Abstract
Enhancing the visibility of outdoor images under sandstorm conditions remains a significant challenge in computer vision due to the complex atmospheric interference caused by dust particles. While existing image enhancement algorithms perform well in mild sandstorm scenarios, they often struggle to produce satisfactory results in more severe conditions, where residual color casts and chromatic artifacts become pronounced. These limitations highlight the need for a more robust and adaptable restoration method. In this study, we propose an advanced algorithm designed to restore sand-dust images under varying sandstorm intensities, effectively addressing the aforementioned challenges. The approach begins with a color correction step, achieved through channel compensation and color transfer techniques, which leverage the unique statistical properties of sand-dust images. To further refine the restoration, we improve the boundary constraints of the saturation line prior (SLP) by adjusting the local illumination in the atmospheric light map, enhancing the model’s robustness to environmental variations. Finally, the atmospheric scattering model is employed for comprehensive image restoration, ensuring that color correction and dust removal are optimized. Extensive experiments on real-world sandstorm images demonstrate that the proposed method performs on par with state-of-the-art (SOTA) techniques in weaker sandstorm scenarios, showing marked improvements in more severe conditions. These results highlight the potential of our approach for practical applications in outdoor image enhancement under challenging environmental conditions.
1. Introduction
High-quality images not only bring visual appeal but also provide a reliable source of information for visual systems. However, due to the complexity of weather and environmental conditions, outdoor images often suffer from degradation caused by various adverse factors. In recent years, the frequent occurrence of sandstorms has severely impacted daily life and posed challenges to the visual quality of outdoor imaging systems and the reliability of subsequent computer vision tasks [1,2]. Under sandstorm conditions, the absorption and scattering of light by airborne dust particles results in images with a predominant yellow or red tint and a significant reduction in the visibility of distant objects. Numerous researchers have focused on developing sandstorm image enhancement algorithms to restore the color and details of sandstorm images.
Existing sand-dust image enhancement techniques can be divided into three main types: nonphysical model-based methods, deep learning-based methods, and physical model-based models. Nonphysical model-based sandstorm image enhancement methods have predominantly concentrated on color correction and contrast enhancement [3,4,5]. For example, Xiang et al. [6] proposed an image enhancement algorithm based on channel compensation and brightness partitioning. However, these methods often introduce new chromatic artifacts and exhibit limited de-dust capabilities, primarily due to neglecting the inherent physical characteristics of sandstorm images. In recent years, data-driven approaches have succeeded in image processing tasks such as dehazing and underwater image enhancement. Consequently, researchers have explored their application in sandstorm image restoration [7,8]. However, these methods rely on synthetic datasets, which often fail to generalize to real-world sandstorm images due to domain gaps. In response, some unsupervised frameworks have been proposed [9,10], yet their performance on severely degraded sand-dust images is limited. To reduce the reliance on large-scale datasets and improve the generalization to real-world sandstorm images, a robust paradigm has been proposed that involves the integration of priors with the atmospheric scattering model [11,12]. Moreover, Liu et al. proposed a real-time scene restoration framework, incorporating the rank one prior (ROP) [13] to restore degraded images under varying imaging conditions, and they further enhanced its generalization with the rank one prior plus (ROP+) [14]. However, these methods can struggle to deliver satisfactory results when the priors are invalid.
In summary, while existing methods have successfully mitigated the detrimental effects of sandstorms, several issues persist. Specifically, in severe sandstorm conditions, the current color correction techniques do not sufficiently account for the wavelength-dependent attenuation of color channels, limiting their effectiveness in eliminating the red veil. Moreover, the priors used during the sand-dust removal process do not fully consider the physical properties of sandstorm images, leading to color artifacts. To resolve the issues above, this paper conducts in-depth research. In the color correction process, channel compensation is initially applied to mitigate color shifts, followed by color transfer based on the statistical properties of the mean and variance of color channels, effectively eliminating the red veil. During dust removal, we improve the boundary constraints of the saturation line prior by appropriately adjusting the atmospheric light map, significantly reducing chromatic artifacts. Comprehensive experiments conducted on real-world sandstorm images demonstrate the robustness and effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
The contributions of this research are as follows:
- We present a robust sand-dust image restoration algorithm that decomposes the restoration task into color correction and dust removal components. In mild dust conditions, the proposed method delivers enhanced dust removal effectiveness. In extreme sandstorm situations, the algorithm removes the red veil from the sand-dust images while maintaining stable and robust dust removal performance.
- We propose a novel color correction method that is equally effective for red-dominant sand-dust images. Channel compensation is applied to restore the distribution of the compressed blue and red channels. Color transfer ensures the consistency of the mean and variance across the color channels. Dynamic range expansion is employed to enhance the image’s contrast and brightness.
- We propose a local-block-based atmospheric light estimation strategy and design a novel illuminance adjustment method, significantly reducing color artifacts.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows. Section 2 provides a concise review of existing sand-dust image enhancement and restoration methods, followed by a comprehensive analysis and summary. Section 3 outlines the motivations behind this work. Section 4 presents a detailed description of the components of the proposed sand-dust image restoration algorithm. Section 5 demonstrates the experimental results and an analysis comparing the proposed method with several state-of-the-art approaches. Finally, Section 6 concludes the paper with a summary of the findings.
