Abstract
Estimating the magnetic moment of a magnetic target is a key aspect of magnetic anomaly detection when accurately locating the target. Current methods primarily rely on vector magnetic field signals or gradient signals, which face challenges such as steering errors and the high costs associated with sensor arrays. This paper proposes a magnetic moment estimation algorithm that combines a scalar magnetic field sensor and the three components of the local geomagnetic field with a convolutional neural network (CNN). The simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm performs well in noise environments with a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) greater than −5 dB. At an SNR of −5 dB, the relative error in the magnetic moment magnitude is 4.92%, while the absolute errors in the magnetic moment declination and inclination are and , respectively. The vector angle difference is . The algorithm achieves high estimation accuracy even with a scalar sensor and under poor noise conditions, offering a novel and effective approach for future magnetic moment estimation research.
1. Introduction
Magnetic anomaly detection (MAD) technology is used to detect and localize local magnetic targets by analyzing magnetic anomaly signals [1]. It can be categorized into aeromagnetic, ground-based, and satellite-based surveys, depending on the platform employed for detection. Among these, aeromagnetic surveys involve placing magnetic detectors on aircraft to detect magnetic anomalies. This method offers advantages such as a wide detection range, high operational efficiency, and precise detection accuracy [2]. Aeromagnetic surveys are extensively utilized in various fields, including mineral exploration [3], where they are used for geological mapping as well as anomaly detection, anti-submarine early warning [4,5], and unexploded ordnance detection [6,7], among others.
In airborne MAD surveys, estimating the magnetic moment of magnetic targets from detection data is a critical step [8,9], as it can significantly reduce the false alarm rate [10]. Wynn inverted the magnetic dipole moment information using the magnetic field vector and magnetic gradient signals measured by a magnetic gradiometer and sensor array, thereby estimating the magnetic moment of the target [11]. Wiegert employed a multi-tensor gradiometer and fluxgate array for the triangulation of the magnetic target and proposed the STAR algorithm to estimate the magnetic moment [12]. However, the STAR algorithm is affected by issues such as significant measurement noise and inherent errors due to the tensor contraction assumption. To address these limitations, Liu enhanced the direction vector selection mechanism relying on rotation invariance and optimized the distance estimation, thereby improving positioning accuracy [13]. Sheinker introduced a nonlinear optimization approach using simulated annealing relying on the magnetic dipole model [14]. Ege examined the geometric characteristics of magnetic targets by studying how magnetic materials influence the vertical component of the geomagnetic field [15]. Qin et al. developed an algorithm grounded in a full magnetic gradient orthogonal basis function, which can accurately estimate the vector magnetic moment of the target under low SNR conditions [16]. Ou, Qiu, and colleagues integrated the target speed, movement direction, the distance between the sensor and the magnetic target, and the magnetic dipole model to construct a magnetic dipole motion model, which they used to identify the magnetic target by comparing the waveforms of the model signal with those of the collected signal [17].
Currently, most magnetic moment estimation algorithms rely on magnetic field data collected by vector magnetic sensors and magnetic gradiometers. However, vector magnetic sensors are prone to issues such as large steering errors [18] and low sensitivity, making them less suitable for mobile platforms. In contrast, scalar magnetic sensors offer higher sensitivity and stability [19], making them ideal for use on high-speed airborne platforms. Fan utilized a scalar magnetic sensor array combined with a particle swarm optimization algorithm to perform target detection [20]. Du proposed an estimation method relying on magnetic field data from multiple scalar magnetic sensors, employing orthogonal basis decomposition and average filtering techniques [21]. While these algorithms offer valuable insights, they require a larger number of sensors and more complex data processing, placing high demands on the platform. Jin introduced a correlation detection method established on normalized magnetic moments. This approach performs well for estimating the magnetic moment modulus under low SNR conditions, but it struggles with accurately estimating the direction of the magnetic moment [22]. This paper proposes a magnetic moment estimation algorithm that integrates a scalar magnetic sensor with CNN. The input of algorithm includes the three components of 2D geomagnetic field and 2D scalar magnetic anomaly signal, while the output consists of magnetic moment vector. This approach ensures accurate magnetic moment estimation while maintaining low-cost applicability.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Magnetic Anomaly Detection
2.1.1. Principles and Methods
Magnetic sensors can be classified into scalar magnetic sensors and vector magnetic sensors based on the type of field quantity they measure. A vector magnetic field sensor measures the three components of the total magnetic field, providing directional information [23]. However, vector magnetic field sensors are susceptible to steering errors, making them less suitable for use on moving vehicles. In contrast, scalar magnetic field sensors, which measure the modulus of the total magnetic field, are widely used on flying platforms due to their superior stability.
