. Coco-stuff: Thing and stuff classes in context. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 1209–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Zhao, H.; Puig, X.; Fidler, S.; Barriuso, A.; Torralba, A. Scene parsing through ade20k dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 633–641. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, A.; Chang, A.X.; Savva, M.; Halber, M.; Funkhouser, T.; Nießner, M. Scannet: Richly-annotated 3d reconstructions of indoor scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5828–5839. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, Y.; Thumuluru, S.; Jiang, F.; Yin, R.; Yao, B.; Zhang, K.; Liu, B. An experimental study of automatic water cannon systems for fire protection of large open spaces. Fire Technol. 2014, 50, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, W.; Lin, D.; Zhao, G. Real-time monitoring of jet trajectory during jetting based on near-field computer vision. Sensors 2019, 19, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Pan, L.; Zhao, G. An improved near-field computer vision for jet trajectory falling position prediction of intelligent fire robot. Sensors 2020, 20, 7029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, A.G. MobileNets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Xiong, P.; Fan, H.; Sun, J. Dfanet: Deep feature aggregation for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9522–9531. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Gamal, M.; Siam, M.; Abdel-Razek, M. Shuffleseg: Real-time semantic segmentation network. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.03816. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. Shufflenet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6848–6856. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Wang, J.; Peng, C.; Gao, C.; Yu, G.; Sang, N. Bisenet: Bilateral segmentation network for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 325–341. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Gao, C.; Wang, J.; Yu, G.; Shen, C.; Sang, N. Bisenet v2: Bilateral network with guided aggregation for real-time semantic segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 3051–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Bian, L.; Huang, X.; Wei, H.; Li, J.; Ni, H. DSNet: A Novel Way to Use Atrous Convolutions in Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.03702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, Z.; Luo, G.; Chen, T.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Yu, G.; Shen, C. Topformer: Token pyramid transformer for mobile semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 12083–12093. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Gou, C.; Wu, Q.; Feng, H.; Han, J.; Ding, E.; Wang, J. RTFormer: Efficient design for real-time semantic segmentation with transformer. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 7423–7436. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Q.; Huang, Z.; Lu, J.; Yu, G.; Zhang, L. Seaformer: Squeeze-enhanced axial transformer for mobile semantic segmentation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.13156. [Google Scholar]
- Everingham, M.; Eslami, S.A.; Van Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The pascal visual object classes challenge: A retrospective. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 111, 98–136. [Google Scholar]
- Ros, G.; Sellart, L.; Materzynska, J.; Vazquez, D.; Lopez, A.M. The synthia dataset: A large collection of synthetic images for semantic segmentation of urban scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3234–3243. [Google Scholar]
- Brostow, G.J.; Fauqueur, J.; Cipolla, R. Semantic object classes in video: A high-definition ground truth database. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2009, 30, 88–97. [Google Scholar]
- Bovcon, B.; Muhovič, J.; Perš, J.; Kristan, M. The mastr1325 dataset for training deep usv obstacle detection models. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 3–8 November 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 3431–3438. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Jiang, M.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y. Are we ready for unmanned surface vehicles in inland waterways? The usvinland multisensor dataset and benchmark. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 3964–3970. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, S.; Guan, R.; Wu, Z.; Ni, Y.; Huang, Z.; Liu, R.W.; Yue, Y.; Ding, W.; Lim, E.G.; Seo, H.; et al. WaterScenes: A multi-task 4d radar-camera fusion dataset and benchmarks for autonomous driving on water surfaces. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 16584–16598. [Google Scholar]
- Žust, L.; Perš, J.; Kristan, M. Lars: A diverse panoptic maritime obstacle detection dataset and benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 4–6 October 2023; pp. 20304–20314. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Chen, L.C.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H.; Hua, W.; Yuille, A.L.; Fei-Fei, L. Auto-deeplab: Hierarchical neural architecture search for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 82–92. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Chen, P.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, D.; Huang, Z.; Hou, X.; Cottrell, G. Understanding convolution for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 12–15 March 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1451–1460. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, X.; Han, J.; Ding, G. Scaling up your kernels to 31x31: Revisiting large kernel design in cnns. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 11963–11975. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, M.; Lai, S.; Huang, J.; Wei, X.; Chai, Z.; Luo, J.; Wei, X. Rethinking bisenet for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 9716–9725. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1502.03167. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; et al. Searching for mobilenetv3. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Lu, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, X.; Luo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Feng, J.; Xiang, T.; Torr, P.H.; et al. Rethinking semantic segmentation from a sequence-to-sequence perspective with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 6881–6890. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, E.; Wang, W.; Yu, Z.; Anandkumar, A.; Alvarez, J.M.; Luo, P. SegFormer: Simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 12077–12090. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.H.; Lu, C.Z.; Hou, Q.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, M.M.; Hu, S.M. Segnext: Rethinking convolutional attention design for semantic segmentation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 1140–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Xiong, Z.; Bhattacharyya, S.P. PIDNet: A real-time semantic segmentation network inspired by PID controllers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 19529–19539. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).