2. Related Work
With the increasing frequency of sandstorms, researchers have shown heightened interest in sandstorm image enhancement. This section briefly reviews the existing algorithms for sandstorm image enhancement and restoration.
2.1. Nonphysical Model-Based Methods
Nonphysical model-based methods apply white balance techniques to sand-dust images first, followed by weight maps to fuse multiple enhancement results. For instance, Fu et al. [3] utilized gamma correction to generate two inputs with varying brightness, calculated three weight maps (sharpness, chromaticity, and saliency), and fused them to produce an enhanced image. While effective in enhancing image details, this approach also results in localized darkening and color artifacts. Wang et al. [15] proposed a rapid color balancing technique and an effective fusion strategy to enhance sandstorm images. Shi et al. [4] introduced a contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) method based on normalized gamma transformation, which performed color correction and compensation in the Lab color space. However, this method does not substantially enhance the edges of the dust storm images. Park and Eom [5] devised a color balance algorithm for sandstorm image enhancement, using the mean and standard deviation of RGB channels in the color histogram for adaptive adjustment, followed by the CLAHE method to enhance the contrast. Although this technique produces high-quality results, it does not eliminate color artifacts. Gao et al. [16] introduced a Lab color space-based algorithm for color balancing and sandstorm image enhancement. Xu et al. [17] noted the similarity in contours across the RGB channels of natural scenes and proposed an image enhancement algorithm using a tensor least squares optimization model. However, this method does not restore the original colors of the dust storm images. While nonphysical model-based methods can deliver rapid and effective enhancement results, they remain limited in their effectiveness for complex sandstorm scenes.
2.2. Deep Learning-Based Methods
With robust fitting abilities and flexible architectures, neural networks have proven effective in learning dust removal from extensive datasets. Shi et al. [18] proposed a convolutional neural network (CNN)-based sandstorm image enhancement method that integrated a color restoration subnet with a dust removal subnet. Si et al. [7] established a benchmark for the training of CNNs and the assessment of algorithm performance in sandstorm image reconstruction, utilizing the Pix2Pix network for validation. To address the feature inconsistency between Transformers and CNNs, Shi et al. [8] developed a hybrid framework for effective sandstorm image restoration. These methods leverage the atmospheric scattering model to synthesize training datasets, yielding excellent results under specific conditions. However, the generalization capabilities of these methods require further validation. To mitigate the dependence on paired images, Ding et al. [19] proposed a two-stage sandstorm image restoration method based on style transfer and an unsupervised sand-dust image restoration network (USDR-Net). Gao et al. [9] introduced a cycle-consistent generative adversarial network for image de-dusting (D-CycleGAN). However, it struggled with severely degraded sandstorm images. Recognizing the intrinsic differences between sandstorm and haze images, Meng et al. [10] developed an unpaired learning algorithm for image de-dusting based on Retinex with GANs (DedustGAN). While it effectively removes most dust from images, blurring artifacts are present, especially in the sky regions. More recently, several multi-task integrated frameworks have been proposed [20,21], but their performance remains constrained by the dataset’s quality and the complexity of the models.
2.3. Physical Model-Based Restoration Methods
Sandstorm image restoration algorithms based on the atmospheric scattering model [22] typically require additional prior knowledge to accurately estimate atmospheric light and transmission, enabling the inversion of the model to obtain a clear image. Inspired by the dark channel prior (DCP) [23], Shi et al. [11] proposed a modified DCP method to reduce halo effects and suggested performing color correction in the Lab color space. While this method reduces the halo effect, it introduces new color distortions. Building on the concept of the red channel prior, Gao et al. [24] introduced an inverted blue channel prior for sandstorm image restoration. However, the excessive blue channel caused a bluish tint in the restored images. Dhara et al. [25] developed a novel color shift classifier and designed an adaptive atmospheric light refinement method for the correction of color bias, but the restored images still exhibited significant color distortions. Jong-Ju Jeon et al. [12] introduced a color correction algorithm based on consistent chromatic variance, using gamma correction to estimate the transmission map. This method effectively removed the color veil in dust storm images, but the dust removal effect remained unsatisfactory. Although physical model-based methods can achieve more significant dust removal results, achieving a balanced trade-off between color correction and dust removal remains challenging.
3. Motivation
This paper investigates the restoration of sandstorm images from the perspective of the physical model to improve the reliability of visual tasks under sandstorm conditions. Unlike general image restoration tasks, the degradation factors in sandstorm images are complex and diverse, making it challenging to eliminate their negative impacts through a single process. Therefore, it is essential to account for degradation factors such as color shift, detail blurring, and low contrast and strike a balance between different modules during the restoration process. Recently, promising developments in underwater image enhancement and image dehazing technologies have provided valuable insights. Specifically, the scattering medium in underwater scenes causes color attenuation in the opposite order compared to sandstorm images. This characteristic allows us to adapt the color correction methods used for underwater image enhancement to sandstorm images. Moreover, the broad application of dark channel prior-based algorithms in both underwater image enhancement and sandstorm image restoration not only highlights the robustness of the dark channel prior but also motivates researchers to investigate novel prior knowledge. As such, dividing the restoration process into color correction and dust removal appears to be a rational and promising strategy.