As shown in Figure 1, let , , and represent the total magnetic field, the geomagnetic field, and the magnetic anomaly signal, and the two angles and represent the angles between different vectors, respectively [24]. Using the law of cosines, we can derive the following equation:
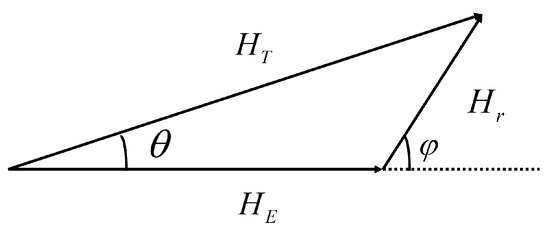
Figure 1.
Vector diagram of signal relationship.
In aeromagnetic surveys, since the magnitude of the geomagnetic field is significantly higher than that of the magnetic anomaly signal, the last term in Equation (2) can be represented as follows:
As mentioned earlier, the last term in Equation (5) can be omitted. Therefore, the measured magnetic field signal can be expressed as follows:
According to Equation (6), the total magnetic field signal can be expressed as the magnitude of the geomagnetic field along with the projection of the magnetic anomaly signal in the direction of the geomagnetic field. The process of generating the magnetic anomaly signal and the principle of aeromagnetic measurement are illustrated in Figure 2.
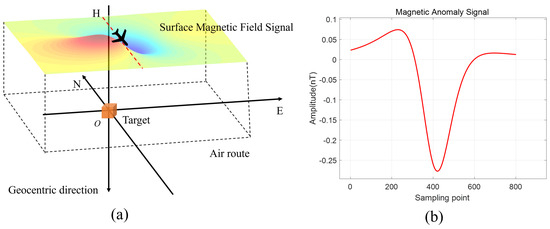
Figure 2.
Magnetic survey map: (a) schematic of magnetic anomaly detection; (b) magnetic anomaly signal.
2.1.2. Geomagnetic Field, Magnetic Moment, and Magnetic Anomaly Signals
As discussed earlier, the magnetic anomaly field is determined by both the geomagnetic field vector and the target magnetic field. To offer a clearer explanation of the magnetic moment angular characteristics, we will now describe the associated angular parameters. According to Figure 3, the angle formed between the magnetic moment and its projection onto the XY plane is defined as the inclination angle, denoted as . Meanwhile, the angle between the projection of the magnetic moment onto the XY plane and the X-axis is defined as the declination angle, denoted as .
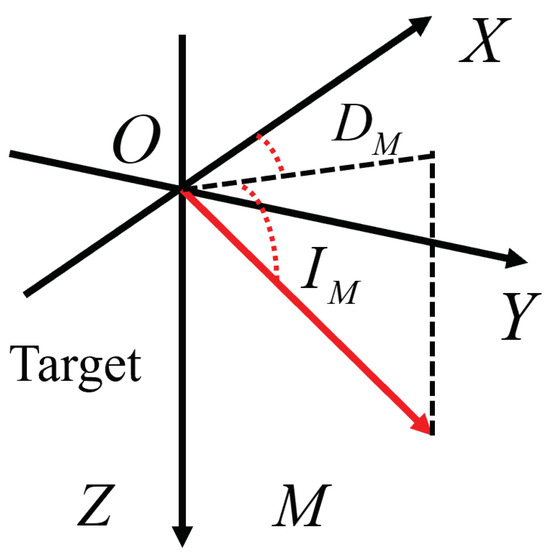
Figure 3.
Illustration of magnetic moment direction information.
Assume that the direction of the geomagnetic field is parallel to the Y-axis, the target is located at , and the observation range spans from to 30 along both axes, with a sampling point interval of . The observation plane is set at , and the directions of the total magnetic moment vector are , , , and . The magnetic field intensity is provided in nanoteslas (nT).
We simulated the magnetic anomaly field under varying magnetic moment orientations within the coordinate system, allowing us to examine the relationship between the magnetic moment direction, the geomagnetic field direction, and the resulting magnetic anomaly field.
The simulation results are shown in Figure 4, which illustrates the impact of changes in the magnetic moment direction on the magnetic anomaly signal while keeping the magnetic moment magnitude constant. Examples are highlighted in the figure, with the red dashed lines representing the magnetic anomaly signal. When the total magnetic moment is orthogonal to the geomagnetic field and parallel to the observation surface, the magnetic anomaly vector exhibits symmetry along the target center, with peaks and troughs symmetrically distributed around the center. In contrast, when the magnetic moment is parallel to the geomagnetic field in the same direction, the magnetic anomaly vector at the center of the observation surface aligns with the geomagnetic field but points in the opposite direction. This results in the largest negative projection of the magnetic anomaly field along the geomagnetic direction, and the angle between the magnetic anomaly vectors on either side of the center and the positive direction of the geomagnetic field is less than , with symmetry around the center. As a result, the total magnetic anomaly field forms a single trough distribution.
