Investigation of the Relationship Between the Anti-Oxidant Effect, Brand Trust, Healthiness, and Intention to Purchase Propolis Products: The Moderating Effect of Nutritional Disclosure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Hypotheses Development
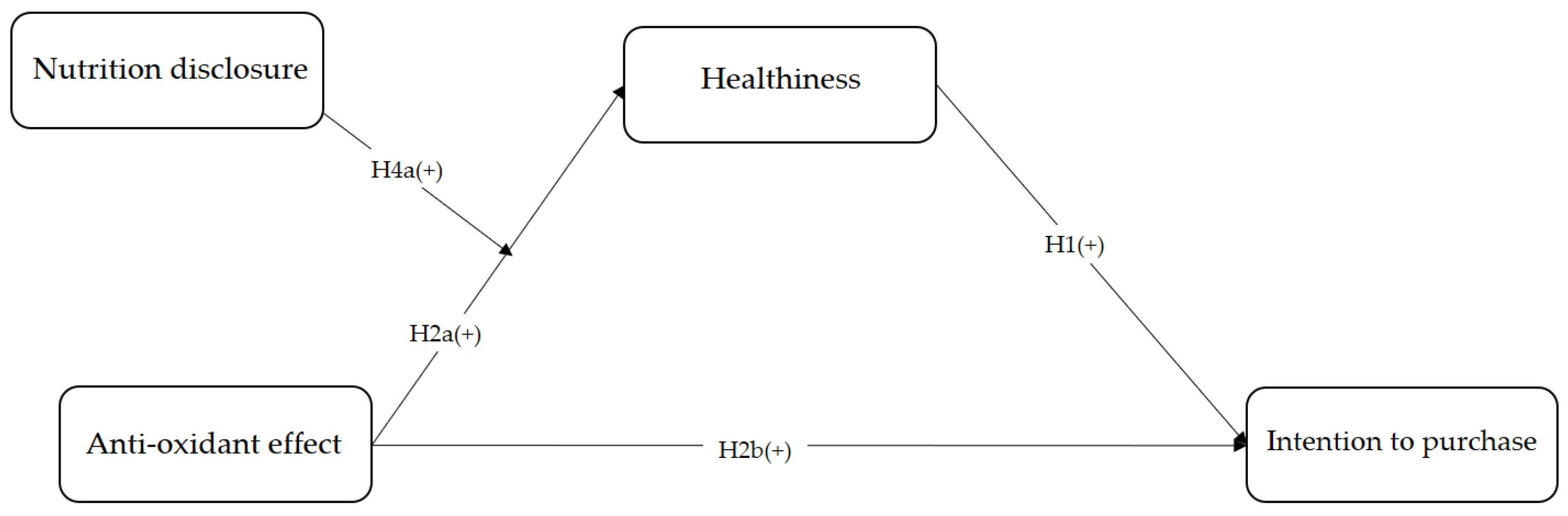
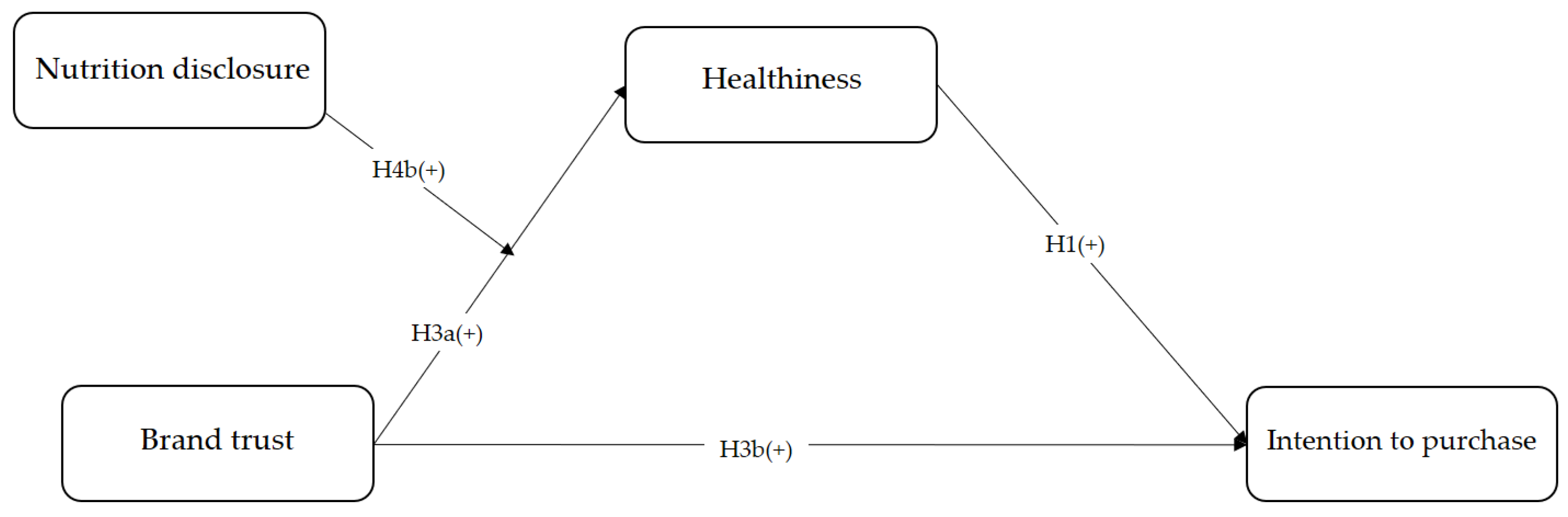
2.1. Healthiness
2.2. Intention to Purchase
2.3. The Anti-Oxidant Effect
2.4. Brand Trust
2.5. The Moderating Effect of Nutrition Disclosure and the Heuristic Effect
3. Method
3.1. The Research Model
3.2. Illustration of Measurement Items
3.3. Recruitment of Survey Participants and Data Analysis
4. Empirical Results
4.1. Confirmatory Factor Analysis
4.2. Results of Hypotheses Testing
5. Discussion
5.1. Discussion of the Empirical Results
5.2. Limitations and Directions for Future Research
6. Conclusions
6.1. Theoretical Implications
6.2. Managerial Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Polaris Market Research. Propolis Market Share, Size, Trends, Industry Analysis Report, Product Type (Capsules and Tablets, Liquids, Others), by Distribution Channel (Retail Store, Online, Others), by Region, and Segment Forecasts, 2024–2032. 2024. Available online: https://www.polarismarketresearch.com/industry-analysis/propolis-market (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Cedeño-Pinos, C.; Marcucci, M.; Bañón, S. Contribution of green propolis to the antioxidant, physical, and sensory properties of fruity jelly candies made with sugars or fructans. Foods 2021, 10, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.J.; Jew, S. Functional food development: Concept to reality. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaner, G.; Ayer, Ç. Evaluation of Honey and Propolis Consumption Habits of Adults During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Süleyman Demirel Üniv. Sağlık Bilim. Derg. 2024, 15, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubowska, D.; Dąbrowska, A.; Pachołek, B.; Sady, S. Behavioral Intention to Purchase Sustainable Food: Generation Z’s Perspective. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witek, L.; Kuźniar, W. Green Purchase Behaviour Gap: The Effect of Past Behaviour on Green Food Product Purchase Intentions among Individual Consumers. Foods 2023, 13, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Lee, S.; Jeon, H. The role of customer experience, food healthiness, and value for revisit intention in GROCERANT. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Temmerman, J.; Heeremans, E.; Slabbinck, H.; Vermeir, I. The impact of the Nutri-Score nutrition label on perceived healthiness and purchase intentions. Appetite 2021, 157, 104995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platta, A.; Mikulec, A.; Radzymińska, M.; Kowalski, S.; Skotnicka, M. Willingness to Consume and Purchase Food with Edible Insects among Generation Z in Poland. Foods 2024, 13, 2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topolska, K.; Florkiewicz, A.; Filipiak-Florkiewicz, A. Functional food—Consumer motivations and expectations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.; Lu, P.; Parrella, J.; Leggette, H. Consumer acceptance toward functional foods: A scoping review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasote, D.; Bankova, V.; Viljoen, A. Propolis: Chemical diversity and challenges in quality control. Phytochem. Rev. 2022, 21, 1887–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katekhaye, S.; Fearnley, H.; Fearnley, J.; Paradkar, A. Gaps in propolis research: Challenges posed to commercialization and the need for an holistic approach. J. Apic. Res. 2019, 58, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, X. The impact of brand trust on consumers’ behavior toward agricultural products’ regional public brand. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0295133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhar, C.; Krishna, S.; Kayal, G.G.; Rana, N. Does brand credibility matter? The case of organic food products. Br. Food J. 2022, 124, 987–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Data Bridge Market Research. Global Propolis Market Size, Share, and Trends Analysis Report—Industry Overview and Forecast to 2031. 2024. Available online: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-propolis-market?srsltid=AfmBOopBGlyZOxW1QQTblXWted6nXUdiJjkM30JqkQIjGjtwCcHNCctg (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Husain, R.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, B.M. The impact of brand equity, status consumption, and brand trust on purchase intention of luxury brands. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2022, 9, 2034234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Sadiq, B.; Bashir, T.; Mahmood, H.; Rasool, Y. Investigating the impact of green marketing components on purchase intention: The mediating role of brand image and brand trust. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobaih, A.; Abdelaziz, A. The impact of nutrition labelling on customer buying intention and behaviours in fast food operations: Some implications for public health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Cronin, J.; Peloza, J. The role of corporate social responsibility in consumer evaluation of nutrition information disclosure by retail restaurants. J. Bus. Ethics 2015, 130, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etco, M.; Sénécal, S.; Léger, P.; Fredette, M. The influence of online search behavior on consumers’ decision-making heuristics. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2017, 57, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheibehenne, B.; Miesler, L.; Todd, P. Fast and frugal food choices: Uncovering individual decision heuristics. Appetite 2007, 49, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.; Babey, S. Contextual influences on eating behaviours: Heuristic processing and dietary choices. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 766–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega-Zamora, M.; Torres-Ruiz, F.J.; Murgado-Armenteros, E.M.; Parras-Rosa, M. Organic as a heuristic cue: What Spanish consumers mean by organic foods. Psychol. Mark. 2014, 31, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.; Zhang, L.S. Is this food healthy? The impact of lay beliefs and contextual cues on food healthiness perception and consumption. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2022, 46, 101348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plasek, B.; Lakner, Z.; Temesi, Á. Factors that influence the perceived healthiness of food. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siipi, H. Is natural food healthy? J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2013, 26, 797–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Lu, J. The impact of package color and the nutrition content labels on the perception of food healthiness and purchase intention. J. Food Prod. Mark. 2016, 22, 191–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrescu, D.C.; Vermeir, I.; Petrescu-Mag, R. Consumer understanding of food quality, healthiness, and environmental impact: A cross-national perspective. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provencher, V.; Jacob, R. Impact of perceived healthiness of food on food choices and intake. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2016, 5, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroni, F.; Esmaeilikia, M.; Rumiati, R.I. What makes a food healthy? Sex differences in what is associated to healthiness evaluations. Food Qual. Prefer. 2022, 96, 104438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richetin, J.; Caputo, V.; Demartini, E.; Conner, M.; Perugini, M. Organic food labels bias food healthiness perceptions: Estimating healthiness equivalence using a Discrete Choice Experiment. Appetite 2022, 172, 105970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.A.; Moon, J. The Relationship between Food Healthiness, Trust, and the Intention to Reuse Food Delivery Apps: The Moderating Role of Eco-Friendly Packaging. Foods 2024, 13, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.P.; Evers, S.; McKenna, M. Determinants of healthy eating in children and youth. Can. J. Public Health 2005, 96, S22–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarar, N.; Machiels, C.; Orth, U. Shaping up: How package shape and consumer body conspire to affect food healthiness evaluation. Food Qual. Prefer. 2019, 75, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.; Nguyen, P. Integrating the theory of planned behavior and the norm activation model to investigate organic food purchase intention: Evidence from Vietnam. Sustainability 2022, 14, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, M.; Gaber, H.; El Essawi, N. Examining the factors that affect consumers’ purchase intention of organic food products in a developing country. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roseira, C.; Teixeira, S.; Barbosa, B.; Macedo, R. How collectivism affects organic food purchase intention and behavior: A study with Norwegian and Portuguese young consumers. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevedo-Silva, F.; Pereira, J. Factors affecting consumers’ cultivated meat purchase intentions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanbur, M.; Eraslan, G.; Silici, S. Antioxidant effect of propolis against exposure to propetamphos in rats. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqui, T.; Farooqui, A. Beneficial effects of propolis on human health and neurological diseases. Front. Biosci. Elite 2012, 4, 779–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordim, J.; Lise, C.; Marques, C.; Oldoni, T.; Varela, P.; Mitterer-Daltoé, M. Potential use of naturally colored antioxidants in the food industry—A study of consumers’ perception and acceptance. J. Sens. Stud. 2021, 36, e12657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekebo, A.; Geba, C.; Bisrat, D.; Jeong, J.; Jung, C. Wound Healing, Anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant activities, and chemical composition of Korean propolis from different sources. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Lu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Deng, Z.; Zheng, L.; Li, H. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoids from propolis via Nrf2 and NF-κB pathways. Foods 2022, 11, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valivand, N.; Aravand, S.; Lotfi, H.; Esfahani, A.; Ahmadpour-Yazdi, H.; Gheibi, N. Propolis: A natural compound with potential as an adjuvant in cancer therapy-a review of signaling pathways. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, A.; van Klinken, R.; Schrobback, P.; Muller, J. Consumer trust in food and the food system: A critical review. Foods 2021, 10, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.A.; Moon, J. Assessing antecedents of restaurant’s brand trust and brand loyalty, and moderating role of food healthiness. Nutrients 2023, 15, 5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konuk, F.A. The impact of retailer innovativeness and food healthiness on store prestige, store trust and store loyalty. Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aureliano-Silva, L.; Spers, E.; Lodhi, R.; Pattanayak, M. Who loves to forgive? The mediator mechanism of service recovery between brand love, brand trust and purchase intention in the context of food-delivery apps. Br. Food J. 2022, 124, 4686–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawley, J.; Susskind, A.; Willage, B. Does information disclosure improve consumer knowledge? Evidence from a randomized experiment of restaurant menu calorie labels. Am. J. Health Econ. 2021, 7, 427–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kees, J.; Royne, M.; Cho, Y. Regulating front-of-package nutrition information disclosures: A test of industry self-regulation vs. other popular options. J. Consum. Aff. 2014, 48, 147–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, E.; Burton, S.; Bates, K.; Huggins, K. Coming to a restaurant near you? Potential consumer responses to nutrition information disclosure on menus. J. Consum. Res. 2009, 36, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchini, A.; Riganelli, C.; Diotallevi, F.; Polenzani, B. Label information and consumer behaviour: Evidence on drinking milk sector. Agric. Food Econ. 2021, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santa, J.C.; Drews, S. Heuristic processing of green advertising: Review and policy implications. Ecol. Econ. 2023, 206, 107760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, A.; Kotz, J.; Al Masri, M.; Allmeta, A.; Purnhagen, K.; König, L. Consumers’ perception of novel foods and the impact of heuristics and biases: A systematic review. Appetite 2024, 196, 107285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazifi, A.; Seyfi, S.; Roschk, H. The role of inferred motive in shaping tourists’ reactions to intentional failures. Curr. Issues Tour. 2024, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Steiger, R.; Scholl-Grissemann, U.; Kallmuenzer, A.; Klier, F.; Peters, M. Tit for tat: How hotel guests can be convinced to do their part to reduce energy consumption. Tour. Manag. 2025, 106, 105010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyle, R. Structural Equation Modeling: Concepts, Issues, and Applications; Sage: Newcastle, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable-variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.; Anderson, R.; Babin, B.; Black, W. Multivariate Data Analysis: A Global Perspective; Pearson: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis: A Regression-Based Approach, 2nd ed.; Guilford Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
| Construct | Code | Item |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-oxidant effect | A1 | Propolis product has an anti-oxidant effect. |
| A2 | Propolis products are useful to get an anti-oxidant impact. | |
| A3 | Propolis product provides me with anti-oxidant outcomes. | |
| A4 | Propolis product improves the anti-oxidant effect of mine. | |
| Brand trust | B1 | I trust the brand of propolis product. |
| B2 | Propolis product brand is trustworthy. | |
| B3 | Propolis product brand is reliable. | |
| B4 | Propolis product brand never disappoints me. | |
| Healthiness | H1 | Propolis product promotes my health condition. |
| H2 | Propolis product is useful for my better health condition. | |
| H3 | Propolis product improves my health condition. | |
| H4 | Propolis product is effective for enhancing my health condition. | |
| Nutrition disclosure | N1 | Propolis product offers nutrition information well. |