3.1. Color Correction
Color cast correction aims to restore the color histogram of sand-dust images to its original distribution. Since the original distribution is unknown, statistical features serve as references for channel compensation and normalization. However, extreme cases may result in residual color casts due to inappropriate reference channels or limited parameter adaptability. In recent advancements in underwater image enhancement, channel compensation-based color correction methods have demonstrated considerable effectiveness [26,27,28,29], prompting our interest in adapting these techniques for sand-dust image restoration. Typically, the color channel with the highest mean value is considered the best-preserved channel and is selected as a reference channel. The mean difference and the reversion of the attenuated channel can serve as adaptive parameters for channel compensation. However, this assumption does not hold for extreme red-dust images, where the blue and red channels suffer severe degradation. In such cases, the pixel values of the blue channel are concentrated around 0, while those of the red channel are concentrated around 255, as shown in Figure 1f. If the lost information is not effectively restored, color bias will remain. Therefore, based on the histogram distribution characteristics of sand-dust images, we propose a new compensation strategy that applies appropriate adjustments to all three RGB channels, effectively recovering the lost color information.
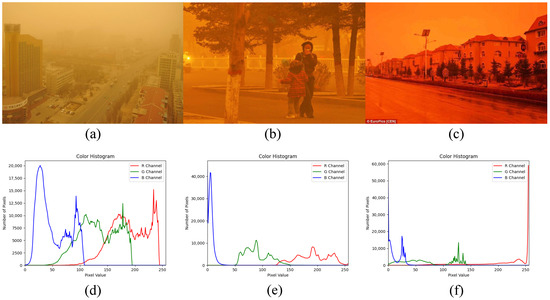
Figure 1.
Sandstorm images from different scenarios with corresponding color histograms: (a–c) are sandstorm images. (d–f) are their corresponding color histograms.
While channel compensation can restore the information in the color channels, it does not eliminate color shift but instead limits it to a controlled range. We can remove the residual color shift via normalization. However, it is crucial to maintain the consistency of the mean and variance across the color channels during this process; otherwise, color bias may persist. For example, Park’s normalization method [5], which retains the mean of the green channel, ensures variance consistency through initial color correction but inevitably causes damage during normalization, leading to color artifacts. Drawing inspiration from color transfer techniques [30,31], we propose an approach where channel compensation first constrains the color shifts to a controllable range, followed by color transfer to eliminate these residual biases.
3.2. Dust Removal
Although color correction establishes a new balance, it disrupts the original color distribution, complicating the dust removal process. Considering that the saturation and brightness components are less affected during color correction, we introduce the saturation line prior [32] to address this issue. While the saturation line prior is effective for dehazing, it may fail in sky regions and near-distance monochromatic targets, leading to color artifacts and dark areas. This problem arises mainly due to the incoordination between atmospheric light and transmission. While there are two possible ways to address this problem, arbitrary modifications would significantly degrade the performance of the saturation line prior. We analyze the causes of color artifacts and hypothesize that, in the worst case, the transmission value is 0, which helps to eliminate the color artifacts.
4. Method
This section provides a detailed explanation of the proposed method. Figure 2 illustrates the overall framework, which consists of three main modules: color correction, atmospheric light estimation, and transmission estimation. The first module restores the lost color information by utilizing the statistical features of sand-dust images, effectively removing the color veil. The second module computes a local atmospheric light map using the dark channel prior and adjusts the illumination of the refined atmospheric light map. The third module estimates the transmission using the saturation line prior. Due to the illumination adjustment in the second module, the boundary constraints of the saturation line prior have been modified. As a result, a clean image can be obtained using the atmospheric scattering model.
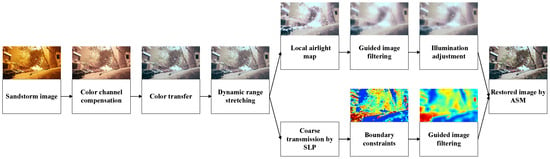
Figure 2.
Overview of the proposed sand dust image restoration algorithm.
4.1. Adaptive Color Correction
Sandstorm images often appear yellow or red due to wavelength-dependent light absorption and scattering. Effective color correction is crucial in restoring their original colors. Unlike haze images, sandstorm images exhibit histograms that are shifted, concentrated, and sequentially distributed [7], as shown in Figure 1.
Inspired by the findings in [33], this paper proposes a novel channel compensation scheme based on the distribution characteristics of sandstorm image histograms. Primarily, we compensate for the severely attenuated blue channel using the red and green channels, as shown in Equation (1):
where represents the compensated blue channel, and , , and denote the original RGB color channels. , , and represent the mean values of the red, green, and blue channels, respectively. When the color attenuation in sand-dust images is minimal, the mean values of the RGB channels are generally above 0.5, causing the denominator to exceed 1. This results in the suppression of the channel compensation. In contrast, when the color attenuation in sand-dust images is severe, the channel compensation receives an additional boost. This strategy effectively prevents under-compensation in images with severe color attenuation and minimizes over-compensation in images with mild color shifts.