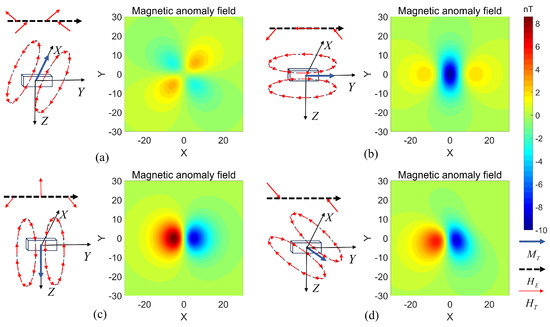
Figure 4.
Distribution of the total magnetic anomaly field on the observation surface for different angles between the target magnetic moment and the geomagnetic field vector: (a) magnetic moment direction ; (b) magnetic moment direction ; (c) magnetic moment direction ; (d) magnetic moment direction .
When the magnetic moment is orthogonal to the geomagnetic field and perpendicular to the observation surface, the magnetic anomaly vector at the center is also perpendicular to the geomagnetic field, resulting in a zero projection along the geomagnetic field direction. This configuration generates a magnetic anomaly field with peaks and troughs symmetrically distributed around the target origin. Lastly, when the magnetic moment is angled relative to the geomagnetic field, the total magnetic anomaly field exhibits a double peak—one positive and one negative—where the peak line is offset from the target origin.
These simulation results confirm that the vector relationship between the magnetic anomaly field and the geomagnetic field primarily governs the distribution of the total magnetic anomaly field signal.
2.2. Magnetic Dipole Model
In magnetic anomaly detection research, the size of the magnetic anomaly target is typically much smaller than the distance between the measurement point and the target. When this distance is 2 to 3 times greater than the target size, the magnetic material can be approximated as a magnetic dipole [25]. Under this assumption, the magnetic field of the dipole can serve as an equivalent representation of the target magnetic field.
Relying on the condition that the magnetic target can be equivalently represented as a magnetic dipole, the magnetic anomaly signal is derived using the magnetic dipole model. A coordinate system is established according to Figure 5, with the magnetic target placed at the origin. The coordinates of the magnetic field sensor are denoted as , and the distance between the magnetic field sensor and the magnetic target is r. The magnetic target is equivalently represented as a magnetic dipole with a magnetic moment . The expression for the magnetic anomaly signal is given as follows:
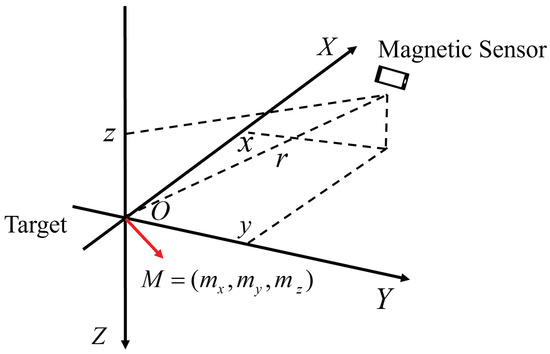
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of magnetic anomaly detection.
By substituting Equation (7) into Equation (6), the magnetic anomaly signal S detected by the scalar magnetic sensor can be expressed as follows:
which expands to:
As seen from the above equation, there are unknown quantities, such as the target position, which prevent the direct calculation of the target magnetic moment by inverting the magnetic anomaly signal. A direct, closed-form linear relationship between the target magnetic moment and the magnetic anomaly signal cannot be established. To address this challenge, a nonlinear model can be used to solve the problem.
Neural networks have undoubtedly become a crucial tool in this context, as they excel at modeling relationships between data that are difficult to describe with linear models [26]. Therefore, we chose to use a 2D CNN to model the relationship between the target magnetic anomaly signal, the geomagnetic field, and the target magnetic moment. Previous studies have employed CNN to process target data and localize the target [27]. This paper proposes a fitting network based on a 2D CNN to establish the relationship between the target magnetic moment and the magnetic anomaly signal.
3. Model and Experiment
3.1. Neural Network Model
CNN comprise deep learning models particularly well-suited for processing data with grid-like structures, such as images, videos, audio, and time series data [28]. In this paper, a 2D CNN architecture is introduced to estimate the target magnetic moment, relying on the three-component geomagnetic field signal and the scalar magnetic anomaly signal obtained from the measured target. Compared to fully connected neural networks, the CNN is better at capturing local information features. By convolving the target magnetic anomaly signal with the geomagnetic field, spatial local features within the signal are extracted. Furthermore, due to the use of convolutional kernels, memory consumption and computational costs are reduced.
The structure of the CNN model proposed in this paper is illustrated in Figure 6 composed of three convolutional layers, two pooling layers, and one fully connected layer, with the detailed settings provided in Table 1. The convolution kernel, compared to larger kernels like , incurs lower computational cost while achieving a larger receptive field through the stacking of multiple kernels. The design of the three convolution layers aims to progressively extract features from low order to high order, striking a balance between feature extraction and computational efficiency. As the number of convolutional layers increases, the receptive field expands, enhancing the network’s ability to capture local features [29]. The network also includes two pooling layers, which downsample the convolutional data to reduce computational complexity and improve the model’s generalization ability. The network achieves a lightweight design while maintaining strong predictive performance.