| N2 | Propolis product nutrition information is easy to attain. | |
| N3 | Propolis product nutrition information is easy to ensure. | |
| N4 | Propolis products discloses nutrition information well. | |
| Intention to purchase | I1 | I intend to use propolis product. |
| I2 | I will purchase propolis product. | |
| I3 | I am willing to buy propolis product. | |
| I4 | I have an intention to purchase propolis product. |
| Item | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Male | 126 | 41.3 |
| Female | 179 | 58.7 |
| 20 s | 47 | 24.3 |
| 30 s | 101 | 33.1 |
| 40 s | 92 | 30.2 |
| 50 s | 33 | 10.8 |
| Older than 60 | 5 | 1.6 |
| Monthly household income | ||
| Less than USD 2500 | 86 | 28.2 |
| USD 2500–USD 4999 | 111 | 36.4 |
| USD 5000–USD 7499 | 48 | 15.7 |
| USD 7500–USD 9999 | 13 | 4.3 |
| More than USD 10,000 | 47 | 15.4 |
| Weekly use frequency | ||
| Less than 1 time | 118 | 38.7 |
| 1–2 times | 121 | 39.7 |
| 3–6 times | 44 | 14.4 |
| More than 7 times | 22 | 7.2 |
| Construct | Code | Loading | Mean (SD) | AVE | CR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-oxidant effect | A1 | 0.806 | 3.77 (0.80) | 0.730 | 0.915 |
| A2 | 0.880 | ||||
| A3 | 0.893 | ||||
| A4 | 0.838 | ||||
| Brand trust | B1 | 0.707 | 3.80 (0.78) | 0.674 | 0.891 |
| B2 | 0.862 | ||||
| B3 | 0.824 | ||||
| B4 | 0.881 | ||||
| Healthiness | H1 | 0.823 | 3.84 (0.86) | 0.742 | 0.920 |
| H2 | 0.858 | ||||
| H3 | 0.872 | ||||
| H4 | 0.892 | ||||
| Nutrition disclosure | N1 | 0.790 | 3.77 (0.80) | 0.647 | 0.880 |
| N2 | 0.797 | ||||
| N3 | 0.839 | ||||
| N4 | 0.791 | ||||
| Intention to purchase | I1 | 0.921 | 3.84 (1.01) | 0.836 | 0.953 |
| I2 | 0.937 | ||||
| I3 | 0.897 | ||||
| I4 | 0.902 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Anti-oxidant effect | 0.828 | ||||
| 2. Brand trust | 0.601 * | 0.820 | |||
| 3. Healthiness | 0.667 * | 0.618 * | 0.861 | ||
| 4. Nutrition disclosure | 0.533 * | 0.661 * | 0.596 * | 0.914 | |
| 5. Intention to purchase | 0.560 * | 0.660 * | 0.684 * | 0.533 * | 0.914 |
| Model 1 Healthiness | Model 2 Intention to Purchase | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | t Value | β | t Value | |
| Constant | −2.077 | −2.83 * | 0.408 | 1.90 |
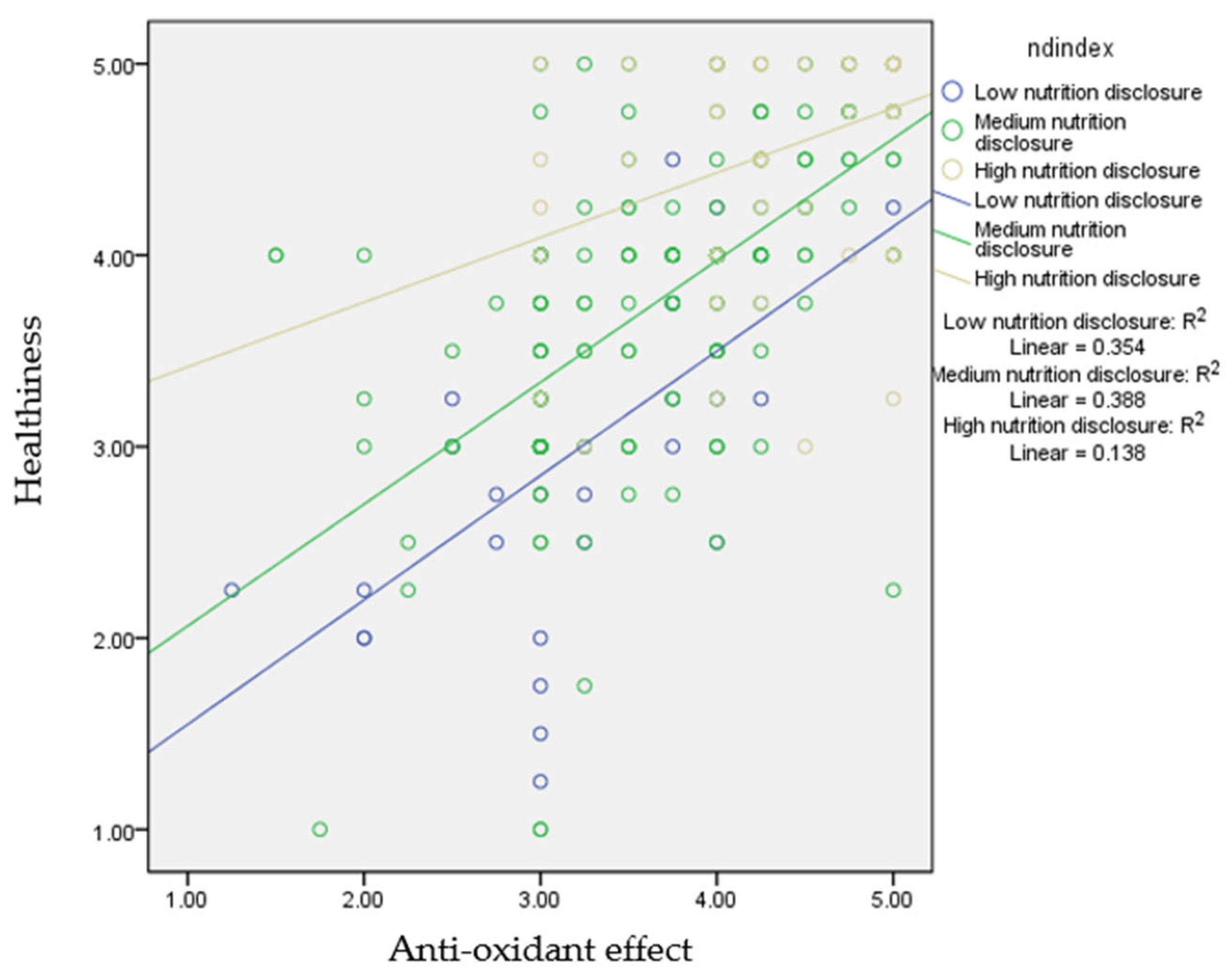
| Anti-oxidant effect | 1.216 | 6.85 * | 0.236 | 3.39 * |
| Nutrition disclosure | 1.068 | 3.27 * | ||
| Interaction | −0.185 | −2.59 * | ||
| Healthiness | 0.661 | 10.10 * | ||