Considering that the green channel may also suffer significant attenuation in extreme red sandstorm images, we use Equation (2) to compensate for the green channel and Equation (3) to attenuate the excessive intensity of the red channel:
While the color channel compensation significantly reduces the color shift in red sandstorm images, it cannot eliminate color distortions. Subsequently, we employ a color transfer method to perform color correction, as shown in Equation (4):
where and represent the mean and standard deviation of channel c. represents the average of the standard deviations of the RGB channels, and denotes the average of the means of the RGB channels. We selected the statistical characteristics of sand-dust images as the targets for color transfer, eliminating the need for additional reference images. The color transfer process largely rectifies the color shift in the sandstorm image, yet the dynamic range remains constrained. Therefore, Equation (5) is applied to stretch the dynamic range accordingly:
where represents the final color-corrected image. and represent the maximum and minimum of the output image, respectively. and correspond to the 99.5% and 0.5% percentiles of the normalized image. By setting to 0.05, the issue of locally dark regions in the image can be effectively mitigated.
4.2. Local Atmospheric Light Estimation
Using the global atmospheric light may lead to the unintended darkening of the image or color artifacts, particularly in complex scenarios. Consequently, it is essential to factor in local illumination disparities when estimating atmospheric light [34]. Drawing from this idea, we evenly divide the color-corrected sandstorm image into rectangular segments and estimate the atmospheric light in each block. Firstly, we calculate the dark channel of the image via Equation (6):
Then, we select the brightest pixel in the dark channel as the local atmospheric light in each block. Upon performing patch-wise computations, a rough local airlight map is generated. However, patch-based calculations introduce noticeable block artifacts. To ensure consistency in local illumination while preserving edges, we refine the local atmospheric map using a guided filter [35]. The window radius of the guided filter is set to 60, while the regularization parameter is set to 0.001.
Existing research [36] indicates that hazy conditions may increase the brightness components of images, leading to overestimated atmospheric light values compared to the actual atmospheric light. Consequently, images restored using the atmospheric scattering model often appear darker than the original hazy images. Sandstorm image restoration, which employs dehazing priors, faces similar challenges. In response to this challenge, we propose an illumination adjustment strategy to adjust the refined local atmospheric map, as shown in Equation (8):
where represents the adjusted local atmospheric light map. Sand-dust images often exhibit low illumination, requiring more illumination compensation than haze images. We selected 0.95 as a general compensation factor, as lower values can further enhance the image brightness but may also degrade the restoration performance due to reduced accuracy in atmospheric light. Additionally, since the dark channel prior assumes that the brightest pixel represents the atmospheric light value, the atmospheric light values should not be smaller than the pixel values within a local region. Therefore, we applied a max operation on the compensated atmospheric light map. Compared to the method in [34], our process delivers superior visual results, as depicted in Figure 3.
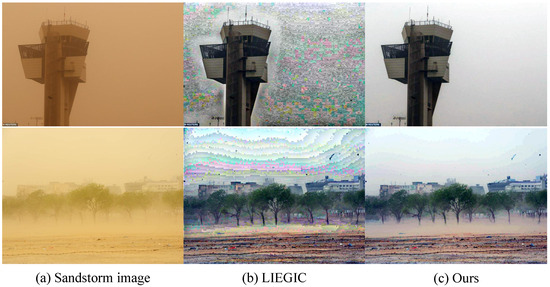
Figure 3.
Comparison of recovery results from different atmospheric light calculation methods.
4.3. Transmission Estimation Based on Saturation Line Prior
The inherent limitations of the DCP have prompted further research into more refined and resilient priors [37,38,39]. However, these priors often encounter failure when applied to sandstorm images. This issue can be primarily due to two factors: first, color correction disrupts the pixel consistency in sandstorm images, causing some properties to shift; second, the intrinsic variation between sandstorms and haze conditions limits the applicability of dehazing priors. This subsection aims to offer a feasible approach.
The advent of the color attenuation prior (CAP) [36] and saturation-based transmission estimation [40] has validated the role of the saturation component in transmission estimation. However, these methods only consider each pixel’s saturation, without accounting for more complex intrinsic relationships among pixels. Recently, the saturation line prior [32] was introduced to address this gap. The saturation line prior describes an approximately linear relationship between the saturation components and the reciprocal of the brightness components of haze images in local blocks. This paper attempts to apply this relationship to sandstorm images.