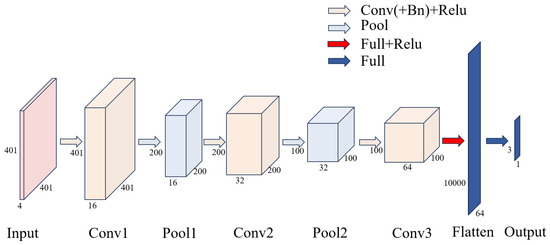
Figure 6.
Neural network architecture diagram.

Table 1.
Detailed settings of the neural network.
The model described in this article was trained on a laptop computer. The training time was approximately 14 min, with 50 training epochs, a learning rate of , and a batch size of 5. The specifications of the computer used for training are as follows:
Processor: 13th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-13500HX 2.50 GHz;
GPU: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4060 Laptop GPU 8 GB;
Memory: 16 GB.
3.2. Dataset
The 2D CNN proposed in this paper uses the three components of the geomagnetic field and the scalar magnetic anomaly signal as input samples. The network consists of three convolutional layers designed to extract feature information from the input samples, with the labels corresponding to the components of the target magnetic moment.
A dataset is generated in MATLAB using the magnetic dipole model. The input dataset consists of the three components of the geomagnetic field from the model and the scalar magnetic anomaly signal. The label data include the three components of the magnetic moment. These three components are defined within the same coordinate system, specifically using the North–East–Down (NED) coordinate system, to facilitate subsequent work. Given the small horizontal detection distance, the plane gradient of the geomagnetic field can be neglected [30], and it is assumed that the geomagnetic field signal remains constant within the detection range. The dataset is generated according to the parameters specified in Table 2:

Table 2.
Simulation target parameters.
- 1.
- The magnitude of the geomagnetic field is 50,000 nT, with a geomagnetic field inclination of and a declination of ;
- 2.
- The simulation range is , with a spatial sampling rate of 0.1 sampling points per meter;
- 3.
- The height varies from 500 m to 1000 m in 100 m steps;
- 4.
- The target magnetic moment modulus ranges from to A·m2, with a step size of A·m2;
- 5.
- The target magnetic moment declination ranges from to , with a step size of . The magnetic moment inclination ranges from to , with a step size of .
The dataset used in this paper consists of 1800 samples, each represented by a matrix, with the output label being a three-dimensional vector. The dataset is divided into a training set (70%), a validation set (15%), and a test set (15%). The samples include scalar magnetic anomaly signals and three-component geomagnetic field signals, generated from various heights, target magnetic moment magnitudes, and magnetic moment angle configurations.
The independent test set ensures that the model is not overfitted to the training data, offering a more accurate evaluation of its final performance and generalization ability. This approach highlights the model’s capacity to handle new data in real-world scenarios.
During aeromagnetic operations, magnetic anomaly signals detected by the magnetic sensor are subject to noise. The performance of the model is evaluated under different noise levels by applying varying SNRs to the dataset. The noise primarily results from the aeromagnetic environment, with the flight vehicle being the main factor influencing the noise level [31]. As a result, the noise impacts both the training and test set data.
Gaussian white noise with SNRs ranging from dB to 50 dB were added to the dataset. Figure 7 illustrates this, where Figure 7a represents the dataset without noise, and Figure 7b shows the dataset after noise has been added.
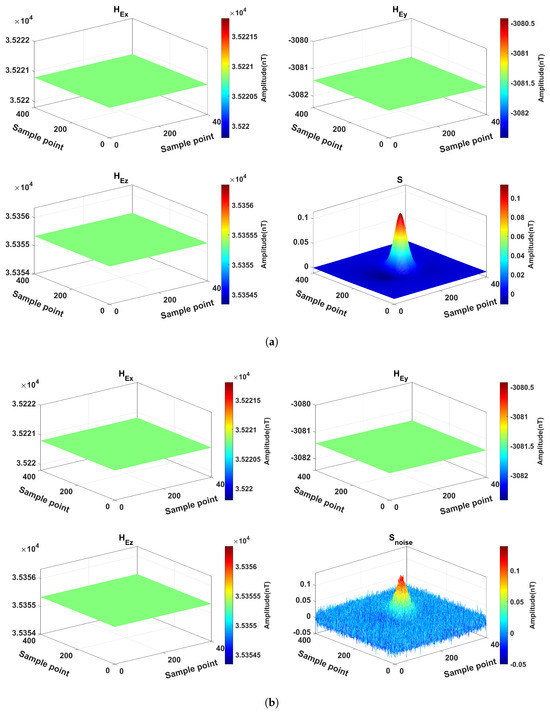
Figure 7.
Sample of magnetic anomaly signal: (a) sample of magnetic anomaly signal without noise. (b) sample of magnetic anomaly signal with noise.