| F-value | 122.04 * | 143.45 * | ||
| R2 | 0.5488 | 0.4872 | ||
| Conditional effect of the focal predictor | ||||
| Nutrition disclosure | ||||
| 3.00 | 0.659 | 10.69 * | ||
| 3.75 | 0.520 | 10.77 * | ||
| 4.75 | 0.334 | 4.74 * | ||
| Index of mediated moderation | Index | LLCI | ULCI | |
| −0.1228 * | −0.2131 | −0.0519 | ||
| Model 3 Healthiness | Model 4 Intention to Purchase | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | t Value | β | t Value | |
| Constant | −0.948 | −1.17 | −0.080 | −0.39 |
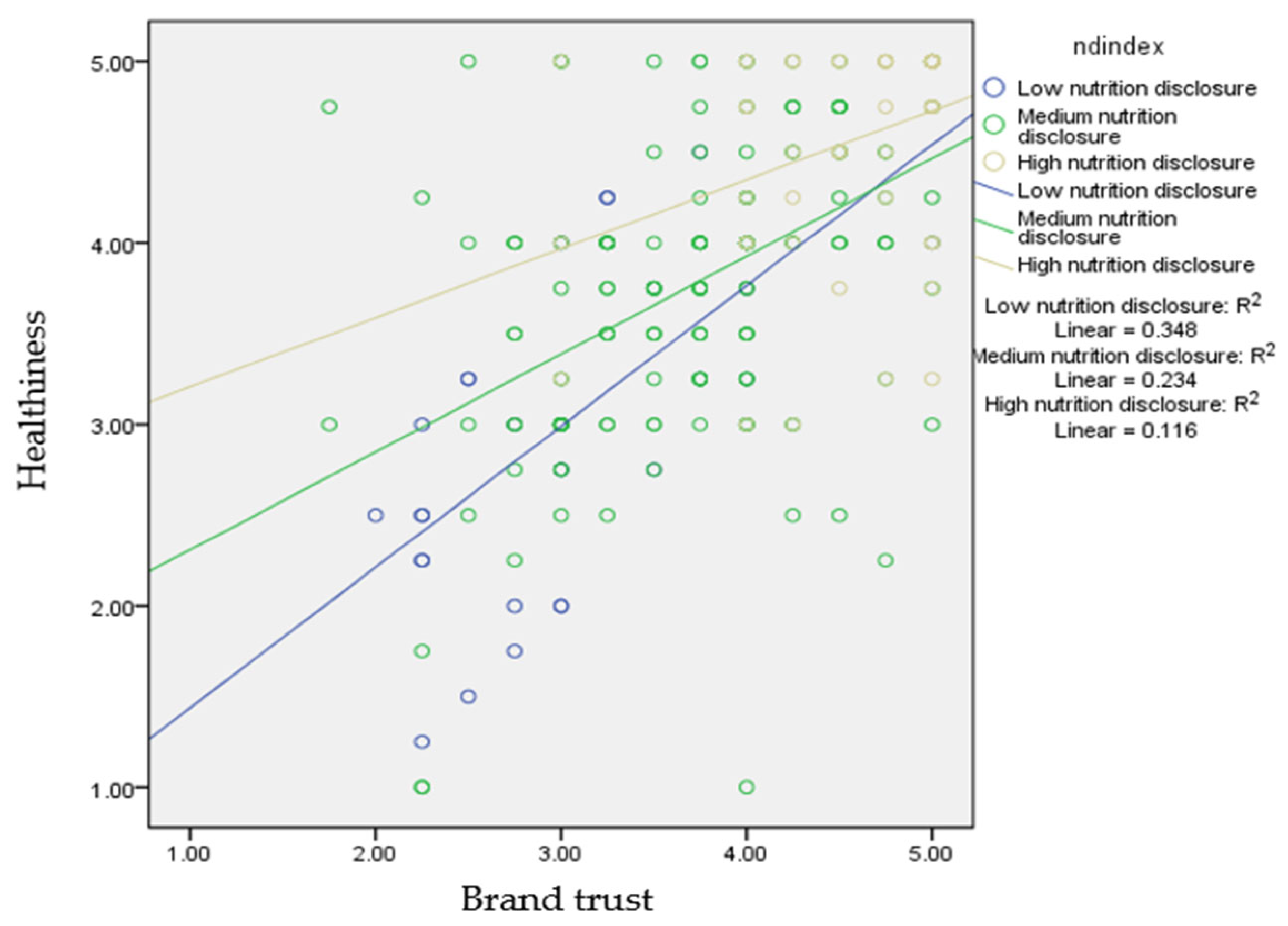
| Brand trust | 0.922 | 6.85 * | 0.496 | 7.89 * |
| Nutrition disclosure | 0.847 | 3.79 * | ||
| Interaction | −0.130 | −2.28 * | ||
| Healthiness | 0.528 | 9.17 * | ||
| F-value | 83.43 * | 191.15 * | ||
| R2 | 0.4540 | 0.4611 | ||
| Conditional effect of the focal predictor | ||||
| Nutrition disclosure | ||||
| 3.00 | 0.532 | 7.08 * | ||
| 3.75 | 0.435 | 7.02 * | ||
| 4.75 | 0.305 | 3.62 * | ||
| Index of mediated moderation | Index | LLCI | ULCI | |
| −0.0687 * | −0.1346 | −0.0067 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.G.; Kim, Y.K.; Moon, J. Investigation of the Relationship Between the Anti-Oxidant Effect, Brand Trust, Healthiness, and Intention to Purchase Propolis Products: The Moderating Effect of Nutritional Disclosure. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2530. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052530
Kim MG, Kim YK, Moon J. Investigation of the Relationship Between the Anti-Oxidant Effect, Brand Trust, Healthiness, and Intention to Purchase Propolis Products: The Moderating Effect of Nutritional Disclosure. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(5):2530. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052530
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Min Gyung, Ye Kang Kim, and Joonho Moon. 2025. "Investigation of the Relationship Between the Anti-Oxidant Effect, Brand Trust, Healthiness, and Intention to Purchase Propolis Products: The Moderating Effect of Nutritional Disclosure" Applied Sciences 15, no. 5: 2530. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052530
APA StyleKim, M. G., Kim, Y. K., & Moon, J. (2025). Investigation of the Relationship Between the Anti-Oxidant Effect, Brand Trust, Healthiness, and Intention to Purchase Propolis Products: The Moderating Effect of Nutritional Disclosure. Applied Sciences, 15(5), 2530. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052530