Firstly, by dividing both sides of the atmospheric scattering model equation by the atmospheric light, we obtain a normalized form, as shown in Equation (9):
where refers to the color channel c of the clear image, and indicates the transmission map. Supposing that and represent the normalized sand-dust image and the clear image, the above equation can be reformulated as
Under the premise of a locally monochromatic surface, the saturation component is locally invariant. According to the definition of saturation, the saturation component of can be formulated as
Let and denote the minimum and maximum color components of , respectively. The above equation can be rewritten as
Equation (12) can be rewritten as
Under the assumption that the RGB channels of the color-corrected sandstorm image share identical transmission, we can derive Equation (14) from Equation (10):
By further simplifying the above equation, we obtain
In the HSV color space, suppose that the brightness component is equal to the maximum color channel, expressed as , with the local saturation and transmission considered as constants. Therefore, we can rewrite Equation (16) as Equation (17):
where , denotes the slope, and represents the intercept. Upon establishing the saturation line, the transmission for the corresponding local block can be derived via Equation (18):
To construct a reliable saturation line, we adopted the approach outlined in [32]. While the saturation line prior works well for most areas, it fails when the local saturation approaches zero or when there is minimal color variation. To recalculate the transmission in regions where the saturation line prior fails, we introduce the boundary constraint in [41], as shown in Equation (19):
where denotes the lower boundary and represents the upper boundary of the color channel. When , the restored image exhibits localized blue artifacts and white patches. We assume that must not be less than . Consequently, cases of yield a transmission value of zero, thereby eliminating chromatic artifacts and white patches. After improving the boundary transmission calculation, we applied a guided filter [35] for smoothing, yielding the final transmission map . In the guided filter, the window radius is set to 30, and the regularization parameter is set to 0.01.
Finally, we substituted the obtained atmospheric light map and transmission map into the atmospheric scattering model to obtain the restored clear image, as illustrated in Equation (20):
The parameter denotes the minimum transmission threshold, calculated as the mean of the bottom 5% of the transmission values. In Algorithm 1, the main steps of the proposed method are outlined.
| Algorithm 1: The Main Steps of the Proposed Method |
Input: Sand-dust image Parameter setting: , , Begin Step 2: Correct the color shift using Equation (4) Step 3: Stretch dynamic range using Equation (5) Step 4: Estimate local atmospheric light via DCP [23] Step 5: Obtain using Equation (7) Step 6: Adjust the illumination of the atmospheric light map using Equation (8) Step 7: Calculate using Equation (18) Step 8: Calculate using Equation (19) Step 9: Restore the dust-free image using Equation (20) End Output: Clear image |
5. Experiments
In this section, we evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed sandstorm image restoration algorithm by conducting comparative experiments with several state-of-the-art methods, including Gray World [42], Shades of Gray [43], the fusion-based enhancing approach (FBE) [3], the halo-reduced dark channel prior (HRDCP) [11], normalized gamma transformation (NGT) [4], ROP [13], successive color balance (SCB) [5], ROP+ [14], chromatic variance consistency (CVC) [12], and DedustGAN [10]. The experiments are conducted on the following platform: Intel i5-12500H CPU @ 3.10GHz, 16.00 GB RAM Windows 11 using MATLAB R2020b and Python 3.8. Due to the lack of publicly available datasets, we collect approximately 1500 real-world sandstorm images from the internet and research papers, selecting 500 high-quality images as our test dataset. For fairness, the codes for the comparative algorithms are provided by the original authors.
5.1. Subjective Evaluation
This subsection aims to evaluate the proposed algorithm by first comparing the performance of color correction. Figure 4 shows six sandstorm images with significant color shifts and the corresponding color-corrected versions.

Figure 4.
Comparison of color correction results.
As shown in Figure 4, the Gray World [42] and Shades of Gray [43] algorithms fail to correct severe redshifts. Their incorrect gain coefficients cause the corrected images to have a blue or yellow tint. SCB [5] and CVC [12] achieve commendable results but fail to effectively suppress the red channel when the intensity of the green channel is low, causing red artifacts in specific regions. In contrast, our method successfully avoids these issues, significantly restoring the original image colors. Note that Figure 4 only shows the color correction results as a reference, with the full results provided later in the text.
To further evaluate the dust removal performance of our algorithm, 18 representative sandstorm images are selected for comparison, as shown in Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7. In mild sandstorm scenarios, most methods are unaffected by color shifts, except HRDCP [11]. Despite showing commendable dust removal capabilities, these traditional methods still struggle to restore distant buildings. DedustGAN [10] introduces color distortion in some cases. In contrast, our algorithm showcases robust sand dust removal performance, almost eliminating dust in the near field and markedly improving the visibility for distant objects, as shown in Figure 5.

Figure 5.
Comparison of recovery results of weak sandstorm images.

Figure 6.
Comparison of recovery results of yellow sandstorm images.

Figure 7.
Comparison of recovery results of severe sandstorm images.
Figure 6 illustrates the experimental outcomes for yellow sandstorm images. The FBE [3] method efficiently removes sand dust, although the enhanced images show localized dark areas. HRDCP [11] significantly enhances the contrast but at the expense of introducing noticeable color distortions. The results from NGT [4] exhibit a grayish-green tint. Lacking a color correction preprocessing step, ROP [13] and ROP+ [14] have a prominent yellow tint in the results. SCB [5] delivers esthetically pleasing results, although some of the results display an unnatural color tone. CVC [12] restores the color effectively but results in an overall darkened image. While DedustGAN [10] successfully restores more details, it introduces noticeable noise and blurriness. In contrast, our algorithm accurately recovers the original colors and maintains proper brightness.