Currently, the noise floor of scalar magnetic field sensors is quite low. For instance, the Quspin QZFM Gen-3 scalar magnetic field sensor has a noise floor of , which has little impact on magnetic field data collection. As a result, the noise from scalar magnetic field sensors does not significantly affect the data, making it acceptable. Introducing noise simulates the impact of environmental noise on the magnetic field data. The environmental magnetic field noise would influence target magnetic moment estimation by inferencing the network’s feature extraction.
3.3. Performance Indicators
This paper uses the Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) to evaluate the magnetic moment modulus. MAPE represents the percentage of the error relative to the true value, is dimensionless, and provides an intuitive measure of the prediction error in relation to the actual value. The calculation equation for MAPE is given in Equation (10), where represents the true value of the modulus and represents the predicted value of the magnetic moment.
The Mean Absolute Error (MAE) is a simple and intuitive metric that directly reflects the average difference between the predicted and true values. It effectively measures the performance of the algorithm, as it provides the same impact for the same error magnitude, regardless of the actual value [32]. Therefore, MAE is used to measure the errors of declination and inclination. The calculation of the prediction error for the deflection and inclination of the magnetic moment is represented by Equation (11).
As in previous sections, and represent the true values of the magnetic moment deflection and inclination, while and represent the predicted values of these parameters.
4. Results
4.1. Ideal State
Seventy percent of the dataset is used for training the network. It is important to note that the selection of the training set is random. The following are the test results after the model training is completed. The test results show that the error in the magnetic moment modulus is 1.85%, and the average absolute errors for the magnetic moment deflection and inclination are and , respectively. The average absolute error between the predicted magnetic moment and the test ranging angle is approximately , the results are shown in Table 3. The model is demonstrated to possess a strong magnetic moment fitting capability, effectively capturing the underlying relationship between the input data and the target magnetic moment. This capability allows the model to achieve highly accurate predictions on the test set, maintaining a relatively small error margin.

Table 3.
Fitting error.
When the inclination angle of the test magnetic moment is close to 90°, small changes in the X and Y components of the magnetic moment can cause significant variations in the magnetic moment deflection, leading to drastic fluctuations in the deflection error. In contrast, the magnetic moment inclination changes less drastically during the calculation process, so the magnetic moment inclination error is smaller than the magnetic moment deflection error.
Since the data are randomly selected, the test set data are arranged for clarity, as shown in Figure 8, Figure 9 and Figure 10.
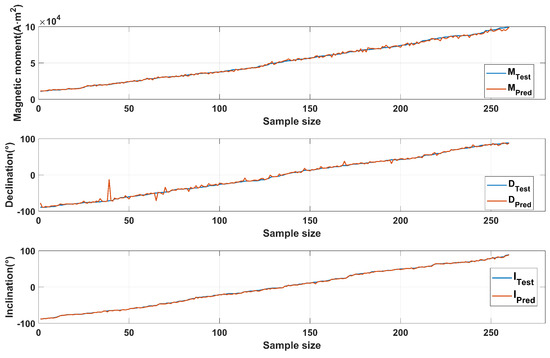
Figure 8.
The estimation diagram of the magnetic moment magnitude, declination, and inclination.
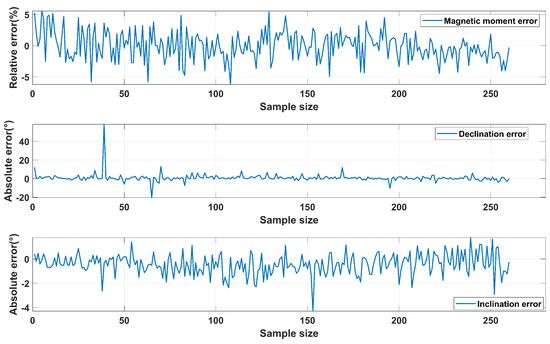
Figure 9.
Fitting errors of the magnetic moment magnitude, declination, and inclination.
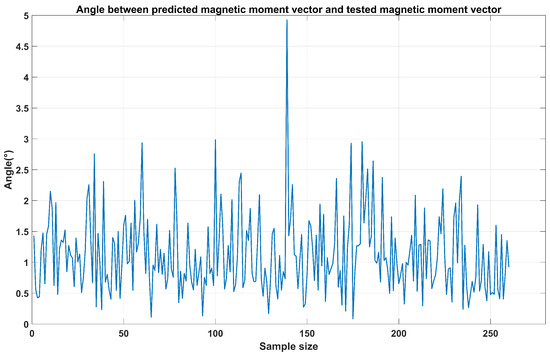
Figure 10.
The difference between the test magnetic moment and the predicted magnetic moment vectors.
4.2. Adding Noise
During aeromagnetic operations, noise inevitably affects the accuracy of the measurements. The performance of the model is evaluated under different noise levels by applying varying signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) to the dataset. The noise primarily originates from the aeromagnetic environment, with the sensor carrier playing a crucial role as the dominant factor influencing the noise level. This influence is particularly evident on moving platforms, where vibrations, orientation changes, and equipment onboard generate additional noise. As a result, noise affects both the training data and the test set.
Gaussian white noise with an SNR ranging from to 50 dB is added to the dataset. The model is then trained using the data segmentation and training methods described above. The following results are obtained: the test results of the model trained with samples at an SNR of dB are shown in Figure 11, Figure 12 and Figure 13.
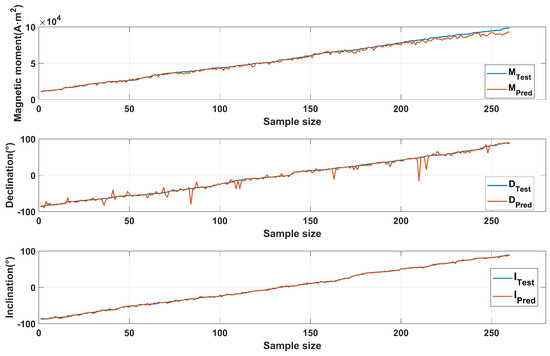
Figure 11.
The estimation diagram of the magnetic moment magnitude, declination, and inclination under noise conditions with SNR = −5 dB.
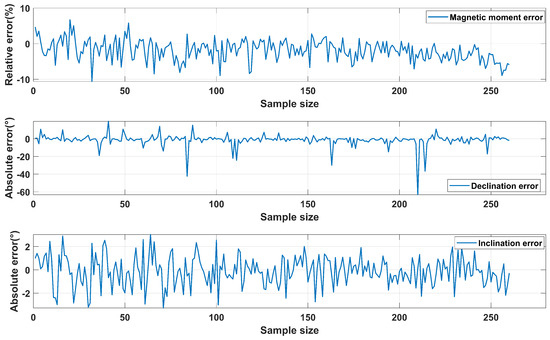
Figure 12.
Fitting errors of the magnetic moment magnitude, declination, and inclination under noise conditions with SNR = −5 dB.
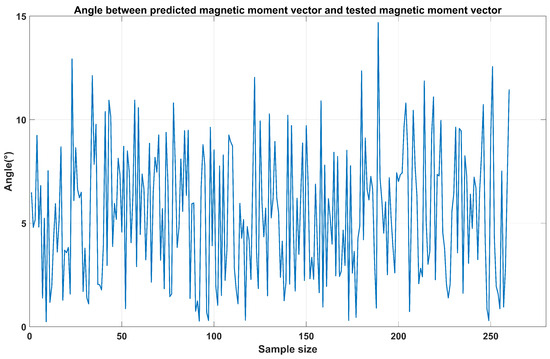
Figure 13.
The angular difference between the test magnetic moment vector and the predicted magnetic moment vector with SNR = −5 dB.
From Figure 14 and Figure 15, it can be observed that as the SNR increases, the error generally decreases and eventually stabilizes. When the SNR = dB, the errors in the three components of the magnetic moment are approximately 7%. The relative error in the magnetic moment magnitude is 4.92%, while the absolute errors in the magnetic moment declination and inclination are and , respectively. The vector angle difference is .
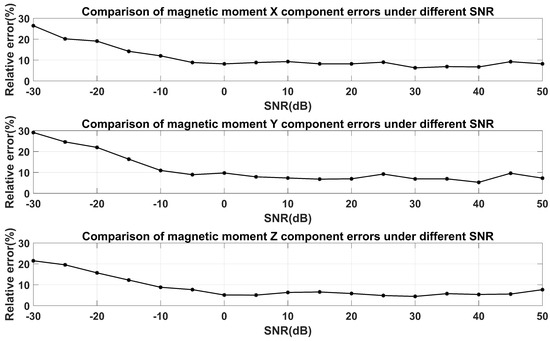
Figure 14.
Errors in different components of the magnetic moment under different SNRs.
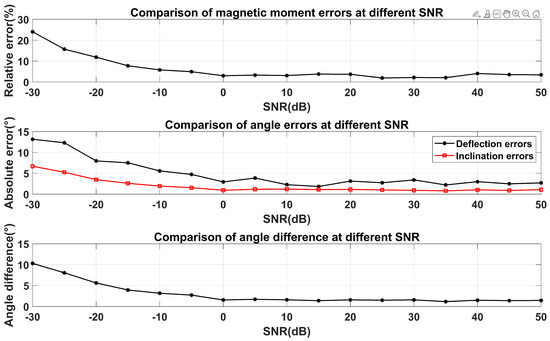
Figure 15.
The error of the model on the test set under different SNRs.
As the model is trained with different samples, the prediction error gradually stabilizes, demonstrating the ability of the model to perform effectively in harsh noise environments. These samples are augmented with noise of gradually increasing SNR, further validating robustness and adaptability of the model to varying levels of noise interference. This behavior highlights potential of the model for reliable performance in real-world scenarios where noise conditions are unpredictable and challenging.