Figure 7 presents the experimental results for red sandstorm images. While FBE [3] effectively mitigates the red veil in the sandstorm images, the results exhibit a yellowish hue. The results of HRDCP [11] and NGT [4] exhibit an orange tint. Due to limited color correction, ROP [13] and ROP+ [14] show significant color cast residues and purple artifacts in the restored results. Although SCB [5] and CVC [12] perform well in color correction, they still leave red artifacts in local areas, and the sky appears bluish. DedustGAN [10] produces results with severe color distortion and purple artifacts. By contrast, our algorithm effectively balances color correction and dust removal, successfully eliminating the red veil while ensuring comprehensive dust removal from the sandstorm images.
To further demonstrate the robustness of the algorithm, restoration results for 12 additional sandstorm images are provided in Figure 8. As shown in Figure 8, the proposed method is highly effective in correcting color biases, restoring fine details, and minimizing color artifacts.

Figure 8.
More experimental results for the proposed method: (a) Restoration results of yellow sandstorm images; (b) Restoration results of red sandstorm images.
5.2. Objective Evaluation
To objectively assess the performance of our algorithm, we employed five widely used no-reference image quality evaluation metrics, including the rate of new visible edges e [44], the geometric mean of visibility level enhancement [44], the natural image quality evaluator (NIQE) [45], the natural scene statistics and perceptual characteristics-based quality index (NPQI) [46], and the structure, naturalness, and perception-driven NIQE (SNP-NIQE) [47]. Theoretically, a higher e value indicates richer detail in the restored result; a higher value signifies a more pronounced enhancement in contrast in the sandstorm images by the algorithm. The NIQE, NPQI, and SNP-NIQE evaluate the image quality based on statistical features, with lower scores indicating better image quality. We initially performed a quantitative comparison using the 18 sandstorm images displayed. Table 1 presents the average values of these metrics, with the best results highlighted in red, the second-best in green, and the third in blue.
As shown in Table 1, HRDCP [11] achieves the most noticeable improvement in the contrast of sand-dust images, while NGT [4] performs best in preserving their natural characteristics. However, both methods demonstrate limited capabilities in edge restoration and fail to recover the true colors of sand-dust images effectively. DedustGAN [10], employing a reference-free image fusion strategy, achieves notable advantages in the quantitative metrics. Nevertheless, while the fusion strategy leverages the strengths of dual-branch networks, it also inherits their weaknesses, resulting in poor visual quality. Although the proposed method does not outperform other methods in the evaluation metrics, it ranks consistently high across all evaluation criteria. When integrating subjective and objective evaluations, our algorithm demonstrates robust restoration performance for sand-dust images across diverse scenarios.
To further confirm the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm in sandstorm removal, we conduct quantitative experiments on a dataset of 500 real-world sandstorm images, with the results summarized in Table 2. The proposed algorithm achieves the best performance in e, NIQE, and NPQI and ranks second in SNP-NIQE, demonstrating its effectiveness in enhancing edge information while significantly improving the overall image quality. However, the less favorable result for indicates a decline in performance due to artifact removal. This compromise arises because color distortion and artifacts, while undesirable, still align with the solution space and contribute positively to the evaluation metrics. To conclude, the proposed sand-dust image restoration method effectively balances the challenges of color correction and dust removal, yielding visually satisfying outcomes in most cases. Moreover, it demonstrates performance on par with that of other methods in terms of objective evaluation metrics.

Table 2.
Average metrics of 500 sandstorm images. The best, second-best and third results are highlighted in red, green and blue, respectively.
5.3. Running Time
This study conducts runtime experiments on sandstorm images at three different resolutions, as shown in Table 3. The experimental results represent the average runtime from ten runs, with the hardware specifications and the experimental platform indicated. From the table, it is evident that, as the resolution increases, the runtime of the proposed algorithm increases approximately linearly. The atmospheric light and transmission estimation modules rely on local patches of size 15 × 15 for computation. As a result, the algorithm’s computational complexity is approximately , where M and N represent the image width and height, respectively. While this block-based computation improves the accuracy of the parameters, it also significantly increases the computational complexity.

Table 3.
Running times of various sandstorm image enhancement methods (unit: seconds).
5.4. Application
To validate the preprocessing capabilities for high-level computer vision tasks, we conducted object detection tests using YOLOv5, with representative outcomes presented in Figure 9. In most scenarios, the proposed algorithm enhances the number and accuracy of detections. However, adverse results occur in specific instances, potentially due to the restoration process altering some image features.

Figure 9.
Visual object detection results for YOLOv5: (a) The detection results of sandstorm images; (b) The detection results of de-dusted images obtained by the proposed method.
5.5. Limitation
Although this study successfully incorporates the saturation line prior into sand-dust image restoration and effectively mitigates the color distortion caused by its failure, the robustness of dust removal heavily depends on the accurate construction of the saturation line. If the saturation line prior fails across most regions, achieving satisfactory restoration results becomes challenging, as shown in Figure 10. In the distant regions near the sky, the boundary constraint is employed to compute the transmission map due to the failure of the saturation line prior. However, as the transmission map is set to 0 in these areas for artifact removal through illumination adjustment, the distant buildings and bridges are not effectively restored, remaining blurred.

Figure 10.
Failure cases of dust removal.