5. Discussion
When calculating the magnetic moment magnitude from the three components, the error in the magnitude may be smaller than the errors in the individual components if the error signs are opposite. Simulation experiments indicate that when the SNR is greater than −5 dB, the model’s performance remains relatively stable. The results indicate that the model proposed upon maintains a reasonable level of accuracy even under low SNR conditions. An advantage of this algorithm is that it relies entirely on scalar magnetic field data, enabling the aircraft to operate with just a single scalar magnetic field sensor, thus reducing hardware requirements. Another advantage is that the model allows for the direct estimation of the target’s magnetic moment size and direction. Additionally, the model demonstrates strong stability in the presence of environmental noise, maintaining high accuracy in magnetic moment estimation even under harsh conditions.
Compared to the STAR algorithm, which requires magnetic field gradient signals from multiple directions around the target, this model uses a simpler signal format and requires fewer sensors. While traditional linear algorithms may struggle to capture the complex relationship between the target magnetic moment and the magnetic anomaly signal, CNN is capable of learning this intricate mapping through activation functions. Furthermore, enhanced stability is provided by the CNN, and it is less sensitive to noise.
However, due to the two-dimensional structure of the input data, the application scenario may be somewhat limited, with the model primarily suited for the magnetic moment estimation of static targets. In practical applications, multiple factors must be considered to ensure the algorithm’s effectiveness. For example, when the target size or number is unclear, or when the sensor is positioned too close to the target, the target may no longer be accurately represented by a magnetic dipole model, leading to inaccurate magnetic moment estimation. Furthermore, the scanning area should be designed to capture the most complete signal possible. It is anticipated that future improvements will help reduce the limitations caused by the data structure.
6. Conclusions
This paper presents a magnetic moment fitting model based on a CNN and scalar magnetic anomaly signals, aimed at uncovering the complex relationship between magnetic anomaly signals, geomagnetic field signals, and the target magnetic moment. The dataset used for training the model includes 2D magnetic anomaly signals and three-component geomagnetic field signals, generated under various heights and magnetic moment conditions, with the three components of the magnetic moment serving as network labels.
Additionally, Gaussian white noise with varying SNRs was added to the dataset. After training the model, the error demonstrated an overall decrease and stabilized as the SNR improved. When the SNR = dB, the model achieved the relative error in the magnetic moment magnitude is 4.92%, while the absolute errors in the magnetic moment declination and inclination are and , respectively. The vector angle difference is . These results highlight the model stability, even in challenging environments.
The primary goal of this model is to minimize the error in magnetic moment fitting under conditions with a scalar magnetic sensor and low SNR, effectively addressing the instability of vector magnetic sensors caused by steering discrepancies. By doing so, it enhances the efficiency of magnetic moment fitting across diverse environmental conditions. The model offers valuable insights into the precise fitting of magnetic moments under low SNR conditions, providing practical strategies for researchers in applications such as unexploded ordnance detection [33], urban pipeline installation [34], and medical robotics [35].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.Y.; methodology, X.Y. and B.C.; software, X.Y. and J.Z.; validation, X.Y., J.Z. and K.Z.; investigation, B.C., K.Z. and X.L.; resources, B.Y. and W.Z.; data curation, J.Z., B.C. and X.L.; Writing original draft preparation, X.Y.; Writing review and editing, J.Z. and K.Z.; supervision, W.Z.; project administration, W.Z.; funding acquisition, B.Y. and W.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was founded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, grant number No. 2023YFB3905002 and Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS No.2023138.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the editors and reviewers for their efforts in helping with the publication of this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| STAR | Scalar Triangulation and Ranging |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio |
| MAPE | Mean absolute percentage error |
| MAE | Mean absolute error |
References
- Lenz, J.E. A review of magnetic sensors. Proc. IEEE 1990, 78, 973–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, P. History of aeromagnetic surveying in Canada. Lead. Edge 2007, 26, 1384–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, P.; Dentith, M. Magnetic responses associated with mineral deposits. AGSO J. Aust. Geol. Geophys. 1997, 17, 145–158. [Google Scholar]
- Polvani, D. Current and future underwater magnetic sensing. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 81, Boston, MA, USA, 16–18 September 1981; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1981; pp. 442–446. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, P.; Lin, C.-s.; Zhang, J.; Tan, B. Adaptive detection of magnetic target in aeromagnetic survey. In Proceedings of the 2010 3rd International Conference on Computer Science and Information Technology, Chengdu, China, 9–11 July 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 2, pp. 497–501. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, G.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, H.; Li, Z.; Ren, G. Detection, localization and classification of multiple dipole-like magnetic sources using magnetic gradient tensor data. J. Appl. Geophys. 2016, 128, 131–139. [Google Scholar]
- Billings, S.D.; Herrmann, F.J. Automatic detection of position and depth of potential UXO using continuous wavelet transforms. In Detection and Remediation Technologies for Mines and Minelike Targets VIII; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2003; Volume 5089, pp. 1012–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, R.; Zhou, C.; Gao, J. Estimation of dipole magnetic moment orientation based on magnetic signature waveform analysis by a magnetic sensor. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 505, 166761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mersch, E.; Yvinec, Y.; Dupont, Y.; Neyt, X.; Druyts, P. Underwater magnetic target localization and characterization using a three-axis gradiometer. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2014-TAIPEI, Taipei, Taiwan, 7–10 April 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Billings, S.D. Discrimination and classification of buried unexploded ordnance using magnetometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, W.; Frahm, C.; Carroll, P.; Clark, R.; Wellhoner, J.; Wynn, M. Advanced superconducting gradiometer/magnetometer arrays and a novel signal processing technique. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1975, 11, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegert, R. Magnetic STAR technology for real-time localization and classification of unexploded ordnance and buried mines. In Detection and Sensing of Mines, Explosive Objects, and Obscured Targets XIV; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2009; Volume 7303, pp. 514–522. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Li, X.; Zeng, X. A real-time magnetic dipole localization method based on cube magnetometer array. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019, 55, 4003609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheinker, A.; Lerner, B.; Salomonski, N.; Ginzburg, B.; Frumkis, L.; Kaplan, B.Z. Localization and magnetic moment estimation of a ferromagnetic target by simulated annealing. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ege, Y.; Sensoy, M.G.; Kalender, O.; Nazlibilek, S. Numerical analysis for remote identification of materials with magnetic characteristics. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2011, 60, 3140–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Li, M.; Li, K.; Pan, Y.; Yang, X.; Ouyang, J. Target magnetic moment orientation estimation method based on full magnetic gradient orthonormal basis function. AIP Adv. 2022, 12, 035035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Qiu, J.; Xie, D.; Wang, Z.; Du, J.; Chang, Q. Research on the moving magnetic object recognition method based on magnetic signature waveform. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2021, 58, 6500108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Xiao, C.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z. Horizontal error calibration method for triaxial fluxgate magnetometer. In Proceedings of the 2008 World Automation Congress, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 28 September–2 October 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Hu, M.; Du, C.; Xia, M. Detection of magnetic dipole target signals by using convolution neural network. In Proceedings of the 2018 Cross Strait Quad-Regional Radio Science and Wireless Technology Conference (CSQRWC), Xuzhou, China, 21–24 July 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.; Kang, C.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, M. An efficient method for tracking a magnetic target using scalar magnetometer array. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, C.; Xia, M.; Huang, S.; Xu, Z.; Peng, X.; Guo, H. Detection of a moving magnetic dipole target using multiple scalar magnetometers. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Wang, H.; Zhuang, Z.; Qian, Q.; Wu, C.; Shi, Y. Underwater target correlation detection and location method based on normalized magnetic moment. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2024, 35, 045114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamoudi, M.; Quesnel, Y.; Dyment, J.; Lesur, V. Aeromagnetic and marine measurements. In Geomagnetic Observations and Models; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 57–103. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; You, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Zhu, W. Inversion of Target Magnetic Moments Based on Scalar Magnetic Anomaly Signals. Electronics 2023, 12, 4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, T.; Shima, A.; Konishi, M.; Yanagisawa, H.; Takada, J.i.; Araki, K. Magnetic dipole signal detection and localization using subspace method. Electron. Commun. Jpn. Part III Fundam. Electron. Sci. 2002, 85, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laoué, N.; Lepers, A.; Deletraz, L.; Faure, C. Neural Network Calibration of Airborne Magnetometers. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 10th International Workshop on Metrology for AeroSpace (MetroAeroSpace), Milan, Italy, 19–21 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Chen, Z.; Pan, M.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, S.; Chen, D.; Hu, J.; Pan, X.; Hu, J.; et al. Magnetic anomaly detection based on full connected neural network. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 182198–182206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L.O. CNN: A vision of complexity. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 1997, 7, 2219–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzubaidi, L.; Zhang, J.; Humaidi, A.J.; Al-Dujaili, A.; Duan, Y.; Al-Shamma, O.; Santamaría, J.; Fadhel, M.A.; Al-Amidie, M.; Farhan, L. Review of deep learning: Concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Li, K.; Yao, C.; Wang, X.; Ouyang, J.; Yang, X. Magnetic anomaly detection using full magnetic gradient orthonormal basis function. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 12928–12940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, B.; Elkattan, M. Cancellation of dynamic ON/OFF effects in airborne magnetic survey. Sens. Imaging 2017, 18, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Myttenaere, A.; Golden, B.; Le Grand, B.; Rossi, F. Mean absolute percentage error for regression models. Neurocomputing 2016, 192, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billings, S.D.; Pasion, C.; Walker, S.; Beran, L. Magnetic models of unexploded ordnance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2115–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Xiang, X.; Lapierre, L.; Zhang, Q. Robust magnetic tracking of subsea cable by AUV in the presence of sensor noise and ocean currents. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2017, 43, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Alici, G. A novel magnetic anchoring system for wireless capsule endoscopes operating within the gastrointestinal tract. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 24, 1106–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).