Furthermore, the saturation line prior assumes equal transmission maps for the RGB channels, which is typically invalid for sand-dust images. To address this issue, we employ a color correction approach. While the color correction process effectively removes the color veil, it tends to result in overcompensation under low-illumination and multi-light-source scenarios, as shown in Figure 11. Since the light sources near the observer are not subject to significant absorption and attenuation, this overcompensation often causes them to appear bluish. Defining a mask for the light sources [48] can alleviate this issue.

Figure 11.
Failure cases of color correction.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we have introduced a novel approach for sandstorm image restoration, emphasizing the importance of channel compensation, color transfer, and illumination adjustment in addressing the challenges posed by such extreme conditions. Through extensive experimentation, we have demonstrated that our algorithm effectively restores the true colors of sandstorm images, successfully eliminating color casts while preserving essential image details. Furthermore, the method exhibits robust sand-dust removal capabilities, even in severe sandstorm scenarios, which sets it apart from existing solutions. However, despite these promising results, some limitations remain. Specifically, the saturation line prior may not yield optimal performance in some environments, and the local block-based approach can be computationally demanding, especially when dealing with high-resolution images. Given these findings, we suggest that future studies could focus on two main aspects: investigating faster and more accurate approaches for local atmospheric light estimation and employing more robust priors to calculate transmission in regions where the saturation line prior fails. Moreover, combining detail and texture enhancement methods could improve the algorithm’s performance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.Z. and F.S.; methodology, S.Z. and F.S.; software, S.Z. and F.S.; validation, S.Z., G.W. and J.H.; formal analysis, S.Z. and F.S.; investigation, S.Z., G.W. and J.H.; resources, S.Z. and F.S.; data curation, S.Z. and F.S.; writing—original draft preparation, S.Z.; writing—review and editing, S.Z., F.S., Z.J., G.W. and J.H.; visualization, S.Z.; supervision, F.S. and Z.J.; project administration, F.S. and Z.J.; funding acquisition, F.S. and Z.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang (Grant 2022D01C58), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 62261053), the Tianshan Talent Training Project—Xinjiang Science and Technology Innovation Team Program (Grant 2023TSYCTD0012), the Tianshan Innovation Team Program of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region of China (Grant 2023D14012), and the Scientific Research Plan of Universities of Xinjiang (Grant XJEDU2019Y006).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SLP | Saturation line prior |
| SOTA | State-of-the-art |
| ROP | Rank one prior |
| ROP+ | Rank one prior plus |
| CLAHE | Contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| USDR-Net | Unsupervised sand-dust image restoration network |
| D-CycleGAN | Cycle-consistent generative adversarial network for image de-dusting |
| DedustGAN | Image de-dusting based on Retinex with generative adversarial networks |
| DCP | Dark channel prior |
| CAP | Color attenuation prior |
| FBE | Fusion-based enhancing approach |
| HRDCP | Halo-reduced dark channel prior |
| NGT | Normalized gamma transformation |
| SCB | Successive color balance |
| CVC | Chromatic variance consistency |
| NIQE | Natural image quality evaluator |
| NPQI | Natural scene statistics and perceptual characteristics-based quality index |
| SNP-NIQE | Structure, naturalness, and perception-driven NIQE |
References
- Ma, J.; Lin, M.; Zhou, G.; Jia, Z. Joint Image Restoration For Domain Adaptive Object Detection In Foggy Weather Condition. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 27–30 October 2024; pp. 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, A.; Mandal, M.; Narang, P.; Chamola, V. ReViewNet: A Fast and Resource Optimized Network for Enabling Safe Autonomous Driving in Hazy Weather Conditions. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 4256–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Huang, Y.; Zeng, D.; Zhang, X.P.; Ding, X. A fusion-based enhancing approach for single sandstorm image. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 16th international workshop on multimedia signal processing (MMSP), Jakarta, Indonesia, 22–24 September 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, E.; He, L. Normalised gamma transformation-based contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalisation with colour correction for sand–dust image enhancement. IET Image Process. 2020, 14, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.H.; Eom, I.K. Sand-dust image enhancement using successive color balance with coincident chromatic histogram. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 19749–19760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, P.; Chen, C.; Liu, G.; Pang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Hu, J. Image Enhancement of Degraded Sand-dust Images Based on Channel Compensation and Brightness Partitioning. In Proceedings of the 2023 2nd International Conference on Robotics, Artificial Intelligence and Intelligent Control (RAIIC), Mianyang, China, 11–13 August 2023; pp. 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Yang, F.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y. A comprehensive benchmark analysis for sand dust image reconstruction. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2022, 89, 103638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wei, B.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, L. Sandformer: CNN and Transformer under Gated Fusion for Sand Dust Image Restoration. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023-2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–9 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.; Lai, H.; Jia, Z. Unsupervised image dedusting via a cycle-consistent generative adversarial network. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Huang, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Teng, S.; Grau, A. DedustGAN: Unpaired learning for image dedusting based on Retinex with GANs. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 243, 122844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, E.; He, L. Let you see in sand dust weather: A method based on halo-reduced dark channel prior dehazing for sand-dust image enhancement. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 116722–116733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.J.; Park, T.H.; Eom, I.K. Sand-dust image enhancement using chromatic variance consistency and gamma correction-based dehazing. Sensors 2022, 22, 9048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Sun, J.; Zeng, T. Rank-One Prior: Toward Real-Time Scene Recovery. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 14802–14810. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Liu, R.W.; Sun, J.; Zeng, T. Rank-one prior: Real-time scene recovery. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 8845–8860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wei, B.; Kang, Z.; Hu, L.; Li, C. Fast color balance and multi-path fusion for sandstorm image enhancement. Signal Image Video Process. 2021, 15, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Lai, H.; Wang, L.; Jia, Z. Color balance and sand-dust image enhancement in lab space. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 15349–15365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wang, X.; Xu, X. Single image enhancement in sandstorm weather via tensor least square. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2020, 7, 1649–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Liu, C.; Ren, W.; Shuangli, D.; Zhao, M. Convolutional neural networks for sand dust image color restoration and visibility enhancement. Chin. J. Image Graph 2022, 27, 1493–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Chen, H.; Xu, L.; Zhang, R. Restoration of single sand-dust image based on style transformation and unsupervised adversarial learning. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 90092–90100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Qi, T.; Zeng, T. Scene recovery: Combining visual enhancement and resolution improvement. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 153, 110529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yang, D.; Gao, Y.; Liu, R.W.; Liu, J.; Guo, Y. AoSRNet: All-in-One Scene Recovery Networks via multi-knowledge integration. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2024, 294, 111786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, S.G.; Nayar, S.K. Vision and the atmosphere. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2002, 48, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Sun, J.; Tang, X. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 33, 2341–2353. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.; Lai, H.; Jia, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Sand-dust image restoration based on reversing the blue channel prior. IEEE Photonics J. 2020, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhara, S.K.; Roy, M.; Sen, D.; Biswas, P.K. Color cast dependent image dehazing via adaptive airlight refinement and non-linear color balancing. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 31, 2076–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yuan, J.; Cai, Z. ACCE: An Adaptive Color Compensation and Enhancement Algorithm for Underwater Image. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, S.; Lin, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Sohel, F. A Pixel Distribution Remapping and Multi-Prior Retinex Variational Model for Underwater Image Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 7838–7849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Ruan, R.; Zhuang, P.; Xie, X.; Li, C. Underwater Image Quality Improvement via Color, Detail, and Contrast Restoration. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 1726–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Dong, L.; Xu, W. Retinex-inspired color correction and detail preserved fusion for underwater image enhancement. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 192, 106585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Ren, P.; Zhang, W. Underwater Image Color Correction via Color Channel Transfer. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, X.; Peng, Y.; Li, B.; Zhai, Y. Maximum Information Transfer and Minimum Loss Dehazing for Underwater Image Restoration. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2024, 49, 622–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, P.; Chen, H.; Tan, X.; Jin, Y.; Chen, E. Single image dehazing using saturation line prior. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 3238–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancuti, C.O.; Ancuti, C.; De Vleeschouwer, C.; Bekaert, P. Color Balance and Fusion for Underwater Image Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.M.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Li, B.; Zheng, J. Adaptive single image dehazing using joint local-global illumination adjustment. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2019, 22, 1485–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Sun, J.; Tang, X. Guided image filtering. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 35, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Mai, J.; Shao, L. A fast single image haze removal algorithm using color attenuation prior. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 3522–3533. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bui, T.M.; Kim, W. Single image dehazing using color ellipsoid prior. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 27, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, D.; Treibitz, T.; Avidan, S. Single image dehazing using haze-lines. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 42, 720–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.T.; Cao, K.; Cosman, P.C. Generalization of the dark channel prior for single image restoration. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 2856–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.E.; Park, T.H.; Eom, I.K. Fast single image dehazing using saturation based transmission map estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 29, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, G.; Wang, Y.; Duan, J.; Xiang, S.; Pan, C. Efficient image dehazing with boundary constraint and contextual regularization. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 617–624. [Google Scholar]
- Buchsbaum, G. A spatial processor model for object colour perception. J. Frankl. Inst. 1980, 310, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, G.D.; Trezzi, E. Shades of gray and colour constancy. In Proceedings of the 12th Color and Imaging Conference: Color Science and Engineering Systems, Technologies, and Applications, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 9–12 November 2004; pp. 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Hautiere, N.; Tarel, J.P.; Aubert, D.; Dumont, E. Blind contrast enhancement assessment by gradient ratioing at visible edges. Image Anal. Stereol. 2008, 27, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Soundararajan, R.; Bovik, A.C. Making a “completely blind” image quality analyzer. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2012, 20, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gu, K.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Blind image quality assessment by natural scene statistics and perceptual characteristics. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. (TOMM) 2020, 16, 1–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhai, G.; Zhao, D.; Gao, W. Unsupervised blind image quality evaluation via statistical measurements of structure, naturalness, and perception. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2019, 30, 929–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancuti, C.O.; Ancuti, C.; De Vleeschouwer, C.; Sbert, M. Color Channel Compensation (3C): A Fundamental Pre-Processing Step for Image Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 2653–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).